Advanced Refinement of Geopolymer Composites for Enhanced 3D Printing via In-Depth Rheological Insights
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geopolymer-Based Composite Formulations
2.1. Material Characterization
2.2. Mix Design Method
2.3. Rheological Protocol
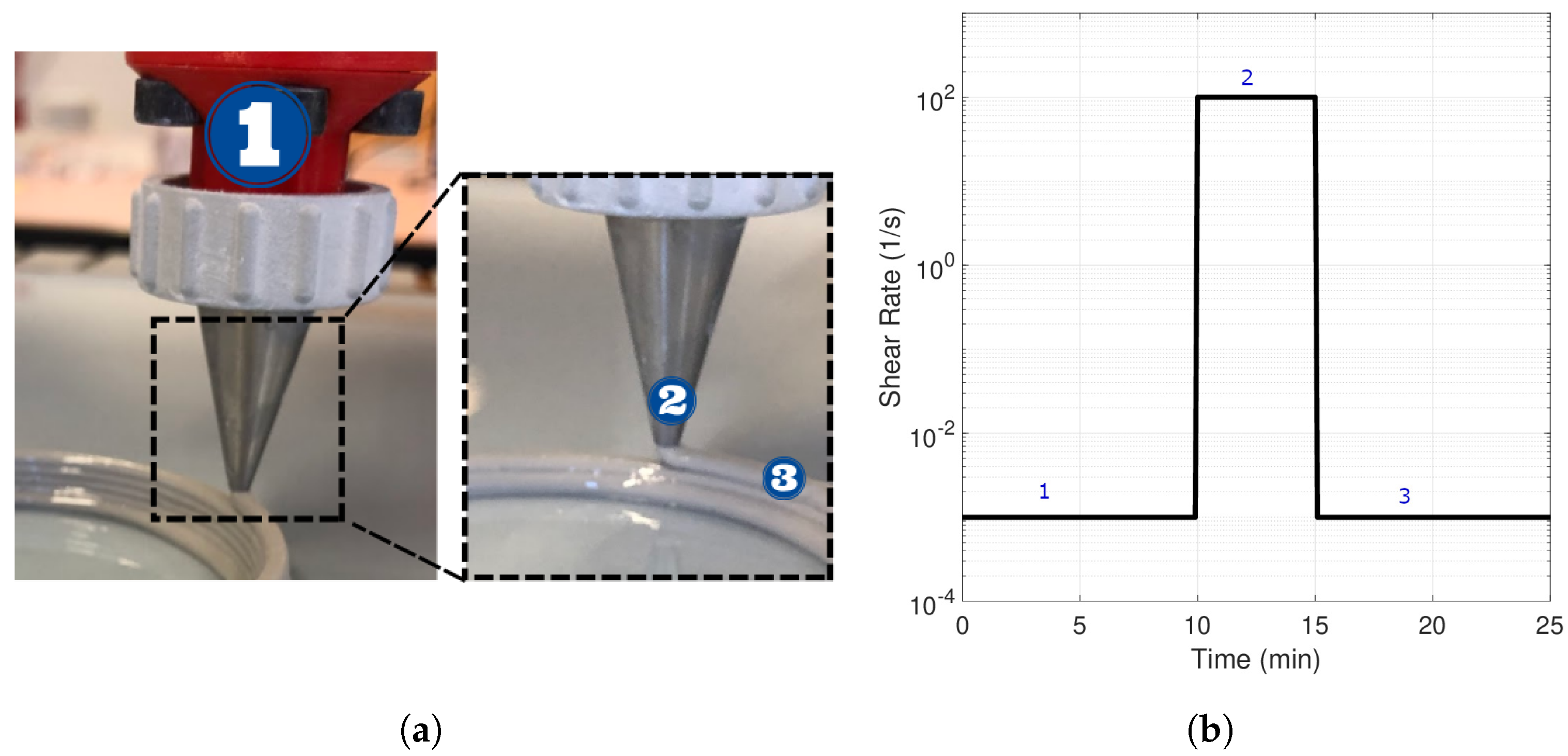
2.3.1. Shearing Tests
2.3.2. Oscillatory Tests
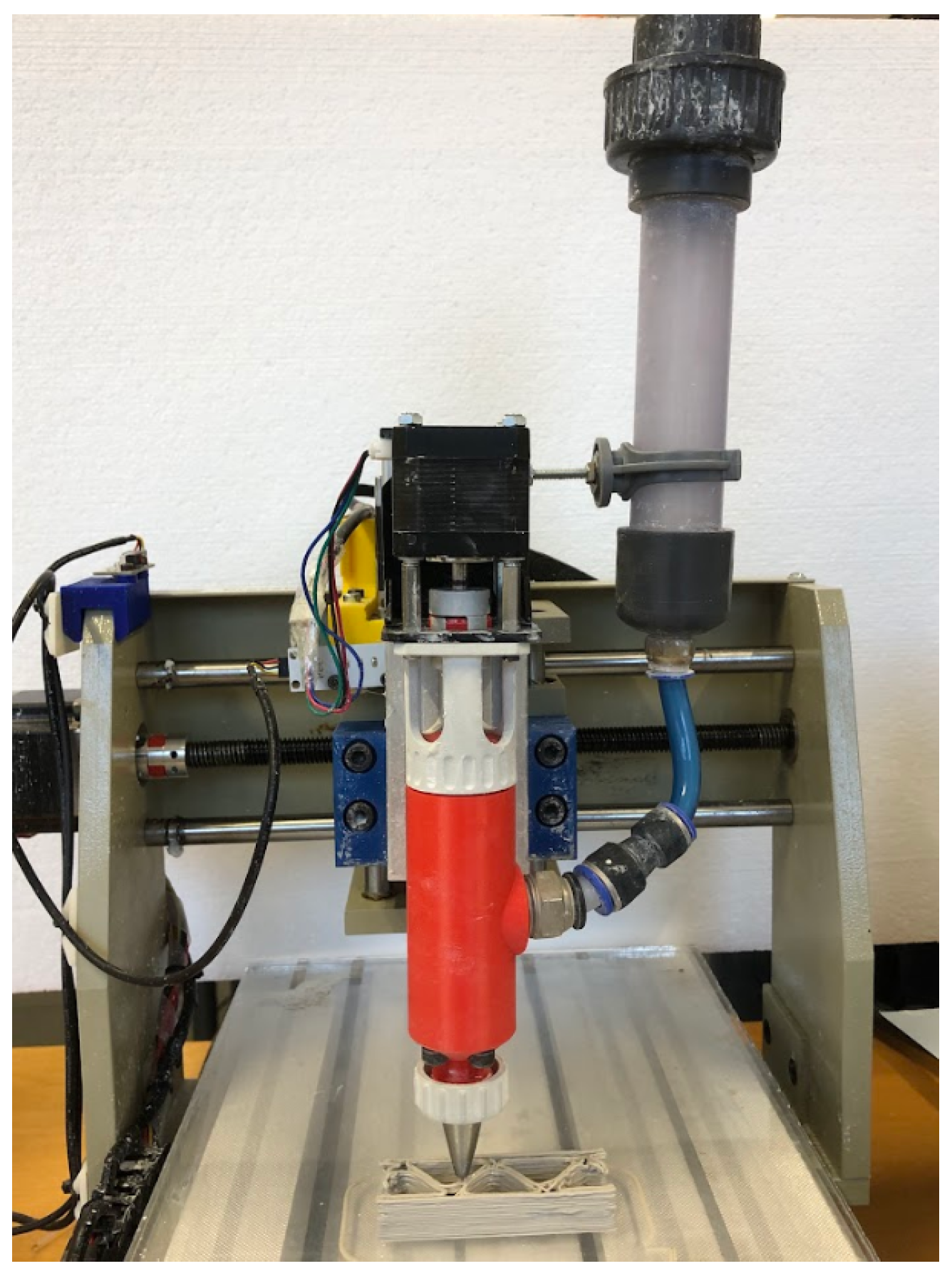
2.4. Three-Dimensional Printing Protocol
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rheometry Development for Extrusion-Based 3D Printing of Geopolymer Composites
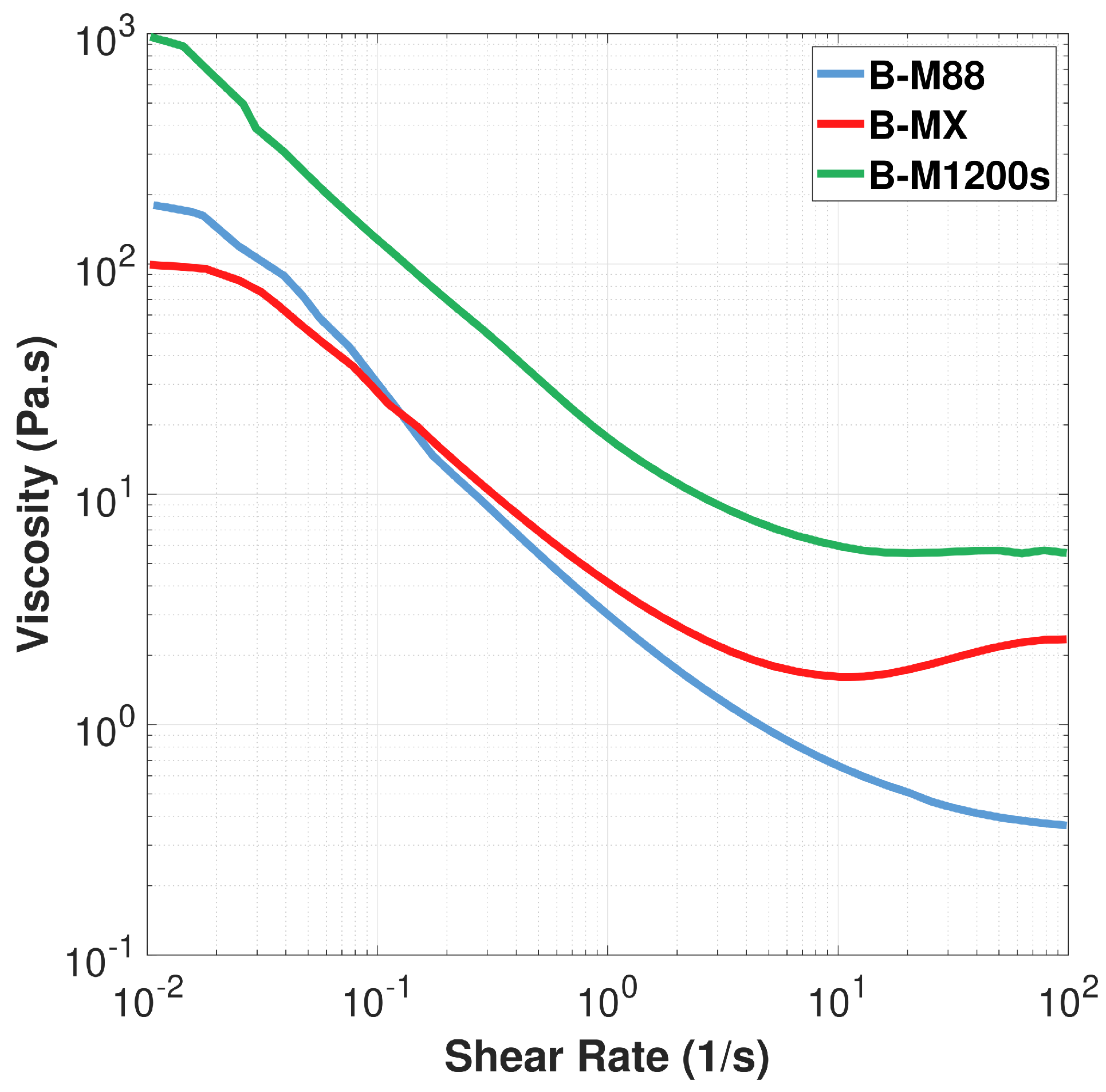
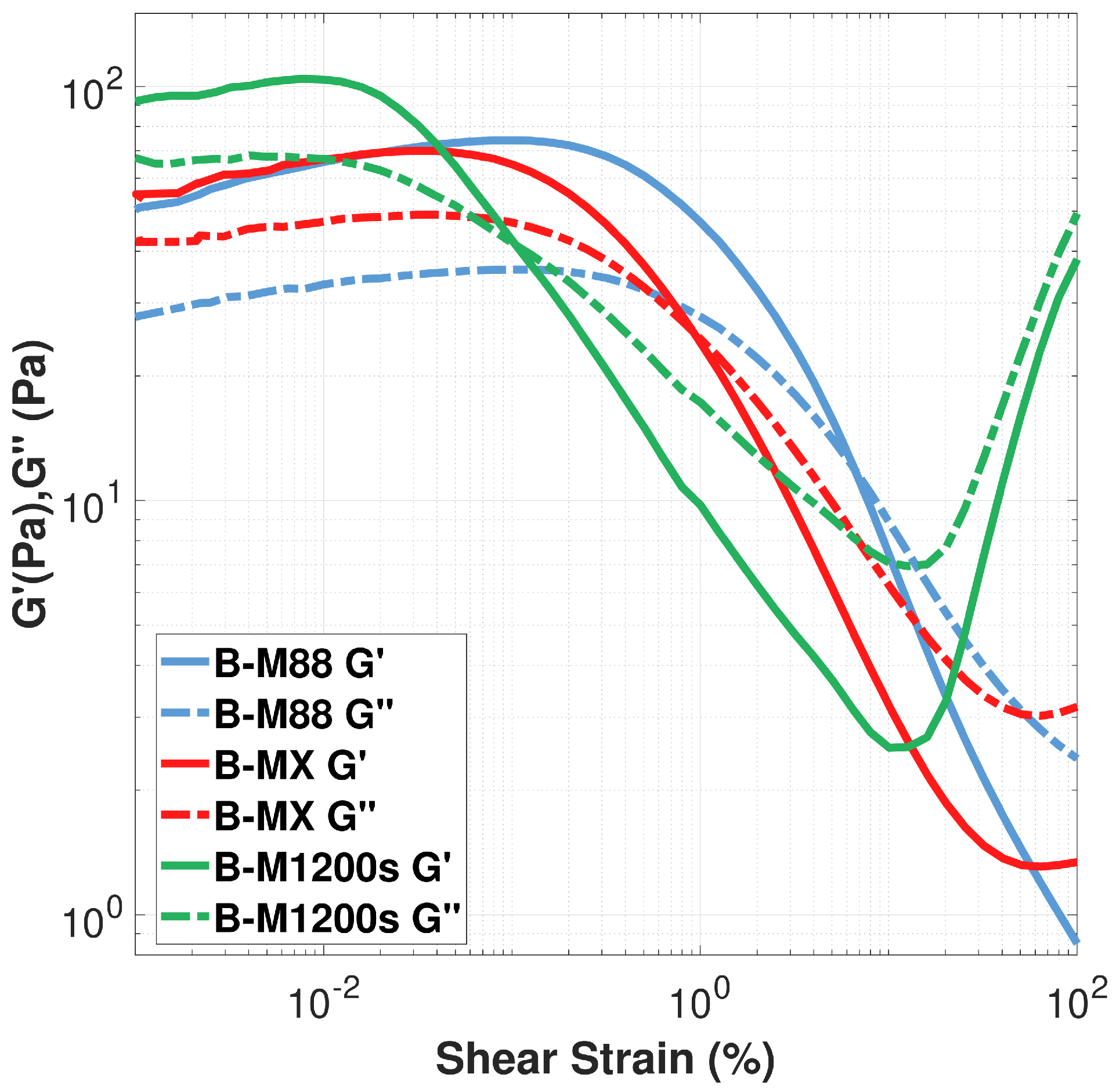
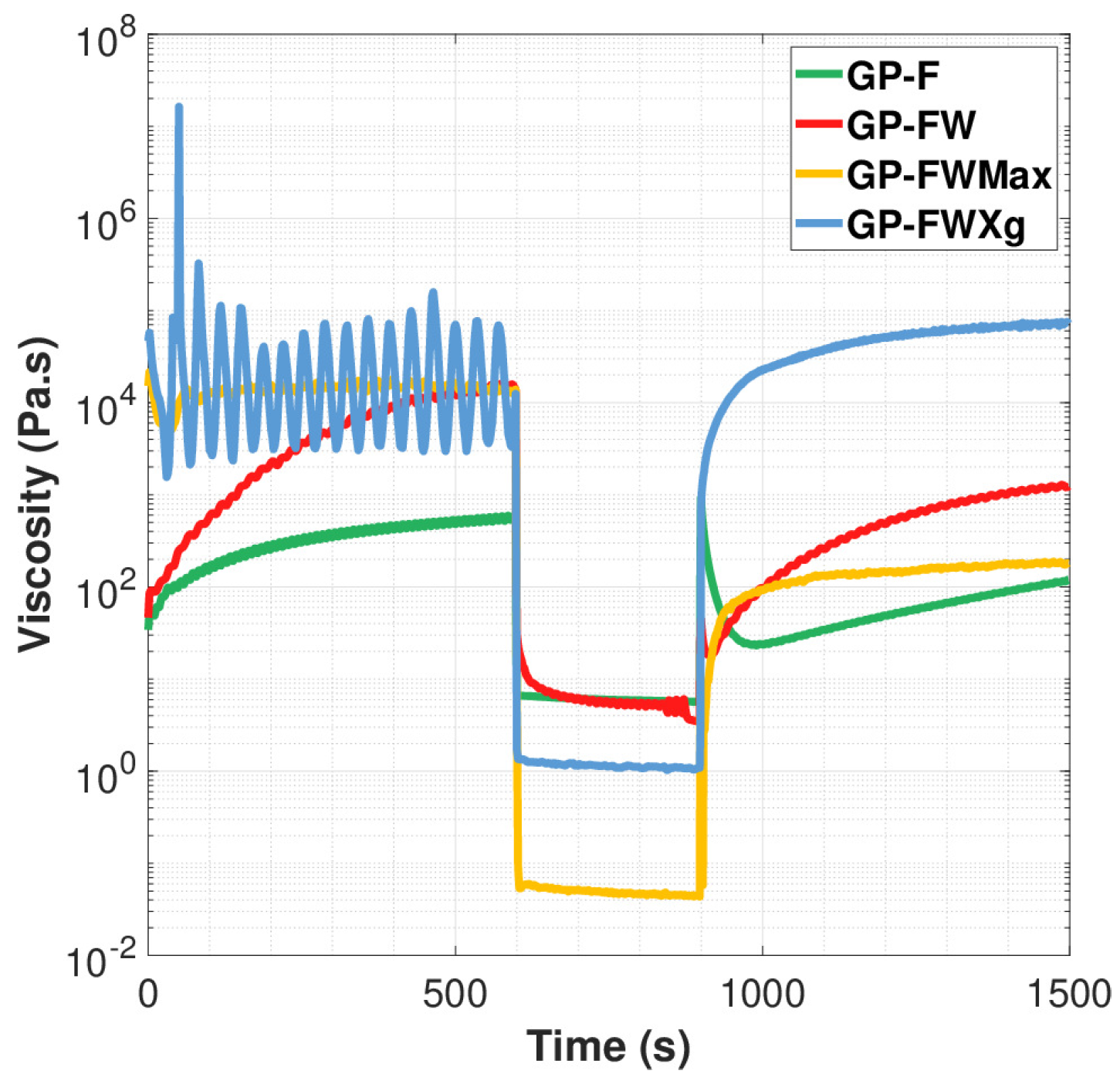
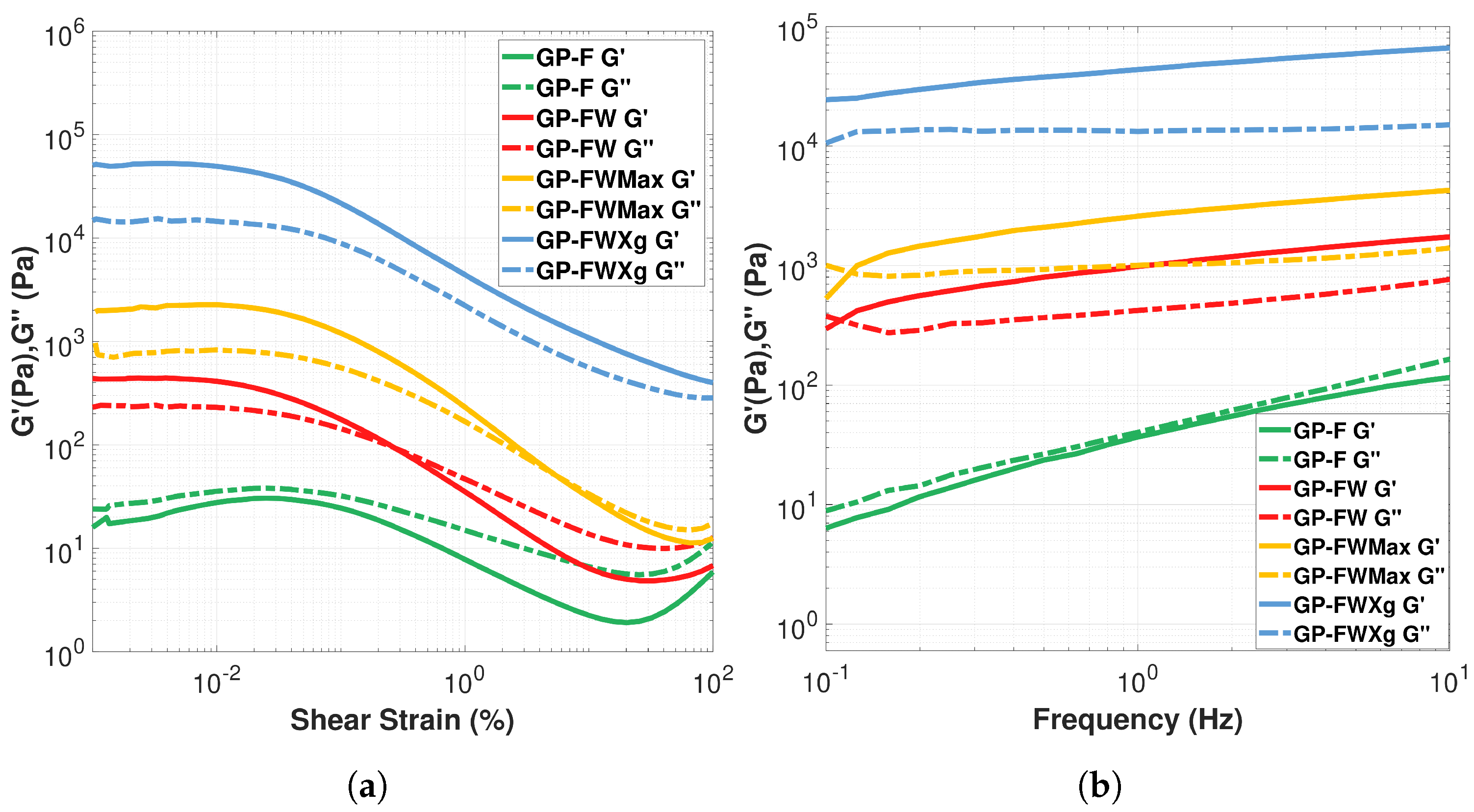
3.1.1. Comparative Analysis of Binders: Rheological Behavior Evaluation
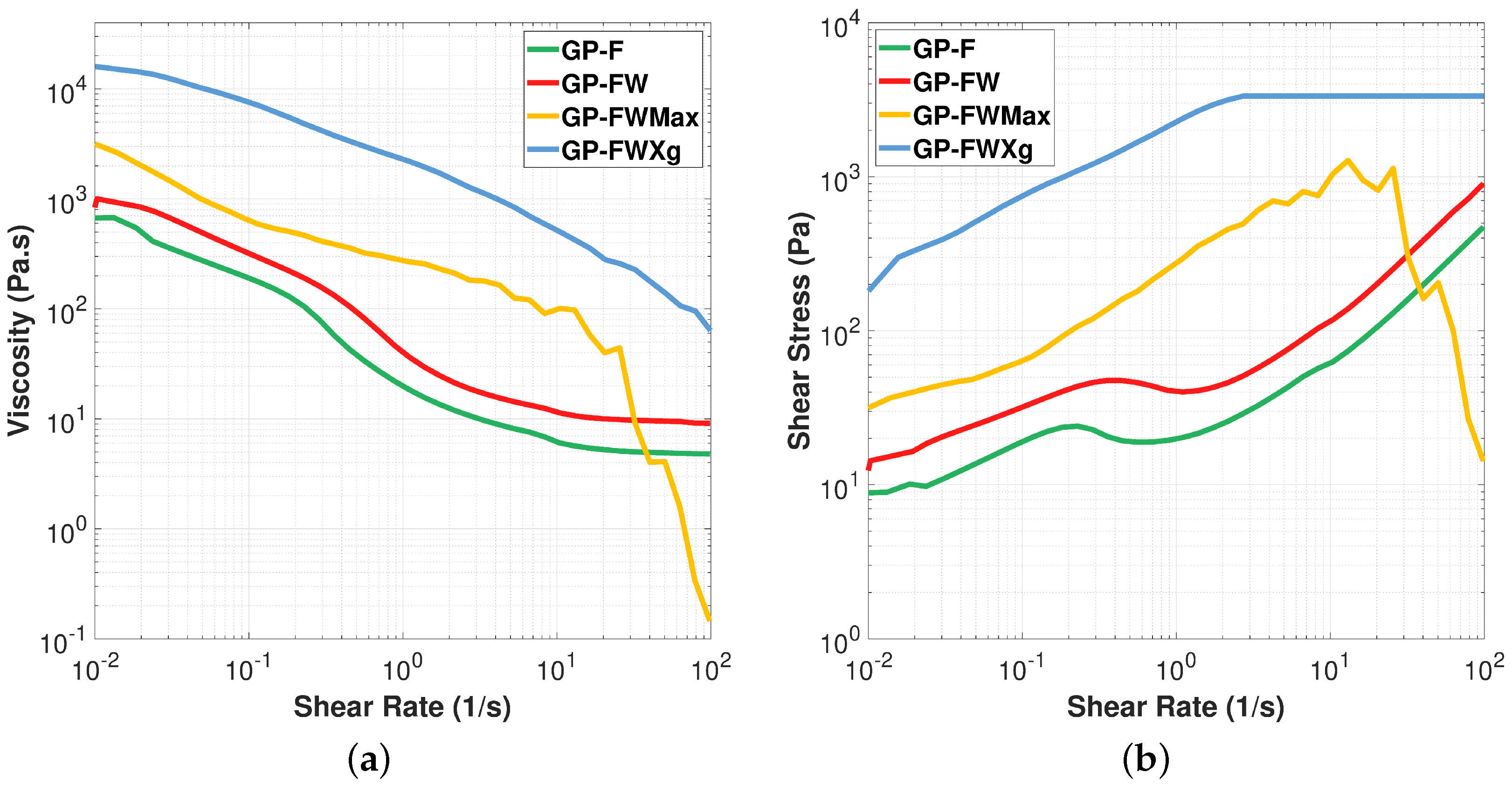
3.1.2. Filler Optimization and Effect of Adding Gelling Agent: Rheological Behavior Evaluation
3.2. Printable Geopolymer-Based Composite Paste
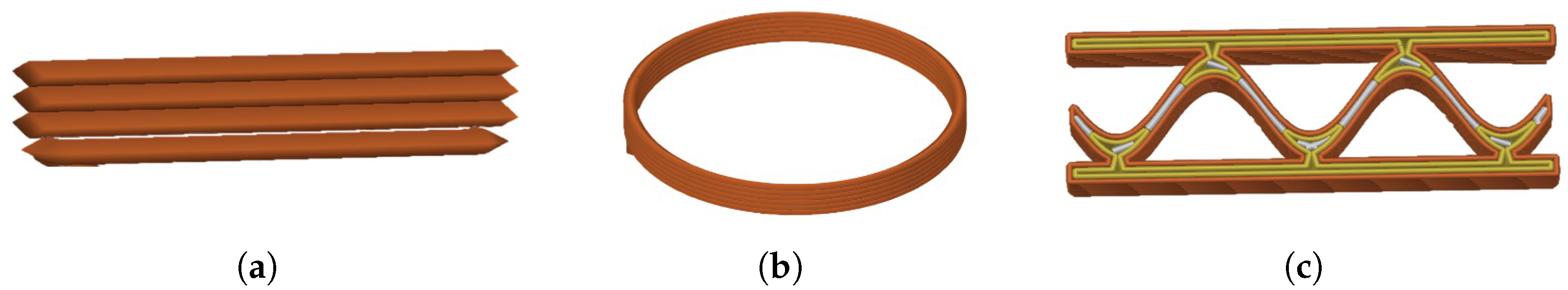
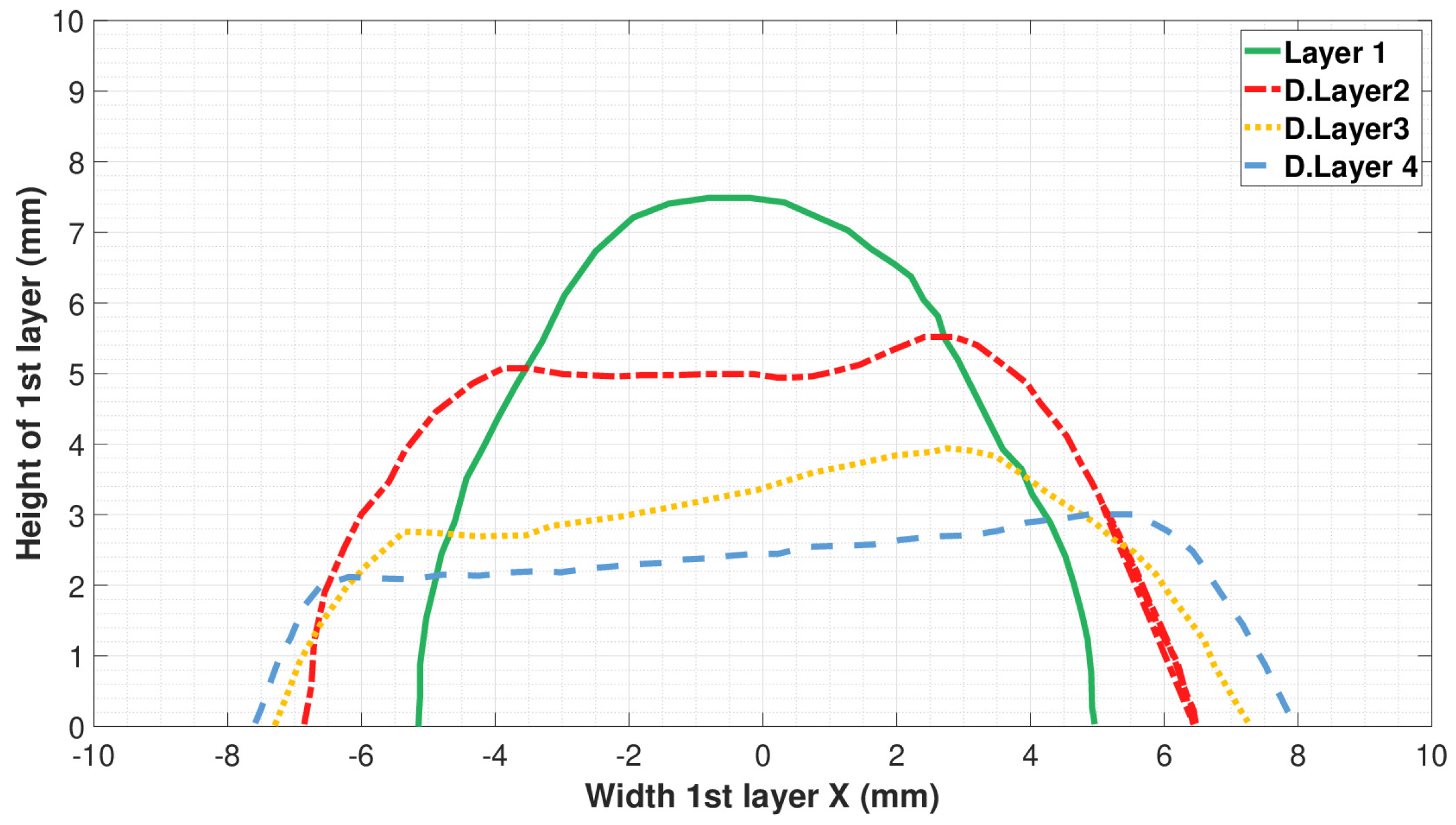
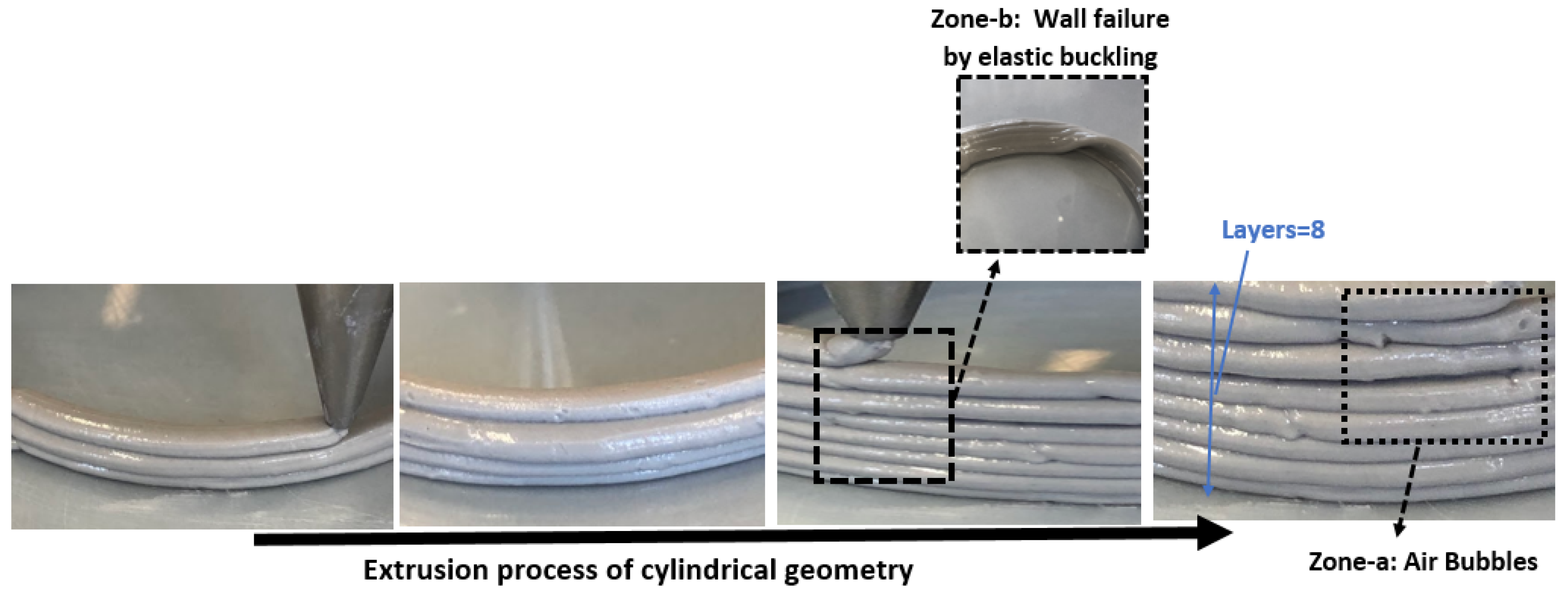
3.2.1. Three-Dimensional Printing of Geopolymer-Based Composite Formula “GP-FWMax”
3.2.2. Three-Dimensional Printing of Geopolymer-Based Composite Formula “GP-FWXg”
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodžić, S.; Šikić, T.F.; Dogan, E. Green environment in the EU countries: The role of financial inclusion, natural resources and energy intensity. Resour. Policy 2023, 82, 103476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satone, S.R.; Parbat, D.K.; Badar, A.M.; Varghese, V.P.; Satone, D.S.; Kawalkar, M.A. Application of green material on durability behaviour of green concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, P.; Legendre, C. Raw Materials Critical for the Green Transition: Production, International Trade and Export Restrictions; OECD: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoodi, O.; Siad, H.; Lachemi, M.; Dadsetan, S.; Şahmaran, M. Optimized application of ternary brick, ceramic and concrete wastes in sustainable high strength geopolymers. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, C.; Li, N.; Jiao, D.; Yuan, Q. Rheology of alkali-activated materials: A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 121, 104061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymer Chemistry and Applications; Institute Geopolymer: Saint-Quentin, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Jiménez, A.F.; Palomo, A. New cements for the 21st century: The pursuit of an alternative to Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers: Ceramic-like inorganic polymers. J. Ceram. Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 335–350. [Google Scholar]
- Hegab, H.; Khanna, N.; Monib, N.; Salem, A. Design for sustainable additive manufacturing: A review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2023, 35, e00576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, D.; Srinivas, D.; Panda, B.; Suraneni, P.; Sitharam, T. Use of industrial waste materials for 3D printing of sustainable concrete: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Tang, Y.; Kim, S.; Rosen, D.W. Human-machine collaborative additive manufacturing. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 66, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N. Rheological requirements for printable concretes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 112, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botti, R.; Innocentini, M.; Faleiros, T.; Mello, M.; Flumignan, D.; Santos, L.; Franchin, G.; Colombo, P. Additively manufactured geopolymer structured heterogeneous catalysts for biodiesel production. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 23, 101022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoude, C.; Prud’homme, E.; Johannes, K.; Gremillard, L. The Mechanical Properties of Geopolymers as a Function of Their Shaping and Curing Parameters. Ceramics 2024, 7, 873–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchin, G.; Scanferla, P.; Zeffiro, L.; Elsayed, H.; Baliello, A.; Giacomello, G.; Pasetto, M.; Colombo, P. Direct ink writing of geopolymeric inks. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 2481–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Fu, S.; Zhao, S.; He, P.; Ma, G.; Wang, M.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y. Direct ink writing of geopolymer with high spatial resolution and tunable mechanical properties. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 46, 102202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, A.; Subhani, T.; Yun, T.S.; Nagesh, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Exploring the Structural Performance of 3D-Printed Geopolymer-based Architectural Components. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 27, 102382. [Google Scholar]
- Ricciotti, L.; Apicella, A.; Perrotta, V.; Aversa, R. Geopolymer materials for extrusion-based 3D-printing: A review. Polymers 2023, 15, 4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; He, P.; Wang, M.; Yan, S.; Jia, D.; He, P.; Wang, M.; Yan, S. Geopolymers and Their Matrix Composites: A State-of-the-Art Review. Geopolymer Geopolymer Matrix Compos. 2020, 311, 7–34. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, B.; Singh, G.V.P.B.P.; Unluer, C.; Tan, M.J. Synthesis and characterization of one-part geopolymers for extrusion based 3D concrete printing. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovářík, T.; Hájek, J.; Hervert, T.; Deshmukh, K.; Pola, M.; Jansa, Z.; Beneš, J.; Svoboda, M. Silica-based geopolymer spherical beads: Influence of viscosity on porosity architecture. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 124, 104261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, P.; d’Ávila, M.; Anand, R.; Moldenaers, P.; Van Puyvelde, P.; Bloemen, V. Insights on shear rheology of inks for extrusion-based 3D bioprinting. Bioprinting 2021, 22, e00129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Fu, S.; Yang, T.; Li, K.; Chen, G.; Dong, Q.; He, P.; Sun, Z.; Duan, X.; Jia, D.; et al. Unveiling the critical role of rheology modifiers in additive manufacturing of geopolymers and their mechanical properties. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 78, 103826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilcan, H.; Sahin, O.; Kul, A.; Ozcelikci, E.; Sahmaran, M. Rheological property and extrudability performance assessment of construction and demolition waste-based geopolymer mortars with varied testing protocols. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 136, 104891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Y.; Phuhongsung, P. Improving 3D/4D printing characteristics of natural food gels by novel additives: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofelice, M.; Messia, M.C.; Marconi, E.; Cuomo, F.; Lopez, F. Effect of the xanthan gum on the rheological properties of alginate hydrogels. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 142, 108768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, N.P.; Olhero, S.M.; Labrincha, J.A.; Novais, R.M. 3D-printed red mud/metakaolin-based geopolymers as water pollutant sorbents of methylene blue. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Pan, J.; Zhu, B.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Meng, L.; Cai, J. Improving mechanical properties of 3D printable ‘one-part’geopolymer concrete with steel fiber reinforcement. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 75, 107077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, R.; Khan, M.A.; Alyousef, R.; Javed, M.F.; Ali, M. Promoting the green construction: Scientometric review on the mechanical and structural performance of geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 368, 130502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilar, F.A.; Ganachari, S.V.; Patil, V.B.; Bhojaraja, B.; Khan, T.Y.; Almakayeel, N. A review of 3D printing of geopolymer composites for structural and functional applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 400, 132869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunothayan, A.R.; Nematollahi, B.; Khayat, K.H.; Ramesh, A.; Sanjayan, J.G. Rheological characterization of ultra-high performance concrete for 3D printing. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 136, 104854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymer Chemistry and Applications, 5th ed.; Institut Géopolymère, Geopolymer Institute: Saint-Quentin, France, 2020; Chapter 21. [Google Scholar]
- Sabbatini, A.; Vidal, L.; Pettinari, C.; Sobrados, I.; Rossignol, S. Control of shaping and thermal resistance of metakaolin-based geopolymers. Mater. Des. 2017, 116, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favier, A. Mécanisme de Prise et Rhéologie de Liants Géopolymères Modèles. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris-Est, Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Keskin-Topan, Y.; Bessaies-Bey, H.; Petit, L.; Tran, N.C.; d’Espinose de Lacaillerie, J.B.; Rossignol, S.; Roussel, N. Effect of maximum packing fraction of powders on the rheology of metakaolin-based geopolymer pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2024, 179, 107482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tuohey, J.; Amini, N.; Morton, D.A.; Hapgood, K.P. 3D printing of customised particles for powder rheology, mixing and segregation study. Powder Technol. 2023, 425, 118576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávila, J.; d’Ávila, M. Rheological evaluation of Laponite/alginate inks for 3D extrusion-based printing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 101, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Chen, S.; Zeng, Q.; Xu, S.; Li, H. Correlating the elastic properties of metakaolin-based geopolymer with its composition. Mater. Des. 2016, 95, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hass, L.; Bos, F. Bending and pull-out tests on a novel screw type reinforcement for extrusion-based 3D printed concrete. In Proceedings of the Second RILEM International Conference on Concrete and Digital Fabrication: Digital Concrete 2020, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 6–8 July 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 632–645. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjayan, J.; Jayathilakage, R.; Rajeev, P. Vibration induced active rheology control for 3D concrete printing. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 140, 106293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, R.I. Engineering Rheology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; Volume 52. [Google Scholar]
- Graessley, W.W. The entanglement concept in polymer rheology. In The Entanglement Concept in Polymer Rheology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 1–179. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, H.A.; Hutton, J.F.; Walters, K. An Introduction to Rheology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Rovnaník, P.; Rovnanikova, P.; Vyšvařil, M.; Grzeszczyk, S.; Janowska-Renkas, E. Rheological properties and microstructure of binary waste red brick powder/metakaolin geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 188, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnoli, M.; Leonelli, C.; Kamse, E.; Gualtieri, M. Rheology of geopolymer by DOE approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewoldt, R.H.; Johnston, M.T.; Caretta, L.M. Experimental challenges of shear rheology: How to avoid bad data. In Complex Fluids in Biological Systems: Experiment, Theory, and Computation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 207–241. [Google Scholar]
- Guy, C.; Jean-Louis, G.; Nicolas, H. Initiation à la Rhéologie (4 Éd.): Bases Théoriques et Applications Expérimentales; Lavoisier: Paris, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- de Andrade, R.; Paim, T.C.; Bertaco, I.; Naasani, L.S.; Buchner, S.; Kovářík, T.; Hájek, J.; Wink, M.R. Hierarchically porous bioceramics based on geopolymer-hydroxyapatite composite as a novel biomaterial: Structure, mechanical properties and biocompatibility evaluation. Appl. Mater. Today 2023, 33, 101875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Rosas, R.; Tejada-Ortigoza, V.; Cuan-Urquizo, E.; Mendoza-Cachú, D.; Morales-de La Pena, M.; Alvarado-Orozco, J.M.; Campanella, O.H. Evaluation of rheology and printability of 3D printing nutritious food with complex formulations. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 58, 103030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, A.; Kulichikhin, V.; Ilyin, S. A modern look on yield stress fluids. Rheol. Acta 2017, 56, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Bhandari, B.; Prakash, S.; Mantihal, S.; Zhang, M. Linking rheology and printability of a multicomponent gel system of carrageenan-xanthan-starch in extrusion based additive manufacturing. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.D.; Akroyd, T.; Kee, D.C.D.; Zhu, L. Yield stress measurements in suspensions: An inter-laboratory study. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2006, 18, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kolli, R. Experimental investigation on mechanical properties of fly ash-GGBFS based GO-geopolymer concrete using mineral sand (Quartz-Feldspar) as fine aggregate. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 60, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, L.; Feng, W.; Ma, H.; Zhang, S.; Shi, H. Investigation on the microstructure and mechanism of geopolymer with different proportion of quartz and K-feldspar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 147, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bong, S.H.; Nematollahi, B.; Xia, M.; Nazari, A.; Sanjayan, J. Properties of one-part geopolymer incorporating wollastonite as partial replacement of geopolymer precursor or sand. Mater. Lett. 2020, 263, 127236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archez, J.; Texier-Mandoki, N.; Bourbon, X.; Caron, J.F.; Rossignol, S. Influence of the wollastonite and glass fibers on geopolymer composites workability and mechanical properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 257, 119511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, A.; Bhandari, B.; Dong, X.; Prakash, S. Feasibility study of hydrocolloid incorporated 3D printed pork as dysphagia food. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 107, 105940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, C.S.; Therriault, D.; Heuzey, M.C. Development of aqueous protein/polysaccharide mixture-based inks for 3D printing towards food applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulayt, A.; Jaafri, R.; Samouh, H.; El Idrissi, A.C.; Roziere, E.; Moussa, R.; Loukili, A. Stability of a new geopolymer grout: Rheological and mechanical performances of metakaolin-fly ash binary mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 181, 420–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.; Im, J.; Prasidhi, A.K.; Cho, G.C. Effects of Xanthan gum biopolymer on soil strengthening. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 74, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Qing, L.; Ma, G.; Zhang, D.; Wei, C. Numerical investigation into effects of rheological properties on grout flow in rock fracture using Herschel-Bulkley model. Eng. Geol. 2024, 329, 107402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, H.; Ikeda, A.; Kawasaki, T.; Miyazaki, K. Universal mechanism of shear thinning in supercooled liquids. Commun. Phys. 2024, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosti, M.E.; Takagi, S. Shear-thinning and shear-thickening emulsions in shear flows. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 083319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, A.; Levato, R.; D’Este, M.; Piluso, S.; Eglin, D.; Malda, J. Printability and shape fidelity of bioinks in 3D bioprinting. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 11028–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, B.; Unluer, C.; Tan, M.J. Extrusion and rheology characterization of geopolymer nanocomposites used in 3D printing. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 176, 107290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mewis, J.; Wagner, N.J. Thixotropy. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 147, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, S.; Rao, K.H.; Forsling, W. Dissolution of wollastonite and its flotation and surface interactions with tallow-1, 3-diaminopropane (duomeen T). Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Aziz, N.A.; Shafri, H.Z.M.; Ahmad, K.A.B. Computational fluid dynamics study on cemented paste backfill slurry. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 369, 130558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, J.F. The rheological behavior of concentrated colloidal dispersions. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 99, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brader, J.M. Nonlinear rheology of colloidal dispersions. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 363101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamipour-Shirazi, A.; Norton, I.T.; Mills, T. Designing hydrocolloid based food-ink formulations for extrusion 3D printing. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniasadi, H.; Kimiaei, E.; Polez, R.T.; Ajdary, R.; Rojas, O.J.; Österberg, M.; Seppälä, J. High-resolution 3D printing of xanthan gum/nanocellulose bio-inks. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery, M.P.; Klein, S.; Richardson, R.; Bartlett, P.; Adams, G.; Dickin, F.; Simske, S. The rheology of dense colloidal pastes used in 3D-printing. In Proceedings of the Nip & Digital Fabrication Conference, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–11 September 2014; Society for Imaging Science and Technology: Springfield, IL, USA, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 140–145. [Google Scholar]
- Quemada, D.; Berli, C.L.A. Interactions Dans Les Dispersions; Stabilisation; Lavoisier: Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kröger, M.; Vermant, J. The Structure and Rheology of Complex Fluids; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Suiker, A.S.; Wolfs, R.J.; Lucas, S.M.; Salet, T.A. Elastic buckling and plastic collapse during 3D concrete printing. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 135, 106016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
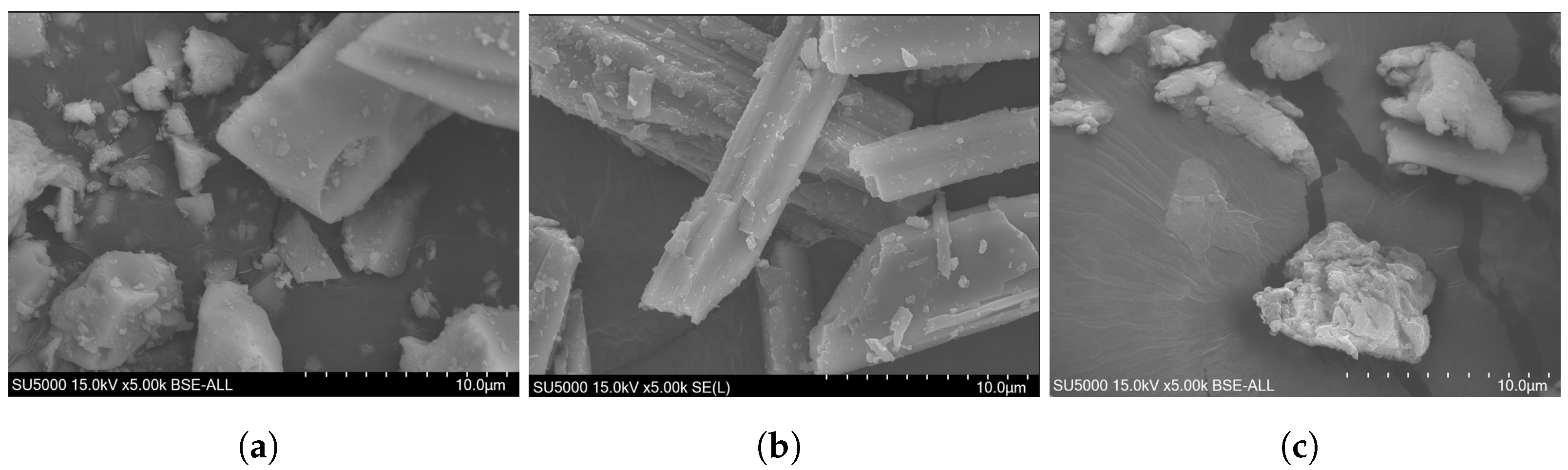
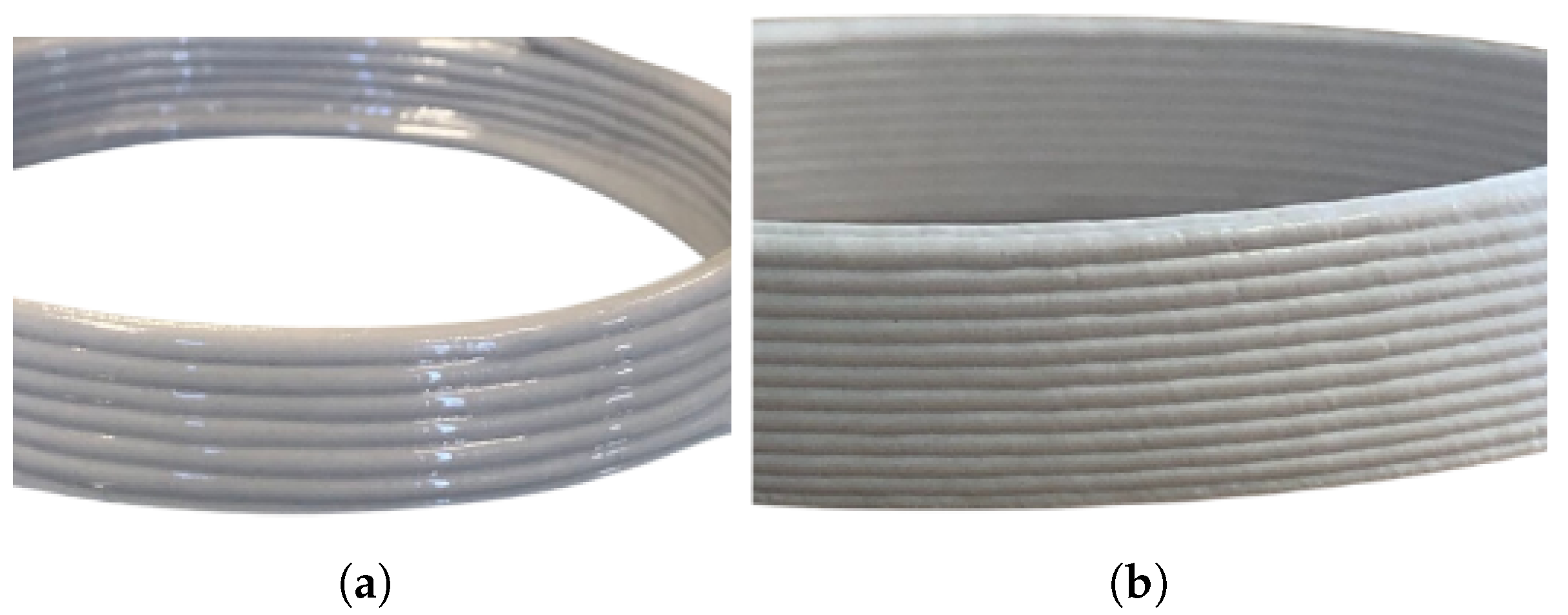
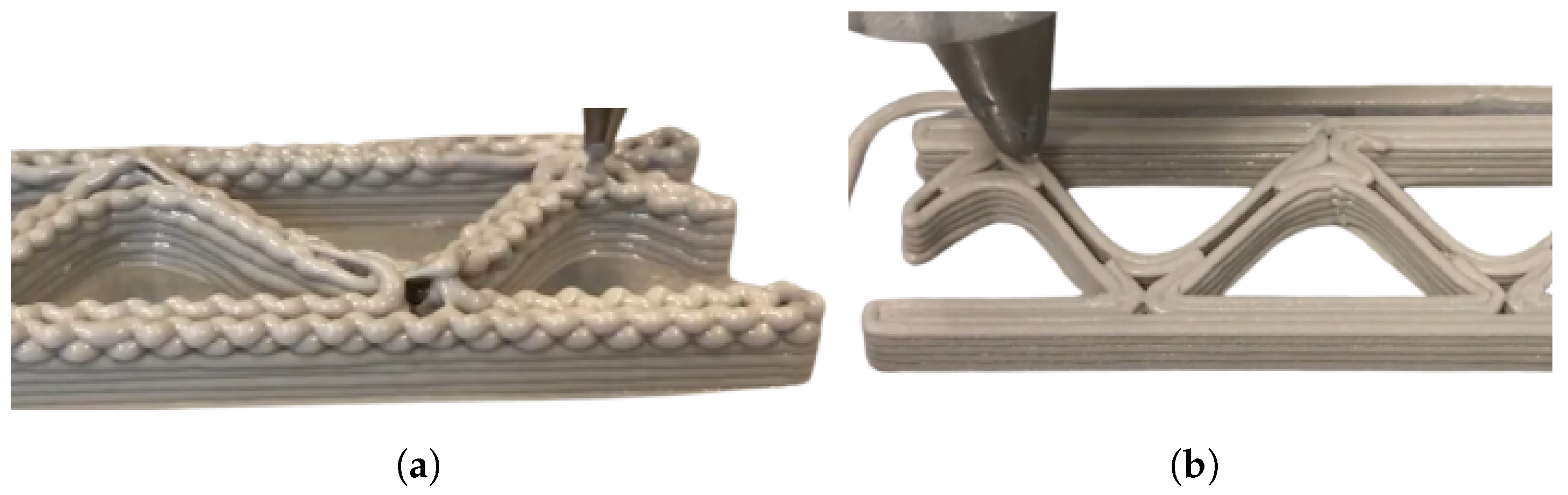
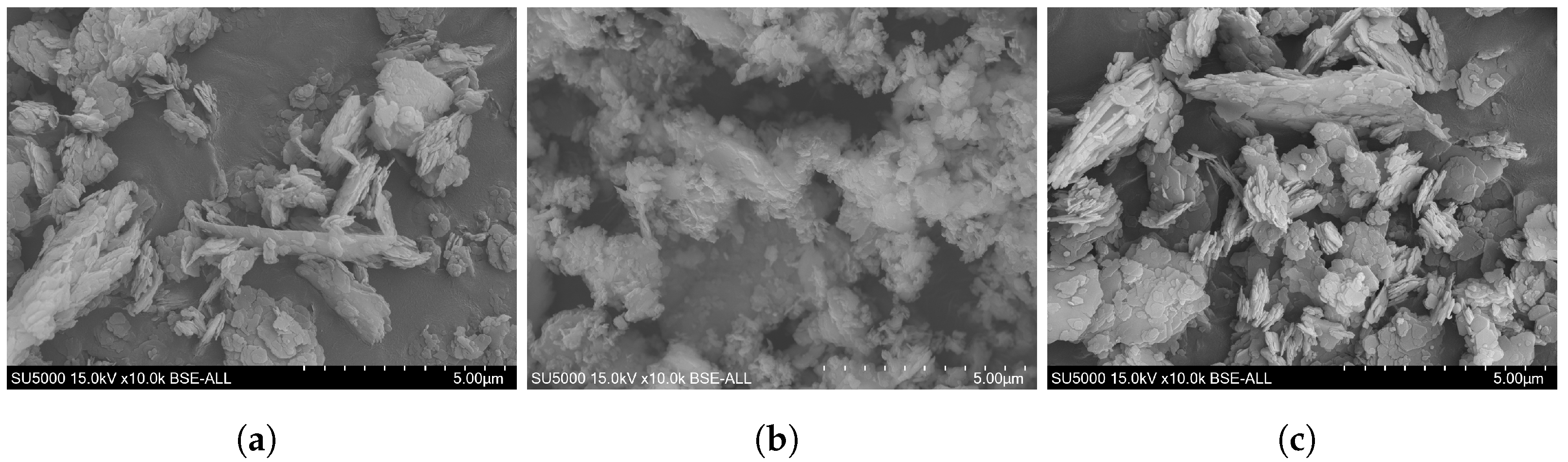

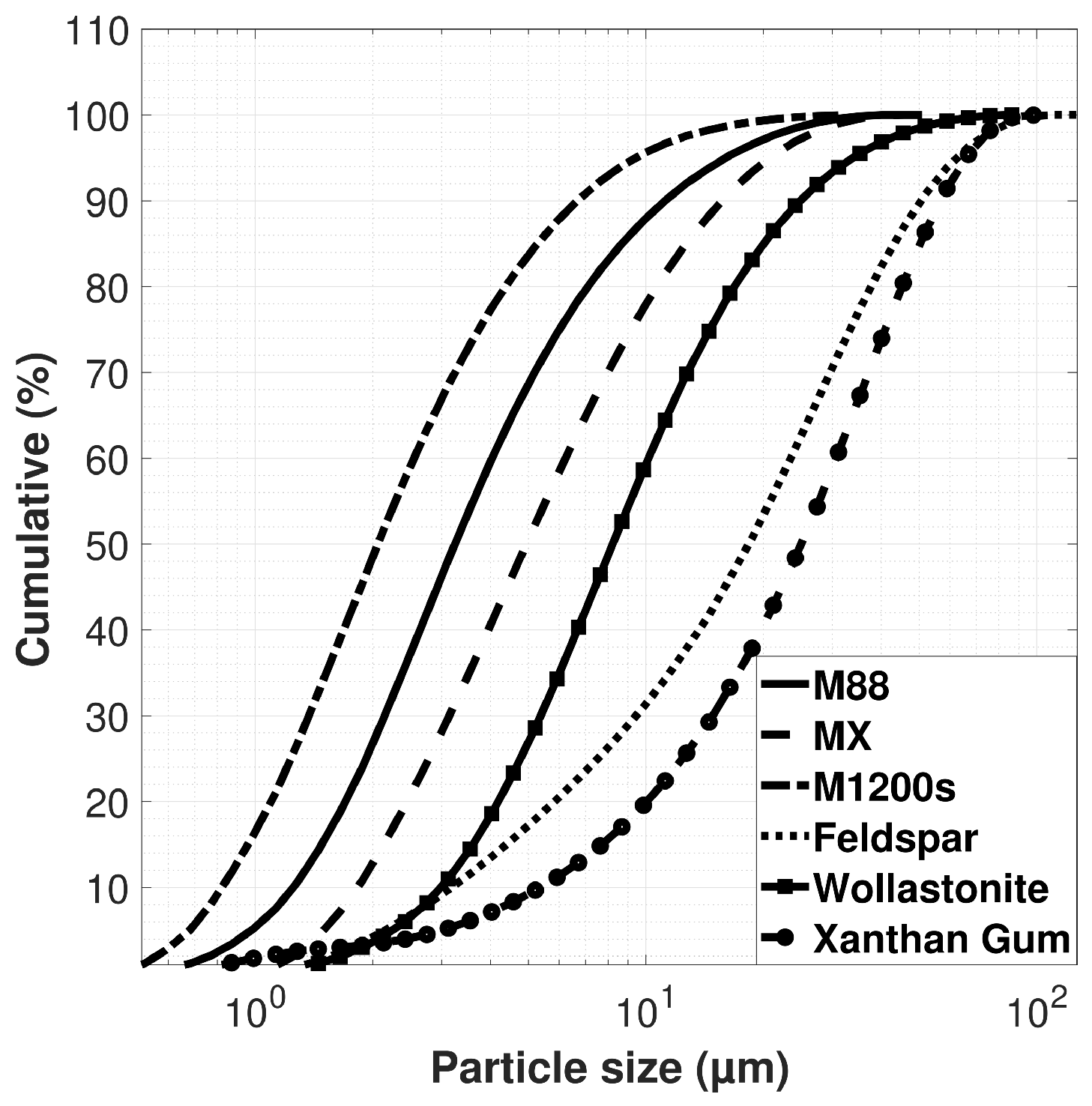

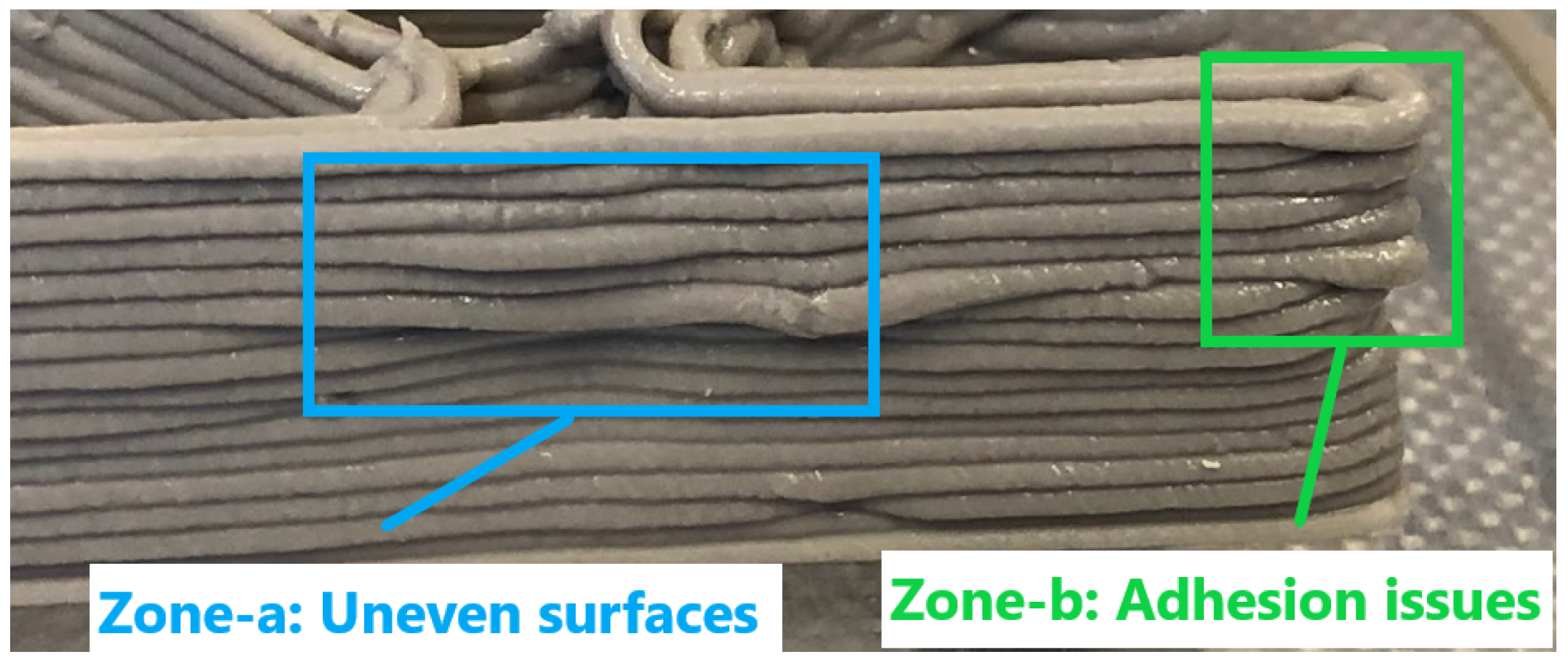
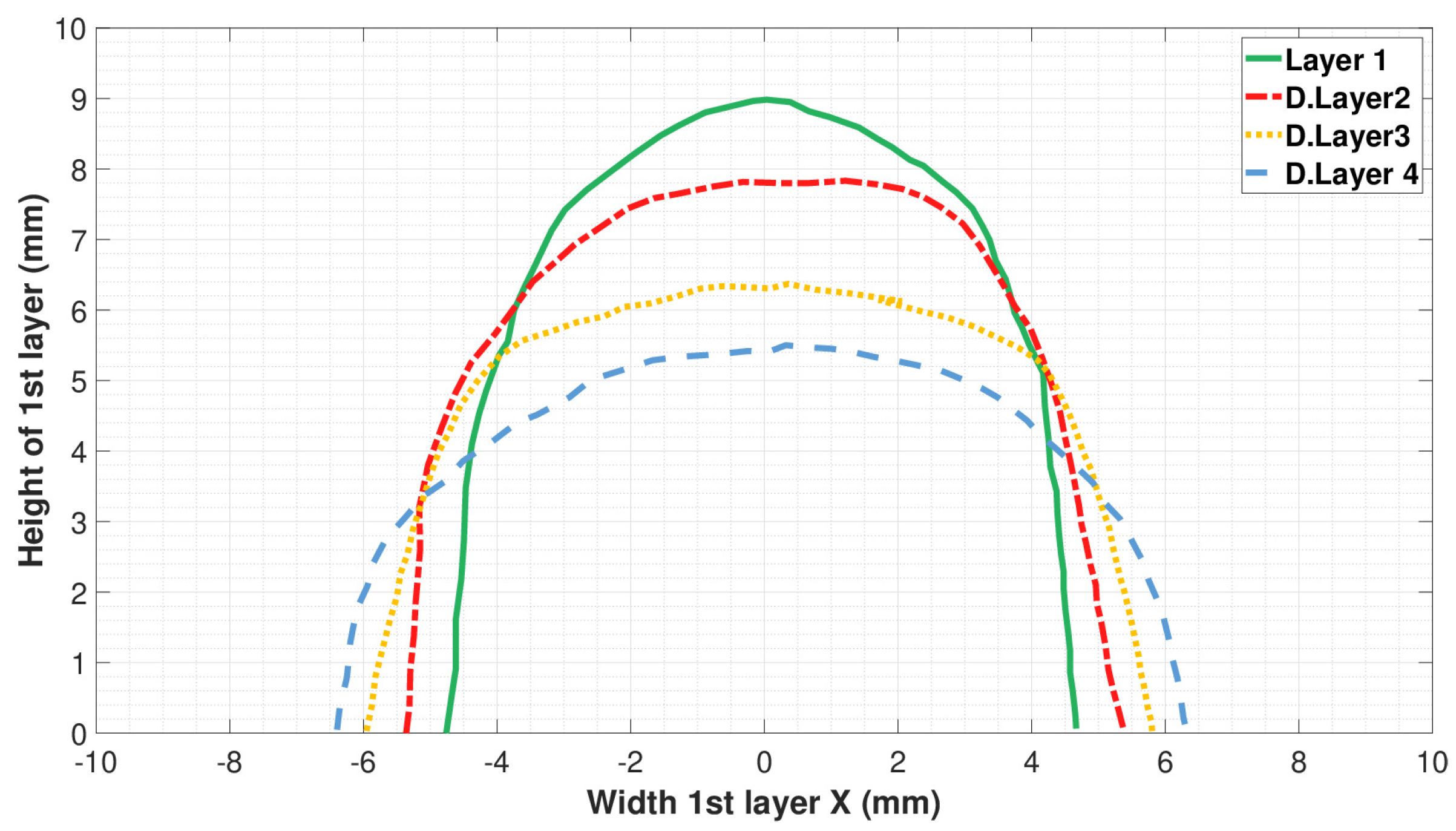


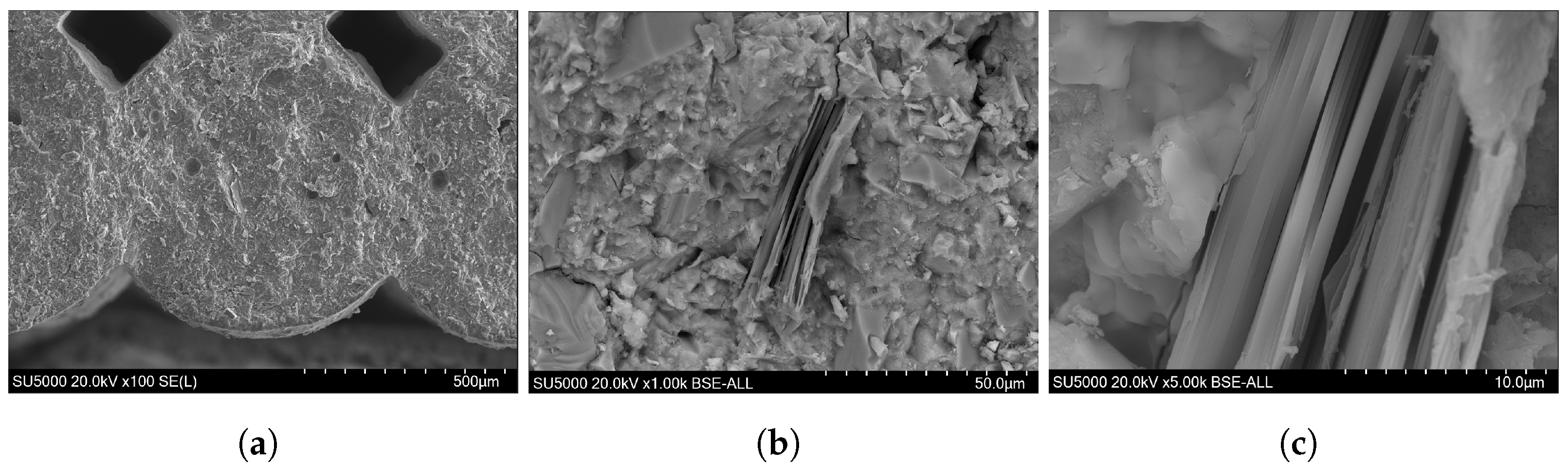
| Sample | O | Na | Al | Si | P | S | K | Ca | Ti | Fe | Zr | Mg | Cl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tempozz M88 | 51.52 | 0.14 | 22.38 | 22.88 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.86 | 0.40 | 1.24 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Metamax | 52.40 | 0.27 | 19.36 | 20.79 | 0.65 | 0.42 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.95 | 0.19 | 4.66 | 0.28 | 0.04 |
| Argical M1200s | 51.11 | 0.08 | 18.52 | 22.07 | 0.60 | 0.15 | 0.70 | 0.12 | 0.52 | 1.24 | 4.03 | 0.84 | 0.01 |
| Feldspar IMX424 | 52.20 | 0.25 | 4.41 | 38.50 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 4.65 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Wollastonite 1250 mesh | 48.99 | 0.00 | 0.28 | 20.16 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 30.27 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.31 | 0.00 |
| Sample | Argical M1200s | Metamax | Tempozz M88 | Feldspar IMX4224 | Wollastonite 1250 Mesh |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median particle size (m) | 2 | 5 | 3 | 20 | 10 |
| Specific surface Area (m2/g) | 29.673 | 22.864 | 25.104 | 3.851 | 51.523 |
| Formula | Feldspar/Fillers (%) | Wollastonite/Fillers (%) | Xanthan Gum/Fillers (%) | Total Weight Fillers (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GP-F | 100 | 0 | 0 | 40 |
| GP-FW | 80 | 20 | 0 | 40 |
| GP-FWMax | 80 | 20 | 0 | 55 |
| GP-FWXg | 79.5 | 20 | 0.5 | 40 |
| Geopolymer Formulas | Viscosity (Pa.s) | (Pa) | K (Pa.s) | n | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GP-F | 566 | 9.01 | 4.624 | 0.912 | 0.993 |
| GP-FW | 1001 | 14.32 | 8.883 | 0.898 | 0.998 |
| GP-FWMax | 2620 | 36.83 | 277.223 | 0.588 | 0.988 |
| GP-FWXg | 15,970 | 181.41 | 2110.793 | 0.413 | 0.976 |
| Formulas | Viscosity (Pa.s) | Recovery (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GP-F | 478.8 | 924.1 | 88.51 | 26.25 | 24.18 | 119.8 | 25.02 |
| GP-FW | 36.92 | 18.59 | 46.26 | 69.56 | 8.98 | ||
| GP-FWMax | 7.22 | 24.6 | 68 | 93 | 179 | 1.16 | |
| GP-FWXg | 914 | 89.24 | |||||
| Time measurement (s) | 500 | 900 | 920 | 950 | 1000 | 1500 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gasmi, A.; Pélegris, C.; Davidovits, R.; Guessasma, M.; Tortajada, H.; Jean, F. Advanced Refinement of Geopolymer Composites for Enhanced 3D Printing via In-Depth Rheological Insights. Ceramics 2024, 7, 1316-1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics7040087
Gasmi A, Pélegris C, Davidovits R, Guessasma M, Tortajada H, Jean F. Advanced Refinement of Geopolymer Composites for Enhanced 3D Printing via In-Depth Rheological Insights. Ceramics. 2024; 7(4):1316-1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics7040087
Chicago/Turabian StyleGasmi, Abrar, Christine Pélegris, Ralph Davidovits, Mohamed Guessasma, Hugues Tortajada, and Florian Jean. 2024. "Advanced Refinement of Geopolymer Composites for Enhanced 3D Printing via In-Depth Rheological Insights" Ceramics 7, no. 4: 1316-1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics7040087
APA StyleGasmi, A., Pélegris, C., Davidovits, R., Guessasma, M., Tortajada, H., & Jean, F. (2024). Advanced Refinement of Geopolymer Composites for Enhanced 3D Printing via In-Depth Rheological Insights. Ceramics, 7(4), 1316-1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics7040087









