Effect of Electrode Profile and Polarity on Performance of Pressurized Sparkgap Switch
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
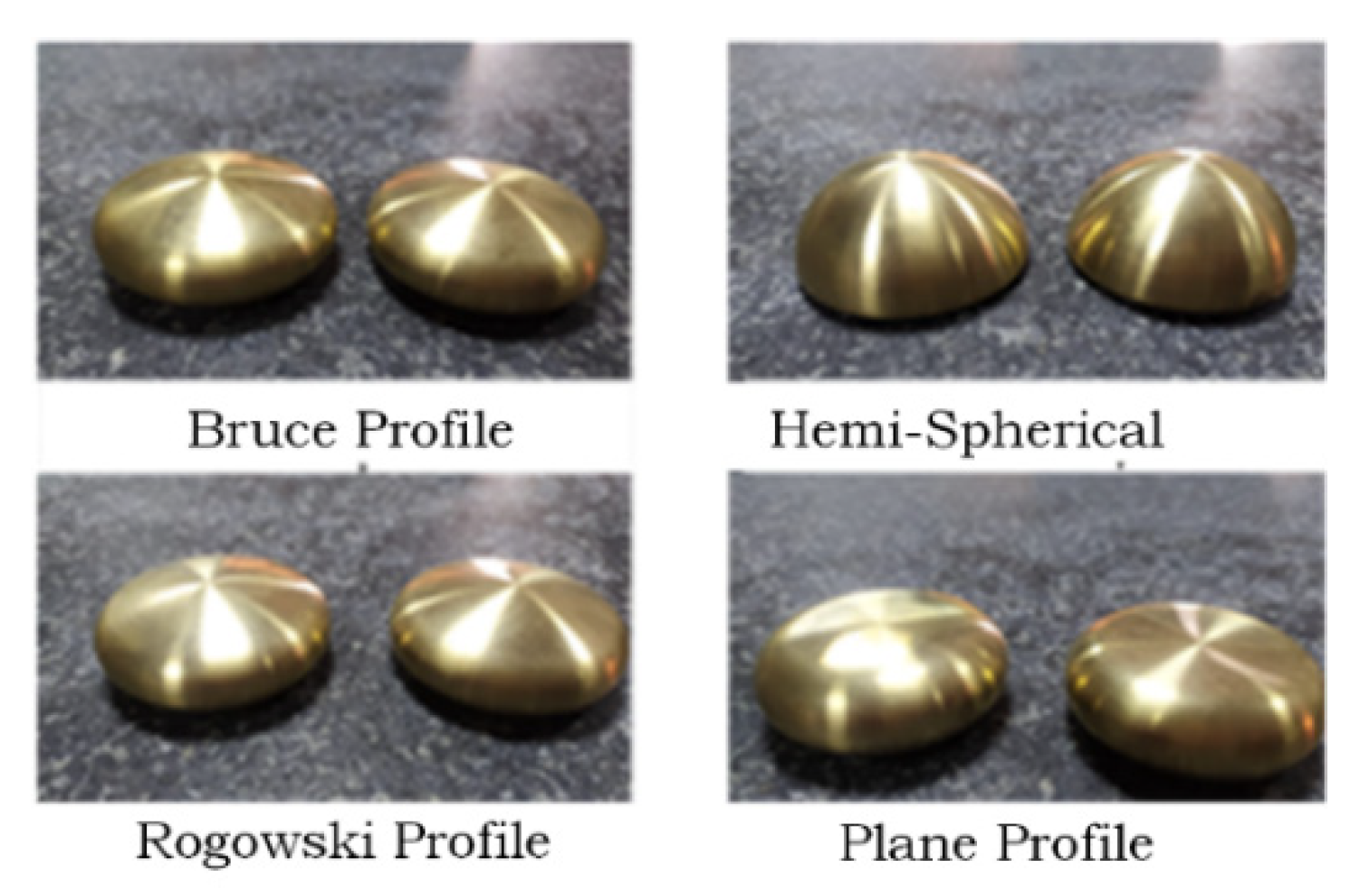
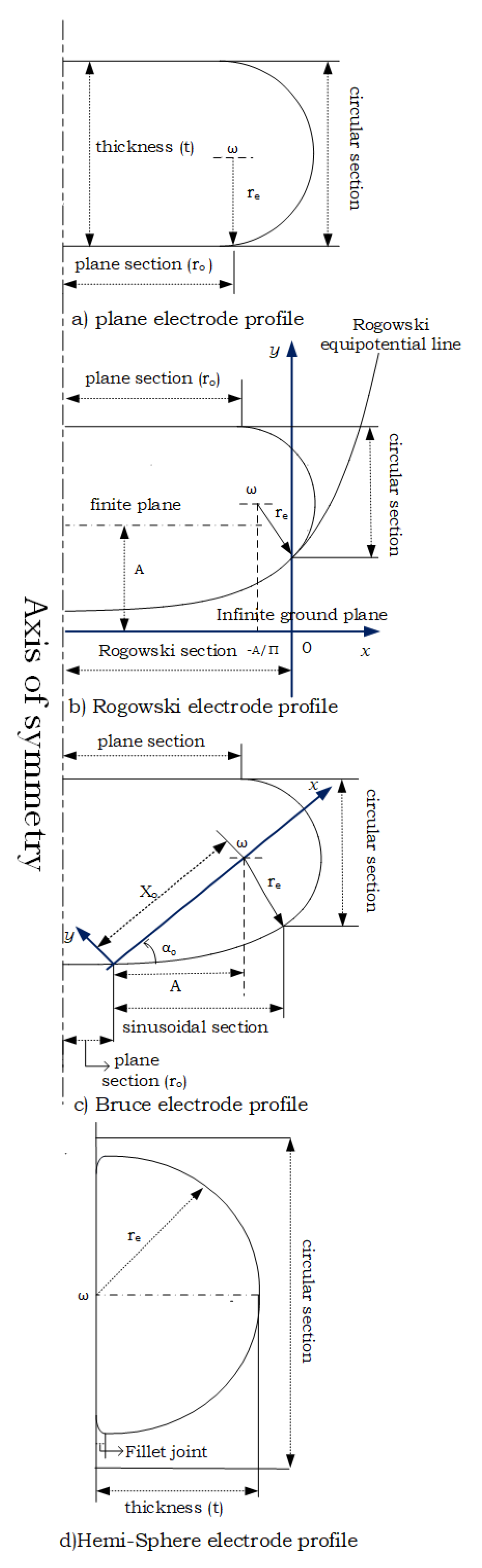
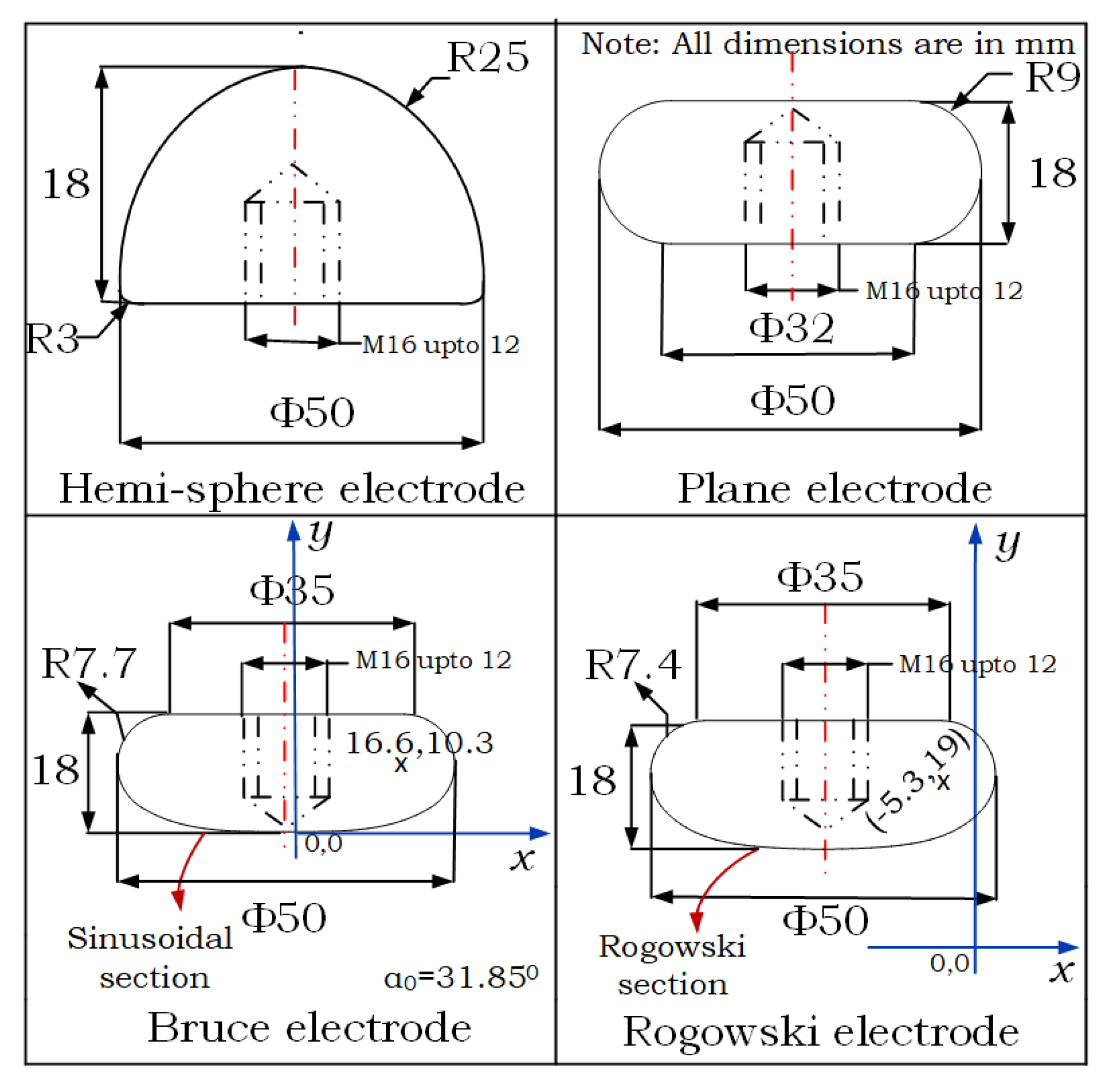
2.1. Test Electrode Configuration
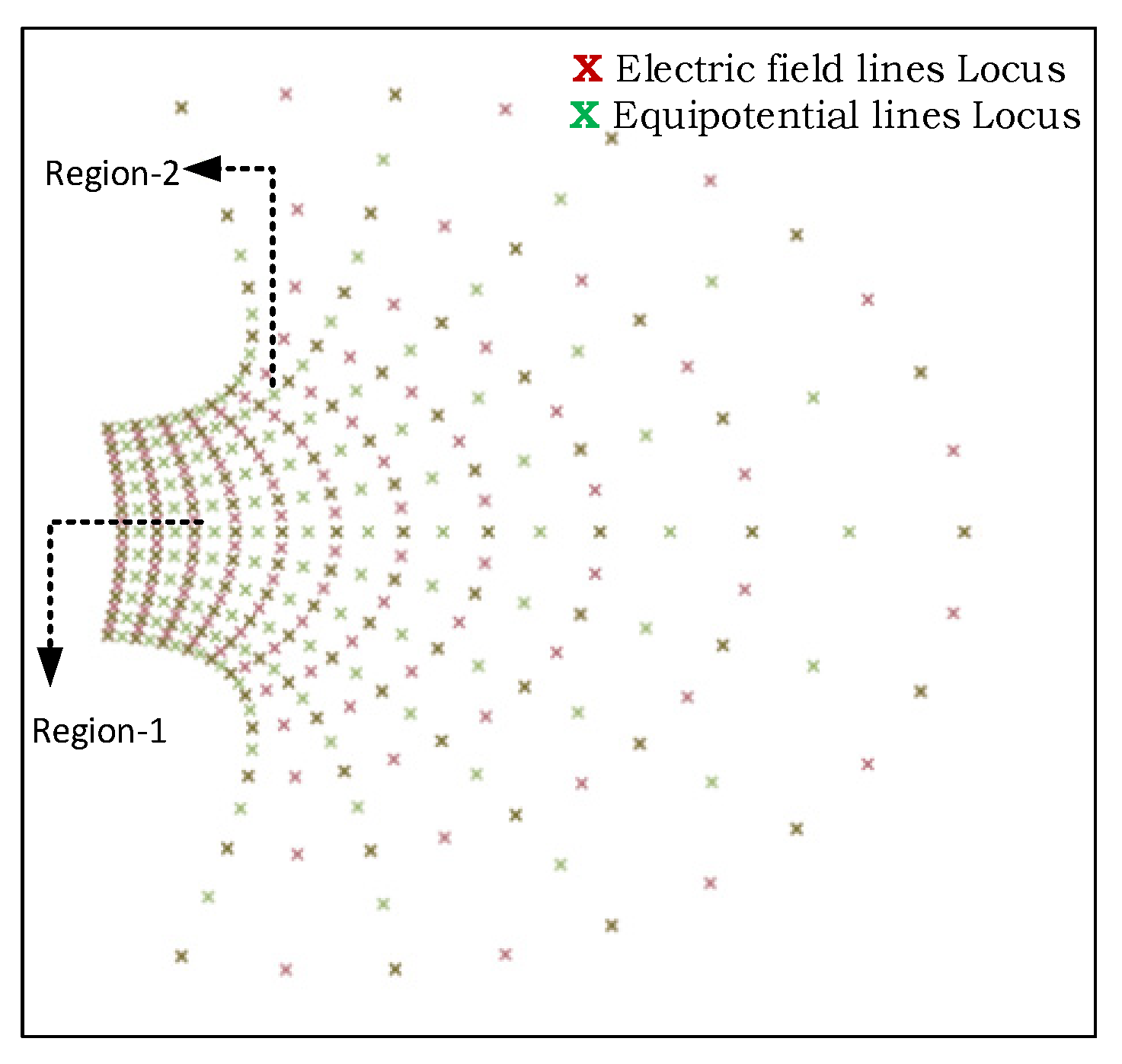
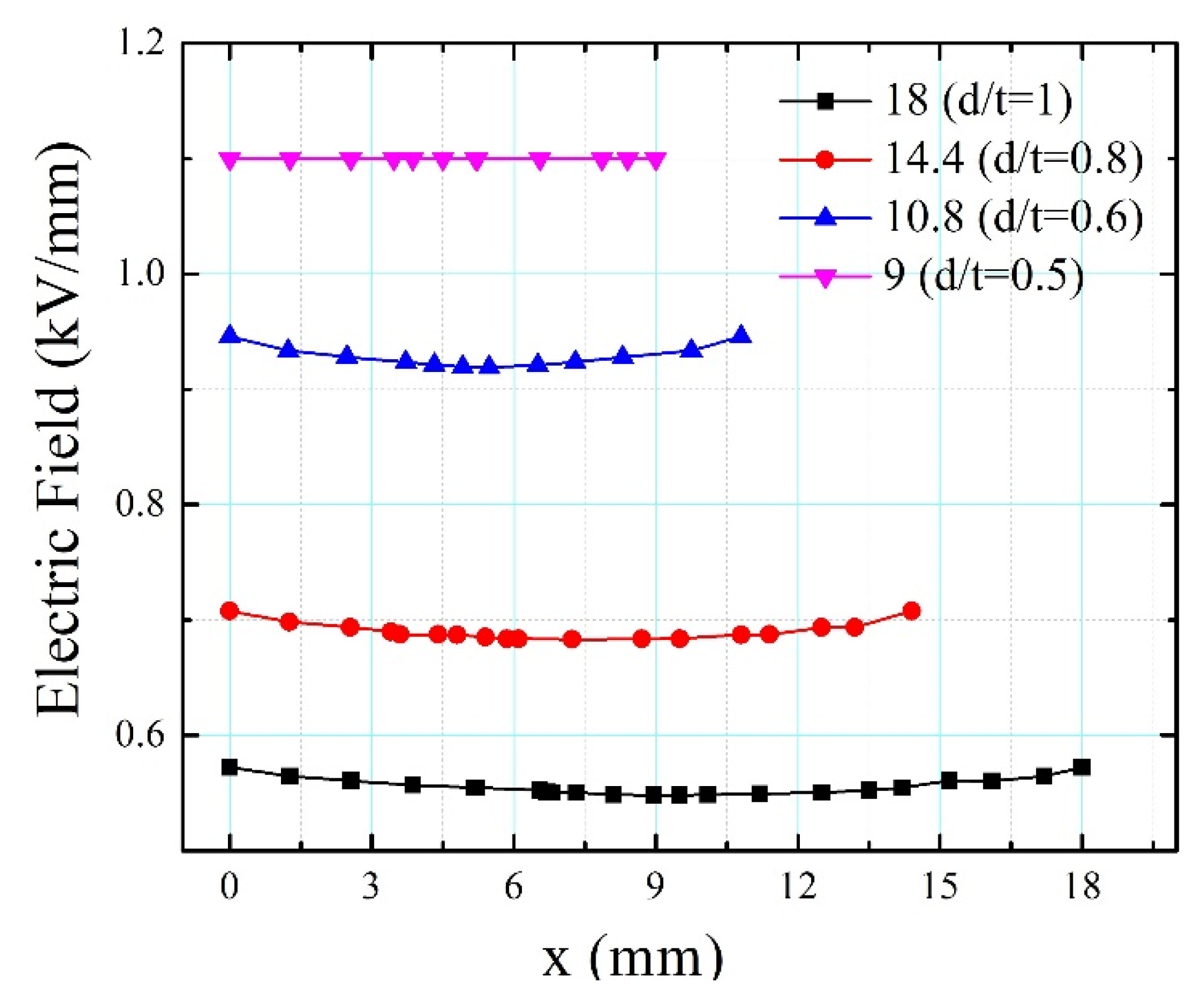
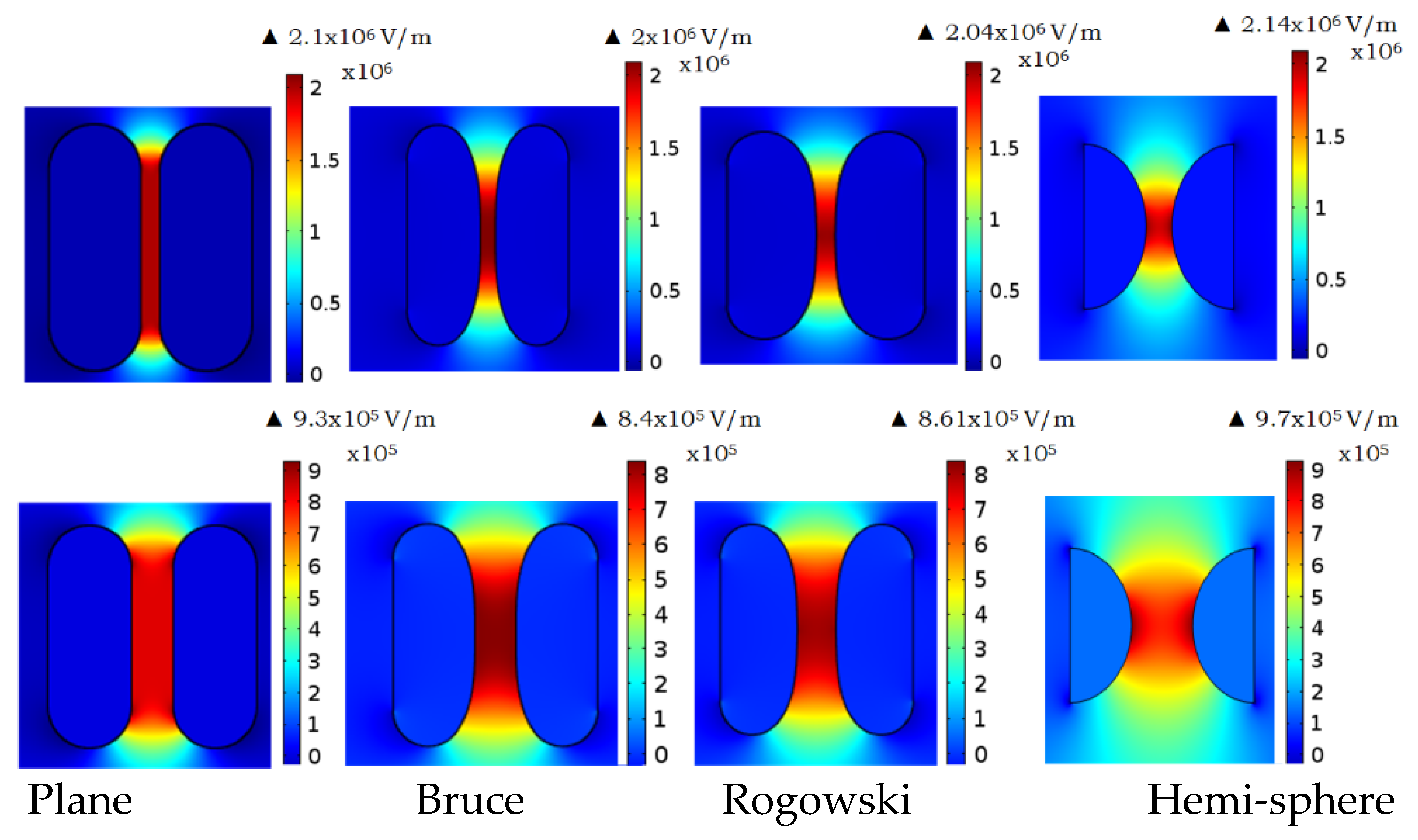
2.2. Simulation Results and Analysis
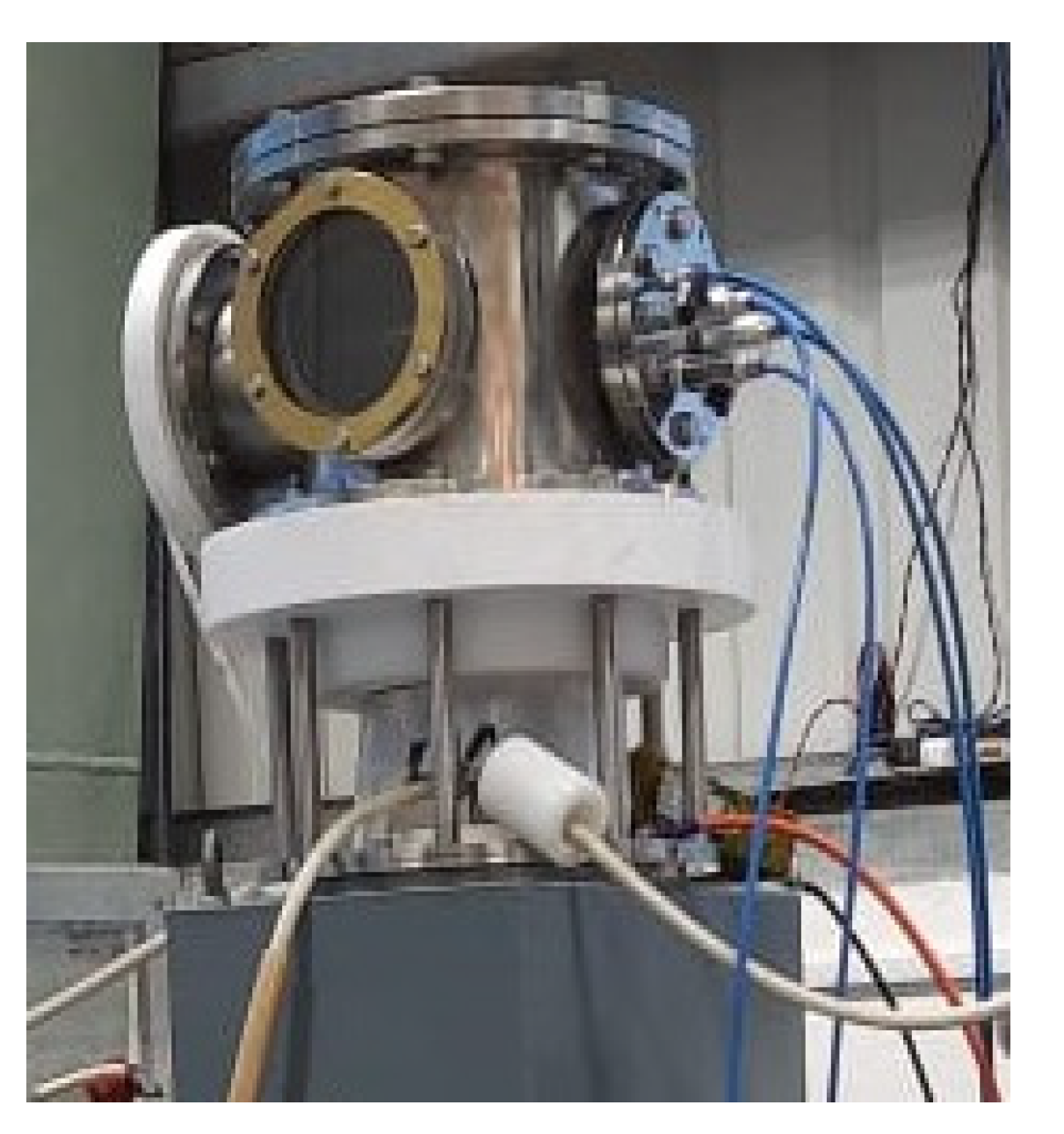
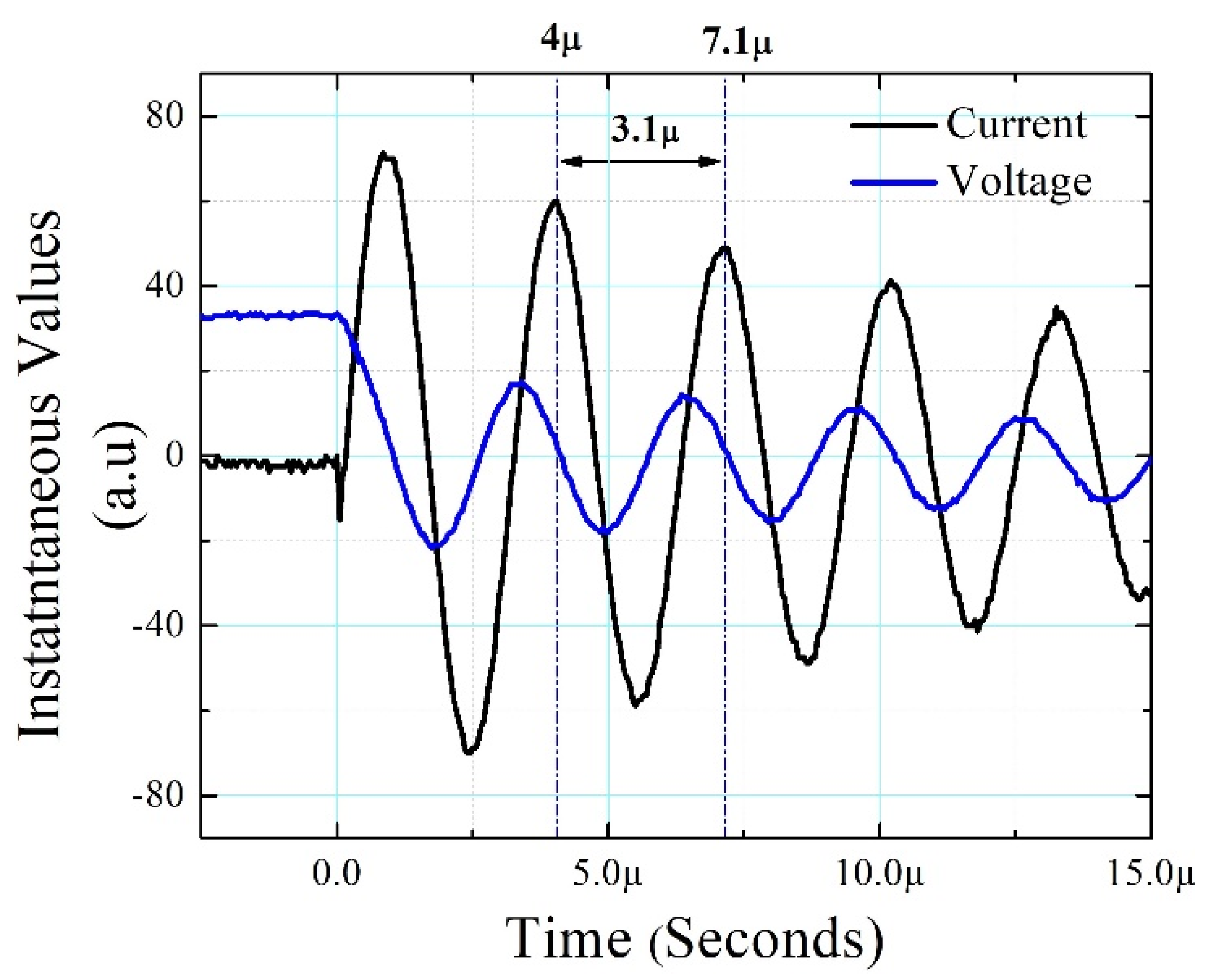
2.3. Experimental Setup and Diagnostics
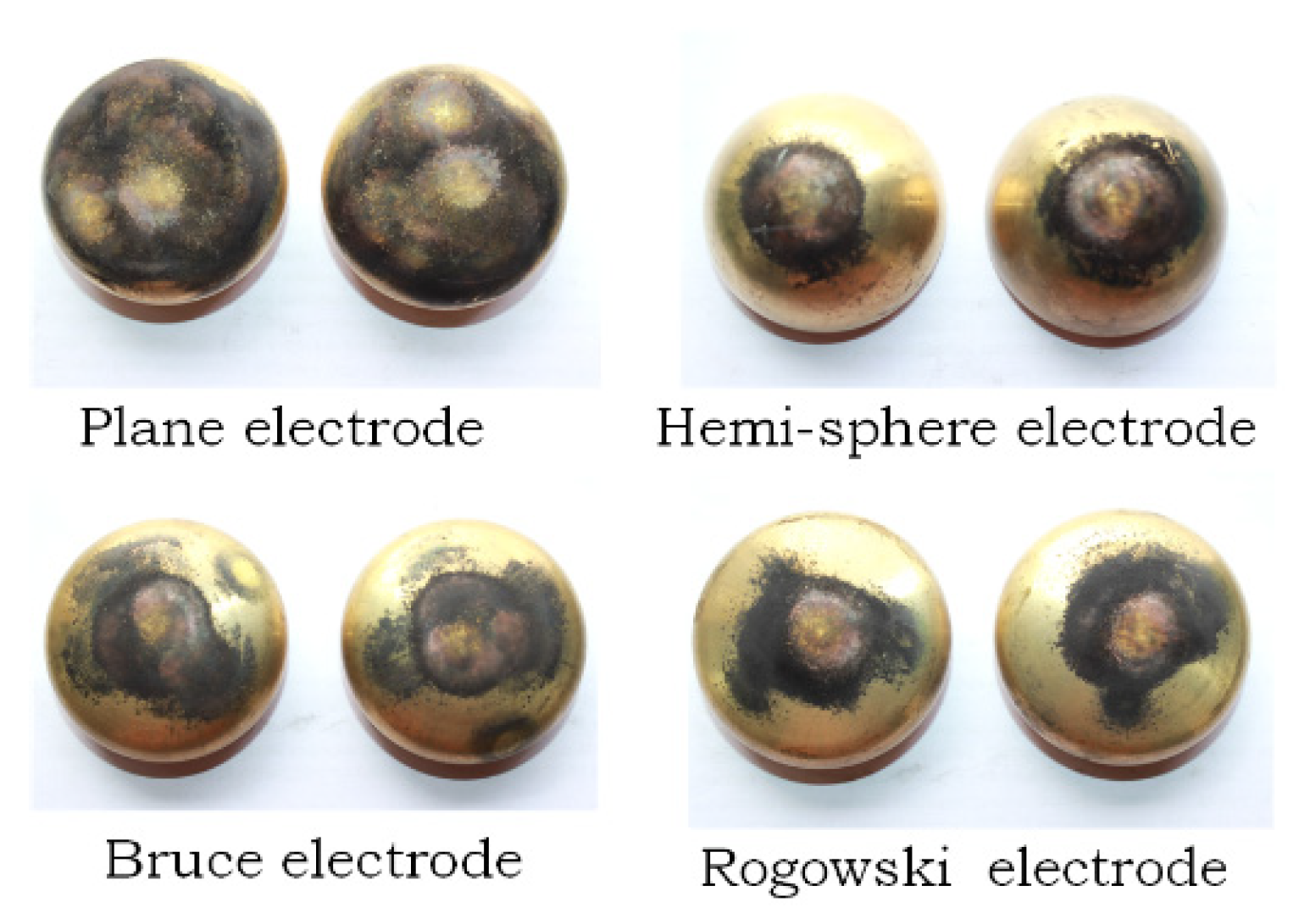
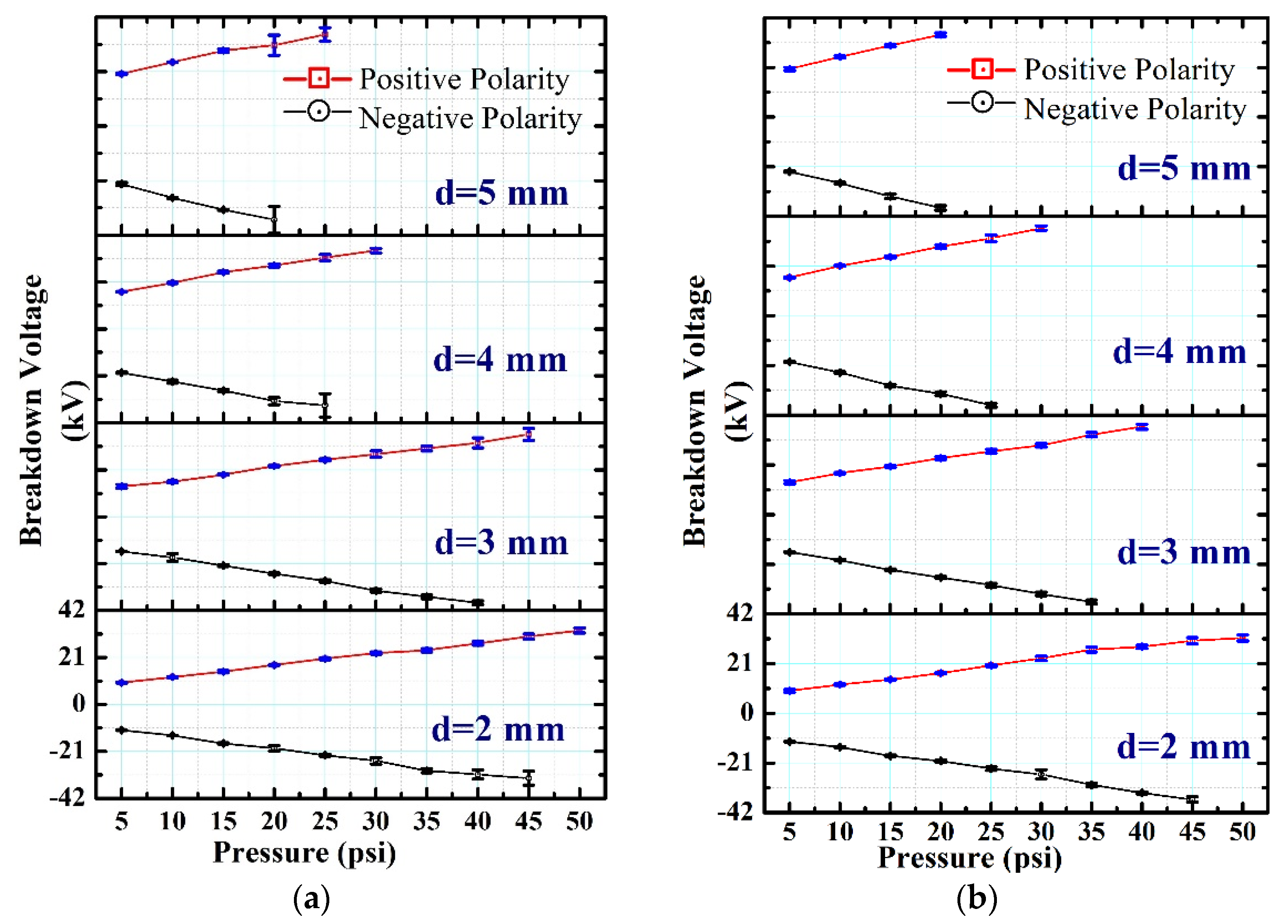
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- The analysis of spatial electric field distribution provides a generalized criterion for choosing major dimensions of sparkgap electrode and gap length to ensure uniform field in the inter-electrode region. Experimental investigation performed on four different types of electrode profiles mainly reveals the comparison of stability in breakdown characteristics of each profile so that their suitability is independently judged for use in appropriate operating voltage range.
- To ensure uniform electric field in the discharge gap region d/t ≤ 0.5 (this results in a stable breakdown behavior as electric field is more focused in the discharge region rather than at edges).
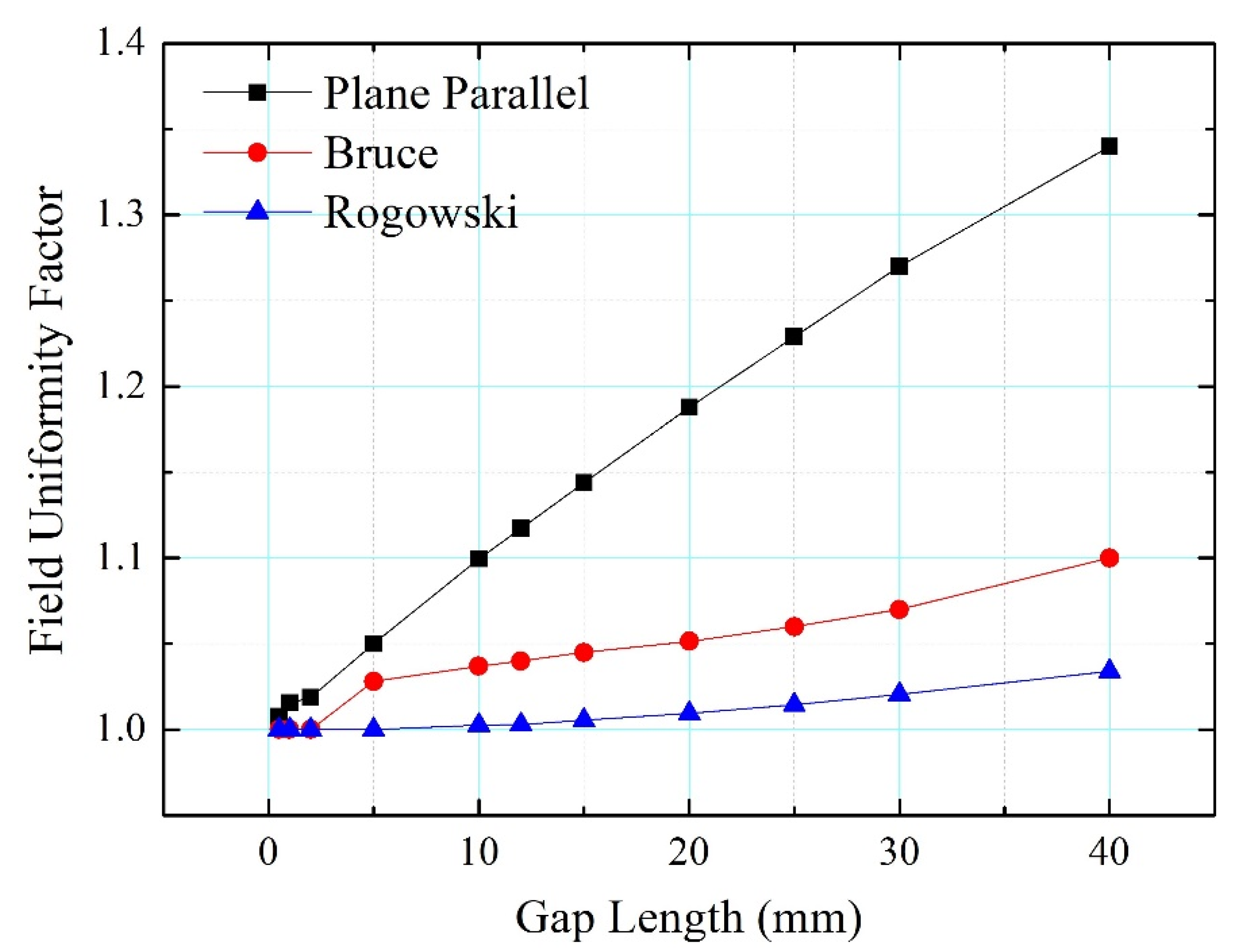
- The variation of field uniformity factor η with inter-electrode gap length d dictates the breakdown behavior of sparkgap. With increase in the gap length, very steep raise, moderate change, and marginal variation in η is observed for plane parallel, Bruce, and Rogowski profiles respectively. As a result, even in the widest range of gap lengths Rogowski profile exhibits uniform electric field resulting in most stable breakdown behavior as compared to the remaining profiles.
- In Hemi-sphere electrode profile, η improves with increase in gap length and hence it is a preferred choice in applications where large gap length is required to obtain very high hold-off voltage.
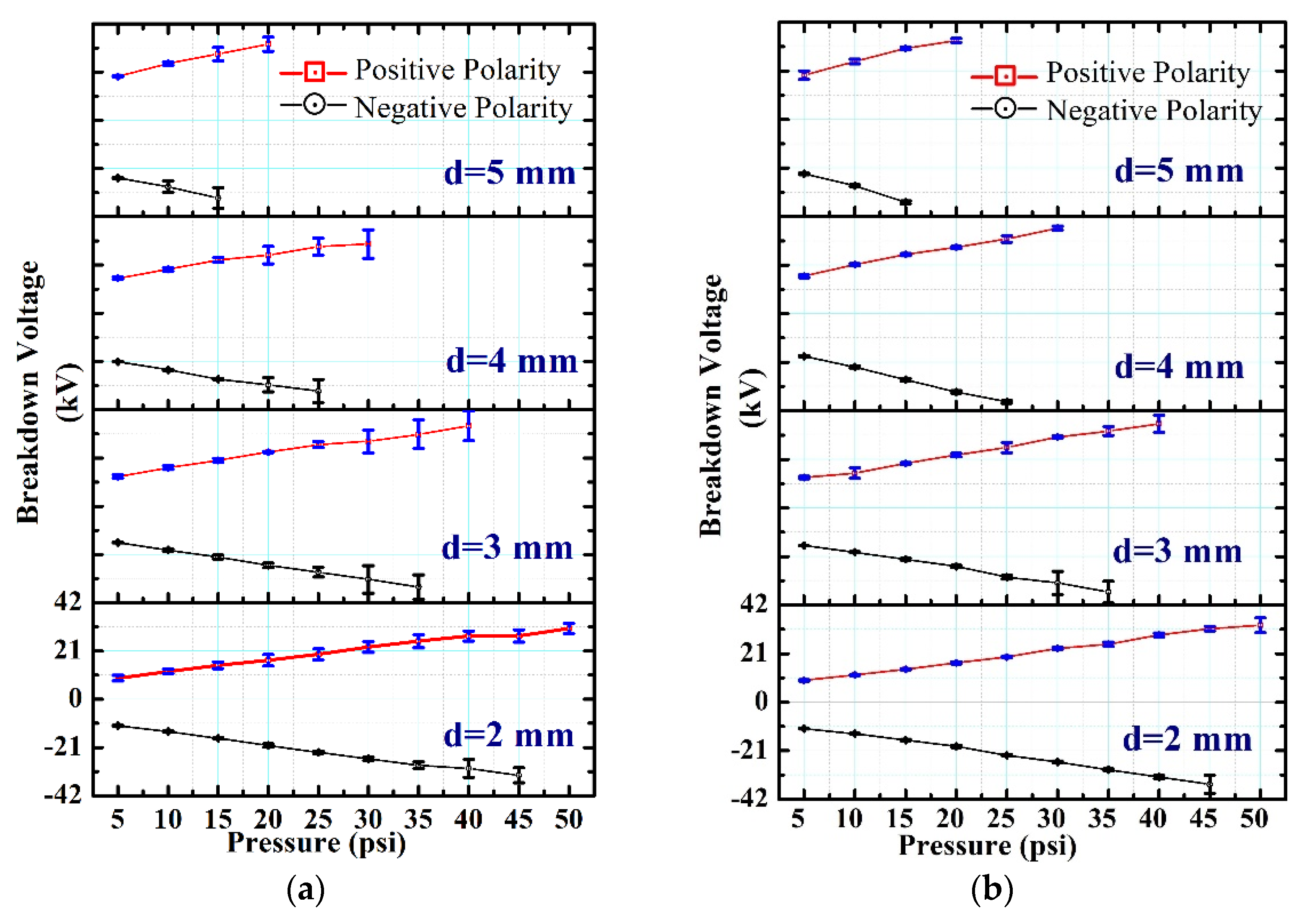
- Experimental investigation on the effect of polarity evidences higher SBV in all cases with negative polarity as a consequence of space charge build-up in the discharge gap. However, the extent of difference in SBV was found to be pressure dependent.
- In the time-resolved investigation of breakdown delay with positive and negative polarity it was recurrently noticed that switch closure is marginally fast with positive bias as a consequence of higher propagation velocity of positive streamer than the negative streamer.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bluhm, H. Pulsed Power Systems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Ren, J.; Li, J. Repetitive Gas-Discharge Closing Switches for Pulsed Power Applications. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2019, 47, 4237–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, J.S.; Harrison, J.A. A uniform field electrode for use in a discharge chamber of restricted size: Design and performance. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1969, 2, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.Y. Improved Uniform-Field Electrode Profiles for TEA Laser and High-Voltage Applications. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1973, 44, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva, I.; Guerra, J. Design Note: A compacted Ernst-electrodes profile for pulsed high-pressure lasers. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, N1–N2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raote, P.; Patil, G.; Prasad, M.B.S.; Nilaya, J.P.; Biswas, J.D. Switch-less operation of a TEA CO2 laser with extended electrodes. Opt. Commun. 2008, 281, 2213–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezh, A. Practical approach for the design of uniform-field electrodes in transversely excited CO2 lasers. Appl. Opt. 2021, 60, 4690–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anufrik, S.S.; Volodenkov, A.P.; Znosko, K.F. Selection of electrodes profile for excimer lasers. In Proceedings of the 2010 10th International Conference on Laser and Fiber-Optical Networks Modeling, Sevastopol, Ukraine, 12–14 September 2010; pp. 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, G.G.; Loeb, L.B. Streamer Mechanism and Main Stroke in the Filamentary Spark Breakdown in Air as Revealed by Photomultipliers and Fast Oscilloscopic Techniques. Phys. Rev. 1961, 123, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujotzek, M.; Seeger, M.; Schmidt, F.; Koch, M.; Franck, C. Experimental investigation of streamer radius and length in SF6. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 245201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, L.B. Streamer Breakdown and Sparking Thresholds. Phys. Rev. 1951, 81, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, F.; Pfeiffer, W.; Wang, G.; He, R. Study of Formation and Propagation of Streamers in SF6 and Its Gas Mixtures with Low Content of SF6 Using a One-Dimensional Fluid Model. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2012, 14, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- El-Hawary, H.H.; Abdel-Salam, M.; Hashem, A.A.-R.; Turky, A.-H.A. A New Computer Simulation of Avalanche Evolution and Its Transition Into Anode- and Cathode-Directed Streamers in Short Uniform Field Gaps. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2020, 48, 3740–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, S.; Han, Y.; Cressault, Y. Experimental studies on power frequency breakdown voltage of CF3I/N2 mixed gas under different electric fields. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 92901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sham, N.M.B.; Zahid, N.Z.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Jamail, N.A.M.; Abd-Rahman, R. Breakdown Characteristic of N2- CO2 Gas Mixtures under AC and DC Test Voltages. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1874, 12027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffel, E.; Zaengal, W.S. High Voltage Engineering Fundamentals, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Woburn, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gibert, A.; Dupuy, J.; Domens, P.; Riquel, G.; Hutzler, B. Dielectric behaviour of SF6 in non-uniform fields. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1993, 26, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Tarasenko, V.F.; Zhang, C.; Beloplotov, D.S.; Yang, W.; Lomaev, M.I.; Zhou, Z.; Sorokin, D.A.; Yan, P. Abnormal polarity effect in nanosecond-pulse breakdown of SF6 and N2. Phys. Lett. A 2014, 378, 1828–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, R.W.; Wilson, M.P.; MacGregor, S.J.; Timoshkin, I.V.; Given, M.J.; Wang, T. Characterization and Statistical Analysis of Breakdown Data for a Corona-Stabilized Switch in Environmentally Friendly Gas Mixtures. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2018, 46, 3557–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korasli, C.; Farish, O. Corona and Breakdown in Coaxial-Electrode Geometry in SF6 and SF6/N2 Mixtures. In Gaseous Dielectrics III.; Christophorou, L.G., Ed.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, Z. Effect of switch parameters and polarity on the repetitive performance of a corona-stabilized switch viewed from behavior of space charge. Phys. Plasmas 2020, 27, 43509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, M.G.; Timoshkin, I.V.; Mcgregor, S.J.; Wilson, M.P.; Given, M.J. Polarity effects on breakdown of short gaps in a point-plane topology in air. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardikyan, K. Breakdown strength of air, SF6 and a mixture of air plus SF6 containing a small amount of SF6. Eur. Trans. Electr. Power 1999, 9, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.P.; Boekhoven, W.; Timoshkin, I.V.; Given, M.J.; MacGregor, S.J.; Wang, T.; Lehr, J.M. Performance of a corona-stabilised switch activated by fast-rising trigger pulses. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Power Modulator and High Voltage Conference (IPMHVC), San Diego, CA, USA, 3–7 June 2012; pp. 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, A.; Yap, D.; Lim, Y.W. Time jitter studies of a corona-stabilised closing switch. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Pulsed Power Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 19–23 June 2011; pp. 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, C. Effect of pressure on repetitive performance of a corona-stabilized plasma closing switch. Phys. Plasmas 2020, 27, 23508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zeng, B.; Cheng, J.; Su, J.; Li, R.; Zhao, L. Experimental Investigation on the Breakdown Voltage Jitter of Corona-Stabilized Switch at Low Repetition Rate. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2017, 45, 2351–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persephonis, P.; Vlachos, K.; Georgiades, C.; Parthenios, J. The inductance of the discharge in a spark gap. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 71, 4755–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesyats, G.A. Pulsed Power and Electronics; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Siahlo, S.E.; Tikhomirov, V. Residual resistance simulation of an air spark gap switch. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.07499. [Google Scholar]
- Bindu, S.; Mangalvedekar, H.A.; Parekh, M.; Sharma, A.; Chakravarthy, D.P.; Mittal, K.C. Electrodynamic Simulation of High-Voltage Peaking Switch. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2012, 40, 3093–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Mishra, E.; Sagar, K.; Meena, M.; Shyam, A. Transmission line transformer for reliable and low-jitter triggering of a railgap switch. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 95117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, N.G. Electrode Design for Testing in Uniform Field Gaps. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1980, PAS-99, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J. A computer study of uniform-field electrodes. Br. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 18, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cst Studio Suite-Electric Field Simulation; Dassault Systèmes Simulia Corp: Vélizy-Villacoublay, France, 2010.
- Guenther, A.H.; Martin, T.H.; Kristiansen, M. J.C. Martin on Pulsed Power; Advances in Pulsed Power Technology Series; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman, H.; Heo, H.; Park, S.S.; Nam, S.H. Design of a SF6 Gas-Filled Spark Gap Switch for High-Voltage Application. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2010, 38, 2758–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayle, P.; Cornebois, B. Propagation of ionizing electron shock waves in electrical breakdown. Phys. Rev. A 1985, 31, 1046–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, R.W.; Bragg, J.K.; Thomas, V.G. Space Charge Formation and the Townsend Mechanism of Spark Breakdown in Gases. Phys. Rev. 1954, 96, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, A.; Ratushnaya, V.; Ebert, U. Positive and negative streamers in ambient air: Modelling evolution and velocities. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 234005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gandi, V.K.; Verma, R.; Warrier, M.; Sharma, A. Effect of Electrode Profile and Polarity on Performance of Pressurized Sparkgap Switch. Plasma 2022, 5, 130-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma5010010
Gandi VK, Verma R, Warrier M, Sharma A. Effect of Electrode Profile and Polarity on Performance of Pressurized Sparkgap Switch. Plasma. 2022; 5(1):130-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma5010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleGandi, Vinod Kumar, Rishi Verma, Manoj Warrier, and Archana Sharma. 2022. "Effect of Electrode Profile and Polarity on Performance of Pressurized Sparkgap Switch" Plasma 5, no. 1: 130-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma5010010
APA StyleGandi, V. K., Verma, R., Warrier, M., & Sharma, A. (2022). Effect of Electrode Profile and Polarity on Performance of Pressurized Sparkgap Switch. Plasma, 5(1), 130-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma5010010





