Abstract
In gear transmissions, vibration causes noise and malfunction. In actual applications, misalignments contribute to intensifying the destructive effect of vibrations. In this paper, the nonlinear dynamics of a spiral bevel gear pair, with small helix angle, considering different misalignments, are deeply investigated. Axial misalignment, radial misalignment, and the combination of these two types are considered in this study. The governing equation is numerically solved through an implicit Runge–Kutta scheme. Since the main goal of this study is the analysis of the dynamic scenario, the mesh stiffness of the gear pair is obtained from the literature. The dynamical system is nonlinear and time-varying; it is analyzed through time responses, phase portraits, Poincaré maps, and bifurcation diagrams. Results show that, among the considered three cases with different types of misalignments, the spiral bevel gear with axial misalignment is the worst destructive case; aperiodic, subharmonic, and multiperiod responses are observable for this case. It is interesting that the chaotic responses for the case, having both types of misalignments, are less likely for the case with axial misalignment, only.
1. Introduction
The role of a bevel gears is undeniable, as they are extensively utilized to transfer the power between nonparallel shafts. Bevel gears consist of a different type of geometries, the most important of them being the spiral bevel gears (SBG). The vibrations affect the stress distribution, the contact pressure, and the fatigue life of a geartrain. The nonlinear behavior of SBG is worthy of investigation; see, e.g., [1]. Various parameters, such as backlash and time-varying mesh stiffness, exert a prominent influence on the nonlinearity. Moreover, one of the important sources of the driveline noise and the vibration is the gear mesh transmission error.
A wide range of methods has been used to study gear pairs [2,3,4,5,6]. The nonlinear vibration of actual gear pairs, with some likely faults and conditions, has become the main issue among researchers due to vast ranges of applications of the gear systems. Simon [7] examined the influence of tooth errors and misalignments on angular displacements with different angular velocity ratios. Truncated contacts and edge loading are caused by misalignment, which directly affect the contact pattern. Consequently, it results in the high edge stresses on the teeth flank, which leads to micropitting [8]. In [9], Buzzoni et al. proposed a methodology to assess the contact pattern for straight bevel gears based on gear parameters, different speeds, and surface finishing. Spievak et al. [10] investigated and simulated the effect of a crack in SBG. Moreover, the tooth load is considered a function of time and location. The dynamic model of SBG considering the friction and elastic contact deformation has been studied by Yu-jing et al. [11].
Most of the methods for the evaluation of time-varying mesh stiffness are mainly based on the fact that the gear pair is perfectly mounted and located at their theoretical location. To overcome this limitation, Luo et al. [12] came up with a gear mesh kinematic model, which was capable of calculating the actual contact positions of teeth with time-varying mesh stiffness. The suggested kinematic model helped to compute the actual time-varying mesh stiffness of both cracked and healthy teeth. Li [13] studied the effects of tooth profile modifications and the effects of misalignments of gear shafts for spur gears. Their study clarified that the tooth profile modification has a significant effect on tooth contact stresses, load sharing ratios, and mesh stiffnesses. Driot and Perret-Liaudet [14] analyzed a spur gear pair considering the manufacturing errors. Moreover, they investigated the effect of shaft misalignment and gear tooth profile errors. In order to diagnose faults, shaft misalignment, and rotor unbalance in a gear system and monitor the condition of rotating, Jalan and Mohanty [15] presented a method based on residual generation technique. Hotait et al. [16] studied how shaft misalignments affect the root stresses of the gears with or without the lead crown. The study aimed to develop an experimental test program for helical gears with misalignments and lead crown. Various shaft misalignments and different crowns, as well as a wide range of torques, were taken into consideration in these experiments. Mu et al. [17] found that working under a condition of heavy load or misalignment could lead to edge contact, even though a spiral bevel gear with high contact ratio is designed theoretically perfectly. To avoid the edge contact, the tooth surface modification method based on cutter blade profile correction is proposed. To validate their method, a face-milling spiral bevel gear is simulated by means of TCA and FEM methods, and their results are compared with the results of the proposed method. This method, which is based on corrected the cutter blade profile, could effectively increase the avoidance of edge contact. Vevit et al. [18] presented an efficient TCA model for spiral bevel gears with misalignment. Their model could be used in order to predict the transmission error and contact pressures of a gear pair with misalignment more accurately. An et al. [19] represented a model for the spiral bevel gear based on geometric elements, which is insensitive to the angle misalignment and enhances the load capacity. Their proposed model is validated by the experimental test results.
The overall objective of the present paper is to investigate the nonlinear dynamics of an SBG pair with small helix angle, which is based on the influence of misalignment in actual SBG manufacturing. The dynamic simulation of SBG is main purpose of the present works; the mesh stiffness of the system [1] is the starting point. The novelty of the present study is the investigation of misalignment effect on the dynamic behavior of the spiral bevel gear pair. Due to the backlash and mesh stiffness fluctuation, the governing equations of motion are nonlinear and time-dependent. Therefore, for the investigation of the vibration behavior, a numerical method, based on an implicit Runge–Kutta method, is applied. This study illustrates the dynamic behavior of SBG affected by different misalignments.
2. Physical Model
Consider the bevel gear pair of Figure 1: the translational degrees of freedom for both driver and driven gears are constrained in all directions; the gears can rotate around their axes, but other rotations are not allowed. Furthermore, some assumptions are considered: pure involute profile, dry and frictionless contact; moreover, thermal effects are not considered. To investigate the effect of misalignments on dynamic behavior, three cases are considered as follows [1]:
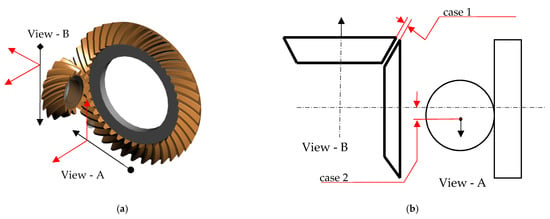
Figure 1.
Geometric definition of misalignment errors; case 3 is the combination of the cases 1 and 2. (a) 3-D view of the SBG model. (b) 2-D view of the model to show the radial and axial misalignments.
- Case 1: Axial misalignment (offset 0.01 mm);
- Case 2: Radial misalignment (offset 0.015 mm);
- Case 3: Combination of the axial and radial misalignments (0.01 mm and 0.015 mm, respectively).
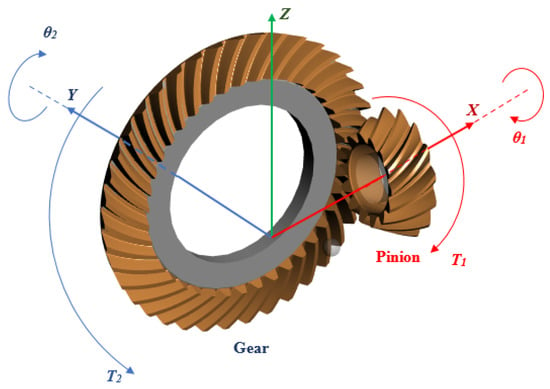
Figure 2.
The dynamic model of a gear system with rotational degrees of freedom.
Due to mounting and manufacturing error or teeth profile modifications, the backlash between mating teeth varies; it is called geometric transmission error, or e(t). The linear dynamic transmission error (DTE) along the line of action is defined as . Let , the speed ratio. The two equations are merged, and the following equation is obtained.
where , , and . Equation (2) presents the dimensional equivalent rotational displacement of the gear mesh.
is the backlash function of the rotational displacement (Equation (3)). The backlash function times the stiffness returns the restoring force [3]. Whenever is between and , the contact loss happens [24]. For , the contact occurs in forwarding face flank, while if undesired backside contact happens; see [22]. Besides, the torsional mesh stiffness of the gear set is a time-varying function, which is periodic with fundamental mesh frequency . In Figure 3, the mesh stiffness and the loaded transmission error (LTE) are presented withing a meshing period [1]. The equivalent mesh stiffness Fourier series is given by:
where , , and are determined by MATLAB function for Fourier series. In this study, the main goal is to investigate the effects of different types of misalignments on spiral bevel gear dynamics. Consequently, the time-varying mesh stiffnesses for all cases are brought from the study, which is done previously by Hu [1] on the mesh stiffness of the spiral bevel gear.
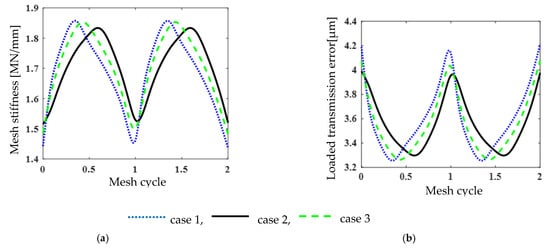
Figure 3.
Mesh stiffness (a) and loaded transmission error (b) of the pinion.
Table 1 shows the peak-to-peak of mesh stiffness and LTE for the mentioned cases. It is to be noted that the case 1 (axial misalignment) is the one that has the maximum peak-to-peak of LTE and mesh stiffness. In addition, the peak-to-peak for case 3 (both radial and axial misalignments) is bigger than the peak-to-peak for case 2, but it is smaller than the case 1, see Table 1.

Table 1.
The peak-to-peak amount of LTE and mesh stiffness.
In order to normalize the governing equation, new parameters are introduced as follows:
Consequently, Equations (2)–(4) can be rewritten as follows:
Equation (6) is a nonlinear differential equation with time-varying parameters. This governing equation is solved numerically “RADAU scheme”, which is an implicit scheme of the Runge–Kutta algorithm; see, e.g., [2,3,22,25,26].
3. Numerical Results
The numerical data of the considered SBG pair are listed in Table 2. It is to be noted that gear pairs with small helix angle are used in power transmission gearbox in aerospace applications, due to its high loaded tooth contact performance [1,27]. The time response for each case is calculated, and phase portrait and Poincaré map are extracted from these results. Bifurcation diagrams and root mean square (RMS) are obtained by varying the excitation frequency, i.e., the pinion rotational speed.

Table 2.
Geometric parameters of the SBG pairs.
The time response of the SBG is simulated for different mesh frequencies, i.e., different rotational speeds [26]. For each frequency, the transient is separated from the steady-state; the first 1000 periods are considered as transient parts, and after that, we assume that the effect of frequency variation is expired. The bifurcation diagrams of Poincaré maps, the amplitude frequency diagram, and the phase portraits are extracted from the last at least ten periods of the time responses. The Poincaré maps are extracted from time-consuming integration for 3000 periods after transient removal.
Figure 4 and Figure 5 illustrate the bifurcation diagrams of Poincaré maps vs. the mesh frequency ratio of the spiral bevel pinion with axial misalignment (case 1). Figure 4 represents the case of backward speed variations, and Figure 5 presents the forward. For each frequency, the final condition of each response is considered as the initial condition of the subsequent frequency. In Figure 4 and Figure 5, one can see three diverse trends: periodic (single line), 2T subharmonic (2 lines), and unsteady (cloud of points), each of which is depicted by a different color: black, blue, and red, respectively. Note that unsteady can be chaotic or quasiperiodic.
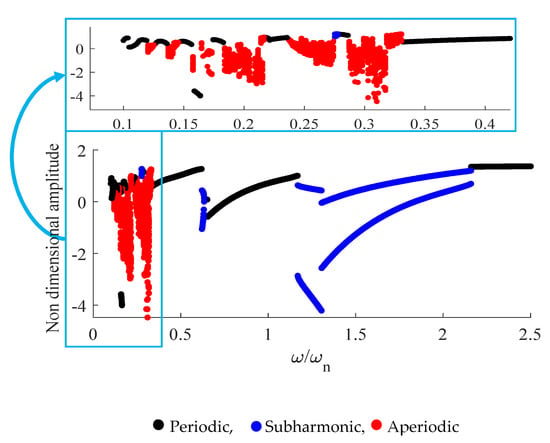
Figure 4.
Bifurcation diagram based on backward simulation, case 1.
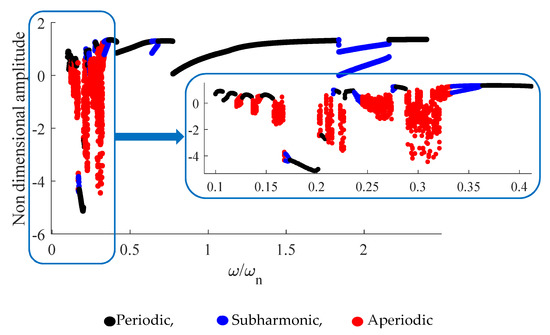
Figure 5.
Bifurcation diagram based on forward simulation, case 1.
Simulations are carried out in the range of . For the backward and forward simulations, initially, the vibration is periodic for the range of ; from , nonsmooth subharmonic bifurcation takes place. In the backward simulation, the periodic motion occurs for the range of . This range for the forward simulation is . However, from 0.633 to 0.620 for backward simulation and from 0.678 to 0.642 for the forward simulation, the subharmonic behavior appears again. For in the backward simulation and in the forward simulation, periodic responses are observed, although chaotic, periodic, and subharmonic motions alternate in these narrow intervals.
Figure 6 shows the dynamic behavior for the radial misalignment (case 2). Similarly, Figure 7 shows the dynamic behavior for the combination of axial and radial misalignments (case 3). In each figure, results are deeply investigated based on the backward simulation and also on the forward simulation. Periodic response and subharmonic response are recognizable in these bifurcation diagrams. In spite of case 1 (axial misalignment), there is no chaotic response for cases 2 and 3. Firstly, during the backward simulation, periodic behavior starts from to for two cases 2 and 3 (Figure 6a and Figure 7a, respectively), and then, decreasing the speed, the periodic response switches to subharmonic. Two branches emerge until the frequency ratio approaches to about 1.29 for cases 2 and 3. It is observed that cases 2 and 3 have the same behavior in the backward simulation for ; however, this behavior is completely different for . Secondly, in the case of the forward simulation, subharmonic occurs twice for the cases 2 and 3, the longest of which starts at about and continues up to 1.9 (Figure 6b and Figure 7b). At about , it is seen that the bifurcation trend experiences a jump with different amplitudes. Although periodic orbits are observed for both cases (cases 2 and 3), some jumps occur, leading 1T to 2T responses and vice versa.
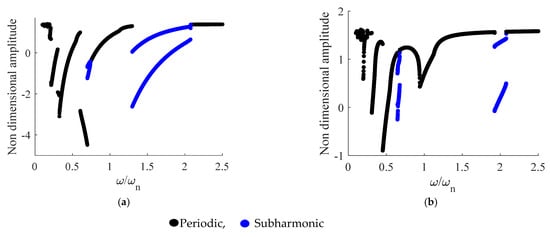
Figure 6.
Bifurcation diagram based on (a) backward and (b) forward simulations, case 2.
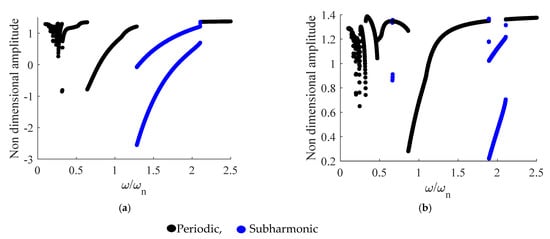
Figure 7.
Bifurcation diagram based on (a) backward and (b) forward simulations, case 3.
Figure 8 shows the amplitude–frequency diagram for the case 1 in terms of backward and forward simulations. Similarly, Figure 9 shows amplitude–frequency diagram for case 2, Figure 9a, and case 3, Figure 9b. The primary resonance is identified, as well as superharmonic resonances (), and a parametric resonance (). These results show that, for the first case (axial misalignment), aperiodicity is more likely with respect to cases 2 and 3. For case 1, the system experiences unsteady phenomena when it approaches superharmonic resonances . It means the axial misalignment plays a destructive role in the vibration; this is not evident for radial misalignment or radial and axial misalignments. By considering the bifurcation diagram (Figure 4 and Figure 5) for case 1, a chaotic response occurred when .
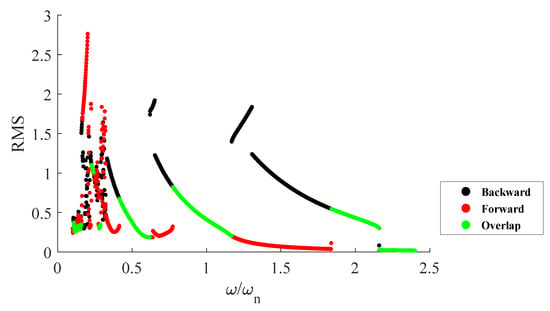
Figure 8.
RMS diagram of the forward and backward simulations, case 1.
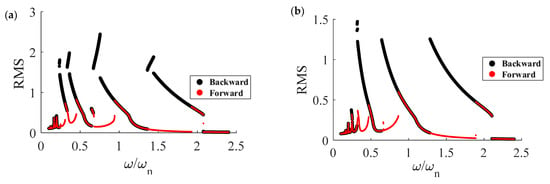
Figure 9.
RMS diagram, (a) case 2, (b) case 3.
Figure 10 shows the nonlinear dynamics for specific operating conditions by means of three types of representations: time history, phase portrait, and Poincaré map. For the sake of brevity, only the results of the first case are presented here, while no complex dynamics are observed for cases 2 and 3. Six frequencies with different operating conditions are brought in Figure 10. The analysis of Figure 10, in particular, the Poincaré maps, shows that the unsteady responses are probably chaotic dynamics; indeed, the Poincaré maps show an interesting fractal structure.
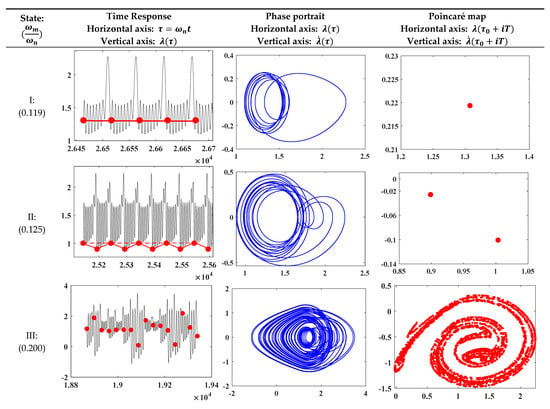
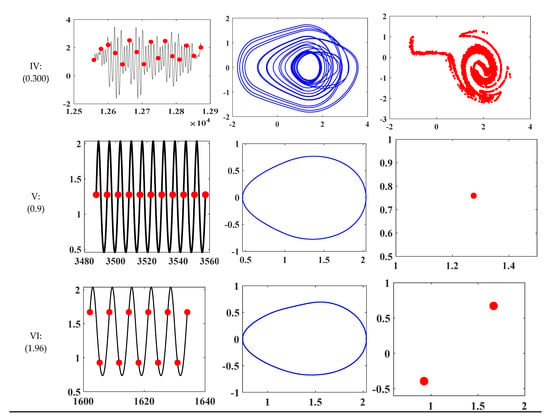
Figure 10.
Nonlinear vibration behavior in different frequency ratios for backward simulation, case 1.
It is evident that there is a high probability of unsteady response at low speed (see Figure 10). As a consequence, the maximum value of the dynamic response (as shown in the time response graph) has higher amplitude when the system with axial misalignment works for the frequency ranges with possessing chaos phenomena even at low speeds; see cases 3 and 4. By increasing the speed, the behavior of the system gets steadier, and the only phenomenon that occurred is subharmonics.
4. Conclusions
This paper investigates the effect of misalignments on the dynamics of spiral bevel gears with small helix angle. Due to the time-varying mesh stiffness and backlash, the nonlinear equation with variable parameters is simulated by means of a Runge–Kutta method. The results of this manuscript are listed as follows:
- For axial misalignment, bifurcation analysis shows three diverse scenarios: periodic, subharmonic, and aperiodic. It is notable that, while , chaotic phenomena frequently occur.
- There is no chaotic response for the case with radial misalignment and the combination of the radial and axial misalignments. These two cases have the same behavior for ; however, this behavior is completely different for .
- The third case introduces the SBG with both axial and radial misalignments; thus, it is expected that the relevant dynamic behavior is worse than the case with just axial misalignment. However, in contrast with case 1, the case with both types of considered misalignment demonstrates less chaotic responses.
The most important result of this paper is that the vibration response for the case with the combination of both two axial and radial misalignments is less than the case with only axial misalignment. To explain this phenomenon, we should point out that the peak-to-peak of mesh stiffness for the case with axial misalignment is bigger than the peak-to-peak of mesh stiffness for the case with the combination of misalignments. Finally, one can conclude that adding radial misalignment to the axial misalignment may decrease the wrecking effect of the axial misalignment.
It should be mentioned that there are some assumptions in order to drive the governing equations: no-friction and one degree of freedom. Therefore, for further research, it would be of great benefit if it is possible to investigate the dynamics of the spiral bevel gear pairs without this simplification and increase the number of degrees of freedom. Moreover, in this study, only two different types of misalignments and their combination are considered; for future works, one suggestion is to investigate the effect of all different types of misalignments and their combinations on the dynamics of the spiral bevel gear.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.P. and F.S.S.; data curation, F.P. and F.S.S.; methodology, F.P. and F.S.S.; validation, F.S.S. and M.M.; formal analysis, F.P., F.S.S. and M.M.; investigation, F.P., F.S.S. and M.M.; resources, F.P.; writing—original draft preparation, F.S.S. and M.M.; writing—review and editing, F.P.; software, M.M.; visualization, M.M.; supervision, F.P. and F.S.S.; project administration, F.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors thank the Region Emilia Romagna for supporting this research through the project “DiaPro4.0—Sistema “cost effective” multisensore di Diagnostica- Prognostica integrato in azionamenti meccanici dell’Industria 4.0”—(PG/2018/632156).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in the current study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Nomenclature
| aj, bj | Fourier coefficients |
| c | Damping coefficient between the mesh gear teeth of the pairs |
| Ceq | Equivalent damping coefficient |
| E | Module of elasticity |
| eθ(t) | Time-varying circumferential no-load transmission error |
| I1, I2 | Rotary inertia of pinion and gear |
| Ieq | Equivalent rotary inertia |
| N1 | Teeth number of pinion |
| n | Gear ratio of the gear pair |
| Np | Number of samples for mesh stiffness computation |
| k0 | Average value of torsional mesh stiffness of the gear pair |
| k | Time-varying mesh stiffness of the gear pair |
| Keq | Equivalent mesh stiffness of the gear pair |
| Km | Equivalents of the torsional mesh stiffness of the gear pair |
| rb1, rb2 | Base radii of pinion and gear |
| S | Number of harmonics |
| T1 | Constant driver torque |
| T2 | Constant breaking torque |
| w | Face width |
| α | Pressure angle |
| γs | Input shaft speed |
| ζ | Damping ratio |
| θ1 | Driver angular displacement |
| θ2 | Driven angular displacement |
| θb | Angular backlash |
| λ | Linear dynamic transmission error along the line of action |
| λθ | Angular dynamic transmission error |
| ν | Poisson ratio |
| ωm | Fundamental mesh frequency |
References
- Hu, Z.; Ding, H.; Peng, S.; Tang, Y.; Tang, J. Numerical determination to loaded tooth contact performances in consideration of misalignment for the spiral bevel gears. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 151, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaie, M.; Samani, F.S.; Motahar, H. Nonlinear vibration of crowned gear pairs considering the effect of Hertzian contact stiffness. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samani, F.S.; Molaie, M.; Pellicano, F. Nonlinear vibration of the spiral bevel gear with a novel tooth surface modification method. Meccanica 2019, 54, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgüven, H.N.; Houser, D.R. Mathematical models used in gear dynamics—A review. J. Sound Vib. 1988, 121, 383–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H. Dynamic modelling and parametric optimization of a full hybrid transmission. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part K J. Multi-Body Dyn. 2019, 233, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paouris, L.; Rahmani, R.; Theodossiades, S.; Rahnejat, H.; Hunt, G.; Barton, W. Inefficiency predictions in a hypoid gear pair through tribodynamics analysis. Tribol. Int. 2018, 119, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, V. Influence of tooth errors and misalignments on tooth contact in spiral bevel gears. Mech. Mach. Theory 2008, 43, 1253–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisaus, V.; Mohammadpour, M.; Theodossiades, S.; Rahnejat, H. Effect of teeth micro-geometrical form modification on contact kinematics and efficiency of high performance transmissions. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part K J. Multi-Body Dyn. 2017, 231, 538–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buzzoni, M.; D’Elia, G.; Mucchi, E.; Dalpiaz, G. A vibration-based method for contact pattern assessment in straight bevel gears. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 120, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spievak, L.E.; Wawrzynek, P.A.; Ingraffea, A.R.; Lewicki, D.G. Simulating fatigue crack growth in spiral bevel gears. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2001, 68, 53–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Y.-J.; Yao, L.-G.; Zhang, J. Nonlinear Finite Element Simulation and Analysis of Double Circular Arc Spiral Bevel Gear Nutation Drive. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications, Shenyang, China, 8–11 August 2019; Springer: New York, NY, USA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Baddour, N.; Liang, M. Effects of gear center distance variation on time varying mesh stiffness of a spur gear pair. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2017, 75, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. Effects of misalignment error, tooth modifications and transmitted torque on tooth engagements of a pair of spur gears. Mech. Mach. Theory 2015, 83, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driot, N.; Perret-Liaudet, J. Variability of modal behavior in terms of critical speeds of a gear pair due to manufacturing errors and shaft misalignments. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 292, 824–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalan, A.K.; Mohanty, A. Model based fault diagnosis of a rotor–bearing system for misalignment and unbalance under steady-state condition. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 327, 604–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotait, M.; Kahraman, A. Experiments on root stresses of helical gears with lead crown and misalignments. J. Mech. Des. 2008, 130, 074502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Li, W.; Fang, Z. Tooth surface modification method of face-milling spiral bevel gears with high contact ratio based on cutter blade profile correction. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 106, 3229–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivet, M.; Tamarozzi, T.; Desmet, W.; Mundo, D. On the modelling of gear alignment errors in the tooth contact analysis of spiral bevel gears. Mech. Mach. Theory 2021, 155, 104065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Zhang, L.; Qin, S.; Lan, G.; Chen, B. Mathematical design and computerized analysis of spiral bevel gears based on geometric elements. Mech. Mach. Theory 2021, 156, 104131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yinong, L.; Guiyan, L.; Ling, Z. Influence of asymmetric mesh stiffness on dynamics of spiral bevel gear transmission system. Math. Probl. Eng. 2010, 2010, 124148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang-Jian, C.-W. Nonlinear dynamic analysis for bevel-gear system under nonlinear suspension-bifurcation and chaos. Appl. Math. Model. 2011, 35, 3225–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonori, G. Static and Dynamic Modeling of Gear Transmission Error. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, Modena, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kahraman, A.; Lim, J.; Ding, H. A dynamic model of a spur gear pair with friction. In Proceedings of the 12th IFToMM World Congress, Besançon, France, 17–21 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Parker, R.G. Nonlinear dynamics of idler gear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 2008, 53, 345–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motahar, H.; Samani, F.S.; Molaie, M. Nonlinear vibration of the bevel gear with teeth profile modification. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016, 83, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggioni, M.; Samani, F.S.; Bertacchi, G.; Pellicano, F. Dynamic optimization of spur gears. Mech. Mach. Theory 2011, 46, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, H.; Tang, J. Accurate numerical computation of loaded tooth surface contact pressure and stress distributions for spiral bevel gears by considering time-varying meshing characteristics. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2019, 135, 102683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenship, G.; Kahraman, A. Steady state forced response of a mechanical oscillator with combined parametric excitation and clearance type non-linearity. J. Sound Vib. 1995, 185, 743–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).