Features of Pinch Plasma, Electron, and Ion Beams That Originated in the AECS PF-1 Plasma Focus Device
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
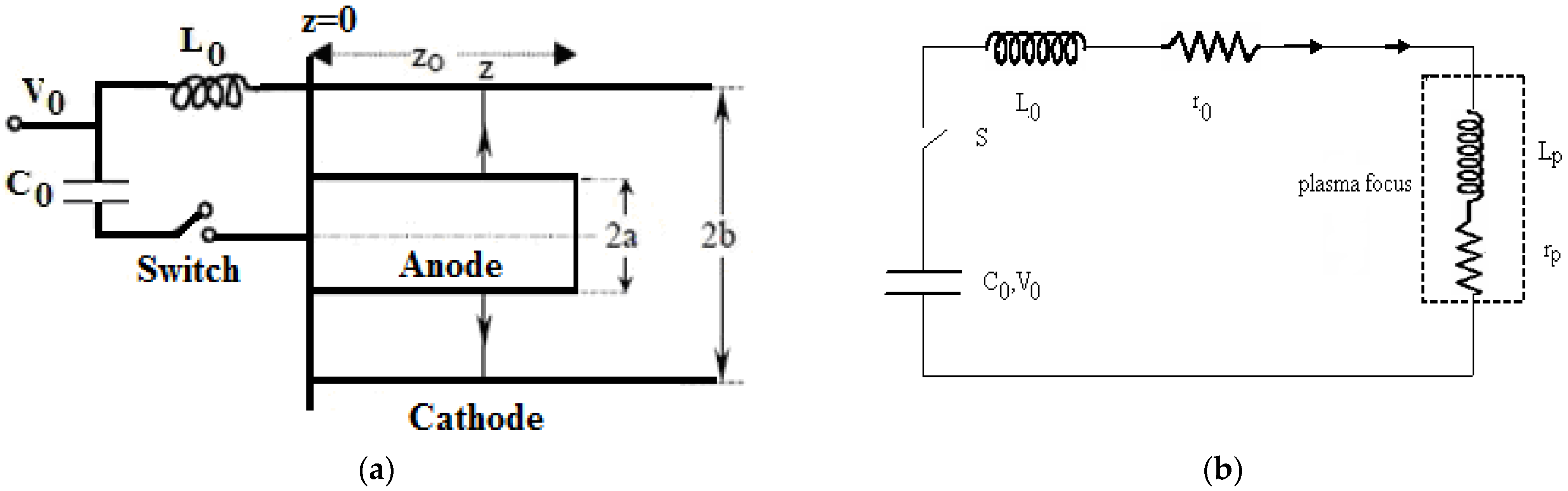
2.1. Experimental Set up and Diagnostic Tools
2.2. The Lee Model Code Used for the Ion and Electron Beam Computation
3. Results and Discussion
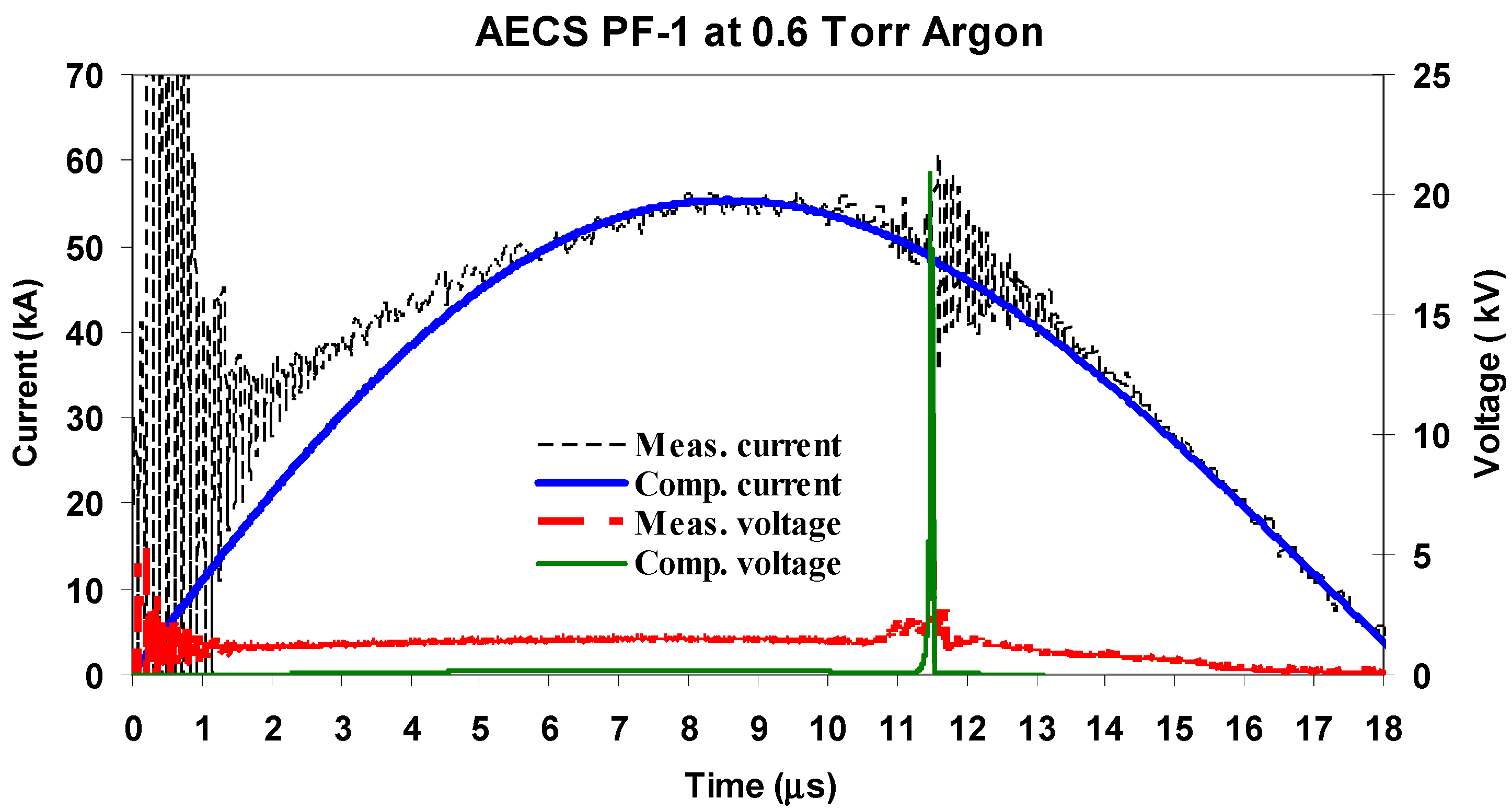
3.1. Fitting Procedures of the Current Waveforms
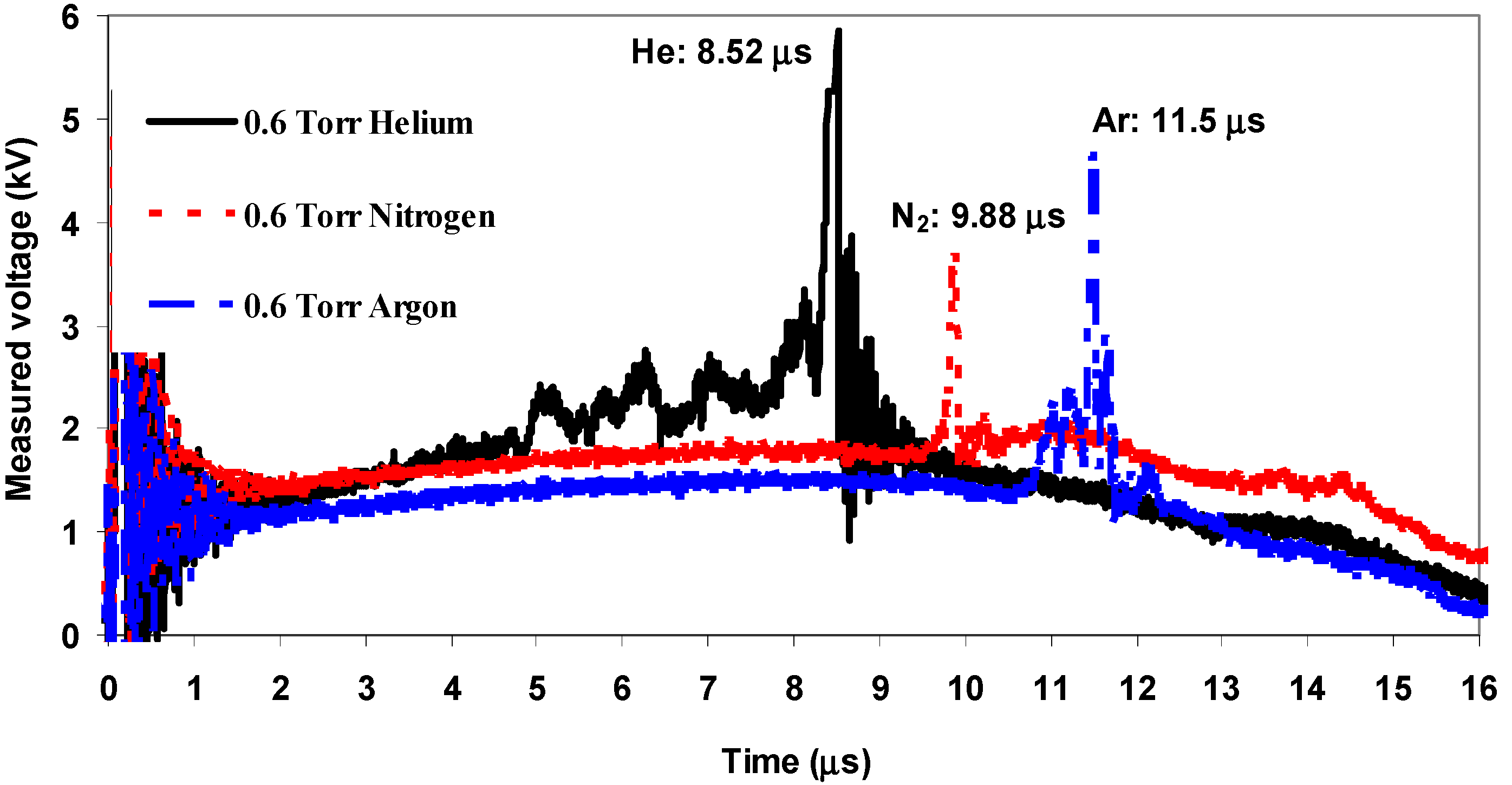
3.2. Plasma Parameters Generated in the AECS PF-1 Device
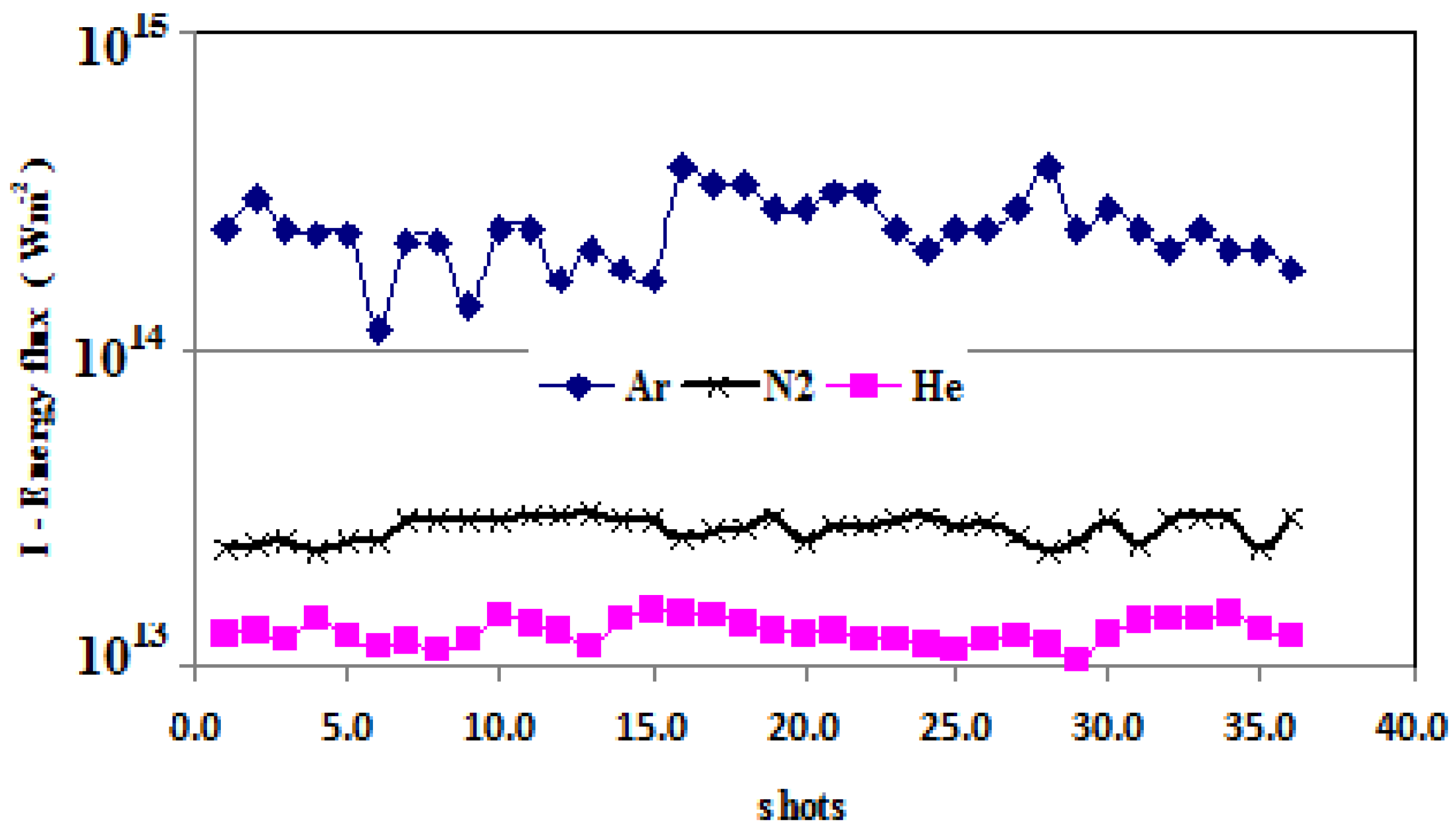
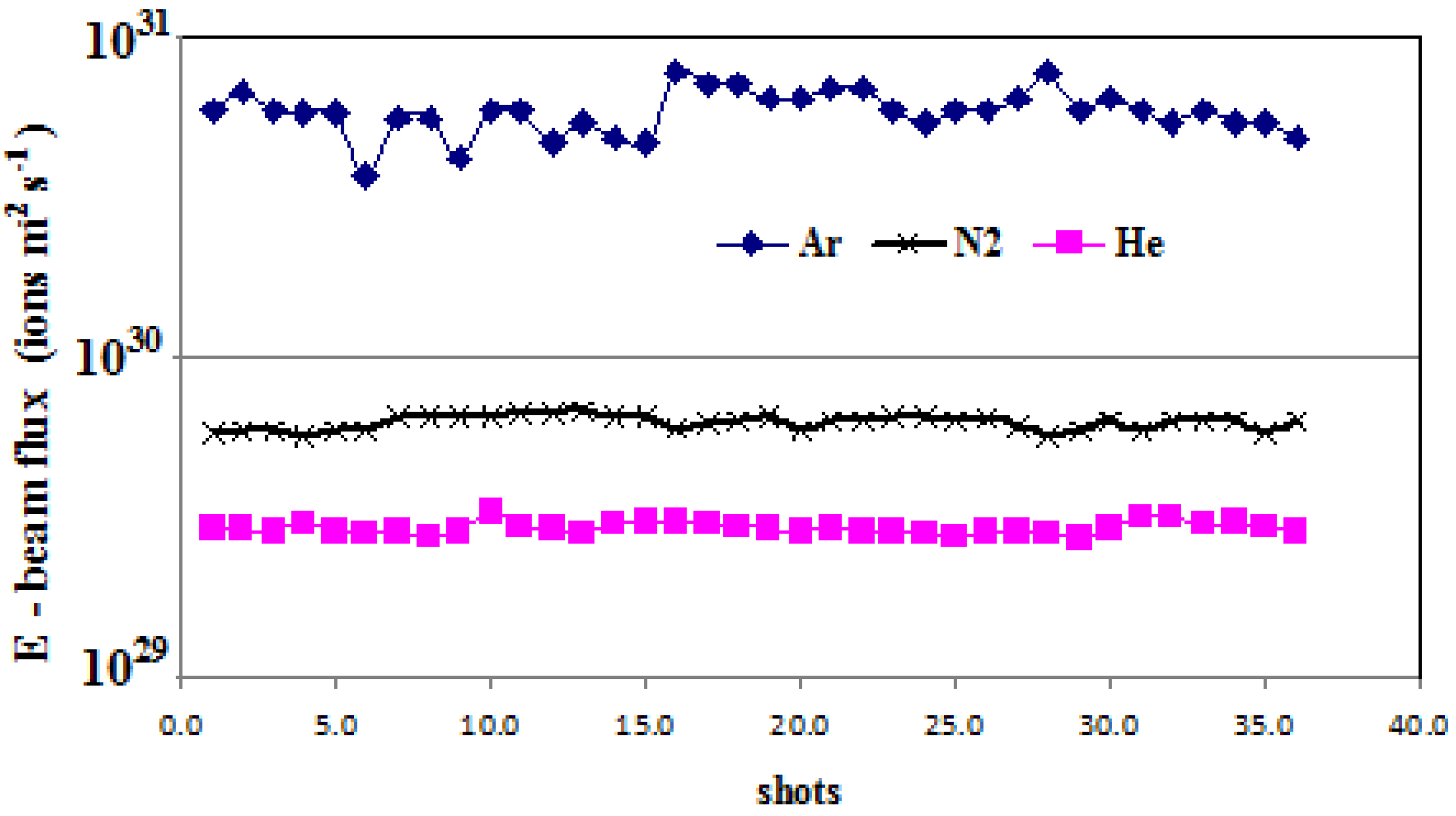
3.3. Ion Beam Properties of the AECS PF-1 Device
3.4. Electron Beam Properties of the AECS PF-1 Device
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Auluck, S.; Kubes, P.; Paduch, M.; Sadowski, M.J.; Krauz, V.I.; Lee, S.; Soto, L.; Scholz, M.; Miklaszewski, R.; Schmidt, H.; et al. Update on the Scientific Status of the Plasma Focus. Plasma 2021, 4, 450–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, K.; Kaneko, I.; Shimoda, K.; Yamamoto, T. A method for measuring electron energy distribution in a plasma focus. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 29, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Lin, J.; Patran, A.; Wong, D.; Hassan, S.M.; Mahmood, S.; White, T.; Tan, T.L.; Springham, S.V.; Lee, S.; et al. Optimization of a plasma focus device as an electron beam source for thin film deposition. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2007, 16, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.; Lim, L.K.; Yap, S.L.; Wong, C.S. Imperative function of electron beams in low-energy plasma focus device. Pramana J. Phys. 2015, 85, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.; Ling, Y.S.; Yaqoob, I.; Kumar, N.N.; Kuang, L.L.; San, W.C. Effects of different mineral admixtures on the properties of fresh concrete. Scient. World J. 2014, 2014, 240729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartari, A.; Da, A.R.; Bonifazzi, C.; Marziani, M. Formation of Nano-Crystalline Phase in Hydrogenated Amorphous Silicon Thin Film by Plasma Focus Ion Beam Irradiation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2004, 213, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowski, L.; Sadowski, M.J. Hot-spots in plasma-focus discharges as intense sources of different radiation pulses. Braz. J. Phys. 2002, 32, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouzo, J.; Acuna, H.; Milanese, M.; Moroso, R. Relativistic electron beams detection in a dense plasma focus. Eur. Phys. J. D 2002, 21, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patran, A.; Stoenescu, D.; Rawat, R.S.; Springham, S.V.; Tan, T.L.; Tan, L.C.; Rafique, M.S.; Lee, P.; Lee, S. A magnetic electron analyzer for plasma focus electron energy distribution studies. J. Fusion Energy 2006, 25, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Saw, S.H.; Ali, J. Numerical experiments on radiative cooling and collapse in plasma focus operated in krypton. J. Fusion Energy 2013, 32, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akel, M.; Lee, S. Radiative Collapse in Plasma Focus Operated with Heavy Noble Gases. J. Fusion Energy 2013, 32, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akel, M.; Lee, S.; Saw, S.H. Numerical Experiments in Plasma Focus Operated in Various Gases. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2012, 40, 3290–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Saw, S.H. Plasma focus ion beam fluence and flux—For various gases. Phys. Plasmas 2013, 20, 062702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, H.A.R.; Khan, I.A.; Ikhlaq, U.; Hussnain, A. Variation of ion energy flux with increasing working gas pressures using faraday cup in plasma focus device. J. Nat. Sci. Math. 2008, 48, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.; Qayyum, A.; Ahmad, R.; Murtaza, G.; Zakaullah, M. Nitriding of titanium by using an ion beam delivered by a plasma focus. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.R.; Neog, N.K.; Bhuyan, H.; Rout, R.K.; Rawat, R.S.; Lee, P. Effect of anode designs on ion emission characteristics of a plasma focus device. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 46, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, H.; Lepone, A.; Marquez, A.; Sadowski, M.J.; Baranowski, J.; Skladnik-Sadowska, E. Analysis of the nitrogen ion beam generated in a low-energy plasma focus device by a Faraday cup operating in the secondary electron emission mode. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 1998, 26, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, M.; Habibi, M.; Yousefi, H.R.; Roshani, G.H. Angular Distribution Analysis of Nitrogen Ions in a Low Energy Dense Plasma Focus Device. Contrib. Plasma Phys. 2013, 53, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feugeas, J.N.; Sanchez, G.; De Gonzalez, C.; Hermida, J.D.; Scordia, G. Pulsed ion implantation of nitrogen in pure titanium. Rad. Rad. Eff. Defects Solids 1993, 25, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Habibi, M. Angular distribution of ion beam emitted from a 3.5 kJ plasma focus device using different shapes of anodes. Phys. Lett. A 2016, 380, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. Radiative Dense Plasma Focus Computation Package: RADPF. Available online: https://www.plasmafocus.net (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Gribkov, V.A.; Banaszak, A.; Bienkowska, B.; Dubrovsky, A.V.; Ivanova-Stanik, I.; Jakubowski, L.; Karpinski, L.; Miklaszewski, R.A.; Paduch, M.; Sadowski, M.J.; et al. Plasma dynamics in the PF-1000 device under full-scale energy storage: II. Fast electron and ion characteristics versus neutron emission parameters and gun optimization perspectives. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 3592–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pimenov, V.N.; Elena, V.; Demina, S.A.; Maslyaev, L.; Ivanov, I.; Vladimir, A.; Gribkov, A.V.; Dubrovsky, Ü.; Ugaste, T.; Laas, M.S.; et al. Damage and modification of materials produced by pulsed ion and plasma streams in Dense Plasma Focus device. Nukleonika 2008, 53, 111–121. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Saw, S.H. Plasma focus ion beam fluence and flux—Scaling with stored energy. Phys. Plasmas 2012, 19, 112703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akel, M.S.; Salo, A.; Saw, S.H.; Lee, S. Properties of Ion Beams Generated by Nitrogen Plasma Focus. J. FusionEnergy 2014, 33, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akel, M.S.; Salo, A.; Saw, S.H.; Lee, S. Ion Beam Features Produced by Two Plasma Focus Machines Operated with Different Gases. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2014, 42, 2202–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akel, M.S.; Salo, A.; Saw, S.H.; Lee, S. Electron Beam Properties Emitted From Deuterium Plasma Focus: Scaling Laws. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2017, 45, 2303–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akel, M.; AL-Hawat, S.; Lee, S.; Saw, S.H. Characterization of electron beams emitted from dense plasma focus machines using argon, neon and nitrogen. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 32, 1850397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hawat, S. Axial velocity measurement of current sheath in a plasma focus device using a magnetic probe. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2004, 32, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hawat, S.; Soukieh, M.; Abou Kharoub, M.; Al-Sadat, W. Using Mather-type plasma focus device for surface modification of AISI304 steel. Vacuum 2010, 84, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hawat, S.; Akel, M.; Saw, S.H.; Lee, S. Model parameters vs. gas pressure in two different plasma focus devices operated in Argon and Neon. J. Fusion Energy 2012, 31, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. Plasma focus radiative model: Review of the Lee model code. J. Fusion Energy 2014, 33, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Operating Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Capacitance | 25 µF |
| Operating charging voltage | 15 kV |
| Stored energy (E0) | 2.8 kJ |
| Peak discharge current | 54 kA |
| Inductance of circuit | 1400 nH |
| Anode length | 16 cm |
| Anode radius | 0.95 cm |
| Cathode radius | 3.2 cm |
| Rise time of the current | ~10 μs |
| Working gases | Nitrogen, argon, and helium |
| AECS PF-1 | He | N2 | Ar |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average of 36 Shots | Average of 36 Shots | Average of 36 Shots | |
| Peak current Ipeak (kA) | 50 | 53 | 55 |
| Pinch current Ipinch (kA) | 34 | 36 | 34 |
| Plasma temperature Te, (eV) | 350 | 105 | 126 |
| pinch radius rp (cm) | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.03 |
| Length of the pinch zp (cm) | 1.4 | 1.35 | 1.65 |
| Pinch duration τ (ns) | 11.2 | 13.8 | 17 |
| Induced voltage Vmax (kV) | 5.7 | 6 | 21.7 |
| Plasma density Ni (×1023 m−3) | 0.7 | 2.3 | 9.1 |
| The peak axial speed Va (cm/μs) | 4.5 | 2.5 | 2.1 |
| The shock speed Vs (cm/μs) | 24 | 14.4 | 11.4 |
| The peak radial piston speed Vp (cm/μs) | 16.5 | 10.2 | 9 |
| AECS PF-1 | He | N2 | Ar |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average of 36 Shots | Average of 36 Shots | Average of 36 Shots | |
| Ion beam(IB) fluence (×1020 m−2) | 0.3 | 0.22 | 1.1 |
| Ion flux (×1027 m−2 s−1) | 2.4 | 1.6 | 6.6 |
| Ion energy (keV) | 35 | 105 | 223 |
| En fluence (×106 J m−2) | 0.14 | 0.37 | 4.1 |
| En flux (×1014 Wm−2) | 0.13 | 0.27 | 2.4 |
| Ion number (×1013) | 13 | 6.2 | 3.8 |
| IB energy (J) | 0.75 | 1.05 | 1.34 |
| IB energy (%E0) | 0.025 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| IB current (kA) | 3.8 | 4.1 | 3.6 |
| IB current (%Ipeak) | 8 | 7.75 | 6.5 |
| IB curr. den. (×1010 A m−2) | 0.1 | 0.15 | 1.1 |
| Damage factor (×1010 Wm−2s0.5) | 0.14 | 0.32 | 3.1 |
| AECS PF-1 | He | N2 | Ar |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average of 36 Shots | Average of 36 Shots | Average of 36 Shots | |
| Electron beam (EB) fluence (×1022 m−2) | 0.35 | 0.86 | 9.7 |
| EB flux (×1030 m−2 s−1) | 0.3 | 0.62 | 5.9 |
| The kinetic energy of the relativistic electrons Erel (keV) | 18 | 19.5 | 23.1 |
| Energy fluence (×108 J m−2) | 0.1 | 0.27 | 3.73 |
| Energy flux (Heat flux) (×1016 Wm−2) | 0.09 | 0.2 | 2.2 |
| Electron number (×1014) | 2.7 | 3.99 | 5.48 |
| EB energy (J) | 0.78 | 1.25 | 2 |
| EB energy (%E0Stored energy) | 0.028 | 0.045 | 0.072 |
| EB current (kA) | 3.9 | 4.6 | 5.2 |
| EB current (%Ipeak) | 8.12 | 8.78 | 9.36 |
| EB curr. den. (×1011 A m−2) | 0.47 | 1 | 9.4 |
| Damage factor (×1012 Wm−2 s0.5) | 0.1 | 2.3 | 2.87 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akel, M.; AL-Hawat, S.; Ahmad, M.; Ballul, Y.; Shaaban, S. Features of Pinch Plasma, Electron, and Ion Beams That Originated in the AECS PF-1 Plasma Focus Device. Plasma 2022, 5, 184-195. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma5020014
Akel M, AL-Hawat S, Ahmad M, Ballul Y, Shaaban S. Features of Pinch Plasma, Electron, and Ion Beams That Originated in the AECS PF-1 Plasma Focus Device. Plasma. 2022; 5(2):184-195. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma5020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkel, Mohamad, Sharif AL-Hawat, Muthanna Ahmad, Yamen Ballul, and Soliman Shaaban. 2022. "Features of Pinch Plasma, Electron, and Ion Beams That Originated in the AECS PF-1 Plasma Focus Device" Plasma 5, no. 2: 184-195. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma5020014
APA StyleAkel, M., AL-Hawat, S., Ahmad, M., Ballul, Y., & Shaaban, S. (2022). Features of Pinch Plasma, Electron, and Ion Beams That Originated in the AECS PF-1 Plasma Focus Device. Plasma, 5(2), 184-195. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma5020014






