l-Dopa and Fluoxetine Upregulate Astroglial 5-HT2B Receptors and Ameliorate Depression in Parkinson’s Disease Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. 6-OHDA Treatment
2.3. Drug Treatment
2.4. Behavioral Tests
2.5. Acute Isolation of Cells
2.6. Primary Cultures of Astrocytes
2.7. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Statistics
2.10. Materials
3. Results
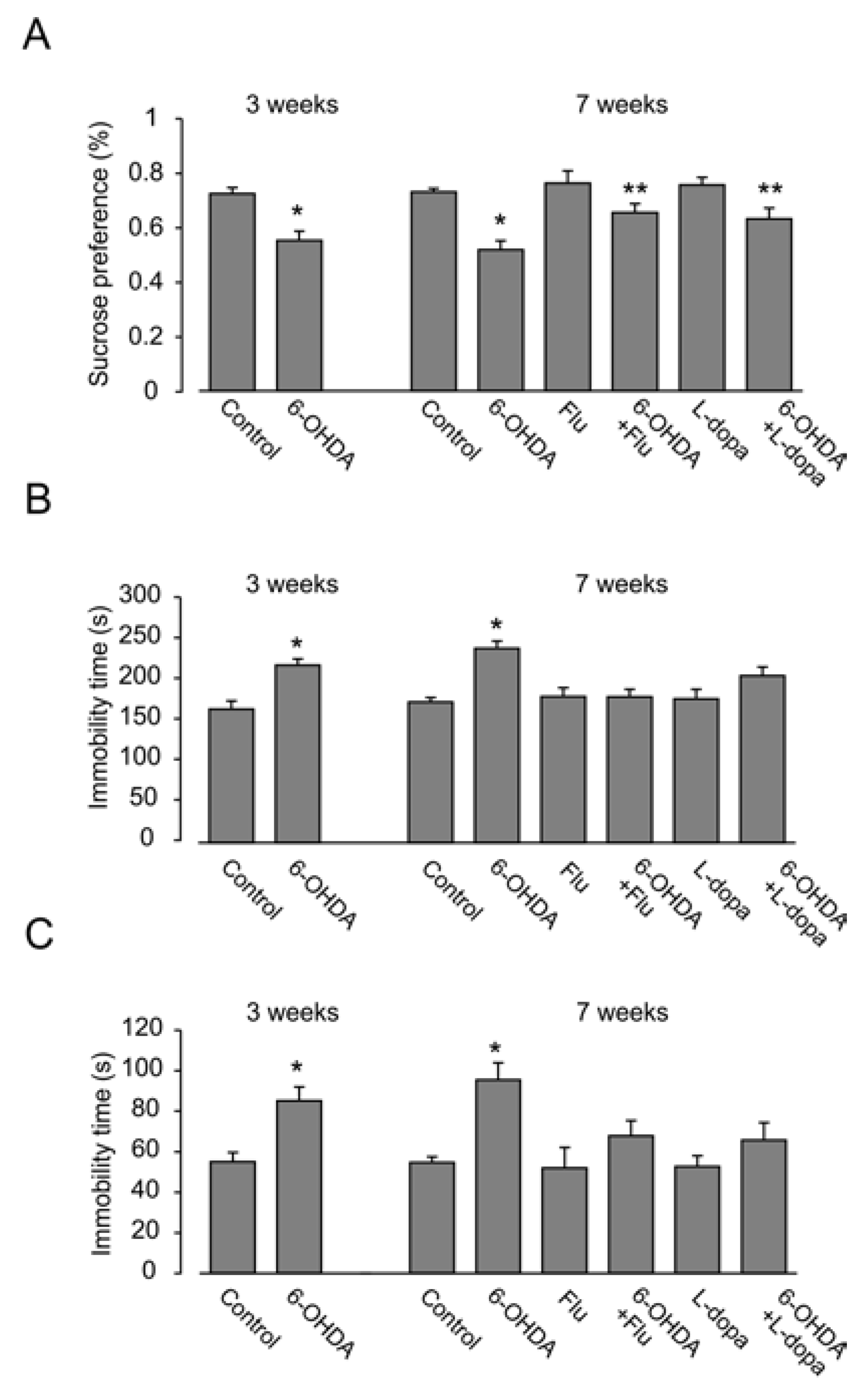
3.1. Depressive Behavior
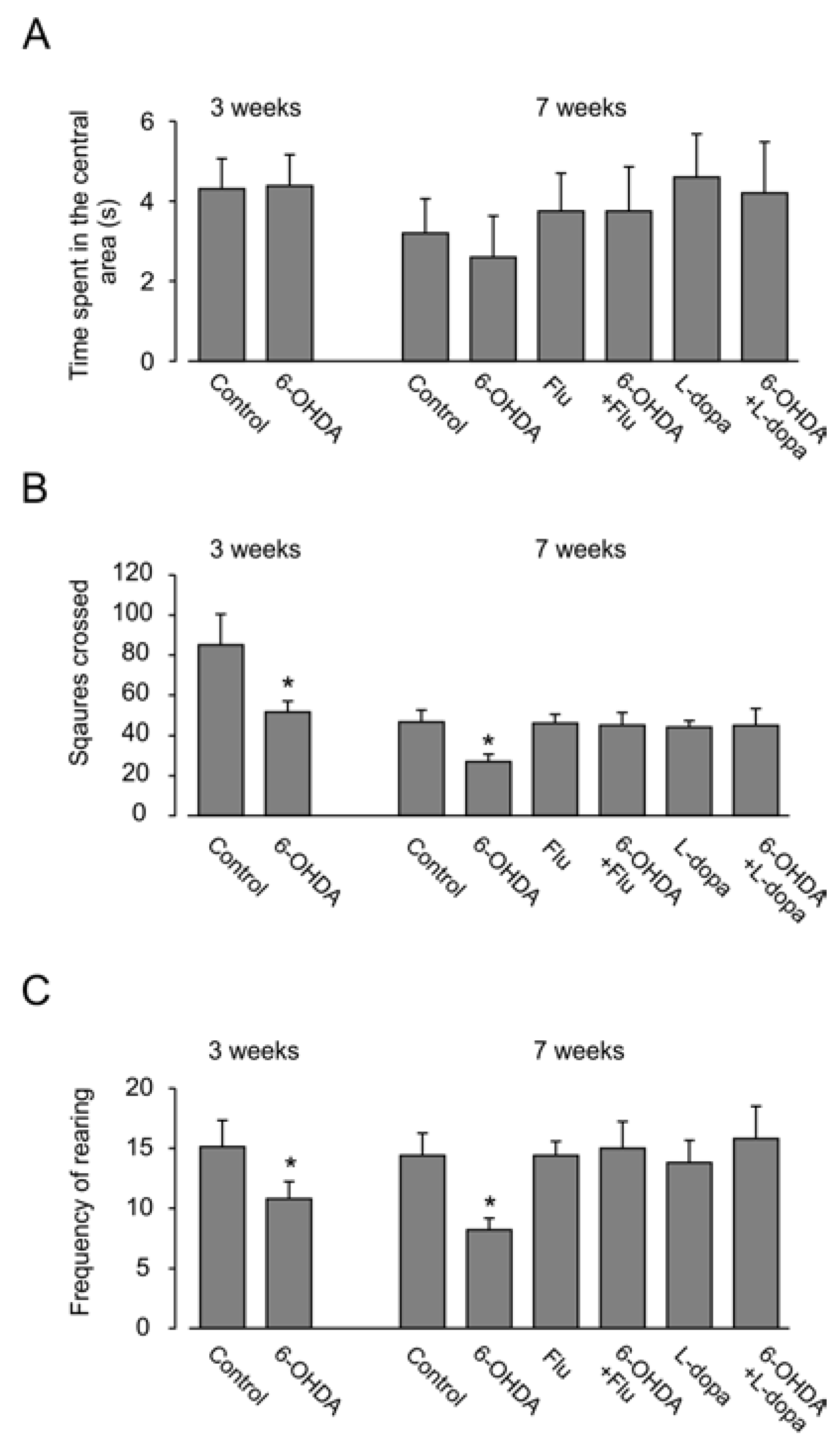
3.2. Motor Activity
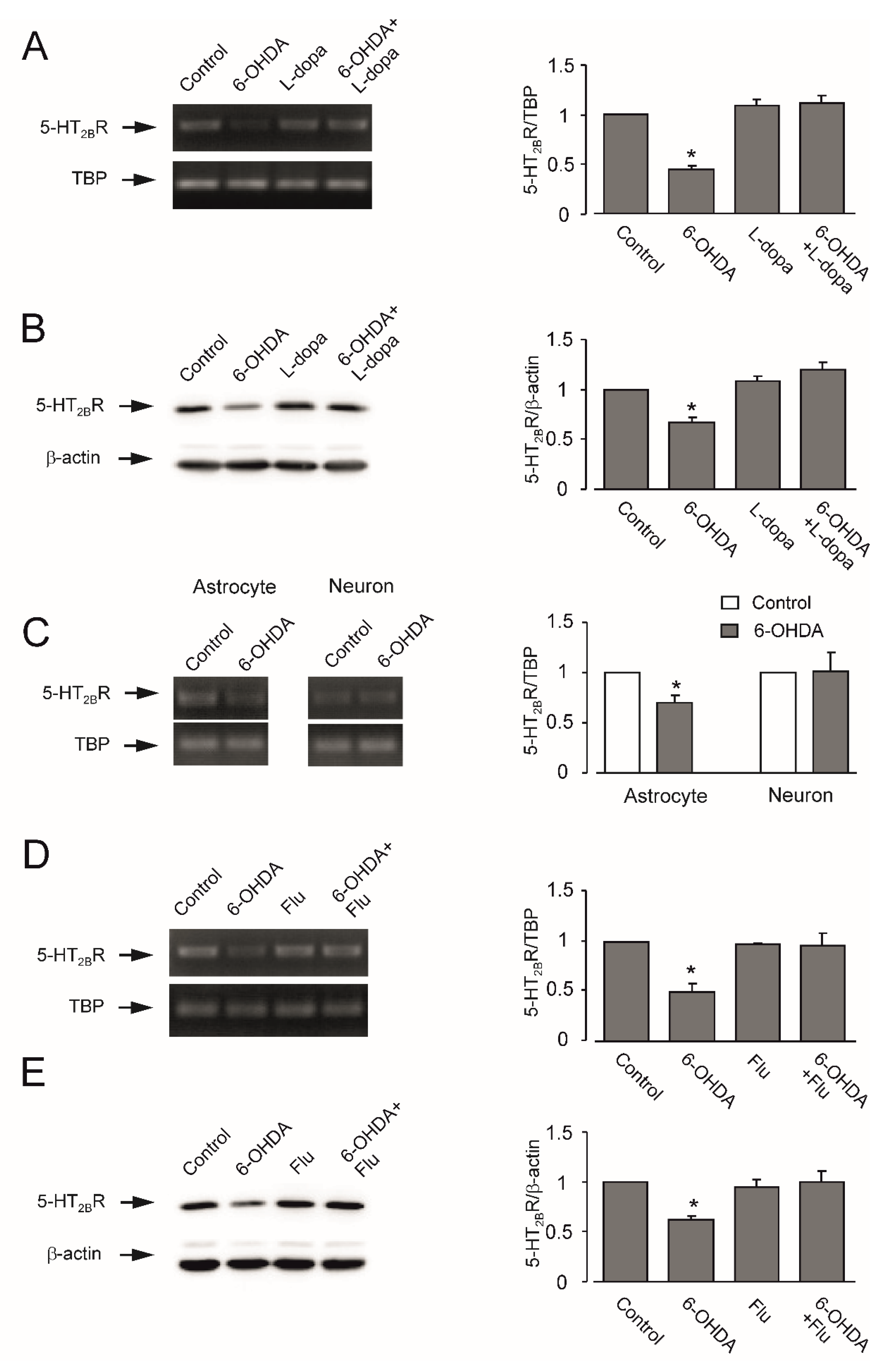
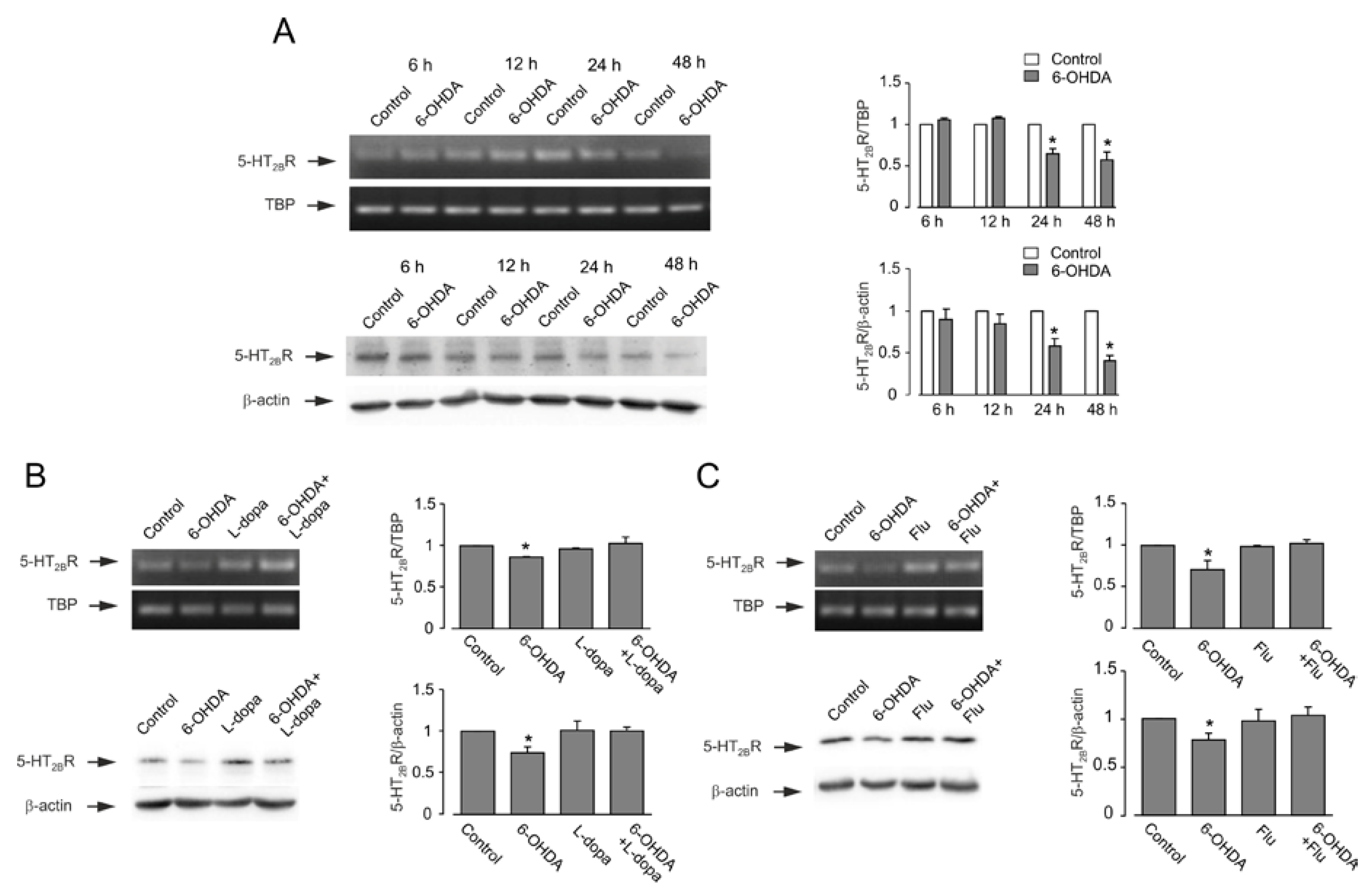
3.3. Expression of mRNA and Protein of 5-HT2B Receptor
4. Discussion
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hornykiewicz, O.; Kish, S.J. Biochemical pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Adv. Neurol. 1987, 45, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chiu, W.H.; Depboylu, C.; Hermanns, G.; Maurer, L.; Windolph, A.; Oertel, W.H.; Ries, V.; Höglinger, G.U. Long-term treatment with l-DOPA or pramipexole affects adult neurogenesis and corresponding non-motor behavior in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropharmacology 2015, 95, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, F.H.; Rosso, A.L.; Maultasch, H.; Nicaretta, D.H.; Vincent, M.B. Depression in Parkinson’s disease: Diagnosis and treatment. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2012, 70, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskow Jaunarajs, K.L.; Angoa-Perez, M.; Kuhn, D.M.; Bishop, C. Potential mechanisms underlying anxiety and depression in Parkinson’s disease: Consequences of l-DOPA treatment. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, S.H.; Chuang, R.; Brotchie, J.M. Serotonin and Parkinson’s disease: On movement, mood and madness. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, H.D.E.; Hirst, W.D.; Wade-Martins, R. The role of astrocyte dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Trends Neurosci. 2017, 40, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Steardo, L.; Parpura, V.; Montana, V. Translational potential of astrocytes in brain disorders. Prog. Neurobiol. 2016, 144, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Rodríguez, J.J.; Steardo, L. Astrogliopathology: A central element of neuropsychiatric diseases? Neuroscientist 2014, 20, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Parpura, V. Astrogliopathology in neurological, neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 85, 254–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Nu, W.; Cai, L.; Hertz, L.; Peng, L. Fluoxetine-mediated 5-HT2B receptor stimulation in astrocytes causes EGF receptor transactivation and ERK phosphorylation. Psychopharmacology 2008, 201, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dong, L.; Wang, B.; Cai, L.; Jiang, N.; Peng, L. Cell type-specific gene expression and editing responses to chronic fluoxetine treatment in the in vivo mouse brain and their relevance for stress-induced anhedonia. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 37, 2480–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Li, B.; Verkhratsky, A.; Peng, L. Cell type-specific in vivo expression of genes encoding signalling molecules in the brain in response to chronic mild stress and chronic treatment with fluoxetine. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 2827–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Song, D.; Gu, L.; Ren, Y.; Verkhratsky, A.; Peng, L. Decrease of gene expression of astrocytic 5-HT2B receptors parallels development of depressive phenotype in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blesa, J.; Phani, S.; Jackson-Lewis, V.; Przedborski, S. Classic and new animal models of Parkinson’s disease. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 845618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, K.; Kabuto, H.; Makino, H.; Ogawa, N. Pole test is a useful method for evaluating the mouse movement disorder caused by striatal dopamine depletion. J. Neurosci. Methods 1997, 73, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovatt, D.; Sonnewald, U.; Waagepetersen, H.S.; Schousboe, A.; He, W.; Lin, J.H.; Han, X.; Takano, T.; Wang, S.; Sim, F.J.; et al. The transcriptome and metabolic gene signature of protoplasmic astrocytes in the adult murine cortex. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 12255–12266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Li, B.; Hertz, L.; Peng, L. Contributions in astrocytes of SMIT1/2 and HMIT to myo-inositol uptake at different concentrations and pH. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 61, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertz, L.; Peng, L.; Lai, J.C. Functional studies in cultured astrocytes. Methods 1998, 16, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertz, L.; Bock, E.; Schousboe, A. GFA content, glutamate uptake and activity of glutamate metabolizing enzymes in differentiating mouse astrocytes in primary cultures. Dev. Neurosci. 1978, 1, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertz, L.; Juurlink, B.H.J.; Szuchet, S. Cell cultures. In Handbook of Neurochemistry; Lajtha, A., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, E.; Hertz, L.; Schousboe, A. Neurotransmitters as developmental signals. Neurochem. Int. 1991, 19, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, E.K.; Peng, L.; Chen, Y.; Yu, A.C.; Hertz, L. Up-regulation of 5-HT2B receptor density and receptor-mediated glycogenolysis in mouse astrocytes by long-term fluoxetine administration. Neurochem. Res. 2002, 27, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Marjou, A.; Delouvée, A.; Thiery, J.P.; Radvanyi, F. Involvement of epidermal growth factor receptor in chemically induced mouse bladder tumour progression. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 2211–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Nedergaard, M. Astroglial cradle in the life of the synapse. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Nedergaard, M. Physiology of astroglia. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 239–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pitta, M.; Brunel, N.; Volterra, A. Astrocytes: Orchestrating synaptic plasticity? Neuroscience 2016, 323, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallerac, G.; Rouach, N. Astrocytes as new targets to improve cognitive functions. Prog. Neurobiol. 2016, 144, 48–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorec, R.; Horvat, A.; Vardjan, N.; Verkhratsky, A. Memory formation shaped by astroglia. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekny, M.; Pekna, M.; Messing, A.; Steinhäuser, C.; Lee, J.M.; Parpura, V.; Hol, E.M.; Sofroniew, M.V.; Verkhratsky, A. Astrocytes: A central element in neurological diseases. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 323–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkowska, G.; Stockmeier, C.A. Astrocyte pathology in major depressive disorder: Insights from human postmortem brain tissue. Curr. Drug Targets 2013, 14, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niciu, M.J.; Henter, I.D.; Sanacora, G.; Zarate, C.A., Jr. Glial abnormalities in substance use disorders and depression: Does shared glutamatergic dysfunction contribute to comorbidity? World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 15, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Verkhratsky, A.; Gu, L.; Li, B. Targeting astrocytes in major depression. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2015, 15, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Li, B.; Verkhratsky, A. Targeting astrocytes in bipolar disorder. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2016, 16, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankiewicz, K.S.; Oldfield, E.H.; Chiueh, C.C.; Doppman, J.L.; Jacobowitz, D.M.; Kopin, I.J. Hemiparkinsonism in monkeys after unilateral internal carotid artery infusion of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP). Life Sci. 1986, 39, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bové, J.; Perier, C. Neurotoxin-based models of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 2012, 211, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meredith, G.E.; Totterdell, S.; Potashkin, J.A.; Surmeier, D.J. Modeling PD pathogenesis in mice: Advantages of a chronic MPTP protocol. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2008, 14 (Suppl. S2), S112–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossowska, K.; Lorenc-Koci, E. Depression in Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 1545–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, A.; Jackson, D.; Manley, M.S.; Young, S.J.; Groves, P.M. Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase immunoreactive cells in the rat striatum: A possible site for the conversion of exogenous l-DOPA to dopamine. Brain Res. 1995, 704, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatsua, T.; Sawadab, M. l-Dopa therapy for Parkinson’s disease: Past, present and future. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2009, 15 (Suppl. 1), S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyushin, M.Y.; Huertas, A.; Kucheryavykh, Y.V.; Kucheryavykh, L.Y.; Tsydzik, V.; Sanabria, P.; Eaton, M.J.; Skatchkov, S.N.; Rojas, L.V.; Wessinger, W.D. l-DOPA uptake in astrocytic endfeet enwrapping blood vessels in rat brain. Parkinson’s Dis. 2012, 321406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.K.; Kim, I.J.; Hwang, S.; Kook, J.H.; Lee, M.C.; Shin, B.A.; Bae, C.S.; Yoon, J.H.; Ahn, S.G.; Kim, S.A. System l-amino acid transporters are differently expressed in rat astrocyte and C6 glioma cells. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 50, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.J.; Lee, E.H. Characterization of l-DOPA transport in cultured rat and mouse astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 1996, 43, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inazu, M.; Kubota, N.; Takeda, H.; Zhang, J.; Kiuchi, Y.; Oguchi, K.; Matsumiya, T. Pharmacological characterization of dopamine transport in cultured rat astrocytes. Life Sci. 1999, 64, 2239–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inazu, M.; Takeda, H.; Ikoshi, H.; Uchida, Y.; Kubota, N.; Kiuchi, Y.; Oguchi, K.; Matsumiya, T. Regulation of dopamine uptake by basic fibroblast growth factor and epidermal growth factor in cultured rat astrocytes. Neurosci. Res. 1999, 34, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asanuma, M.; Miyazaki, I.; Murakami, S.; Diaz-Corrales, F.J.; Ogawa, N. Striatal astrocytes act as a reservoir for l-DOPA. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stansley, B.J.; Yamamoto, B.K. l-Dopa-induced dopamine synthesis and oxidative stress in serotonergic cells. Neuropharmacology 2013, 67, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prigione, A.; Begni, B.; Galbussera, A.; Beretta, S.; Brighina, L.; Garofalo, R.; Andreoni, S.; Piolti, R.; Ferrarese, C. Oxidative stress in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with Parkinson’s disease: Negative correlation with levodopa dosage. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 23, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colamartino, M.; Padua, L.; Meneghini, C.; Leone, S.; Cornetta, T.; Testa, A.; Cozzi, R. Protective effects of l-dopa and carbidopa combined treatments on human catecholaminergic cells. DNA Cell Biol. 2012, 31, 1572–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostrzewa, J.P.; Kostrzewa, R.A.; Kostrzewa, R.M.; Brus, R.; Nowak, P. Perinatal 6-hydroxydopamine to produce a lifelong model of severe Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blohberger, J.; Buck, T.; Berg, D.; Berg, U.; Kunz, L.; Mayerhofer, A. l-DOPA in the human ovarian follicular fluid acts as an antioxidant factor on granulosa cells. J. Ovarian Res. 2016, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Fang, M.; Zhu, X.L.; Zhao, Y.X.; Liu, X.Y. Low-dose levodopa protects nerve cells from oxidative stress and up-regulates expression of pCREB and CD39. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Hertz, L.; Peng, L. Serotonin increases ERK1/2 phosphorylation in astrocytes by stimulation of 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptors. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 57, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, B.; Lovatt, D.; Xu, J.; Song, D.; Goldman, S.A.; Nedergaard, M.; Hertz, L.; Peng, L. 5-HT2B receptors are expressed on astrocytes from brain and in culture and are a chronic target for all five conventional ‘serotonin-specific reuptake inhibitors’. Neuron Glia Biol. 2010, 6, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Huang, J. Astrocytic 5-HT2B receptor as in vitro and in vivo target of SSRIs. Recent Pat. CNS Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertz, L.; Rothman, D.L.; Li, B.; Peng, L. Chronic SSRI stimulation of astrocytic 5-HT2B receptors change multiple gene expressions/editings and metabolism of glutamate, glucose and glycogen: A potential paradigm shift. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Hertz, L.; Peng, L. Chronic treatment of astrocytes with therapeutically relevant fluoxetine concentrations enhances cPLA2 expression secondary to 5-HT2B-induced, transactivation-mediated ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Psychopharmacology 2009, 207, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, S.L.; Doly, S.; Narboux-Nême, N.; Fernández, S.; Mazot, P.; Banas, S.M.; Boutourlinsky, K.; Moutkine, I.; Belmer, A.; Roumier, A.; et al. 5-HT2B receptors are required for serotonin-selective antidepressant actions. Mol. Psychiatry 2012, 17, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, D.; Ma, K.; Verkhratsky, A.; Peng, L. l-Dopa and Fluoxetine Upregulate Astroglial 5-HT2B Receptors and Ameliorate Depression in Parkinson’s Disease Mice. Neuroglia 2018, 1, 48-62. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia1010006
Song D, Ma K, Verkhratsky A, Peng L. l-Dopa and Fluoxetine Upregulate Astroglial 5-HT2B Receptors and Ameliorate Depression in Parkinson’s Disease Mice. Neuroglia. 2018; 1(1):48-62. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia1010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Dan, Kangli Ma, Alexei Verkhratsky, and Liang Peng. 2018. "l-Dopa and Fluoxetine Upregulate Astroglial 5-HT2B Receptors and Ameliorate Depression in Parkinson’s Disease Mice" Neuroglia 1, no. 1: 48-62. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia1010006
APA StyleSong, D., Ma, K., Verkhratsky, A., & Peng, L. (2018). l-Dopa and Fluoxetine Upregulate Astroglial 5-HT2B Receptors and Ameliorate Depression in Parkinson’s Disease Mice. Neuroglia, 1(1), 48-62. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia1010006






