The Neuroimmunological Nexus of Multiple Sclerosis: Deciphering the Microglial Transcriptomic Tapestry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Neuroimmunological Landscape of Multiple Sclerosis: Microglia as a Central Nexus
3. Microglia as a Sabotaging Agent in Multiple Sclerosis
3.1. Unsettled Role of Microglial Phagocytosis, Phagoptosis, and Trogocytosis
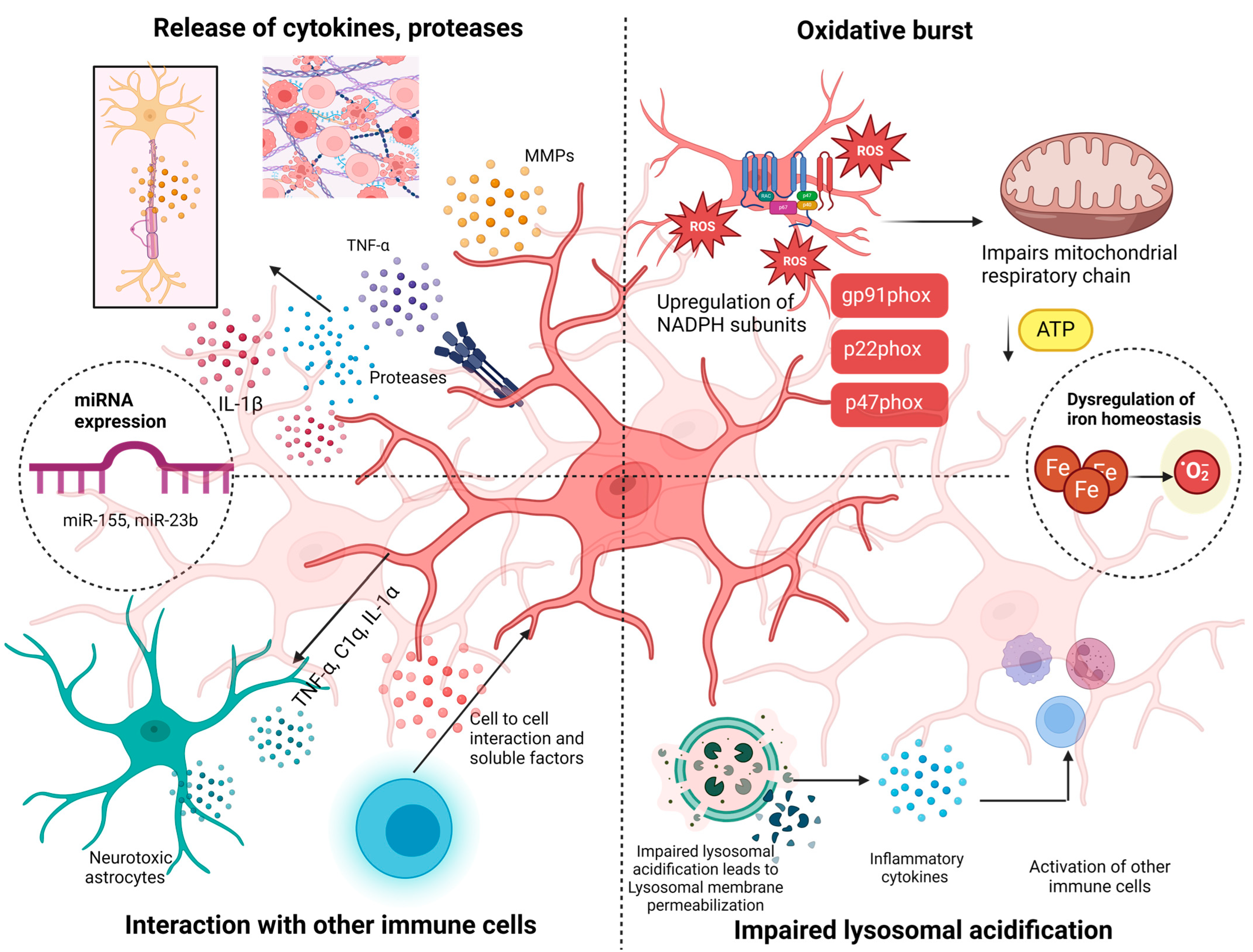
3.2. Involvement of Indirect Pathways in Microglial’s Cascading Effects
4. Paradigm Shift in Microglia—Reconstructing the Microglia in Multiple Sclerosis
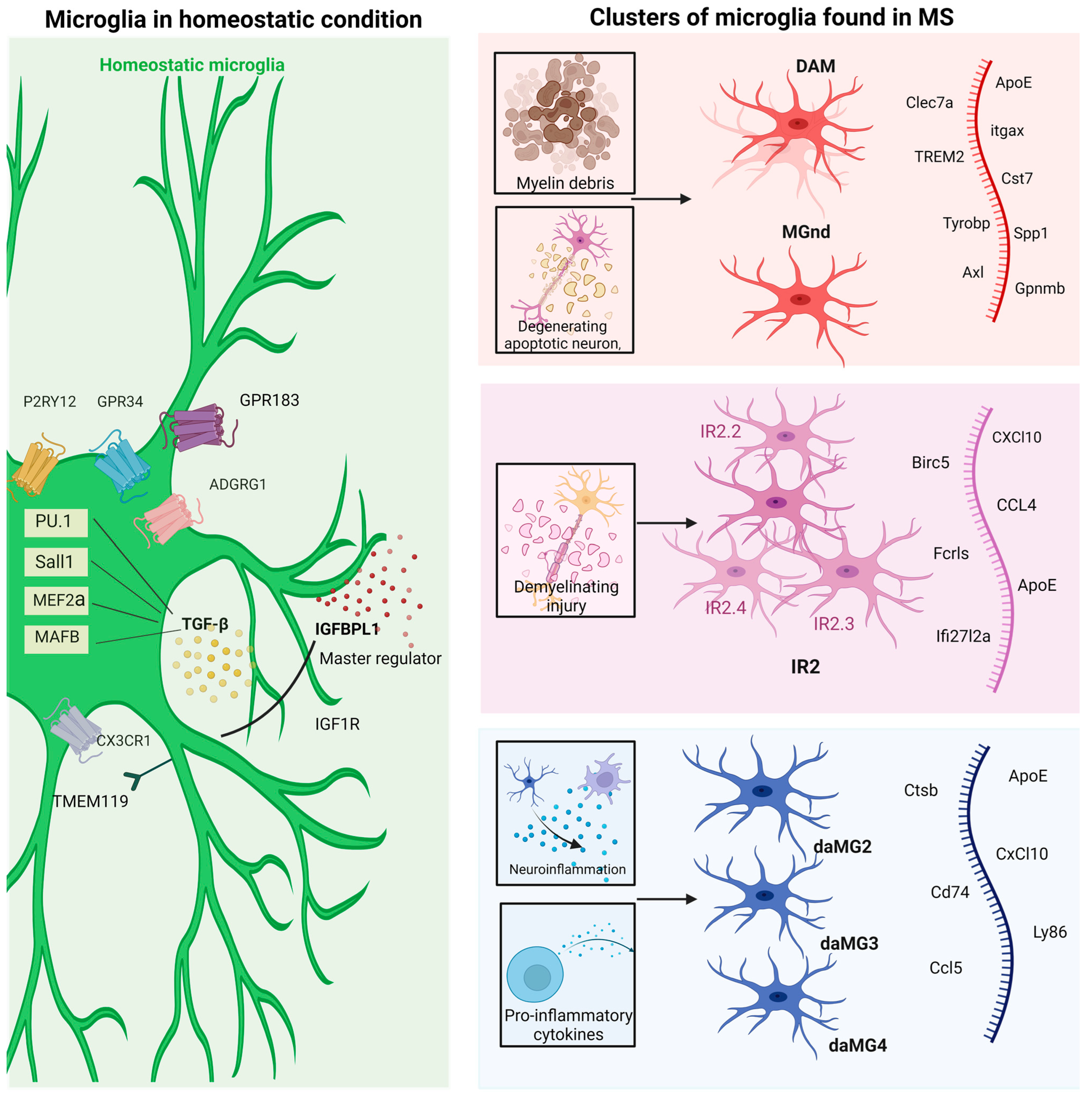
Redefining Physiological Microglia—Homeostatic or Resting Microglia
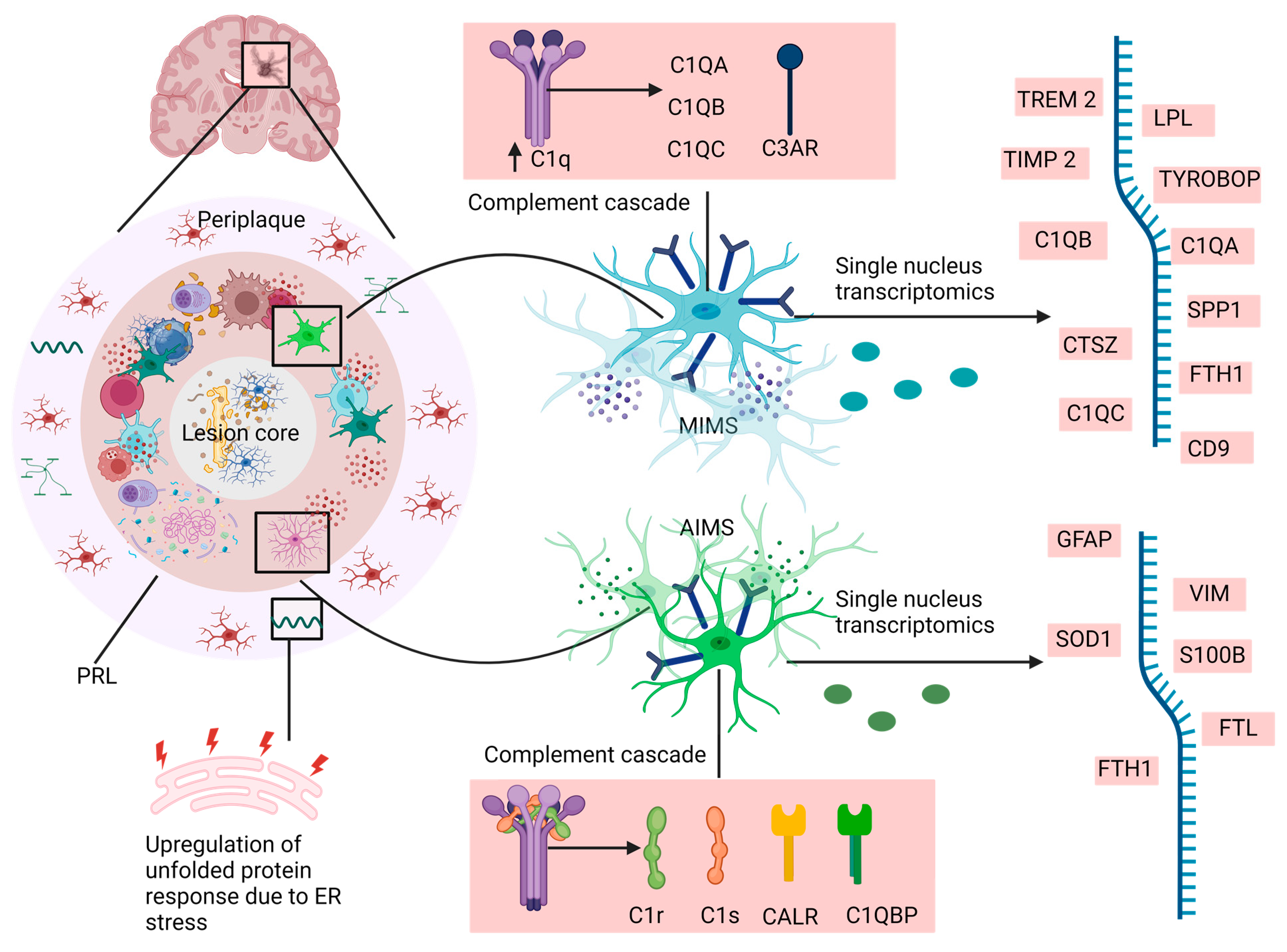
5. The Uncharted Territory of Microglia Transcriptomics in Multiple Sclerosis
6. MS-Associated Microglia versus Neurodegenerative Disorder-Associated Microglia
7. Homeostatic Microglia and Disease-Associated Microglia—Another Transcriptomic Landscape of Microglia in Multiple Sclerosis
8. Morphological Cues—Microglial Morphological Topology
9. Indiscretion of M1 versus M2 Framework
10. Discussion
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, W.M.; Colonna, M. The identity and function of microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat. Immun. 2018, 19, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, I.; Han, S.J.; Kaur, G.; Crane, C.; Parsa, A.T. The role of microglia in central nervous system immunity and glioma immunology. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2010, 17, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.A.; Boddeke, H.W.G.M.; Kettenmann, H. Microglia in physiology and disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 619–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vattoth, S.; Kadam, G.H.; Gaddikeri, S. Revised McDonald Criteria, MAGNIMS consensus and other relevant guidelines for diagnosis and follow up of MS: What radiologists need to know? Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. 2021, 50, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, D.L.J.N.E.J.M.; Daniel, S.; Reich, M.D.; Claudia, F.; Lucchinetti, M.D.; Peter, A.; Calabresi, M.D. Multiple Sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 378, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Deczkowska, A.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Weiner, A.; Colonna, M.; Schwartz, M.; Amit, I. Disease-associated microglia: A universal immune sensor of neurodegeneration. Cell 2018, 173, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolicelli, R.C.; Sierra, A.; Stevens, B.; Tremblay, M.-E.; Aguzzi, A.; Ajami, B.; Amit, I.; Audinat, E.; Bechmann, I.; Bennett, M.; et al. Microglia states and nomenclature: A field at its crossroads. Neuron 2022, 110, 3458–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasemann, S.; Madore, C.; Cialic, R.; Baufeld, C.; Calcagno, N.; El Fatimy, R.; Beckers, L.; O’Loughlin, E.; Xu, Y.; Fanek, Z.; et al. The TREM2-APOE pathway drives the transcriptional phenotype of dysfunctional microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Immunity 2017, 47, 566–581.E9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Absinta, M.; Maric, D.; Gharagozloo, M.; Garton, T.; Smith, M.D.; Jin, J.; Fitzgerald, K.C.; Song, A.; Liu, P.; Lin, J.-P. A lymphocyte–microglia–astrocyte axis in chronic active multiple sclerosis. Nature 2021, 597, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, T.R.; Dufort, C.; Dissing-Olesen, L.; Giera, S.; Young, A.; Wysoker, A.; Walker, A.J.; Gergits, F.; Segel, M.; Nemesh, J.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing of microglia throughout the mouse lifespan and in the injured brain reveals complex cell-state changes. Immunity 2019, 50, 253–271.E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschallinger, J.; Iram, T.; Zardeneta, M.; Lee, S.E.; Lehallier, B.; Haney, M.S.; Pluvinage, J.V.; Mathur, V.; Hahn, O.; Morgens, D.W.; et al. Lipid-droplet-accumulating microglia represent a dysfunctional and proinflammatory state in the aging brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, K.; Lee, S.-J.; Mook-Jung, I. White matter-associated microglia: New players in brain aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 75, 101574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinz, M.; Jung, S.; Priller, J. Microglia biology: One century of evolving concepts. Cell 2019, 179, 292–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendimu, M.Y.; Hooks, S.B. Microglia phenotypes in aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Cells 2022, 11, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherafat, A.; Pfeiffer, F.; Reiss, A.M.; Wood, W.M.; Nishiyama, A. Microglial neuropilin-1 promotes oligodendrocyte expansion during development and remyelination by trans-activating platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons, V.; Rivest, S. Beneficial Roles of Microglia and Growth Factors in MS, a Brief Review. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, H.; Young, K.; Qureshi, M.; Rowe, R.K.; Lifshitz, J. Quantitative microglia analyses reveal diverse morphologic responses in the rat cortex after diffuse brain injury. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, A.G.; Orr, A.L.; Li, X.-J.; E Gross, R.; Traynelis, S.F. Adenosine A2A receptor mediates microglial process retraction. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dendrou, C.A.; Fugger, L.; Friese, M.A. Immunopathology of multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, B.F.G.; Pirko, I.; Lucchinetti, C.F. Pathology of multiple sclerosis: Where do we stand? CONTINUUM Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2013, 19, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, C.K.; Saijo, K.; Winner, B.; Marchetto, M.C.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms Underlying Inflammation in Neurodegeneration. Cell 2010, 140, 918–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charabati, M.; Wheeler, M.A.; Weiner, H.L.; Quintana, F.J. Multiple sclerosis: Neuroimmune crosstalk and therapeutic targeting. Cell 2023, 186, 1309–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierhansl, L.; Hartung, H.-P.; Aktas, O.; Ruck, T.; Roden, M.; Meuth, S.G. Thinking outside the box: Non-canonical targets in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 578–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baecher-Allan, C.; Kaskow, B.J.; Weiner, H.L. Multiple Sclerosis: Mechanisms and Immunotherapy. Neuron 2018, 97, 742–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandolesi, G.; Gentile, A.; Musella, A.; Fresegna, D.; De Vito, F.; Bullitta, S.; Sepman, H.; Marfia, G.A.; Centonze, D. Synaptopathy connects inflammation and neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubé, B.; Lévesque, S.A.; Paré, A.; Chamma, É.; Kébir, H.; Gorina, R.; Lécuyer, M.-A.; Alvarez, J.I.; De Koninck, Y.; Engelhardt, B.; et al. Neutrophils mediate blood–spinal cord barrier disruption in demyelinating neuroinflammatory diseases. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 2438–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal-Bianco, A.; Grabner, G.; Kronnerwetter, C.; Weber, M.; Höftberger, R.; Berger, T.; Auff, E.; Leutmezer, F.; Trattnig, S.; Lassmann, H.; et al. Slow expansion of multiple sclerosis iron rim lesions: Pathology and 7 T magnetic resonance imaging. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 133, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, E.; Galeel, A.A.; Ramadan, I.; Gaber, D.; Mustafa, H.; Mekky, J. Iron deposition in multiple sclerosis: Overall load or distribution alteration? Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2022, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zierfuss, B.; Wang, Z.; Jackson, A.N.; Moezzi, D.; Yong, V.W.; Disorders, R. Iron in multiple sclerosis–Neuropathology, immunology, and real-world considerations. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2023, 78, 104934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkady, A.M.; Cobzas, D.; Sun, H.; Blevins, G.; Wilman, A.H. Progressive iron accumulation across multiple sclerosis phenotypes revealed by sparse classification of deep gray matter. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 1464–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipnis, J. Multifaceted interactions between adaptive immunity and the central nervous system. Science 2016, 353, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Microbiota and neuroimmune signalling—Metchnikoff to microglia. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louveau, A.; Harris, T.H.; Kipnis, J. Revisiting the mechanisms of CNS immune privilege. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-R.; Seong, K.-J.; Kim, W.-J.; Jung, J.-Y. Epigallocatechin gallate protects against hypoxia-induced inflammation in microglia via NF-κB suppression and Nrf-2/HO-1 activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, J.; Xu, Z.; Yan, H.; Tang, B.; Liu, C.; Chen, C.; Meng, Q. Microglia-containing human brain organoids for the study of brain development and pathology. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 28, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galatro, T.F.; Holtman, I.R.; Lerario, A.M.; Vainchtein, I.D.; Brouwer, N.; Sola, P.R.; Veras, M.M.; Pereira, T.F.; Leite, R.E.P.; Möller, T.; et al. Transcriptomic analysis of purified human cortical microglia reveals age-associated changes. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Sagare, A.P.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood–brain barrier breakdown in Alzheimer disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendiola, A.S.; Yan, Z.; Dixit, K.; Johnson, J.R.; Bouhaddou, M.; Meyer-Franke, A.; Shin, M.-G.; Yong, Y.; Agrawal, A.; MacDonald, E.; et al. Defining blood-induced microglia functions in neurodegeneration through multiomic profiling. Nat. Immunol. 2023, 24, 1173–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium. Multiple sclerosis genomic map implicates peripheral immune cells and microglia in susceptibility. Science 2019, 365, eaav7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correale, J.; Hohlfeld, R.; Baranzini, S.E. The role of the gut microbiota in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2022, 18, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, J.R.; Veiga-Fernandes, H. Neuroimmune circuits in inter-organ communication. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 20, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothhammer, V.; Borucki, D.M.; Tjon, E.C.; Takenaka, M.C.; Chao, C.-C.; Ardura-Fabregat, A.; De Lima, K.A.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Hewson, P.; Staszewski, O.; et al. Microglial control of astrocytes in response to microbial metabolites. Nature 2018, 557, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agirman, G.; Yu, K.B.; Hsiao, E.Y. Signaling inflammation across the gut-brain axis. Science 2021, 374, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelman, J.S.; Martin, L.B. Vertebrate sickness behaviors: Adaptive and integrated neuroendocrine immune responses. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2009, 49, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardiguian, S.; Ladds, E.; Turner, R.; Shepherd, H.; Campbell, S.J.; Anthony, D.C. The contribution of the acute phase response to the pathogenesis of relapse in chronic-relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalitis models of multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbierato, M.; Borri, M.; Facci, L.; Zusso, M.; Skaper, S.D.; Giusti, P. Expression and differential responsiveness of central nervous system glial cell populations to the acute phase protein serum amyloid A. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, S.J.; Meier, U.; Mardiguian, S.; Jiang, Y.; Littleton, E.T.; Bristow, A.; Relton, J.; Connor, T.J.; Anthony, D.C. Sickness behaviour is induced by a peripheral CXC-chemokine also expressed in Multiple Sclerosis and EAE. Brain, Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voet, S.; Prinz, M.; van Loo, G. Microglia in central nervous system inflammation and multiple sclerosis pathology. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosselin, D.; Skola, D.; Coufal, N.G.; Holtman, I.R.; Schlachetzki, J.C.M.; Sajti, E.; Jaeger, B.N.; O’Connor, C.; Fitzpatrick, C.; Pasillas, M.P.; et al. An environment-dependent transcriptional network specifies human microglia identity. Science 2017, 356, eaal3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, V.W. Microglia in multiple sclerosis: Protectors turn destroyers. Neuron 2022, 110, 3534–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Noort, J.M.; Baker, D.; Kipp, M.; Amor, S. The pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis: A series of unfortunate events. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2023, 214, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distéfano-Gagné, F.; Bitarafan, S.; Lacroix, S.; Gosselin, D. Roles and regulation of microglia activity in multiple sclerosis: Insights from animal models. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2023, 24, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Yang, B.; Liu, W.; Tan, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, X. Emerging role of non-coding RNAs in neuroinflammation mediated by microglia and astrocytes. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.-T.; Sharma, R.; Lim, J.L.; Haider, L.; Frischer, J.M.; Drexhage, J.; Mahad, D.; Bradl, M.; van Horssen, J.; Lassmann, H. NADPH oxidase expression in active multiple sclerosis lesions in relation to oxidative tissue damage and mitochondrial injury. Brain 2012, 135, 886–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikalov, S. Cross talk between mitochondria and NADPH oxidases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.C.; Neher, J.J. Microglial phagocytosis of live neurons. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, G. Synaptic nibbling. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, T.K.; Ruthazer, E.S. Microglial trogocytosis and the complement system regulate axonal pruning in vivo. Elife 2021, 10, e62167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G.C.; Neher, J.J. Eaten alive! Cell death by primary phagocytosis:’phagoptosis’. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012, 37, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, C.A.; Popescu, A.S.; Kitchener, E.J.; Allendorf, D.H.; Puigdellívol, M.; Brown, G.C. Microglial phagocytosis of neurons in neurodegeneration, and its regulation. J. Neurochem. 2021, 158, 621–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, D.; Shi, Z.; Smith, A.D.; Li, W.; Gao, Y. Central nervous system diseases related to pathological microglial phagocytosis. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2021, 27, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Beja-Glasser, V.F.; Nfonoyim, B.M.; Frouin, A.; Li, S.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Merry, K.M.; Shi, Q.; Rosenthal, A.; Barres, B.A.; et al. Complement and microglia mediate early synapse loss in Alzheimer mouse models. Science 2016, 352, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Wu, X.; Fan, B.; Li, N.; Lin, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ma, J. Up-regulation of microglial cathepsin C expression and activity in lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Han, C.; Liang, J.; Hou, C.; Xiao, H.; Ikenaka, K.; Ma, J. The induction of neuronal death by up-regulated microglial cathepsin H in LPS-induced neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, H. Cathepsin regulation on microglial function. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2020, 1868, 140465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quick, J.D.; Silva, C.; Wong, J.H.; Lim, K.L.; Reynolds, R.; Barron, A.M.; Zeng, J.; Lo, C.H. Lysosomal acidification dysfunction in microglia: An emerging pathogenic mechanism of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarisbrick, I.A.; Blaber, S.I.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Genain, C.P.; Blaber, M.; Rodriguez, M. Activity of a newly identified serine protease in CNS demyelination. Brain 2002, 125, 1283–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, W.; Sun, Y.; Wu, M. New insight on microglia activation in neurodegenerative diseases and therapeutics. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1308345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siao, C.-J.; Fernandez, S.R.; Tsirka, S.E. Cell type-specific roles for tissue plasminogen activator released by neurons or microglia after excitotoxic injury. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 3234–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teesalu, T.; Hinkkanen, A.E.; Vaheri, A. Coordinated induction of extracellular proteolysis systems during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 2227–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarisbrick, I.J.A.i.m.S.; Diseases, E.D. The multiple sclerosis degradome: Enzymatic cascades in development and progression of central nervous system inflammatory disease. Adv. Mult. Scler. Exp. Demyelinating Dis. 2008, 318, 133–175. [Google Scholar]
- Ramaglia, V.; Hughes, T.R.; Donev, R.M.; Ruseva, M.M.; Wu, X.; Huitinga, I.; Baas, F.; Neal, J.W.; Morgan, B.P. C3-dependent mechanism of microglial priming relevant to multiple sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegenhain, C.; Vieth, B.; Parekh, S.; Reinius, B.; Guillaumet-Adkins, A.; Smets, M.; Leonhardt, H.; Heyn, H.; Hellmann, I.; Enard, W. Comparative Analysis of Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Methods. Mol. Cell 2017, 65, 631–643.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuste, R.; Hawrylycz, M.; Aalling, N.; Aguilar-Valles, A.; Arendt, D.; Armañanzas, R.; Ascoli, G.A.; Bielza, C.; Bokharaie, V.; Bergmann, T.B.; et al. A community-based transcriptomics classification and nomenclature of neocortical cell types. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 1456–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettas, S.; Karagianni, K.; Kanata, E.; Chatziefstathiou, A.; Christoudia, N.; Xanthopoulos, K.; Sklaviadis, T.; Dafou, D. Profiling Microglia through Single-Cell RNA Sequencing over the Course of Development, Aging, and Disease. Cells 2022, 11, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Jiang, J.; Tan, Y.; Chen, S. Microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: Mechanism and potential therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.-Y. From bulk, single-cell to spatial RNA sequencing. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2021, 13, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Bisht, K.; Eyo, U.B. A Comparative Biology of Microglia Across Species. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geirsdottir, L.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Weiner, A.; Bohlen, S.C.; Neuber, J.; Balic, A.; Giladi, A.; Sheban, F.; Dutertre, C.-A.; et al. Cross-Species Single-Cell Analysis Reveals Divergence of the Primate Microglia Program. Cell 2019, 179, 1609–1622.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benarroch, E.E. Microglia: Multiple roles in surveillance, circuit shaping, and response to injury. Neurology 2013, 81, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmerjahn, A.; Kirchhoff, F.; Helmchen, F. Resting Microglial Cells Are Highly Dynamic Surveillants of Brain Parenchyma in Vivo. Science 2005, 308, 1314–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raivich, G. Like cops on the beat: The active role of resting microglia. Trends Neurosci. 2005, 28, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vankriekelsvenne, E.; Chrzanowski, U.; Manzhula, K.; Greiner, T.; Wree, A.; Hawlitschka, A.; Llovera, G.; Zhan, J.; Joost, S.; Schmitz, C.; et al. Transmembrane protein 119 is neither a specific nor a reliable marker for microglia. Glia 2022, 70, 1170–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenkhuis, B.; Somarakis, A.; Kleindouwel, L.R.; van Roon-Mom, W.M.; Höllt, T.; van der Weerd, L. Co-expression patterns of microglia markers Iba1, TMEM119 and P2RY12 in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2022, 167, 105684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Cho, K.-S.; Wei, X.; Xu, F.; Lennikov, A.; Hu, G.; Tang, J.; Guo, S.; Chen, J.; Kriukov, E.; et al. IGFBPL1 is a master driver of microglia homeostasis and resolution of neuroinflammation in glaucoma and brain tauopathy. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, C.-C.; Sankowski, R.; Prinz, M.; Smolders, J.; Huitinga, I.; Hamann, J. GPCRomics of Homeostatic and Disease-Associated Human Microglia. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 674189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Sankowski, R.; Staszewski, O.; Prinz, M. Microglia Heterogeneity in the Single-Cell Era. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, T.; Sankowski, R.; Staszewski, O.; Böttcher, C.; Amann, L.; Sagar; Scheiwe, C.; Nessler, S.; Kunz, P.; Van Loo, G.; et al. Spatial and temporal heterogeneity of mouse and human microglia at single-cell resolution. Nature 2019, 566, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zia, S.; Rawji, K.S.; Michaels, N.J.; Burr, M.; Kerr, B.J.; Healy, L.M.; Plemel, J.R. Microglia Diversity in Health and Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.; Ikezu, T. Transcriptional and Epigenetic Regulation of Microglia in Health and Disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, P.S.; Dando, O.; Emelianova, K.; He, X.; McKay, S.; Hardingham, G.E.; Qiu, J. Microglial identity and inflammatory responses are controlled by the combined effects of neurons and astrocytes. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamma, E.; Lasisi, W.; Libner, C.; Ng, H.S.; Plemel, J.R. Central nervous system macrophages in progressive multiple sclerosis: Relationship to neurodegeneration and therapeutics. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittner, S.; Zipp, F. A lymphocyte-glia connection sets the pace for smoldering inflammation. Cell 2021, 184, 5696–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangaraju, S.; Dammer, E.B.; Raza, S.A.; Rathakrishnan, P.; Xiao, H.; Gao, T.; Duong, D.M.; Pennington, M.W.; Lah, J.J.; Seyfried, N.T.; et al. Identification and therapeutic modulation of a pro-inflammatory subset of disease-associated-microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2018, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, M.N.; Sethi, I.; Harris, T.H. Microglia in CNS infections: Insights from Toxoplasma gondii and other pathogens. Trends Parasitol. 2022, 38, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Revilla, J.; Boza-Serrano, A.; Espinosa-Oliva, A.M.; Soto, M.S.; Deierborg, T.; Ruiz, R.; de Pablos, R.M.; Burguillos, M.A.; Venero, J.L. Galectin-3, a rising star in modulating microglia activation under conditions of neurodegeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Li, X. Different phenotypes of microglia in animal models of Alzheimer disease. Immun. Ageing 2022, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordão, M.J.C.; Sankowski, R.; Brendecke, S.M.; Sagar; Locatelli, G.; Tai, Y.-H.; Tay, T.L.; Schramm, E.; Armbruster, S.; Hagemeyer, N. Single-cell profiling identifies myeloid cell subsets with distinct fates during neuroinflammation. Science 2019, 363, eaat7554. [Google Scholar]
- van der Poel, M.; Ulas, T.; Mizee, M.R.; Hsiao, C.-C.; Miedema, S.S.M.; Adelia, N.; Schuurman, K.G.; Helder, B.; Tas, S.W.; Schultze, J.L.; et al. Transcriptional profiling of human microglia reveals grey–white matter heterogeneity and multiple sclerosis-associated changes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Itriago, A.; Radford, R.A.W.; Aramideh, J.A.; Maurel, C.; Scherer, N.M.; Don, E.K.; Lee, A.; Chung, R.S.; Graeber, M.B.; Morsch, M. Microglia morphophysiological diversity and its implications for the CNS. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 997786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Platas, S.G.; Cruceanu, C.; Chen, G.G.; Turecki, G.; Mechawar, N. Evidence for increased microglial priming and macrophage recruitment in the dorsal anterior cingulate white matter of depressed suicides. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 42, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madry, C.; Kyrargyri, V.; Arancibia-Cárcamo, I.L.; Jolivet, R.; Kohsaka, S.; Bryan, R.M.; Attwell, D. Microglial ramification, surveillance, and interleukin-1β release are regulated by the two-pore domain K+ channel THIK-1. Neuron 2018, 97, 299–312.e6. [Google Scholar]
- Reddaway, J.; Richardson, P.E.; Bevan, R.J.; Stoneman, J.; Palombo, M. Microglial morphometric analysis: So many options, so little consistency. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1211188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, T.R.F.; Murphy, S.M.; Rowe, R.K. Comparisons of quantitative approaches for assessing microglial morphology reveal inconsistencies, ecological fallacy, and a need for standardization. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cătălin, B.; Stopper, L.; Bălşeanu, T.-A.; Scheller, A. The in situ morphology of microglia is highly sensitive to the mode of tissue fixation. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2017, 86, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolhoseini, M.; Kluge, M.G.; Walker, F.R.; Johnson, S.J. Segmentation, Tracing, and Quantification of Microglial Cells from 3D Image Stacks. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Pardon, M.C.; Agostini, A.; Faas, H.; Duan, J.; Ward, W.O.; Easton, F.; Auer, D.; Bai, L. Novel Methods for Microglia Segmentation, Feature Extraction, and Classification. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2016, 14, 1366–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, W.Y.; Ma, C.H.E. Bipolar/rod-shaped microglia are proliferating microglia with distinct M1/M2 phenotypes. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7279. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.E.; Morganti-Kossmann, C.; Lifshitz, J.; Ziebell, J.M. Rod microglia: A morphological definition. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, K.R.; Denman, C.R.; Dubisch, P.S.; Akhter, M.; Lifshitz, J. An update on the rod microglia variant in experimental and clinical brain injury and disease. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcaa227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, F.; Sun, M.; Wu, N.; Liu, B.; Yi, X.; Ge, R.; Fan, X. Microglia in the context of multiple sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1157287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prineas, J.W.; Lee, S.J.J.o.N.; Neurology, E. Microglia subtypes in acute, subacute, and chronic multiple sclerosis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2023, 82, nlad046. [Google Scholar]
- Bisht, K.; Sharma, K.; Lacoste, B.; Tremblay, M. Dark microglia: Why are they dark? Commun. Integr. Biol. 2016, 9, e1230575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonk, F.; Roux, P.; Flamant, P.; Fiette, L.; Bozza, F.A.; Simard, S.; Lemaire, M.; Plaud, B.; Shorte, S.L.; Sharshar, T.; et al. Phenotypic clustering: A novel method for microglial morphology analysis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, G.; Cubero, R.J.A.; Kanari, L.; Venturino, A.; Schulz, R.; Scolamiero, M.; Agerberg, J.; Mathys, H.; Tsai, L.-H.; Chachólski, W. Microglial MorphOMICs unravel region- and sex-dependent morphological phenotypes from postnatal development to degeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Mills, C.D.; Kincaid, K.; Alt, J.M.; Heilman, M.J.; Hill, A.M.J.T.J.o.i. M-1/M-2 macrophages and the Th1/Th2 paradigm. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 6166–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.E.; Damle, S.S.; Wancewicz, E.V.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Hart, C.E.; Mazur, C.; Swayze, E.E.; Kamme, F. A modular analysis of microglia gene expression, insights into the aged phenotype. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransohoff, R.M. A polarizing question: Do M1 and M2 microglia exist? Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Schmidt, S.V.; Sander, J.; Draffehn, A.; Krebs, W.; Quester, I.; De Nardo, D.; Gohel, T.D.; Emde, M.; Schmidleithner, L.; et al. Transcriptome-based network analysis reveals a spectrum model of human macrophage activation. Immunity 2014, 40, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sale, A.; Berardi, N.; Maffei, L. Environment and Brain Plasticity: Towards an Endogenous Pharmacotherapy. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 189–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohlen, C.J.; Bennett, F.C.; Tucker, A.F.; Collins, H.Y.; Mulinyawe, S.B.; Barres, B.A. Diverse Requirements for Microglial Survival, Specification, and Function Revealed by Defined-Medium Cultures. Neuron 2017, 94, 759–773.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotti, A.; Ransohoff, R.M. Microglial Physiology and Pathophysiology: Insights from Genome-wide Transcriptional Profiling. Immunity 2016, 44, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, J.D.; Olschowka, J.A.; O’Banion, M.K. Neuroinflammation and M2 microglia: The good, the bad, and the inflamed. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, W.; Zhang, J. A richer and more diverse future for microglia phenotypes. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmetzyanova, E.; Kletenkov, K.; Mukhamedshina, Y.; Rizvanov, A. Different Approaches to Modulation of Microglia Phenotypes After Spinal Cord Injury. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; You, Z. Switching of the Microglial Activation Phenotype Is a Possible Treatment for Depression Disorder. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.-L.; Yuan, Y.; Tian, L. Microglial regional heterogeneity and its role in the brain. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 25, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, V.H.; Cunningham, C.; Holmes, C. Systemic infections and inflammation affect chronic neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koussounadis, A.; Langdon, S.P.; Um, I.H.; Harrison, D.J.; Smith, V.A. Relationship between differentially expressed mRNA and mRNA-protein correlations in a xenograft model system. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep10775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, T.; Güell, M.; Serrano, L. Correlation of mRNA and protein in complex biological samples. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 3966–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, S.E.; Kamath, T.; Dissing-Olesen, L.; Hammond, T.R.; de Soysa, T.Y.; Young, A.M.H.; Murphy, S.; Abdulraouf, A.; Nadaf, N.; Dufort, C.; et al. Dissection of artifactual and confounding glial signatures by single-cell sequencing of mouse and human brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwecka, M.; Rajewsky, N.; Rybak-Wolf, A. Single-cell and spatial transcriptomics: Deciphering brain complexity in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2023, 19, 346–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanamsagar, R.; Bilbo, S.D. Environment matters: Microglia function and dysfunction in a changing world. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2017, 47, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharjee, S.; Gordon, P.M.K.; Lee, B.H.; Read, J.; Workentine, M.L.; Sharkey, K.A.; Pittman, Q.J. Characterization of microglial transcriptomes in the brain and spinal cord of mice in early and late experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis using a RiboTag strategy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, I.C.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Wheeler, M.A.; Li, Z.; Rothhammer, V.; Linnerbauer, M.; Sanmarco, L.M.; Guo, L.; Blain, M.; Zandee, S.E.J.; et al. Barcoded viral tracing of single-cell interactions in central nervous system inflammation. Science 2021, 372, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransohoff, R.M.; Kivisäkk, P.; Kidd, G. Three or more routes for leukocyte migration into the central nervous system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, F.-L.; Chithanathan, K.; Lilleväli, K.; Yuan, X.; Tian, L. Differences of microglia in the brain and the pinal cord. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 504. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jha, A.; Kumar, H. The Neuroimmunological Nexus of Multiple Sclerosis: Deciphering the Microglial Transcriptomic Tapestry. Neuroglia 2024, 5, 234-253. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia5030017
Jha A, Kumar H. The Neuroimmunological Nexus of Multiple Sclerosis: Deciphering the Microglial Transcriptomic Tapestry. Neuroglia. 2024; 5(3):234-253. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia5030017
Chicago/Turabian StyleJha, Akanksha, and Hemant Kumar. 2024. "The Neuroimmunological Nexus of Multiple Sclerosis: Deciphering the Microglial Transcriptomic Tapestry" Neuroglia 5, no. 3: 234-253. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia5030017
APA StyleJha, A., & Kumar, H. (2024). The Neuroimmunological Nexus of Multiple Sclerosis: Deciphering the Microglial Transcriptomic Tapestry. Neuroglia, 5(3), 234-253. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia5030017




