Abstract
3D printing of ceramics has started gaining traction in architecture over the past decades. However, many existing paste-based extrusion techniques have not yet been adapted or made feasible in ceramics. A notable example is coextrusion, a common approach to extruding multiple materials simultaneously when 3D-printing thermoplastics or concrete. In this study, coextrusion was utilized to enable multi-material 3D printing of ceramic elements, aiming to achieve functionally graded porosities at an architectural scale. The research presented in this paper was carried out in two consecutive phases: (1) The development of hardware components, such as distinct material mixtures and a dual extruder setup including a custom nozzle, along with software environments suitable for printing gradient materials. (2) Material experiments including material testing and the production of exemplary prototypes. Among the various potential applications discussed, the developed coextrusion method for clay-based composites was utilized to fabricate ceramic objects with varying material properties. This was achieved by introducing a combustible as a variable additive while printing, resulting in a gradient porosity in the object after firing. The research’s originality can be summarized as the development of clay-based material mixtures encompassing porosity agents for 3D printing, along with comprehensive material-specific printing parameter settings for various compositions, which collectively enable the successful creation of functionally graded architectural building elements. These studies are expected to broaden the scope of 3D-printed clay in architecture, as it allows for performance optimization in terms of structural performance, insulation, humidity regulation, water absorption and acoustics.
1. Introduction
In the field of architecture, there is a growing interest in 3D-printing clay [1]. Yet, paste-based 3D printing of ceramics is not as technologically advanced as it is with other materials such as polymers, metals or concrete [2]. Gradient materials, along with the concept of coextrusion (also referred to as simultaneous extrusion), are utilized in various research fields and scales. Coextrusion is a manufacturing process that involves combining two or more different materials, often in the form of polymers or composite materials, and simultaneously extruding them through a single die or nozzle. This results in a single continuous product with distinct layers or components. This section aims to provide an overview of the relevant references from various disciplines, categorized based on nozzle diameter: micro scale (nozzle diameter < 1 mm) and macro scale (nozzle diameter > 1 mm). Beyond the scale of the material being printed, porosity can be found within the designed object itself, defined by the printing path, to form complex internal geometries [3].
Controlled gradient porosity offers performance optimization potential [4], as varying material densities perform differently in terms of load bearing, insulating and humidity regulating [5], and have been discussed regarding architectural features for over a decade [6]. In combination with the coextrusion concept, this approach enables the incorporation of porosity within a contained extrusion while maintaining control over the surface quality [7]. On a micro scale, the 3D printing of functionally graded porosities is predominantly bio-inspired [8,9]. There is in-depth research regarding its effects on the mechanical properties [10] and thermal conductivity of porous materials [11], as well as corrosion resistance and environmental adaptation [12]. At this scale, porosity in ceramics is achieved by utilizing foam [13] or electrochemical gradation [14], among other things. On a macro scale, multi-materials are being well established in order to create gradient properties, such as color, in deposition modeling (FDM) printing [15,16]. References also show that there are methods for the functionally graded 3D printing of concrete, where materials are mixed right before being extruded [17]. However, the number of references for the multi-material paste-based extrusion of clay at the scale of building components is comparatively low. An early example of mixing up to four materials, including ceramics and metals, for 3D printing is Robocasting Technology [18]. This method involved the printing of layers of combustible support material within the object, which were subsequently incinerated after firing, thereby creating voids within the final object. Relevant test samples were produced with nozzle sizes around 1 mm in diameter. Investigations on a gradient material change while printing have continued in recent research [19]. The most notable example for coextrusion, regarding its relation to architectural applications, is a project named Janus Printing [20], where the coextrusion of different types of clay is utilized in order to color printed objects differently. The discussion of their research suggests the use of coextrusion to create gradient material properties such as density/porosity. Further, various artists [21,22,23,24], as well as commercially available 3D clay printers capable of dual material extrusion [25], are using multi-material approaches in order to color designs differently. Additionally, biological foaming techniques have been used to successfully create porosity in unfired clay bodies [26]. However, challenges exist in digitally representing multi-materials with gradient material changes for digital simulations [27]. The current software is particularly limiting when it comes to representing material distributions and porosities at different scales within a single object [28].
This work advances the development of functionally graded 3D-printed ceramics in architecture in that it goes beyond the current research by taking into account what potential will unfold for clay-based multi material printed objects when fired.
2. Materials and Methods
The research was carried out in two phases: (1) The development of hardware components, including suitable material mixtures, a custom nozzle, a dual extruder setup (described in Section 2.1) and a software work environment (described in Section 2.2). (2) The second phase focused primarily on material experiments and the subsequent analysis of the results. This included tests to evaluate the printing parameters for different material compositions (described in Section 3.1 and Section 3.2), as well as the production of exemplary prototypes (described in Section 3.3). To determine changes in the porosity of the ceramic, a method involving the measurement of the water absorption difference was utilized [29].
2.1. Hardware Setup
In order to achieve a controlled coextrusion of clay, various hardware components, including suitable material mixtures, a custom nozzle and a dual extruder setup, had to be designed and produced as prototypes.
2.1.1. Material Mixtures
An initial investigation was performed to develop a suitable clay mixture for the primary material to be positioned on the outside of the extrusion (in the following, referred to as the primary material). Additionally, a material mixture containing porosity agent additives (in the following, referred to as secondary material) was developed for placement at the center of the extrusion. The following criteria were used for evaluating a suitable material composition: printability, compatibility of the primary and secondary material and solidification or combustibility during the firing process.
For the primary material, a mixture of clay powder and water was prepared at a weight ratio of 10:3. The clay powder type 208 (Goerg & Schneider, Boden, Germany) was chosen based on existing knowledge regarding its printability, shrinkage behavior and properties after firing at various temperatures from preliminary work. This clay type is classified as semi-fat to fat, indicating a strong binding ability, which is especially advantageous when mixed with porosity agents. Compared to clay mass, clay powder has the advantage of allowing the water content to be determined exactly. Further, powder has proven more reliable in achieving homogeneity when mixed with additives, as described in the following paragraphs. The clay powder is composed of 75.0% SiO2, 19.8% Al2O3, 2.2% K2O, 1.4% TiO2, 0.9% Fe2O3, 0.3% MgO, 0.2% CaO and 0.10% Na2O. We aimed to keep the amount of water as low as possible to decrease the effect of shrinkage or potential cracking during the drying process, while still being able to print it under the conditions suggested by the manufacturer of the printer.
The composition of the secondary material was based on common porosity agents used for the production of commercially available ceramic bricks. Measurements carried out by one of the co-authors in [30] show the pore structure caused by such porosity agents in fired clay. To give the reader an idea of the pore spaces that can be generated in this way, examples of results from micro-computed tomography measurements and electron microscopy images are shown in Figure 1.
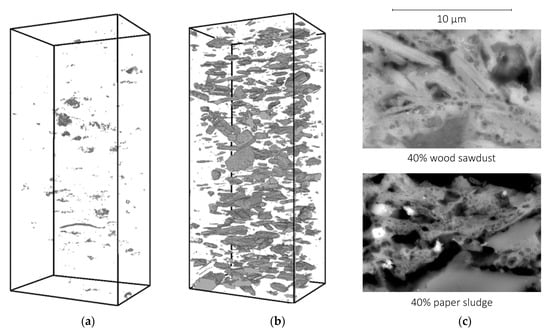
Figure 1.
Pore structures visualized using an lCT40 micro-computed tomography device from Scanco, Switzerland. (a) 10 vol.-% paper sludge, (b) 10 vol.-% sawdust—both on 6 × 5 × 15 mm3 samples. (c) Micropores in fired clay as captured using scanning electron microscopy.
The material experimentation phase started with mixing dry clay powder and (1) paper fibers, (2) wood sawdust and (3) lignite (brown coal). We aimed to make use of materials that are clarified as waste materials by other industries for sustainability reasons. Additionally, the chosen material should be locally available and have a value approximately equivalent to that of the used clay powder. A set of various material compositions was produced, with the ratio of porosity agent to clay powder ranging from 1:7 to 1:1. All mixtures were created by mixing the dry clay powder with the porosity agent first, while water was added as a second step to ensure a homogeneous distribution of the porosity agent within the material mixture. After the initial experiments, paper fibers exhibiting a clumping behavior, which caused the nozzle of the 3D printer to clog while printing, were excluded from further experiments. Viable results were obtained while using both wood sawdust and lignite. Due to the comparatively difficult acquisition of lignite and its greater environmental impact compared to wood [31], subsequent experiments focused on working with wood sawdust. The oak wood sawdust, sourced from the byproduct of a nearby wood workshop, underwent sieving to achieve a particle size of <1 mm or <2 mm, aiming to ensure material homogeneity and an uninterrupted printing process. Due to the water-binding behavior of wood sawdust, it was necessary for the secondary material to be softer than the primary one. This fact influenced the parameters of the nozzle design discussed in Section 2.1.2. Further, it was observed that wood sawdust, characterized by its intact cellulosic fibers, slightly increased the tensile strength of the dried mixture compared to those containing lignite. This provides greater design flexibility for objects to be 3D-printed. For each material composition containing wood sawdust as a porosity agent, cubic testing samples measuring 5 cm × 5 cm × 5 cm and flat samples measuring 1 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm were fabricated. All mixtures were manually shaped by filling molds with them after adding 35% to 50% of the dried mixture’s weight in water. In order to evaluate the effects of different amounts of porosity agents, the set of test objects was fired at 1070 °C. For firing, a Top 60/R (Nabertherm, Lilienthal, Germany) top loader kiln was used. The firing procedure was programmed to include the following phases: 0 °C to 600 °C in 5 h, 600 °C to 1070 °C in 6 h, remaining at 1070 °C for 20 min, followed by a cooldown phase undefined in time (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Cubic samples, unfired and fired, of material mixtures of wood sawdust and clay ranging from weight ratios of 2:7 (left) to the printable maximum of 1:3 (center) and 1:1 (right).
The objective was to determine the maximum amount of wood sawdust that could be added to the clay while maintaining printability and stability after firing. The stability was classified into low, medium and high brittleness based solely on qualitative measures. A weight ratio of sawdust to clay powder at 1:2 was identified as the maximum for maintaining stability after firing at a peak temperature of 1070 °C; exceeding this ratio caused the porous samples to burst. Additionally, a weight ratio of 1:3 was found to be the maximum for printing with the hardware setup used for extruding the secondary material, as discussed in the following section. Higher ratios of wood sawdust would require increased air pressure for extrusion, leading to water separation and a significant slowdown in the printing process.
Subsequent experiments demonstrated that higher levels of porosity could be achieved via the incorporation of additional binding agents alongside the clay. The tested binding agents included glue (based on methylcellulose), agar-agar, and alginate, which helped prevent water separation from the material mixture. Moreover, it was observed that adding oil or grease to the mixture eased the cleaning of the 3D printer components, especially in clay-based mixtures with a high water content (<40%), which tend to adhere to surfaces. It is important to note that the use of lubricants is recommended only for the secondary material as it may otherwise weaken the layer bond of the primary material during printing. However, for subsequent experiments, no additives were introduced to minimize the number of influencing parameters and to ensure the comprehensibility of the results.
In order to measure the effects of the different porosities of the material mixtures, the water absorption capacity was assessed. For this purpose, the fired samples were immersed in a water bath for 72 h, and the difference in weight before and after was measured (Table 1). The variation in water absorption provided insights into the different levels of porosity. The table below illustrates that with an increasing amount of porosity agent, water absorption increases significantly. It is assumed that values deviating from the average ascending curve are due to irregularities during the manual filling of the molds.

Table 1.
Comparison of different material compositions fired at 1070 °C regarding water absorption and brittleness. In these mixtures, oak wood sawdust with a maximum particle size of 1 mm was employed as the porosity agent. Entries marked with an asterisk (*) were mixed with a maximum particle size of 2 mm.
2.1.2. Coextrusion Nozzle
The design of a custom nozzle was crucial for successful coextrusion. A set of initial nozzle designs was printed from PLA using a commercially available FDM 3D printer. We aimed to design the nozzle by placing the secondary material at the center of the primary material. Therefore, a nozzle with an extrusion diameter of 4 mm was incorporated into a larger nozzle with an extrusion diameter of 10 mm. While the larger nozzle extruding the primary material was directly connected to the extruder XL of the printer mounted directly above, the smaller nozzle extruding the secondary material was fed from the additional standard extruder mounted next to it, entering the nozzle from the side (Figure 3, left). In designing the nozzle geometry, it was necessary to ensure that both nozzles ended at the same height to prevent mutual blockage of the material flow. For the production of the final nozzle, the Saturn 8K resin 3D printer (Elegoo, Shenzhen, China) was used. It utilized Anycubic Standard Photopolymer Resin and SLA (stereolithography) technology to achieve thinner wall thicknesses compared to PLA prototypes, essential for preventing air entrapment within the two extrusions. Compared to prototypes from FDM (fused deposition modeling) printers, the SLA-printed nozzles exhibited smoother surfaces, eliminating the need for additional surface smoothing procedures. After the fabrication process, the prints were detached from the printing bed and then hardened using an Anycubic Wash and Cure 2.0 in a specialized liquid for a duration of 20 min. When comparing equal material quantities, no significant differences in hardness were observed during iterative physical testing. Finally, the nozzles were mounted on the screw thread of the extruder and a tube feeding the secondary material mixture was attached.
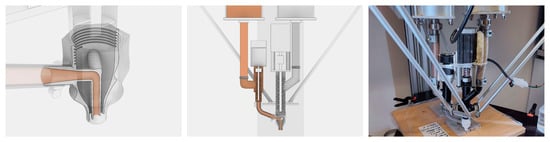
Figure 3.
The custom nozzle to enable coextrusion being designed in 3D (left), schematic drawing of the hardware setup (center) and the dual extruder setup (right).
2.1.3. Dual Extruder Setup
An LDM (Liquid Deposition Modeling) 3D printer from Italian company WASP named Delta WASP Clay 40100 (Massa Lombarda, RA, Italy), which is especially designed for printing clay, served as the starting point for the hardware setup. The printer operates using a pressurized material tank that feeds a moveable extruder. Inside, a stepper motor controls the amount of material being extruded by rotating a screw conveyor. For printing multiple materials, the printer was extended by a second material tank, equipped with a second pressure reducer, and a second extruder. For extruding the primary material, the LDM WASP Extruder XL 2.0 was used. For extruding the secondary material, a smaller variant, the LDM WASP Extruder 2.0, was used (Figure 3, center). A second material tank with a separate pressure regulator was attached, and both extruders were mounted in such a way that the printer’s Delta system’s freedom of movement remained unrestricted (Figure 3, right). Further, several modifications had to be made to the printer itself. Unused output pins at the motherboard of the printer were used to control the second stepper motor by sending step and direction signals to an external stepper motor driver. To achieve this, it was necessary to install firmware typically used for controlling a continuous feeding system, which includes a large degassing extruder that replaces the pressurized tank.
2.2. Software
Version 7 SR 20 of the Rhinoceros 3D (McNeel Europe S.L. C/de Roger de Flor, 32, 08018 Barcelona, Spain) modeling software and its programming tool Grasshopper were used for providing the necessary machine data. A digital model of the hardware setup was used to simulate the printing procedure. This allowed for designing while also providing a tangible sense of the actual scale, and prevented collisions with the attached hardware components, such as the second extruder and the connecting tube for the custom nozzle. For this research, a Grasshopper plugin, named Termite [32], previously written for generating G-codes for clay printing, was extended with functions to control both extruder motors independently. This improvement enables the design and provision of machine data to be accomplished within a single software platform, ensuring a highly streamlined workflow. Distributing desired segments of printing paths on different layers within Rhinoceros determines the composition of the extrusion at a given area within the printed object.
3. Material Experimentation and Results
In order to assess the viability of the previously defined variables, such as the ratios of material mixtures, pressure settings and the nozzle design, and to further clarify which additional parameters are required for multi-material printing, three experiments were conducted. These experiments included sets of test objects with varying material compositions.
3.1. Experiment 1: On/Off Distribution
To enable visual differentiation of the secondary material, red clay type 302 (Goerg & Schneider, Boden, Germany) was utilized as secondary material with a weight ratio of clay, water and wood sawdust of 4:2:1, allowing printing at a minimum speed of up to 1500 mm/m. The comparable characteristics of the differently colored clay masses, including flow behavior, shrinkage and water absorption, facilitated the coextrusion of both materials without the occurrence of cracks or deformation during the drying process. The first set of printed test objects consisted of rectangular-shaped bodies measuring 100 mm × 100 mm × 15 mm exhibiting three layers of printing paths. The objects were printed along a continuous path throughout the entire piece. After drying, the test pieces were cut open to observe the composition of the extrusion. A test object was labeled successful when it met the following criteria: (1) The outside dimensions of all extrusions deviated by less than 1 mm from the planned cross section of 10 mm × 5 mm. (2) There were no visible cracks in the primary material exposing the inside due to overpressure on the secondary material. (3) No visible air inclusions were present within an extrusion. An effective controlled distribution of the secondary material was evident, as several test objects demonstrated the successful placement of the secondary material within selected extrusions (Figure 4).

Figure 4.
Test specimens exhibiting distinct material distribution within individual printed objects comprising standard extrusion with only the primary material (left), with a continuous coextrusion of primary and secondary material (center) and switching between standard extrusion and coextrusion according to printing path information (right) without affecting the overall geometry of the test specimens.
As a next step, test samples measuring 15 cm × 15 cm and composed of 32 horizontal layers were printed to include different patterns in order to further evaluate the successful positioning of the secondary material within a more elaborate framework. After drying, the samples were fired at 900 °C. The samples were meticulously sanded using a LaboPol-35 (Struers, Copenhagen, Denmark) grinding and polishing machine to reveal the material distribution within the extrusion. The first prints showed a delay of the secondary material caused by the distance between the auger and end of nozzle. For the next set of test specimens, this delay was measured and successfully compensated for by informing the printing paths (Figure 5).

Figure 5.
Sanded test specimens comparing consistent printing settings (left) with the successful positioning of the inside material according to multiple user-defined patterns such as circular arrangement (center) and crossed arrangement (right).
3.2. Experiment 2: Gradient Distribution
After several iterations, adjustments to independent stepper motors as well as the pressure on the individual tanks were achieved in order to meet all previously mentioned criteria. According to the viscosity of the material mixtures described in the previous section, the pressure of each tank was adjusted to ensure the proper extrusion of the material. The higher the pressure, the faster the material was fed to the extruder. When the pressure was too low, the screw conveyor was not able to extrude its full volume, as the supply of material from the tank proved insufficient for the printing speed of 300 mm/m used. When the pressure was too high, the material tended to squeeze out the water content when being congested, resulting in an inhomogeneous material supply. The machine is built for a maximum pressure of 8 bar. The pressure for the primary material was set to 6 to 8 bar, while the pressure for the secondary material was set to 3 bar, both leaving a buffer for moments where irregularities in the material mixtures would cause problems. In the context of this research, the gradient, which has a theoretically infinite resolution, was discretized into five distinct settings, resulting in five different mixtures. This approach was adopted to illustrate the potential of the developed technique. It is worth noting that this number can be expanded as desired, as it merely depends on digital information. Table 2 contains a summary of the printing parameters and the resulting material compositions, while Figure 6 shows the cross-sections of the printed pieces.

Table 2.
Overview of printing parameters resulting in different material compositions.

Figure 6.
Cross-sections of different material compositions within one extrusion. From left to right, Mixtures 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 as described in Table 2.
3.3. Experiment 3: Architectural Prototype
Finally, to demonstrate the application at an architectural scale, exemplary prototypes of multiple facade panels with gradient porosities were fabricated, which would not have been possible using conventional 3D printing methods for clay (Figure 7, left). The final prototype fabricated within a printing speed range of 200 to 300 mm/m exhibited no notable decline in accuracy within regions featuring multiple material compositions. The prototypes measure 30 cm × 30 cm with a front side that can be freely designed. The double-wall structure allows the object to be spiralized within a continuous print path, thus reducing the production time and achieving a higher surface quality. The backside includes multiple bracings as well as a rail that enables elements to be hung on a metal substructure. Several overlapping elements are installed, similar to roof tiles, to prevent water penetration. Additionally, the overlapping compensates for any inaccuracies in dimensions. The prototypes are printed lying on their side to allow for 90° overhangs in the final positioning (Figure 7, middle). Based on results of Experiments 1 and 2, the printing paths of the front face of the facade element were designed so that the gradient porosity inside would achieve an area-specific humidity control and cooling effect. The drying process was conducted in an indoor room environment with an average humidity level of 60%. Temperature fluctuations ranging from 18 °C to 22 °C were not considered during the drying process. While monitoring the drying process of the ceramic elements, it was observed that the designated areas of the object were able to successfully store water for a longer period of time, thereby increasing the cooling effect of the environment without affecting the surface quality on the outside (Figure 7, right).

Figure 7.
Concept drawing visualizing the cooling effect (left), printing process of the architectural prototype (center) and a mockup of printed objects exhibiting varying water absorption (right).
4. Discussion
We successfully developed hardware and software components in order to produce 3D-printed ceramic building elements including gradient porosities. It can be assumed that the pore structure introduced by the porosity agents consists mainly of compact pores at different length scales (see Figure 1). This is ideal for high thermal resistance. This was achieved by using a dual extruder setup including a custom-designed nozzle for coextrusion and introducing a combustible material mixture as the filling material. This opens up the possibility for completely new designs of 3D-printed ceramics that are not only more customized but also highly functional and material-efficient.
Currently, the main limitation is the need for low viscosity in the secondary material, which restricts the number of layers that can be printed without the structure collapsing under its own weight. Printed objects with multi-material compositions were observed to be more prone to warping behavior caused by the detachment or debonding of the printed layers during the firing process when compared to objects composed solely of clay. To mitigate such defects, it is crucial to ensure optimal layer bonding by ensuring adequate material flow and thoughtfully designed printing paths, along with a controlled deceleration of the drying and firing processes. Another aspect that requires consideration pertains to the expenses associated with the necessary fabrication equipment and the need for proficient personnel to utilize the developed software tools for real-life applications. With the increasing adoption of 3D printing in the ceramic building industry, machine prices are expected to decrease and workers will become more proficient through education on the application of the required software. Multi-material printing presents a meaningful extension of the conventional methods of 3D-printing clay. Objects with gradient porosities have the potential for industrial production, both in the high-performance sector of the building industry and in various other fields.
5. Perspectives
While this research introduced the use of porosity agents in order to change the porosity of the printed object, various other material combinations and corresponding applications are enabled by the concept of the coextrusion of clay-based materials. Having a combustible secondary material allows for hollow extrusions once fired. The created tubes can be used to contain cold or hot water in order to regulate temperature or humidity [4]. The use of gel-like support materials [33] allows the removal of the inside material without the need for firing by using air pressure, allowing hollow structures also to occur in unfired clay. Further, applications of unfired coextruded clay components are viable, e.g., when organic material is used as the inside material in order to act as a substrate for mycelial growth, allowing for fiber reinforcement as well as acting as a binding agent of multiple components [34]. Filament or thread materials can be used inside the extrusion as a reinforcement in order to support the clay while printing, resulting in the increased bringing ability of wet clay [35,36], thus allowing for more spatial and net-like designs to be fabricated [37,38]. Further, magnetic materials can be introduced in order to support extrusion from the inside while printing [39]. When engaging in multi-material printing, it is necessary to consider the shrinkage characteristics of both materials to accommodate the drying and firing processes [4]. However, it is also conceivable that disparate behaviors can be utilized advantageously. A secondary material could be used to prestress certain areas to compensate for shrinkage or to enable self-formation. As the amount of water dictates the process of drying and shrinking, the drying behavior can be gradually controlled within the composite [40]. Considering the drying process, the secondary material can function as a heat conductor, allowing for a more homogenous drying process. This is because the drying of the objects is not solely dependent on the overall geometry once the areas that lead to different drying times are exposed or enclosed. Instead, the objects can be additionally heated from the inside in order to provide more consistent drying. Further, it is imaginable to shift the focus from clay as a final material toward being a reusable support material [41]. Thermoplastics or other viscous materials could be printed inside a clay extrusion to create spring-like prints when unfired clay is washed off. Another potential application involves utilizing the two distinct diameters of the custom nozzle with the same material. This allows for different resolutions within a single print without the need to change the nozzle [20].
From a mechanical point of view, the first sophisticated micromechanical models for fired clay were recently developed by co-authors of this work. These are able to predict the stiffness [42], thermal conductivity and strength [43,44] of fired clay depending on the pore volume and pore morphology. With the development of these models, this proposed work becomes especially relevant. The varying porosities could be seamlessly translated into material property distributions. With the primary emphasis of this study being on production and its associated processes, a future research task will be to apply these models to the material presented in this study in order to provide a more detailed mechanical characterization. This will pave the way for material-informed design concepts for such structures in the future.
While the primary emphasis of this research was placed on quantifying porosity using water absorption measurements, the upcoming phase of the study is set to encompass material testing, including: (1) Compressive strength, (2) thermal conductivity and (3) acoustic absorption. Further research will be conducted on extending the criteria for suitable porosity agents with the aim of reducing the energy needed for firing and limiting the emission of air pollutants. Finally, with respect to the porosity distribution in the material composition, future endeavors will involve integrating informed toolpaths using optimization software, particularly in the context of enhancing structural performance. This strategy is anticipated to yield an optimized material distribution in forthcoming applications of our developed method.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.J.; methodology, J.J.; software, J.J.; resources, L.G. and K.R.; writing—review and editing, H.V. and J.F.; supervision, M.S.; funding acquisition, M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) project F77 (SFB “Advanced Computational Design”). Open Access Funding by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request.
Acknowledgments
We are most grateful to the Institute of Applied Geosciences, Graz University of Technology for preparing the ceramic samples for analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rael, R.; San Fratello, V. Printing Architecture: Innovative Recipes for 3D Printing; Chronicle Books: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Lao, C.; Fu, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; He, Y. 3D Printing of Ceramics: A Review. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 661–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiorgio, V.; Parisi, F.; Fieni, F.; Parisi, N. The New Boundaries of 3D-Printed Clay Bricks Design: Printability of Complex Internal Geometries. Sustainability 2022, 14, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, D. Clay Printing: The Fourth Generation Brickwork; Springer Vieweg: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2022; ISBN 978-3-658-37160-9. [Google Scholar]
- Knaack, U.; Witte, D.; Mohsen, A.; Bilow, M.; Tessmann, O. Imagine 10 Rapids 2.0; nai010 Publishers: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 978-94-6208-293-9. [Google Scholar]
- Oxman, N.; Keating, S.; Tsai, E. Functionally Graded Rapid Prototyping. In Innovative Developments in Virtual and Physical Prototyping; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 483–489. ISBN 978-0-415-68418-7. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Maharma, A.; Patil, S.; Markert, B. Effects of Porosity on the Mechanical Properties of Additively Manufactured Components: A Critical Review. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 122001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ritchie, R. Functional Gradients and Heterogeneities in Biological Materials: Design Principles, Functions, and Bioinspired Applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 88, 467–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, S.; Hazell, P.; Wang, H.; Escobedo, J.; Ameri, A. Lessons from Nature: 3D Printed Bio-Inspired Porous Structures for Impact Energy Absorption—A Review. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 58, 103051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorey, R.A.; Yeomans, J.A.; Smith, P.A. Effect of Pore Clustering on the Mechanical Properties of Ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 22, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Alzina, A.; Bourret, J.; Nait-Ali, B.; Pennec, F.; Tessier-Doyen, N.; Otsu, K.; Matsubara, H.; Elser, P.; Gonzenbach, U. Thermal Conductivity of Porous Materials. J. Mater. Res. 2013, 28, 2260–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Heer, B. Additive Manufacturing of Multi-Material Structures. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2018, 129, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minas, C.; Carnelli, D.; Tervoort, E.; Studart, A. 3D Printing of Emulsions and Foams into Hierarchical Porous Ceramics. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9993–9999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieback, B.; Neubrand, A.; Riedel, H. Processing Techniques for Functionally Graded Materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 362, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuipers, T.; Doubrovski, E.; Verlinden, J. 3D Hatching: Linear Halftoning for Dual Extrusion Fused Deposition Modeling. In Proceedings of the 1st Annual ACM Symposium on Computational Fabrication, Cambridge, MA, USA, 12–13 June 2017; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Martínez, J.; Bedell, P.; Vennin, N.; Lefebvre, S. Colored Fused Filament Fabrication. ACM Trans. Graph. 2019, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craveiro, F.; Bártolo, H.; Duarte, J.; Bártolo, P.J. A Multi-Material Extrusion Nozzle for Functionally Graded Concrete Printing. In Industry 4.0–Shaping The Future of The Digital World; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 130–135. ISBN 978-0-367-82308-5. [Google Scholar]
- Cesarano, I. A Review of Robocasting Technology. MRS Proc. 1998, 542, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Martin, A.; Kroehler, B.; Henderson, A.; Huang, T.; Watts, J.; Hilmas, G.; Leu, M. Fabricating Functionally Graded Materials by Ceramic On-Demand Extrusion with Dynamic Mixing. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 13–15 August 2018; pp. 1087–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Seibold, Z.; Mhatre, S.; López, J.; Alhadidi, S.; Bechthold, M. Janus Printing: Co-Extrusion Based Multi-Material Additive Manufacturing for Ceramics. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the Association for Computer-Aided Design in Architecture (ACADIA), Austin, TX, USA, 24–26 October 2019; pp. 576–585. [Google Scholar]
- ELstudio Print&Burn 3D Printing with Clay & More. Available online: https://www.elstudio.nl/?p=1784 (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Emerging Objects Bad Ombres v.2. Available online: https://emergingobjects.com/project/bad-ombres-v-2/ (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- van Herpt, O. Dunes. Available online: https://oliviervanherpt.com/dunes/ (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Peters, B. Dyadic Series. Available online: https://www.brian-peters.com/collectibles (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Vormvrij Dual Extruder for LUTUM 4. Available online: https://vormvrij.nl/brutum/products/brutum-web-store/#!/DUAL-extruder-upgrade-kit/p/177834339/category=47492119 (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Menchavez, R.; Intong, L.-A. Red Clay-Based Porous Ceramic with Pores Created by Yeast-Based Foaming Technique. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 6511–6520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriadis, K. Mixed Matters: The Problems of Designing with Multi-Materials. In Proceedings of the What’s the Matter? Materiality and Materialism at the Age of Computation, Barcelona, Spain, 4–6 September 2014; pp. 211–226. [Google Scholar]
- Michalatos, P.; Payne, A.O. Working with Multi-Scale Material Distributions. ACADIA Proc. 2013, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmang, H.; Scholze, H.; Telle, R. Keramik; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1982; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Kariem, H.; Hellmich, C.; Kiefer, T.; Jäger, A.; Füssl, J. Micro-CT-Based Identification of Double Porosity in Fired Clay Ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 9411–9428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saosee, P.; Sajjakulnukit, B.; Gheewala, S.H. Environmental Externalities of Wood Pellets from Fast-Growing and Para-Rubber Trees for Sustainable Energy Production: A Case in Thailand. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2022, 14, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauk, J. Termite. 2023. Available online: https://www.food4rhino.com/en/app/termite (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Keating, S. From Bacteria to Buildings: Additive Manufacturing Outside the Box. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jauk, J.; Gosch, L.; Vašatko, H.; Christian, I.; Klaus, A.; Stavric, M. MyCera. Application of Mycelial Growth within Digitally Manufactured Clay Structures. Int. J. Archit. Comput. 2022, 20, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-Q.; Klug, C.; Schmitz, T. Fiber-Reinforced Clay: An Exploratory Study on Automated Thread Insertion for Enhanced Structural Integrity in LDM. Ceramics 2023, 6, 1365–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauk, J.; Gosch, L.; Vašatko, H.; Königsberger, M.; Schlusche, J.; Stavric, M. Filament-Reinforced 3D Printing of Clay. Materials 2023, 16, 6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenwasser, D.; Mantell, S.; Sabin, J. Clay Non-Wovens: Robotic Fabrication and Digital Ceramics. In Proceedings of the ACADIA 2017 DISCIPLINES & DISRUPTION: 37th Annual Conference of the Association for Computer Aided Design in Architecture, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2–4 November 2017; pp. 2–4. [Google Scholar]
- Alothman, S.; Im, H.C.; Jung, F.; Bechthold, M. Spatial Print Trajectory. In Robotic Fabrication in Architecture, Art and Design 2018; Willmann, J., Block, P., Hutter, M., Byrne, K., Schork, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 167–180. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.; Fiore, B.; Erb, R. Designing Bioinspired Composite Reinforcement Architectures via 3D Magnetic Printing. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheder-Bieschin, L.; Margariti, G.; Körner, A.; Suzuki, S.; Knippers, J. Tailoring Self-Formation Fabrication and Simulation of Membrane-Actuated Stiffness Gradient Composites. In Proceedings of the IASS Annual Symposia, Boston, MA, USA, 16–20 July 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, E.; Arthur, H. Hexcrete Modular and Recyclable Paper Clay Formwork. In Proceedings of the eCAADe 41, Graz, Austria, 20–23 September 2023; Volume 1—Digital Design Reconsidered. pp. 429–438. [Google Scholar]
- Buchner, T.; Kiefer, T.; Königsberger, M.; Jäger, A.; Füssl, J. Continuum Micromechanics Model for Fired Clay Bricks: Upscaling of Experimentally Identified Microstructural Features to Macroscopic Elastic Stiffness and Thermal Conductivity. Mater. Des. 2021, 212, 110212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchner, T.; Königsberger, M.; Jäger, A.; Füssl, J. A Validated Multiscale Model Linking Microstructural Features of Fired Clay Brick to Its Macroscopic Multiaxial Strength. Mech. Mater. 2022, 170, 104334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchner, T.; Königsberger, M.; Gaggl, W.; Früh, G.; Kiefer, T.; Füssl, J. A Continuum Micromechanics Model Challenged to Predict Thermo-Mechanical Properties of 18 Different Clay Bricks and Sensitivity Analysis Revealing Effects of Compositional and Microstructural Features. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 403, 132601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).