Experimental Study on Temperature Distribution Characteristics Under Coordinated Ventilation in Underground Interconnected Tunnels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Maximum Temperature Below the Ceiling at Different Fire Locations
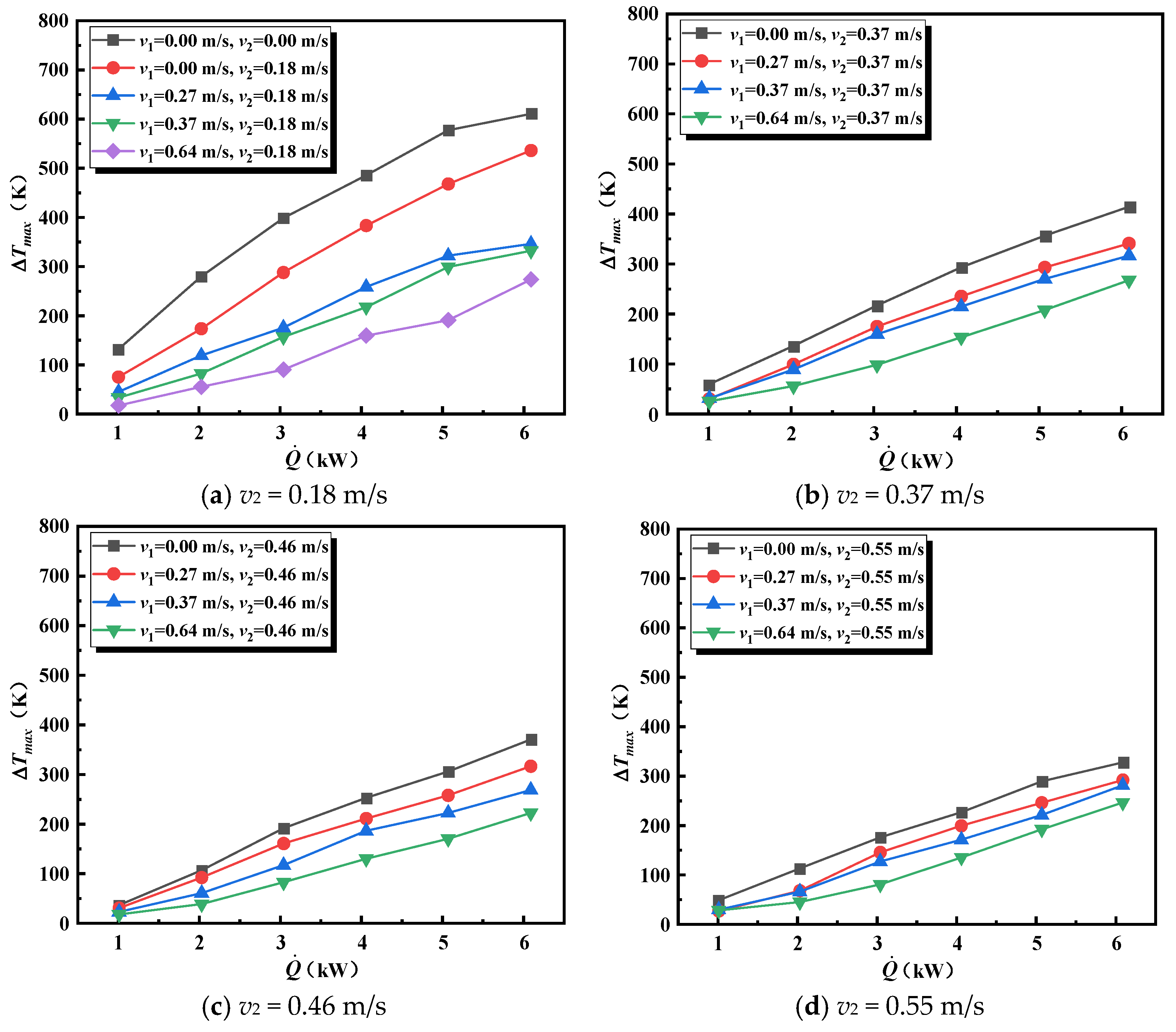
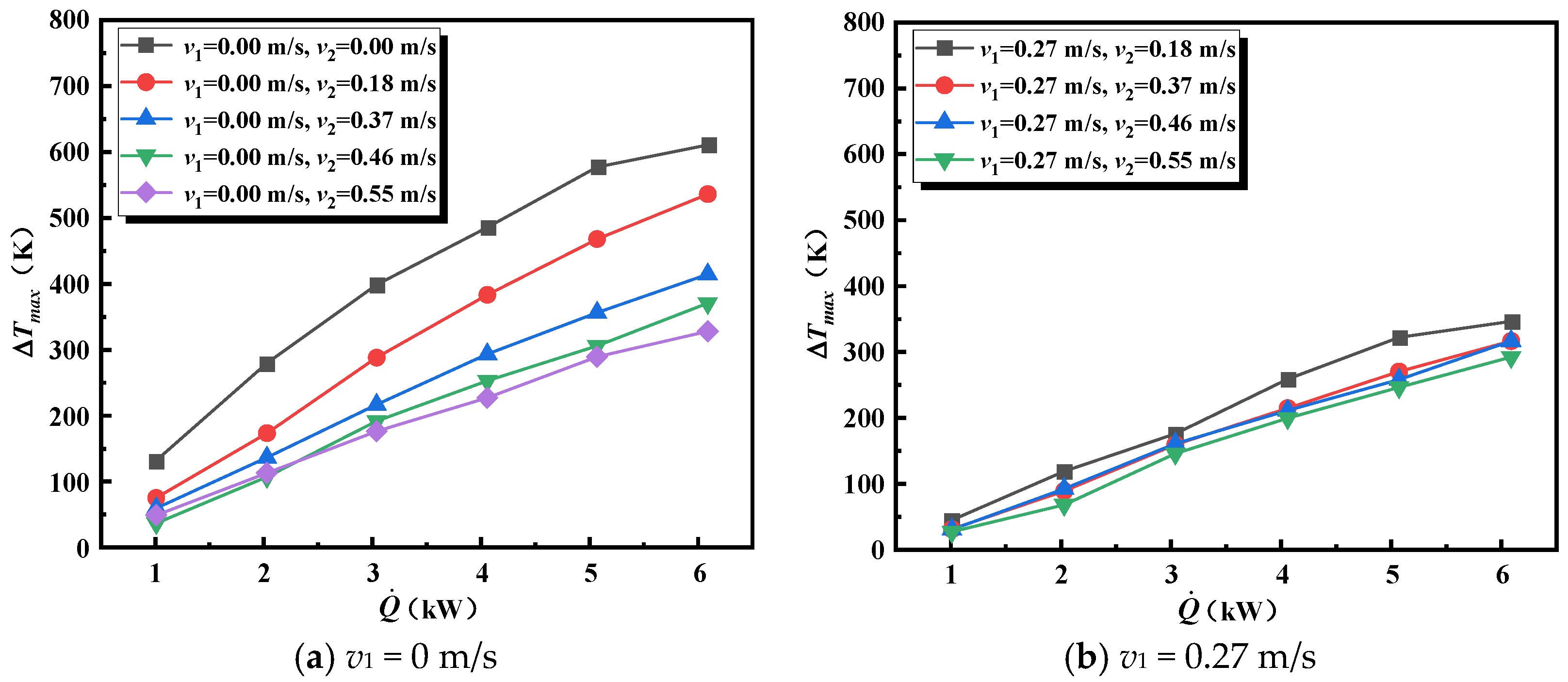
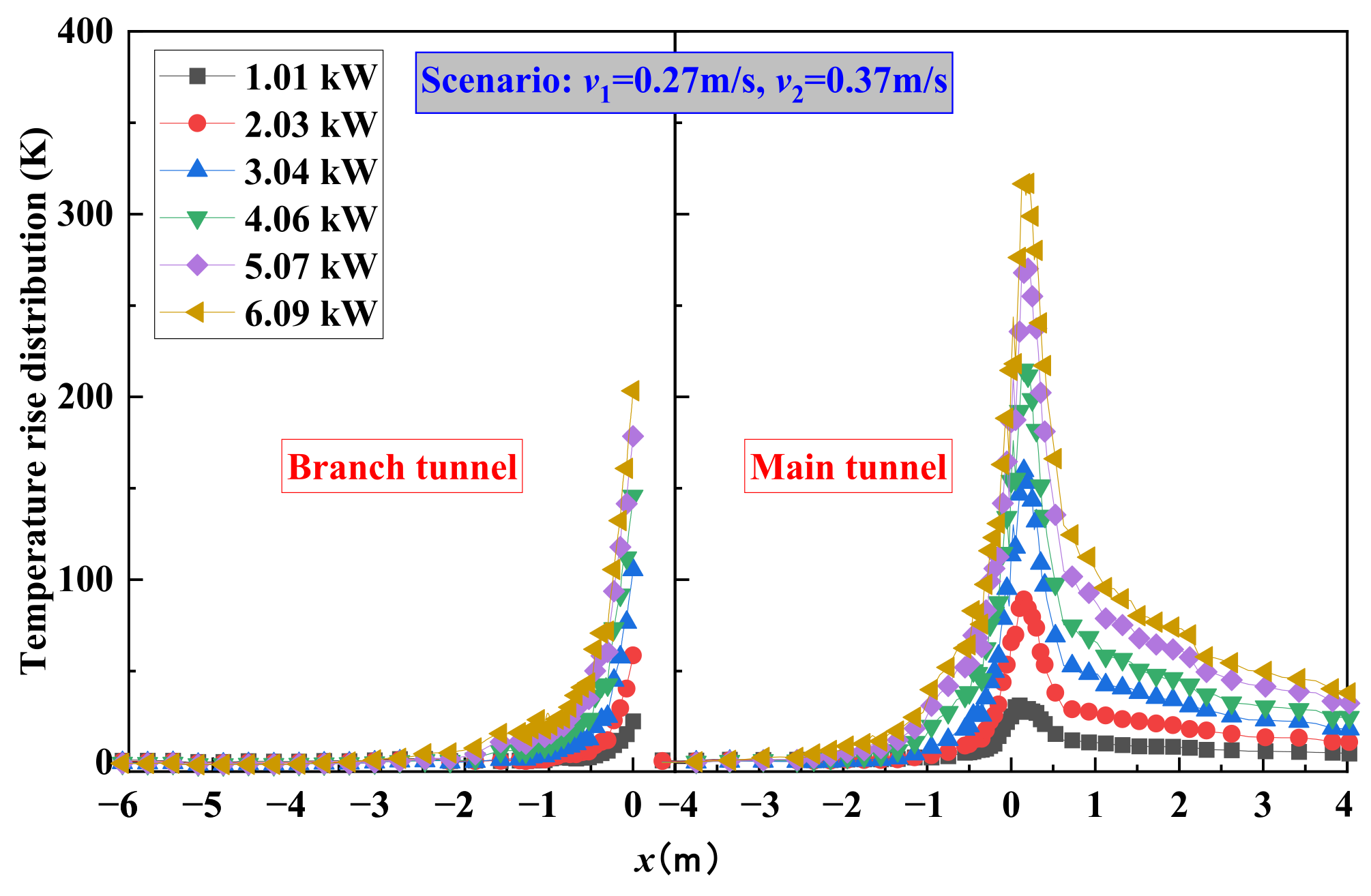
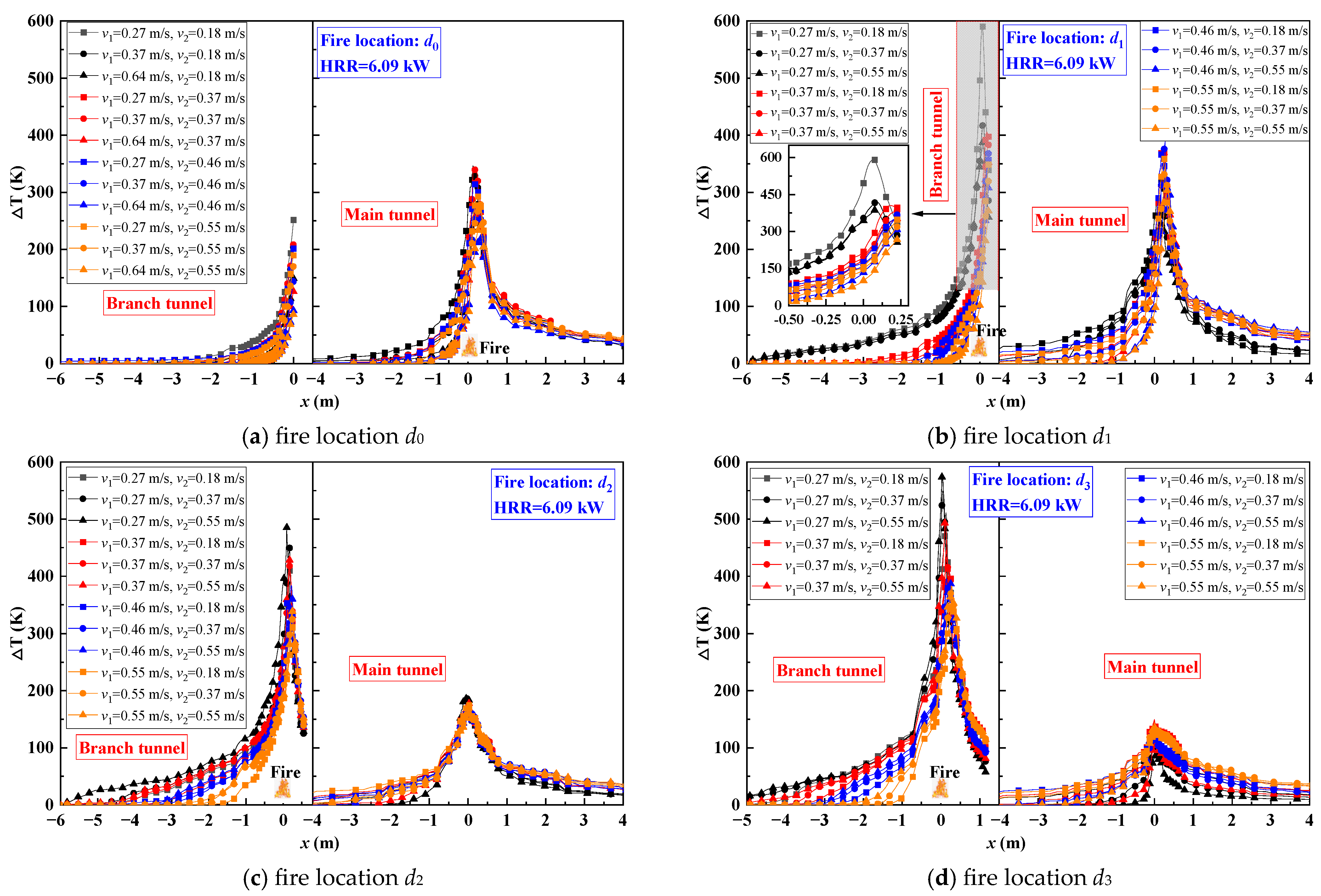
3.1.1. Maximum Temperature at Location d0
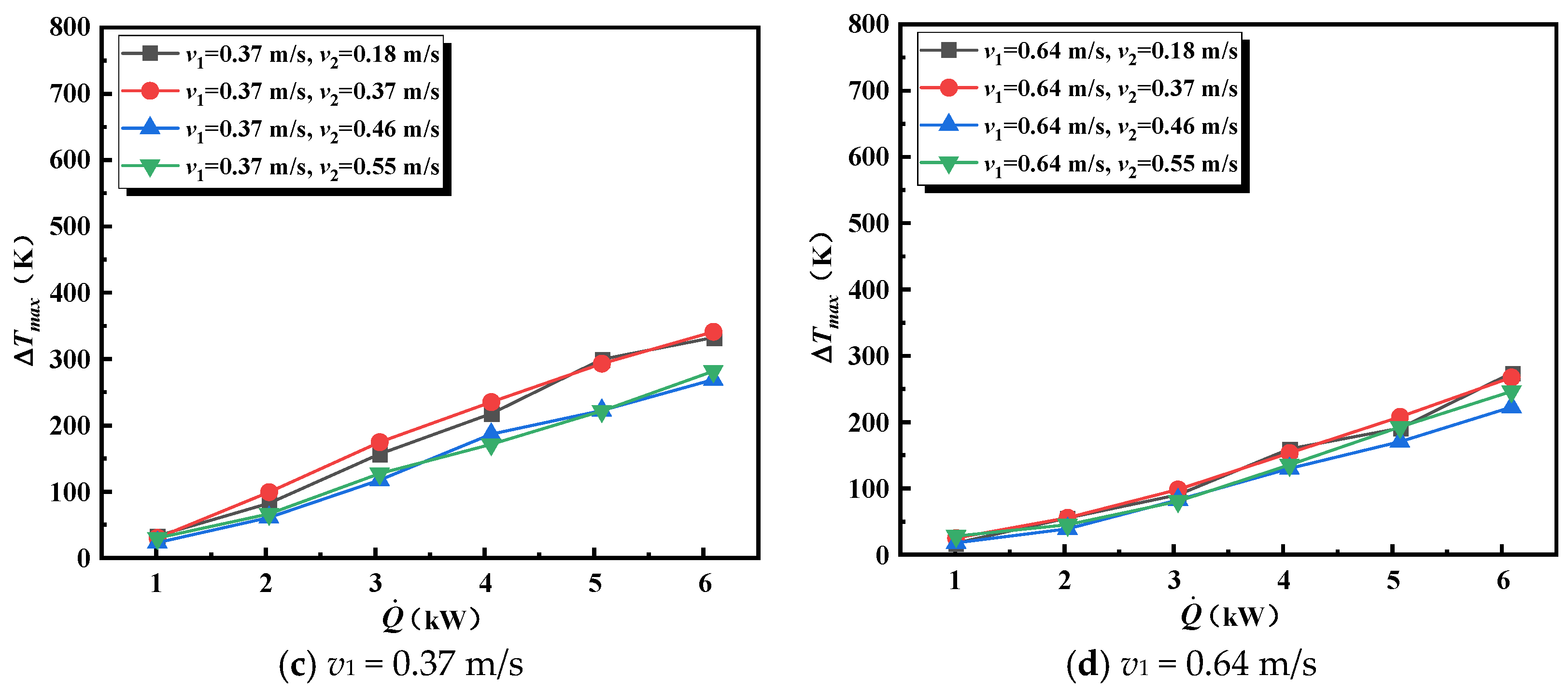
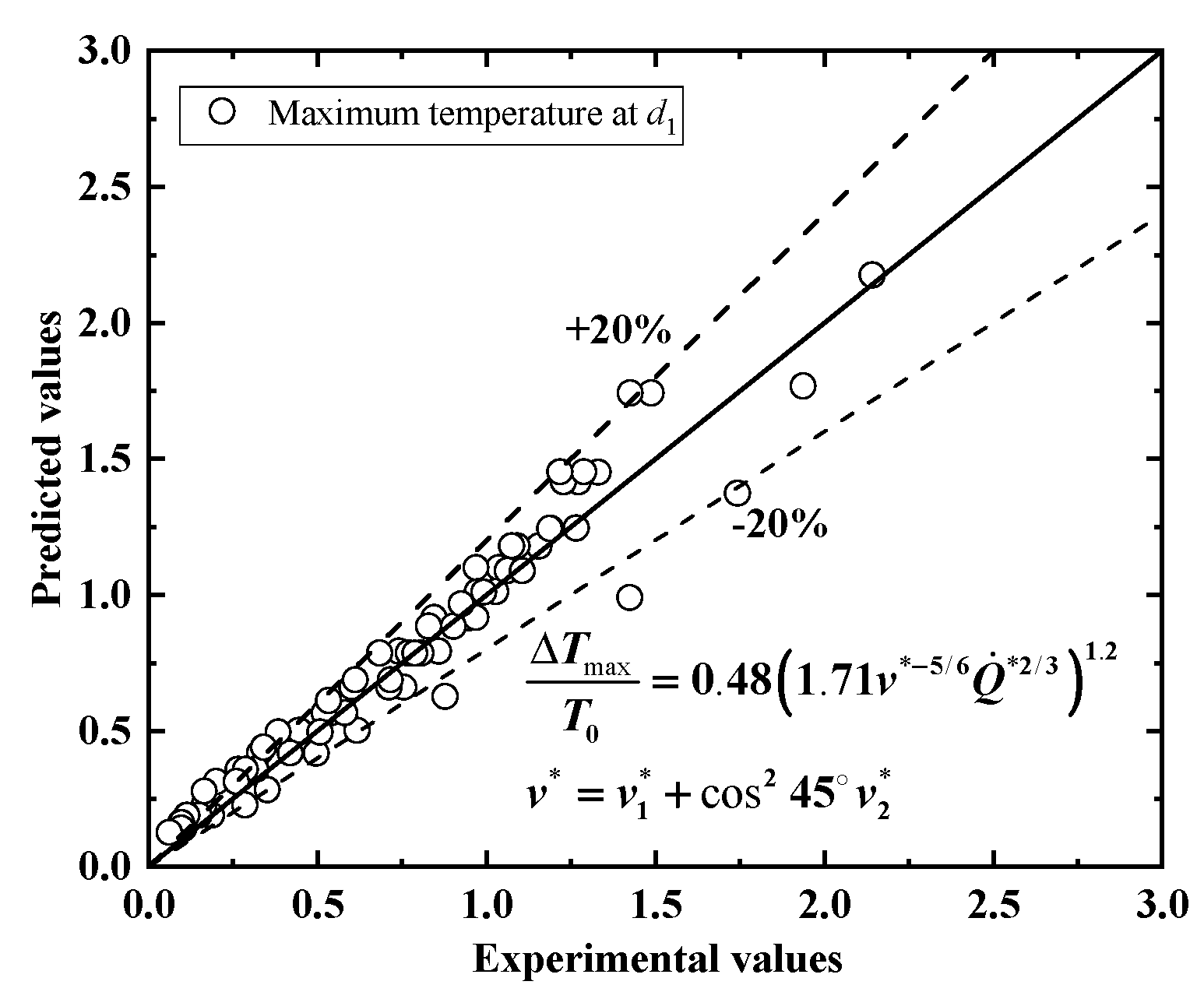
3.1.2. Maximum Temperature at Location d1
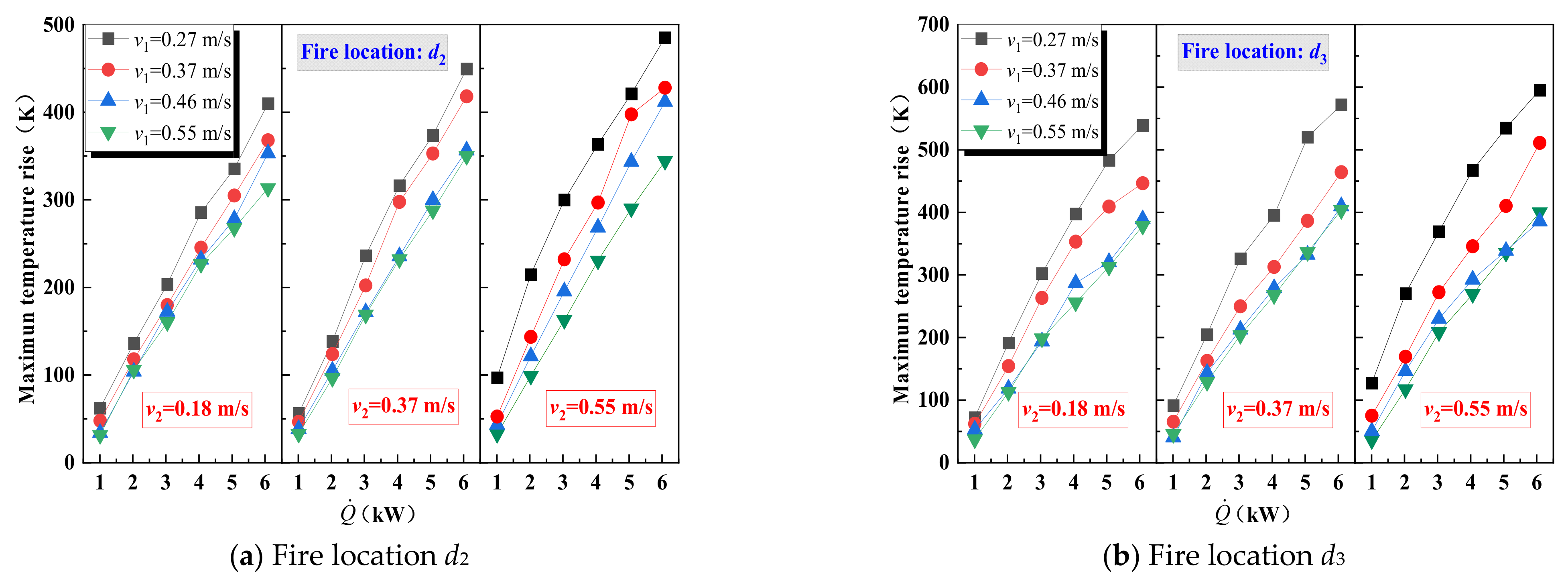
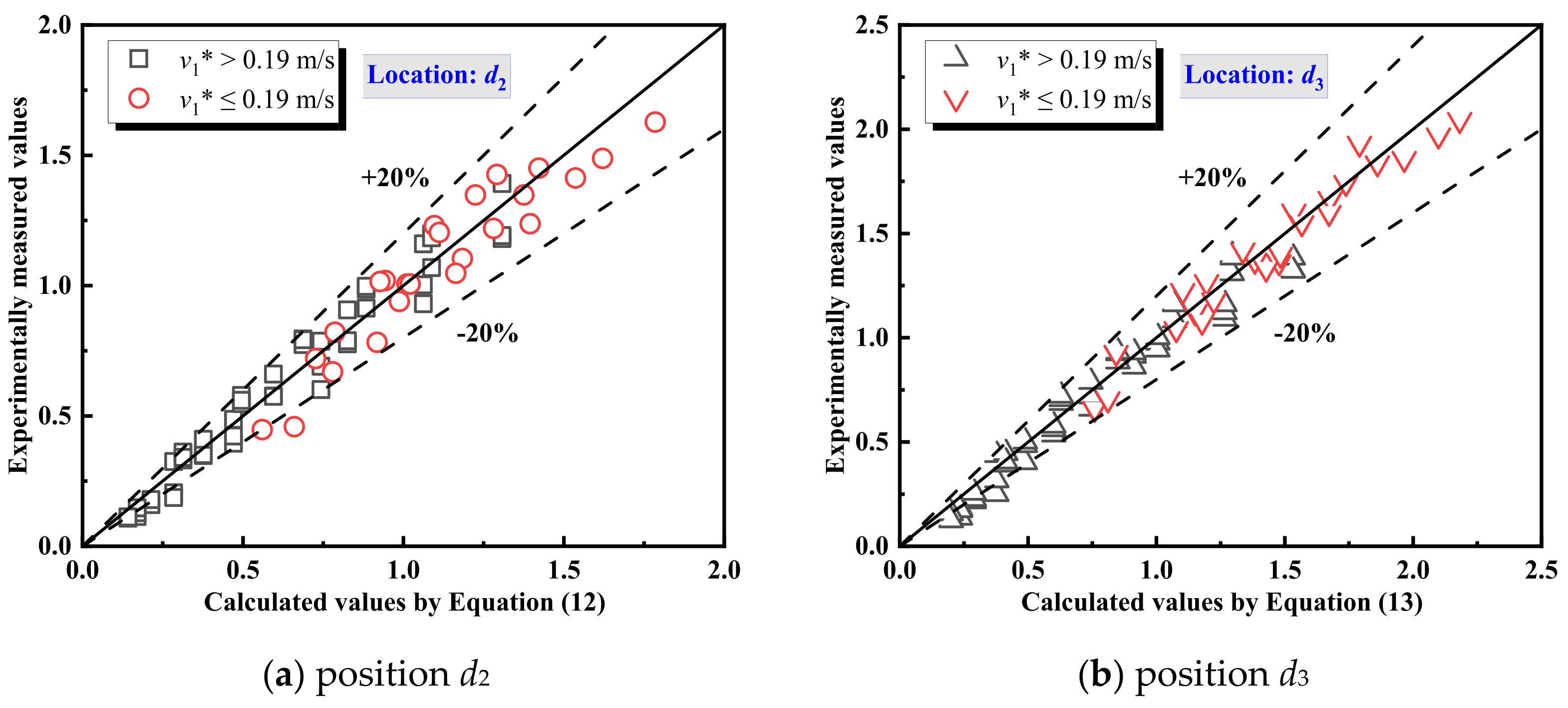
3.1.3. Maximum Temperature for Positions d2 and d3
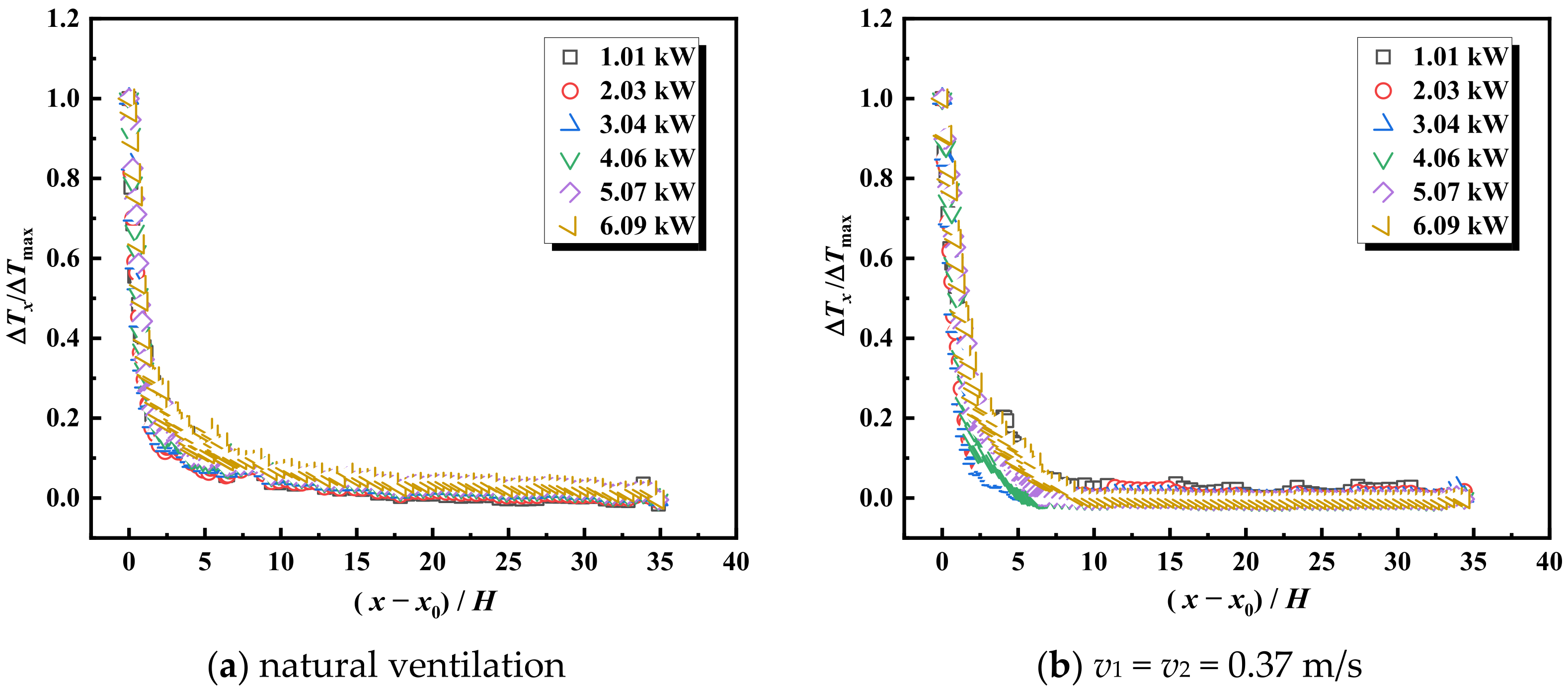
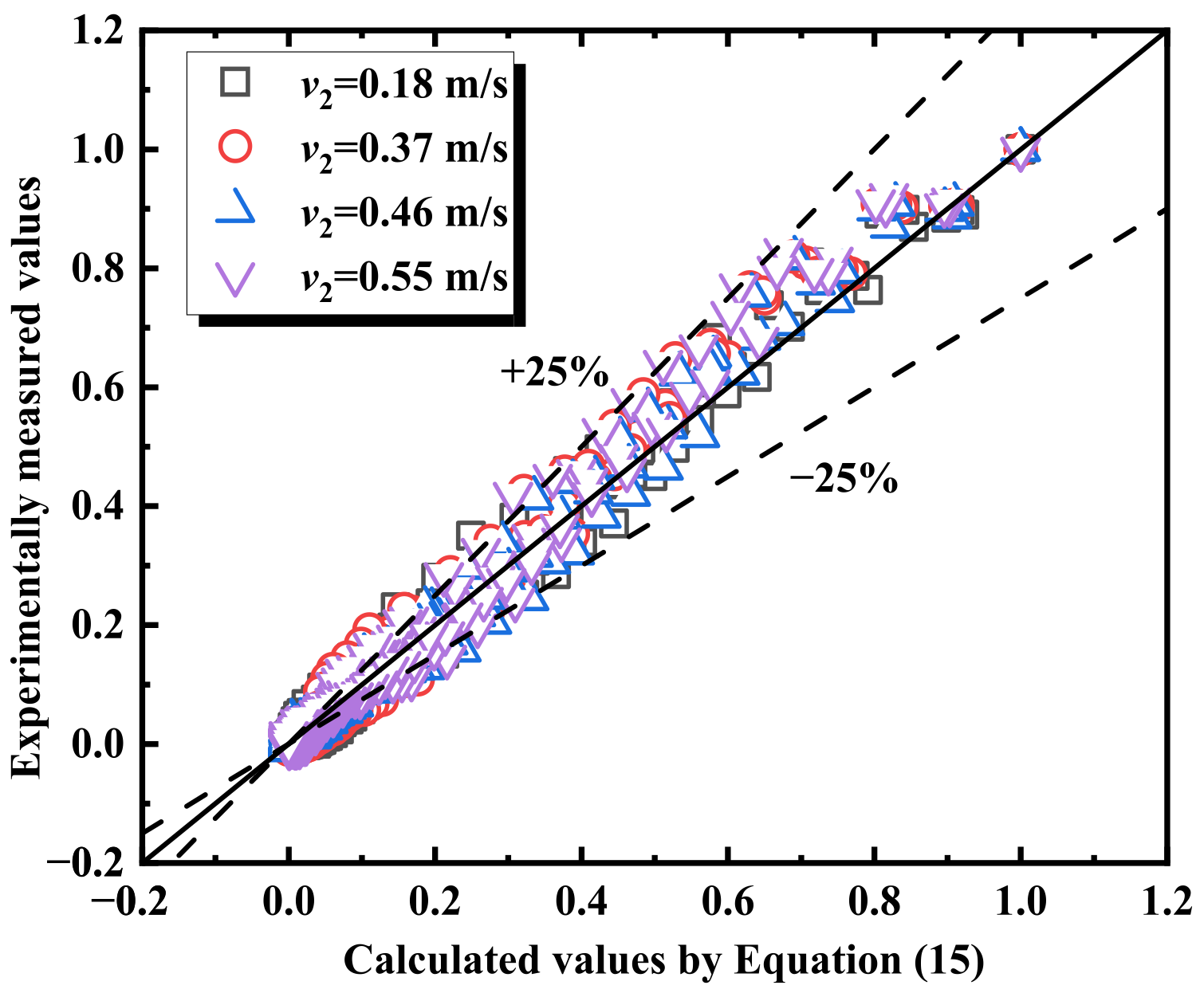
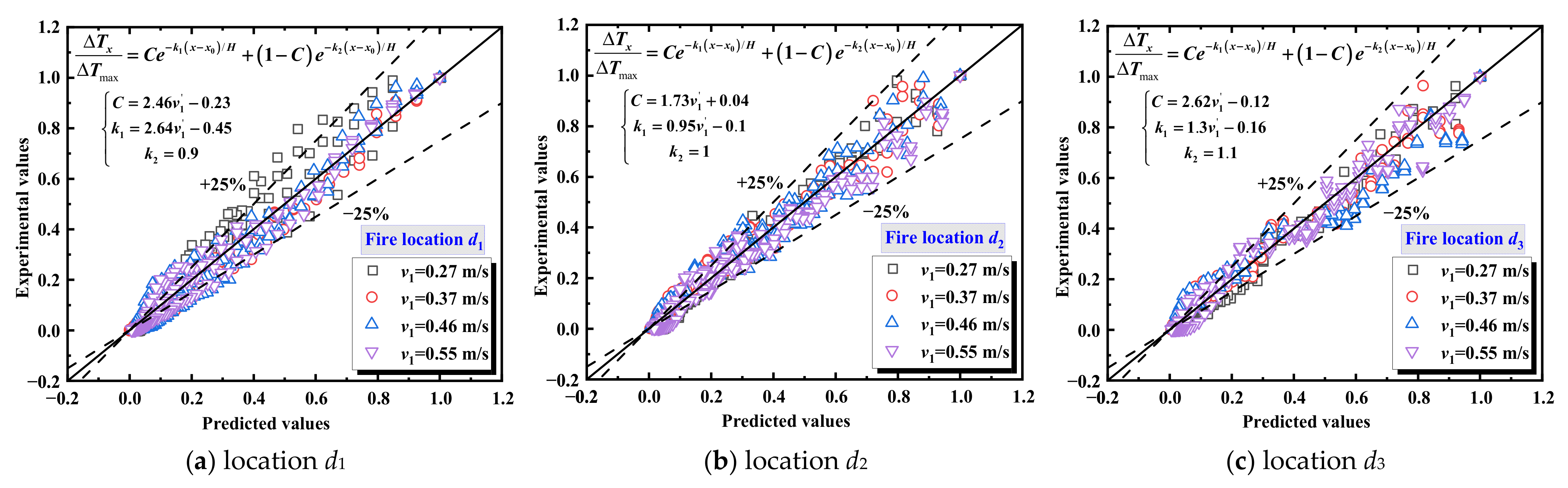
3.2. Analysis of Longitudinal Temperature Distribution Upstream of the Branch Tunnel Under Cooperative Ventilation
3.3. Characteristics of Smoke Propagation in Tunnels
4. Conclusions
- (1)
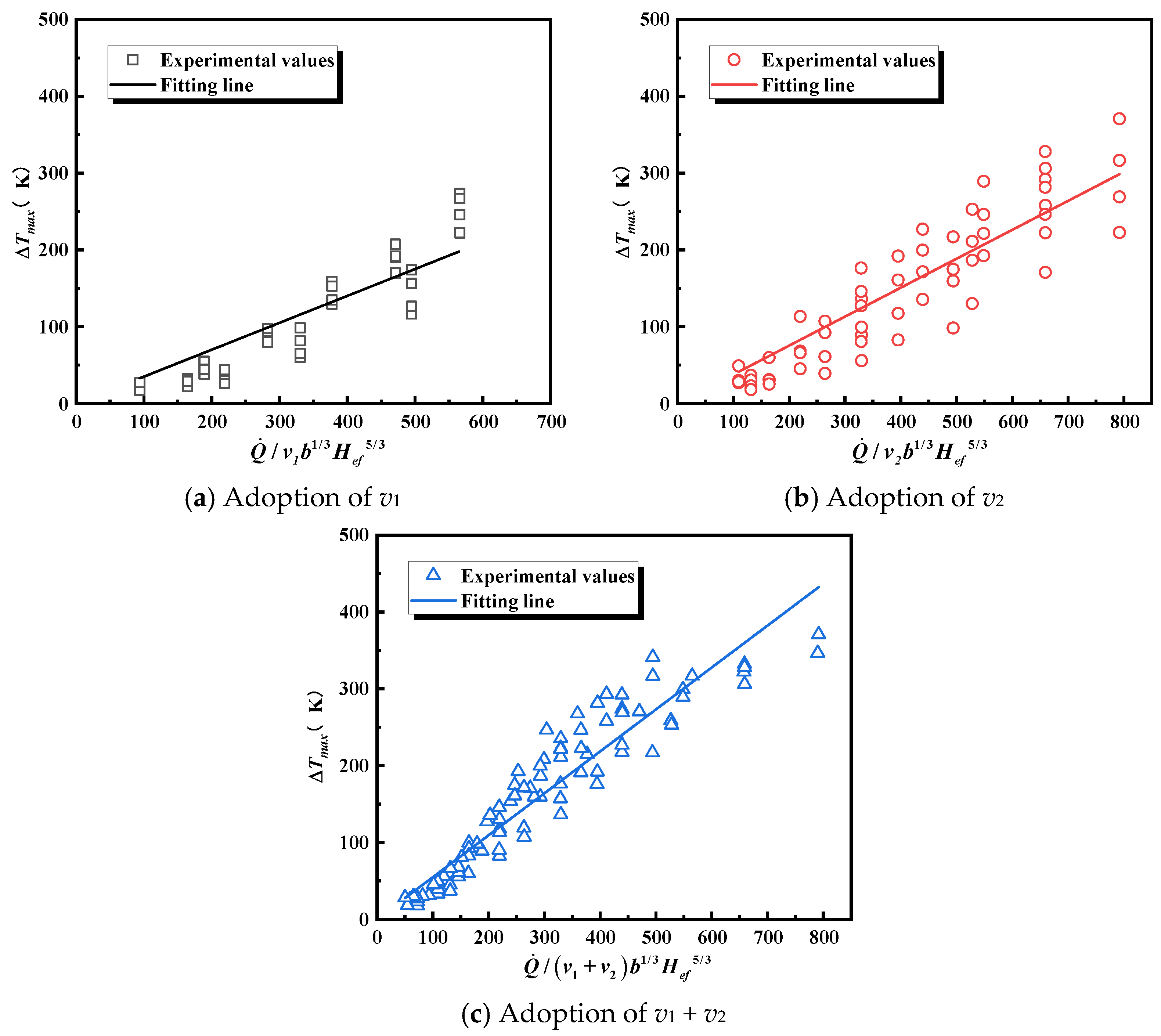
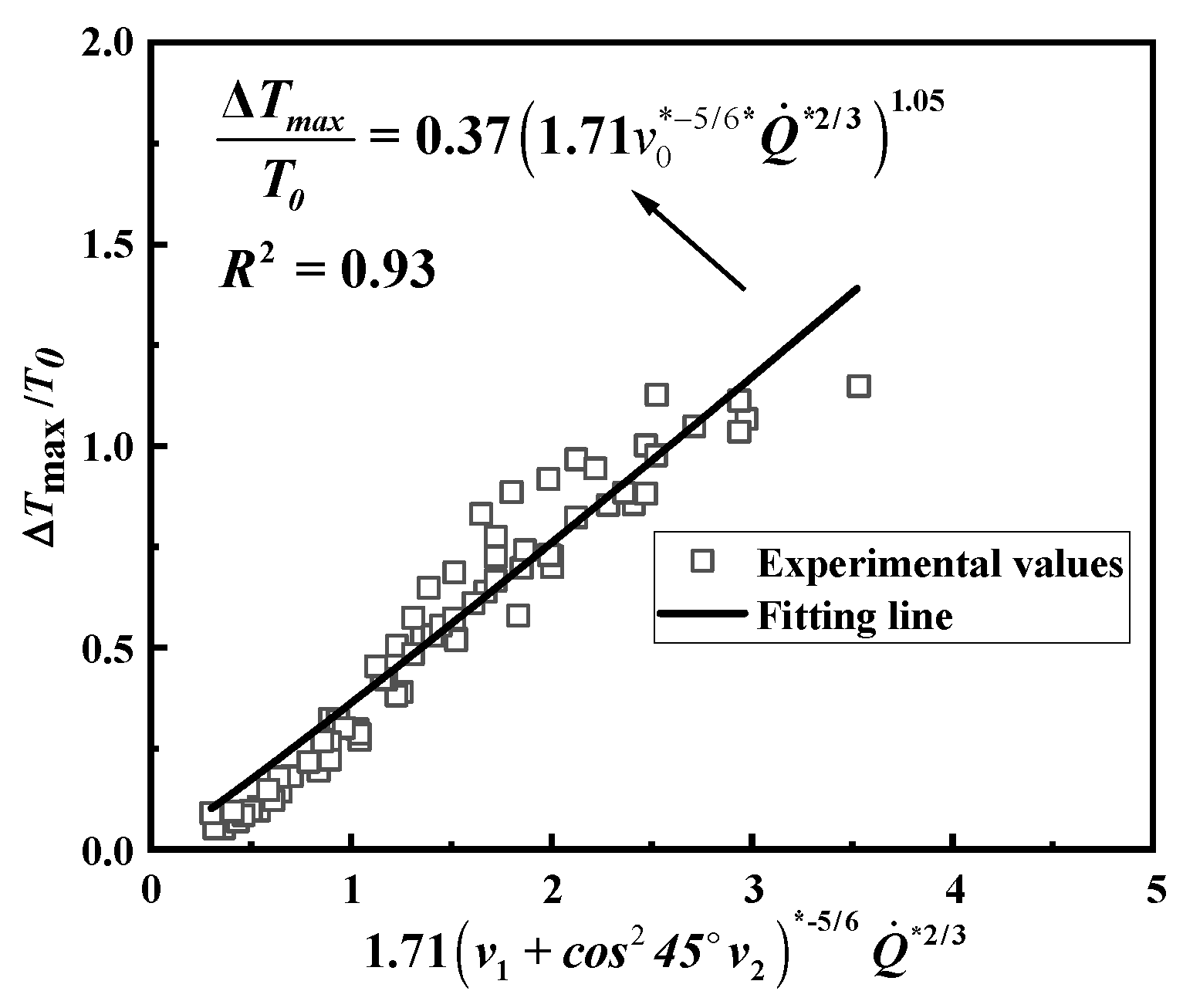
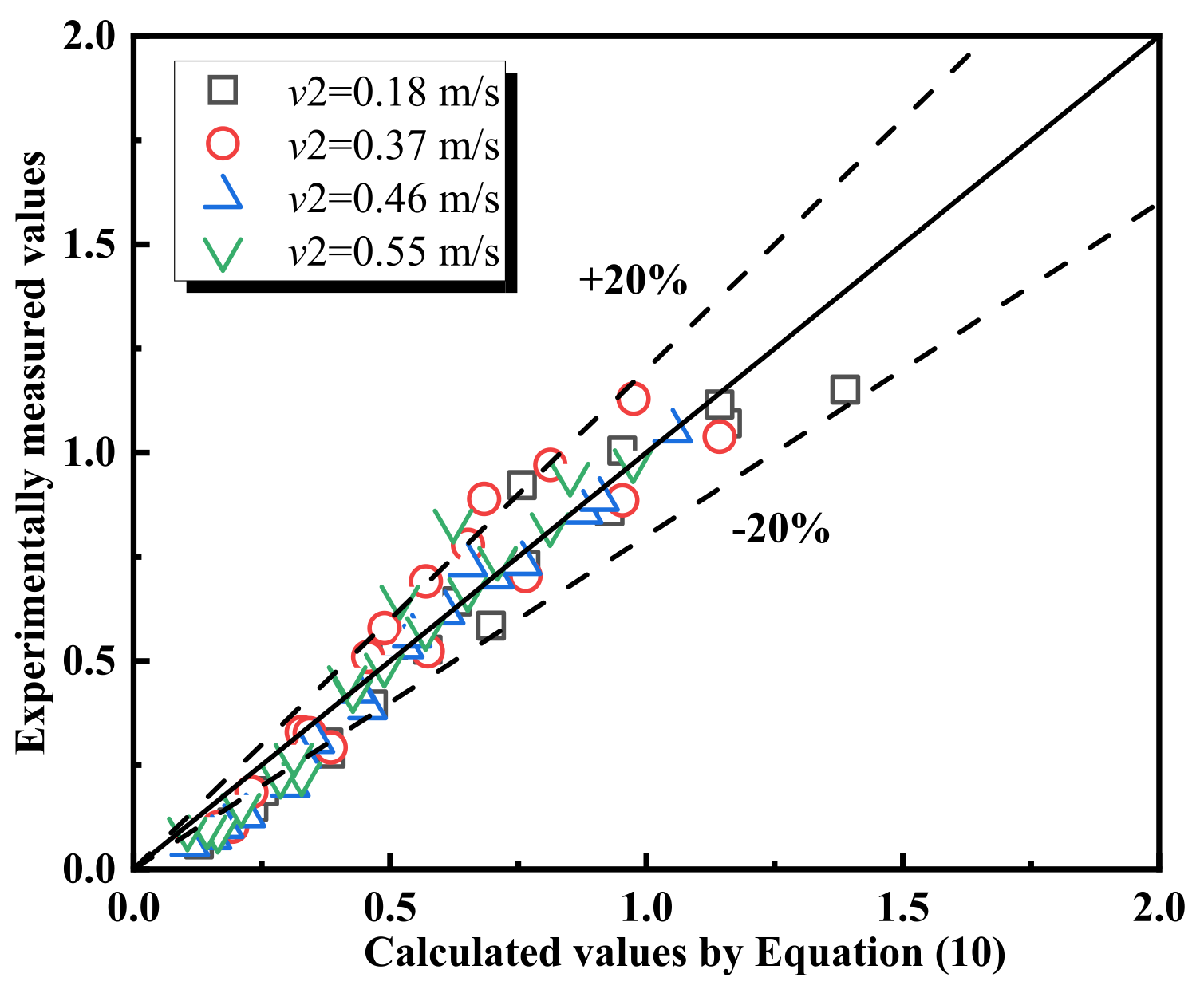
- The maximum temperature rise is jointly determined by the HRR and cooperative ventilation. A higher HRR leads to a larger . The influence of cooperative ventilation can be categorized based on the fire location. Before the fire enters the branch tunnel, ventilation in both the main and branch tunnels reduces . After the fire moves into the branch tunnel, ventilation in the main tunnel transitions to increasing . Considering variations in fire location, HRR, and cooperative ventilation, a prediction model for the maximum temperature in interconnected tunnels has been proposed.
- (2)
- The dimensionless longitudinal temperature distribution is minimally affected by the HRR. When fire is at the intersection of the central axis (d0), the temperature decay upstream of the branch tunnel is closely related to v2. However, after the fire source moves to the entrance or inside the branch tunnel, the influence of the main tunnel’s airflow becomes minimal. Combining cooperative ventilation and the HRR, a predictive model for the temperature decay upstream of the branch tunnel under different fire locations in interconnected tunnel has been proposed.
- (3)
- A higher HRR enhances the thermal driving force of smoke, leading to a broader spread range. The spread of smoke within the tunnel is jointly affected by the fire location and cooperative ventilation. Before the fire enters the branch tunnel, ventilation in both the main and branch tunnels can effectively control smoke spread. The smoke spread range decreases with increasing velocity. After the fire moves into the branch tunnel, the impact of ventilation airflow transitions from suppressing smoke spread to increasing its diffusion range in the interconnected tunnel.
- (4)
- In underground interconnected tunnels, smoke movement characteristics are complex and variable. To better ensure personnel safety, smoke control strategies should be formulated based on the existing tunnel smoke extraction system (longitudinal smoke exhaust mode or centralized smoke exhaust mode) and actual fire scenarios (fire location).
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tao, H.W.; Xu, Z.S.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhang, X.C.; Fan, C.G. Application of the longitudinal ventilation system in the underground interconnected infrastructure: Assessment of flow distribution and confluence ratio. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerod. 2023, 239, 105466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babrauskas, V.; Gann, R.G.; Levin, B.C.; Paabo, M.; Yusa, S. A methodology for obtaining and using toxic potency data for fire hazard analysis. Fire Saf. J. 1998, 31, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hietainemi, J.; Kallonen, R.; Mikkola, E. Burning characteristics of selected substances: Production of heat, smoke and chemical species. Fire Mater. 1999, 23, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, R.L. Calculation of response time of ceiling-mounted fire detectors. Fire Technol. 1972, 8, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Fan, C.G.; Zhong, W.; Shen, X.B.; Sun, J.H. Experimental investigation on influence of different transverse fire locations on maximum smoke temperature under the tunnel ceiling. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 2012, 55, 4817–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, R.L. Turbulent ceiling-jet induced by large-scale fires. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1975, 11, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Lei, B.; Ingason, H. The maximum temperature of buoyancy-driven smoke flow beneath the ceiling in tunnel fires. Fire Saf. J. 2011, 46, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurioka, H.; Oka, Y.; Satoh, H.; Sugawa, O. Fire properties in near field of square fire source with longitudinal ventilation in tunnels. Fire Saf. J. 2003, 38, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.H.; Ji, J.; Fan, C.G.; Sun, J.H.; Zhu, J.P. Influence of sidewall restriction on the maximum ceiling gas temperature of buoyancy-driven thermal flow. Energy Build. 2014, 84, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.H.; Ji, J.; Fan, C.G.; Sun, J.H. Experimental analysis of the influence of accumulated upper hot layer on the maximum ceiling gas temperature by a modified virtual source origin concept. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 2015, 84, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.H.; Chen, L.F.; Wu, L.; Li, Y.F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Meng, N. An experimental investigation and correlation on buoyant gas temperature below ceiling in a slopping tunnel fire. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 51, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Wan, H.X.; Li, K.Y.; Han, J.Y.; Sun, J.H. A numerical study on upstream maximum temperature in inclined urban road tunnel fires. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 2015, 88, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yu, L.X.; Weng, M.C.; Lu, X.L. Study on longitudinal temperature distribution of fire-induced ceiling flow in tunnels with different sectional coefficients. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 54, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Ingason, H. The maximum ceiling gas temperature in a large tunnel fire. Fire Saf. J. 2012, 48, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Ingason, H. Position of maximum ceiling temperature in a tunnel fire. Fire Technol. 2014, 50, 889–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.L.; Li, J.; Xu, X. Full-scale tests on smoke temperature distribution in long-large subway tunnels with longitudinal mechanical ventilation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 109, 103784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhong, M.H.; Tian, X.L.; Zhang, P.H.; Xiao, Y.; Mei, Q. Experimental and numerical study on fire-induced smoke temperature in connected area of metro tunnel under natural ventilation. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 138, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.B.; Li, Y.F.; Li, J.M.; Li, J.X.; Wu, K.; Zhu, K.; Li, H.H. Experimental investigation on maximum gas temperature beneath the ceiling in a branched tunnel fire. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 145, 105997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Chen, C.K.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xu, T.; Sun, H.K. Experimental study on temperature profile in a branched tunnel fire under natural ventilation considering different fire locations. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 159, 106631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.S.; Gao, Y.J.; Li, X.S.; Mao, P.F.; Zhang, Y.C.; Jin, K.Y.; Li, T.; Chen, L.F. Effects of transverse fire locations on flame length and temperature distribution in a bifurcated tunnel fire. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 112, 103893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.W.; Xu, Z.S.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhang, X.C.; Fan, C.G. An experimental study on the smoke spread in underground interconnected infrastructure with longitudinal ventilation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 142, 105381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.F.; Mao, P.F.; Zhang, Y.C.; Xing, S.S.; Li, T. Experimental study on smoke characteristics of bifurcated tunnel fire. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 98, 103295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.F.; Zhou, S.X.; Lan, Y.J.; Liu, X.Y.; Yang, Y.P.; Li, X.S.; Yan, X.E.; Chen, H.F. Experimental study on fire characteristics of the bifurcated tunnel under multi-directional ventilation. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 185, 108072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delichatsios, M.A. The flow of fire gases under a beamed ceiling. Combust. Flame 1981, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.H.; Huo, R.; Chow, W.K.; Wang, H.B.; Yang, R.X. Decay of buoyant smoke layer temperature along the longitudinal direction in tunnel fires. J. Appl. Fire Sci. 2005, 13, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.L.; Zeng, Y.H. Effect of single-side centralized exhaust on smoke control and temperature distribution in longitudinal ventilation tunnel fires. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 119, 104241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.L.; Zeng, Y.H.; Li, J.; Yang, G.C.; Fang, Y.; Li, B.J. Study on the maximum temperature and temperature decay in single-side centralized smoke exhaust tunnel fires. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 172, 107277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingason, H.; Li, Y.Z. Model scale tunnel fire tests with longitudinal ventilation. Fire Saf. J. 2010, 45, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.B.; Li, Y.F.; Li, J.X.; Wu, K.; Li, H.H.; Zhu, K. Experimental study on the temperature longitudinal distribution induced by a branched tunnel fire. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 170, 107175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.A.; Jiang, L.; Li, S.Y.; Shen, N.; Zhang, Y.C.; Sun, J.H. Theoretical and experimental study on longitudinal smoke temperature distribution in tunnel fires. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2016, 102, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.L.; Xu, Z.S.; Liu, Q.L.; Zhen, Y.X.; Tao, H.W.; Yu, Z.H.; Zhao, J.M. Experimental study on the impact of blockage ratio on smoke propagation in underground interconnected tunnel. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2024, 203, 109150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

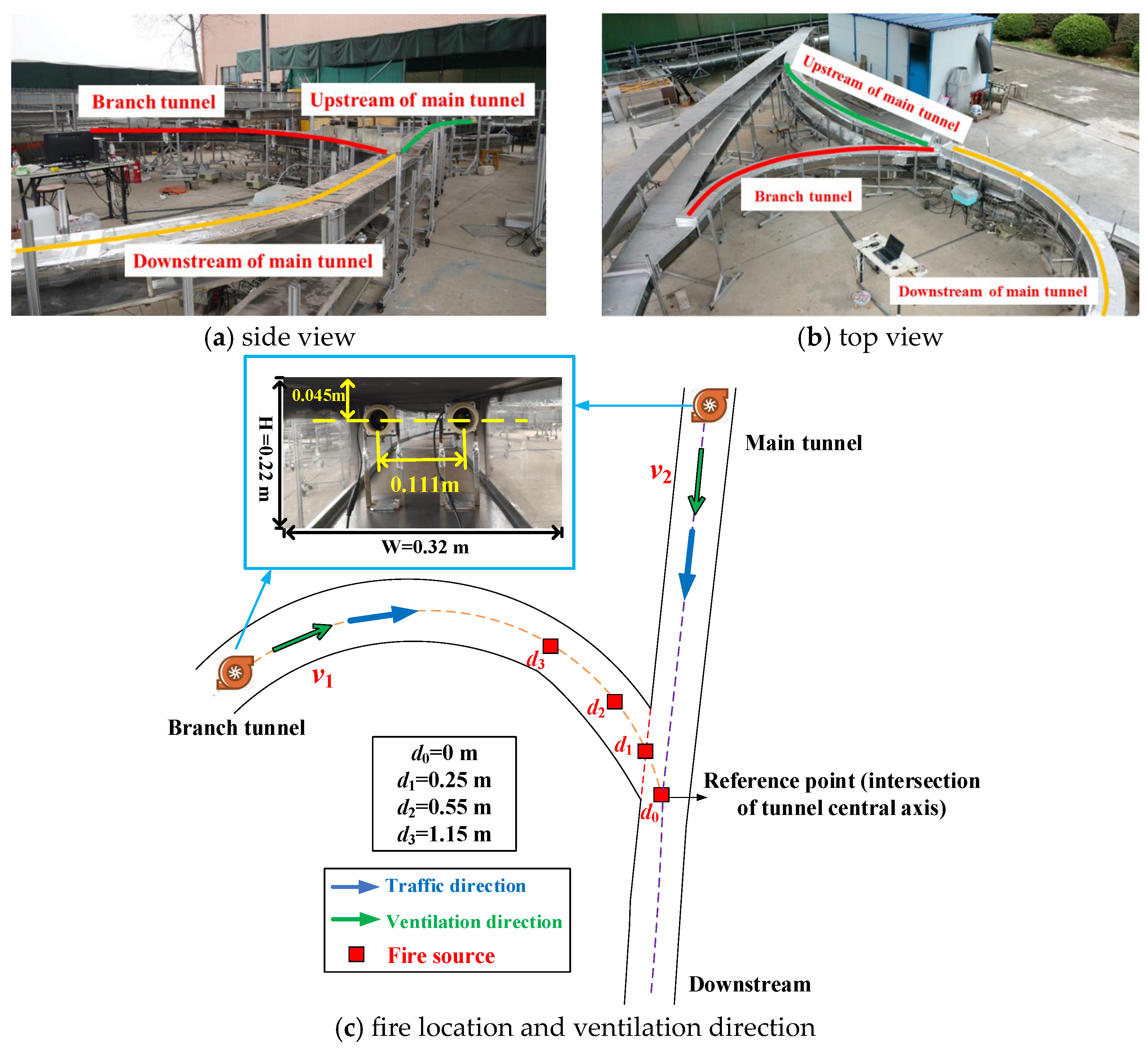
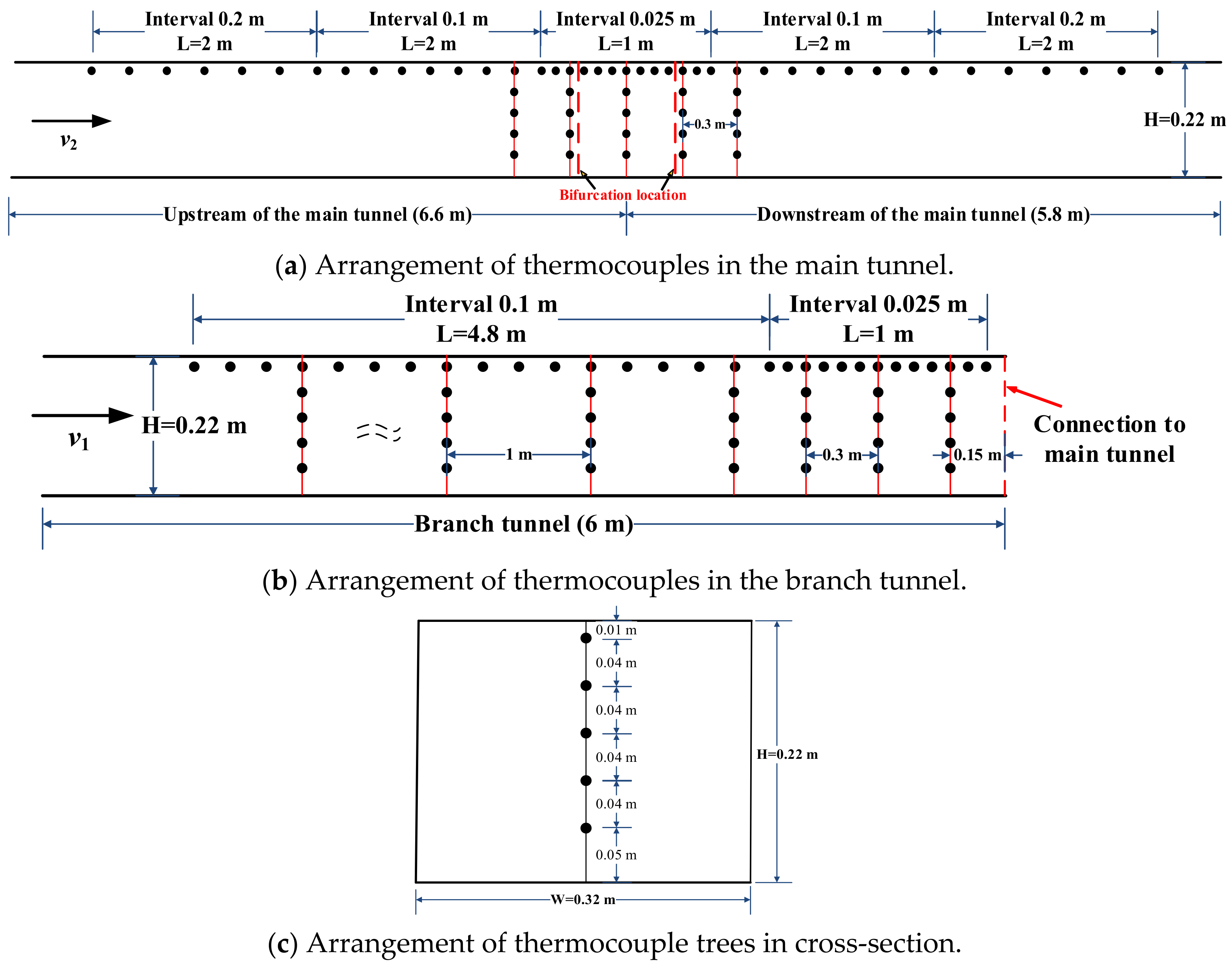



| Tests | Fire Location | Heat Release Rate (kW) | Longitudinal Ventilation Velocity of the Branch Tunnel v1 (m/s) | Longitudinal Ventilation Velocity of the Main Tunnel v2 (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base01~06 | d0 (0 m) | 1.01, 2.03, 3.04, 4.06, 5.07, 6.09 | 0 | 0 |
| A01~A96 | d0 (0 m) | 0, 0.27, 0.37, 0.64 | 0.18, 0.37, 0.46, 0.55 | |
| B01~B72 | d1 (0.25 m) | 0.27, 0.37, 0.46, 0.55 | 0.18, 0.37, 0.55 | |
| C01~C72 | d2 (0.55 m) | 0.27, 0.37, 0.46, 0.55 | 0.18, 0.37, 0.55 | |
| D01~D72 | d3 (1.15 m) | 0.27, 0.37, 0.46, 0.55 | 0.18, 0.37, 0.55 |
| Case | Coefficient C | Coefficient k1 | Coefficient k2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| v2 = 0.18 m/s | 0.26 | v1 = 0 m/s, k1 = 0.06 v1 = 0.27 m/s, k1 = 0.16 v1 = 0.37 m/s, k1 = 0.26 v1 = 0.64 m/s, k1 = 0.81 | 0.9 |
| v2 = 0.37 m/s | 0.24 | ||
| v2 = 0.46 m/s | 0.14 | ||
| v2 = 0.55 m/s | 0.15 |
| Fire Location | Case | Coefficient C | Coefficient k1 | Coefficient k2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| d1 | v1 = 0.27 m/s | 0.28 | 0.09 | 0.9 |
| v1 = 0.37 m/s | 0.39 | 0.22 | 0.94 | |
| v1 = 0.46 m/s | 0.55 | 0.38 | 0.88 | |
| v1 = 0.55 m/s | 0.76 | 0.61 | 0.89 | |
| d2 | v1 = 0.27 m/s | 0.39 | 0.10 | 0.99 |
| v1 = 0.37 m/s | 0.49 | 0.13 | 1.12 | |
| v1 = 0.46 m/s | 0.57 | 0.18 | 1.05 | |
| v1 = 0.55 m/s | 0.74 | 0.29 | 1.02 | |
| d3 | v1 = 0.27 m/s | 0.41 | 0.11 | 1.04 |
| v1 = 0.37 m/s | 0.56 | 0.17 | 1.11 | |
| v1 = 0.46 m/s | 0.71 | 0.24 | 1.08 | |
| v1 = 0.55 m/s | 0.93 | 0.37 | 1.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ying, H.; Xu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Jiao, W. Experimental Study on Temperature Distribution Characteristics Under Coordinated Ventilation in Underground Interconnected Tunnels. Fire 2025, 8, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8030110
Ying H, Xu Z, Yu Z, Yin Y, Jiao W. Experimental Study on Temperature Distribution Characteristics Under Coordinated Ventilation in Underground Interconnected Tunnels. Fire. 2025; 8(3):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8030110
Chicago/Turabian StyleYing, Houlin, Zhisheng Xu, Zihan Yu, Yaolong Yin, and Weibing Jiao. 2025. "Experimental Study on Temperature Distribution Characteristics Under Coordinated Ventilation in Underground Interconnected Tunnels" Fire 8, no. 3: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8030110
APA StyleYing, H., Xu, Z., Yu, Z., Yin, Y., & Jiao, W. (2025). Experimental Study on Temperature Distribution Characteristics Under Coordinated Ventilation in Underground Interconnected Tunnels. Fire, 8(3), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8030110






