Effect of Web Flexibility in Gear Engagement: A Proposal of Analysis Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model Description
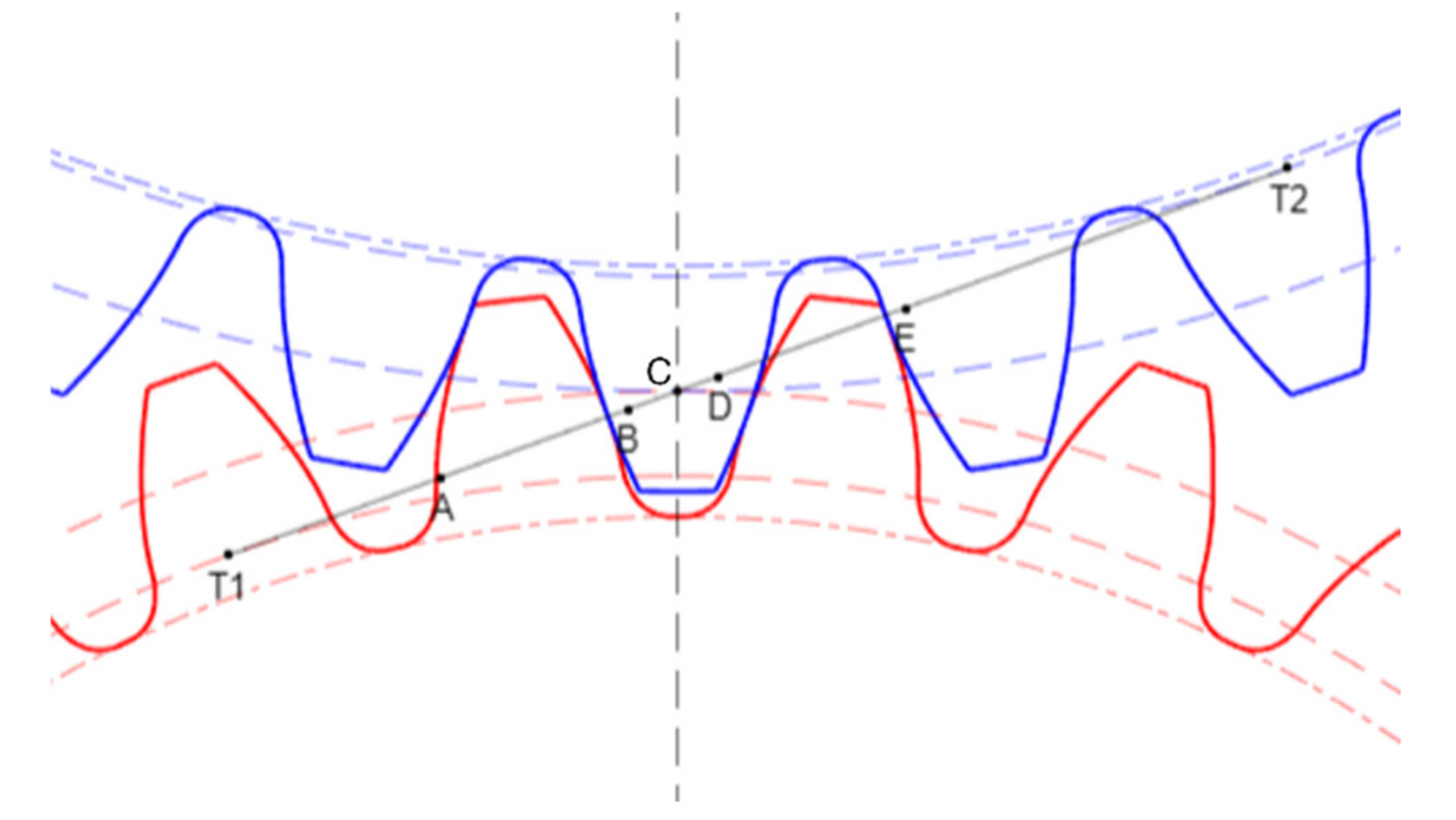
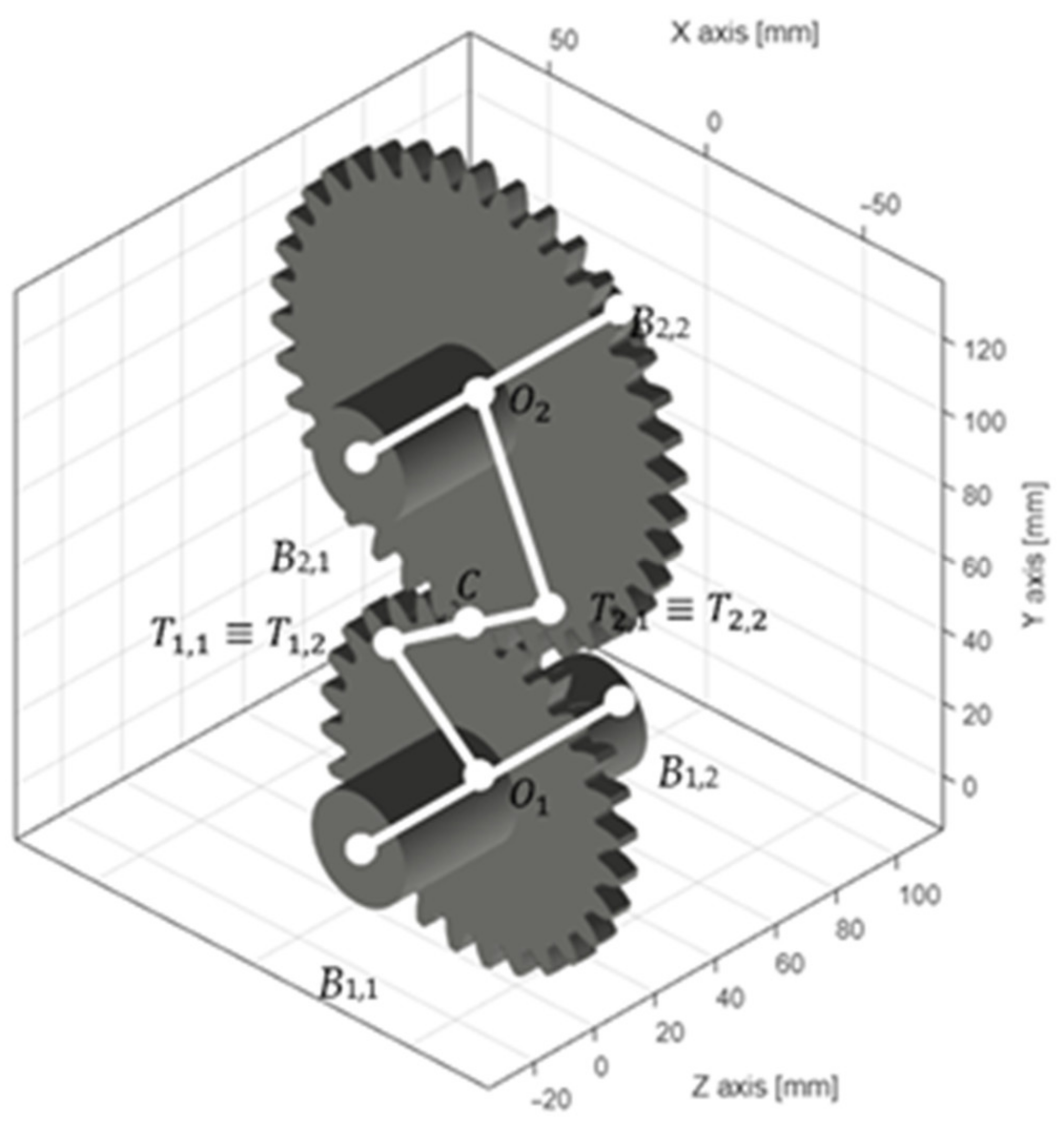
2.1.1. Rigid Gear Body
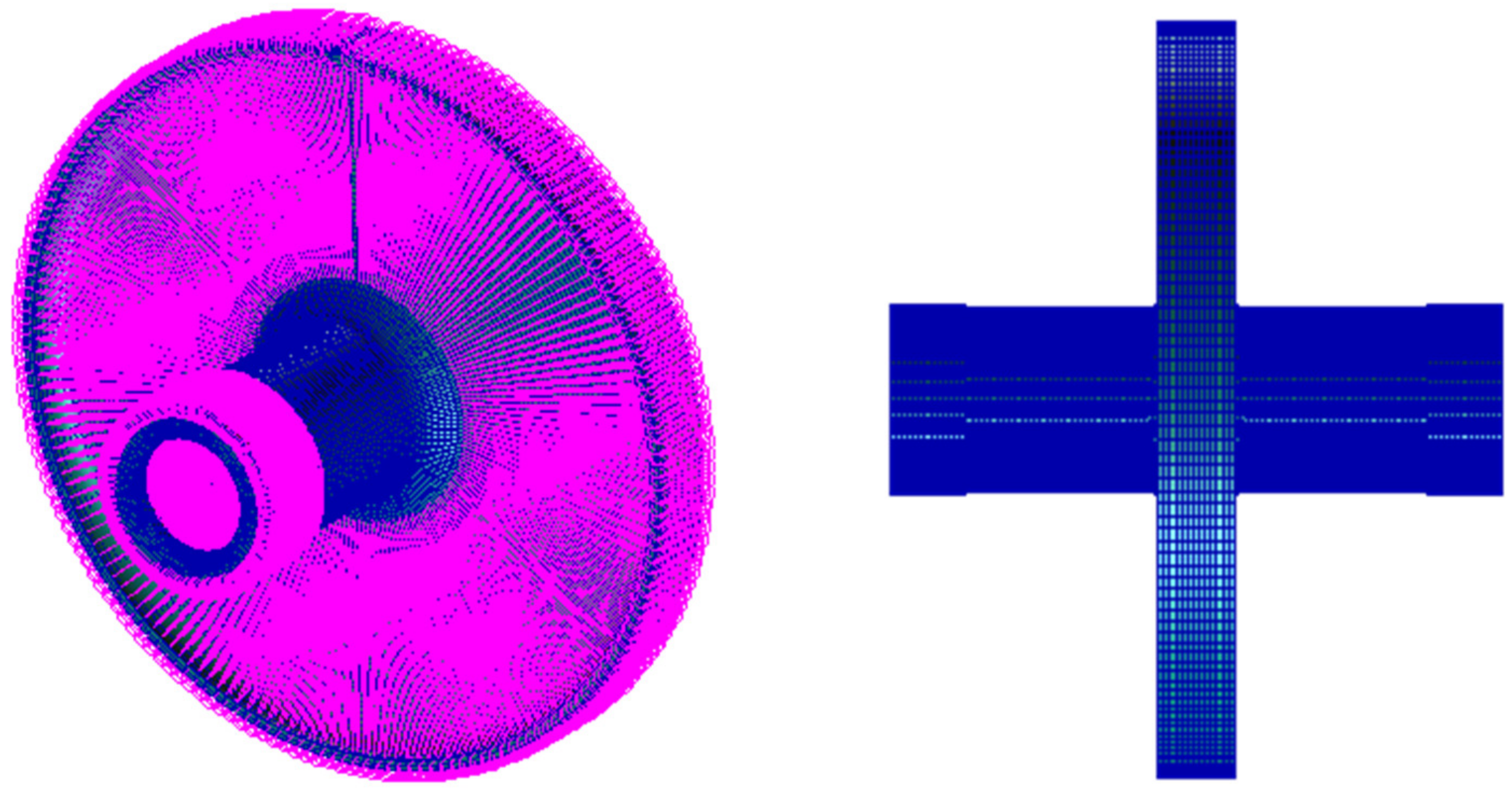
2.1.2. Flexible Gear Body
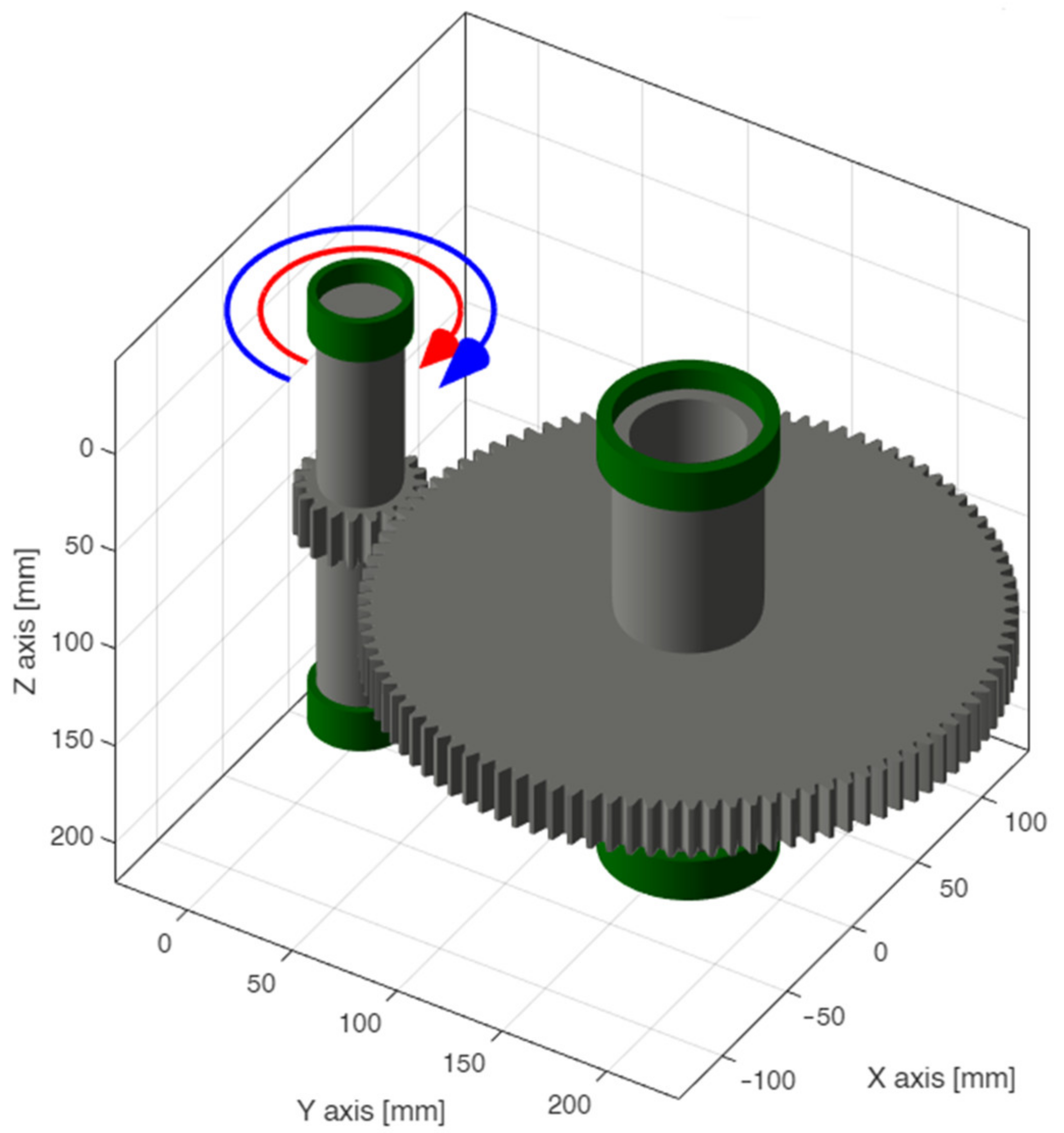
2.2. Case Study
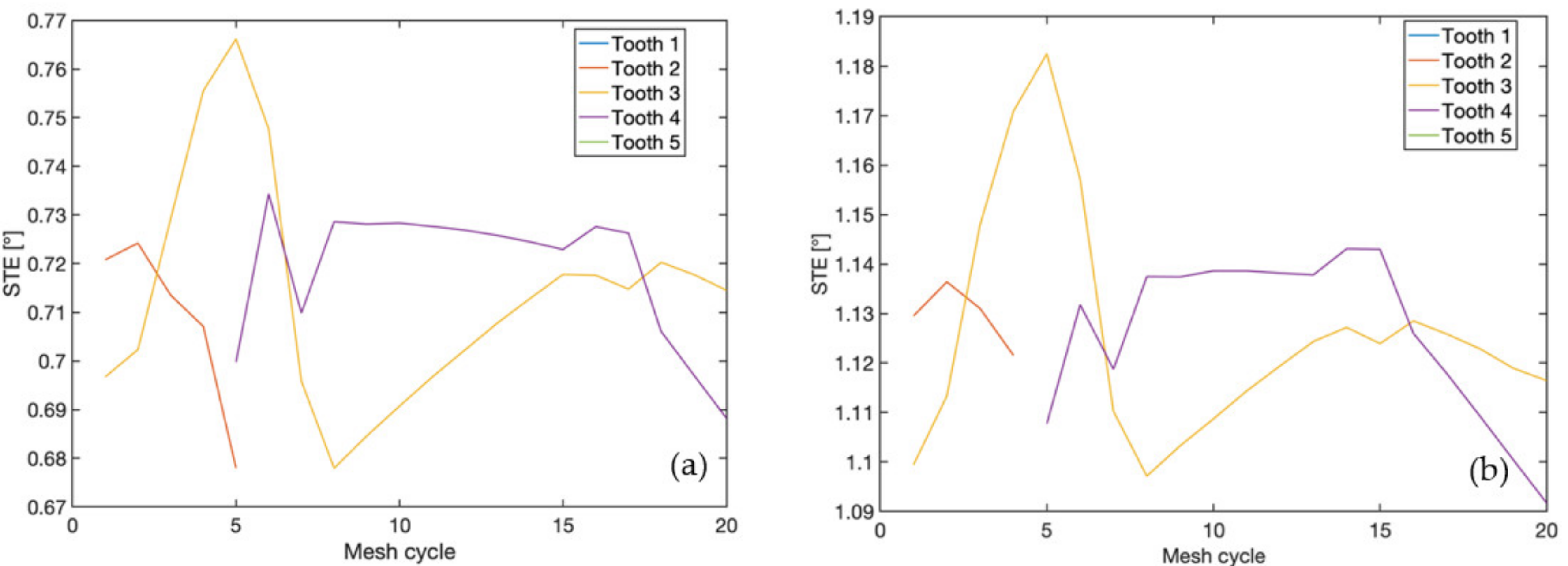
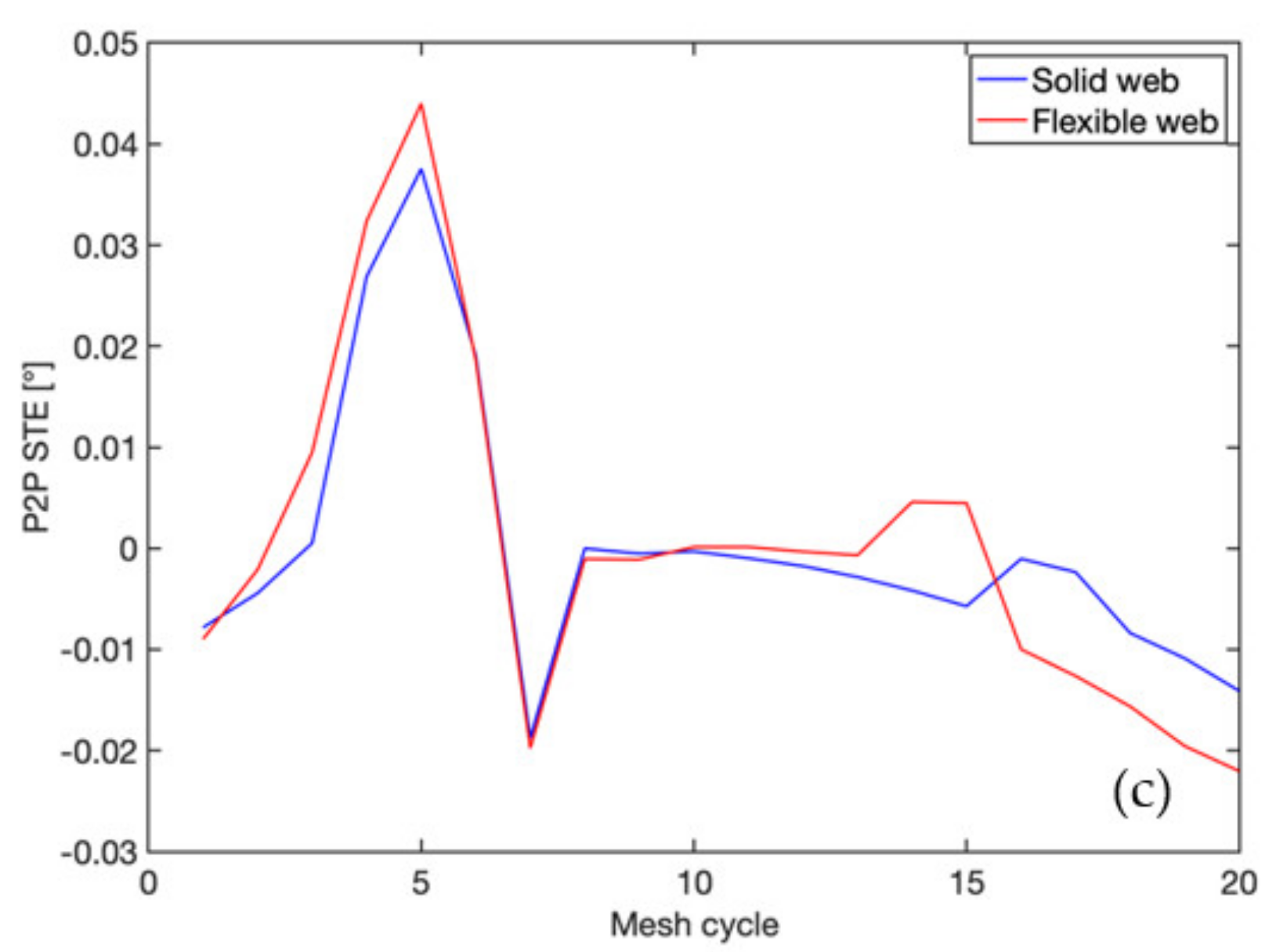
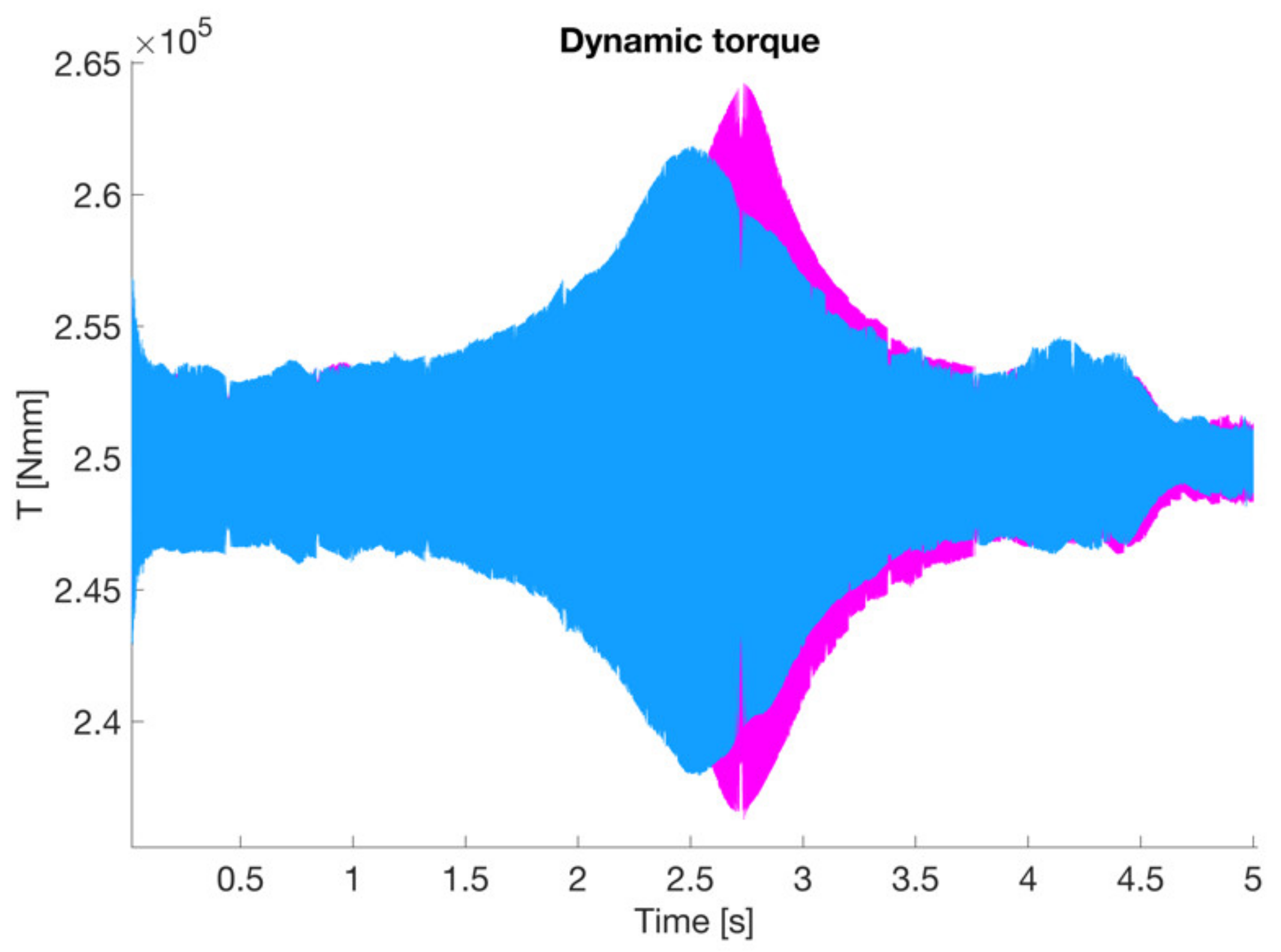
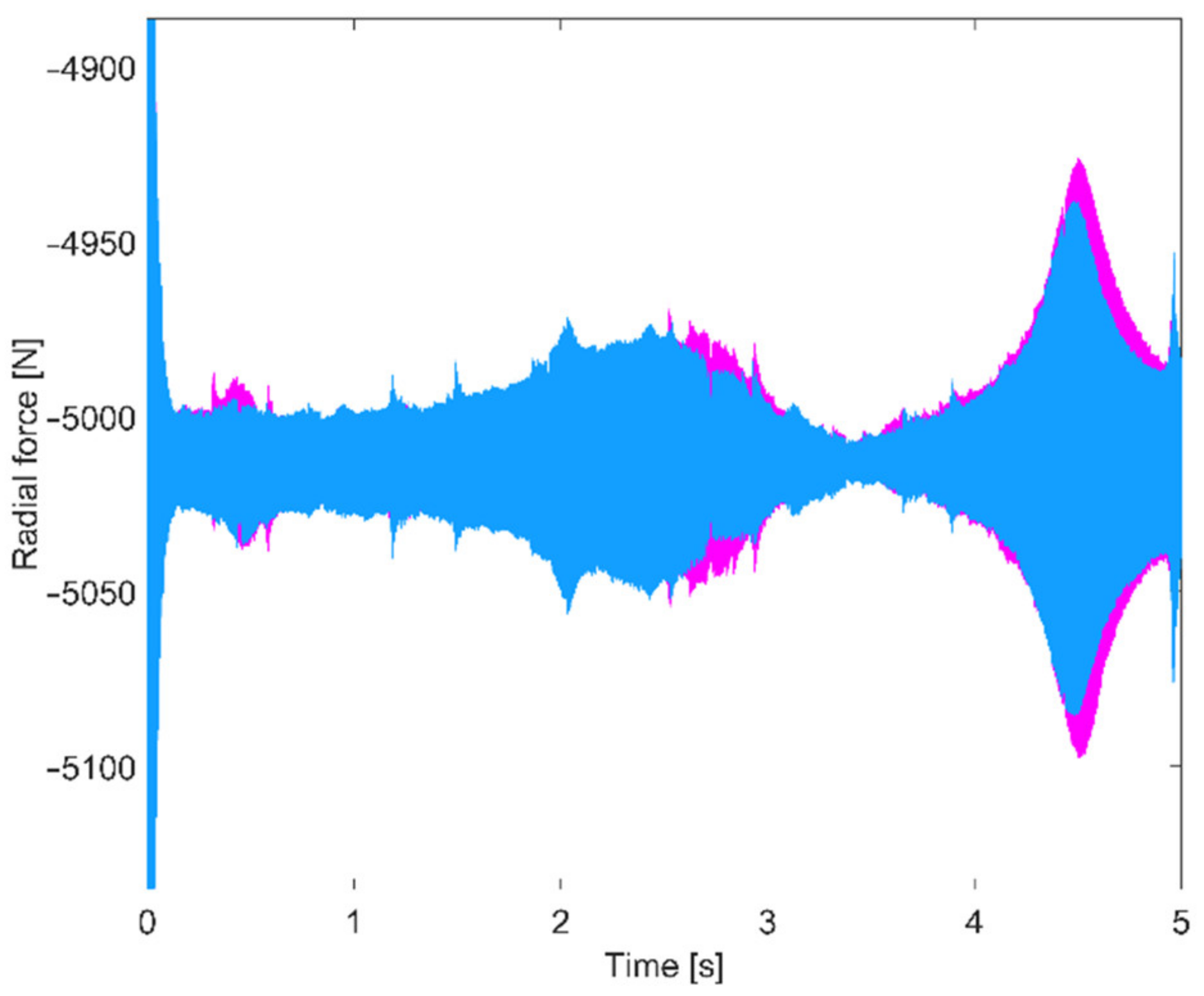
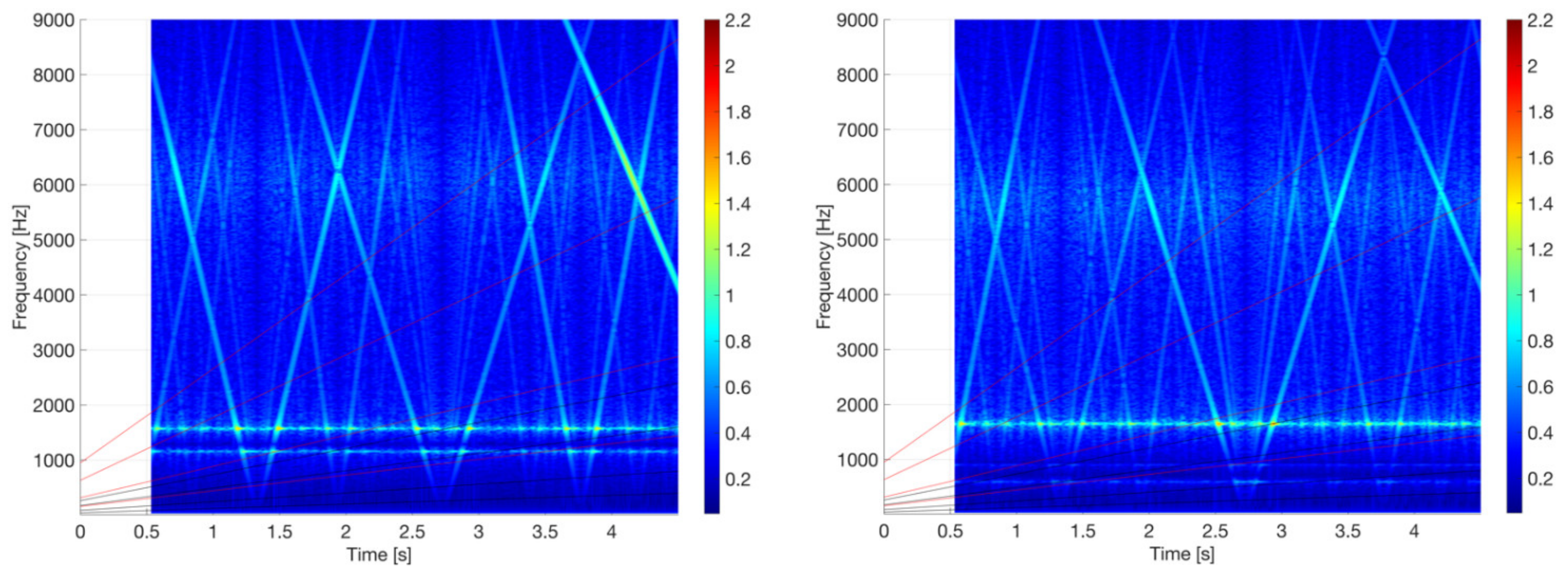
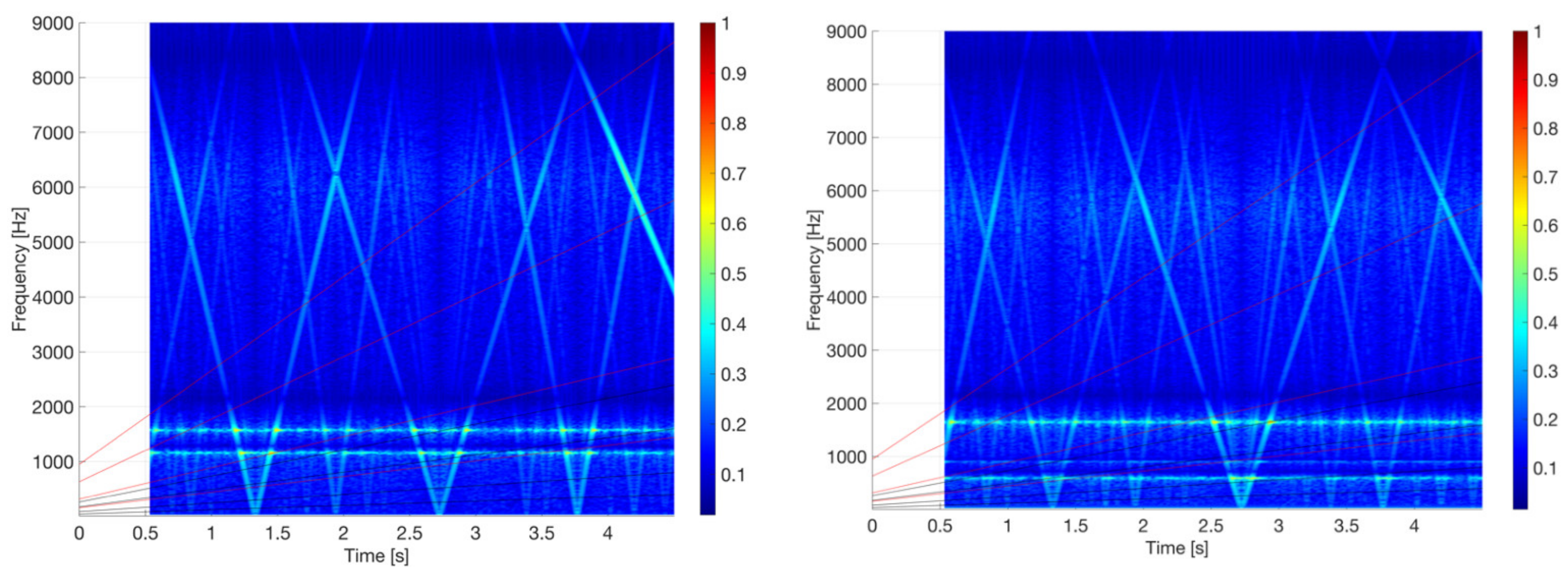
3. Results
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Curà, F.; Mura, A.; Rosso, C. Effect of rim and web interaction on crack propagation paths in gears by means of XFEM technique. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2015, 38, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curà, F.; Mura, A.; Rosso, C. Investigation of crack propagation path in tube gears. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2017, 7, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozguven, H.N.; Houser, D.R. Mathematical models used in gear dynamics—A review. J. Sound Vib. 1988, 121, 383–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abersek, B.; Flasker, J.; Glodez, S. Review of mathematical and experimental models for determination of service life of gears. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2004, 71, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasil, L.; Mackerle, J. Finite element analyses and simulations of gears and gear drives a bibliography 1997–2006. Int. J. Comput.-Aided Eng. Softw. 2008, 25, 196–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, F.; Rosso, C. Sources of excitation and models for cylindrical gear. Machines 2020, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozguven, H.N.; Houser, D.R. Dynamic analysis of high speed gears by using the loaded static transmission error. J. Sound Vib. 1988, 125, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.L. Dynamic loads on teeth of spur gears. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1958, 172, 87–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velex, P.; Ajmi, M. On the modelling of excitations in geared systems by transmission errors. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 290, 882–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velex, P.; Ajmi, M. Dynamic tooth loads and quasi-static transmission errors in helical gears–Approximate dynamic factor formulae. Mech. Mach. Theory 2007, 42, 1512–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velex, P.; Chapron, M.; Fakhfakh, H.; Bruyere, J.; Becquerelle, S. On transmission errors and profile modifications minimising dynamic tooth loads in multi-mesh gears. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 379, 28–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, F.; Maggi, T.; Marcellini, C.; Rosso, C.; Delprete, C. Evaluation of the effect of profile modifications in gears subjected to sudden torque inversion. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1038, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, C.; Bruzzone, F.; Maggi, T.; Marcellini, C. Influence of Micro Geometry Modification on Gear Dynamics; No. 2020-01-1323; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kahraman, A.; Singh, R. Non-linear dynamics of a spur gear pair. J. Sound Vib. 1990, 142, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.G.; Vijayakar, S.M.; Imajo, T. Non-linear dynamic response of a spur gear pair: Modelling and experimental comparisons. J. Sound Vib. 2000, 237, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahraman, A.; Singh, R. Interactions between time-varying mesh stiffness and clearance non-lMinearities in a geared system. J. Sound Vib. 1991, 146, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenship, G.W.; Kahraman, A. Steady state forced response of a mechanical oscillator with combined parametric excitation and clearance type non-linearity. J. Sound Vib. 1995, 185, 743–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theodossiades, S.; Natsiavas, S. Non-linear dynamics of gear-pair systems with periodic stiffness and backlash. J. Sound Vib. 2000, 229, 287–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodossiades, S.; Natsiavas, S. On geared rotordynamic systems with oil journal bearings. J. Sound Vib. 2001, 243, 721–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodossiades, S.; Natsiavas, S. Periodic and chaotic dynamics of motor-driven gear-pair systems with backlash. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2001, 12, 2427–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eritnel, T.; Parker, R.G. Three-dimensional nonlinear vibration of gear pairs. J. Sound Vib. 2012, 331, 3628–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Eritnel, T.; Ericson, T.M.; Parker, R.G. Vibro-acoustic propagation of gear dynamics in a gear-bearing-housing system. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 5762–5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigaud, E.; Sabot, J. Effect of elasticity of shafts, bearings, casing and couplings on the critical rotational speeds of a gearbox. arXiv 1996, arXiv:physics/0701038, 833–845. [Google Scholar]
- Palermo, A.; Mundo, D.; Hadjit, R.; Desmet, W. Multibody element for spur and helical transmission error and the dynamic stress factor of spur gear pairs. Mech. Mach. Theory 2013, 62, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, F.; Maggi, T.; Marcellini, C.; Rosso, C. 2D nonlinear and non-Hertzian gear teeth deflection model for static transmission error calculation. Mech. Mach. Theory 2021, 166, 104471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.G.; Agashe, V.; Vijayakar, S.M. Dynamic response of a planetary gear system using a finite element/contact mechanics model. J. Mech. Des. 2000, 122, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, A.; Ligata, H.; Singh, A. Influence of ring gear rim thickness on planetary gear set behavior. J. Mech. Des. 2010, 132, 021002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kahraman, A.; Ligata, H. Internal gear strains and load sharing in planetary transmissions. J. Mech. Des. 2008, 130, 072602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowper, G.R. The shear coefficient in Timoshenko’s beam theory. J. Appl. Mech. 1966, 33, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvin, F.L. Gear Geometry and Applied Theory; P.T.R. Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Ziekiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, R.L. The Finite Element Method for Solid and Structural Mechanics; Elsevier: Oxford, UK; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bruzzone, F.; Maggi, T.; Marcellini, C.; Rosso, C. Gear Teeth Deflection Model for Spur Gears: Proposal of a 3D Nonlinear and Non-Hertzian Approach. Machines 2021, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newmark, N.M. A Method of Computation for Structural Dynamics. J. Eng. Mech. Div. 1959, 85, 67–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Cooley, C.G.; Parker, R.G. An efficient hybrid analytical-computational method for nonlinear vibration of spur gear pairs. J. Vib. Acoust. 2018, 141, 011006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, C.G.; Parker, R.G.; Vijayakar, S.M. A frequency domain finite element approach for three-dimensional gear dynamics. In Proceedings of the International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 30 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Cooley, C.G.; Parker, R.G. Dynamic tooth root strains and experimental correlations in spur gear pairs. Mech. Mach. Theory 2016, 101, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eritnel, T.; Parker, R.G. Nonlinear vibration of gears with tooth surface modifications. J. Vib. Acoust. 2013, 135, 051005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ajmi, M.; Velex, P. A model for simulating the quasi-static and dynamic behaviour of solid wide-faced spur and helical gears. Mech. Mach. Theory 2005, 40, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eritnel, T.; Parker, R.G. An investigation of tooth mesh nonlinearity and partial contact loss in gear pairs using a lumped-parameter model. Mech. Mach. Theory 2012, 56, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonisoli, E.; Delprete, C.; Rosso, C. Proposal of a modal-geometrical-based master nodes selection criterion in modal analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2009, 23, 606–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boashash, B. Estimating and interpreting the instantaneous frequency of a signal. I. Fundamentals. Proc. IEEE 1992, 80, 520–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejdic, E.; Djurovic, I.; Jiang, J. Time–frequency feature representation using energy concentration: An overview of recent advances. Digit. Signal Process. 2009, 19, 153–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, C.G.; Parker, R.G. Vibration of high-speed rotating rings coupled to spatial space-fixed stiffness. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 2631–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, C.; Maggi, T.; Marcellini, C.; Bruzzone, F. Test Bench for Static Transmission Error Evaluation in Gears; No. 2020-01-1324; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
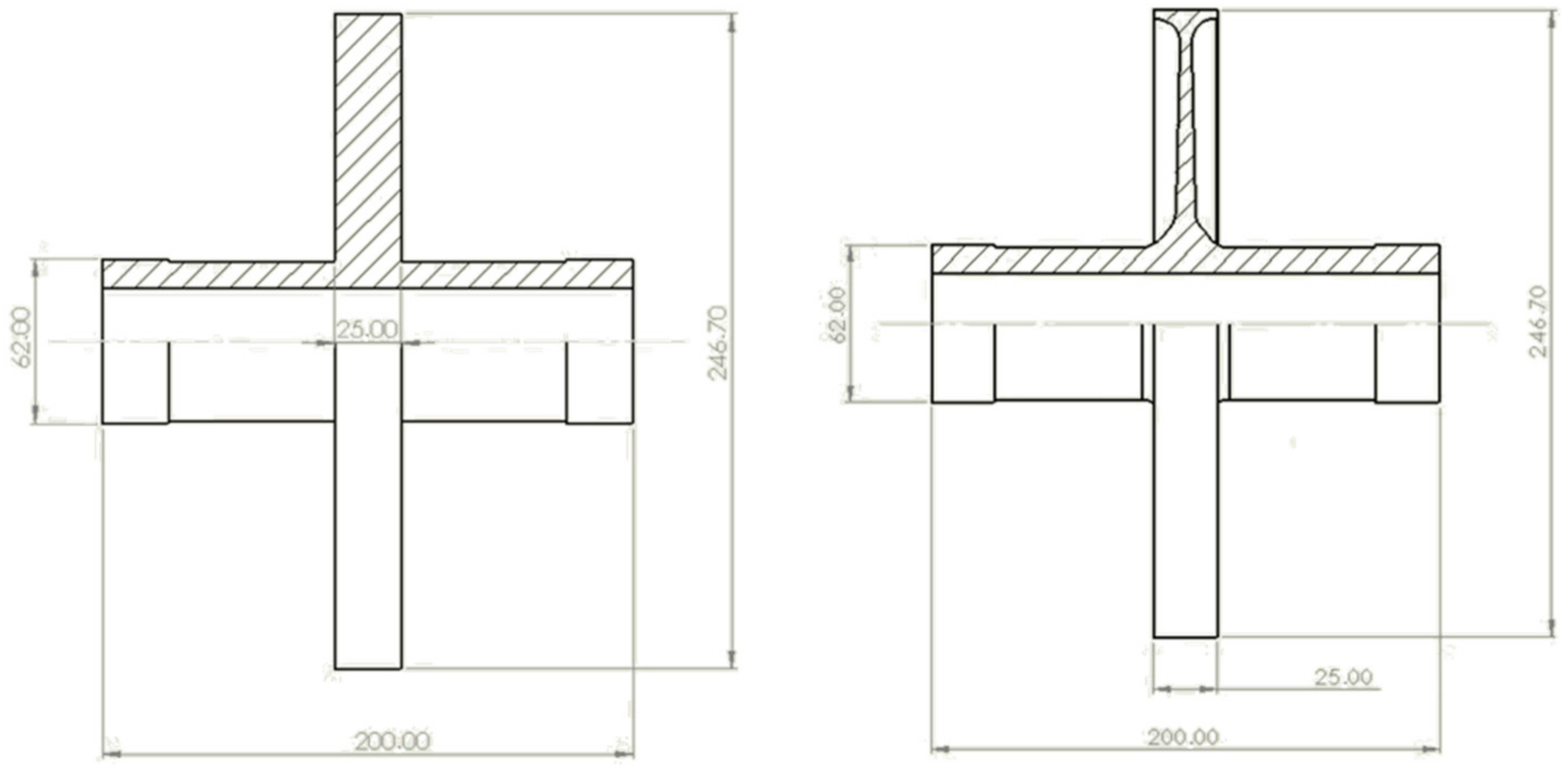
| Thick Web | Thin Web | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinion | Gear | Pinion | Gear | |
| 19 | 100 | 19 | 100 | |
| 2.625 | 2.625 | |||
| 20 | 20 | |||
| 0 | 0 | |||
| 25 | 25 | |||
| constant | 25 | variable | 4 to 8 | |
| 60 | 40 | 60 | 40 | |
| 200 | ||||
| Material: Steel | ||||
| 200,000 | ||||
| 0.3 | ||||
| 7800 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bruzzone, F.; Rosso, C. Effect of Web Flexibility in Gear Engagement: A Proposal of Analysis Strategy. Vibration 2022, 5, 200-212. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration5020013
Bruzzone F, Rosso C. Effect of Web Flexibility in Gear Engagement: A Proposal of Analysis Strategy. Vibration. 2022; 5(2):200-212. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration5020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleBruzzone, Fabio, and Carlo Rosso. 2022. "Effect of Web Flexibility in Gear Engagement: A Proposal of Analysis Strategy" Vibration 5, no. 2: 200-212. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration5020013
APA StyleBruzzone, F., & Rosso, C. (2022). Effect of Web Flexibility in Gear Engagement: A Proposal of Analysis Strategy. Vibration, 5(2), 200-212. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration5020013







