1. Introduction
Forest fire risk forecasting aims to predict the likelihood of forest fires occurring and calculate a series of fire behavior indicators exhibited after ignition; this is based on known weather conditions, fuel characteristics, firebrands, and topographic factors [
1,
2]. It primarily helps to tailor prevention measures to the risk level, enabling analysts to scientifically determine the focus and intensity of daily forest fire prevention efforts according to the severity of the fire risk. Therefore, accurate risk forecasting is a prerequisite for effective forest fire prevention. Currently, the fire risk forecasting models used in China primarily rely on statistical methods, seeking to establish relationships between weather elements and fire occurrence [
3]. However, this approach has significant limitations: it not only fails to adequately consider the states of fuel materials—i.e., the carriers of forest fires—but also neglects to consider how topographic factors and other aspects influence potential fire behavior. Moreover, the weather–fire occurrence probability model was developed in 2007. In the context of global climate warming, and with recent adjustments in forest fire management policies, this relationship is no longer applicable [
4].
A recent report by the United Nations Environment Programme and GRID-Arendal indicates that climate change and land use transformations will lead to more frequent and intense forest fires, projecting a 14%, 30%, and 50% increase in the number of global extreme wildfire events by 2030, 2050, and the end of the century, respectively [
5,
6]. Nowell contends that the increasing complexity of forest fires highlights the need for institutional adaptation [
7], necessitating in-depth research on forest fire risk forecasting methodologies to enhance the accuracy in calculating fire occurrence probabilities—this is a critical advancement in order to strengthen forest fire prevention efforts [
8,
9].
Forest fire occurrence forecasting, which is a critical component of fire risk assessment, involves determining the likelihood of forest fires being ignited within specific timeframes and geographical areas [
10,
11,
12]. This probability is not only influenced by meteorological factors but also intrinsically linked to the firebrand availability and fuel conditions [
13]. The limitations of the current forecasting methodologies arise from their exclusive focus on the impact of weather conditions on the fire probability while neglecting the contributions of the firebrand and fuel. Consequently, it is crucial to develop a novel computational approach that couples the effects of the firebrand, weather, and fuel characteristics in order to address existing methodological deficiencies and enhance the forecasting capabilities under climate change scenarios.
Theoretically, the forest fire occurrence probability can be expressed as the product of three probabilities: the firebrand occurrence probability, the ignition probability (i.e., the likelihood of a fuel being ignited), and the post-ignition spread-to-damage probability [
4,
14]. The firebrand occurrence probability is primarily influenced by the socioeconomic development level, human activity intensity, and forest road accessibility [
15,
16,
17,
18]. The ignition probability depends mainly on the fuel moisture content, firebrand type, and meteorological conditions [
19,
20,
21,
22], while the post-ignition spread-to-damage probability is predominantly associated with potential spread rates following initial ignition [
14]. The accurate quantification of these three probabilities at specific spatiotemporal scales enables the precise calculation of the forest fire occurrence probability for risk forecasting, effectively addressing the disparities between predicted fire risk ratings and actual fire occurrence probabilities. Currently, while the ignition probability has been extensively researched, studies on the firebrand occurrence probability and spread-to-damage probability remain scarce. The National Fire Danger Rating System (NFDRS) determines ignition probabilities through laboratory experiments involving the matchstick ignition of shortleaf pine needles combined with preheating thermal energy calculations. It also estimates the spread-to-damage probability using the Rothermel fire spread model, defining the product as the ignition component (IC)—representing the probability of reportable fires caused by specific firebrands [
14]. Sun and Zhang demonstrated the IC’s efficacy in predicting the forest fire occurrence probability in China’s Greater Khingan Range, particularly in areas with sparse firebrands, thereby reducing the discrepancies between predicted fire risk levels and actual fire occurrences [
20]. Thus, this study adopts the IC to advance forest fire occurrence probability research and enhance the predictive accuracy.
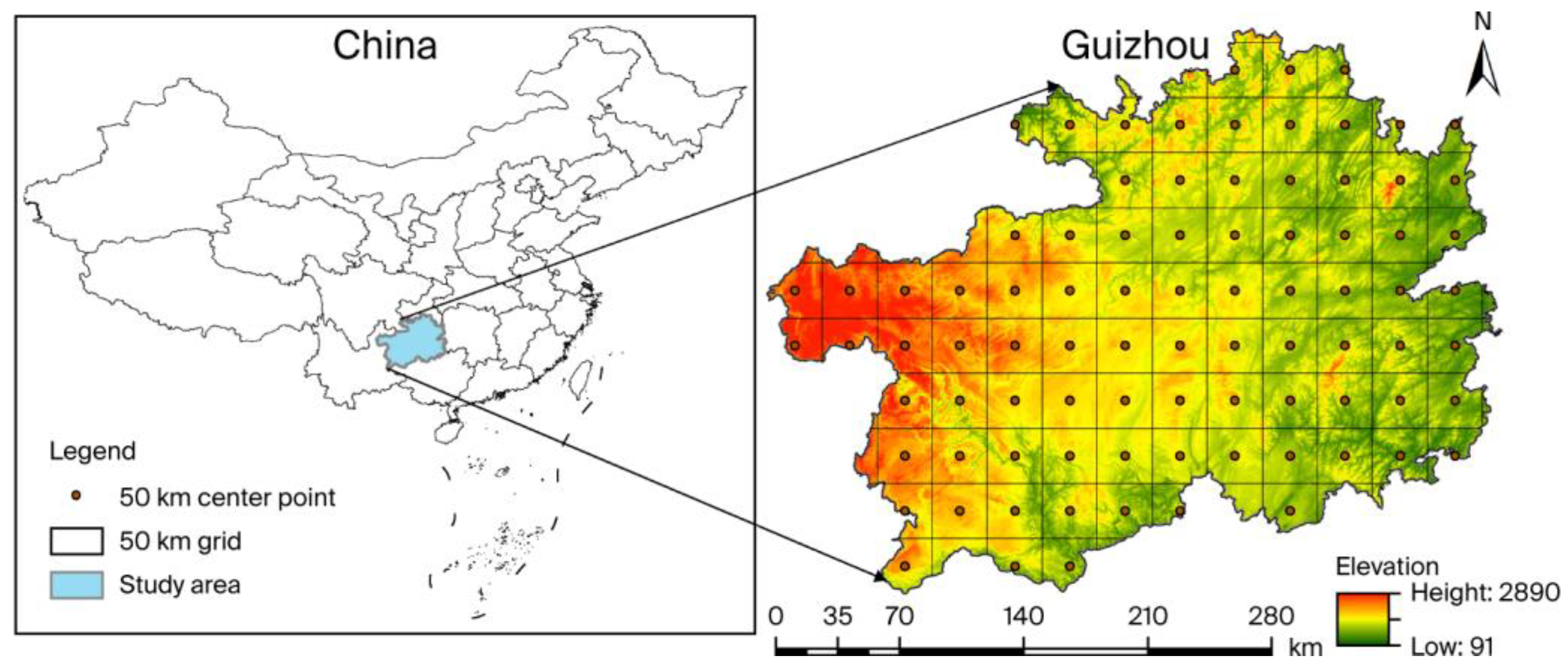
Guizhou Province, China, characterized by its distinctive topography consisting of 80% mountains, 10% water, and 10% farmland, exhibits a pronounced agroforestry mosaic landscape, where forest fires pose significant challenges in terms of containment and elevated risks when ignited [
23]. Since 2022, elevated numbers of forest fire incidents have been recorded across the province, with multiple concurrent forest fires occurring in various regions. In particular, there was an abrupt surge in fire frequencies during early 2024, resulting in many casualties. Therefore, it is crucial to investigate the forest fire occurrence probability in Guizhou by integrating the firebrand occurrence probability with the IC in order to advance forest fire prevention and suppression strategies under climate change.
However, Guizhou Province exhibits significant differences in firebrands, fuel characteristics, and weather conditions compared to regions such as the United States and China’s Greater Khingan Range. Furthermore, socioeconomic development induces temporal variations in the firebrand occurrence probability. Consequently, this study leverages historical forest fire data from Guizhou to investigate the forest fire occurrence probability, integrating the firebrand occurrence probability with the IC to address three key research questions: (1) Does the direct application of the NFDRS methodology for IC calculation demonstrate a significant correlation with the observed forest fire occurrence probabilities in Guizhou? (2) Given the significant IC–fire probability correlation, what temporal scale optimally balances the effective characterization of the firebrand occurrence probability with low-error fire occurrence prediction? (3) How can a spatially explicit fire occurrence probability prediction model combining the firebrand and IC be developed and validated for Guizhou? This research resolves critical limitations in current fire risk forecasting by integrating firebrands, fuel dynamics, and meteorological factors—quantifying the probabilistic mechanisms governing the forest fire initiation-to-spread continuum—thereby establishing a theoretical foundation and technical framework for enhanced fire risk prediction in Guizhou, while providing scientific support for forest fire management decisions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Situated in Southwestern China (103°36′–109°35′ E, 24°37′–29°13′ N), Guizhou Province exhibits pronounced topographical heterogeneity, characterized by a general descending elevation gradient from west to east and dominated by plateau mountains (accounting for ~61% of the total area), hills (~32%), and basins (~7%), with mountainous terrain accounting for approximately 93% of the provincial land area. The study region experiences a humid subtropical monsoon climate, featuring a mean annual temperature of ~15 °C, annual precipitation of 1000–1400 mm, and perennial relative humidity exceeding 70%. Winters remain mild (January mean: 4–6 °C), while summers stay cool (July mean: 15–23 °C). With its forest coverage reaching 63%, it has extensively distributed coniferous forests, primarily consisting of Pinus massoniana Lamb., Pinus yunnanensis Franch., and Abies fabri Craib., complemented by broadleaved species including Quercus glauca Thunb., Quercus fabri Hance., Populus przewalskii Maxim., and Cinnamomum camphora Presl.
2.2. IC Calculation Method
The IC is calculated as the product of the ignition probability and post-ignition spread-to-damage probability. While the most accurate method to determine these probabilities involves using predictive models derived from ignition and combustion experiments, such an approach is prohibitively time- and resource-intensive. The NFDRS provides computational methods for two types of probabilities, which have been widely adopted globally. Although the calculation model was originally developed based on environmental conditions in the United States and may introduce certain errors when applied elsewhere, the underlying principles of fuel physics—such as the relationship between the moisture content and ignition probability—and the heat transfer equations are universally applicable. Moreover, as this research primarily constitutes an exploratory investigation into regional fire probability prediction methods and predominantly adopts the physically based computational approaches from the NFDRS, rather than relying on purely empirical statistical models, the methodologies outlined in reference within the NFDRS framework are directly applied in this study [
14]. The following equations are used:
where
denotes the ignition probability (%),
denotes the pre-ignition heat energy (cal/g),
denotes the air temperature (°F),
denotes the relative humidity (%),
denotes the equilibrium moisture content of a fuel (%), and
denotes the moisture content of the fuel (%). The fuel moisture content can be derived from
and
measurements, thus determining
.
The spread-to-damage probability is calculated according to Equation (5) [
24]:
where
SC (spread component) is derived from Rothermel’s fire spread rate model [
25] and represents the computed spread rate rounded to the nearest integer;
SCm (minimum spread rate threshold) denotes the lowest rate of spread sufficient to initiate forest fires within the study area, typically determined by developers or land managers [
24]. If
, then
.
Given that surface fires dominate the study area, and fine surface fuels are typically ignited first, this study uses parameters for
Pinus massoniana needles (see
Table 1) as the input for the Rothermel model.
2.3. Model Data
This study integrates forest fire point records, meteorological and topographic datasets, and fuel characteristics for the target region.
(1) Forest fire point data: Forest fire occurrence exhibits temporal patterns that are influenced by policy adjustments, socioeconomic development, and lifestyle changes [
26]. Post-2016, Guizhou experienced a marked decline in the frequency of fires attributable to these factors [
27]. Given data availability constraints, the analysis period spanned 2016–2020. Fire locations were extracted from the MCD64A1 wildfire products processed by the Global Wildfire Information System
https://gwis.jrc.ec.europa.eu (accessed on 3 January 2025), with each fire point containing unique identifiers, date stamps, and geographic coordinates. Forested areas were delineated using land cover data with a 1 km resolution, derived from the Resource and Environment Science and Data Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences
https://www.resdc.cn/DOI/DOI.aspx?DOIID=54 (accessed on 3 January 2025). The downloaded fire point data were spatially intersected with the forestland data of Guizhou Province to extract fire points located within forested areas. To minimize errors and ambiguous positives in forest fire detection, only fire points with a confidence level ≥ 80% were retained. Furthermore, to ensure spatial independence [
28], only the earliest detected fire point was preserved among clusters of points separated by less than 1 km. This procedure resulted in the final forest fire dataset for Guizhou Province, covering the period of 2016–2020 and including attributes such as the timing of fire occurrence. All processing steps were performed using ArcGIS 10.8.
(2) Meteorological data: For 2016–2020, daily observations of the air temperature, relative humidity, wind speed, and precipitation were sourced from data with a 4 km resolution from the Gridded Daily Meteorological Dataset for China (2000–2020;
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10963932 (accessed on 3 January 2025)), providing high-precision inputs for fuel moisture, ignition, and spread probability calculations.
(3) Topographic data: Slope parameters for potential spread modeling were derived from data with a 30 m resolution from GDEMV2 digital elevation models
http://www.gscloud.cn (accessed on 3 January 2025). Slope rasters were processed in ArcGIS 10.8 using the Slope tool (3D Analyst > Raster Surface), with point extraction via Extract Multi Values to Points.
(4) Fuel data: The fuel conditions (e.g., type and load) in the study area changed repeatedly during the research period, and it was difficult to track these variations. As an exploratory study on fire probability calculation methods in the study area, this research prioritized the establishment and validation of the methodological framework. To mitigate interference due to vegetation heterogeneity and enable a clear assessment of the method’s performance, we controlled for fuel complexity by focusing on a single, fixed fuel type. Consequently,
Pinus massoniana forests—the most widespread and fire-prone forest type in the study area, accounting for approximately 20% of the total forested land—were selected as the research subject. This choice allowed for the most efficient evaluation of the method’s applicability. Moreover, due to the high resin content of
Pinus massoniana needles and the species’ status as a key target for fire prevention in this region, this typical forest stand carries clear ecological and practical management significance. Fuel parameters for daily spread rate calculations were obtained through field surveys, laboratory analyses, and literature synthesis [
23,
29]. To ensure that interannual variations in the fire probability were driven primarily by meteorological and ignition factors rather than changes in fuel characteristics—thereby establishing a stable baseline for method evaluation—these parameters were assumed to remain constant throughout the study period (
Table 2).
2.4. Grid Partitioning of Study Area
Computing forest fire occurrence probabilities requires sufficient sample sizes. Treating Guizhou Province as a single unit would yield inadequate samples while obscuring the spatial heterogeneity in the meteorological and topographic conditions, compromising the reliability of fuel moisture content and spread component calculations. To enhance the data fidelity, the study area was partitioned into subregions, with central-point meteorological and topographic values representing each unit. Aligned with Article 15 of China’s Regulations on Forest Fire Prevention, mandating county-based forest fire danger zoning, and considering Guizhou’s 176,167 km
2 area, encompassing 88 counties/districts, we established an 83-cell grid system (50 km × 50 km) for analytical efficiency and regulatory compliance. This configuration provided 83 replicates, each averaging 250,000 hectares (
Figure 1).
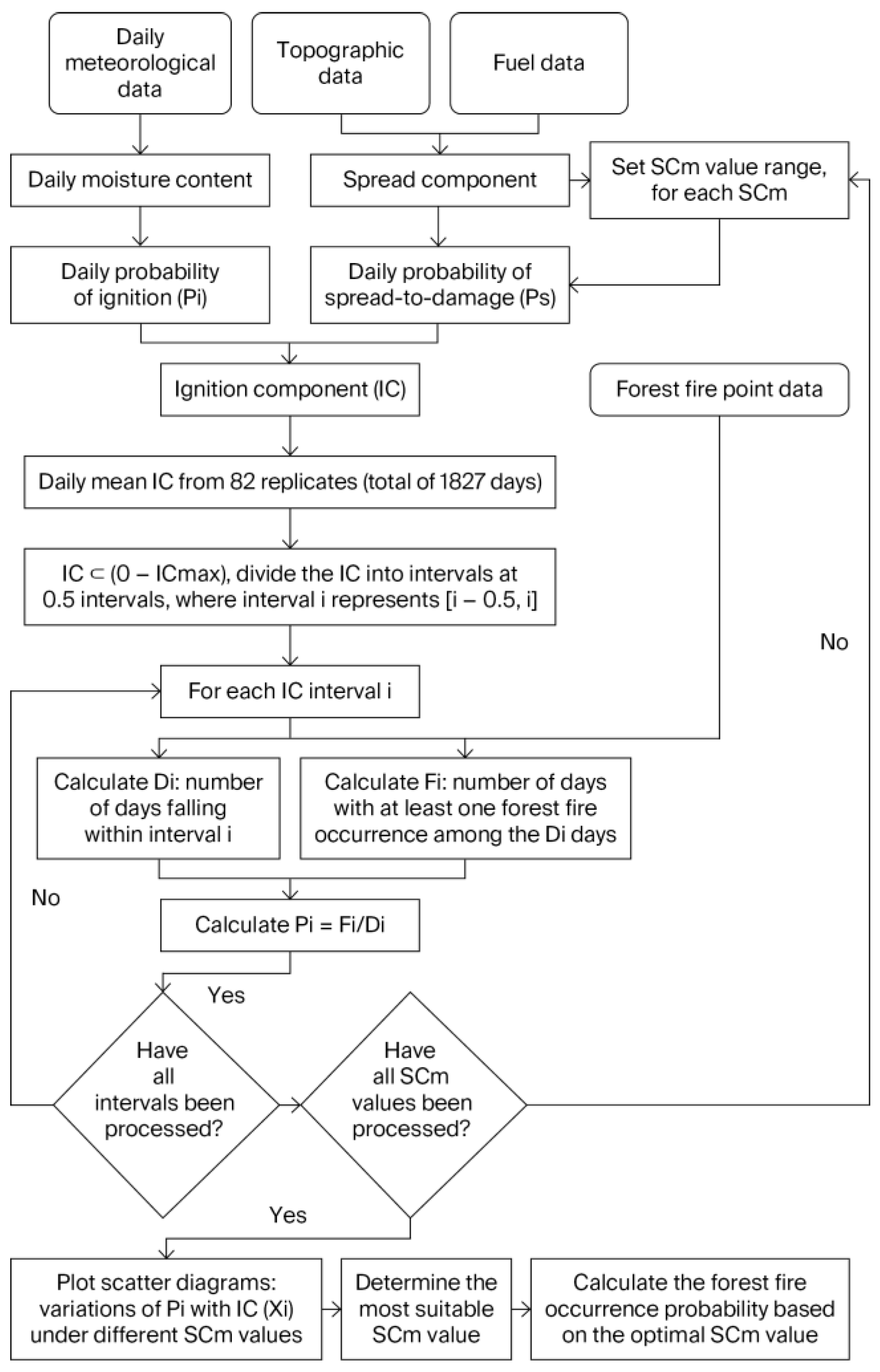
2.5. Forest Fire Occurrence Probability Calculation
For the 83 grids in the study area, the daily EMC and fuel moisture content (FMC) of each grid were calculated based on meteorological data from grid center points and Equations (3) and (4), focusing on the period of 2016–2020 (totaling 1827 days). Subsequently, the daily ignition probabilities of the fuels in each grid were determined based on the air temperature and FMC values.
Based on the rate of spread in Rothermel’s model, the daily potential rate of spread within each grid was calculated by integrating the fuel physicochemical properties from
Table 1 and daily FMC values. The resulting value was rounded and recorded as SC. Since
SCm remains constant across periods and is independent of factors such as the firebrand type [
20], determining the appropriate
SCm value for the study area requires an examination of the statistical relationship between the calculated
IC and the forest fire occurrence probability under defined
SCm values.
Based on the daily calculated SC for each grid, class intervals and step sizes were rationally defined. The probability of a fuel point igniting and subsequently spreading into a disaster was calculated for different SC thresholds (
SCm). The IC (dimensionless) was then defined as 100 times the product of the ignition probability and the spread-to-disaster probability, resulting in values ranging from 0 to 100. This study utilized 83 replicates. The mean IC value across these 83 replicates was computed for each day, yielding a total of 1827 daily IC values. The maximum IC value observed over these 1827 days was recorded as ICmax. Consequently, the range of IC values during the study period was 0 to ICmax. The IC value domain was partitioned into ICmax subintervals at intervals of 0.5. Subinterval
i is defined as [
I − 0.5,
i). For each subinterval
i, the number of days (
Di) where the IC value fell within this interval was calculated. By correlating this with the forest fire point data, the number of days within
Di on which at least one forest fire occurred (
Fi) was determined. The probability of at least one forest fire occurring when the IC belongs to subinterval [
I − 0.5,
i) is calculated as
. The midpoint of subinterval [
I − 0.5,
i) is
Xi =
i − 0.25, where
i = 0.5, 1, 1.5, …, int(ICmax) + 0.5 (where int(ICmax) represents the integer part of ICmax). Scatter plots depicting the IC against
were generated for different
SCm values. These plots were analyzed to assess the influence of
SCm on the forest fire occurrence probability. The optimal
SCm value for the study area was identified. Subsequent calculations of the forest fire occurrence probability and further analyses within this study were then conducted based on this determined
SCm value. The calculation flowchart is shown in
Figure 2.
2.6. Data Processing
2.6.1. Statistics for the Basic Situation
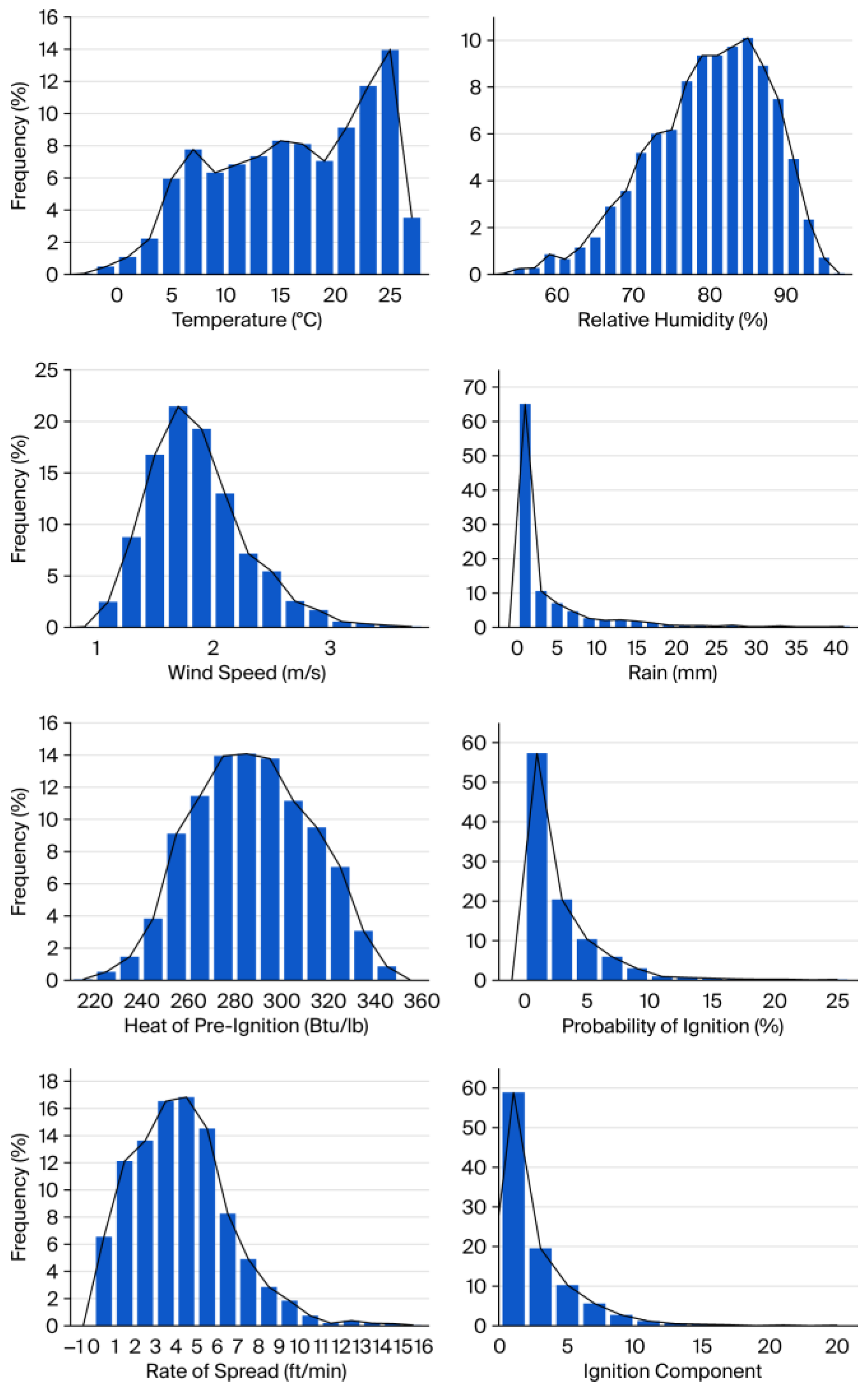
A basic overview and frequency distribution plots were generated for meteorological elements (including the air temperature, relative humidity, wind speed, and precipitation) and key variables (including Qig, the ignition probability, the potential spread rate, and the IC) within the study area during the period 2016–2020. These visualizations were analyzed to characterize their distribution patterns over this timeframe.
2.6.2. Analysis of Influencing Factors
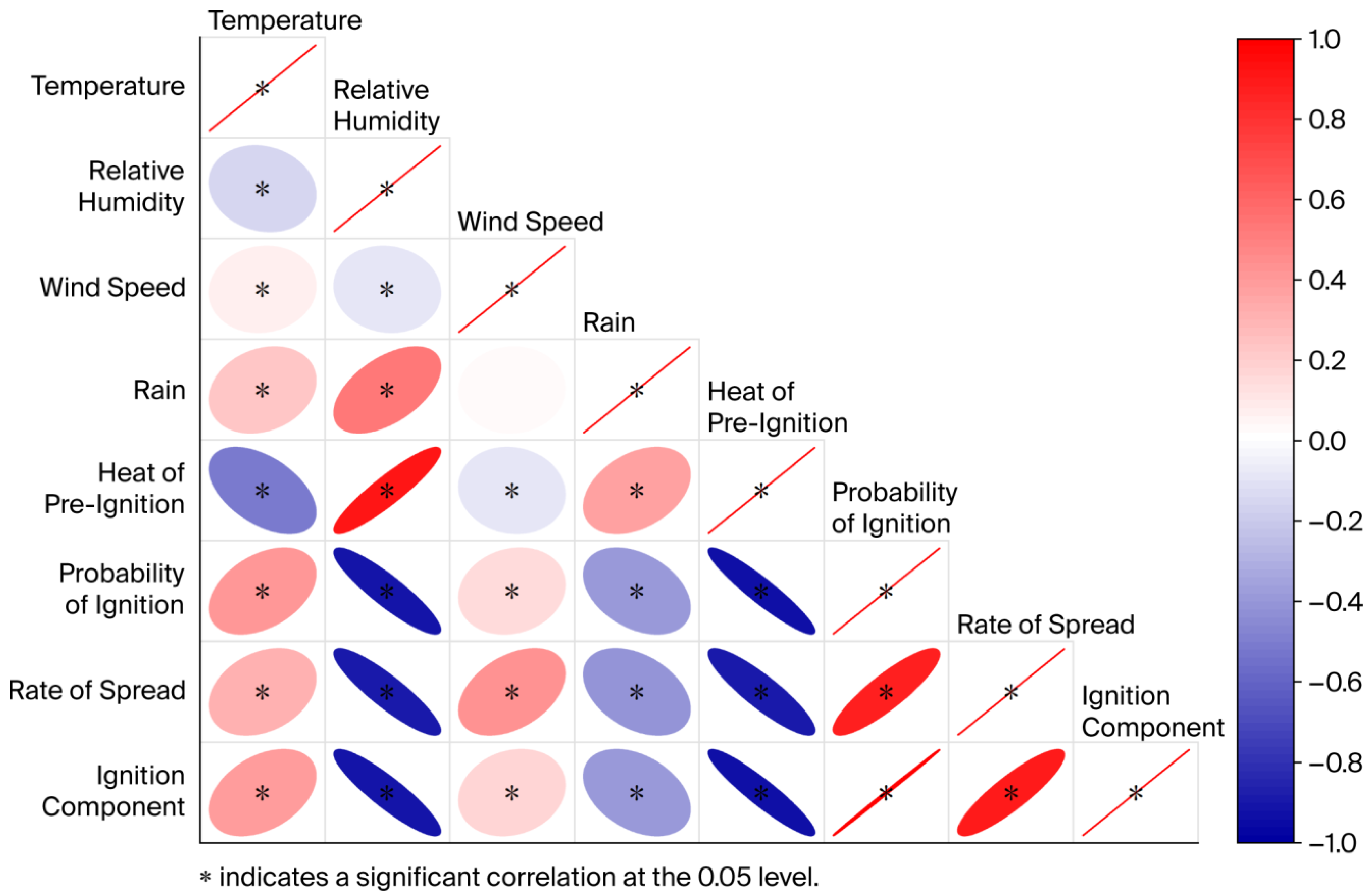
Spearman’s rank correlation analysis was employed. A correlation heatmap was generated to visualize the relationships between meteorological elements and key variables. This analysis revealed the influences of the meteorological elements on the key variables, establishing a basis for the subsequent investigation into the correlation between the IC and forest fire occurrence probability.
2.6.3. Investigation of Impact of Time Span on Forest Fire Occurrence Prediction Based on IC
(1) Correlation analysis between IC and forest fire occurrence probability across difference time spans: Considering that variations in the study duration may influence the relationship between the forest fire occurrence probability and IC, this study set the maximum research time span to five years (covering 2016–2020). We analyzed the correlation between the forest fire occurrence probability and IC across different time spans to determine whether the IC was significantly correlated with the forest fire occurrence probability within different time intervals.
(2) Development of predictive model for forest fire occurrence probability based on IC: Based on the results of the influencing factor analysis and the curve depicting the variation in the forest fire occurrence probability with the IC, an appropriate equation form was selected. Using the forest fire occurrence probability as the dependence variable and the IC as the independent variable, model fitting was conducted separately for different time spans. The mean absolute error (MAE) and mean relative error (MRE) in predicting the forest fire occurrence probability based on the IC under each time span were calculated. This study employed an n-fold cross-validation approach for equation fitting. For a dataset containing n samples, each iterative fitting procedure utilized n − 1 samples for model training and the remaining one for validation. This methodology enabled the evaluation of the prediction performance across each IC interval, thereby mitigating overfitting and ensuring the verifiability of the results. Based on preliminary experiments, the following functional form was selected for the predictive model: P = (100*IC)/(a + IC) (where P indicates the forest fire occurrence probability, IC indicates the ignition component, and a indicates the parameter to be fitted in the model).
A line chart was plotted with the time span (years) as the x-axis and the MAE and MRE as the y-axis. Difference testing was performed to analyze the impact of the time span on the prediction accuracy of the method. The optimal time span for the study was subsequently identified through joint consideration of the correlation coefficient and the magnitude of the prediction errors.
2.6.4. Development of Predictive Model for Forest Fire Occurrence Probability Based on IC
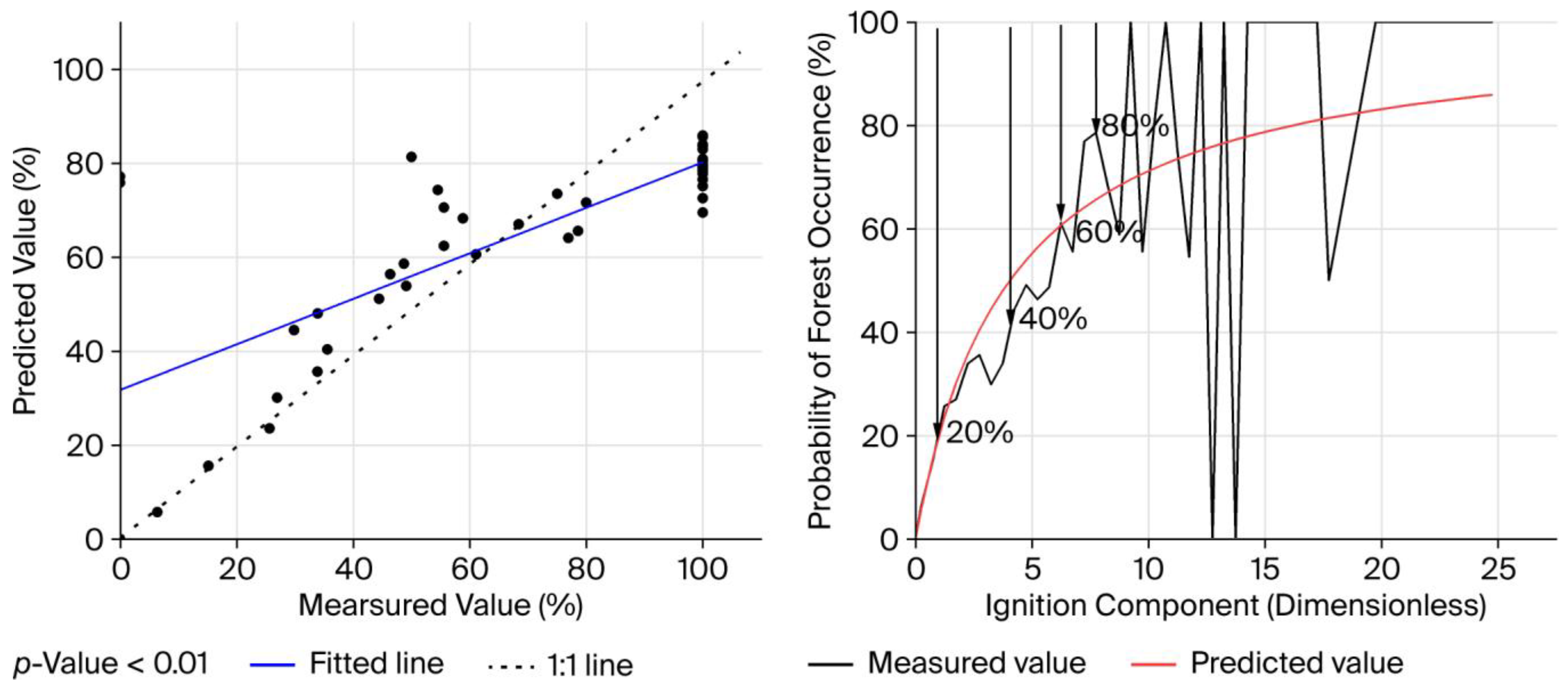
Based on the determined optimal time span, the predictive model and methodology for the forest fire occurrence probability using the IC were established. A 1:1 plot of the measured versus predicted values and a dynamic variation curve of the predictions were generated. These visualizations were used to compare and identify the specific value intervals where the predictive method tended to produce errors.
4. Discussion
4.1. Forest Fire Environmental Analysis
Research indicates that high temperatures, low humidity, and strong winds significantly reduce the moisture content in surface forest fuels [
30,
31,
32]. However, in Guizhou Province, during 2016–2020, the mean relative humidity reached 79.96%, with the minimum recorded at 53.97%. This persistently high humidity results in elevated daily moisture levels in fine surface fuels, consequently increasing the heat required for ignition. In this study, the average pre-ignition heat of fuels was 287.33 Btu/lb, with the maximum ignition probability being only 24.67%. Furthermore, on over 85% of all days, the ignition probability remained below 5%. Sun and Zhang reported an IC range of 0–100 for forest fire probability modeling in the Greater Khingan Mountains [
20]. In contrast, our study observed a maximum IC value of only 24.67, suggesting inherently unfavorable environmental conditions for forest fires in the study area when firebrands are excluded. Nevertheless, 2666 forest fires points occurred during the study period (averaging 1.46 daily occurrences), indicating a high probability of firebrands. Thus, enhancing anthropogenic firebrand management is imperative to reduce the forest fire incidence in this region.
4.2. Influence of SCm on Fire Occurrence Probability
This study demonstrates that SCm exerts no significant effect on the variation in the forest fire occurrence probability with the IC, aligning with the findings of Sun and Zhang [
20]. This phenomenon may be attributed to the characteristics of the fire environment in the study area. As detailed in
Section 4.1, the probability of successful fuel ignition remained low during the study period. Once a firebrand occurs, it invariably indicates extreme environmental conditions (e.g., critical weather and fuel moisture levels). Under such thresholds, any potential rate of spread invariably results in sustained fire propagation and consequential damage [
33]. Consequently, the SCm values do not significantly alter the relationship between the IC and fire occurrence probability.
4.3. Impact of IC on Forest Fire Occurrence Probability
Regardless of the study period (timespan), the IC remained highly significantly correlated with the forest fire occurrence probability, confirming the feasibility of using the IC to predict the forest fire occurrence probability in the study area. This also reveals the influence mechanism of the fuel–meteorology system on the forest fire occurrence probability. As shown in
Figure 4, when the IC exceeds a certain threshold, the forest fire occurrence probability exhibits significant fluctuations, with instances of zero probability frequently observed. The primary reason for this is that, once the IC surpasses this critical value, the theoretical fire occurrence probability should be 100%. However, since forest fire risk forecasting in the study area primarily relies on meteorological elements (the IC itself incorporates meteorological factors), exceeding this threshold generally indicates an extremely high fire risk, which, in practice, triggers strict human intervention and governmental fire prevention measures. These stringent management actions effectively reduce the probability of human-caused ignitions. As a result, although the actual fire environment (fuel and meteorological conditions) becomes highly hazardous, the observed fire occurrence probability does not continue to increase with the rising IC [
34,
35]. Instead, it decreases or remains at zero, displaying notable fluctuations.
Sun and Zhang reported a fire occurrence probability of zero when the IC fell below a specific threshold [
20], whereas the present study demonstrates that forest fires can occur even at IC values below 0.5. This discrepancy primarily stems from differences in regional characteristics. The study area considered by Sun and Zhang was located at a high latitude and is typically covered by snow during early spring and late autumn, when the IC values are low, thereby inhibiting fire ignition. In contrast, the present study area consists of evergreen forest regions, where conditions that are conducive to fire occurrence persist even under low IC values [
36].
4.4. Influence of Study Time Span on Forest Fire Occurrence Prediction Based on IC
As the time span increased, the correlation between the IC and forest fire occurrence probability, while not showing statistically significant differences across individual time spans, exhibited a discernible downward trend overall. When predicting the forest fire occurrence probability based on the IC, the 5-year time span yielded significantly lower prediction errors compared to other time spans, with the errors also generally decreasing over extended time spans. This pattern can be attributed to the inherent regularity of forest fire occurrence in specific regions [
37,
38], combined with the relative stability of key socioeconomic factors—such as the economic development level and lifestyle patterns—during the relatively short 5-year period selected in this study [
39,
40,
41,
42]. Therefore, expanding the studied time span helps to more accurately capture the true relationship between the forest fire occurrence probability and IC in the region, thereby reducing the prediction errors. However, it is reasonable to anticipate that, if the studied time span extends beyond the period during which these key factors remain stable—for instance, by encompassing phases of marked socioeconomic transition—more pronounced variations in both the correlation coefficients and prediction errors are likely to occur [
43].
4.5. IC-Based Forest Fire Probability Research and Fire Management
This study confirms the feasibility of directly utilizing the IC from the NFDRS for forest fire probability prediction. Based on the nonlinear relationship observed between the IC and fire probability, the Michaelis–Menten equation was selected for model fitting. The resulting prediction model, in which P = (100*IC)/(4.06 + IC), led to an MAE of 11.27% and an MRE of 14.75%, with the primary source of errors occurring under extremely high ICs. This can be attributed to the direct application of the NFDRS calculation method, combined with the limitation of considering only a single fuel type. According to the Michaelis–Menten equation, when the IC equals the model coefficient of 4.06, the forest fire occurrence probability in the study area reaches 50%, representing a critical threshold for probability variation. Consequently, daily fire management operations can incorporate IC calculations derived from this methodology for fire probability assessment and risk rating forecasting. Of particular significance, elevated IC values indicate that the fuel–meteorology environment has reached critical ignition thresholds. Under such conditions, comprehensive reinforcement of firebrand control is imperative, as any firebrand event will likely trigger rapid fire propagation. Region-specific measures should prioritize enhanced anthropogenic firebrand management (e.g., agricultural fire permits, recreation activity restrictions) and science outreach programs to increase public awareness of fire prevention protocols.
4.6. Limitations and Future Practical Applications
This study directly employed the NFDRS models to calculate the probability of ignition and the subsequent probability of fire spread. However, potential discrepancies in the ecological characteristics and fuel properties within the study area may limit the model’s applicability. Consequently, future research should incorporate ignition and fire behavior experiments on regionally typical fuel types to develop localized predictive models, which is crucial to enhance the forecasting accuracy. Furthermore, the exclusive focus on Pinus massoniana constrains the spatial transferability of the model. The Karst landscape of the studied region supports diverse vegetation types—such as evergreen broadleaf forests—besides Masson pine stands. Variations in the physicochemical properties of these fuels mean that treating the entire study area as consisting of homogeneous Masson pine coverage may result in prediction biases in non-pine areas. Additionally, over the five-year study period, factors such as the stand structure and fuel load were subject to change, thereby influencing the fire risk. The assumption of constant fuel properties over five years could have obscured or misrepresented seasonal peaks in fire risks, indicating spatiotemporal limitations. Future work will integrate multitemporal remote sensing data to differentiate major vegetation types and monitor their phenological dynamics, thereby advancing the current static, single-fuel model towards a spatiotemporally dynamic multifuel framework.
Therefore, prior to practical application, the localized calibration of the NFDRS models specific to the study region is necessary to further enhance the prediction accuracy. Specifically, the following steps are recommended for future model improvement. First, the systematic collection of typical fuel samples from the study area should be conducted to obtain key combustion parameters through laboratory measurements of physicochemical properties, ignition probability experiments, and fire behavior simulations. Coupled with long-term field monitoring of the fuel moisture content, these data will support the development of a high-accuracy fuel moisture prediction model. Second, multitemporal remote sensing imagery (e.g., Sentinel-2) should be integrated to precisely identify the dominant vegetation types and capture their phenological dynamics, thereby enabling the construction of a spatiotemporally resolved, multicategory fuel model. Subsequently, operational trial runs could be carried out in representative areas, with fire incident records and field observation data collected during these trials for model feedback and iterative refinement. It is anticipated that, through these systematic model enhancements and validation efforts, a mature IC index-based fire risk probability assessment framework can be established. The successful experience gained may also serve as a valuable reference for other regions, underscoring the practical significance and application potential of this research.
5. Conclusions
It is concluded that the daily forest fire occurrence probability in the study area can be expressed as a nonlinear function of the IC; this validates the applicability of the methodology established in this study—integrating the IC indicator, which comprehensively reflects the fuel–meteorology complex—for the assessment of the fire occurrence probability. As the research time span increases, the prediction error in the forest fire occurrence probability based on the IC indicator exhibits a decreasing trend. When predicting the daily fire occurrence probability using a 5-year research period, the model demonstrates an MAE of 11.27% and an MRE of 14.75%. Therefore, fire occurrence probability estimation, fire risk rating forecasting, and corresponding fire prevention preparations in the study area can be effectively informed by the IC values.
This study preliminarily validated the feasibility of using the IC index—which comprehensively reflects the combined characteristics of meteorology and fuels—to assess the forest fire risk probability. Although the current work establishes only a foundational framework, it provides an algorithmic basis for the development of more accurate and refined operational forest fire probability forecasting systems. By effectively addressing the limitations of existing fire risk assessments that rely solely on meteorological factors, the proposed approach demonstrates promising application potential.