The Control of an Active Seat Suspension Using an Optimised Fuzzy Logic Controller, Based on Preview Information from a Full Vehicle Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
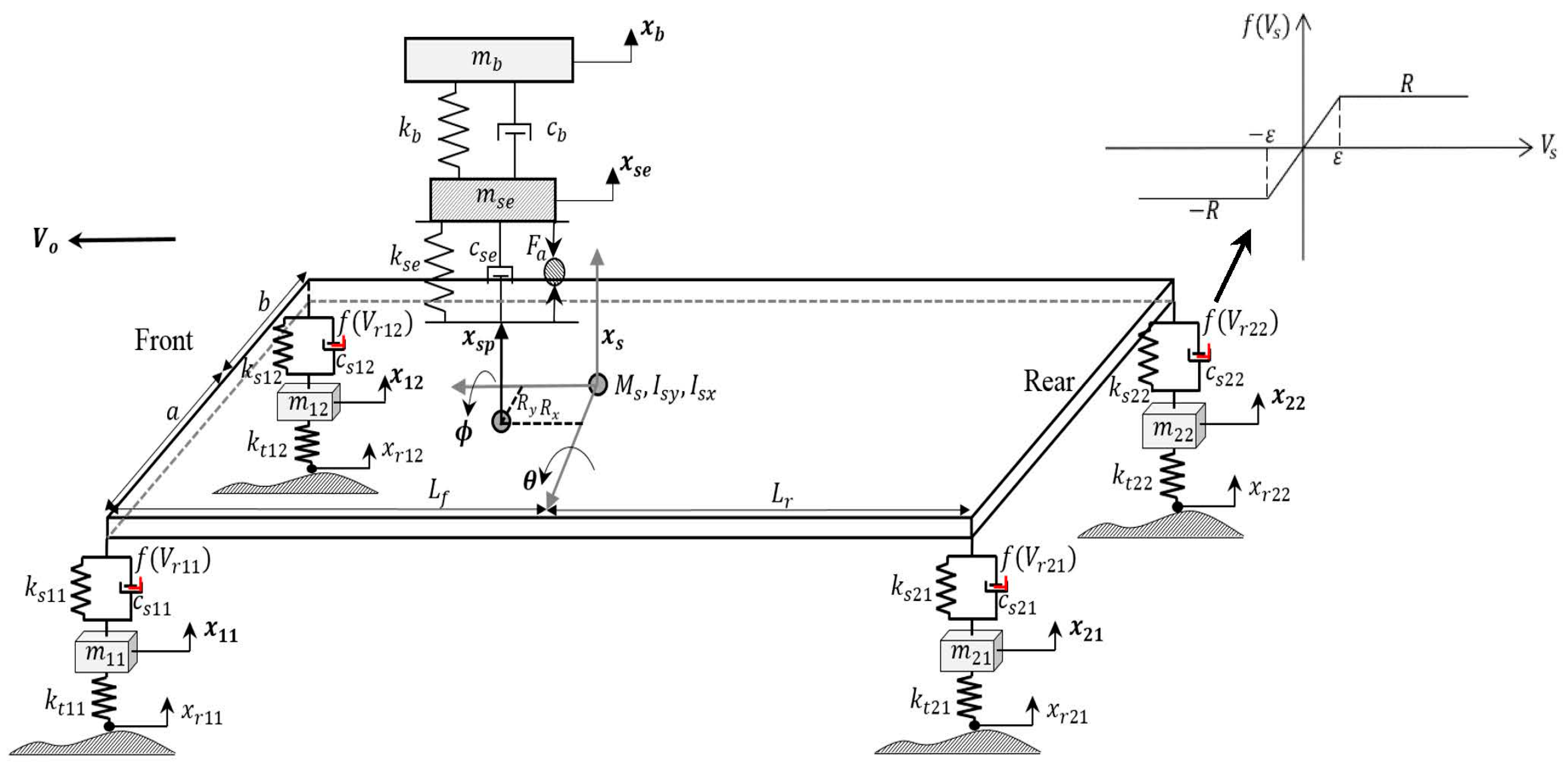
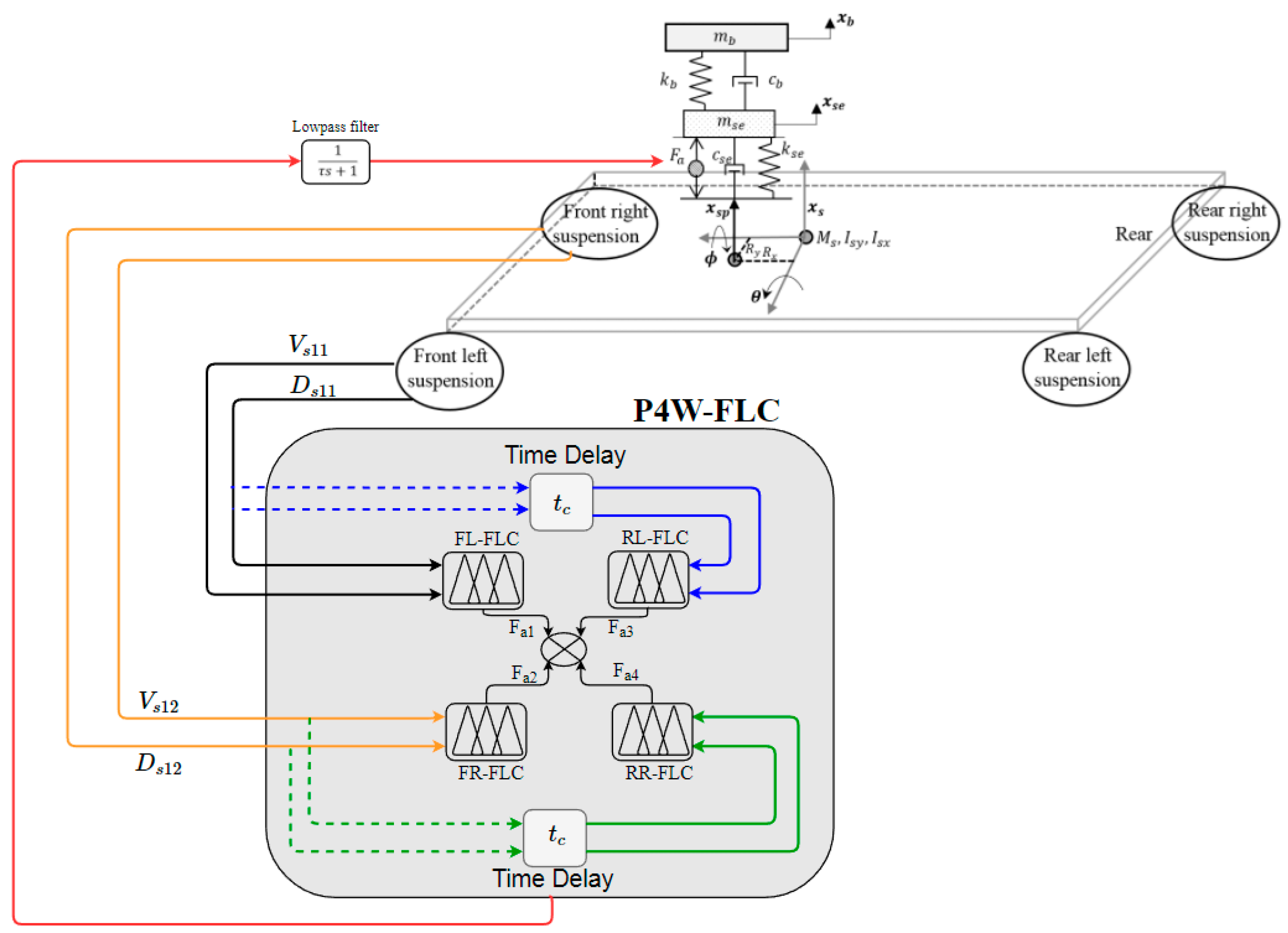
1.1. Integrated Model
- (1)
- Vehicle body motion:
- (a)
- Bouncewhere is the suspension dynamic force at each vehicle suspension, given by:while is the dry friction force of the suspension damper at each wheel, is the seat suspension force, and is the controller force.
- (b)
- Pitch
- (c)
- Roll
- (2)
- Un-sprung masses
- (3)
- Seat suspension
- (4)
- Driver’s body
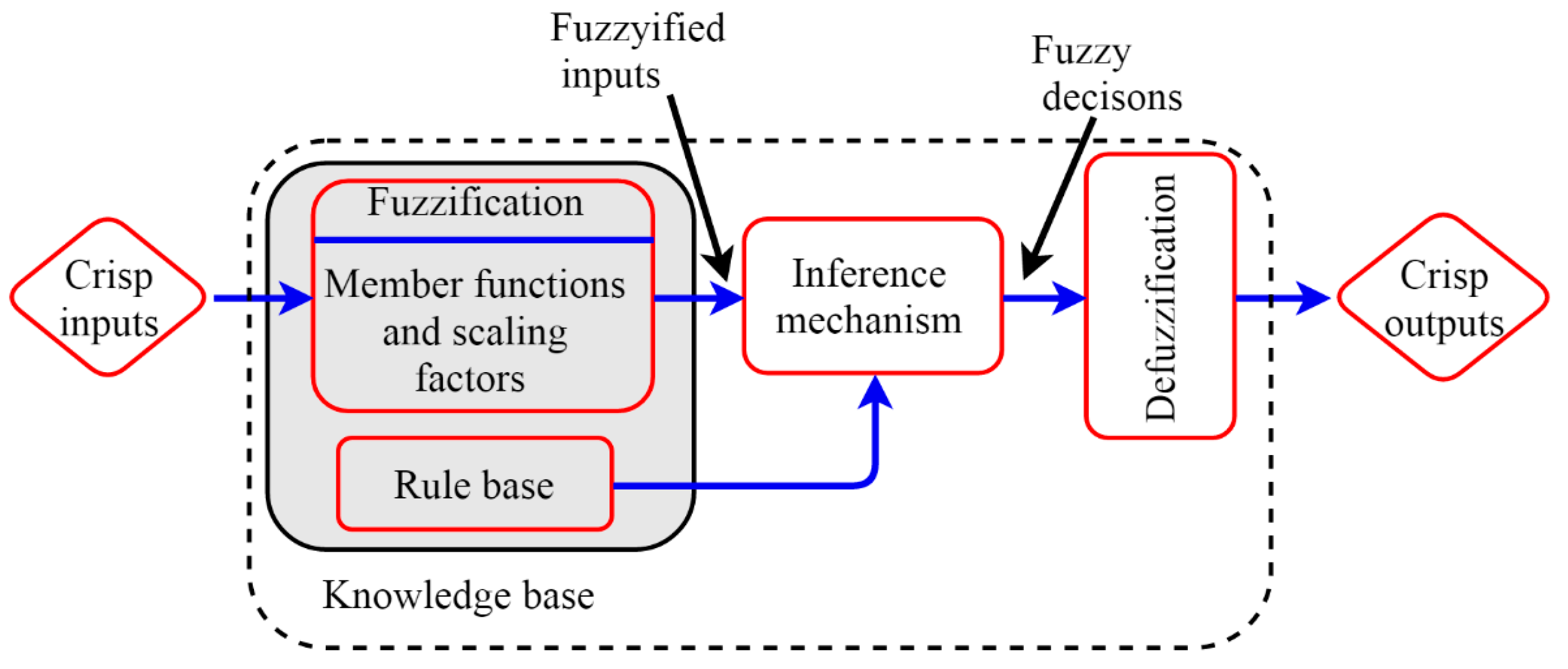
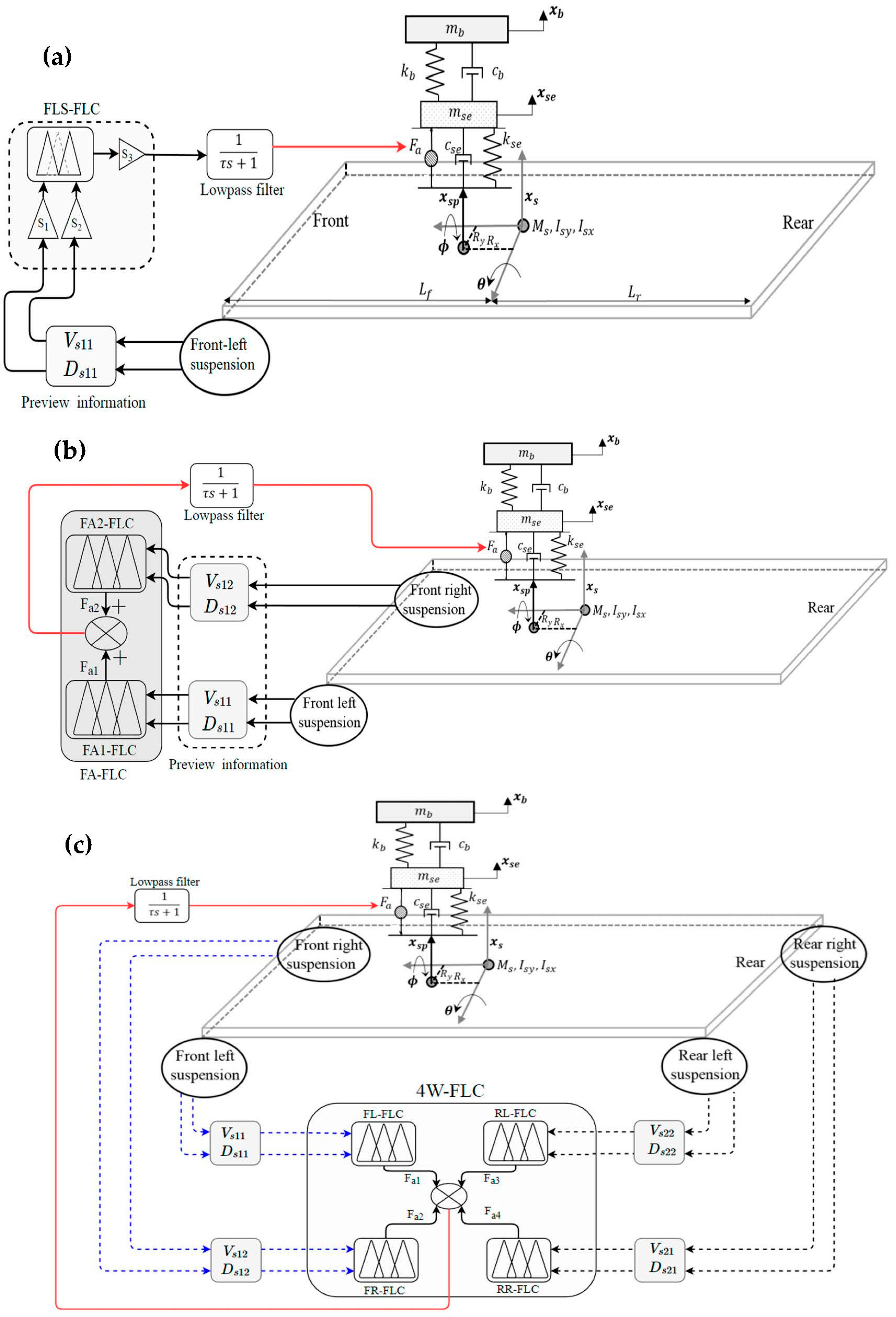
1.2. Fuzzy Logic Controller
- (1)
- A fuzzification interface, which changes the controller inputs to linguistic variables that can be utilised in the inference mechanism.
- (2)
- A rule-base (RB), which is a set of linguistic (“if-then”) rules that stores the knowledge of how to control the process.
- (3)
- An inference mechanism, which uses the linguistic inputs and the RB to produce the control decision.
- (4)
- A defuzzification interface, which converts the linguistic outputs into crisp ones.
1.3. Optimisation Process
2. Simulation Analysis
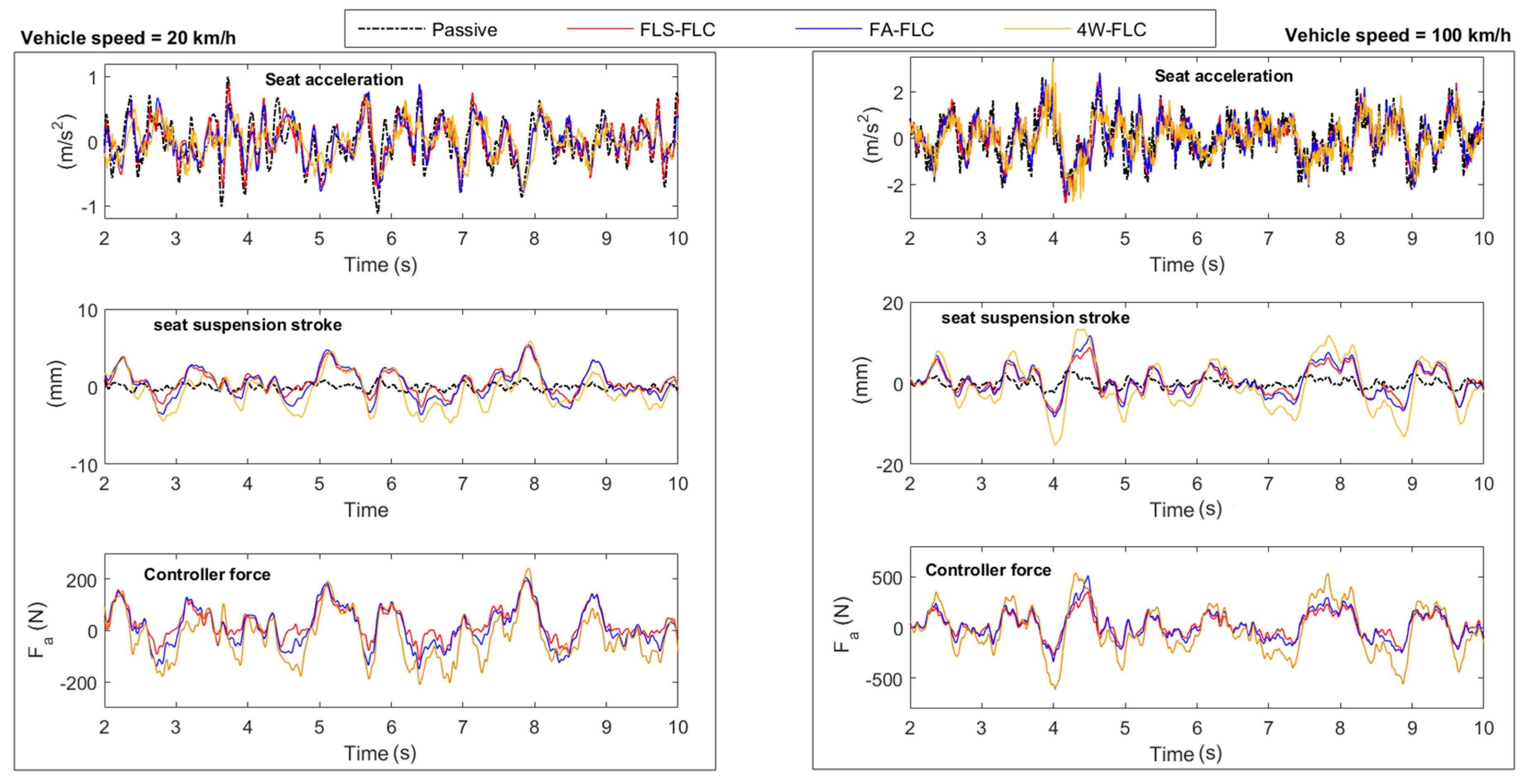
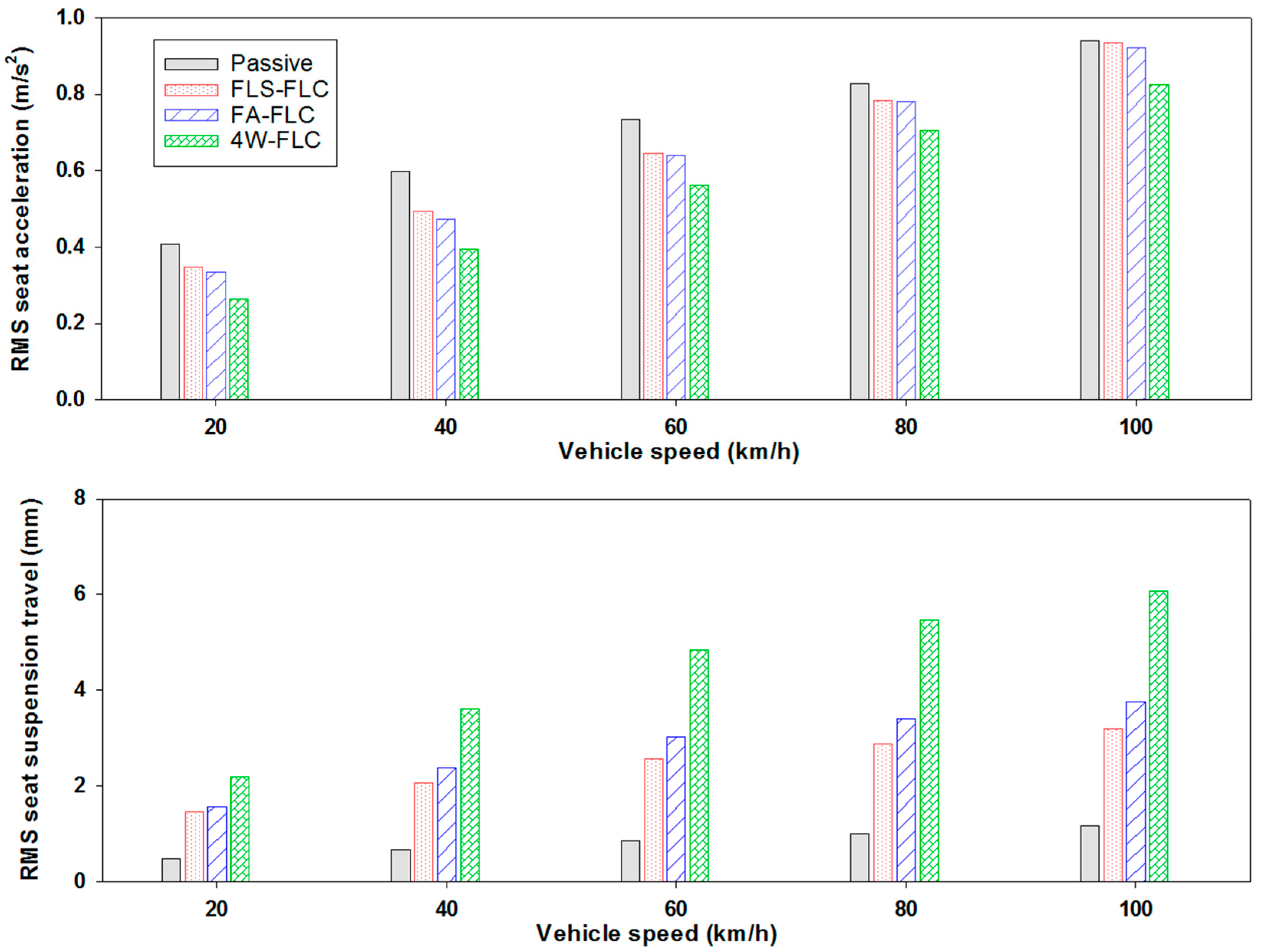
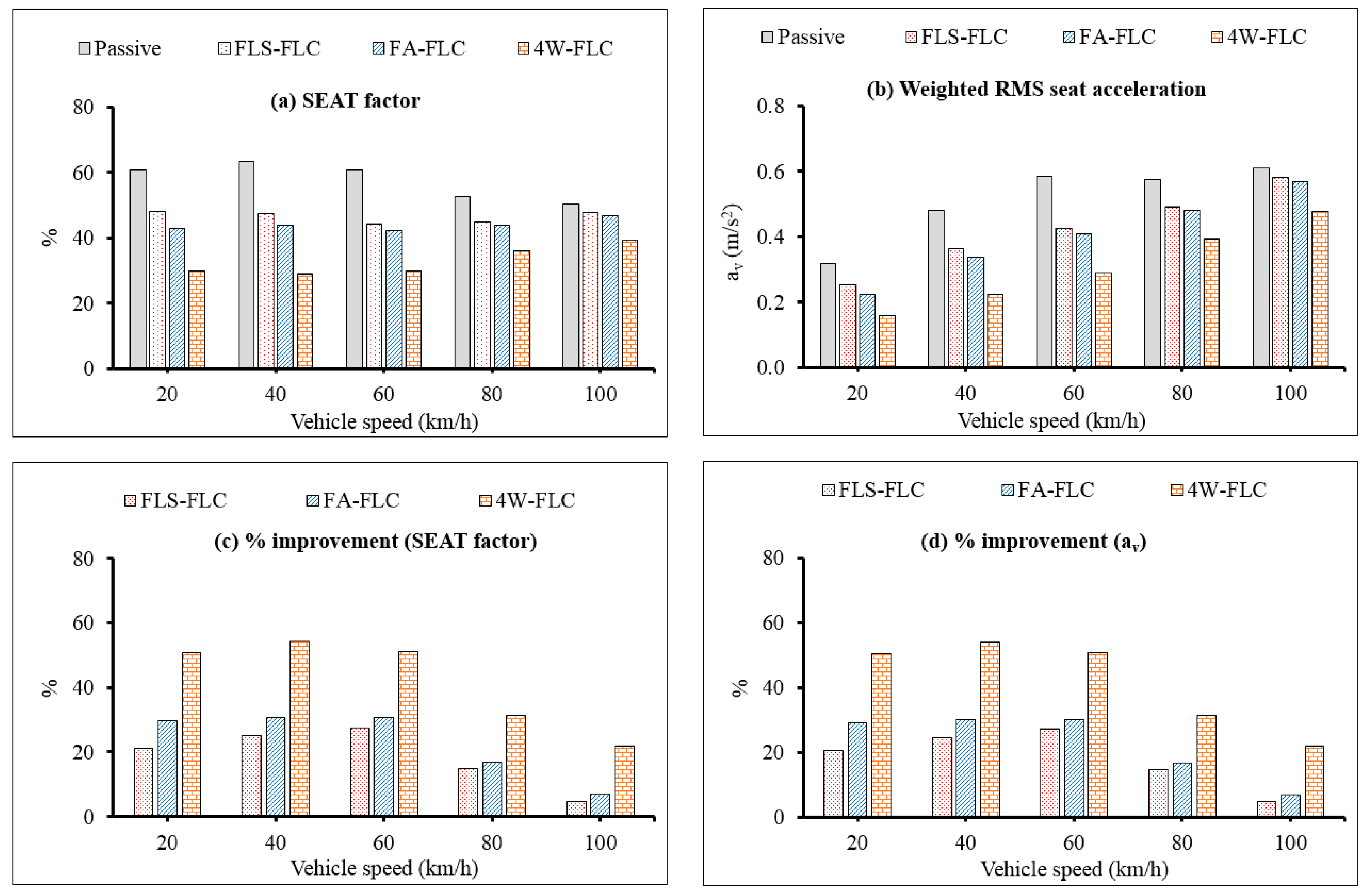
2.1. Random Road
2.2. Parameter Uncertainties
2.3. Road “Bump” Input
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Notation
| 4W | Four wheel |
| 4W-FLC | Four wheel fuzzy logic controller |
| ACGIH | American Conference of Government Industrial Hygienists |
| DOFs | Degrees of freedom |
| FA | Front axle |
| FA-FLC | Front axle fuzzy logic controller |
| FLC | Fuzzy logic controller |
| FLS | Front left suspension |
| FLS-FLC | Front left suspension fuzzy logic controller |
| ISO | International standard organization |
| LMS | Least Mean squares |
| MFs | Membership functions |
| P4W-FLC | Practical four wheel fuzzy logic controller |
| PSD | Power spectral density |
| PSO | Particle swarming optimisation |
| RB | Rule base |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| SEAT | Seat Effective Amplitude Transmissibility factor |
| TLVs | Threshold limit values |
| Symbol | Description |
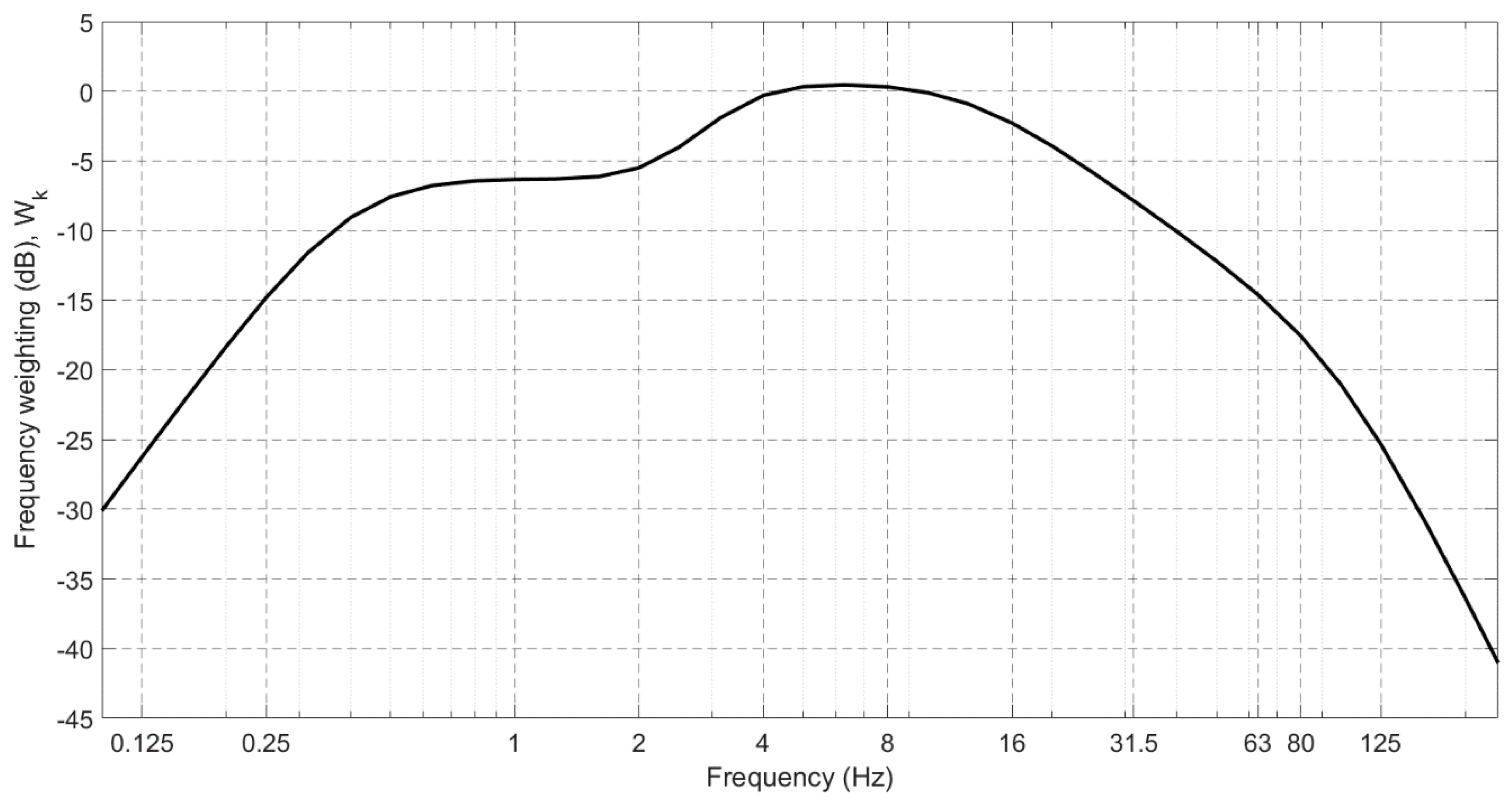
| Frequency-weighted RMS acceleration | |
| Frequency-weighting value at the centre frequency | |
| Weighted root mean square vertical acceleration at the seat’s base | |
| Weighted root mean square of the vertical seat acceleration | |
| Maximum seat stroke | |
| Minimum seat stroke | |
| Vertical acceleration of the sprung mass | |
| Vertical acceleration of the seat | |
| Vertical acceleration of the usprung mass | |
| Vehicle suspension displacement | |
| Actuator control force | |
| Vehicle suspension dynamic force | |
| Seat suspension dynamic force | |
| Moment of inertia in the longitudinal direction | |
| Moment of inertia in the lateral direction | |
| Rx | Lateral distance from the driver’s seat to C.G |
| Longitudinal distance from the driver’s to C.G | |
| Vehicle suspension velocity, | |
| Forward vehicle speed | |
| Vehicle suspension displacement, | |
| Damping coefficient of the vehicle suspension | |
| Damping coefficient of the seat suspension | |
| Stiffness of the vehicle suspension | |
| Stiffness of the seat suspension | |
| Stiffness of the tyre | |
| Human body mass | |
| Human body spring rate | |
| Damping coefficient of human body | |
| maximum allowable seat stroke | |
| minimum allowable seat stroke | |
| vertical displacement of the seat | |
| vertical displacement of the usprung mass | |
| Pitch angular acceleration | |
| Roll angular acceleration | |
| R | Dry friction force limit |
| Dry friction force (full vehicle model) | |
| Viscous band | |
| Pitch rotation angle | |
| Cut-off frequency | |
| Roll rotation angle |
References
- Anna, D.H. The Occupational Environment: Its Evaluation, Control and Management; American Industrial Hygiene Association: Dayton, OH, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Maciejewski, I.; Meyer, L.; Krzyzynski, T. Modelling and multi-criteria optimisation of passive seat suspension vibro-isolating properties. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 324, 520–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnopp, D. Active and semi-active vibration isolation. Trans. ASME J. Vib. Acoust. 1995, 117, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawana, M.; Shimogo, T. Active suspension of truck seat. Shock Vib. 1998, 5, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, Z.; Fei, S.; Tian, E. Robust control of automotive active seat-suspension system subject to actuator saturation. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control Trans. ASME 2014, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Sun, S.; Li, H.; Du, H.; Li, W. Active control of an innovative seat suspension system with acceleration measurement based friction estimation. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 384, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, H. Vibration control for active seat suspension systems via dynamic output feedback with limited frequency characteristic. Mechatronics 2011, 21, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Hillis, A.J.; Darling, J. Adaptive control of an active seat for occupant vibration reduction. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 349, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillis, A.J. Adaptive Control of Active Engine Mounts. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sezgin, A.; Hacioglu, Y.; Yagiz, N. Sliding Mode Control for Active Suspension System with Actuator Delay. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology. Int. J. Mech. Aerosp. Ind. Mechatron. Manuf. Eng. 2016, 10, 1356–1360. [Google Scholar]
- Yagiz, N.; Yuksek, I.; Sivrioglu, S. Robust Control of Active Suspensions for a Full Vehicle Model Using Sliding Mode Control. JSME Int. J. Ser. C Mech. Syst. Mach. Elem. Manuf. 2000, 43, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, T.; Kume, A.; Kurimoto, M.; Hino, J. Construction of an active suspension system of a quarter car model using the concept of sliding mode control. J. Sound Vib. 2001, 239, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eski, I.; Yıldırım, Ş. Vibration control of vehicle active suspension system using a new robust neural network control system. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2009, 17, 778–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.V.C.; Prahlad, V. A tunable fuzzy logic controller for vehicle-active suspension systems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1997, 85, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guclu, R. Fuzzy Logic Control of Seat Vibrations of a Non-Linear Full Vehicle Model. Nonlinear Dyn. 2005, 40, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurel, J.; Mandow, A.; García-Cerezo, A. Tuning a fuzzy controller by particle swarm optimization for an active suspension system. In Proceedings of the IECON 2012 38th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Montreal, QC, Canada, 25–28 October 2012; pp. 2524–2529. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, S.Y.; Kwon, W.H. Genetic-based fuzzy control for half-car active suspension systems. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 1998, 29, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkawy, A.B. Fuzzy and adaptive fuzzy control for the automobiles’ active suspension system. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2005, 43, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskin, Y.; Hacioglu, Y.; Yagiz, N. The use of fuzzy-logic control to improve the ride comfort of vehicles. Strojniski Vestn. 2007, 53, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Taskin, Y.; Hacioglu, Y.; Yagiz, N. Experimental evaluation of a fuzzy logic controller on a quarter car test rig. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2017, 39, 2433–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; Koch, G.; Pellegrini, E.; Spirk, S.; Lohmann, B. Multi-objective preview control of active vehicle suspensions: Experimental results. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2nd International Conference on Advanced Computer Control (ICACC), Shenyang, China, 27–29 March 2010; pp. 497–502. [Google Scholar]
- El Madany, M.; Abduljabbar, Z.; Foda, M. Optimal preview control of active suspensions with integral constraint. Modal Anal. 2003, 9, 1377–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Madany, M.M.; Al Bassam, B.A.; Fayed, A.A. Preview control of slow-active suspension systems. J. Vib. Control 2011, 17, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Madany, M.M. Control and evaluation of slow-active suspensions with preview for a full car. Math. Probl. Eng. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HAĆ, A. Optimal Linear Preview Control of Active Vehicle Suspension. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 1992, 21, 167–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitching, K.J.; Cebon, D.; Cole, D.J. An experimental investigation of preview control. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 1999, 32, 459–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lam, J.; Cheung, K.C. Multi-objective control for active vehicle suspension with wheelbase preview. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 5269–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagiri, S.; Doi, S.; Shoh-no, S.; Hiraiwa, N. Improvement of Ride Comfort by Preview Vehicle-Suspension System; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, H.-S.; Park, Y. Observer-based wheelbase preview control of active vehicle suspensions. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 1998, 12, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, E.K. Optimum linear preview control with application to vehicle suspension. J. Basic Eng. 1968, 90, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, K.; Jawahar, P.M.; Tamilporai, P. Active Suspension System with Preview Control-A Review; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sarami, S. Development and Evaluation of a Semi-Active Suspension System for Full Suspension Tractors; Fachbereich Konstruktion von Maschinensystemen: Berlin, Germany, 2009; Available online: https://opus4.kobv.de/opus4-tuberlin/files/2402/sarami_shahriar.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2017).
- Alvanagh, A.A. Multi-Objective H∞/GH2 Preview Control of Active Vehicle Suspensions. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Control Engineering, Munich Polytechnic University, Munich, Germany, 2008. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.428.480&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 14 July 2017).
- Alfadhli, A.; Darling, J.; Hillis, A.J. The control of an active seat with vehicle suspension preview information. J. Vib. Control 2017, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, J.-S.; Tsai, S.-H.; Liu, M.-T. A PSO-based adaptive fuzzy PID-controllers. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2012, 26, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishkenari, H.N.; Mahboobi, S.H.; Alasty, A. Optimum synthesis of fuzzy logic controller for trajectory tracking by differential evolution. Sci. Iran. 2011, 18, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, J.-S.; Liu, M.-T. Using fuzzy logic controller and evolutionary genetic algorithm for automotive active suspension system. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2009, 10, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaldas, M.; Caliskan, K.; Henze, R.; Küçükay, F. Preview Enhanced Rule-Optimized Fuzzy Logic Damper Controller. SAE Int. J. Passeng. Cars Mech. Syst. 2014, 7, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazeri-Gh, M.; Soleymani, M. Genetic optimization of a fuzzy active suspension system based on human sensitivity to the transmitted vibrations. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J. Autom. Eng. 2008, 222, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Li, P.; Liu, H.; Brown, D. Adaptive fuzzy controller for vehicle active suspensions with particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Symposium on Instrumentation and Control Technology, Beijing, China, 13 October 2008; p. 712922. [Google Scholar]
- Rajeswari, K.; Lakshmi, P. PSO optimized fuzzy logic controller for active suspension system. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advances in Recent Technologies in Communication and Computing (ARTCom), Kottayam, India, 16–17 October 2010; pp. 278–283. [Google Scholar]
- Bingül, Z.; Karahan, O. A Fuzzy Logic Controller tuned with PSO for 2 DOF robot trajectory control. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazinica, A. Particle Swarm Optimization; In-Tech Kirchengasse: Graz, Austria, 2009; Available online: http://personnel.sju.edu.tw/%E6%94%B9%E5%96%84%E5%B8%AB%E8%B3%87%E7%A0%94%E7%A9%B6%E6%88%90%E6%9E%9C/98%E5%B9%B4%E5%BA%A6/%E8%91%97%E4%BD%9C/86.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2017).
- Shi, Y. Particle swarm optimization: Developments, applications and resources. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Seoul, Korea, 27–30 May 2001; pp. 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Bouazara, M.; Richard, M.J.; Rakheja, S. Safety and comfort analysis of a 3-D vehicle model with optimal non-linear active seat suspension. J. Terramechanics 2006, 43, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passino, K.M.; Yurkovich, S. Fuzzy Control Menlo Park; Addison-Wesley: Harlow, CA, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-201-18074-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Bose, B.K. Evaluation of membership functions for fuzzy logic controlled induction motor drive. In Proceedings of the IEEE 28th Annual Conference of the Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 2002), Sevilla, Spain, 5–8 November 2002; pp. 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, M. Handbook of Human Vibration; Academic Press: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 2631-1:1997. Mechanical Vibration and Shock—Evaluation of Human Exposure to Whole-Body Vibration—Part 1: General Requirements; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997; p. 31. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 8608:1995. Mechanical Vibration—Road Surface Profiles—Reporting of Measured Data. Available online: http://www.iso.org/iso/catalogue_detail.htm?csnumber=15913 (accessed on 10 January 2017).
- Ren, H.B.; Chen, S.Z.; Wu, Z.C. Model of excitation of random road profile in time domain for a vehicle with four wheels. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Mechatronic Science, Electric Engineering and Computer (MEC), Jilin, China, 19–22 August 2011; pp. 2332–2335. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, N. Integrated seat and suspension control for a quarter car with driver model. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2012, 61, 3893–3908. [Google Scholar]
- Threshold Limit Values (TLVs) for Chemical Substances and Physical Agents and Biological Exposure Indices (BEIs); American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH): Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2002; pp. 124–131.
- D’Amato, F.J.; Viassolo, D.E. Fuzzy control for active suspensions. Mechatronics 2000, 10, 897–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

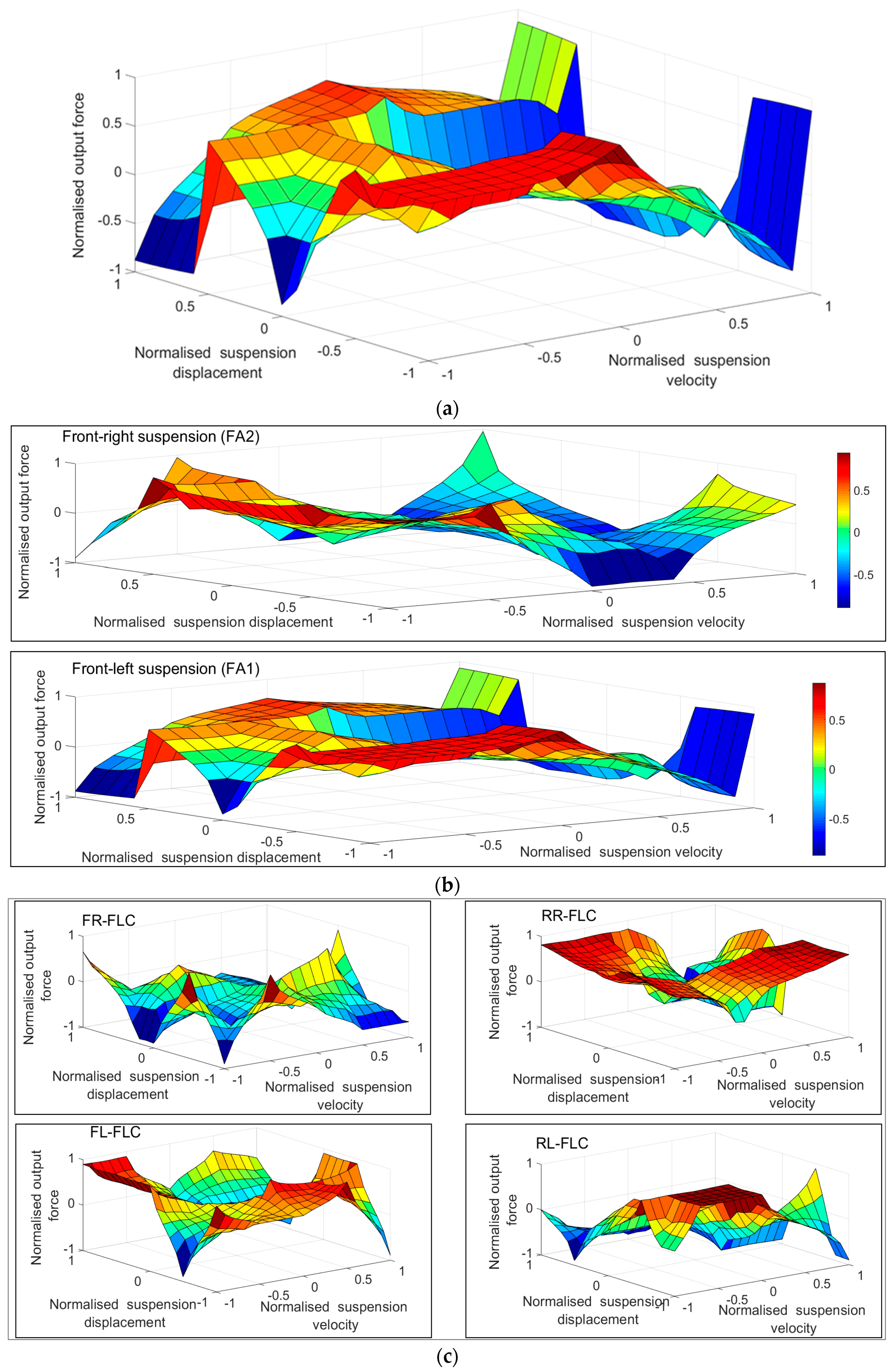
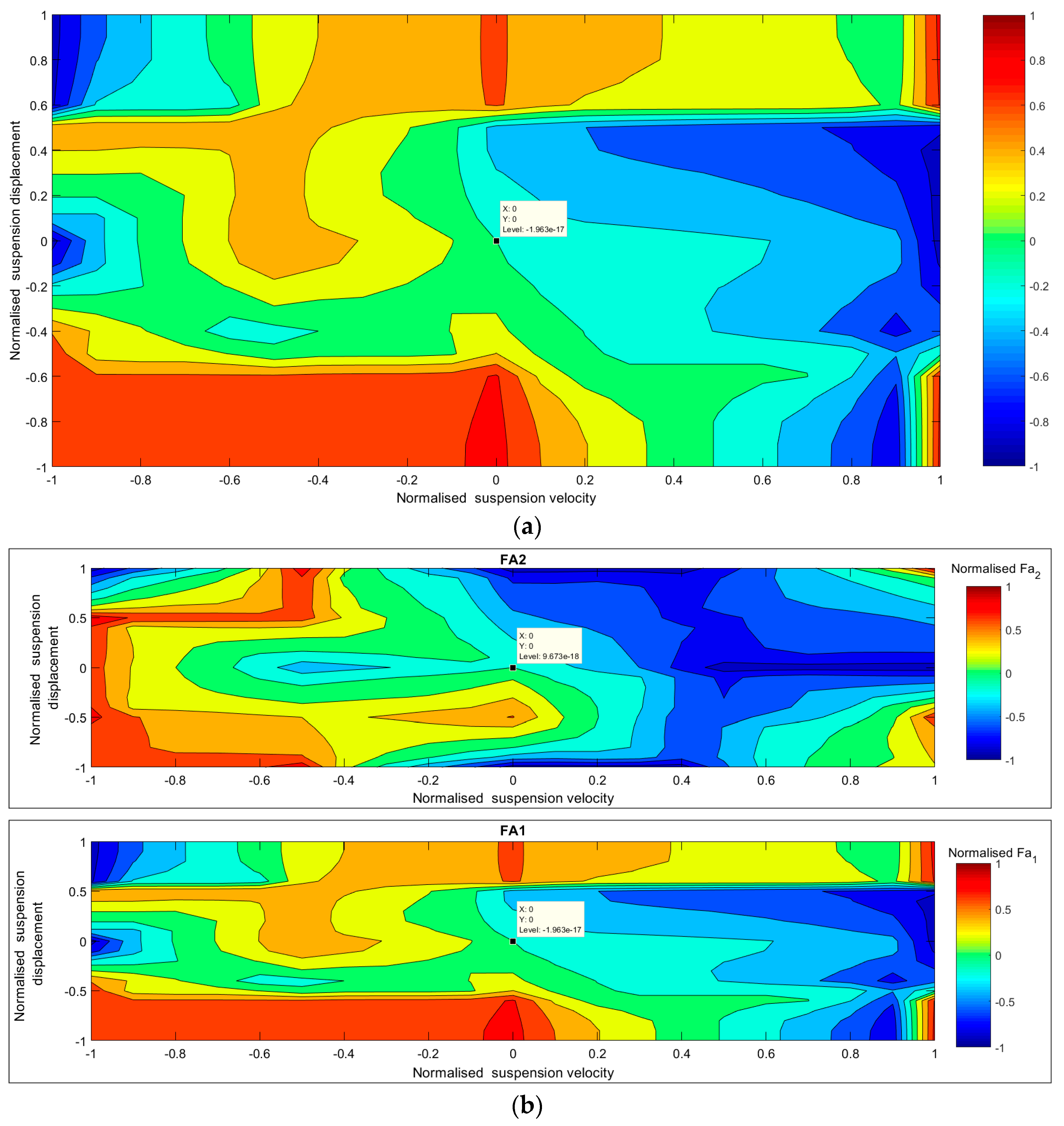
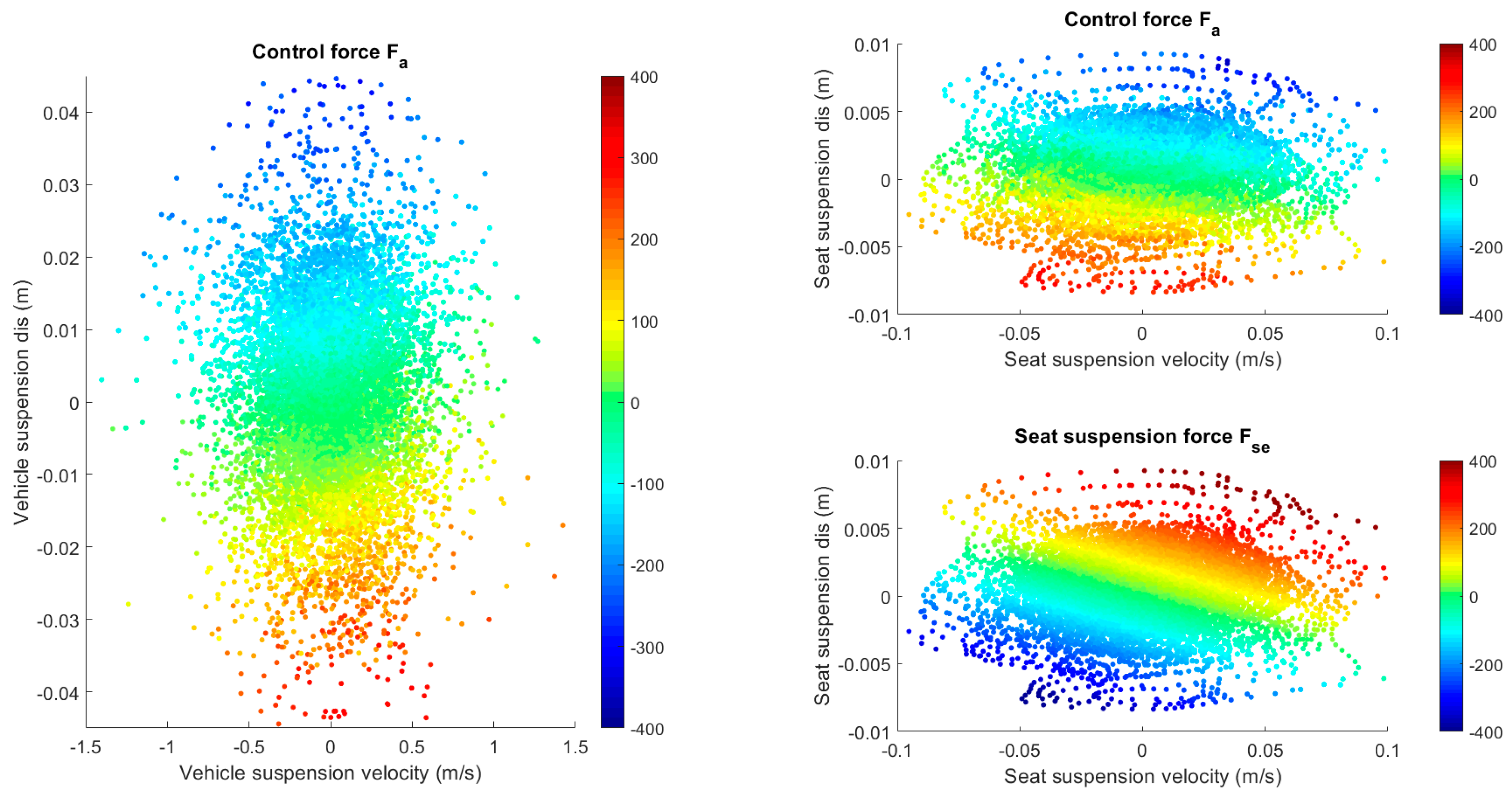
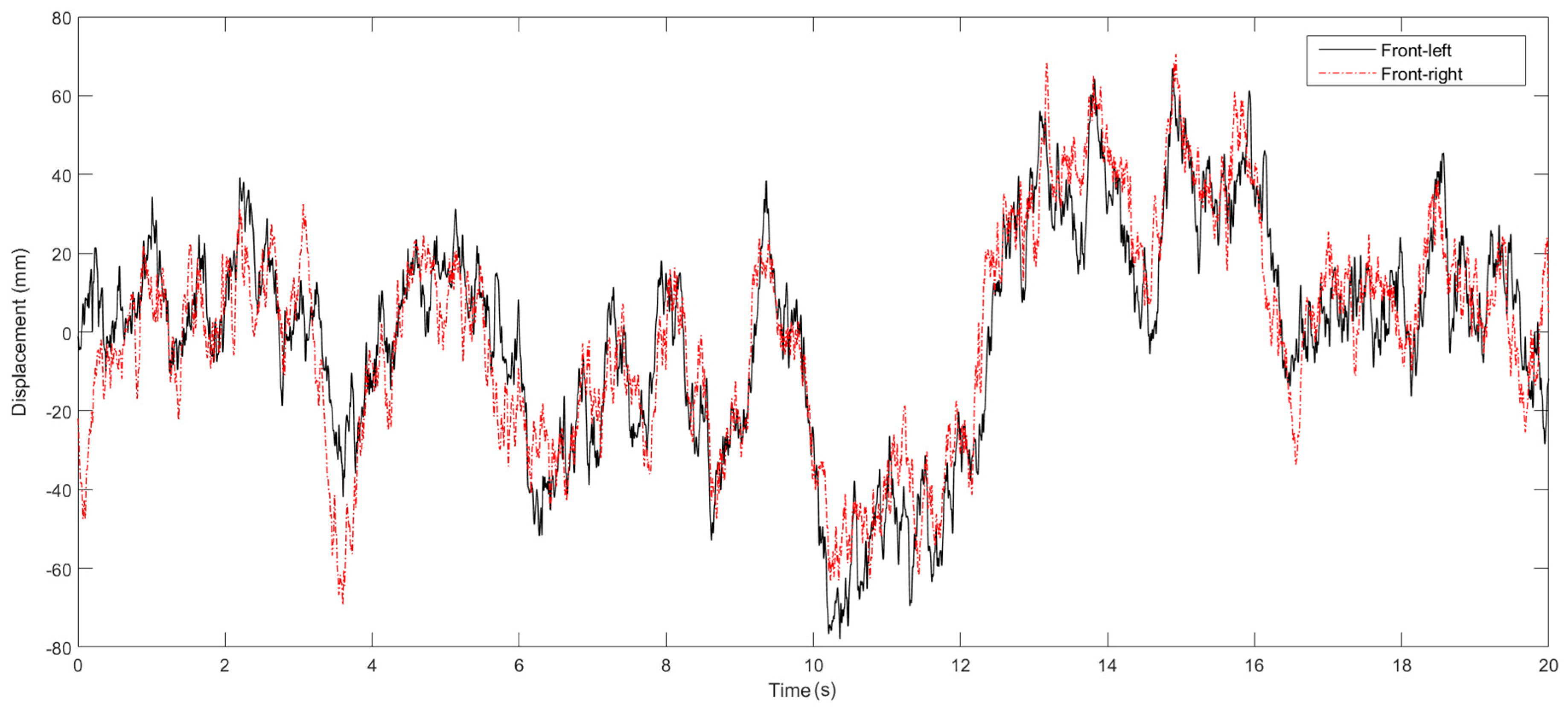

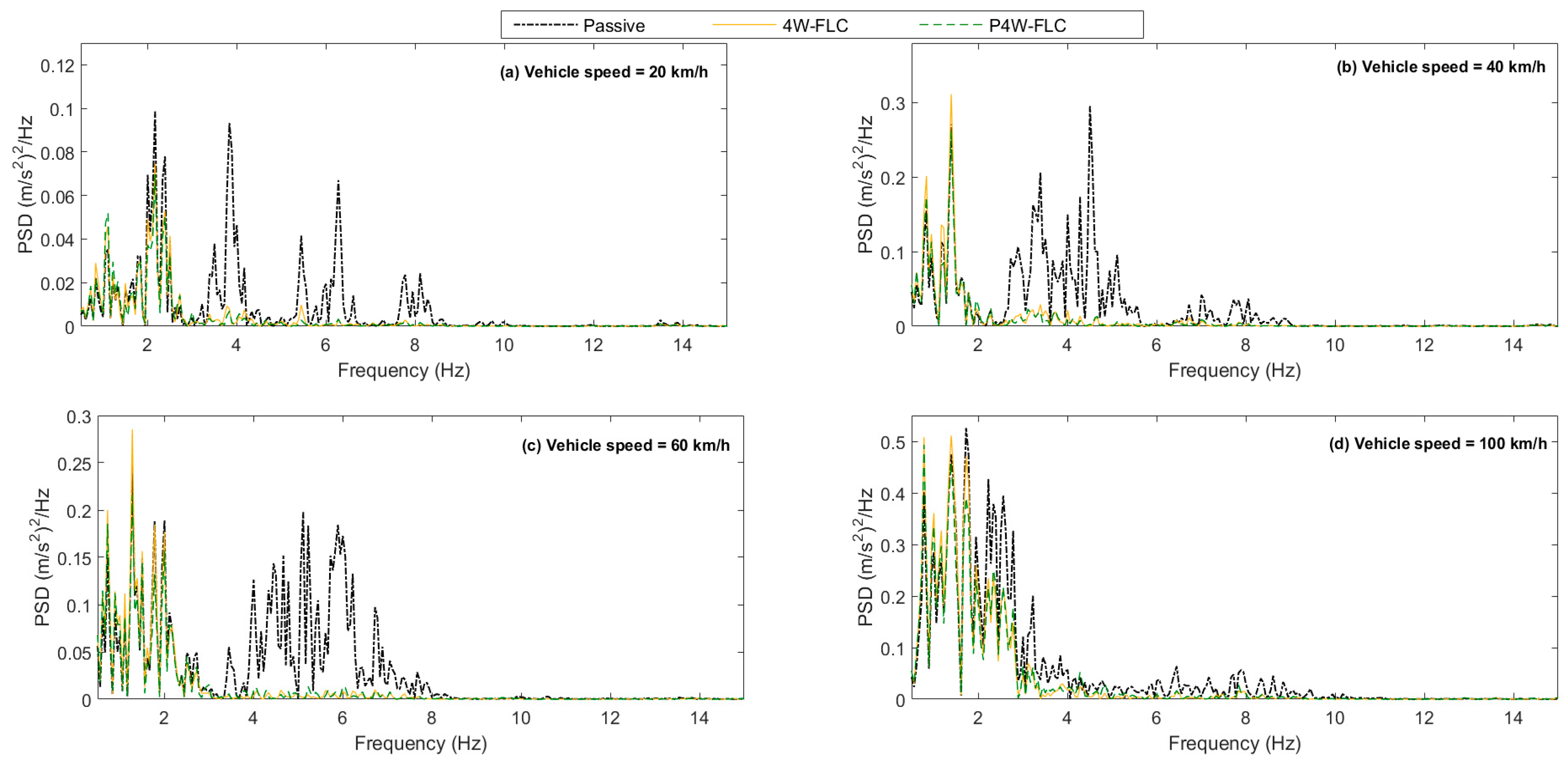
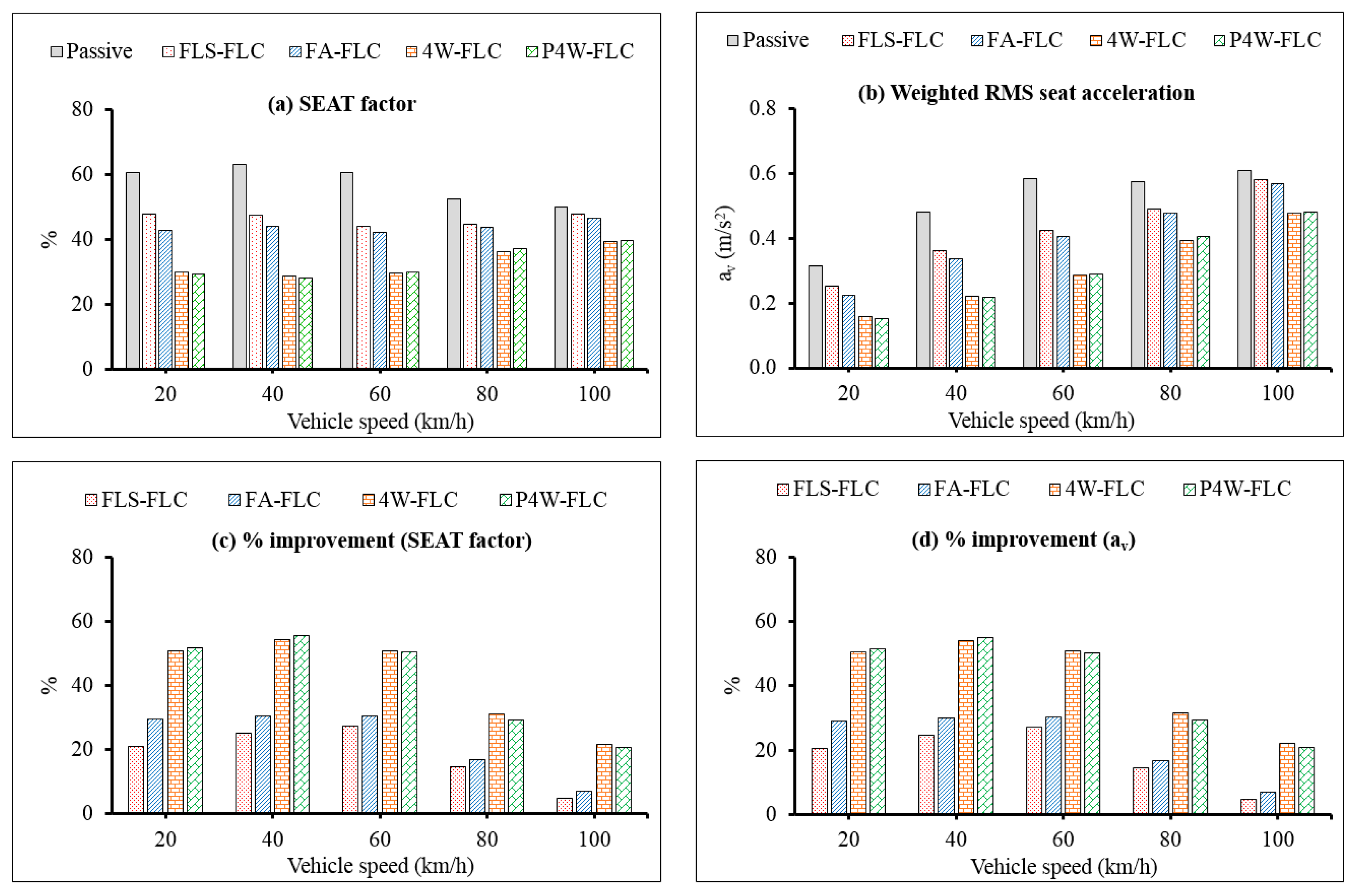

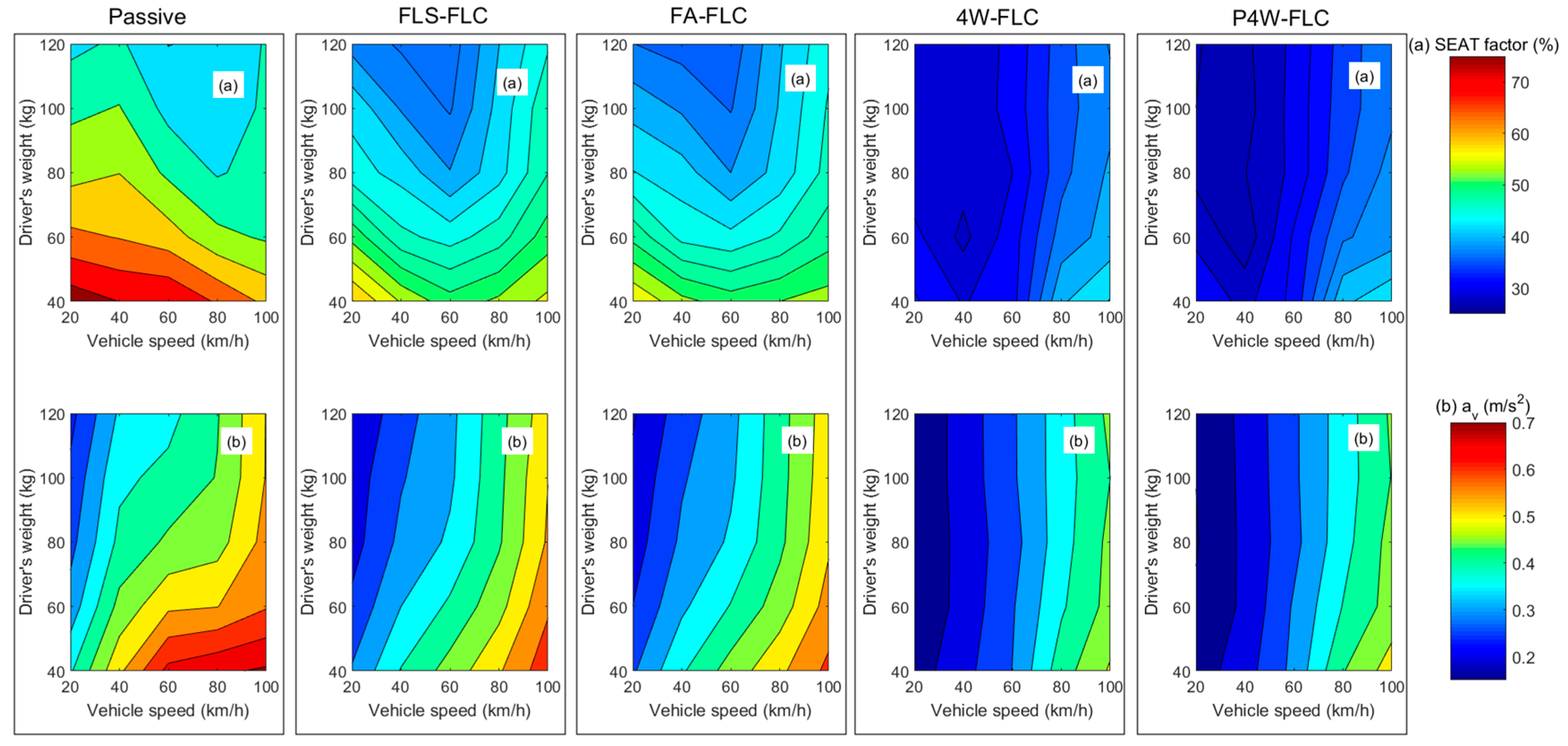
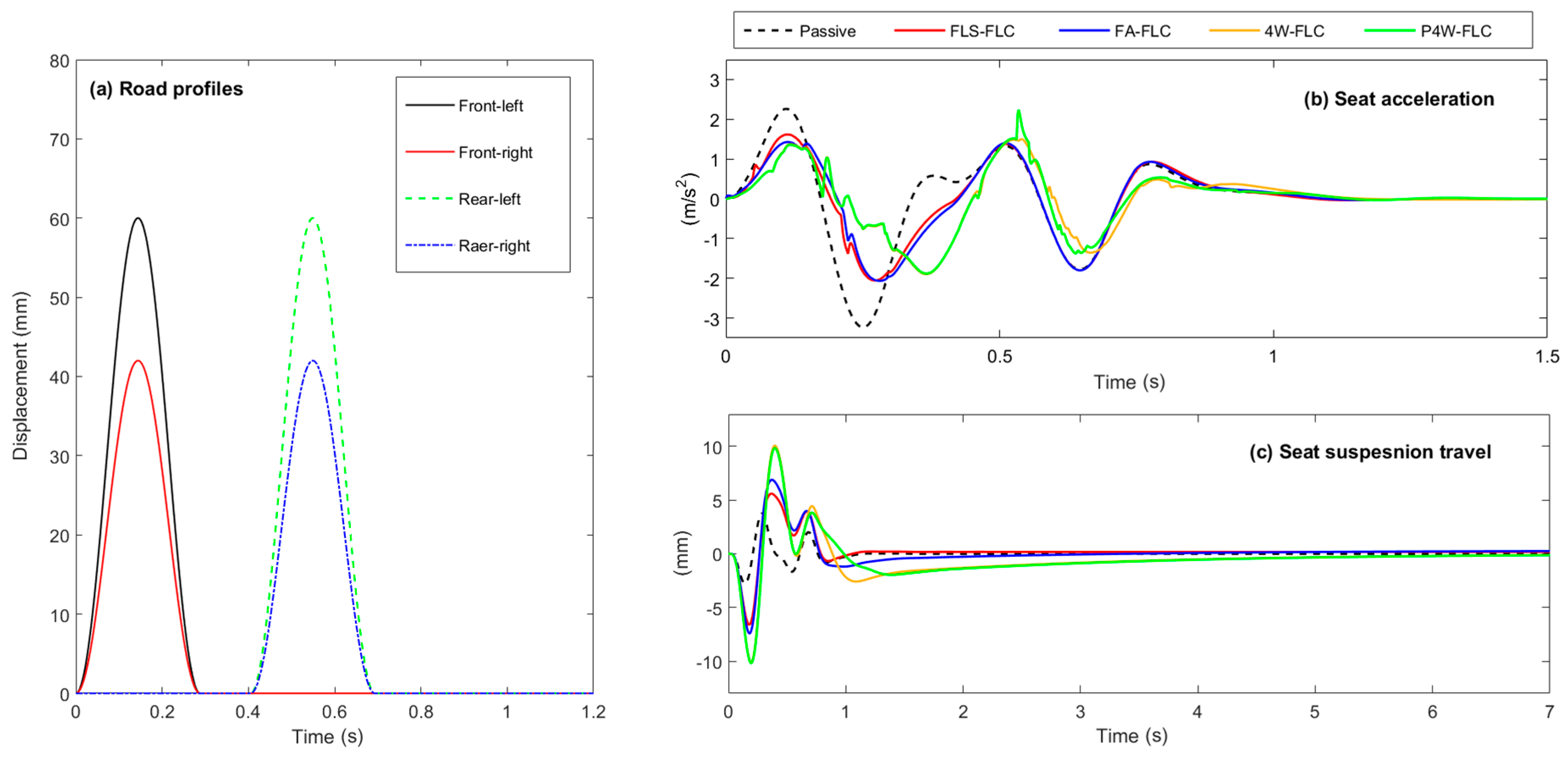
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| 1200.0 | Kg | |
| 20.0 | Kg | |
| 2100.0 | Kg·m2 | |
| 460.0 | Kg·m2 | |
| 10.0 | kN/m | |
| 2000.0 | N·s/m | |
| 180.0 | kN/m | |
| 1.011 | m | |
| Lr | 1.803 | m |
| 0.761 | kN·s/m | |
| 0.761 | kN/m | |
| 0.3 | m | |
| 0.25 | m | |
| R | 22.0 | N |
| 0.0012 | m/s | |
| 5.0 | Kg | |
| 55.25 | Kg | |
| 2.10 | kN·s/m | |
| 42.0 | kN/m | |
| 0.9 | kN·s/m | |
| 280.0 | kN/m |
| System | Seat Acceleration | Seat Suspension Travel | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMS (m/s2) | Peak (m/s2) | RMS (mm) | Peak (mm) | |
| Passive | 1.031 | 3.236 | 1.238 | 3.749 |
| FLS-FLC | 0.825 | 2.055 | 2.720 | 6.595 |
| FA-FLC | 0.802 | 2.060 | 3.057 | 11.840 |
| 4W-FLC | 0.728 | 1.895 | 4.349 | 10.090 |
| P4W-FLC | 0.734 | 2.228 | 4.192 | 10.183 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfadhli, A.; Darling, J.; Hillis, A.J. The Control of an Active Seat Suspension Using an Optimised Fuzzy Logic Controller, Based on Preview Information from a Full Vehicle Model. Vibration 2018, 1, 20-40. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration1010003
Alfadhli A, Darling J, Hillis AJ. The Control of an Active Seat Suspension Using an Optimised Fuzzy Logic Controller, Based on Preview Information from a Full Vehicle Model. Vibration. 2018; 1(1):20-40. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration1010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfadhli, Abdulaziz, Jocelyn Darling, and Andrew J. Hillis. 2018. "The Control of an Active Seat Suspension Using an Optimised Fuzzy Logic Controller, Based on Preview Information from a Full Vehicle Model" Vibration 1, no. 1: 20-40. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration1010003
APA StyleAlfadhli, A., Darling, J., & Hillis, A. J. (2018). The Control of an Active Seat Suspension Using an Optimised Fuzzy Logic Controller, Based on Preview Information from a Full Vehicle Model. Vibration, 1(1), 20-40. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration1010003




