Generation of Negative Air Ions by Use of Piezoelectric Cold Plasma Generator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. The PCPG Operation Principle
2.2. Setup for NAI Measurement
2.3. Ozone Concentration Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Non-Potted PDD
3.1.1. Influence of Airflow
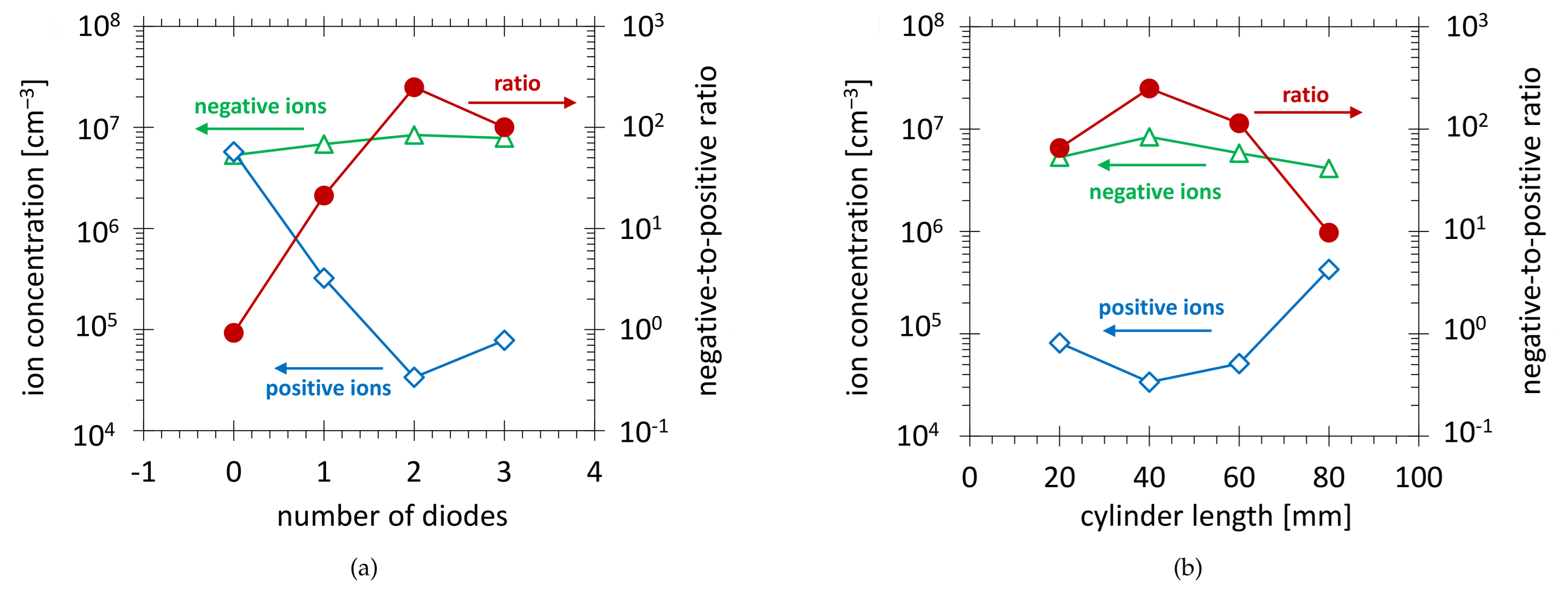
3.1.2. Influence of Number of Diodes
3.1.3. Influence of Cylinder Length
3.2. Potted PCPGs
3.2.1. Potted vs. Non-Potted
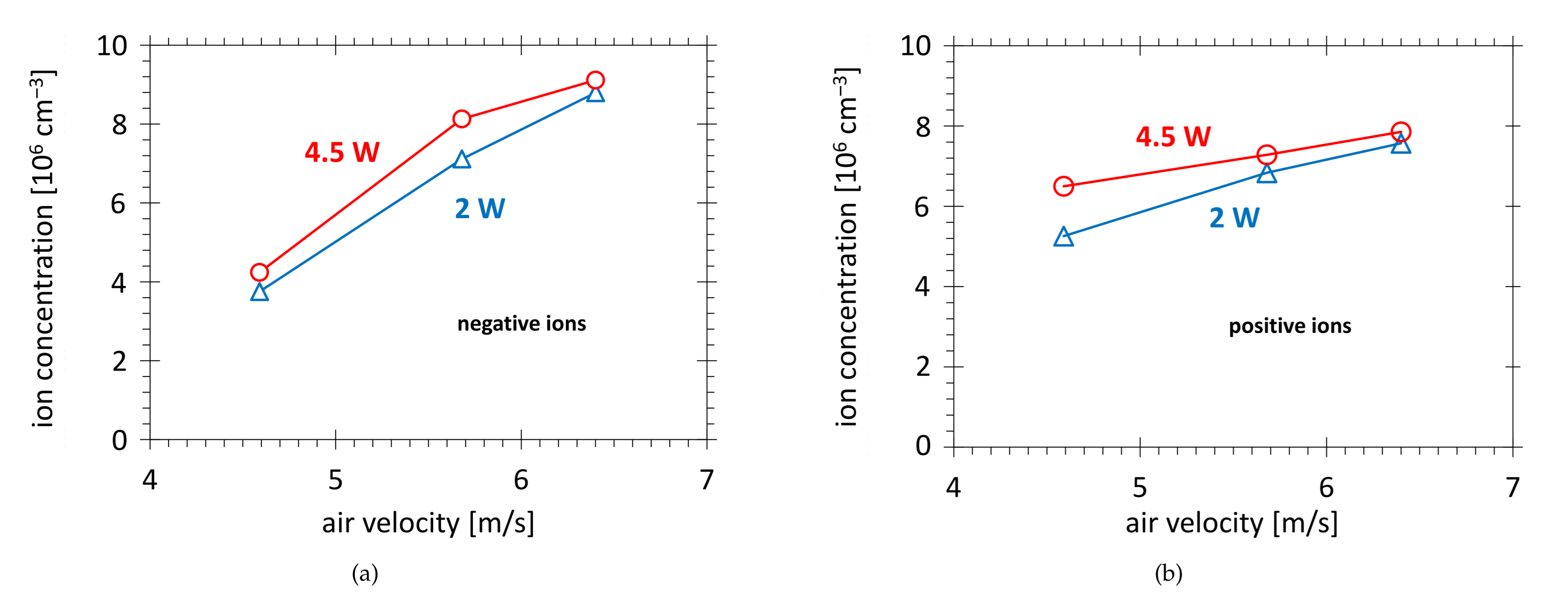
3.2.2. Influence of Power
3.2.3. Ozone Concentration Control
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, S.Y.; Ma, A.; Ramachandran, S. Negative air ions and their effects on human health and air quality improvement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Ma, L.; Xu, X.; Luo, J. Effects of the position reversal of friction pairs on the strength of tribocharging and tribodischarging. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1709.08067. [Google Scholar]
- Beattie, J.K. The mechanism of spray electrification: The waterfall effect. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Zheng, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Deng, C.; Ye, D. Research on generation of negative air ions by plants and stomatal characteristics under pulsed electrical field stimulation. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2017, 19, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.F.; Lin, J.M. Generation and determination of negative air ions. J. Anal. Test. 2017, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.P. Enhancement of the deposition of ultrafine secondary organic aerosols by the negative air ion and the effect of relative humidity. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 62, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, M.; Okuyama, K.; Kousaka, Y. Simple evaluation method of bipolar diffusion charging of aerosol particles and its application to smoke detectors. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1987, 7, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barn, P. Residential Air Cleaner Use to Improve Indoor Air Quality and Health: A Review of the Evidence. National Collaborating Centre for Environmental Health. 2010. Available online: https://www.ncceh.ca/sites/default/files/Air_Cleaners_Oct_2010.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2021).
- Shiue, A.; Hu, S.C.; Tu, M.L. Particles removal by negative ionic air purifier in cleanroom. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2011, 11, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, V.; Meena, G.; Jadhav, D. Effect of negative air ions on fog and smoke. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, V. Removal of particulate matter by using negative electric discharge. Int. J. Eng. Innov. Technol. 2013, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrynin, D.; Friedman, G.; Fridman, A.; Starikovskiy, A. Inactivation of bacteria using dc corona discharge: Role of ions and humidity. New J. Phys. 2011, 13, 103033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, B.W.; King, D.J. Effect of negative air ionization on airborne transmission of Newcastle disease virus. Avian Dis. 1994, 38, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagbom, M.; Nordgren, J.; Nybom, R.; Hedlund, K.O.; Wigzell, H.; Svensson, L. Ionizing air affects influenza virus infectivity and prevents airborne-transmission. Nat. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwama, H. Negative air ions created by water shearing improve erythrocyte deformability and aerobic metabolism. Indoor Air 2004, 14, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, G.; Reischl, G.P. The effect of carrier gas contaminants on the charging probability of aerosols under bipolar charging conditions. J. Aerosol Sci. 2012, 54, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallner, P.; Kundi, M.; Panny, M.; Tappler, P.; Hutter, H.P. Exposure to air ions in indoor environments: Experimental study with healthy adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 14301–14311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, Y.; Pu, J. Negative oxygen ion (NOI) production by enhanced photocatalytic TiO2/GO composites anchored on wooden substrates. Holzforschung 2019, 73, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, L.A.; Gaunt, L.F.; Beggs, C.B.; Shepherd, S.J.; Sleigh, P.A.; Noakes, C.J.; Kerr, K.G. Bactericidal action of positive and negative ions in air. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, S. “On the ionization of air for removal of noxious effluvia” (Air ionization of indoor environments for control of volatile and particulate contaminants with nonthermal plasmas generated by dielectric-barrier discharge). IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2002, 30, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Fujimoto, T.; Kuga, Y.; Sakurai, H.; Seto, T. Characteristics of aerosol charge distribution by surface-discharge microplasma aerosol charger (SMAC). Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manirakiza, E.; Seto, T.; Osone, S.; Fukumori, K.; Otani, Y. High-efficiency unipolar charger for sub-10 nm aerosol particles using surface-discharge microplasma with a voltage of sinc function. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- EPCOS AG. CeraPlas® HF Series. Piezoelectric Based Plasma Generator. Data Sheet. 2018. Available online: https://www.mouser.de/datasheet/2/400/ceraplas-db-1487530.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2021).
- EPCOS AG. Evaluation Kit CeraPlas® HF Driver for CeraPlas® Series. Data Sheet. 2018. Available online: https://www.mouser.de/datasheet/2/400/ceraplas-driving-circuit-user-guide-1487527.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- Britigan, N.; Alshawa, A.; Nizkorodov, S.A. Quantification of ozone levels in indoor environments generated by ionization and ozonolysis air purifiers. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 2006, 56, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakober, C.; Phillips, T. Evaluation of Ozone Emissions from Portable Indoor Air Cleaners: Electrostatic Precipitators and Ionizers; Technical Report; California Environmental Protection Agency: Sacramento, DA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.; Go, D.B. Piezoelectric transformers for low-voltage generation of gas discharges and ionic winds in atmospheric air. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, B.; Hirth, M.; Kogelschatz, U. Ozone synthesis from oxygen in dielectric barrier discharges. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1987, 20, 1421–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzec, D.; Hoppenthaler, F.; Nettesheim, S. Piezoelectric direct discharge: Devices and applications. Plasma 2021, 4, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzec, D.; Hoppenthaler, F.; Shestakov, A.; Burger, D.; Shapiro, A.; Andres, T.; Lerach, S.; Nettesheim, S. Multi-device piezoelectric direct discharge for large area plasma treatment. Plasma 2021, 4, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ON Semiconductor. MUR180E and MUR1100E SWITCHMODE Power Rectifiers Ultrafast E Series with High Reverse Energy Capability. Data Sheet. 2006. Available online: https://datasheet.octopart.com/MUR1100EG-ON-Semiconductor-datasheet-598048.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- Molina, L.T.; Molina, M.J. Absolute absorption cross sections of ozone in the 185- to 350-nm wavelength range. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 14501–14508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daumont, D.; Brion, J.; Charbonnier, J.; Malicet, J. Ozone UV spectroscopy I: Absorption cross-section at room temperautre. J. Atmos. Chem. 1992, 15, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchin, A.; Ehrhart, S.; Leppä, J.; Nieminen, T.; Gagné, S.; Schobesberger, S.; Wimmer, D.; Duplissy, J.; Riccobono, F.; Dunne, E.M.; et al. Experimental investigation of ion–ion recombination under atmospheric conditions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 7203–7216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppä, J.; Anttila, T.; Kerminen, V.M.; Kulmala, M.; Lehtinen, K.E.J. Atmospheric new particle formation: Real and apparent growth of neutral and charged particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4939–4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrov, N.; Anokhin, E.; Kindysheva, S.; Kirpichnikov, A.; Kosarev, I.; Nudnova, M.; Starikovskaia, S.; Starikovskii, A. Plasma decay in air and O2 after a high-voltage nanosecond discharge. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 255202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, S.W.; Axworthy, A.E. Mechanism of the gas phase, thermal decomposition of ozone. J. Chem. Phys. 1957, 26, 1718–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Korzec, D.; Neuwirth, D.; Nettesheim, S. Generation of Negative Air Ions by Use of Piezoelectric Cold Plasma Generator. Plasma 2021, 4, 399-407. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma4030029
Korzec D, Neuwirth D, Nettesheim S. Generation of Negative Air Ions by Use of Piezoelectric Cold Plasma Generator. Plasma. 2021; 4(3):399-407. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma4030029
Chicago/Turabian StyleKorzec, Dariusz, Daniel Neuwirth, and Stefan Nettesheim. 2021. "Generation of Negative Air Ions by Use of Piezoelectric Cold Plasma Generator" Plasma 4, no. 3: 399-407. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma4030029
APA StyleKorzec, D., Neuwirth, D., & Nettesheim, S. (2021). Generation of Negative Air Ions by Use of Piezoelectric Cold Plasma Generator. Plasma, 4(3), 399-407. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma4030029





