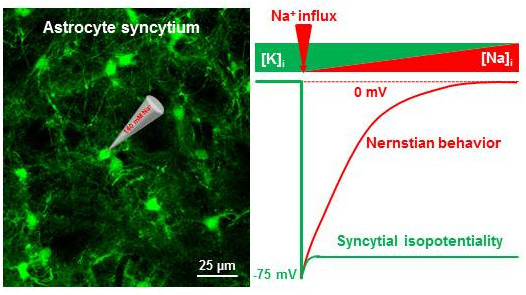
Syncytial Isopotentiality: An Electrical Feature of Spinal Cord Astrocyte Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Preparation of Acute Spinal Cord Slices
2.3. Sulforhodamine 101 Staining
2.4. Confocal Imaging of Spinal Cord Astrocyte Syncytia
2.5. Imaging Acquisition for Astrocyte Identification In Situ
2.6. Electrophysiology
2.7. Chemical Reagents
2.8. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Organization of Astrocyte Syncytium in Cervical Spinal Cord
3.2. Electrophysiological Properties of Grey Matter Astrocytes in the Spinal Cord
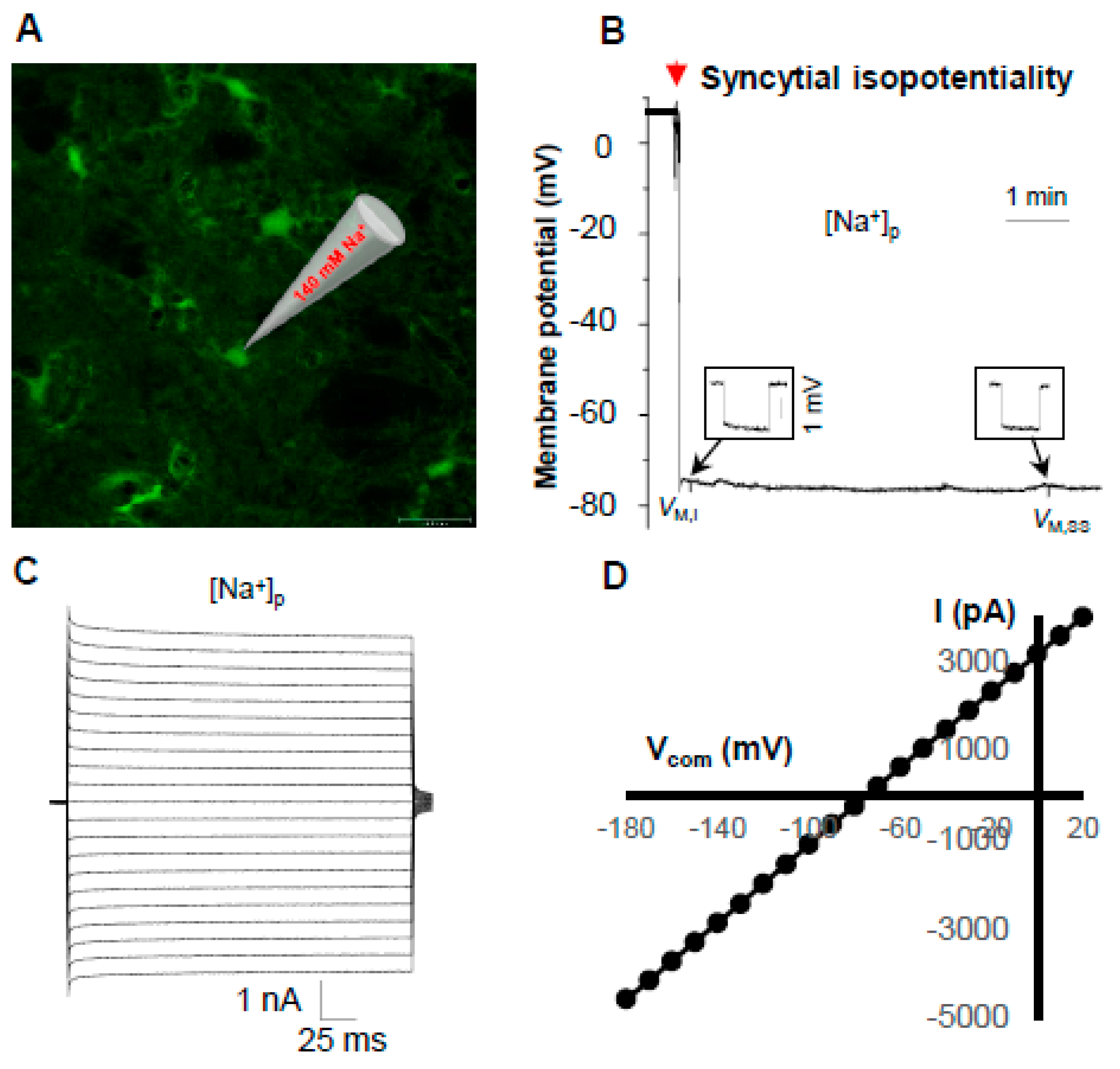
3.3. Syncytial Isopotentiality—An Electrical Feature of Spinal Cord Astrocyte Networks
4. Discussion
4.1. Anatomical Characteristics of Grey Matter Spinal Cord Astrocyte Networks
4.2. Spinal Cord Astrocytes Establish Syncytial Isopotentiality in Their Networks
4.3. Pathological Implications Affecting Astrocyte Syncytial Isopotentiality
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scemes, E.; Suadicani, S.O.; Spray, D.C. Intercellular communication in spinal cord astrocytes: Fine tuning between gap junctions and P2 nucleotide receptors in calcium wave propagation. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, W.T.; Cornell-Bell, A.H.; Sontheimer, H. Astrocytes exhibit regional specificity in gap-junction coupling. Glia 1994, 11, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmerjahn, A.; Bergles, D.E. Large-scale recording of astrocyte activity. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2015, 32, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Nedergaard, M. Physiology of Astroglia. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 239–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Buckalew, R.; Du, Y.; Kiyoshi, C.M.; Alford, C.C.; Wang, W.; McTigue, D.M.; Enyeart, J.J.; Terman, D.; Zhou, M. Gap junction coupling confers isopotentiality on astrocyte syncytium. Glia 2016, 64, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, C.M. Gap-junctional communication in mammalian cortical astrocytes: Development, modifiability and possible functions. In Gap Junctions in the Nervous System; Spray, D.C., Ed.; RG Landes Company: Austin, TX, USA, 1996; pp. 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyoshi, C.M.; Du, Y.; Zhong, S.; Wang, W.; Taylor, A.T.; Xiong, B.; Ma, B.; Terman, D.; Zhou, M. Syncytial isopotentiality: A system-wide electrical feature of astrocytic networks in the brain. Glia 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Houades, V.; Rouach, N.; Ezan, P.; Kirchhoff, F.; Koulakoff, A.; Giaume, C. Shapes of astrocyte networks in the juvenile brain. Neuron Glia Biol. 2006, 2, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houades, V.; Koulakoff, A.; Ezan, P.; Seif, I.; Giaume, C. Gap junction-mediated astrocytic networks in the mouse barrel cortex. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 5207–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, L.; Benchenane, K.; Rothstein, J.D.; Bonvento, G.; Giaume, C. Plasticity of astroglial networks in olfactory glomeruli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18442–18446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nadarajah, B.; Thomaidou, D.; Evans, W.H.; Parnavelas, J.G. Gap junctions in the adult cerebral cortex: Regional differences in their distribution and cellular expression of connexins. J. Comp. Neurol. 1996, 376, 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, L.; Chiang, M.S.R.; Higashimori, H.; Shoneye, T.; Iyer, L.K.; Yelick, J.; Tai, A.; Yang, Y. Molecular and Functional Properties of Regional Astrocytes in the Adult Brain. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 8706–8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Barres, B.A. Astrocyte heterogeneity: An underappreciated topic in neurobiology. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2010, 20, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Du, Y.; Kiyoshi, C.M.; Ma, B.; Alford, C.C.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, M. Electrophysiological behavior of neonatal astrocytes in hippocampal stratum radiatum. Mol. Brain 2016, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Vidensky, S.; Jin, L.; Jie, C.; Lorenzini, I.; Frankl, M.; Rothstein, J.D. Molecular comparison of GLT1+ and ALDH1L1+ astrocytes in vivo in astroglial reporter mice. Glia 2011, 59, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Putra, A.; Schools, G.P.; Ma, B.; Chen, H.; Kaczmarek, L.K.; Barhanin, J.; Lesage, F.; Zhou, M. The contribution of TWIK-1 channels to astrocyte K(+) current is limited by retention in intracellular compartments. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, M.L.; Higashimori, H.; Campbell, S.L.; Hablitz, J.J.; Sontheimer, H. Functional expression of Kir4.1 channels in spinal cord astrocytes. Glia 2006, 53, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, G.; Wang, W.; Kimelberg, H.K.; Zhou, M. Electrical coupling of astrocytes in rat hippocampal slices under physiological and simulated ischemic conditions. Glia 2010, 58, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficker, C.; Rozmer, K.; Kato, E.; Ando, R.D.; Schumann, L.; Krugel, U.; Franke, H.; Sperlagh, B.; Riedel, T.; Illes, P. Astrocyte-neuron interaction in the substantia gelatinosa of the spinal cord dorsal horn via P2X7 receptor-mediated release of glutamate and reactive oxygen species. Glia 2014, 62, 1671–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Minkel, H.R.; Anwer, T.Z.; Arps, K.M.; Brenner, M.; Olsen, M.L. Elevated GFAP induces astrocyte dysfunction in caudal brain regions: A potential mechanism for hindbrain involved symptoms in type II Alexander disease. Glia 2015, 63, 2285–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, Y.; Ma, B.; Kiyoshi, C.M.; Alford, C.C.; Wang, W.; Zhou, M. Freshly dissociated mature hippocampal astrocytes exhibit similar passive membrane conductance and low membrane resistance as syncytial coupled astrocytes. J. Neurophysiol. 2015, 113, 3744–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Haim, L.; Rowitch, D.H. Functional diversity of astrocytes in neural circuit regulation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayraktar, O.A.; Fuentealba, L.C.; Alvarez-Buylla, A.; Rowitch, D.H. Astrocyte development and heterogeneity. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 7, a020362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Barres, B.A. Reactive Astrocytes: Production, Function, and Therapeutic Potential. Immunity 2017, 46, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaume, C.; Koulakoff, A.; Roux, L.; Holcman, D.; Rouach, N. Astroglial networks: A step further in neuroglial and gliovascular interactions. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.J.; Kress, B.; Han, X.; Moll, K.; Peng, W.; Ji, R.R.; Nedergaard, M. Astrocytic CX43 hemichannels and gap junctions play a crucial role in development of chronic neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury. Glia 2012, 60, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Theriault, E.; Frankenstein, U.N.; Hertzberg, E.L.; Nagy, J.I. Connexin43 and astrocytic gap junctions in the rat spinal cord after acute compression injury. J. Comp. Neurol. 1997, 382, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, M.; Du, Y.; Kiyoshi, C.M.; Wu, X.; Askwith, C.C.; McTigue, D.M.; Zhou, M. Syncytial Isopotentiality: An Electrical Feature of Spinal Cord Astrocyte Networks. Neuroglia 2018, 1, 271-279. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia1010018
Huang M, Du Y, Kiyoshi CM, Wu X, Askwith CC, McTigue DM, Zhou M. Syncytial Isopotentiality: An Electrical Feature of Spinal Cord Astrocyte Networks. Neuroglia. 2018; 1(1):271-279. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia1010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Mi, Yixing Du, Conrad M. Kiyoshi, Xiao Wu, Candice C. Askwith, Dana M. McTigue, and Min Zhou. 2018. "Syncytial Isopotentiality: An Electrical Feature of Spinal Cord Astrocyte Networks" Neuroglia 1, no. 1: 271-279. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia1010018
APA StyleHuang, M., Du, Y., Kiyoshi, C. M., Wu, X., Askwith, C. C., McTigue, D. M., & Zhou, M. (2018). Syncytial Isopotentiality: An Electrical Feature of Spinal Cord Astrocyte Networks. Neuroglia, 1(1), 271-279. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia1010018