Abstract
Fire accidents have been reported frequently in Chinese townships over the past few years, where people’s lives and properties have been subjected to huge losses. As a result, a considerable number of traditional villages have disappeared. In this study, field surveys and on-site monitoring were used to study the village of Gao Tuan, while seven scenarios were set up in Pyrosim for simulation and analysis. As indicated by the results of this study, the hidden dangers of Dong traditional settlements in the western Hunan region were identified in terms of the construction materials, street width, and fire use. The Pyrosim simulation analysis results were as follows: scenarios 1/2 show that by utilizing the topography and layout, the wind speed was reduced layer by layer, which reduced the fire spreading disaster by nearly half; scenarios 3/4/5/6 show that, except for the 1000 mm wide street, the degree of fire spreading was negatively correlated with the width of the street, and the fire could no longer be spread to the other side of the street when it was 8000 mm; and scenario 7 shows that, in the case of a fire in a residential house, it is safer to evacuate the people in the building in a unit within 320 s. Based on the survey and Pyrosim simulation results of fire spreading, the strengths and weaknesses of Gaotuan Village in the face of fire events were analyzed, and targeted recommendations are made based on the study for the Dong traditional settlement in the western Hunan region for fire prevention.
1. Introduction
Fire endows mankind with light and hope while also having brought disaster to mankind. Since ancient times, fire has affected the development of architecture, and buildings must prevent fire, while the use of fire should be considered [,,,]. Over the years, fires have occurred in traditional buildings and historic districts around the world, causing irreparable damage to architectural history and culture [,,,,]. Fire prevention has been confirmed as a point of great concern for traditional Chinese buildings, where wood is the main building material []. The ancient people formed a unique fire prevention strategy for wooden buildings in their long productive life []. The rich experience of fire prevention from the existing villages and dwellings can be summarized and applied to the fire prevention strategy of buildings in the new era, while the limitations of fire prevention should be analyzed and improved. The previous fire data suggest that thousands of village fires occurred in China between 1997 and 2017, where people’s lives and properties have been subjected to great loss; numerous traditional villages have disappeared [,]. Accordingly, the vast rural areas and the considerable traditional villages still require targeted fire prevention strategies, and many scholars have been committed to investigating fire risk and fire prevention strategies for ancient buildings [].
Through a review of the existing literature, the academic research presented on ancient building fires was found to fall into research on risk assessment and assessment frameworks [,,,,,,,], and research on fire prevention strategies and mitigation strategies [,,,,,]. For research on risk assessment and risk assessment frameworks, Salazar et al. [] reviewed existing indicator-based fire risk assessment methods and proposed 22 vulnerability indicators, which were classified into four categories that can be adopted to develop fire risk assessment methods specifically for cultural heritage buildings. Yuan et al. [] investigated brick and wood buildings that comprise heritage villages to investigate village fire hazards and provide an assessment of fire safety. Using the analytical hierarchy method, Ibrahim et al. [] examined the criteria and attributes for assessing fire risk in buildings. Wu et al. [] constructed a system of indicators for the sensitivity of heritage value, village fire danger, and evacuation accessibility using Chengkan Village as an example given the complexity and openness of the heritage village system. For research on fire prevention strategies and mitigation strategies, Marrion [] studied hazard-associated information and adopted a detailed, risk-free approach to more effectively address the abovementioned fire-associated hazards and protect the cultural heritage. Zhang et al. [] analyzed the fire risk and strategies for continuous wood-frame dwellings of ethnic minorities in the western Hunan region based on field mapping data and CFD simulations. Zhou et al. [] conducted a fire hazard survey of the Tianjin tenement and developed the corresponding control and mitigation methods that take on great significance in guiding the development of policies and procedures to incorporate fire prevention and protection features into the abovementioned buildings. Bertetto et al.’s [] CFD-based computer fire simulation model determined the spread of fire and smoke from the roof of Notre Dame de Paris to the roof structure, carefully evaluating the evolution of the residual strength ratio and compressive strength of the injured structure. In addition, some scholars tested the fire resistance of timber, wooden windows, and wooden doors, as well as columns, beams, and other components of ancient buildings [,,,]. Most research on fire protection in ancient buildings has been committed to risk assessment, and mitigation strategies have been proposed for existing ancient buildings through a combination of field surveys and subjective analyses, whereas quantitative analyses and simulations of multi-level fire protection between buildings and clusters have rarely been conducted. Coupled with the rapid urbanization and socio-economic development in China, this has brought development opportunities, as well as challenges to rural areas. Due to the excessive speed of development, remote mountainous areas have been notably affected by modern civilization such that their traditional villages have been hollowed out and their fire protection systems have collapsed [,,,].
This study was conducted in China’s western Hunan region, i.e., one of the crucial gathering places of traditional villages in China with colorful ethnic architecture and regional characteristics [,]. The abovementioned traditional villages fully demonstrate the typical characteristics of Hunan villages in terms of village site selection, street layout, and dwelling types [,]. Thus, this study took Gaotuan Village, a typical Dong village in the western Hunan region, as the sample, and used Pyrosim fire simulation software to study the fire prevention strategies of Dong traditional villages in the western Hunan region from three levels (i.e., village, street, and building) to provide a relatively comprehensive and scientific quantitative analysis of the Dong traditional villages in western Hunan. On this basis, the strengths and weaknesses of the Dong traditional villages for fire prevention were analyzed, reasonable aspects of fire prevention were proposed, and targeted fire prevention suggestions were proposed following a practical scenario.
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Area
The Western Hunan region investigated in this study is the western region of Hunan province in the cultural sense, i.e., the collective name of the northwestern and southwestern Hunan Province, which comprises the Xiangxi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture, Zhangjiajie City, Huaihua City, Yongzhou City, and part of Shaoyang City where minority groups live, but not the Xiangxi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture in the administrative division. Tongdao Dong Autonomous County, which is at the southern end of Huaihua City, Hunan Province, is located in the transition zone of the South Ridge Mountains of the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau, which is the junction area of Xiang and Guizhou provinces. Gaotuan Village (Figure 1) has been developed for more than a thousand years since its ancestors came here in the early years of the Northern Song Dynasty to set up a fortress and settle down. Since then, Gaotuan Village has grown from a dozen families at the beginning to more than 160 families and 700 people, mainly of Dong ethnicity. Gaotuan Village has preserved the original architectural features of the Dong people, as well as the ethnic culture, and it was listed in the fourth batch of Chinese traditional villages in November 2016.
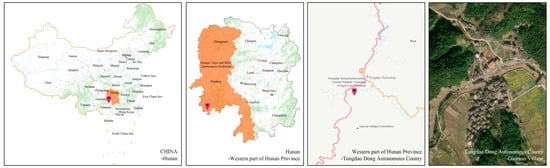
Figure 1.
Study area.
2.2. Sample Village Case Studies
2.2.1. Analysis of Sample Villages
- 1.
- Village Layout
Gaotuan Village is surrounded by mountains on three sides, and the Pingtan River crosses the village from west to east, with the Wayao Mountain in the northeast acting as the highest point and the farmland on both sides of the Pingtan River serving as the lowest point. To be specific, Gaotuan Village refers to a typical traditional village of the foothills-and-river-valley type. The two mountains in the northeast and northwest of Gaotuan Village are capable of effectively resisting the cold north wind in winter and welcoming the warm and humid southeast monsoon in spring and summer such that a good local climate microenvironment is formed, which is fully indicated in the ancient wisdom of “the unity of heaven and man” in buildings. The layout of the village not only provides the inhabitants of the village with shelter from the terrain but also a supply of water and other basic needs for survival. Furthermore, under the effect of the above-described layout, an improved local climate is formed, the wind speed is reduced, and the north wind is resisted such that the risk of spreading in case of a fire can be lowered.
Gaotuan Village expanded from a single village to a “main village–secondary village” layout pattern. To be specific, the central village on the south side of the Pingtan River serves as the main village, and the Shuangyinshan group and Wayao Mountain group on the north side of the Pingtan River act as secondary villages. Regarding the village group, Gaotuan Village falls into three first-class fire protection groups (i.e., A, B, and C). There are relatively spacious rivers and roads between each group such that a natural fireproof isolation zone is formed. Among them, group A serves as the most primitive group, and the residential houses in its group were first formed in the Ming Dynasty, and the group was formed in the late Qing Dynasty. Furthermore, groups B and C were mostly built in the late Qing Dynasty and the Republic of China, and thus, the building density of group A is notably higher than that of groups B and C. Based on the division of the A, B, and C primary fire protection groups, the three primary fire protection groups fell into 11, 5, and 6 secondary fire protection zones according to the width of the streets, the density of dwellings, and the construction time (Figure 2).
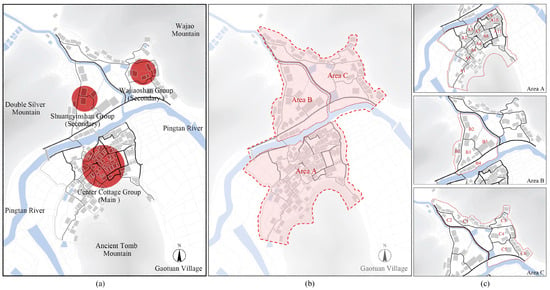
Figure 2.
(a) The surrounding environment of Gaotuan Village and the location of the three groups; (b) the zoning of the primary firefighting group; (c) the zoning of the secondary firefighting group.
- 2.
- Street Layout
The layout of the streets and alleys in Gaotuan Village is correlated with following the terrain while displaying a zigzag and free layout. Following the width and function of the streets, they can be categorized into alleys, minor streets, major streets, and village arterial roads to satisfy the needs of modern vehicular traffic and firefighting. The four intertwine to divide the village into individual neighborhoods of varying sizes. Except for the village arterial roads, which are concrete, the streets and alleys have generally been paved since the Ming and Qing dynasties, with slabs of green stone as the main material, some of which have been repaired with cement after damage. The narrow and winding streets and alleys, with a width-to-height ratio (D/H) mostly less than 1, contribute to land saving for the relatively tight land use in the foothills and valleys, while the narrow streets and alleys can lead to improved village security. However, narrow streets and alleys tend to have small residential spacing and high building density, which are not conducive to fire prevention.
- 3.
- Architectural Form
The traditional dwelling in Gaotuan Village has been reported as a typical dry apartment style, mostly comprising three floors. To be specific, the bottom floor is elevated and employed for stacking firewood and miscellaneous items. Moreover, the third floor is primarily used for stacking miscellaneous items, even without walls surrounding it, and the structure is exposed. Moreover, the second floor serves as the major functional space of the dwelling, and the main rooms (e.g., bedroom and kitchen) are on the second floor. The arrangement of the lower elevated floor can facilitate moisture and insects and snakes, while the upper unused floor is arranged to prevent sunlight and heat insulation. In general, the main entrance of the residence is located on the side of the building, with an external staircase leading directly to the second floor. After entering the second floor, there is a gray space set out as a “T”-shaped corridor. This “T”-shaped corridor has a long corridor on one side, which is completely open to the outside, while the other side is recessed to the inside, which is equivalent to a living room, and is responsible for activities (e.g., resting, chatting, receiving guests, and family work). The fire pits are arranged on the second floor, which has a wooden floor, and are made of larger stones for fire prevention. Furthermore, besides the dwelling houses, Dong people have public buildings (e.g., drum tower, wind and rain bridge, village gate, pavilion, theater stage, and a sa-yeon altar).
2.2.2. Fire House Risk Assessment
- 1.
- Building Materials
“The history of Chinese architecture is written in wood.” This shows the importance of wood in traditional Chinese architecture. As a typical Dong traditional village, the building material of Gaotuan Village is primarily wood, except for the roofs, pillar bases, and other components (Figure 3). The good performance of wood has also enabled the preservation of the buildings in Gaotuan Village to this day. The freshly cut wood used as building materials has a moisture content of more than 50%, but after a period of natural drying, its moisture content will drop to less than 20%, becoming “air-dried wood”, while the wood used in the houses of Gaotuan Village has been weathered and dried for hundreds of years, and its moisture content is notably lower than that of “air-dried wood” and is considered to be “fully dried wood” []. The “air-dried wood” and “full-dry wood” are very easy to burn since the wood exhibits a low water content.

Figure 3.
Typical wooden buildings of the Dong ethnic group.
- 2.
- Daily and Ceremonial Fire Behavior
Fire has been an inseparable part of daily life since ancient times. In ancient Chinese production life, fire was indispensable from worshipping the gods down to daily cooking. For ethnic minorities in the western Hunan region, fire pits are the core space of their dwellings, which are responsible for the survival activities of daily life, the social activities of family gatherings and friendships, and the worship of gods and ancestors. In addition, the local people use wood as fuel for fire pits to keep warm and cook food, and the fire pits are always kept burning to show their respect for fire and the gods. Accordingly, local people usually store considerable amounts of firewood in the storage room or the corner of the house for backup. Through fieldwork, we found that the demand for fire is very high (Figure 4), and thus, the frequent use of fire and flammable construction materials lead to a large fire hazard in the traditional villages of the Dong people in the western Hunan region.

Figure 4.
Typical fire behavior of the Dong people.
2.3. Monitors
2.3.1. Village Wind Speed
To monitor the practical wind speed to simulate the spread of fire between houses in Gaotuan Village, we conducted a 1-week field survey in January 2022 in Gaotuan Village. To avoid the influence of the external environment on the local wind speed, we fixed the handheld automatic detector Testo 425 around the village and the open area inside the village to obtain the practical wind speed in Gaotuan Village, and the specific placement locations are shown in Figure 5.
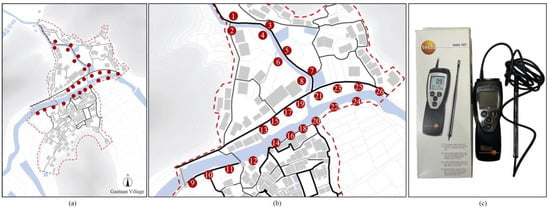
Figure 5.
(a) Location of village wind speed monitoring points; (b) monitoring point numbers; (c) monitoring instrument.
2.3.2. Street Wind Speed
Under an identical external wind speed environment, streets of different widths have a certain influence on the local wind speed of the streets. Gaotuan Village, like other traditional Dong settlements in the western Hunan region, relies on the topography of the terrain to lay out its dwellings, and thus, its streets and alleys also mostly follow the natural topography, forming a pattern of winding and interlocking roads. According to the width of the streets and alleys, we divided them into four levels (i.e., alleys, secondary streets, main streets, and rural arteries). The practical wind speed in identical external environments can be different when the wind enters different streets because of the different widths of the streets to guide the wind. We used a Testo 425 anemometer to monitor the wind speed at two locations in the alleys, secondary streets, main streets, and rural arteries of Gaotuan Village (Figure 6).
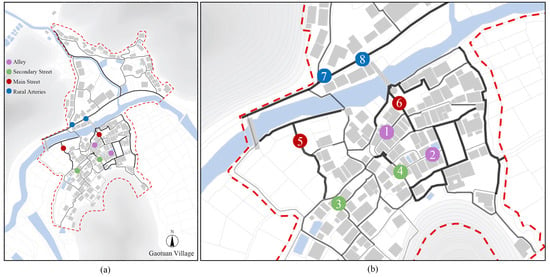
Figure 6.
(a) The location of street wind speed monitoring points; (b) monitoring point numbers.
2.3.3. Building Wind Speed
We selected a typical residential house in Gaotuan Village to monitor its wind speed. Because it is impossible to define indoor and outdoor in the Pyrosim simulation software, a total of eight Testo 425 anemometers were fixed on the outdoor walls of the first and second floors of the selected typical house to monitor the local wind speed.
2.4. Simulation
To ensure the accuracy of the simulation, the common parameters required at the village, street, and building levels were unified following the field mapping data from the field survey and the monitoring data from the nearest meteorological measurement points. The average annual temperature of Gaotuan Village reaches 18 °C, and the wind direction is mostly northerly and southerly. During the field survey, the wind direction of Gaotuan Village was northerly, and the average wind speed of meteorological monitoring points reached 2.17 m/s. At the building level, the local houses were mostly made of wooden boards as the main building material, the roof was made of small green tiles, the ignition temperature of the wooden boards was set at 260 °C, the exothermic rate was 160 kW/m2, and the tile roof was set as a non-combustible material.
2.4.1. Village Fire Simulation
- 1.
- Simulation Model
Based on the field survey field mapping data, a village model of Gaotuan Village was created in SketchUp, and the created SketchUp village model was substituted into Pyrosim in DXF format to build a village fire simulation model. The measured average wind speed and the average wind speed of the nearest meteorological measurement point were defined as scenario 2 and scenario 1, respectively, to simulate the fire in Gaotuan Village by setting the appropriate parameters in Pyrosim.
- 2.
- Grid Settings
Under the effect of the special nature of Pyrosim simulation software, the simulation grid should be set, and the setting of the grid size significantly affected the accuracy and efficiency of the simulation. For the setting of the grid cell size, the empirical value of the grid size and the ratio of the characteristic flame diameter in the Pyrosim software user manual were set to 0.25 m × 0.25 m × 0.25 m, and the ratio was 0.126, which is consistent with the more appropriate value range. The empirical value of the grid size relationship is expressed as Equation (1), and the characteristic flame diameter relationship is expressed as Equation (2):
where x, y, and z are the dimensions of the x, y, and z axes of the cell grid, respectively;
where is the heat release rate of the fire source; is the air density, taking 1.2 kg/m3; is the specific heat capacity of air, taking 1 kJ/(kg-K); is the ambient air temperature, taking 293.15 K; and g is the acceleration of gravity, taking 9.8 m/s2.
The core area of the most typical central cottage group in Gaotuan Village was selected, and the volume size of the grid area was obtained as 12.5 m × 12.5 m × 2 m through the simulation, totaling 312.5 m3, such that a total of 20,000 grids existed in the village fire simulation of Gaotuan Village.
- 3.
- Parameter Settings
Based on the investigation of the wind speed and direction in Gaotuan Village over the past year, the fire source was set at the windward entrance on the north side, which was upwind and was the place with the highest wind speed in the central cottage group. The abovementioned setting conformed to the most unfavorable principle of fire scenario determination, i.e., selecting the place with the maximum probability of fire occurrence and most likely to cause damage, from which the fire started to spread. Following the technical standards of the building smoke management system, the heat release rate of the fire source reached 6 MW, and the initial fire area size was set to 0.1 m × 0.1 m. The t2 fire growth model was used as the fire source type, and the fire growth type was rapid based on the type and location of combustible materials. Moreover, the fire development coefficient was set to 0.0469 kW/s2. Table 1 lists the specific external parameters of the combustion simulation. Furthermore, the ambient temperature was set to 18 °C, and the relative humidity was set to 40%. Furthermore, the average value of the practical wind speed examined in the village of Gaotuan Village and the wind speed of the meteorological monitoring points in Dong Autonomous County of the channel simultaneously served as the Pyrosim simulated wind speed with a simulation duration of 3600 s. Table 2 briefly lists the surface materials of the objects in the model and their thermal properties.

Table 1.
Village combustion simulation parameter settings.

Table 2.
Building surface material and thermal properties.
2.4.2. Street Fire Simulation
- 1.
- Simulation Model
The most typical street in Gaotuan Village was selected as the base sample, with a simulated street length of nearly 65 m and an area of 2600 m2. To avoid the maximum interference of the street house layout on the fire simulation results, the street widths of the selected typical street areas were set to 1000 mm/2000 mm/4000 mm/8000 mm in the Pyrosim simulation software and defined as scenario 3, scenario 4, scenario 5, and scenario 6, respectively. Furthermore, the fire simulation was conducted under the examined wind speed in the village.
- 2.
- Grid Settings
Following Equations (1) and (2) in Section 2.4.1, the grid cell size of scenarios 3/4/5/6 was set to 1.0 m × 1.0 m × 1.0 m, and the volume size of the grid area for the street simulation was determined to be 65 m × 78 m × 9 m, total 45,630 m3, with 45,630 grids in total.
- 3.
- Parameter Settings
The fire source size was set to 1.0 m × 1.0 m, and the fire simulation duration was set to 3600 s. The other parameter settings were identical to those of the village fire simulation in Section 2.4.1, and the specific parameters of each scene were set (Table 3).

Table 3.
Street combustion simulation parameter settings.
2.4.3. Building Fire Simulation
- 1.
- Simulation Model
The most typical residential house in Gaotuan Village was selected as the research sample, and a fire simulation was conducted in Pyrosim simulation software and defined as scenario 7. Due to the existence of wind pressure in the room, the sparks in the fire pit could easily flutter with the wind; according to the principle of examining the situation most prone to disasters, the location of the fire source was set up in the sofa armrests in the fire pit room on the second floor. Moreover, the measurement points were set in the respective room of the second-floor living space, for a total of six measurement points that were 1.4 m above ground level (Figure 7).
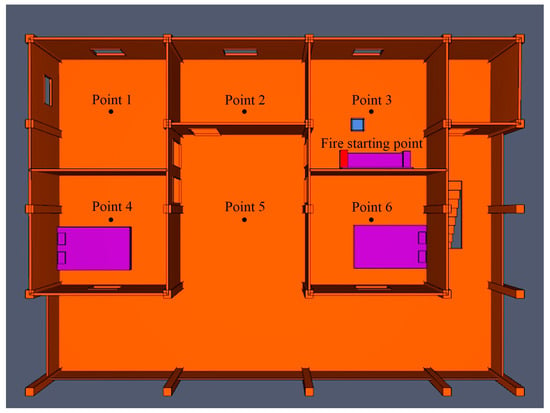
Figure 7.
Simulated measurement point location.
- 2.
- Grid Settings
Based on Equations (1) and (2) in Section 2.4.1, the grid cell size of the building monolith was set to 1.0 m × 1.0 m × 1.0 m, and the volume size of the grid area of the building monolith simulation was calculated as 20 m × 17 m × 13 m, a total of 35,360 m3, with a total of 35,360 grids.
- 3.
- Parameter Settings
The fire source size was set to 0.20 m × 0.50 m, the fire simulation duration was set to 960 s, and the specific parameter settings were set for the scenario (Table 4). The other parameter settings were identical to those for the village fire simulation in Section 2.4.1, and Table 5 lists the properties of the respective material in the specific building monolith model. When combustion occurred, the specific composition of the combustion products was ignored, as well as the by-products of combustion that do not undergo other chemical reactions.

Table 4.
Building combustion simulation parameter settings.

Table 5.
Properties of each material within the building monolith model.
The fixed fire load density of the building monolithic model was calculated [] using Equation (3):
where q is the fire load density in the burning space (MJ/m2), M is the mass of a single combustible in the room on fire (kg), is the effective calorific value of a single combustible (MJ/kg), and is the area of the ground in the room on fire (m2).
The final calculation result was 410 MJ/m2. As the model was simplified in the calculation, the combustible materials were mainly spongy sofas and a wooden enclosure, which were different from other combustible materials piled up in the actual residential house, and there was a certain limitation on the accuracy of the model.
Boom ignition occurs after the initial stage of the fire. It is an extremely dangerous phenomenon where the indoor fire from the slow-burning localized fire transitions to the rapid burning of the fire. After the completion of the transition, all combustible surfaces in the room began to burn []. To determine whether a booming fire occurs in a building can be judged by calculating the critical heat release rate of the room at the point of ignition according to the Thomas model, which is expressed as Equation (4). It was calculated that the residential house would not be bombarded with combustion.
where is the minimum heat release rate (kW), the area of the opening (m2), is the difference between the area inside the room and the area of the opening (m2), and is the height of the opening (m).
3. Results
3.1. Measurement Results
3.1.1. Village Measurement Results
The village of Gaotuan fell into 22 secondary fire protection zones following its natural topography and the texture of the village roads. Moreover, the fire partition area of the respective secondary fire partition was examined and then analyzed (Figure 8), where the minimum area was 195 m2 and the maximum area was 2918 m2. To be specific, less than 1000 m2 and less than 2000 m2 accounted for 22.7% and 77.3% of the total number of clusters, respectively. The area of each of its secondary partitions was less than 3000 m2, which is consistent with the fire prevention and control needs of ancient towns and villages that should be satisfied by building groups with lower fire resistance ratings in China’s current practice. The group buildings were divided into main streets, secondary streets, and alleys, avoiding the continuity of large areas of buildings so that the spread of fire can be significantly reduced.
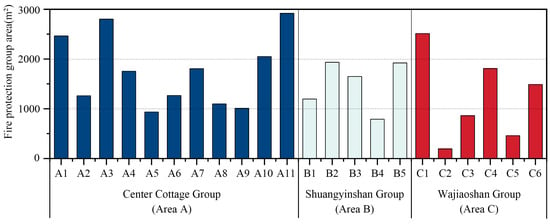
Figure 8.
Areas of secondary fire protection groups in Gaotuan Village.
3.1.2. Street Measurement Results
Following the summary of the mapping data, the main streets of Gaotuan Village fell into four levels (i.e., alleys, secondary streets, main streets, and rural arteries), whose corresponding street widths were 0.0–1.5 m, 1.5–3.0 m, 3.0–6.0 m, and 6.0–9.0 m. Under the effect of certain differences in building heights on both sides, the corresponding width-to-height ratios of its four types of streets were determined to be 0.00–0.20, 0.20–0.40, 0.40–0.70, and 0.70–1.0. Gaotuan Village is located in a valley and river bank, the terrain is relatively flat, and its dwellings are lined up along the contour of the mountain on the south side such that its streets and alleys displayed a more significant difference between the relatively flat place and the mountain out. The classification of its streets and alleys suggested that alleys, secondary streets, main streets, and rural arteries accounted for nearly 23.8%, 37.7%, 21.3%, and 17.2% of the entire village roads, respectively. The existence of relatively considerable streets with width-to-height ratios below 0.5 in Gaotuan Village showed a close correlation with the natural geographic environment of Gaotuan Village. Furthermore, following the fire spacing requirements of Chinese wooden buildings, most of the streets and alleys in Gaotuan Village do not conform to the current fire codes in force.
3.1.3. Building Measurement Results
Figure 9 presents a typical dwelling in Gaotuan Village. The basic plan of the Dong traditional dwelling in Gaotuan Village had three openings, mostly with three floors. The second floor served as the main living space, and the staircase went up to a “T”-shaped corridor, acting as the area for receiving guests, communicating, resting, and working. The hall was behind the “T”-shaped corridor, where the statue of the deity was placed for the residents to worship while serving as the ritual center of the house. A storage room was at the back of the hall. The fire pit room was adjacent to the hall, i.e., the center of family activities in the building. The bedrooms were on the left and right of the hall. Furthermore, the residential structure of Gaotuan Village mostly comprised five columns and eight melons.
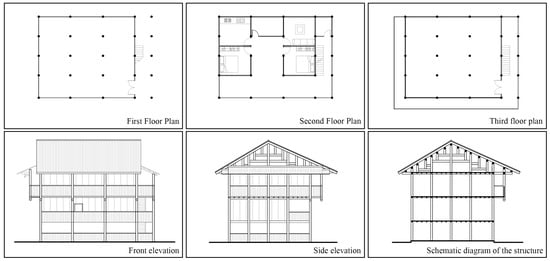
Figure 9.
Typical house in Gaotuan Village.
3.2. Monitoring Results
3.2.1. Village Wind Speed
Figure 10 presents the monitoring results of the village wind speed. Moreover, the data of the meteorological station nearest to Gaotuan Village at the same time were extracted and then compared. The maximum wind speed, minimum wind speed, and average wind speed of the respective village monitoring point in Gaotuan Village reached 2.68 m/s, 0.17 m/s, and 1.14 m/s, respectively, whereas the maximum wind speed, minimum wind speed, and average wind speed of the meteorological station data in the Tongdao county reached 3.44 m/s, 1.24 m/s, and 2.17 m/s, respectively. The maximum, minimum, and average wind speeds in Gaotuan Village were lower than the respective wind speeds at the nearest meteorological measurement points, and the wind speed fluctuations in Gaotuan Village were relatively small. As revealed by the above results, the local wind speed of Gaotuan Village was reduced through the reasonable location and layout of the village. Moreover, the small fluctuation in wind speed suggested that Gaotuan Village was a relatively stable wind environment. Furthermore, the low wind speed and stable wind environment could effectively slow down the fire spread in the case of a fire.
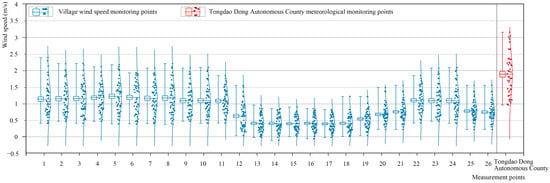
Figure 10.
Village monitoring wind speed and respective meteorological measurement point wind speed.
3.2.2. Street Wind Speed
Figure 11 presents the wind speed monitoring results of streets and alleys in Gaotuan Village with four stratum widths and a total of eight measurement points. The average wind speed of the respective measurement point of its alleys, secondary streets, main streets, and rural arteries reached 0.30 m/s, 0.27 m/s, 0.44 m/s, 0.43 m/s, 0.59 m/s, 0.62 m/s, 0.70 m/s, and 0.69 m/s for monitoring points 1–8 in Figure 6, respectively. Notably, the highest wind speed was identified in the rural arteries, followed by the main streets, then the secondary streets, while the lowest wind speed was reported in the alleys, and their wind speed fluctuations decreased in order. As revealed by the above result, there was a correlation between the width of the street and the wind speed; the narrower the street, the lower the wind speed and the less volatility. The smaller wind speed could not facilitate the spread of a house fire, which is conducive to the prevention of fire.
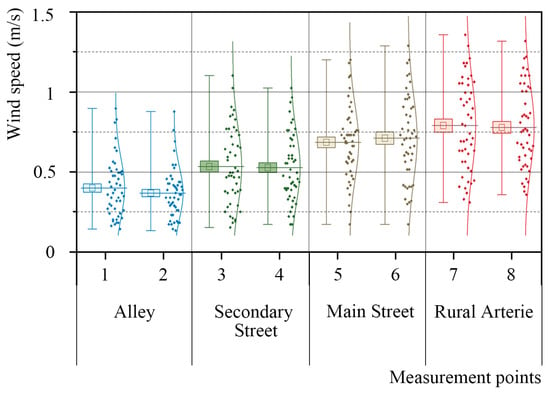
Figure 11.
Street and alley monitoring wind speed.
3.2.3. Building Wind Speed
The wind speed inside and outside of the dwelling was monitored. Under the effect of the village and the street on the weakening of wind speed, the wind speed on the exterior surface of the dwelling was low, and the average wind speed outside the building examined at the monitoring points of the first- and second-floor exterior walls of the dwelling was 0.17 m/s.
3.3. Simulation Results
3.3.1. Village Fire Simulation Results
To corroborate the fire prevention thinking of Dong traditional settlements in the western Hunan region in terms of site selection, we modeled the core group of Gaotuan Village in Pyrosim software with the same parameters and performed a fire simulation. Figure 12a,c,e show the simulation results of fire spreading, smoke dispersion, and temperature slices for scenario 1 (Gaotuan Village at the average wind speed of the nearest meteorological measurement point); Figure 12b,d,f show the simulation results of fire spreading, smoke dispersion, and temperature slices for scenario 2 (Gaotuan Village at the average wind speed of the nearest measurement point).
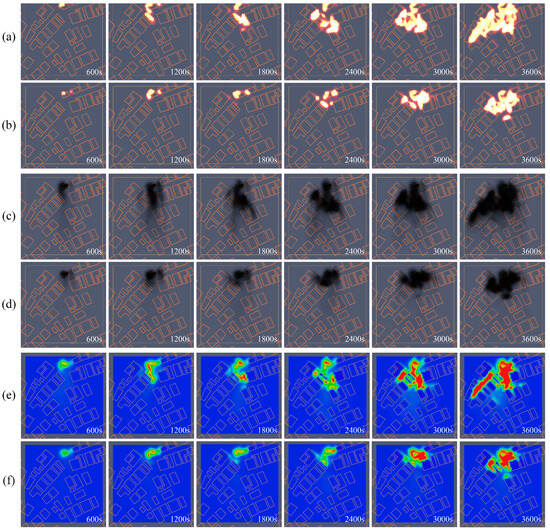
Figure 12.
(a) Scenario 1 fire spread simulation results; (b) scenario 2 fire spread simulation results; (c) scenario 1 smoke dispersion simulation results; (d) scenario 2 smoke dispersion simulation results; (e) scenario 1 temperature slicing simulation results; (f) scenario 2 temperature slicing simulation results.
As indicated by the simulation results, the fire, smoke, and temperature spread in all directions from the location of the fire source following the wind direction after the fire started. For the fire spread, scenarios 1 and 2 started to burn at 600 s at the source of the fire while beginning to spread to nearby residences. To be specific, scenario 1 started to spread downwind at 1200 s and spread in all directions at 3000 s, whereas, in scenario 2, the fire only started to spread downwind at 2400 s and spread in all directions at 3600 s. The smoke diffusion suggested that the speed and extent of smoke diffusion in scenario 1 exceeded those of scenario 2 at the identical time node, and the diffusion of smoke also happened to be an important way for the fire to spread. From the results of the temperature slices, the temperature of combustion and smoke, and the diffusion speed and range of scenario 1 were larger than that of scenario 2 at the same time point. In brief, under identical combustion conditions, the combustion in scenario 1 was more serious than that of scenario 2, and the spreading speed of scenario 1 was notably larger than that of scenario 2. As indicated by the above result, under identical conditions, the local wind speed in Gaotuan Village was effectively reduced by good village siting such that the extent of fire, smoke, and temperature spread under fire conditions was effectively mitigated, and the risk of fire spreading was greatly reduced.
Figure 13 shows the number of dwellings burned in this fire simulation for scenario 1 and scenario 2. At the end of the 3600 s simulation, the number of homes burned in scenario 1 and scenario 2 was 17 and 9, respectively. Under identical village conditions, the local wind speed was reduced due to the good location of Gaotuan Village such that the fire spread rate decreased. The slope of the burn rate curves for scenario 1 and scenario 2 reached 0.00405 and 0.00238, respectively, with nearly double the difference between the slopes of the two curves.
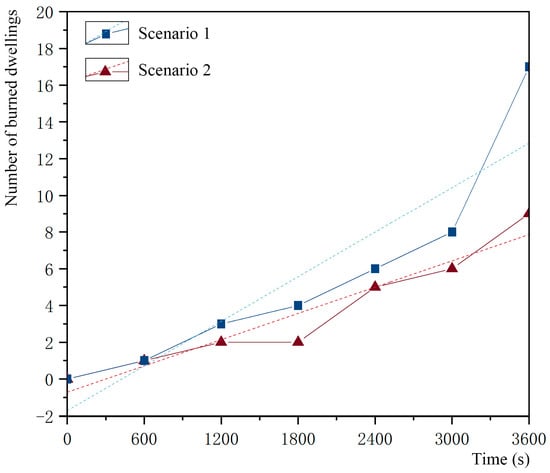
Figure 13.
Number of dwellings burned in the simulations of scenario 1 and scenario 2 at different time points.
3.3.2. Street Fire Simulation Results
Based on the field research, we selected a typical street with a length of about 65 m and the area where there were residential houses on both sides of the street in Gaotuan Village as the research object for the simulation analysis. Figure 14, Figure 15 and Figure 16 show the corresponding fire simulation results, temperature slicing results, and smoke dispersion results from the Pyrosim simulation at the street level, respectively.
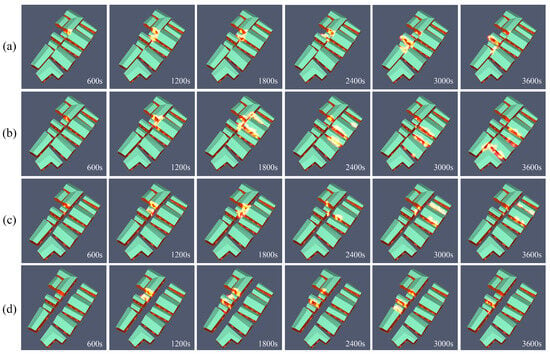
Figure 14.
(a) Scenario 3 fire spread simulation results; (b) scenario 4 fire spread simulation results; (c) scenario 5 fire spread simulation results; (d) scenario 6 fire spread simulation results.
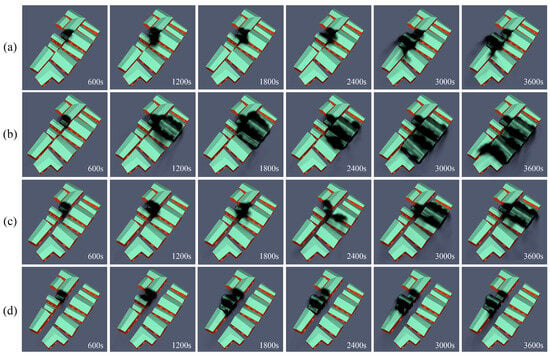
Figure 15.
(a) Scenario 3 smoke dispersion simulation results; (b) scenario 4 smoke dispersion simulation results; (c) scenario 5 smoke dispersion simulation results; (d) scenario 6 smoke dispersion simulation results.
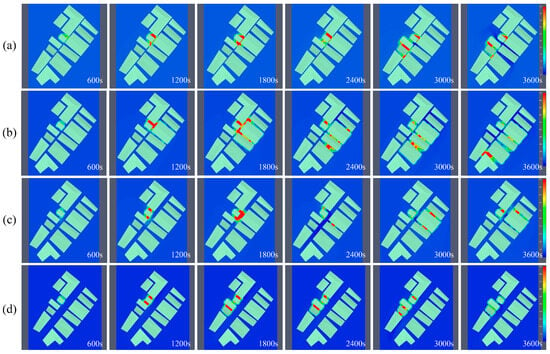
Figure 16.
(a) Scenario 3 temperature slicing simulation results; (b) scenario 4 temperature slicing simulation results; (c) scenario 5 temperature slicing simulation results; (d) scenario 6 temperature slicing simulation results.
From the fire spread, in scenarios 3/4/5/6 at 600 s, the residential house at the point of origin began to burn. In scenario 6, the fire started to spread to both sides of the fire point at 1800 s, and it did not spread to the buildings on the other side of the street till the end of the simulation at 3600 s. In scenario 3, the fire spread to the buildings close to the fire source at 1200 s, and it tended to spread to the buildings on the other side of the street, though it did not cause significant burning to the buildings on the other side of the street till the end of the simulation at 3600 s. In scenario 5, the fire started to spread in all directions at 1800 s, and it had spread to nearly half of the street by the end of the simulation at 3600 s. Moreover, the fire first began to spread in all directions and had spread to nearly half of the buildings on the street near the fire source by the end of the 3600 s simulation. In scenario 4, the fire began to spread in all directions at 1200 s and had spread to the entire street downwind by the end of the 3600 s simulation. As indicated by the smoke dispersion, in scenarios 3 and 6, at the end of the simulation at 3600 s, the smoke had spread along the same side of the street as the fire source, whereas the smoke did not spread to the other side of the street. In scenario 4, the smoke had spread to the other side of the street by 1200 s and had nearly spread to the whole street downwind of the fire source by 3600 s. In scenario 5, the smoke had spread to the other side of the street by 2400 s; at the end of the simulation at 3600 s, the smoke had spread to the buildings close to the fire source and the opposite side of the street. The results of the temperature slices suggested that the maximum temperatures of scenarios 3/4/5/6 reached 610 °C, 765 °C, 625 °C, and 550 °C, respectively, and the range and rate of spread of their temperature slices confirmed the combustion scenarios of this simulation.
By the end of the 3600 s fire simulation, the number of buildings burned in scenarios 3/4/5/6 reached 3, 8, 4, and 4 (Figure 17), respectively. As indicated by the simulation results, the street width played a vital role in the spread of house fires at the street level. The fire scenario was the most severe in the street with a 2000 mm width under identical external conditions. After the fire, the fire, smoke, and temperature spread in all directions from the fire source location following the wind direction.
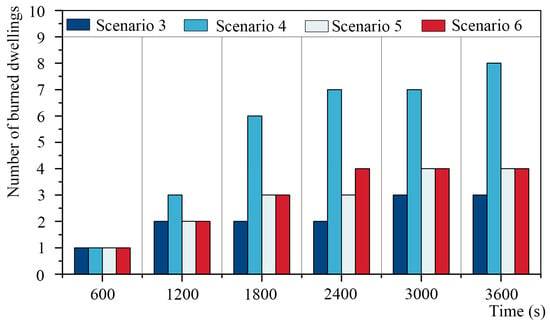
Figure 17.
Number of dwellings burned in the simulations of scenarios 3, 4, 5, and 6 at different time points.
3.3.3. Building Fire Simulation Results
The fire pit is the living fire source of Dong houses, but by the non-combustible nature of the fire pit enclosure, it is not the place where the fire occurs. In the setting of this study, the sparks in the fire pond drifted down to the armrest of the sofa with the wind pressure in the room, and the left side of the sofa started to burn from the left armrest of the sofa.
From the spread of the fire (Figure 18a), the sofa fell into the ignition state at 160 s of the fire. With sufficient oxygen content in the room, the fire tended to expand. At 320 s, the main part of the sofa was judged to be completely burned in the system, i.e., the combustion disappeared, at which time the flames between the fire ponds were mainly concentrated at the window oxygen sufficiency and spread from the wooden envelope to the adjacent rooms. At 480 s, the fire further expanded and spread to the storage room on the west side of the fire ponds, and the floor of the third-floor attic tended to be ignited. At 640 s, the kitchen envelope on the west side was ignited, the two bedrooms on the south side became hot, and the fire on the third floor gradually spread upward to the frame, at which point the fire was nearly out of control. At 800 s, the wooden envelope on the north side was all on fire, and the beds in the bedrooms on the west side showed complete combustion and disappeared. At 960 s, the beds in the bedrooms on the east side were completely burned and disappeared, and the entire second floor fell into a highly dangerous scenario.
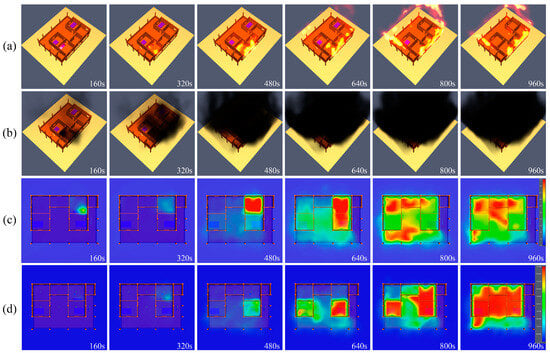
Figure 18.
(a) Scenario 7 fire spread simulation results; (b) scenario 7 smoke dispersion simulation results; (c) scenario 7 temperature slicing simulation results; (d) scenario 7 CO concentration.
Figure 18c shows the temperature slices at a height of 1.4 m from the floor of the second floor. From the temperature slices, a significant temperature change of nearly 300 °C was identified after ignition at the sofa between the fire pits at 160 s. A smaller temperature increase was also reported at the northwest corner of the fire pits. The rest of the space was maintained at a room temperature of 18 °C. At 320 s, the effect of the smoke roof flow jet triggered a slight decrease in temperature at the slices. At 480 s, the temperature of the whole space between the fire pits rose to approximately 800 °C, while the high-temperature smoke spread to other indoor spaces. At 640 s, the temperature of the bedroom connected to the fire pits rose to about 780 °C first, and the temperature of the T-shaped corridor and the west bedroom also rose to about 500 °C. At 800 s, the oxygen was relatively sufficient in the kitchen and storage room on the north side and the corridor on the south side, and the burning high-temperature area was mainly concentrated in the abovementioned locations. At 960 s, the flames spread to the middle of the T-shaped corridor, and the temperature in the middle of the T-shaped corridor also rose to about 750 °C, where the exits of the rooms converged, which was extremely dangerous regarding escape needs.
As indicated by the gas concentration analysis, Figure 18d presents a slice of the CO concentration at a height of 1.4 m on the ground level of the second floor. Carbon monoxide, i.e., an intermediate product in the combustion process, entered human blood through the lungs while being combined with hemoglobin to form carboxyhemoglobin such that the body became hypoxic, and the brain was subjected to the most serious damage. To be specific, at 320 s, the CO concentration at the fire source was increased; at 480 s, the south side of the house was filled with CO, which arose from the window orientation and wind direction, and its concentration was increased to 6.65 × 10−3 mol/mol; at 640 s, the CO concentration in this room reached 6.65 × 10−3 mol/mol, whereas the CO concentration in several rooms was increased to 9.5 × 10−3 mol/mol; at 800 s, all rooms except for the northwest-most room were filled with CO with a concentration of 9.5 × 10−3 mol/mol; at 960 s, CO filled the entire second-floor living space, and the maximum concentrations generally reached 9.5 × 10−3 mol/mol. The volume concentration of gas in the air was 21%; in the event of a fire, oxygen was supplied for combustion, and its concentration then decreased. Figure 19 presents the variation in the oxygen concentration at six monitoring points in the second-floor living space of the building simulation model. At 160 s, the sofa was ignited, and the oxygen concentration began to fluctuate between the fire pits (measurement point 3). When the house started to burn at 320 s, the oxygen concentration of measurement point 1 fluctuated within a scope of 16–6%; the oxygen concentration of measurement point 3 fluctuated between 10 and 6%; and the oxygen concentration of measurement points 2, 4, 5, and 6 decreased rapidly to 6%, reaching an extremely dangerous concentration such that people were likely to suffocate. At 840–900 s, the oxygen concentration of the outdoor measurement point (measurement point 5) recovered to 16%, whereas the oxygen concentration of the indoor measurement points recovered till the end of the simulation at 960 s.
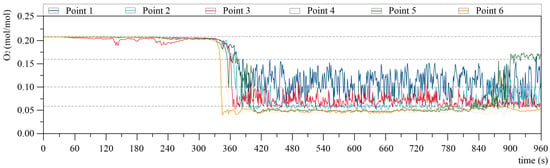
Figure 19.
O2 concentration at each measurement point in scenario 7.
From the case of smoke diffusion, 1 kg of wood generally produced 20 m3 of smoke after burning, and the smoke diffusion of wood frame dwellings was primarily analyzed following the smoke spread area and the height of smoke from the ground. Figure 18b and Figure 20 present the smoke diffusion and height change curves. The smoke spread in the room where the fire originated at 160 s, started to spread to other rooms at 320 s, and then spread to the whole second-floor space at 480 s. Moreover, when the smoke was diffusing, its smoke height continuously decreased from 320 to 360 s. After 360 s, the smoke heights of measurement points 3, 4, 5, and 6 were stabilized at 1.5 m, and measurement points 1 and 2 fluctuated around a height of 1.5 m. On this basis, the indoor smoke that was at high temperatures and toxic posed serious life and safety threats to people, while shading and irritation also exerted a certain effect on the safety judgment regarding evacuation.
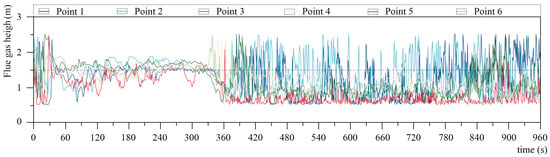
Figure 20.
The smoke height at each measurement point in scenario 7.
- 4.
- Discussion
The Dong traditional settlements in the western Hunan region have been largely constructed of wood, and thus, fire can pose the biggest threat to the survival of their dwellings. However, numerous Dong traditional settlements in the western Hunan region have survived for thousands of years since they follow their ways of survival []. This study aimed at analyzing the spread of fire in Gaotuan Village to clarify the reasonableness and irrationality of Dong traditional settlements in Western Hunan in the face of fire.
From the perspective of fire occurrence, the fire pits of Dong communities in the western Hunan region have been developed to centralize household fires. Although they are not extinguished throughout the year, are enclosed using non-combustible stones of 1000 mm width, which greatly reduces the likelihood of igniting a fire by spreading smoke to nearby wooden buildings and furniture. Regarding combustible materials and combustion aids, the Dong settlements in the western Hunan region do not handle them well. First, the supporting structures and enclosures of their dwellings are made of wood that is easy to burn, which arises from the use of historical construction techniques and access to building materials. Furthermore, considerable dry firewood is kept in reserve at home, which serves as a combustible material and will become fuel in the case of a fire.
From the point of view of fire spread, the Dong traditional villages in the western Hunan region exploit the natural landscape to divide the fire protection zone so that the possibility of fire spreading to other zones can be blocked. Moreover, the location of Dong traditional villages in the western Hunan region contains the ancient Chinese feng shui wisdom of “hiding wind and gathering qi”. The wind speed showed a decreasing trend of “outside–village–street–residence”, with an average wind speed of 2.17 m/s outside the village reduced to 0.17 m/s outside the building through reasonable site selection and layout in Gaotuan Village without mechanical assistance so that the wind speed was reduced layer by layer with the aim of reducing fire spread [,,,]. However, the Dong traditional settlements in the western Hunan region are subject to topographic factors, with relatively small building-to-building spacing and narrow street widths, thus hindering fire prevention. From the fire simulation results, the Dong traditional settlements in the Xiangxi region displayed good siting and layout at the village level such that the risk of fire spreading was reduced. And the fire severity was presented at the street width level in the order of 2000 mm > 4000 mm > 8000 mm > 1000 mm, and the fire spread at 1000 mm street width was not as severe as that at 2000 mm, which was because of too small street space spacing and the wind circulation was not good such that the spread of smoke was not open [,].
From the perspective of a fire escape, when the oxygen volume concentration decreases to 16–12%, the human body appears in obvious discomfort in terms of respiration, pulse rate, and reduced coordination of movement; when the concentration is down to 14–9%, a decline in judgment can appear, along with general deficiency, fainting, and so forth; when the concentration is down to 10–6%, unconsciousness and spasms occur, along with death in 6–8 min; when the concentration is below 6%, people die of asphyxiation in 5 min. Moreover, a healthy adult with a carbon monoxide concentration of 6.4 × 10−3 mol/mol by volume is subjected to nausea and headache in 1–2 min and dies in 10–15 min, and dies in 1–3 min when the concentration reaches 1.28 × 10−3 mol/mol by volume []. After 320 s of fire in the building monolith, the residential house started to burn violently and the smoke spread to the whole second-floor living space, the temperature was elevated, the CO concentration was increased, the oxygen concentration fell, and the smoke height decreased. Accordingly, in the event of a fire in a residential building, it is safer to evacuate the people inside in under 320 s.
The inheritance and development of traditional settlements have always been the focus of research on traditional rural architecture, and there are a considerable number of traditional settlements in China, which are distributed throughout the country and belong to various ethnic groups, representing the traditional culture and regional architectural characteristics of each ethnic group in China []. The Dong traditional settlements in the western Hunan region represent the traditional building techniques of the Dong people, and their study is conducive to suggesting conservation methods and policies that are more in line with the Dong settlements in the western Hunan region. We combined the research data and simulation results to propose targeted arguments for the effective protection of the Dong traditional settlements against fire and their continuation in the face of fire.
4. Questions and Suggestions
Gaotuan Village is a typical Dong traditional village in the western Hunan region. Through this study, Gaotuan Village can reflect the general problems of Dong traditional villages in the western Hunan region, and its suggestions are also applicable to other Dong traditional villages in the western Hunan region. Based on field monitoring and simulation data, we found that most of the Dong traditional villages in the western Hunan region have the following problems.
- 1.
- The site of the village is a remote mountainous area
The location of traditional minority villages in the western Hunan region was selected due to a weighing of many factors. However, in the current harmonious society, remote village siting can trigger longer arrival times for fire trucks. In Gaotuan Village, for instance, it takes 37 min for a fire truck to arrive from the nearest fire station, at which point, the fire is already difficult to control.
- 2.
- Small street width and small building spacing
Narrower streets and alleys primarily aim at conforming to the terrain, and too small street width and building spacing in the event of a fire will spill over and ignite nearby buildings, causing more serious fires. Moreover, the small width of the street will not be reached by fire trucks, and thus, the difficulty of firefighting can be increased.
- 3.
- The construction material is wood
The traditional Dong dwellings in western Hunan are built using the logic of historical inheritance, and their load-bearing frames and maintenance structures are all easily burnable wood, which is the most essential problem for the fire prevention of buildings.
- 4.
- The use of fire
Dong residents in the western Hunan region have been using fire very frequently, and fire takes on critical significance in their daily lives. However, they do not have enough awareness of fire prevention and often fail to do basic fire prevention behaviors, such as people not walking away from fire and keeping flammable objects away from fire sources.
With the development of the social economy and the progress of science and technology, novel fire prevention measures and technologies may be proposed in the future. Nevertheless, under the premise of the current research and technology, the following suggestions were proposed for fire prevention measures for local dwellings based on the results of this study and under the premise of combining the practical local environment and economic factors, as well as preserving and inheriting the unique architectural culture of the Dong traditional dwellings in the western Hunan region.
- 1.
- Increase fire awareness
Fire safety and fire prevention knowledge can be publicized through fire propaganda, cadres’ visits to the countryside and village committee meetings, etc., to enhance the fire awareness of residents and public cadres [,]. Let the residents clearly understand fire safety, always prevent the occurrence of fire, and eliminate fire as a root cause.
- 2.
- Adding basic firefighting facilities
Since the local infrastructure is relatively weak and some villages do not even have running water yet, additional fire hydrants are unlikely to be installed, and thus, only portable firefighting equipment (e.g., additional fire extinguishers) can be installed. This study suggested that two additional fire extinguishers should be installed in public locations in the respective areas to defend against sudden fires following the fire protection zoning of this study. Furthermore, firefighting loops and fighting surfaces can be built to satisfy the requirements for fire truck access and rescue.
- 3.
- Automatic fire alarm system and automatic sprinkler system
An automatic fire alarm system is likely to be built by bringing together vital traditional villages in a city or county []. The residents are largely older and have never left the village and do not know how to contact the fire department. With the addition of an automatic fire alarm system, firefighters can be allowed to be the first to respond to a fire, and the systematic management of fires in remote mountainous villages can be facilitated. Furthermore, the automatic sprinkler system can quickly allow for fire extinguishing [].
- 4.
- Modernization of fire pits
We propose to add modern smoke extraction facilities above the fire pit, i.e., the core space of Dong houses in the western Hunan region, and it should be naturally preserved. Smoke extraction facilities can be added to prevent fires arising from sparks and smoke spreading. Moreover, the indoor air quality can be also improved by adding smoke exhaust facilities.
- 5.
- The use of new materials
Given the characteristics exhibited by wood, the relevant literature was reviewed. As indicated by the result, new coatings can be adopted to enhance the fire resistance of wood [,,,,,]. The use of fireproof coatings on Dong folk dwellings in western Hunan, especially the wooden roof frame, which is a key component can fully preserve the regional architectural culture after use since most of the abovementioned materials are colorless and transparent and can also greatly improve the fire resistance limit of wood.
5. Conclusions
This study took Gaotuan Village, which is a typical Dong traditional village in the western Hunan region, as a research sample and conducted fire simulations of it in Pyrosim software from the three levels of village, street, and residence to study the fire prevention wisdom and deficiencies of the Dong traditional settlements in the western Hunan region. And according to the actual situation of local society and economy, as well as the actual situation of ethnic culture and regional architectural culture, targeted suggestions are put forward. The following conclusions were drawn from the study.
- 1.
- The investigative results show the following:
The traditional houses of the Dong ethnic group in western Hunan use flammable air-dried wood as the main building material, and the spacing between the buildings and the width of the streets is small, which makes it inaccessible to modern fire trucks and does not comply with the fire spacing requirements for wood-framed buildings in China. At the same time, the residents have a weak awareness of fire prevention, with fire pits burning all year round and a large amount of dry wood piled up in their homes. In addition, Gao Tuan Village is located on the riverbank of a valley and relies on the topography to maintain the local climate by blocking the cold northwestern monsoon winds in winter. The topography and layout of the village reduce the wind speed, where the average wind speed was reduced from 2.17 m/s as the external wind speed to 0.17 m/s on the outside surface of the buildings, which slows down the spread of the fire when it occurs.
- 2.
- The simulation results show the following:
In the village level simulation up to 3600 s, the number of burned houses in scenarios 1 and 2 were 17 and 9, respectively, and the burning rate was nearly double. During the street-level simulation to 3600 s, the number of burned buildings in scenarios 3, 4, 5, and 6 were 3, 8, 4, and 4, respectively. During the building-level simulation, at 320 s, the house in scenario 7 started to burn violently, the smoke spread to the entire second-floor living space, the temperature rose with the increase in the concentration of CO, the concentration of oxygen and the height of the smoke decreased, and the safety of the people in the house was greatly threatened until the house was fully burned at 960 s.
Moreover, certain shortcomings were present in this study. The fires were simulated in three aspects (i.e., Dong village, street space, and traditional dwelling) in the Xiangxi region in the Pyrosim software of this study, where the scene model was simplified, while the practical burning scenario was more complex and variable compared with the simulated scenario. Moreover, Gaotuan Village was the selected object of this study, i.e., a typical Dong traditional village in the western Hunan region. On this basis, the findings of this study can only apply to Dong traditional villages in the western Hunan region. In our subsequent research, we will study the fire prevention strategies of the Dong tribes in the Xiangxi region and other minority tribes in the Xiangxi region to supplement the deficiencies in the ancient Chinese fire prevention strategies and justify the fire prevention strategies through quantitative analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L. (Zhezheng Liu) and X.L.; methodology, Z.L. (Zhezheng Liu) and Z.L. (Zhe Li); software, Z.L. (Zhezheng Liu) and X.L.; validation, Z.L. (Zhezheng Liu) and X.L.; formal analysis, L.X. and J.J.; investigation, Z.L. (Zhezheng Liu) and X.L.; resources, Z.L. (Zhe Li); data curation, Z.L. (Zhezheng Liu) and X.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.L. (Zhezheng Liu) and J.J.; writing—review and editing, Z.L. (Zhezheng Liu) and X.L.; visualization, Z.L. (Zhezheng Liu) and X.L.; supervision, Z.L. (Zhe Li) and L.X.; project administration, Z.L. (Zhe Li); funding acquisition, Z.L. (Zhe Li). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 52078484.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy considerations. Please contact the corresponding author before use.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank C.C. and M.C. for their excellent technical support, data curation, and investigation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Romão, X.; Bertolin, C. Risk protection for cultural heritage and historic centres: Current knowledge and further research needs. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 67, 102652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobes, M.; Helsloot, I.; de Vries, B.; Post, J.G. Building Safety and Human Behaviour in Fire: A Literature Review. Fire Saf. J. 2010, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Jiao, H. How Does Information Affect Fire Risk Reduction Behaviors? Mediating Effects of Cognitive Processes and Subjective Knowledge. Nat. Hazards 2018, 90, 1461–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Na, I.Y.; Jang, H.K.; Kim, H.D.; Kim, G.T. Anisotropic Electrical and Thermal Characteristics of Carbon Nanotube-Embedded Wood. Cellulose 2019, 26, 5719–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrion, C.E. More Effectively Addressing Fire/Disaster Challenges to Protect Our Cultural Heritage. J. Cult. Herit. 2016, 20, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.M.; Vicente, R.; Raimundo Mendes da Silva, J.A.; Varum, H.; Costa, A.; Maio, R. Urban Fire Risk: Evaluation and Emergency Planning. J. Cult. Herit. 2016, 20, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozo Neto, J.; Ferreira, T.M. Assessing and Mitigating Vulnerability and Fire Risk in Historic Centres: A Cost-Benefit Analysis. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 45, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuello Bertetto, A.; D’Angella, P.; Fronterre’, M. Residual Strength Evaluation of Notre Dame Surviving Masonry after the Fire. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 122, 105183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorlton, B.; Gales, J. Fire Performance of Heritage and Contemporary Timber Encapsulation Materials. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 29, 101181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, A.; Kioumarsi, M.; Plevris, V.; Stamatopoulos, H. Structural Vulnerability Assessment of Heritage Timber Buildings: A Methodological Proposal. Forests 2020, 11, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, T. Traditional Wisdom for Disaster Mitigation in History of Japanese Architectures and Historic Cities. J. Cult. Herit. 2016, 20, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xiao, C. Large-Scale Fire Spread Model for Traditional Chinese Building Communities. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 67, 105899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tian, F.; Zheng, X.; Sun, Z. Spatial Configuration of Fire Protection for Historical Streets in China Using Space Syntax. J. Cult. Herit. 2023, 59, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.Y.; Liu, B. Chinese Historic Buildings Fire Safety and Countermeasure. Procedia Eng. 2013, 52, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Du, F.; Okazaki, K.; Ochiai, C. Disaster Coping Capacity of a Fire-Prone Historical Dong Village in China: A Case Study in Dali Village, Guizhou. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2017, 21, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazi, Y.S.; Tahoon, D.; Abdel-Fattah, N.A.; El-Alfi, M.F. Socio-Spatial Vulnerability Assessment of Heritage Buildings through Using Space Syntax. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, L.; Gu, Y. Assessing the Accessibility to Fire Hazards in Preserving Historical Towns: Case Studies in Suburban Shanghai, China. Front. Archit. Res. 2022, 11, 731–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granda, S.; Ferreira, T.M. Assessing Vulnerability and Fire Risk in Old Urban Areas: Application to the Historical Centre of Guimarães. Fire Technol. 2019, 55, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementi, F.; Gazzani, V.; Poiani, M.; Lenci, S. Assessment of Seismic Behaviour of Heritage Masonry Buildings Using Numerical Modelling. J. Build. Eng. 2016, 8, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copping, A.G. The Development of a Fire Safety Evaluation Procedure for the Property Protection of Parish Churches. Fire Technol. 2002, 38, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Jiao, H. Insights into the Effects of Cognitive Factors and Risk Attitudes on Fire Risk Mitigation Behavior. Comput. Econ. 2018, 52, 1213–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzi, N.C.; Juliá, P.B.; Ferreira, T.M.; Rosas, J.; Monsalve, M.; de la Llera, J.C. Fire Risk Assessment of Historic Urban Aggregates:An Application to the Yungay Neighborhood in Santiago, Chile. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2023, 86, 105899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinciturk, N.; Kilic, M. A Study on the Fire Protection of Historic Cumalikizik Village. J. Cult. Herit. 2004, 5, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qin, R. Performance-Based Firefighting in Dense Historic Settlements: An Exploration of a Firefighting Approach Combining Value and Risk Assessment with Numerical Simulation. Front. Archit. Res. 2022, 11, 1134–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.Y.; Jun, S. Fire Risk Assessment Models Using Statistical Machine Learning and Optimized Risk Indexing. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, L.G.F.; Romão, X.; Paupério, E. Review of Vulnerability Indicators for Fire Risk Assessment in Cultural Heritage. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 60, 102286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; He, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, P. Fire Hazards in Heritage Villages: A Case Study on Dangjia Village in China. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2018, 28, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.N.; Abdul-Hamid, K.; Ibrahim, M.S.; Mohd-Din, A.; Yunus, R.M.; Yahya, M.R. The Development of Fire Risk Assessment Method for Heritage Building. Procedia Eng. 2011, 20, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Q. Fire Risk Assessment of Heritage Villages: A Case Study on Chengkan Village in China. Fire 2023, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shi, L.; Liu, S.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J. CFD-Based Framework for Fire Risk Assessment of Contiguous Wood-Frame Villages in the Western Hunan Region. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 54, 104607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biao, Z.; Xiao-meng, Z.; Ming-yong, C. Fire Protection of Historic Buildings: A Case Study of Group-Living Yard in Tianjin. J. Cult. Herit. 2012, 13, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Qi, F. Burning Characteristics of Ancient Wood from Traditional Buildings in Shanxi Province, China. Forests 2022, 13, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, D.; Zhou, B.; Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, X. Influence of Air Gap Ratio of the Chinese Historical Wooden Window on the Vertical Flame Spread Performance. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2022, 32, 101308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panno, C.; Gonçalves, J.; Prager, G.; Bolina, F.L.; Tutikian, B.F. Analysis of the Fire Resistance of Normal Wooden Doors Exposed to Fire Conditions. Rev. Constr. 2020, 19, 359–369. [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi, H.; Igarashi, S.; Nagaoka, T. Development of Wood Structural Elements for Fire Resistant Buildings. J. Struct. Fire Eng. 2018, 9, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Wall, G.; Mitchell, C.J.A. Creative Destruction and the Water Town of Luzhi, China. Tour. Manag. 2008, 29, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, J. Recognition of Values of Traditional Villages in Southwest China for Sustainable Development: A Case Study of Liufang Village. Sustain. 2021, 13, 7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Long, B.; Zhao, Y. Creative Destruction and Commercialization of Traditional Villages: Likeng, Wangkou, and Jiangwan in Wuyuan, China. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 592, 012109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Shen, Z.; Tian, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Pan, R.; Wang, H.; Jiao, S.; Kou, W. Fire Risk Level Prediction of Timber Heritage Buildings Based on Entropy and XGBoost. J. Cult. Herit. 2023, 63, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. Western Hunan Houses; China Construction Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Yang, G.; Xie, L. Correlation Analysis of Health Factors of Elderly People in Traditional Miao Dwellings in Western Hunan. Buildings 2023, 13, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhou, J.; Deng, Y. Heritage Values of Ancient Vernacular Residences in Traditional Villages in Western Hunan, China: Spatial Patterns and Influencing Factors. Build. Environ. 2021, 188, 107473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Burley, J.B. Expert Opinion Dimensions of Rural Landscape Quality in Xiangxi, Hunan, China: Principal Component Analysis and Factor Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shi, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, C.; Xiang, T. The Traditional Wisdom in Fire Prevention Embodied in the Layout of Ancient Villages: A Case Study of High Chair Village in Western Hunan, China. Buildings 2022, 12, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, C.; Xiao, Z. Fire Spreading Hazard Analysis of Traditional Village Houses. Build. Sci. 2016, 32, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M. Simulation Study on Fire Boom Ignition and Group Fire Spreading in Wooden Structured Hammock Buildings. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.H.; Huo, R.; Yang, D. Large Eddy Simulation of Fire-Induced Buoyancy Driven Plume Dispersion in an Urban Street Canyon under Perpendicular Wind Flow. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yang, H.; Xu, T.; Wang, F.; Li, C.; Xu, L. Effects of Ambient Pressure on Fire-Induced Buoyancy Driven Plume Dispersion and Re-Entrainment Behavior in a Street Canyon. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, L.; Tang, F.; Wang, Q. Large Eddy Simulation of Fire Smoke Re-Circulation in Urban Street Canyons of Different Aspect Ratios. Procedia Eng. 2013, 62, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lu, K.; Feng, L.; Tao, Y.; Wang, J.; Ding, Y.; Shi, C. Simulation on Smoke Re-Circulation Transition in an Urban Street Canyon for Different Fire Source Locations with Cross Wind. Saf. Sci. 2020, 127, 104716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Wang, K.; Liu, Q.; He, P.; Liu, Q. Simulation Investigation of Fire Smoke Behavior above Simulation Investigation of Fire Smoke Behavior above Simulation Investigation of Fire Smoke Behavior above Simulation Investigation of Fire Smoke Behavior above Simulation Investigation of Fire Smoke. Procedia Eng. 2018, 211, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Deng, L. Fire Risk Assessment; Machinery Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y. Fifty Years of Chinese Folk House Research. J. Archit. 2007, 11, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Cvetković, V.M.; Dragašević, A.; Protić, D.; Janković, B.; Nikolić, N.; Milošević, P. Fire Safety Behavior Model for Residential Buildings: Implications for Disaster Risk Reduction. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 76, 102981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hasemi, Y.; Nozoe, Y.; Nagasawa, M. Study on Strategy for Fire Safety Planning Based on Local Resident Cooperation in a Preserved Historical Mountain Village in Japan. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 56, 102081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.-J.; Hsieh, S.-H. Real-Time Fire Protection System Architecture for Building Safety. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 67, 105913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.Y.; Tang, C.H.; Lin, C.Y. Estimation of Magnitude and Heat Release Rate of Fires Occurring in Historic Buildings-Taking Churches as an Example. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Yang, Q.; Yan, L.; Wang, N. Facile Fabrication of Multifunctional Transparent Fire-Retardant Coatings with Excellent Fire Resistance, Antibacterial and Anti-Aging Properties. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 169, 106925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Qin, Y.; Huang, X.; Gollner, M. Use of Pre-Charred Surfaces to Improve Fire Performance of Wood. Fire Saf. J. 2023, 136, 103745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Liang, C.; Zhang, J. Novel Ti3C2Tx MXene/Epoxy Intumescent Fire-Retardant Coatings for Ancient Wooden Architectures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, M.; Guo, H. Synergistic Flame Retardant Effects of Different Zeolites on Intumescent Fire Retardant Coating for Wood. BioResources 2017, 12, 5369–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Sun, P.; Hai, Y.; Jiang, S. A Self-Healing, Recyclable, and Degradable Fire-Retardant Gelatin-Based Biogel Coating for Green Buildings. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 5231–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kutty, R.G.; Zheng, Q.; Eswariah, V.; Sreejith, S.; Liu, Z. Hexagonal Boron Nitride Nanosheets as High-Performance Binder-Free Fire-Resistant Wood Coatings. Small 2017, 13, 1602456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).