Novel Catalysts Based on Synthetic Mesoporous Silicates of the MCM-41 Type and Hydroxyapatite for Desulfurization of Model Fuel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Samples
2.2. Sample Characterization
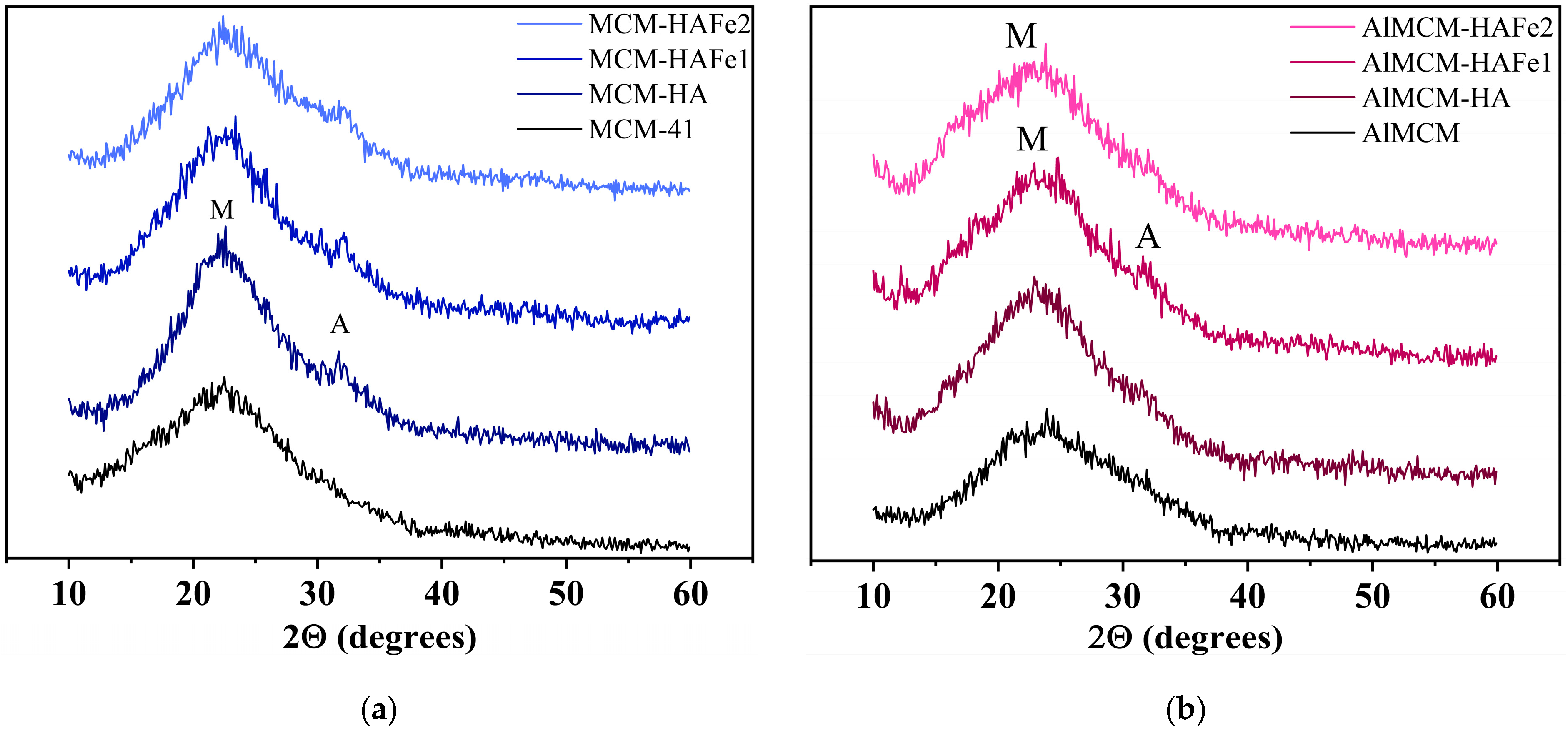
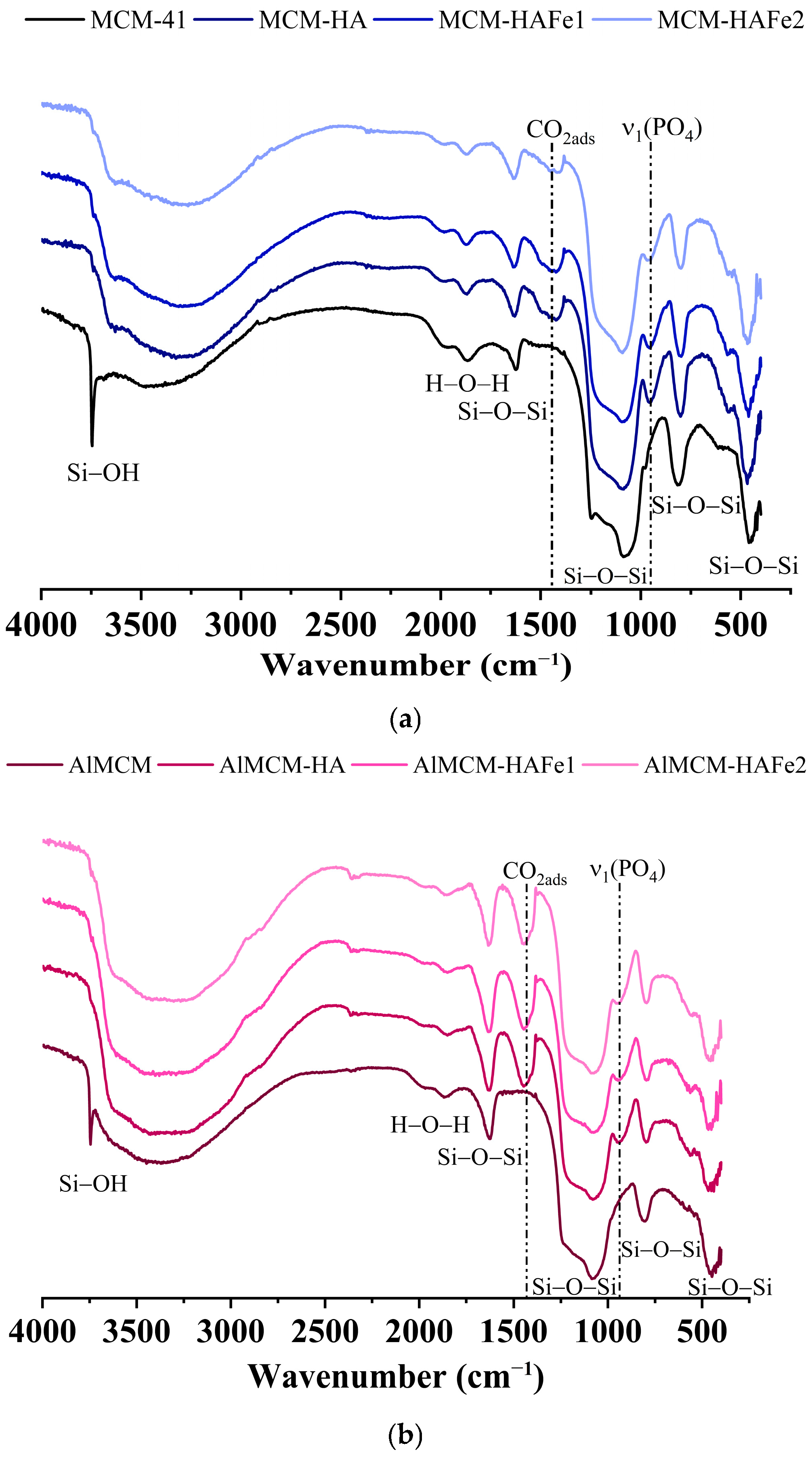
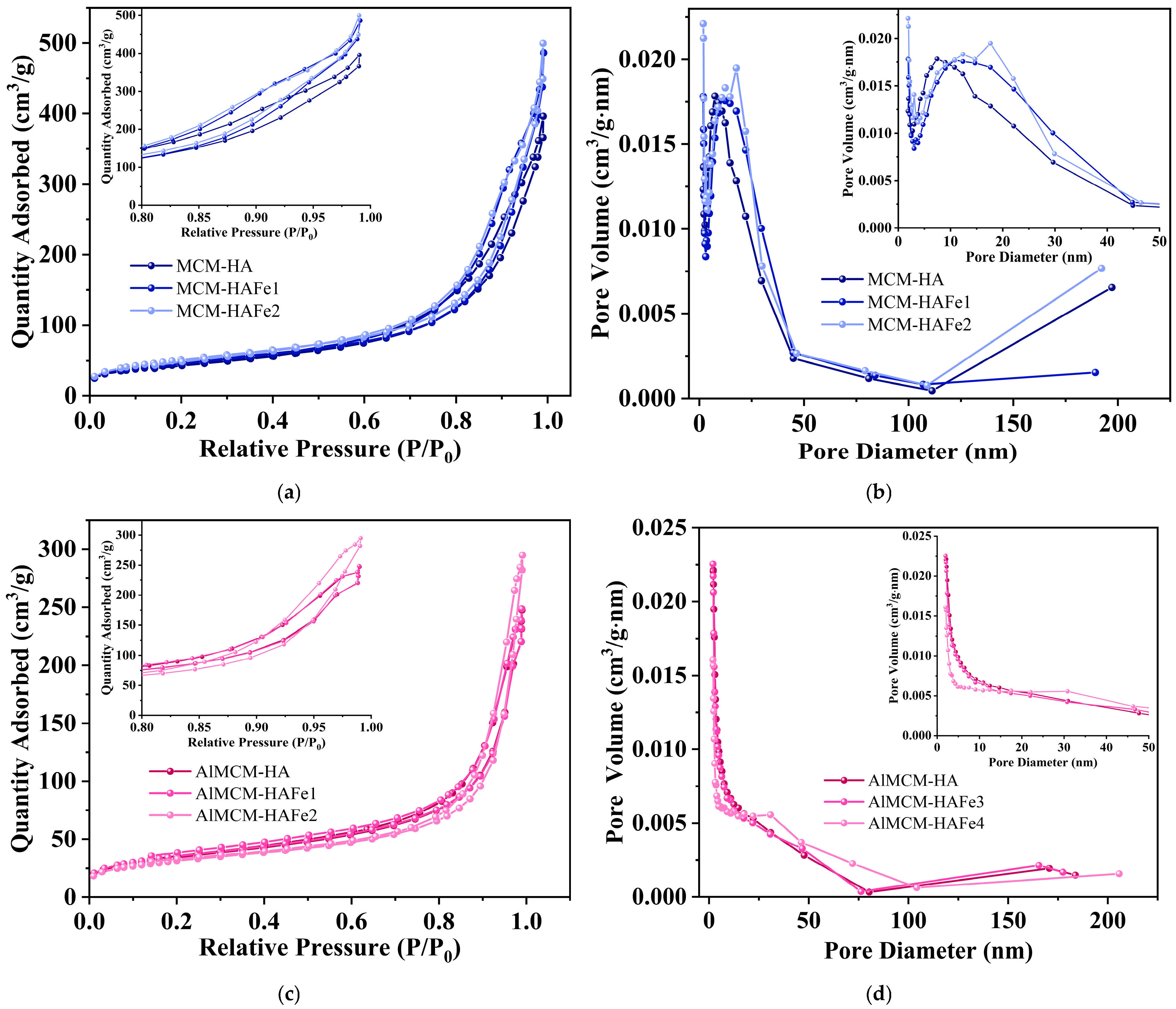
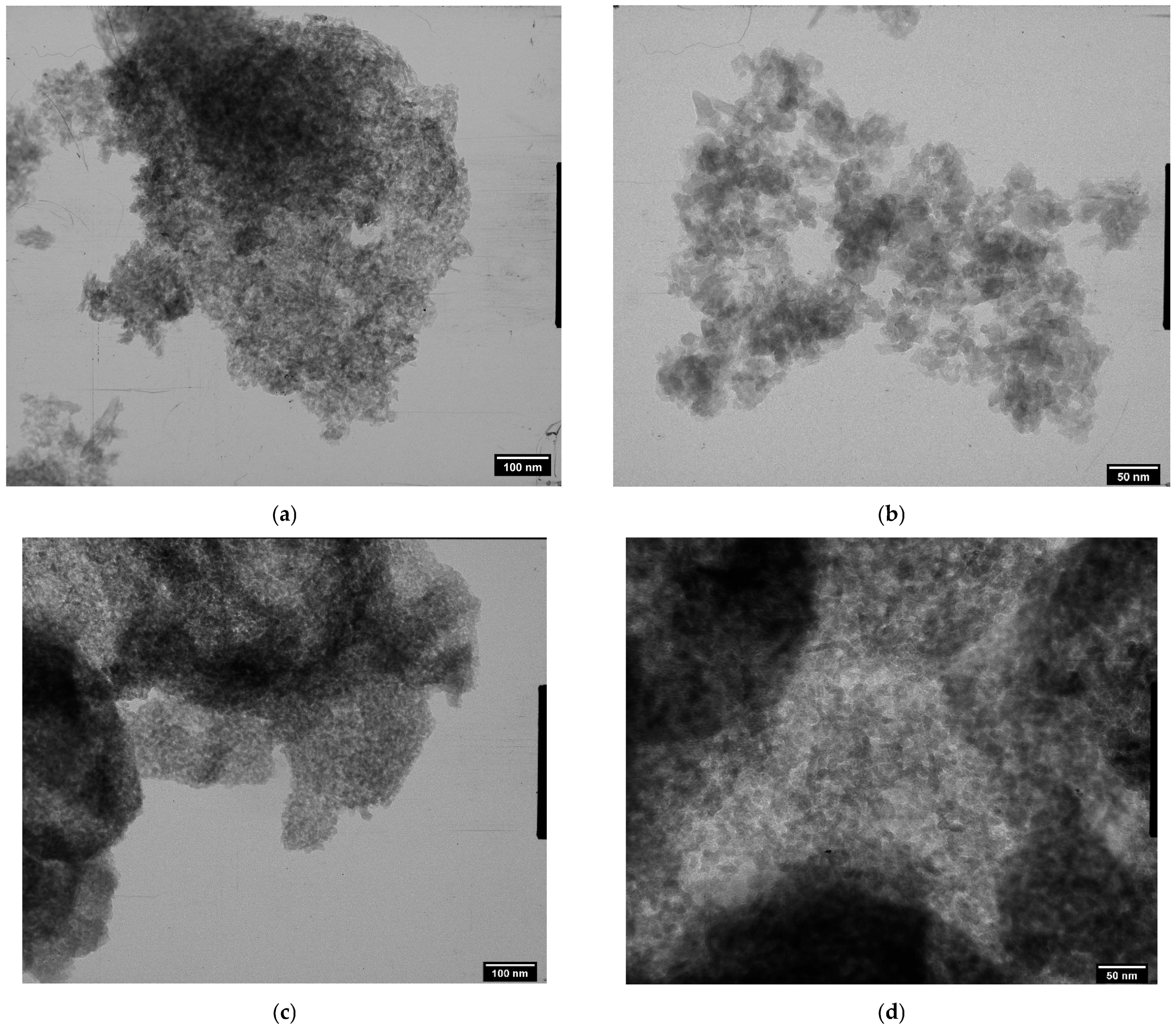
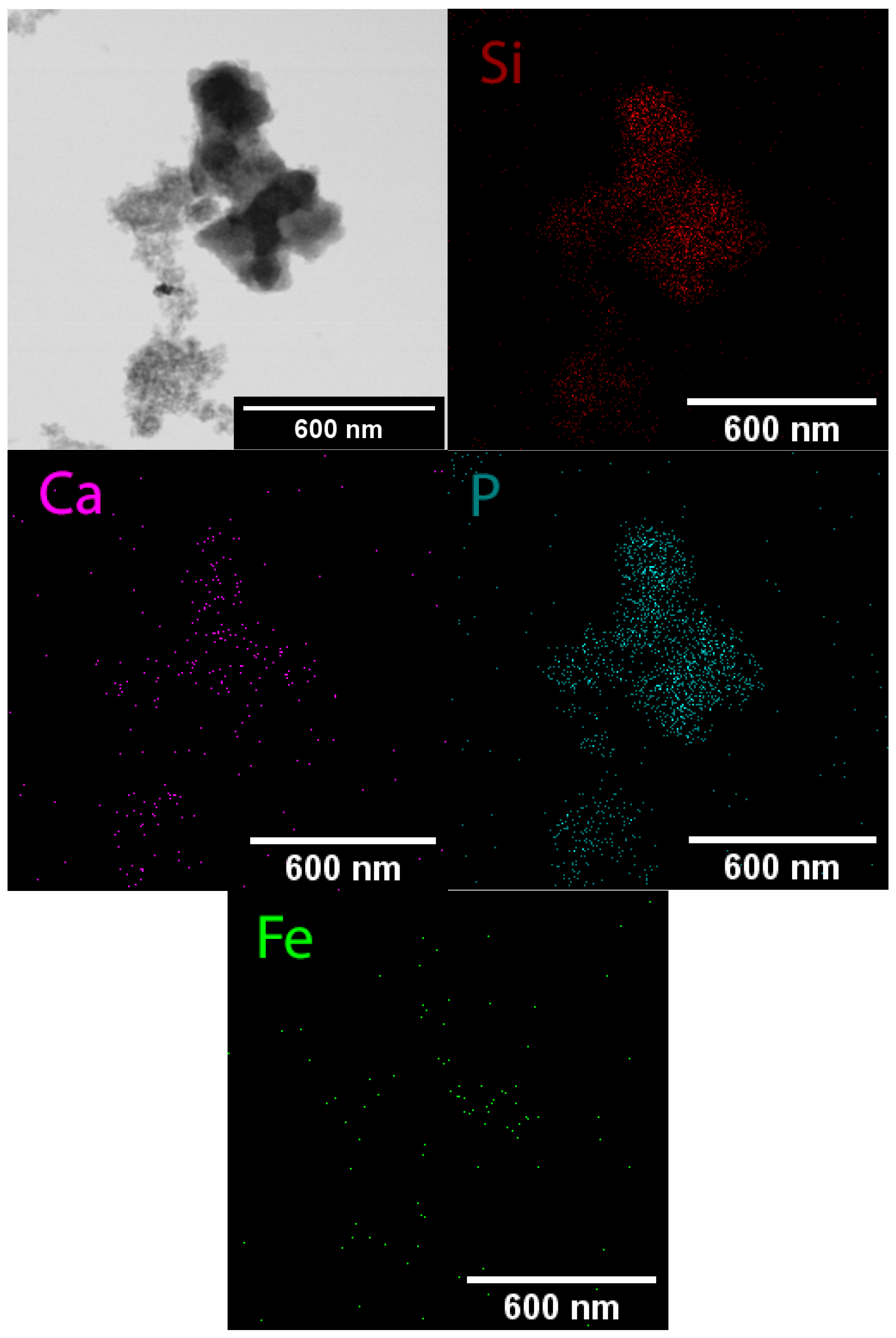
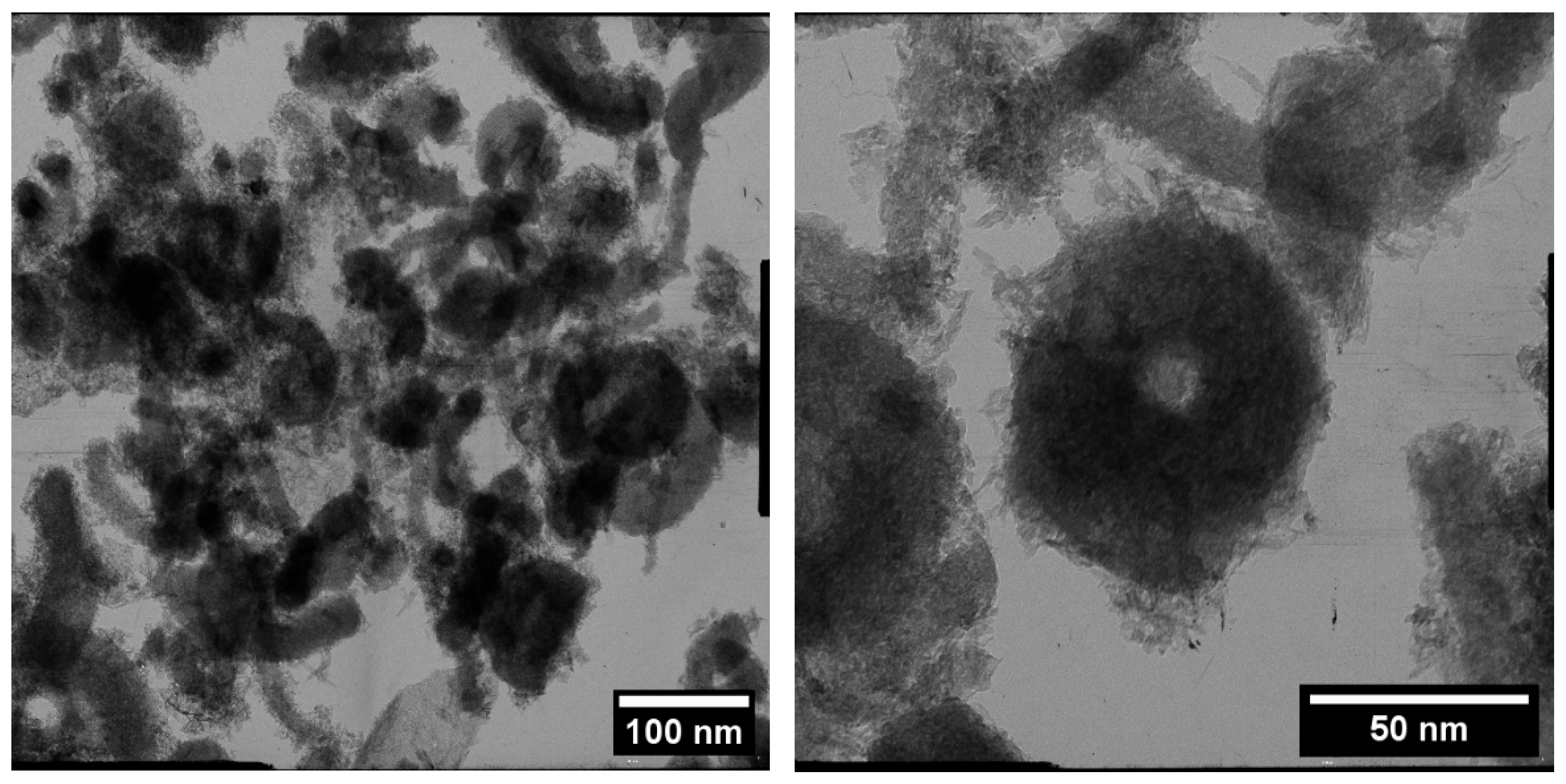
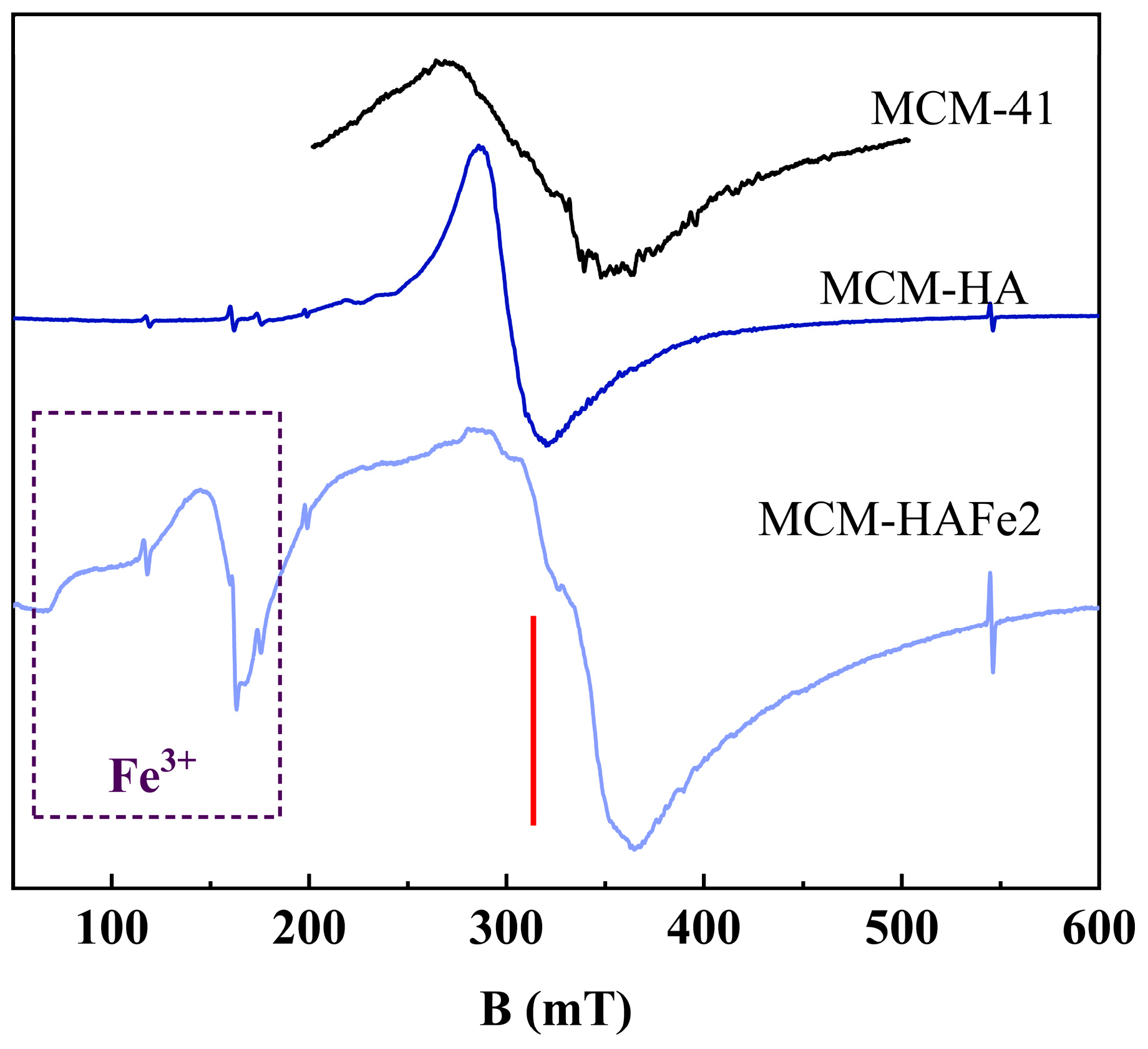
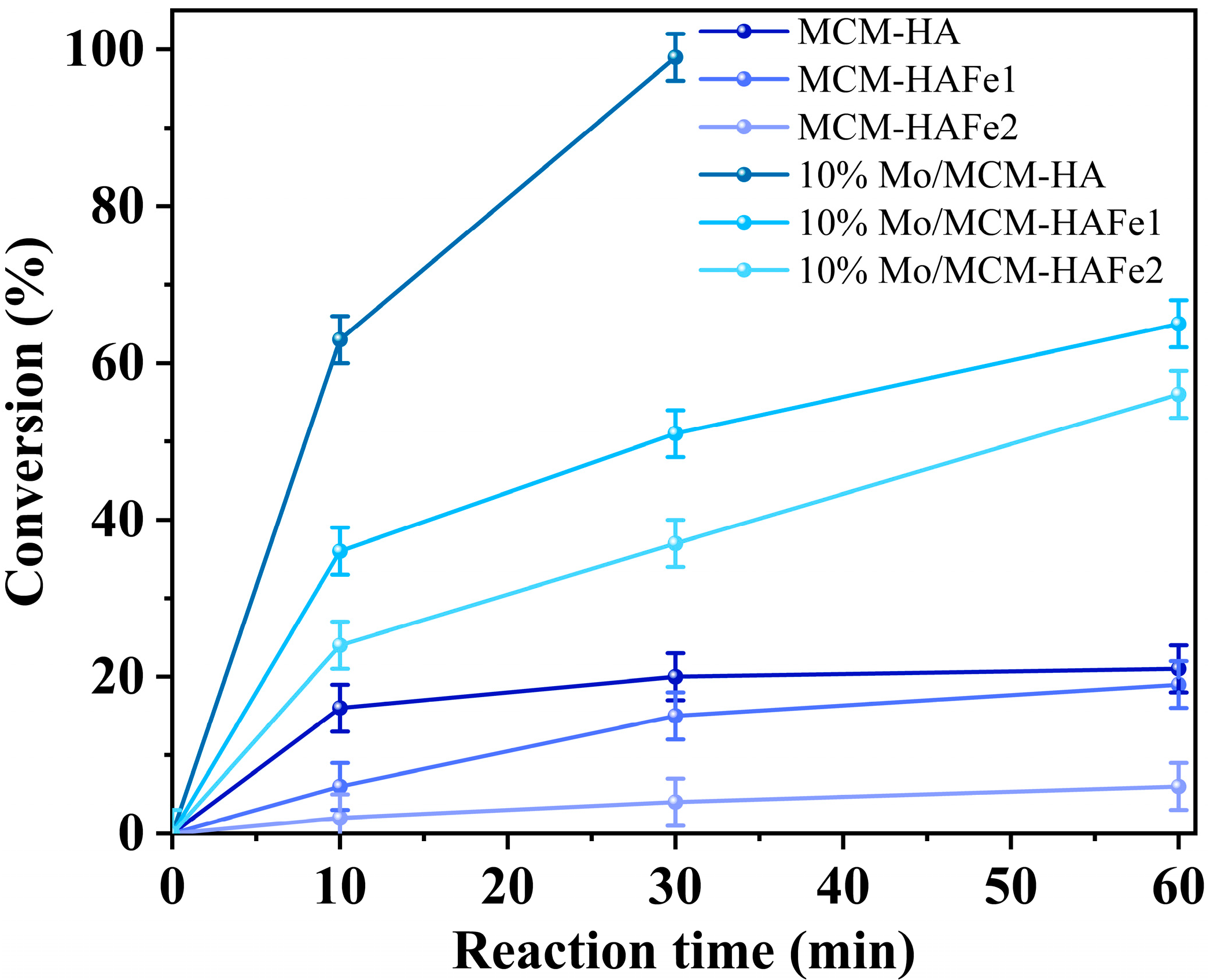
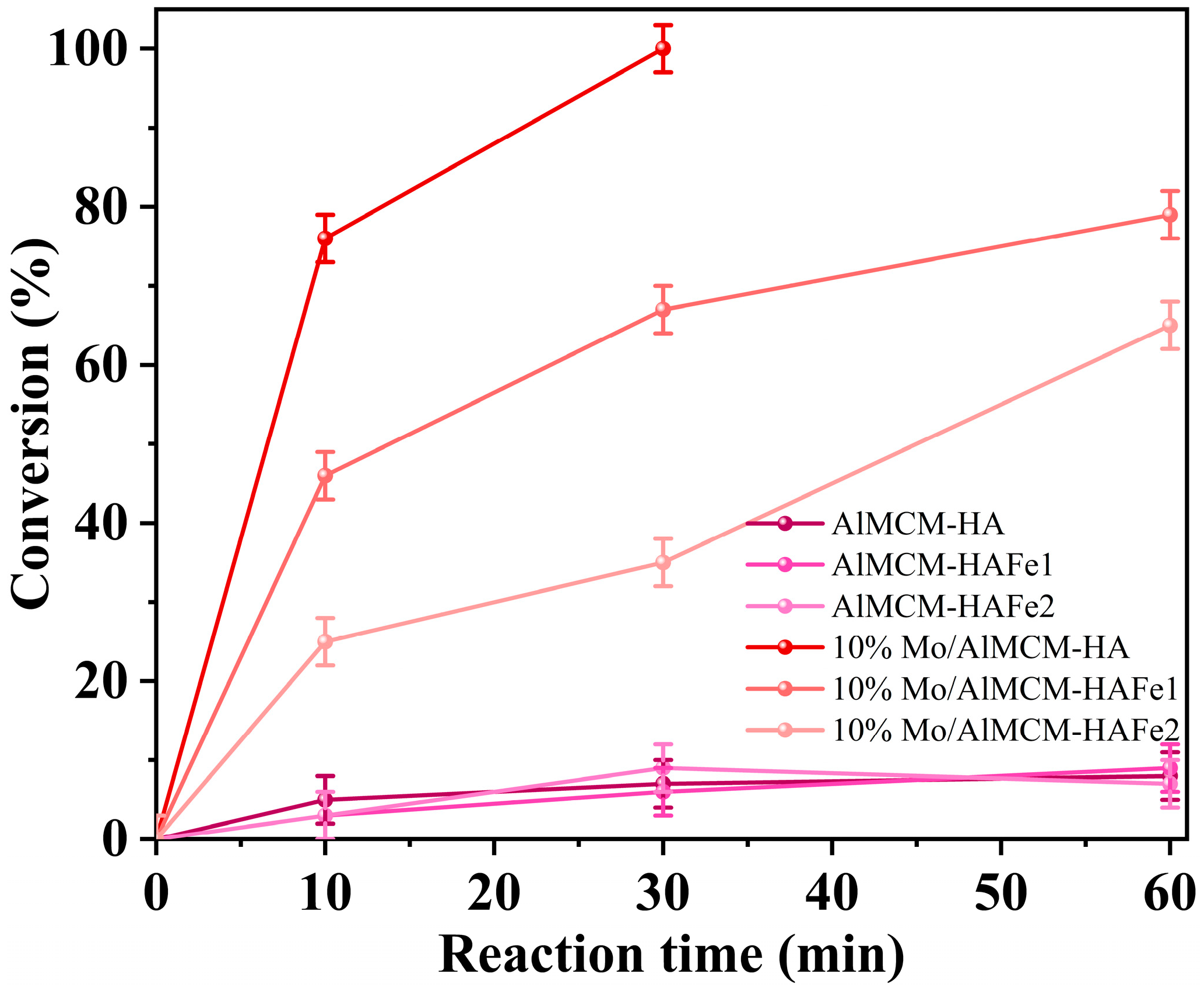
3. Results
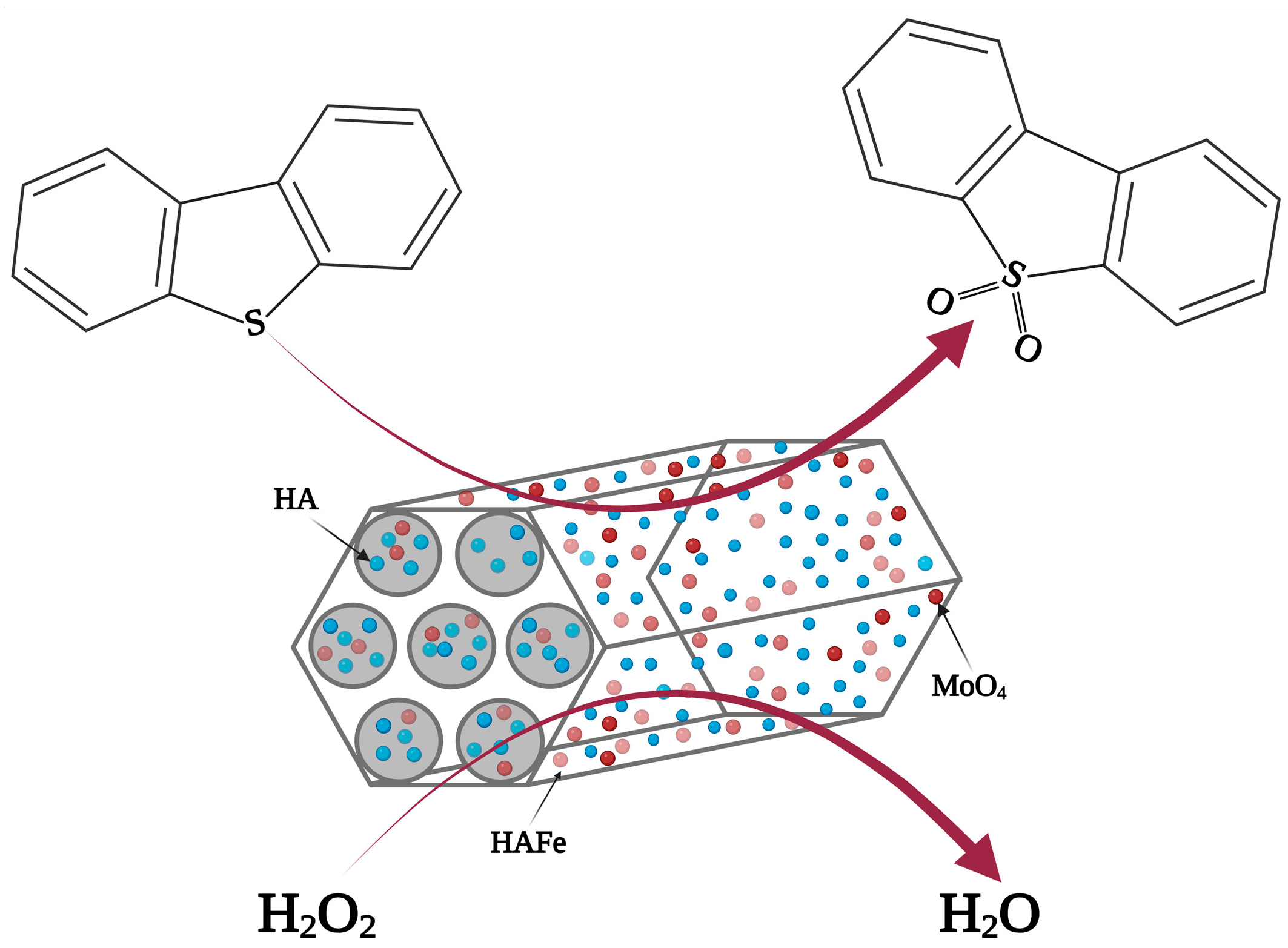
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finley, M. BP Statistical Review of World Energy June 2017; Annual Report; BP: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Babich, I.V.; Moulijn, J.A. Science and Technology of Novel Processes for Deep Desulfurization of Oil Refinery Streams: A Review☆. Fuel 2003, 82, 607–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houda, S.; Lancelot, C.; Blanchard, P.; Poinel, L.; Lamonier, C. Oxidative Desulfurization of Heavy Oils with High Sulfur Content: A Review. Catalysts 2018, 8, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismagilov, Z.; Yashnik, S.; Kerzhentsev, M.; Parmon, V.; Bourane, A.; Al-Shahrani, F.M.; Hajji, A.A.; Koseoglu, O.R. Oxidative Desulfurization of Hydrocarbon Fuels. Catal. Rev. 2011, 53, 199–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra Srivastava, V. An Evaluation of Desulfurization Technologies for Sulfur Removal from Liquid Fuels. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 759–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinamarca, M.A.; Ibacache-Quiroga, C.; Baeza, P.; Galvez, S.; Villarroel, M.; Olivero, P.; Ojeda, J. Biodesulfurization of Gas Oil Using Inorganic Supports Biomodified with Metabolically Active Cells Immobilized by Adsorption. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2375–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barinov, S.M. Calcium Phosphate-Based Ceramic and Composite Materials for Medicine. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2010, 79, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.A.; Smirnov, V.V.; Teterina, A.Y.; Barinov, S.M.; Komlev, V.S. Trends in Development of Bioresorbable Calcium Phosphate Ceramic Materials for Bone Tissue Engineering. Polym. Sci. Ser. D 2018, 11, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq Alam, M.; Kumar, S.; Gopan, G.; Mani, M.; Kannan, S. Fabrication, Mechanical, Finite Element and In Vitro Evaluation of 3D Printed Polylactide/Biphasic Calcium Phosphate Composite Blends. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 318, 129306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, R.O.; Bulut, N.; Kaygili, O. Hydroxyapatite Biomaterials: A Comprehensive Review of Their Properties, Structures, Medical Applications, and Fabrication Methods. J. Chem. Rev. 2024, 6, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sebti, S.; Tahir, R.; Nazih, R.; Saber, A.; Boulaajaj, S. Hydroxyapatite as a New Solid Support for the Knoevenagel Reaction in Heterogeneous Media without Solvent. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2002, 228, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas, R.N.; Leonardo, B.; Silva, L.C.; Fernandes, L.D.; Augusto, B.L.; Mendes, M.F. Study of the Use of Hydrotalcite—Hydroxyapatite as Heterogeneous Catalysts for Application in Biodiesel Using By—Product as Raw Material. Catal. Lett. 2020, 150, 3642–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Hara, T.; Mizugaki, T.; Ebitani, K.; Kaneda, K. Controlled Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite-Supported Palladium Complexes as Highly Efficient Heterogeneous Catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 11572–11573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharissova, O.V.; Méndez, Y.P.; Kharisov, B.I.; González, L.T.; Dorozhkin, S.V. Hydroxyapatite-Based Materials as Catalysts: A Review. Particuology 2025, 96, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruselle, M.; Tõnsuaadu, K.; Gredin, P.; Len, C. Apatites Based Catalysts: A Tentative Classification. Mol. Catal. 2022, 519, 112146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makshakova, O.N.; Shurtakova, D.V.; Vakhin, A.V.; Grishin, P.O.; Gafurov, M.R. Incorporation of Iron(II) and (III) in Hydroxyapatite—A Theoretical Study. Crystals 2021, 11, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.C. Structure and Chemistry of the Apatites and Other Calcium Orthophosphates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Kaygili, O.; Keser, S. Sol-Gel Synthesis and Characterization of Sr/Mg, Mg/Zn and Sr/Zn Co-Doped Hydroxyapatites. Mater. Lett. 2015, 141, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.A.; Donskaya, N.O.; Valeev, D.V.; Fomin, A.S.; Murzakhanov, F.F.; Leonov, A.V.; Konovalov, A.A.; Antonova, O.S.; Shoppert, A.A.; Kudryavtsev, E.A.; et al. Mesoporous Molybdate-Substituted Hydroxyapatite Nanopowders Obtained via a Hydrothermal Route. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 17404–17418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaud, C.; Thomas, C.; Brouri, D.; Millot, Y.; Miche, A.; Costentin, G. Surface Immobilization Mechanisms of Cobalt Ions on Hydroxyapatite Catalyst Supports. Catal. Today 2024, 432, 114621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larina, O.V.; Zikrata, O.V.; Shcherban, N.D.; Yaremov, P.S.; Rostas, A.M.; Khalakhan, I.; Veltruská, K.; Mali, G.; Soloviev, S.O.; Orlyk, S.M. Carbon-Supported Hydroxyapatite Hybrid Catalysts for Butan-1-Ol Conversion: Effect of the Nature of Carbon Support on Process Selectivity. Carbon 2024, 227, 119272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipadeola, A.K.; Chitt, M.; Abdelgawad, A.; Eid, K.; Abdullah, A.M. Graphene-Based Catalysts for Carbon Monoxide Oxidation: Experimental and Theoretical Insights. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 17434–17467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazloo, E.K.; Moheimani, N.R.; Ennaceri, H. Graphene-Based Catalysts for Biodiesel Production: Characteristics and Performance. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydari, N.; Bikas, R.; Shaterian, M.; Lis, T. Selective Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohols by Silica-Supported Heterogeneous Catalyst Containing Dioxidotungsten(VI) Core. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2023, 37, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosun, R.B.; Hamaloğlu, K.Ö.; Tuncel, A. Bimetallic Pd-Au Nanoparticles Supported Monodisperse Porous Silica Microspheres as an Efficient Heterogenous Catalyst for Fast Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202201646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Miao, C.; Wang, R.; Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Yao, J. Advances in Morphology-Controlled Alumina and Its Supported Pd Catalysts: Synthesis and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 5014–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durak, H.; Genel, S. Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Cellulose in the Presence of Sodium Fluoride-Doped Alumina Catalyst. Catal. Lett. 2024, 154, 1336–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, R.E.; Purnomo, H.; Aziz, A.; Holilah, H.; Bahruji, H.; Asikin-Mijan, N.; Suprapto, S.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Jalil, A.A.; Hartati, H.; et al. The Mechanism of Oleic Acid Deoxygenation to Green Diesel Hydrocarbon Using Porous Aluminosilicate Catalysts. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 49, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunns, J.A.; Durndell, L.J.; Zhang, X.; Konarova, M.; Lee, A.F.; Wilson, K. Tuning Acid-Metal Synergy in m-Cresol Hydrodeoxygenation over Bifunctional Pt/Aluminosilicate Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 7052–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.T.; Schmitt, K.D.; Chu, C.T.W.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.W.; McCullen, S.B.; et al. A New Family of Mesoporous Molecular Sieves Prepared with Liquid Crystal Templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakhanov, E.; Akopyan, A.; Golubev, O.; Anisimov, A.; Glotov, A.; Vutolkina, A.; Maximov, A. Alkali Earth Catalysts Based on Mesoporous MCM-41 and Al-SBA-15 for Sulfone Removal from Middle Distillates. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 12736–12744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Yang, H. Investigation of the Physicochemical Aspects from Natural Kaolin to Al-MCM-41 Mesoporous Materials. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2012, 369, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.W.; Endo, A.; Inagi, Y.; Harada, A.; Ohmori, T. Synthesis and Characterization of Mono-Dispersed Mesoporous Spheres. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 6463–6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhonoana, M.P.; Coville, N.J. Synthesis of [Si]-MCM-41 from TEOS and Water Glass: The Water Glass-Enhanced Condensation of TEOS under Alkaline Conditions. J. Solgel Sci. Technol. 2010, 54, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Luo, Z.S.; Pang, W.Q.; Fan, Y.W.; Chen, X.H.; Cui, F.Z. Dilute Solution Routes to Various Controllable Morphologies of MCM-41 Silica with a Basic Medium. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, F.; Courtois, X.; Duprez, D. Tungsten-based Catalysts for Environmental Applications. Catalysts 2021, 11, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Bao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xing, M. Molybdenum-Based Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Control of Environmental Pollutants. EcoMat 2021, 3, e12155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polikarpova, P.; Akopyan, A.; Shigapova, A.; Glotov, A.; Anisimov, A.; Karakhanov, E. Oxidative Desulfurization of Fuels Using Heterogeneous Catalysts Based on MCM-41. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 10898–10903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glotov, A.; Vutolkina, A.; Artemova, M.; Demikhova, N.; Smirnova, E.; Roldugina, E.; Stavitskaya, A.; Ivanov, E.; Egazar’yants, S.; Vinokurov, V. Micro-Mesoporous MCM-41/ZSM-5 Supported Pt and Pd Catalysts for Hydroisomerization of C-8 Aromatic Fraction. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 603, 117764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Gu, J.; Yang, S.; Gu, Q.; De Girolamo, A.; Zhang, L. Evolution of the Pd0/PdO Phase Change on Pd-MCM-41 Catalyst for Efficient Production of Furfural from the Fast Pyrolysis of Cellulose. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 154314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D. Shaily Synthesis and Catalytic Applications of Organo-Functionalized MCM-41 Catalyst: A Review. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2023, 37, e7007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, F.J.; Bravo-Ascención, G.; González-Mota, M.; Puente-Lee, I.; Bokhimi, X.; Klimova, T.E. NiMo Catalysts Supported on Al, Nb, Ti or Zr-Containing MCM-41 for Dibenzothiophene Hydrodesulfurization. Catal. Today 2020, 349, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masteri-Farahani, M.; Niakan, M. Heterogenization of Peracids onto the MCM-41 and SBA-16 Mesoporous Materials for the Epoxidation of Cyclooctene. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 195, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadiri, M.; Farzaneh, F.; Ghandi, M.; Alizadeh, M. Immobilized Copper(II) Complexes on Montmorillonite and MCM-41 as Selective Catalysts for Epoxidation of Alkenes. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2005, 233, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.A.; Antonova, O.S.; Donskaya, N.O.; Fomin, A.S.; Murzakhanov, F.F.; Gafurov, M.R.; Konovalov, A.A.; Kotyakov, A.A.; Leonov, A.V.; Smirnov, S.V.; et al. Effects of Various Ripening Media on the Mesoporous Structure and Morphology of Hydroxyapatite Powders. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelekhov, E.V.; Sviridova, T.A. Programs for X-Ray Analysis of Polycrystals. Met. Metal. Sci. Heat. Treat. 2000, 42, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.A.; Akopyan, A.V.; Gafurov, M.R.; Makshakova, O.N.; Donskaya, N.O.; Fomin, A.S.; Polikarpova, P.P.; Anisimov, A.V.; Murzakhanov, F.F.; Leonov, A.V.; et al. Iron-Doped Mesoporous Powders of Hydroxyapatite as Molybdenum-Impregnated Catalysts for Deep Oxidative Desulfurization of Model Fuel: Synthesis and Experimental and Theoretical Studies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 11604–11619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.A.; Gafurov, M.R.; Murzakhanov, F.F.; Fomin, A.S.; Antonova, O.S.; Khairutdinova, D.R.; Pyataev, A.V.; Makshakova, O.N.; Konovalov, A.A.; Leonov, A.V.; et al. Mesoporous Iron(Iii)-Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanopowders Obtained via Iron Oxalate. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenelonov, V.B.; Romannikov, V.N.; Derevyankin, A.Y. Mesopore Size and Surface Area Calculations for Hexagonal Mesophases (Types MCM-41, FSM-16, Etc.) Using Low-Angle XRD and Adsorption Data. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 28, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, H.; de Carvalho, A.L.G.; Costa, F.F.; Nascimento, L.A.S.d.; Mhadmhan, S.; Pineda, A.; Luque, R.; Valença, G.P. Preparation of Novel Mesoporous Ca/P MCM-41-Based Materials for Mechanochemical Diphenyl Sulfide Oxidation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 297, 110017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.; Souza, K.C.; Sousa, E.M.B. Mesoporous Silica/Apatite Nanocomposite: Special Synthesis Route to Control Local Drug Delivery. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, A.T.; Haghighi, N.B.; Sheikh Hossein Pour, M.; Aminian, M.; Molzemi, S. Hydroxyapatite Incorporation into MCM-41 and Study of Ibuprofen Drug Release. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 56, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentys, A.; Pham, N.H.; Vinek, H. Nature of Hydroxy Groups in MCM-41. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1996, 92, 3287–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zuo, G.; Xiong, G.; Luo, H.; Li, Q.; Ma, C.; Li, D.; Gu, F.; Ma, Y.; Wan, Y. The Inhibition of Lamellar Hydroxyapatite and Lamellar Magnetic Hydroxyapatite on the Migration and Adhesion of Breast Cancer Cells. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wachs, I.E. Surface Structures of Supported Molybdenum Oxide Catalysts. Characterization by Raman and Mo L3-Edge XANES. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 10897–10910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.S.; Sane, A.R.; Rêgo de Vasconcelos, B.; Nzihou, A.; Sharrock, P.; Grouset, D.; Pham Minh, D. Hydroxyapatite Supported Bimetallic Cobalt and Nickel Catalysts for Syngas Production from Dry Reforming of Methane. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 224, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munirathinam, R.; Pham Minh, D.; Nzihou, A. Hydroxyapatite as a New Support Material for Cobalt-Based Catalysts in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 18440–18451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasooriya, I.L.; Chen, J.; Gedara, S.M.K.; Han, Y.; Wickramaratne, M.N. Applications of Nano Hydroxyapatite as Adsorbents: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, S.; Kini, S.M.; Selvaraj, R.; Pugazhendhi, A. A Review on the Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite, Its Composites and Adsorptive Removal of Pollutants from Wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya, J.C.; Valdez, R.; Cota, L.; Alvarez-Amparán, M.A.; Olivas, A. Performance of Al-MCM-41 Nanospheres as Catalysts for Dimethyl Ether Production. Catal. Today 2022, 388–389, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Zhao, D.; Dimitrijevic, N.M.; Rajh, T.; Koodali, R.T. Room Temperature Synthesis of Ti-MCM-48 and Ti-MCM-41 Mesoporous Materials and Their Performance on Photocatalytic Splitting of Water. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.A.S.; Paranhos, C.M. Mitigation of Silica-Rich Wastes: An Alternative to the Synthesis Eco-Friendly Silica-Based Mesoporous Materials. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 309, 110570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.A.S.; De Jesus, R.A.; Santos, D.O.; Neris, J.B.; Figueiredo, R.T.; Paranhos, C.M. Synthesis, Functionalization, and Environmental Application of Silica-Based Mesoporous Materials of the M41S and SBA-n Families: A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarath Chandra, V.; Baskar, G.; Suganthi, R.V.; Elayaraja, K.; Ahymah Joshy, M.I.; Sofi Beaula, W.; Mythili, R.; Venkatraman, G.; Narayana Kalkura, S. Blood Compatibility of Iron-Doped Nanosize Hydroxyapatite and Its Drug Release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1200–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, S.; Padmanabhan, V.P.; Kulandaivelu, R.; Sankara Narayanan Nellaiappan, T.S.; Sagadevan, S.; Paiman, S.; Mohammad, F.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Obulapuram, P.K.; Oh, W.C. Influence of Iron Doping towards the Physicochemical and Biological Characteristics of Hydroxyapatite. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 5061–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotti, C.; Farnetti, E. Selective Oxidation of Glycerol Catalyzed by Iron Complexes. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 396, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Wang, W.; Bi, Y. Synthesis of Mesoporous Hydroxyapatite via a Vitamin C Templating Hydrothermal Route. Mater. Lett. 2018, 218, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; He, X.; Wu, Z. Mesoporous Hydroxyapatite: Preparation, Drug Adsorption, and Release Properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 148, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Gao, Y.; Yi, J.; Cui, M.; Hao, H.; Xu, Q. An Ordered Mesoporous Hydroxyapatite: Preparation, Loading, and Sustained Releasing to Ciprofloxacin. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 106, 2679–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anunziata, O.A.; Martínez, M.L.; Beltramone, A.R. Hydroxyapatite/MCM-41 and SBA-15 Nano-Composites: Preparation, Characterization and Applications. Materials 2009, 2, 1508–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, H.R.; Abdouss, M.; Golshekan, M. Hydroxyapatite Incorporated with Fe3O4@MCM-41 Core-Shell: A Promising Nanocomposite for Teriparatide Delivery in Bone Tissue Regeneration. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 41363–41373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefpour, M.; Taherian, Z. The Effects of Ageing Time on the Microstructure and Properties of Mesoporous Silica-Hydroxyapatite Nanocomposite. Superlattices Microstruct. 2013, 54, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polikarpova, P.D.; Koptelova, A.O.; Vutolkina, A.V.; Akopyan, A.V. Combined Heterogeneous Catalyst Based on Titanium Oxide for Highly Efficient Oxidative Desulfurization of Model Fuels. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 48349–48360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teimouri, A.; Mahmoudsalehi, M.; Salavati, H. Catalytic Oxidative Desulfurization of Dibenzothiophene Utilizing Molybdenum and Vanadium Oxides Supported on MCM-41. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 14816–14833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhmanov, E.V.; Tarakanova, A.V.; Valieva, T.; Akopyan, A.V.; Litvinova, V.V.; Maksimov, A.L.; Anisimov, A.V.; Vakarin, S.V.; Semerikova, O.L.; Zaikov, Y.P. Oxidative Desulfurization of Diesel Fraction with Hydrogen Peroxide in the Presence of Catalysts Based on Transition Metals. Pet. Chem. 2014, 54, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Lu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, R.; Zhang, W.; He, D.; Luo, Y. Promotional Effects of Rare-earth Praseodymium (Pr) Modification over Mcm-41 for Methyl Mercaptan Catalytic Decomposition. Processes 2021, 9, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei, S.; Ghadermazi, M. Immobilization of Cerium (IV) and Erbium (III) in Mesoporous MCM-41: Two Novel and Highly Active Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Synthesis of 5-Substituted Tetrazoles, and Chemo- and Homoselective Oxidation of Sulfides. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, J.; He, X.; Chen, X.; Miao, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X. Effect of Interconnected Mesoporous Structure on HCHO Catalytic Oxidation over Transition Metal Doped Ag/MCM-41. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 42, 103373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savel, A.S.; Evdokimova, E.V.; Mamontov, G.V. Pt–Ag Bimetallic Catalysts Supported on Mesoporous Silica MCM-41 in 4-Nitrophenol Reduction. Inorg. Mater. Nanomater. 2024, 69, 1754–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental Mesoporous Sn (IV) Doping MCM-41 Supported Pd Nanoparticles for Enhanced Selective Catalytic Oxidation of 1, 2-Propanediol to Pyruvic Acid. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 253, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, G.; Ning, G. Efficient Oxidative Desulfurization (ODS) of Model Fuel with H 2O2 Catalyzed by MoO3/γ-Al 2O3 under Mild and Solvent Free Conditions. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.P.; Zhao, R.X.; Li, X.P.; Gao, X.H. Preparation of MoO2/g-C3N4 Composites with a High Surface Area and Its Application in Deep Desulfurization from Model Oil. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 434, 1200–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzechowiak, J.R.; Mrozińska, K.; Masalska, A.; Góralski, J.; Rynkowski, J.; Tylus, W. Effect of MCM-41 on the Physicochemical Properties of Mo and NiMo Catalysts and Their Performance in DBT Conversion. Catal. Today 2006, 114, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Du, G.; Chen, S.; Jia, J.; Sun, P.; Chen, T. Efficient Oxidative-Adsorptive Desulfurization over Highly Dispersed Molybdenum Oxide Supported on Hierarchically Mesoporous Silica. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 645, 128922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample Code | Composition | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Mesoporous Silica | HA Concentration, wt.% | Fe Concentration, mol.% | |
| MCM-HA | MCM-41 | 10 | 0 |
| MCM-HAFe1 | MCM-41 | 10 | 5 |
| MCM-HAFe2 | MCM-41 | 10 | 10 |
| AlMCM-HA | aluminum-containing MCM-41 | 10 | 0 |
| AlMCM-HAFe1 | aluminum-containing MCM-41 | 10 | 5 |
| AlMCM-HAFe2 | aluminum-containing MCM-41 | 10 | 10 |
| Sample | SSA (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | D (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCM-41 series | ||||
| MCM-41 | 925.1 | 0.93 | 3.2 | 2.94 |
| MCM-HA | 162.3 | 0.62 | 14.4 | 16.1 |
| MCM-HAFe1 | 173.2 | 0.76 | 16.8 | 15.1 |
| MCM-HAFe2 | 186.6 | 0.78 | 15.9 | 14.0 |
| AlMCM series | ||||
| AlMCM | 843.9 | 1.35 | 5.2 | 3.2 |
| AlMCM-HA | 123.3 | 0.39 | 13.2 | 21.2 |
| AlMCM-HAFe1 | 127.2 | 0.38 | 13.4 | 20.6 |
| AlMCM-HAFe2 | 112.6 | 0.45 | 18.5 | 23.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Donskaya, N.O.; Goldberg, M.A.; Fomin, A.S.; Koptelova, A.O.; Domashkina, P.D.; Eseva, E.A.; Antonova, O.S.; Konovalov, A.A.; Leonov, A.V.; Kudryavtsev, E.A.; et al. Novel Catalysts Based on Synthetic Mesoporous Silicates of the MCM-41 Type and Hydroxyapatite for Desulfurization of Model Fuel. Ceramics 2025, 8, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics8020061
Donskaya NO, Goldberg MA, Fomin AS, Koptelova AO, Domashkina PD, Eseva EA, Antonova OS, Konovalov AA, Leonov AV, Kudryavtsev EA, et al. Novel Catalysts Based on Synthetic Mesoporous Silicates of the MCM-41 Type and Hydroxyapatite for Desulfurization of Model Fuel. Ceramics. 2025; 8(2):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics8020061
Chicago/Turabian StyleDonskaya, Nadezhda O., Margarita A. Goldberg, Alexander S. Fomin, Anna O. Koptelova, Polina D. Domashkina, Ekaterina A. Eseva, Olga S. Antonova, Anatoliy A. Konovalov, Alexander V. Leonov, Egor A. Kudryavtsev, and et al. 2025. "Novel Catalysts Based on Synthetic Mesoporous Silicates of the MCM-41 Type and Hydroxyapatite for Desulfurization of Model Fuel" Ceramics 8, no. 2: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics8020061
APA StyleDonskaya, N. O., Goldberg, M. A., Fomin, A. S., Koptelova, A. O., Domashkina, P. D., Eseva, E. A., Antonova, O. S., Konovalov, A. A., Leonov, A. V., Kudryavtsev, E. A., Murzakhanov, F. F., Gafurov, M. R., Akopyan, A. V., Barinov, S. M., & Komlev, V. S. (2025). Novel Catalysts Based on Synthetic Mesoporous Silicates of the MCM-41 Type and Hydroxyapatite for Desulfurization of Model Fuel. Ceramics, 8(2), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics8020061









