Longitudinal Ceiling Temperature Profile in an Inclined Channel Induced by a Wall-Attached Fire
Abstract
1. Introduction
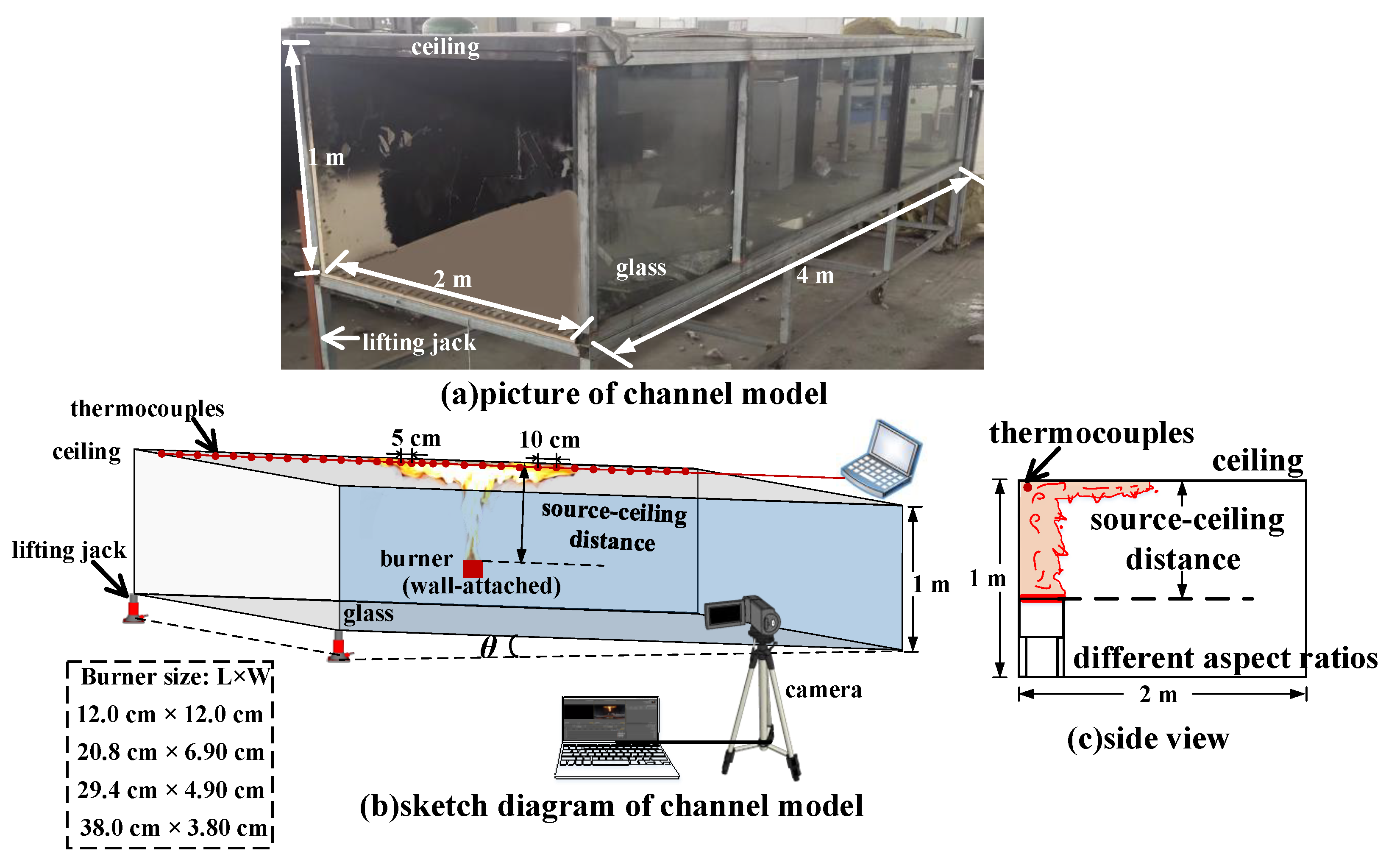
2. Experimental Setup
2.1. Experimental Rig and Measurements
2.2. Experimental Condition Seetings
3. Results and Discussion
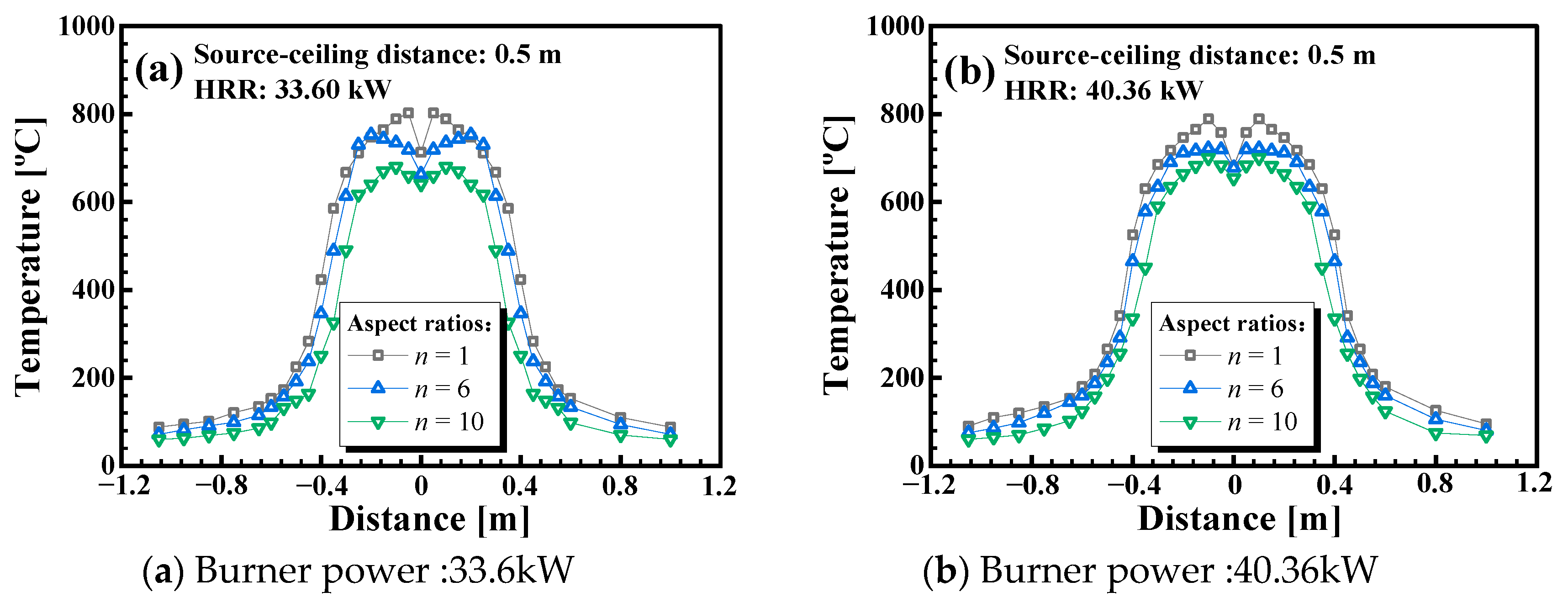
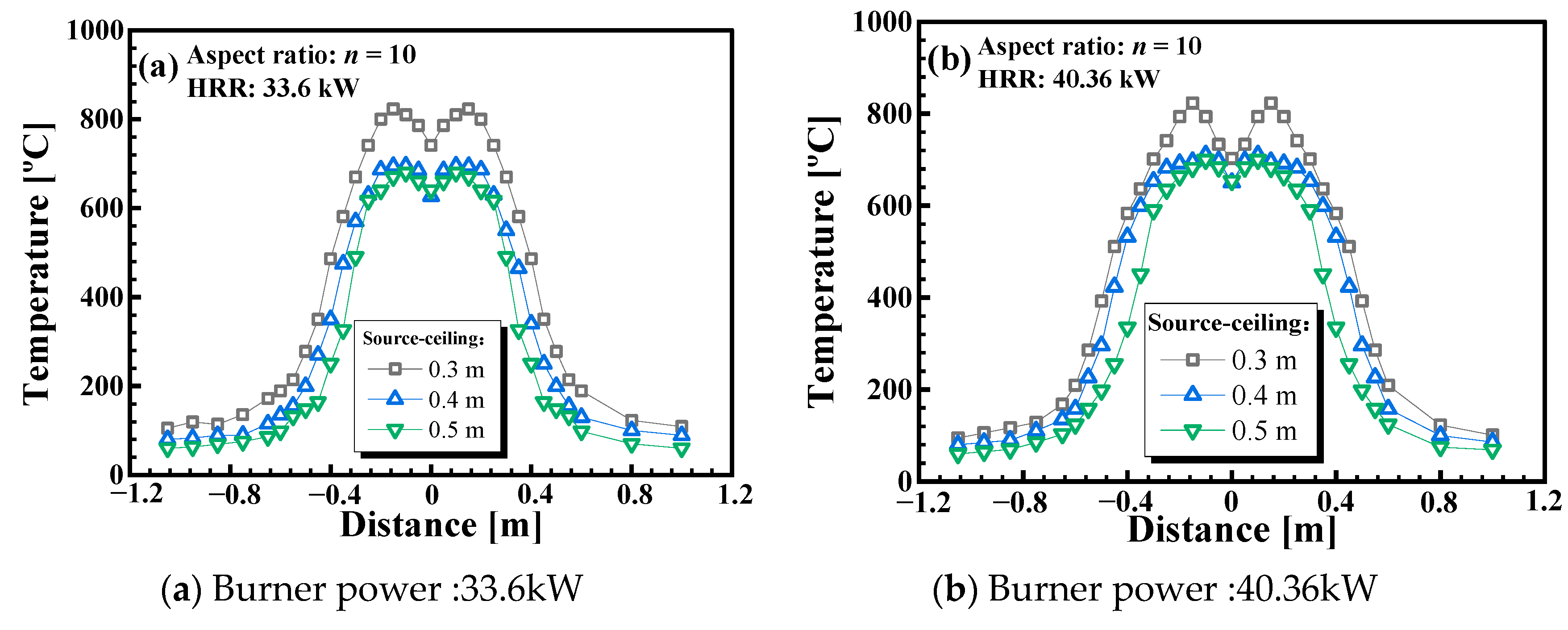
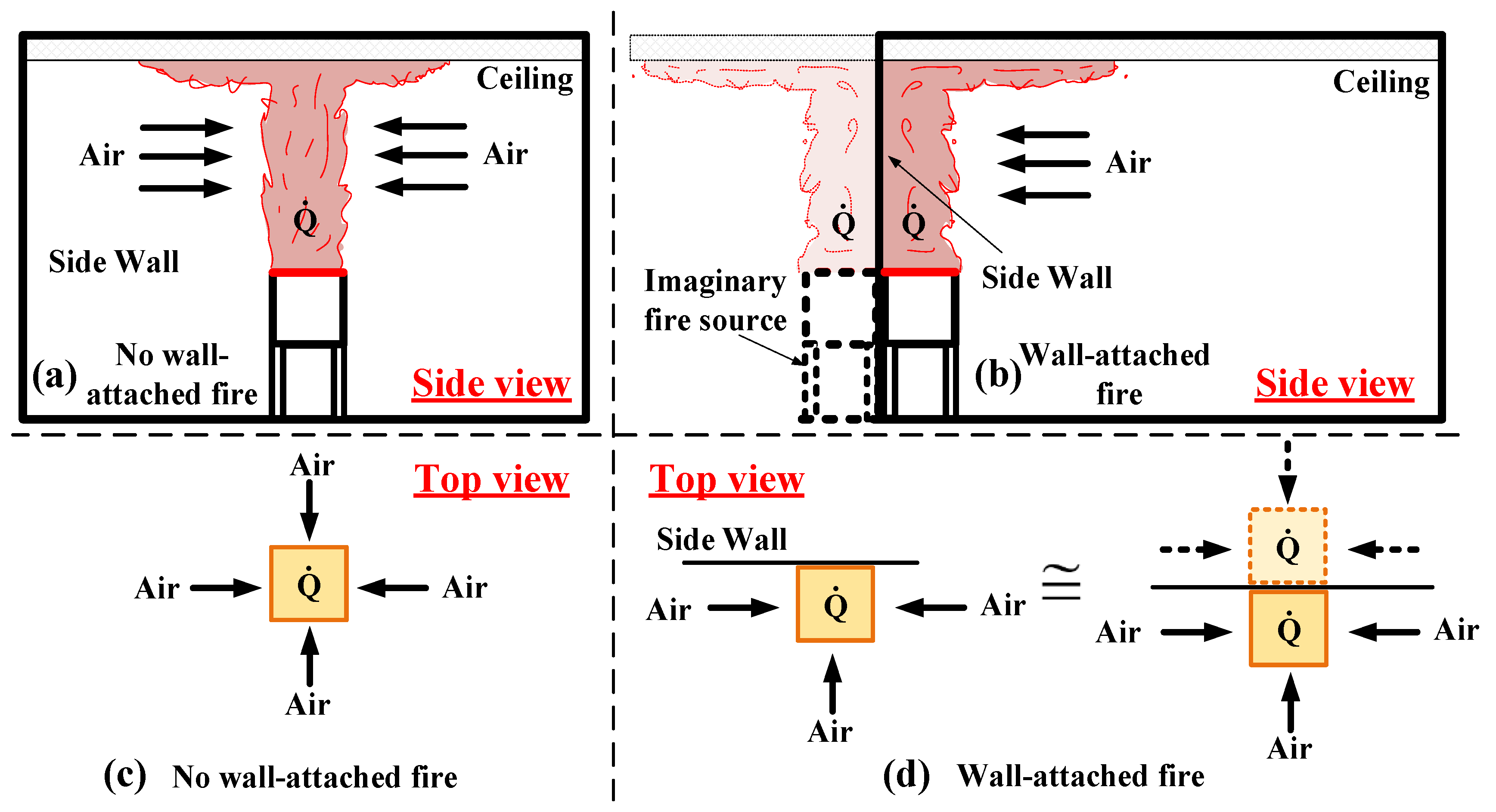
3.1. Influence of the Burner Aspect Ratios and Source-Ceiling Distance on the Longitudinal Temperature Profile Beneath a Horizontal Channel Ceiling
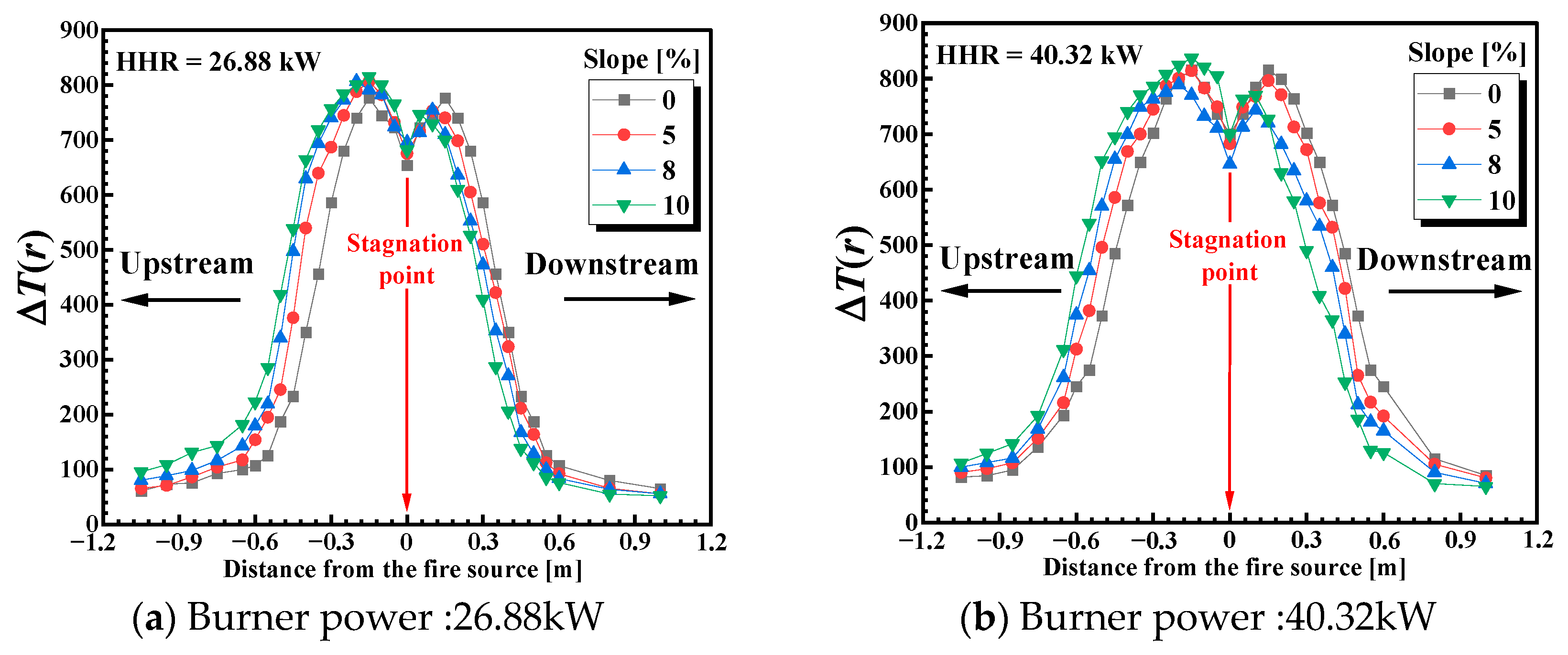
3.2. Influence of the Channel Slopes on the Longitudinal Temperature Profile Under the Ceiling
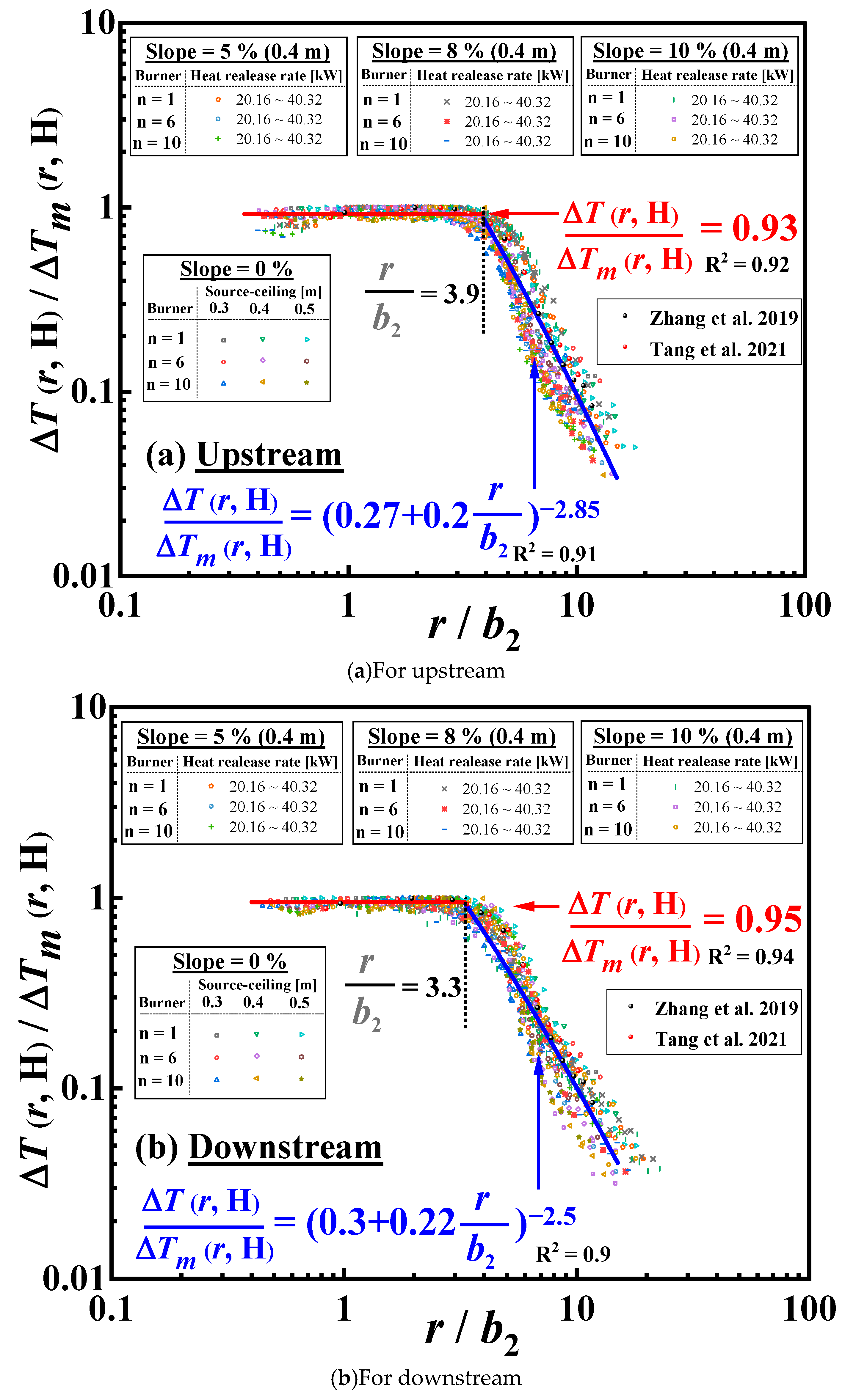
3.3. A Global Correlation of the Longitudinal Ceiling Temperature Profile in an Inclined Channel Ceiling Induced by a Wall-Attached Fire
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- For the channel fire with a horizontal ceiling, the influence of burner aspect ratio and source-ceiling height on the temperature profile is monotonous in the cases considered in this work. With a larger burner aspect ratio and larger source-ceiling distance, more ambient air can be entrained; hence, the longitudinal temperature under the ceiling decays faster.
- (2)
- For the channel fire with an inclined ceiling, when the burner aspect ratio and source-ceiling distance are constant, under a larger channel slope, more hot smoke could be transported upstream due to the asymmetric entrainment effect. Hence, the temperature profile is not symmetric, with higher temperatures upstream and lower temperatures downstream.
- (3)
- Combining the influence of burner aspect ratios, source-ceiling distance, and burner aspect ratio, the characteristic length scale was modified. Based on this, a model describing the ceiling temperature profile was proposed and then verified with previous data.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, R.; Zhou, H.; Hu, Z.; He, S.; Wang, X. Statistical analysis of fire accidents in Chinese highway tunnels 2000–2016. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 83, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Lin, X.; Yuen, R.; Wang, J. Impacts of ceiling height on the combustion behaviors of pool fires beneath a ceiling. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 126, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ni, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, H. Experimental study on the characteristics of wood crib fire in a confined space with different ventilation conditions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 120, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; He, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, P. Experimental study on maximum smoke temperature beneath the ceiling induced by carriage fire in a tunnel with ceiling smoke extraction. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 44, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, N. Fire incident data for Australian road tunnels. Fire Saf. J. 2020, 111, 102909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ni, X.; Zhao, M.; Feng, J.; Zhang, R. Numerical simulation of wood crib fire behavior in a confined space using cone calorimeter data. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 119, 2291–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.G.; Yang, J.; Li, M.H. A theoretical and experimental study of flame length under a tunnel ceiling. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 128, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, S.; Ding, Z. Initial fuel depth effect on the burning characteristics of thin-layer pool fire in a confined enclosure. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 139, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, K. Experimental investigation on carriage fires hazards in the longitudinal ventilated tunnels: Assessment of the smoke stratification features. Saf. Sci. 2020, 130, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Pang, H. Experimental study on the effect of ceiling mechanical smoke extraction system on transverse temperature decay induced by ceiling jet in the tunnel. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2020, 152, 106294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tang, F.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Q. Effect of lateral smoke extraction on transverse temperature distribution and smoke maximum temperature under ceiling in tunnel fires. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 4275–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Cao, Z.; Palacios, A.; Wang, Q. A study on the maximum temperature of ceiling jet induced by rectangular-source fires in a tunnel using ceiling smoke extraction. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 127, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Tao, C.; Zhang, H. Experimental study on fire smoke control using water mist curtain in channel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, R.L. Turbulent ceiling-jet induced by large-scale fires. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1975, 11, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heskestad, G.; Hamada, T. Ceiling jets of strong fire plumes. Fire Saf. J. 1993, 21, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tang, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, L.-J. Experimental study on temperature distribution of ceiling jet in tunnel fires under natural ventilation. Procedia Eng. 2018, 211, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasemi, Y.; Tokunaga, T. Flame geometry effects on the buoyant plumes from turbulent diffusion flames. Fire Sci. Technol. 1984, 4, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasemi, Y.; Nishihata, M. Fuel shape effect on the deterministic properties of turbulent diffusion flames. Fire Saf. Sci. 1989, 2, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X. Flame heights of line-source buoyant turbulent non-premixed jets with air entrainment constraint by two parallel side walls. Fuel 2017, 200, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.H.; Huo, R.; Wang, H.B.; Li, Y.Z.; Yang, R.X. Experimental studies on fire-induced buoyant smoke temperature distribution along tunnel ceiling. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 3905–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, L.; Delichatsios, M.A.; Zhang, J. Experimental study and analysis on flame lengths induced by wall-attached fire impinging upon an inclined ceiling. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2019, 37, 3879–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, L.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L. Flame extension length and temperature profile in thermal impinging flow of buoyant round jet upon a horizontal plate. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 73, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Liu, W.; Hong, W.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, X. A modified thermal radiation model with multiple factors for investigating temperature rise around pool fire. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 379, 120801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delichatsios, M.A. Air entrainment into buoyant jet flames and pool fires. Combust. Flame 1987, 70, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zukoski, E.E. Mass flux in fire plumes. Fire Saf. Sci. 1994, 4, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.X.; Wang, X.S.; Cong, H.Y.; Liu, Y.P.; Zhu, J.P. Temperature profile and flame extension length of a ceiling impinging round jet fire in an inclined tunnel. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 137, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L. A re-examination of entrainment constant and an explicit model for flame heights of rectangular jet fires. Combust. Flame 2014, 161, 3000–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, T.; Sun, H. Experimental study on temperature profile in a branched tunnel fire under natural ventilation considering different fire locations. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 159, 106631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Chen, C.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, T.; Jiao, W. Study on heat allocation and temperature profile in a T-shaped branched tunnel fire with different branch slopes under natural ventilation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 126, 104508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, C.; Lei, P.; Xu, T.; Jiao, W.; Zhang, Y. Experimental study on temperature profile and smoke movement in a model-branched tunnel fire under longitudinal ventilation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 121, 104324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, Z.; Tao, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, A.; Xu, W.; Liu, X. Maximum temperature of thermal plume beneath an unconfined ceiling with different inclination angles induced by rectangular fire sources. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 120, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, S.; Guan, Y.; Lo, S.; Zhang, H. Experiment Investigation on the Influence of Low Pressure on Ceiling Temperature Profile in Aircraft Cargo Compartment Fires. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 89, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Yang, R.; Li, C.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, H. An Experimental Study on Fire Behavior of an Inclined Ceiling Jet in a Low-Pressure Environment. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 138, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, K.; Yang, Z.; Lyu, P.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, L. Numerical study of turbulent flow past a rotating axial-flow pump based on a level-set immersed boundary method. Renew. Energy 2021, 168, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, L.; Sun, X. Temperature Profile of Thermal Flow Underneath an Inclined Ceiling Induced by a Wall-Attached Fire. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 141, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, N.; Wang, Y.; Vilfayeau, S.; Trouvé, A. Large eddy simulation of turbulent vertical wall fires supplied with gaseous fuel through porous burners. Combust. Flame 2016, 169, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, C.; Hu, L. Temperature profile of impingement flow in the corner between wall and inclined ceiling induced by gaseous fuel jet flame. Fuel 2020, 259, 116232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, K.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, D.; Binama, M.; Dai, J. Transient characteristics during power-off process in a shaft extension tubular pump by using a suitable numerical model. Renew. Energy 2021, 164, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintiere, J.G. Scaling applications in fire research. Fire Saf. J. 1989, 15, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Hu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Dong, M. Burning rate and flame tilt characteristics of radiation-controlled rectangular hydrocarbon pool fires with cross air flows in a reduced pressure. Fuel 2015, 139, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Hu, P.; Wen, J. Experimental investigation on lateral ceiling temperature distribution induced by wall-attached fire with various burner aspect ratios in underground space. Fire Saf. J. 2020, 120, 103055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Deng, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q. Effects of burner aspect ratio on heat flux distributions beneath unconfined ceilings with different inclination angles. Combust. Flame 2021, 228, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Qian, Y.; Tang, F.; Wang, Q. Experimental investigations on temperature profile and air entrainment of buoyancy-controlled jet flame from inclined nozzle bounded the wall. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 111, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.F.; Shen, Y.; Zong, R.W.; Tang, F. An experimental study of flame height and air entrainment of buoyancy-controlled jet flames with sidewalls. Fuel 2016, 183, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.F.; Shen, Y.; Zong, R.W. Experimental study on virtual origins of buoyancy-controlled jet flames with sidewalls. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 106, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasemi, Y.; Tokunaga, T. Some experimental aspects of turbulent diffusion flames and buoyant plumes from fire sources against a wall and in a corner of walls. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1984, 40, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Li, Y.; Huo, R.; Yi, L.; Shi, C.; Chow, W.K. Experimental studies on the rise-time of buoyant fire plume fronts induced by pool fires. J. Fire Sci. 2004, 22, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, F.; Su, G.; Chen, S.; Liu, J. Temperature profile beneath an inclined ceiling induced by plume impingement of gas fuel jet flame. Fuel 2018, 223, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H.; He, L.; Tang, F.; Wen, J. Experimental Study on the Radiant Heat Flux of Wall-Attached Fire Plume Generated by Rectangular Sources. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 159, 106605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tao, H.; Xu, W.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, L. Flame Extension Lengths beneath an Inclined Ceiling Induced by Rectangular-Source Fires. Combust. Flame 2017, 176, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malalasekera, W.; Versteeg, H. An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics; World Book Publishing Corp: Chicago, IL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
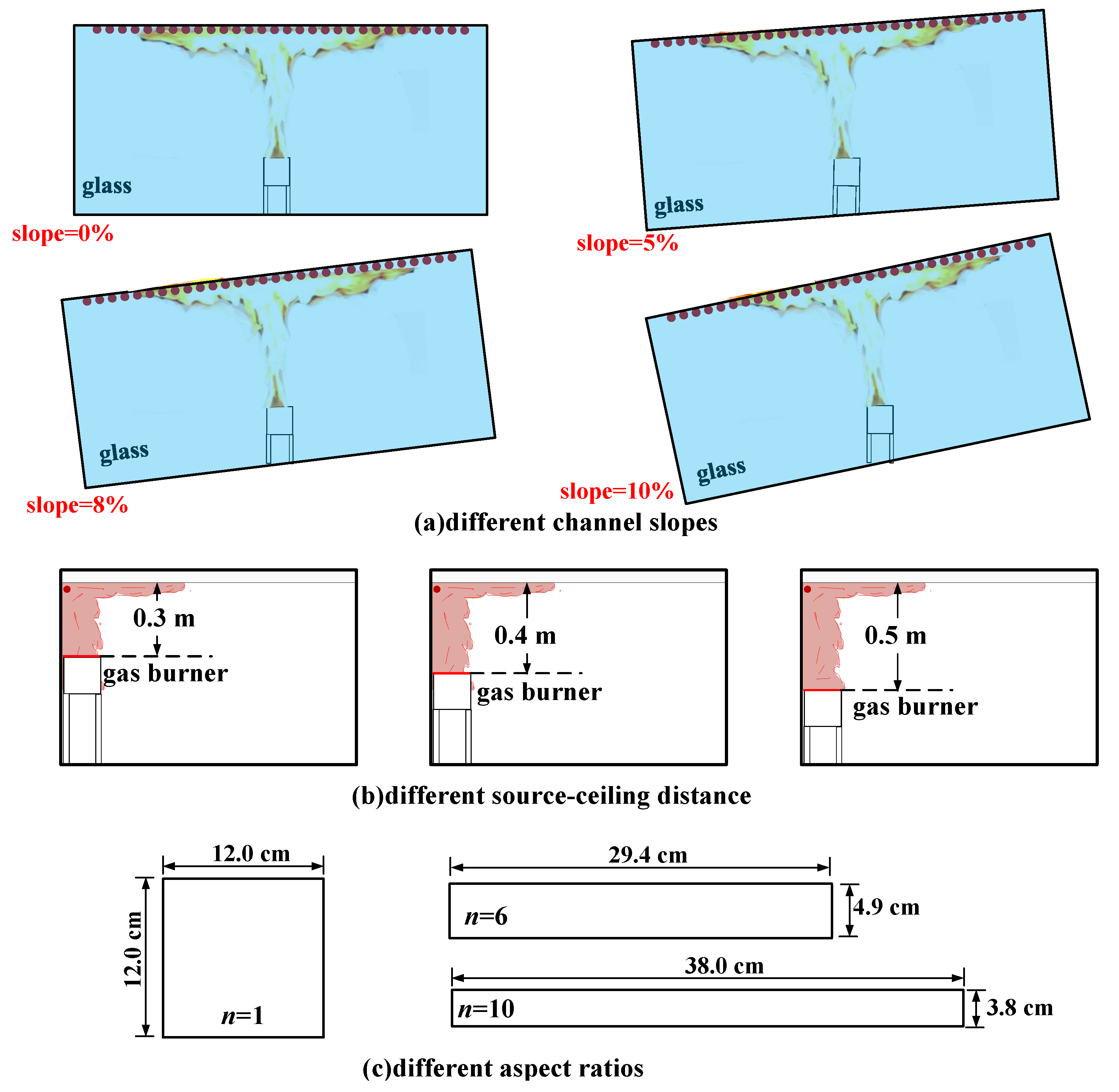



| Test No. | Burner Size [cm × cm] | Aspect Ratio | Slope [%] | Source-Ceiling Distance [m] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1–T12 | 12.0 × 12.0 | 1 | 0 | 0.3, 0.4, 0.5 |
| T13–T24 | 29.4 × 4.90 | 6 | 0 | 0.3, 0.4, 0.5 |
| T25–T36 | 38.0 × 3.80 | 10 | 0 | 0.3, 0.4, 0.5 |
| T37–T48 | 12.0 × 12.0 | 1 | 5, 8, 10 | 0.4 |
| T49–T60 | 29.4 × 4.90 | 6 | 5, 8, 10 | 0.4 |
| T61–T72 | 38.0 × 3.80 | 10 | 5, 8, 10 | 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Tao, Z. Longitudinal Ceiling Temperature Profile in an Inclined Channel Induced by a Wall-Attached Fire. Fire 2025, 8, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8060222
Huang X, Zhang Y, Wang W, Tao Z. Longitudinal Ceiling Temperature Profile in an Inclined Channel Induced by a Wall-Attached Fire. Fire. 2025; 8(6):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8060222
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xubo, Yongfeng Zhang, Wei Wang, and Zhenxiang Tao. 2025. "Longitudinal Ceiling Temperature Profile in an Inclined Channel Induced by a Wall-Attached Fire" Fire 8, no. 6: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8060222
APA StyleHuang, X., Zhang, Y., Wang, W., & Tao, Z. (2025). Longitudinal Ceiling Temperature Profile in an Inclined Channel Induced by a Wall-Attached Fire. Fire, 8(6), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8060222










