Abstract
Laser-induced nuclear reactions in ultra-dense hydrogen H(0) (review in Physica Scripta 2019) create mesons (kaons and pions). These mesons decay mainly to muons. The muons created are useful (patented source) for the muon-induced fusion process. The sign of the muons from the source depends on the initial baryons used. With D(0) (ultra-dense deuterium) the source produces mainly positive muons and with p(0) (ultra-dense protium) the source produces mainly negative muons. Negative muons are required for muon-induced fusion. This charge asymmetry was reported earlier, and has now been confirmed by experiments with a coil current transformer as the beam detector. The current coil detector would give no signal from the muons if charge symmetry existed. The charge asymmetry could indicate unknown processes, for example, caused by the different annihilation processes in D(0) and p(0). The conclusions of a new analysis of the results are presented here. Using D(0) in the muon source, the asymmetry is likely due to the capture of µ- in D atoms and D2 molecules. This leads to emission of excess µ+ from D(0). With p(0) in the muon source, the capture rate of µ- is lower than in D(0). The emitted number of µ+ will be decreased by the reaction between µ+ and the surrounding abundant electrons, forming neutral muonium particles. This effect decreases the amount of emitted µ+ for both p(0) and D(0), and it is proposed to be the main reason for a larger fraction of emitted µ- in the case of p(0). Thus, there is no dominant emission of negative muons which would violate charge conservation.
1. Introduction
The physics of the quantum material ultra-dense hydrogen H(0) was described in a review paper in Physica Scripta in 2019 [1], and the science and technology of its production were reviewed in 2021 [2]. H(0) has an experimental inter-atomic distance of 2.3 ± 0.1 pm in spin level s = 2, [1] and 0.56 pm in spin level s = 1. This means that H(0) is the densest form of material that exists in the universe. Of course, black holes and neutron stars may be denser, but they are hardly considered to be materials. As described previously [1], three different methods have been used to verify the short inter-atomic distances. It is expected [3] that H(0) is superfluid and superconductive. These properties are observed even at room temperature [4,5,6]. Well defined transition temperatures exist to a non-superfluid state at a few hundred K above room temperature [6]. Such transition temperatures must exist for a superfluid and they support the identification of H(0) as a superfluid.
H(0) has been studied using laser-induced Coulomb explosion (CE). This was the first method used to verify the pm inter-nuclear distances. This method has been coupled to time-of-flight (TOF) and time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOF-MS) [1] detection of CE fragments. The second method for verification of the pm distances in H(0) is rotational emission spectroscopy [1] which determines the inter-atomic distances as a function of the spin quantum number s with a precision in the femtometer range.
The third method used for verifying the pm distances in H(0) is based on the observations of nuclear processes in H(0), both spontaneous and laser induced. Such nuclear processes are possible only at pm distances. The laser-induced nuclear processes eject particles in the MeV range, from relatively weak laser pulses of <0.4 J [1,7,8]. As early as in 2015, heat generation above break-even in D(0) was reported using a pulsed laser [9]. This was the first report on sustained nuclear fusion above break-even and, indeed, the first working fusion process that was reported with deuterium as fuel. Later, it was concluded that muon-induced fusion was the fusion process causing these results [9]. Fast mesons and muons from the nuclear processes have been observed at distances up to 2 m in a vacuum [7,8,10,11]. Thus, the meson and muon velocities correspond to 10–500 MeV u−1 per mass unit. Magnetic deflection studies have been used to confirm that many of the initially formed particles are neutral [12]. Thus, they are not trivial protons or electrons. The generation of muons from the laser interaction with H(0) has been confirmed by direct measurements of the accurate decay time for the muons [13]. Other studies [14,15] have confirmed that charged and long-lived neutral kaons as well as charged pions from the laser-induced processes in H(0) decay with their well known decay lifetimes [16,17,18].
Large fluxes of muons are generated by the patented muon generator [19] with application in muon-induced or muon-catalyzed fusion reactors [20]. Since only negative muons can be used for muon-induced fusion [21], the conditions for generating muons with different signs are of great practical importance for the presently ongoing development of this method. Muon-induced fusion is the only sustainable nuclear fusion method since it can use deuterium as a fuel [2,22]. Thus, muon-induced fusion does not require risky handling of radioactive tritium. All other fusion methods under development use D + T fusion [22]. The recent development of the annihilation energy generation method [15] means that tritium will no longer be needed for any type of power generation, since annihilation can use ordinary hydrogen as fuel. The central point in this report is to show that the published muon charge asymmetry can be understood without challenging the standard model of particle physics. This means that the development of muon generators for many different applications can continue.
The generation of muons is important for fundamental studies of muons and studies using muon beams [23,24] as well as for various applications of muons besides the muon-induced fusion method. Of particular interest is the development of muon ionization cooling experiments (MICE) intended for muon beam studies [25,26] and of muons for sensitive muon spin spectroscopy (µSR) [27]. The µSR method should be significantly simplified by the use of the patented muon source, with D(0) as target since this produces mainly positive muons. The advantages are apparent, which include using a table-top muon generator which can be run by one person and easily transported instead of a large stationary particle accelerator that needs a large group of specialists for its use in muon production. The cost of the equipment and the cost of running it is two orders of magnitude smaller for the muon generator with an equipment cost of around 30,000 euros. The radiation safety of this novel muon generator has been studied during more than one hundred running hours with no increased gamma radiation. Due to its low complexity it is highly reliable.
The energy cost of producing muons with the muon source used here is 0.4 J in the laser pulse which produces >1013 muons [20]. This means <4 × 10−14 J per muon. A muon has a mass of 106 MeV or 1.7 × 10−11 J. Thus, the energy required to form a muon in the patented muon source is in the order of 0.2% of its mass-energy. When a particle accelerator is used to create muons, the minimum energy required for any accelerator construction is the muon mass energy. Thus, the patented source is at least a factor of 500 better in energy consumption than any accelerator can ever be. The total power for running the laser and apparatus of the muon source is 1 kW including pumps and heaters. It is conceivable that a particle accelerator requires at least 100 kW for running. Thus, the patented muon source is a factor of 100–500 better than what a particle accelerator can ever be. With 1013 muons with energy around 100 MeV per laser pulse, the total particle energy is 2 × 1015 eV per pulse or 2 × 1016 eV per second with a typical repetition rate of 10 Hz. This is a high-intensity muon source.
2. Background
2.1. Theory of Ultra-Dense Hydrogen H(0)
Ultra-dense hydrogen H(0) is a quantum material. The fundamental physics of it was recently reviewed [1]; thus, only the most important properties for the present study are summarized here. As always, H indicates all the hydrogen isotopes. Thus, D(0) is ultra-dense deuterium, while p(0) is ultra-dense protium normally made from natural hydrogen with a small and unimportant impurity of D. The ultra-dense states are characterized by their spin quantum number s = 1, 2, 3….. [1]. The state s = 2 which is formed most easily in the laboratory at low temperature and pressure, has an H-H distance of 2.3 pm. The state s = 1 is formed from s = 2 both spontaneously at a low rate [28] and by laser pulse induction [29]. In this level s = 1 at an H-H distance of only 0.56 pm [1], it is likely that nuclear reaction takes place rapidly. At similar inter-nuclear distances in muon-catalyzed fusion, the rate constant for fusion D + D is 109 s−1 [21]. This means that the laser field is only required for transferring H(0) from s = 2 to s = 1 at 0.56 pm distance to initiate the nuclear processes, not in any way to drive the nuclear reactions.
2.2. Muon-Induced Fusion
The main reason why muon production is important is the muon-induced fusion process. This fusion process was discovered in 1957 [30,31] and it has been studied by large groups for decades with excellent results [21,32,33]. This method is the only sustainable nuclear fusion method [22] since it employs deuterium as fuel. Tritium is intended to be used by all other fusion methods under development in D + T fusion. Unfortunately, technical development of muon-induced fusion was not done simultaneously with the scientific studies. Instead of developing muon generators, much effort was directed towards finding the maximum length of the muon catalytic chain. This maximum length is how many D + D fusion events that can be induced by one muon before it decays. With the new method of muon production [19] this question is completely irrelevant.
Therefore, the present state-of-the-art in muon-induced fusion is the patented muon generator [19]. There has also recently been serious design work in this field [34].
3. Experimental
The experiments with detection of the sign of the muons from H(0) have been conducted in two main setups, one horizontal setup as used for example in [35] and one vertical setup in as used in [7,11]. The second setup was used for the present experiments. The pressure in the vacuum chamber shown in Figure 1 was 0.2‒2 mbar from the admitted hydrogen (H2, D2) gas. The vacuum pump was an oil-sealed mechanical fore-vacuum pump. The laser was a 5 ns pulsed Nd:YAG laser with pulse energy below 0.5 J. In the H(0) generator, hydrogen gas was catalytically [2] transformed to ultra-dense hydrogen H(0) and fed to the upper surface where the laser induced baryon annihilation reactions. These reactions create kaons and pions, which decay to pions, muons, and other particles such as neutrinos [16,17,18]. A small fraction of the created particles move with high kinetic energy along the vacuum chamber through the current coil as shown in Figure 1. The particle current induces a voltage in the coil which was measured by a fast digital oscilloscope (Tektronix TDS3032 with risetime 1.75 ns). A typical result is shown in Figure 2. This signal clearly shows a chain reaction A → M → N, where A is the annihilating baryon pair in H(0), M is a meson, and N is the muon or pion detected by the current coil.
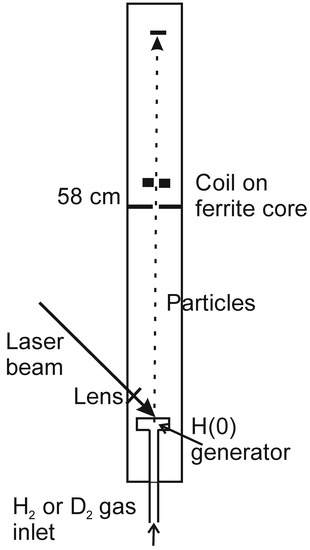
Figure 1.
Schematic drawing of the apparatus. Current coil [30,32] with 19 turns of wire on a ferrite toroid, at 58 cm from the laser target. The connection to the oscilloscope is differential to cancel all signals from the annihilation plasma [35,36].
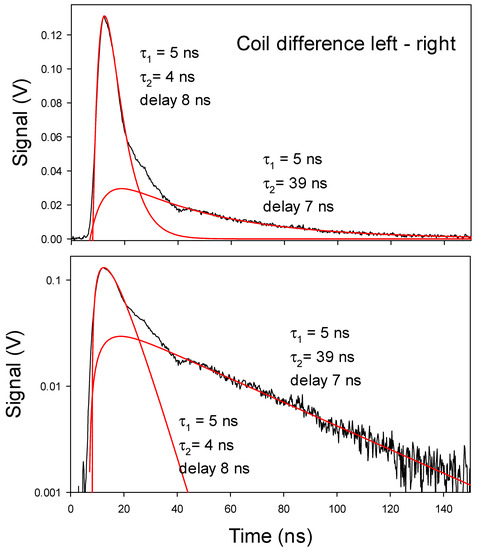
Figure 2.
Linear and logarithmic plots of the differential signal from a current coil with a mainly positive particle signal passing through its center. Laser pulses 0.4 J, 10 Hz pulse repetition, 1064 nm laser light. D(0) in the source in Figure 1, 0.2 mbar D2. The red curves are calculated from Equation (3). The calculated delays of the meson curves after the laser pulse are given. The good exponentials are notable.
The time dependence of the signal is derived from the rate equations for the intermediate meson M (with k1 and k2 being the rate constants in the chain reactions) as:
as
Here nA0 is the number density of the precursor A at time t = 0 thus during the laser pulse. Equation (3) is the solution of Equation (2). The initial number density nM0 of mesons M is set to zero. The curve shape in Equation (3) is used to match the results in Figure 2, as in previous publications [7,8,11,12,14]. The timing results are given as time constants τ = 1/k with suitable indices.
The first peak in Figure 2 follows the laser peak shape (which has a rise time of 2 ns), and thus, has a time constant < 2 ns. It is proposed to be due to pions from the decay of short-lived neutral kaons . The 39 ns time constant signal is due to muons from time-dilated charged pion decay [20,30], with kinetic energy of the pions close to 70 MeV. These pions have mainly been formed in the baryon annihilation [15,37]. The current signals in the first and second distributions in Figure 2 are similar in integrated charge. The origin of the second distribution is mainly (muons from) fast pions directly from the annihilation, while the first distribution is due to (pions from) kaons from the annihilation. As described below, the annihilation creates 2 kaons and 2 fast pions. Thus, the signal intensities should be similar. However, the response of the coil is complex since the velocity of the charged particles will influence the voltage produced in the coil. With p(0) in the source, a negative coil signal is obtained. As described in [35], “In similar coil experiments at higher hydrogen pressure with p(0), the signal is normally negative and concluded to be due to negative muons”.
4. The Nuclear Reaction Process
The reason why the nuclear annihilation processes giving the mesons and muons can take place is, of course, the very short distance between the nucleons, at 0.56 pm in spin state s = 1 for H(0) [1]. From this distance, it is likely that a nuclear reaction takes place rapidly. Most muons formed by meson decay have kinetic energies of >100 MeV [10,11,12]. The meson generating process was identified in [15] as baryon annihilation [38]. The details of this process are partly published [15,37] and more will be published elsewhere.
The nuclear process is a baryon annihilation [15,37]. The energetics for this is typically:
The kinetic energies of the mesons (in parantheses) are shown in Refs. [15,37], measured from their time-dilated decay.
4.1. Kaon and Pion Decay
The decays of kaons and pions are well known [16,17,18]. They often produce muons by processes similar to pair production, or produce muons with the same sign as the decaying charged kaon or pion. Charge is expected to be conserved so equal numbers of positive and negative muons are expected to be formed. In some decays for both neutral and charged kaons, neutral pions are formed instead of charged pions. The neutral pions do not decay to muons but, instead, each neutral pion decays to two high-energy gamma photons. Thus, these processes decrease the number of muons formed.
4.2. Formation and Detection of Muonium
Most mesons decay inside the muon generator, and therefore, the muons are formed there. They have initial kinetic energies of 100–500 MeV since they are from decay of fast kaons and pions [16,17,18]. Thus, they are close to their ionization minimum [39], but they can be slowed down rapidly enough, and therefore, the decay times observed can be close to the values at rest [13]. The hydrogen gas pressure in the muon generator is of the order of mbars and the muons will lose energy both by gas collisions and by collisions in the closely located metal parts in the apparatus. When the muons have reached a low kinetic energy, the possibility of recombination of positive muons with the abundant electrons in the cooled plasma region increases. This produces muonium µ + e−. Such neutral particles are not detectable by wire coils on ferrite toroids, which are used for detecting beams and pulses of charged particles [36] and which have been used in our experiments (Figure 2). It is also likely that muonium particles can pass undetected through the type of Al foil collector used in our previous experiments [10,11,12], since they are neutral. This muonium formation process decreases the number of bare positive muons, and thus it will result in a larger fraction of negative muons in the beam.
It is also possible that negative muonium ions [40] could form in the source. However, the probability of such ions should be low since there is no Coulomb force to form these ions. With slow muons and thermal electrons there is a low probability of muonium ion formation. This effect may produce a slightly larger negative signal in the beam but no clearly observable effect.
5. Discussion of Charge Asymmetry
The charge asymmetry observed in the results from the muon source are based on the different results obtained with p(0) and D(0) at relatively low ejected particle energies (<1 GeV). A comparison with experiments from other groups working at TeV energies [23] is difficult to make. The anti-proton annihilation experiments at low energy [38] do not seem to have checked the charge symmetry of the muons, and there might exist further factors at low energy such as formation of muonium and true muonium. Thus, it was considered necessary to analyze our results carefully. The mesons are created in the annihilation reactions of neutrons with antineutrons or of protons with antiprotons [15,37]. The experiments showing charge asymmetry are published in [13], where it was shown that D(0) as the laser-target material produced mainly positive muons with the correct [18] decay-time 2.23 ± 0.05 µs, while p(0) as target gave shorter lifetimes with a non-exponential decay, probably due to muon capture processes [41] of the negative muons formed in the experiments [13]. It was estimated that p(0) gave 90% negative muons. One important possible mechanism for a charge imbalance could be that the process in D(0) is neutron-antineutron annihilation, while that in p(0) is proton-antiproton annihilation [42]. Since all implications of the annihilation processes are not known, it is important to take care to not miss important information.
These previous asymmetry results have now been confirmed using toroid coils on ferrite cores [35,36] (current transformers) to measure the sign of the particle beam flux in experiments with laser-induced meson pulses. One coil experiment with D(0) is shown in Figure 2, with a positive signal due to pions from decay of short-lived neutral kaons (first peak) and muons from decay of charged pions (second peak and its exponential decay). The muons from the charged pions have the same charge sign as the pions from kaon decay (as described above). Thus, the charge generation is observed for two different formation paths in Figure 2, and the charge asymmetry is still observed. Thus, the charge asymmetry detected in the coil signal must be due to secondary effects, as argued here. If no charge asymmetry existed, the pion and muon distributions in Figure 2 would be invisible or at least weak and distorted. A fundamental process which would give a similar charge asymmetry both for the neutral kaon and the charged pion decays is highly unlikely. The neutral kaon decay produces π+ + π− and the charged pions giving the second contribution in Figure 2 are created by the baryon annihilation as π+ + π−. None of these pair formation processes can create charge, as far as it is known, but this possibility has to be investigated.
From the discussion here, it is concluded that the difference in dominant charge of the muons from D(0) and p(0) is due to the secondary processes in the muon generator. Since negative muons and pions can be captured both in deuterium atoms [41] and deuterium molecules (muon or pion induced fusion), D(0) in the source will result in weaker emission of µ−. Thus, mainly positive muons µ+ will be emitted. Using p(0) in the source will result in much less capture of negative muons µ−, and the likely formation of muonium µ + e− will, instead, decrease the number of positive muons µ+ emitted, such that the main emitted flux of muons is negative in this case.
6. Conclusions
The observed charge asymmetry in the muon emission from the baryon annihilation reactions in the patented muon source is not caused by unknown nuclear processes or by the different annihilation processes, but is due to secondary effects, mainly muon capture and muonium formation. These conclusions will enable further efficient development of intense muon sources with a large fraction of negative muons. Such sources are intended for the only known sustainable fusion process, namely muon-induced (muon-catalyzed) fusion.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data can be received from he author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Holmlid, L.; Zeiner-Gundersen, S. Ultradense protium p(0) and deuterium D(0) and their relation to ordinary Rydberg matter: A review. Phys. Scr. 2019, 94, 075005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlid, L.; Kotarba, A.; Stelmachowski, P. Production of ultra-dense hydrogen H(0): A novel nuclear fuel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 18466–18480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaev, E.; Sudbø, A.; Ashcroft, N.W. A superconductor to superfluid phase transition in liquid metallic hydrogen. Nature 2004, 431, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, P.U.; Holmlid, L. Superfluid ultra-dense deuterium D(-1) at room temperature. Phys. Lett. A 2011, 375, 1344–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, P.U.; Holmlid, L.; Fuelling, S. Search for superconductivity in ultra-dense deuterium D(−1) at room temperature: Depletion of D(−1) at field strength >0.05 T. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2012, 25, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlid, L.; Kotzias, B. Phase transition temperatures of 405-725 K in superfluid ultra-dense hydrogen clusters on metal surfaces. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 45111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlid, L. Two-collector timing of 3-14 MeV/u particles from laser-induced processes in ultra-dense deuterium. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 2013, 22, 1350089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofson, F.; Holmlid, L. Electron-positron pair production observed from laser-induced processes in ultra-dense deuterium D(-1). Laser Part. Beams 2014, 32, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlid, L. Heat generation above break-even from laser-induced fusion in ultra-dense deuterium. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 087129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlid, L. MeV particles in a decay chain process from laser-induced processes in ultra-dense deuterium D(0). Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 2015, 24, 1550026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlid, L. Nuclear particle decay in a multi-MeV beam ejected by pulsed-laser impact on ultra-dense hydrogen H(0). Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 2015, 24, 1550080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlid, L. Mesons from laser-induced processes in ultra-dense hydrogen H(0). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlid, L.; Olafsson, S. Decay of muons generated by laser-induced processes in ultra-dense hydrogen H(0). Heliyon 2019, 5, e01864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlid, L. Laser-induced nuclear processes in ultra-dense hydrogen take place in small non-superfluid HN(0) clusters. J. Clust. Sci. 2018, 30, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlid, L. Energy production by laser-induced annihilation in ultradense hydrogen H(0). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 14592–14595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordling, C.; Österman, J. Physics Handbook; Studentlitteratur: Lund, Sweden, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Burcham, W.E.; Jobes, M. Nuclear and Particle Physics; Pearson: Harlow, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Workman, R.L.; Burkert, V.D.; Crede, V.; Klempt, E.; Thoma, U.; Tiator, L.; Agashe, K.; Aielli, G.; Allanach, B.C.; Amsler, C.; et al. The review of particle physics 2022. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2022, 2022, 083C01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlid, L. Apparatus for Generating Muons with Intended Use in A Fusion Reactor. Swedish Patent nr. SE539684C2, 31 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Holmlid, L. Existing source for muon-catalyzed nuclear fusion can give MW thermal fusion generator. Fusion Sci. Technol. 2018, 75, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balin, D.V.; Ganzha, V.A.; Kozlov, S.M.; Maev, E.M.; Petrov, G.E.; Soroka, M.A.; Schapkin, G.N.; Semenchuk, G.G.; Trofimov, V.A.; Vasiliev, A.A.; et al. High precision study of muon catalyzed fusion in D2 and HD gas. Phys. Part. Nucl. 2011, 42, 185–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlid, L. Muon-catalyzed fusion and annihilation energy generation will supersede non-sustainable T + D nuclear fusion. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2022, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatrchyan, S.; Khachatryan, V.; Sirunyan, A.M.; Tumasyan, A.; Adam, W.; Bergauer, T.; Dragicevic, M.; Erö, J.; Fabjan, C.; Friedl, M.; et al. Measurement of the muon charge asymmetry in pp → W + X production at √s = 7 TeV and an improved determination of light parton distribution functions. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 032004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorringe, T.; Hertzog, D. Precision muon physics. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2015, 84, 73–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogomilov, M.; Karadzhov, Y.; Kolev, D.; Russinov, I.; Tsenov, R.; Vankova-Kirilova, G.; Wang, L.; Xu, F.Y.; Zheng, S.X.; Bertoni, R.; et al. The MICE Muon Beam on ISIS and the beam-line instrumentation of the Muon Ionization Cooling Experiment. J. Instrum. 2012, 7, P05009–P05009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogomilov, M.; Tsenov, R.; Vankova-Kirilova, G.; Song, Y.; Tang, J.; Li, Z.; Bertoni, R.; Bonesini, M.; Chignoli, F.; Mazza, R.; et al. Lattice design and expected performance of the Muon Ionization Cooling Experiment demonstration of ionization cooling. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 2017, 20, 063501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morenzoni, E.; Kottmann, F.; Maden, D.; Matthias, B.; Meyberg, M.; Prokscha, T.; Wutzke, T.; Zimmermann, U. Generation of very slow polarized positive muons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 72, 2793–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmlid, L.; Olafsson, S. Spontaneous ejection of high-energy particles from ultra-dense deuterium D(0). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 10559–10567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlid, L.; Olafsson, S. Charged particle energy spectra from laser-induced processes: Nuclear fusion in ultra-dense deuterium D(0). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, L.W.; Bradner, H.; Crawford, J.F.S.; Falk-Vairant, P.; Good, M.L.; Gow, J.D.; Rosenfeld, A.H.; Solmitz, F.; Stevenson, M.L.; Ticho, H.K.; et al. Catalysis of nuclear reactions by μMesons. Phys. Rev. 1957, 105, 1127–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.D. Catalysis of nuclear reactions between hydrogen isotopes by μMesons. Phys. Rev. 1957, 106, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipowicz, M.; Bystritsky, V.M.; Gerasimov, V.V.; Wozniak, J. Kinetics of muon catalyzed fusion processes in solid H/D mixture. Eur. Phys. J. D 2008, 47, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friar, J.L.; Gibson, B.F.; Jean, H.C.; Payne, G.L. Nuclear transition rates in μ-catalyzed P-D fusion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 66, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.S. Muon Catalyzed Fusion. An investigation of reactor design. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Physics, Imperial College, London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Holmlid, L. Controlling the process of muon formation for muon-catalyzed fusion: Method of non-destructive average muon sign detection. EPJ Tech. Instrum. 2021, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokland, W. Beam Current Monitors. 2009. Available online: https://uspas.fnal.gov/materials/09UNM/BeamCurrentMonitors.pdf.2009 (accessed on 3 May 2021).
- Holmlid, L.; Olafsson, S. Laser-induced annihilation: Relativistic particles from ultra-dense hydrogen H(0). High Energy Density Phys. 2021, 40, 100942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempt, E.; Batty, C.; Richard, J.-M. The antinucleon–nucleon interaction at low energy: Annihilation dynamics. Phys. Rep. 2005, 413, 197–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groom, D.E.; Mokhov, N.V.; Striganov, S.I. Muon stopping power and range tables 10 MeV–100 TeV. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 2001, 78, 183–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, M.; Fukao, Y.; Futatsukawa, K.; Kawamura, N.; Matoba, S.; Mibe, T.; Miyake, Y.; Shimomura, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Hasegawa, K.; et al. Negative muonium ion production with a C12A7 electride film. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1350, 012067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Measday, D. The nuclear physics of muon capture. Phys. Rep. 2001, 354, 243–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlid, L. Novel hydrogen nuclear fuels and their nuclear reactions. Energies 2022. submitted. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).