2. Materials and Methods
Doping of ZrO2 ceramics with MgO oxide in order to evaluate phase polymorphic transformations in zirconium dioxide was carried out using the method of mechanochemical grinding in a planetary mill with various dopant variations from 0.01 to 0.25 molar%. ZrO2 and MgO components of chemical purity 99.95% were used as components for the synthesis; the reagents were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (Sigma, St. Louis, MI, USA).
Ceramics were obtained using the method of mechanochemical solid-phase synthesis. A PULVERISETTE 6 classic line planetary mill (Fritsch, Berlin, Germany) was used for the synthesis. Grinding was carried out at a grinding speed of 400 rpm, and the grinding time was 60 min. For grinding, a grinding cup and balls with a diameter of 10 mm made of tungsten carbide, which has a hardness of 9 on the Mohs scale and a high level of wear resistance, were used. The ratio of grinding media and initial powders in a given molar ratio was 4:1. After grinding, the resulting powder samples were removed from the grinding jars for subsequent thermal annealing. Thermal annealing was carried out in a muffle furnace at an annealing temperature of 1500 °C for 5 h, and the heating rate was 10 °C/min. After holding the samples at a given temperature for 5 h, the samples were cooled for 24 h together with the muffle furnace.
Figure 1 shows a schematic representation of the main processes for the manufacture of ceramics using the method of mechanochemical synthesis.
To compare changes in structural characteristics, and assess the possibility of initiating the processes of polymorphic transformations as a result of mechanochemical grinding and subsequent thermal annealing, a ZrO2 powder sample with a monoclinic type of crystal structure was chosen, which is used as the main element in the preparation of doped ceramics.
Morphological features were studied using the scanning electron microscopy method performed using a Hitachi TM3030 electron microscope (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan).
Analysis of phase transformations associated with the processes of polymorphic transformations was carried out using the method of X-ray phase analysis. For implementation, a D8 Advanced ECO powder diffractometer (Bruker, Berlin, Germany) was used. The diffraction patterns were taken in the Bragg–Brentano geometry, in the angular range of 2θ = 20–100°, with a step of 0.03°. The obtained diffraction patterns were analyzed in order to determine the structural parameters, as well as to establish the main phases in the composition of the ceramics. The phase composition was refined using the PDF-2(2016) database.
Determination of the strength properties was carried out by the method of intensification in order to determine the hardness values of the ceramics, as well as to establish the magnitude of the hardening of the ceramics with a change in the phase composition as a result of polymorphic transformations, as well as changes in the structural parameters. To carry out experimental work to determine the hardness values, a LECO LM700 microhardness tester (LECO, Tokyo, Japan) was used. A Vickers pyramid was used as an indenter, the load on the indenter was 100 N. The Vickers hardness value was calculated using Formula (1) [
25]:
where
P is the applied pressure, and
d is the average length of the imprint diagonal. To collect statistical data and determine the measurement error, all experiments were performed in the form of serial tests of 10–15 consecutive measurements. To measure the hardness, the samples were pressed into tablets 10 mm in diameter and 1 mm thick. Pressing was carried out at room temperature at a pressure of 300 MPa, the pressure was maintained for 30 min, after which the samples were removed for further measurements.
The hardening value was determined by assessing the change in hardness values when compared with the value characteristic of an undoped sample of ZrO2 ceramics prepared in a similar way and annealed at a temperature of 1500 °C.
3. Results and Discussion
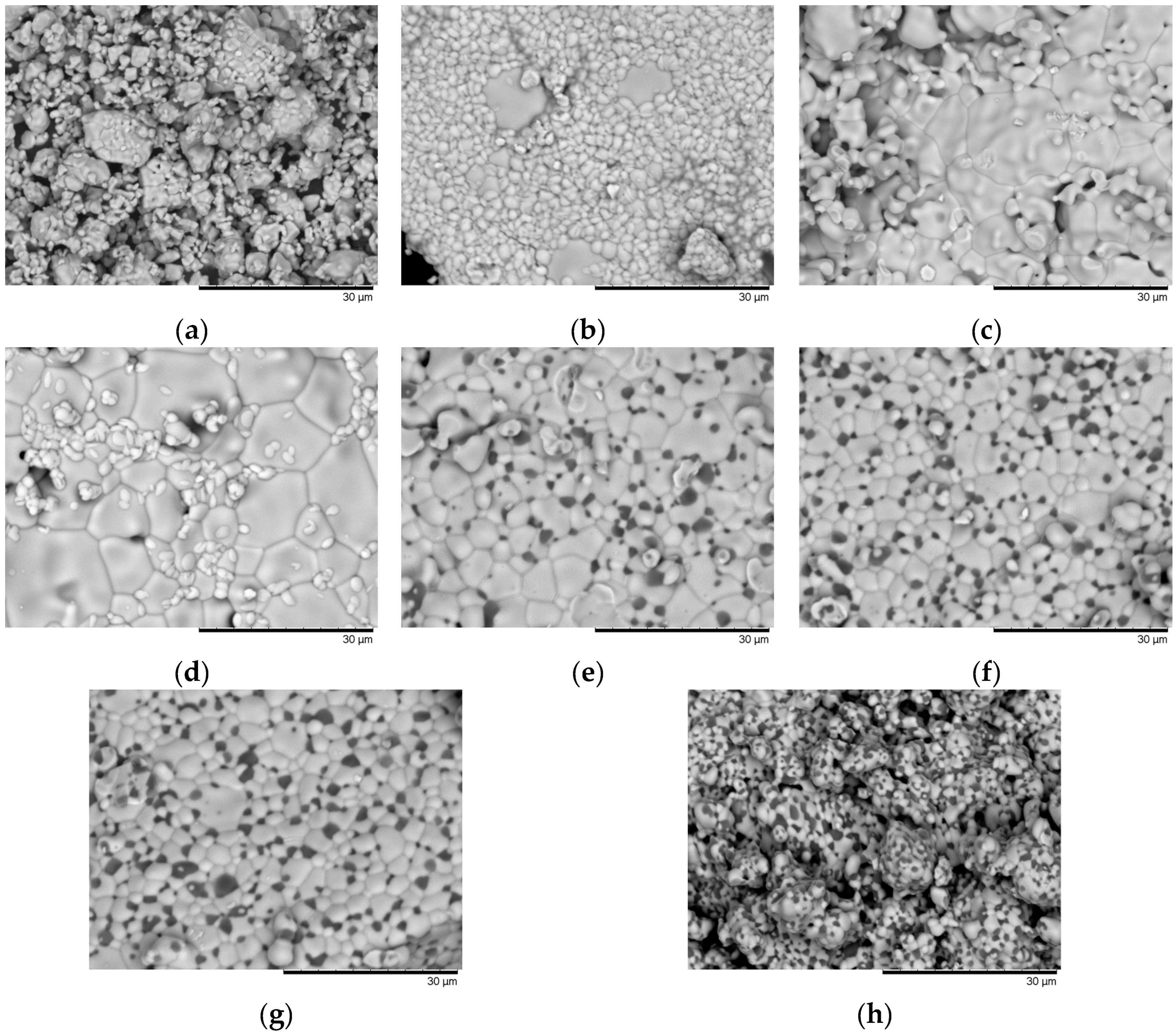
Figure 2 shows the results of the morphological features of synthesized ZrO
2 ceramics doped with MgO with concentrations from 0.01 to 0.20 molar%. In the case of the original sample of ZrO
2 ceramics subjected to mechanochemical grinding, the morphology of the ceramics is a mixture of agglomerates of fine grains, the average size of which varies from 400 to 700 nm. At the same time, the formation of a small number of large grains of irregular rhombic shape, the average size of which exceeds 1.5–3 µm, is also observed in the grain structure. The addition of 0.01 molar% of the MgO dopant to the composition of ceramics leads to the formation of fine grains sintered into large agglomerates, which agglomerate around large grains. Such a change may be due to effects associated with phase transformations of ceramics [
26,
27]. In the case of an MgO dopant concentration of 0.03 molar%, the morphology of ceramics is coarse-grained agglomerates, with a large number of boundary effects near which fine-grained inclusions are formed. At the same time, an increase in the dopant concentration to 0.05 molar% leads to grain compaction, as well as the release of a fine-grained fraction on the ceramic surface or into the interboundary space. At a dopant concentration of 0.10 molar%, inclusions with a different color gradation are observed in the interboundary space, which indicates an excellent phase and elemental composition of these inclusions. It should also be noted that the concentration of such inclusions in the interboundary space increases with increasing concentration, and the effect itself resembles the formation of structures by the type of interboundary introduction of impurity phases.
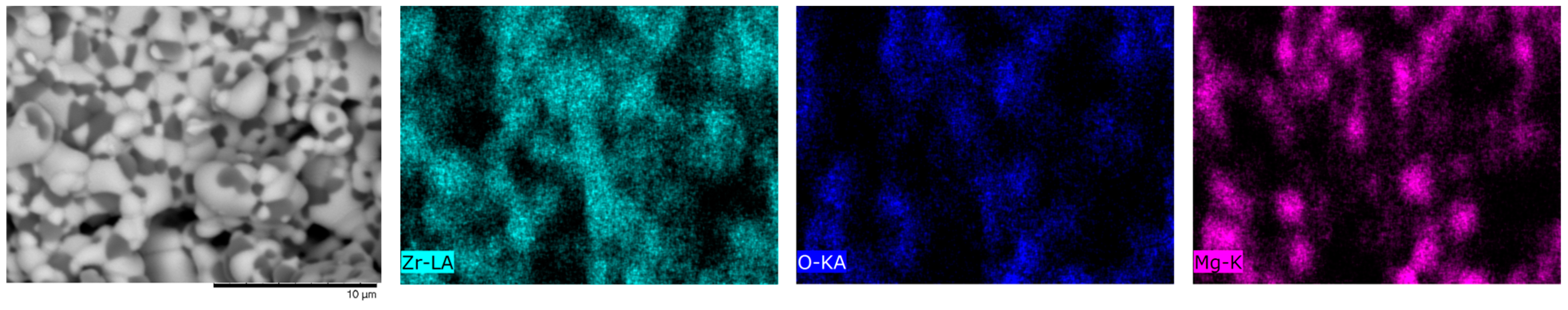
In a detailed analysis using the mapping method of the observed inclusions in the composition of ZrO
2 ceramics (see
Figure 3), which are clearly manifested with an increase in the MgO concentration above 0.10 molar%, it was found that these inclusions are particles of magnesium oxide, the presence of which may be due to the phase transformation processes [
28]. At the same time, it is clearly seen from the presented SEM image data that MgO particles are located at the grain junctions, thereby creating additional boundary effects.
Thus, analyzing the obtained data on morphological features and taking into account the mapping data, we can conclude that with an increase in the concentration of the dopant, the formation of the ceramics structure occurs according to the type of the ZrO
2–MgO solid solution, where the main matrix is zirconium dioxide particles, with magnesium oxide particles embedded in the intergranular space, thereby forming additional boundary effects that can affect the hardening of ceramics. At the same time, an increase in the MgO dopant concentration in the composition of ceramics during thermal annealing leads to a decrease in the grain size, clearly seen in the images of
Figure 2g,h, which can also affect the resistance of ceramics to mechanical and radiation damage.
Based on the obtained SEM image data, it can be concluded that an increase in the MgO dopant concentration leads to the following transformations. At low concentrations of the MgO dopant, grains recrystallize with the formation of a finely dispersed fraction, which agglomerates near the boundaries of large grains with the formation of a fairly dense packing. In the case of an increase in the dopant concentration above 0.10 molar%, a close-packed grain structure is formed, the interboundary space of which is filled with MgO grains. In the case of an increase in the MgO dopant concentration, a decrease in grain size is observed with the formation of a close-packed interstitial solid solution, which is a mixture of ZrO2–MgO in which the interboundary space is filled with MgO grains.
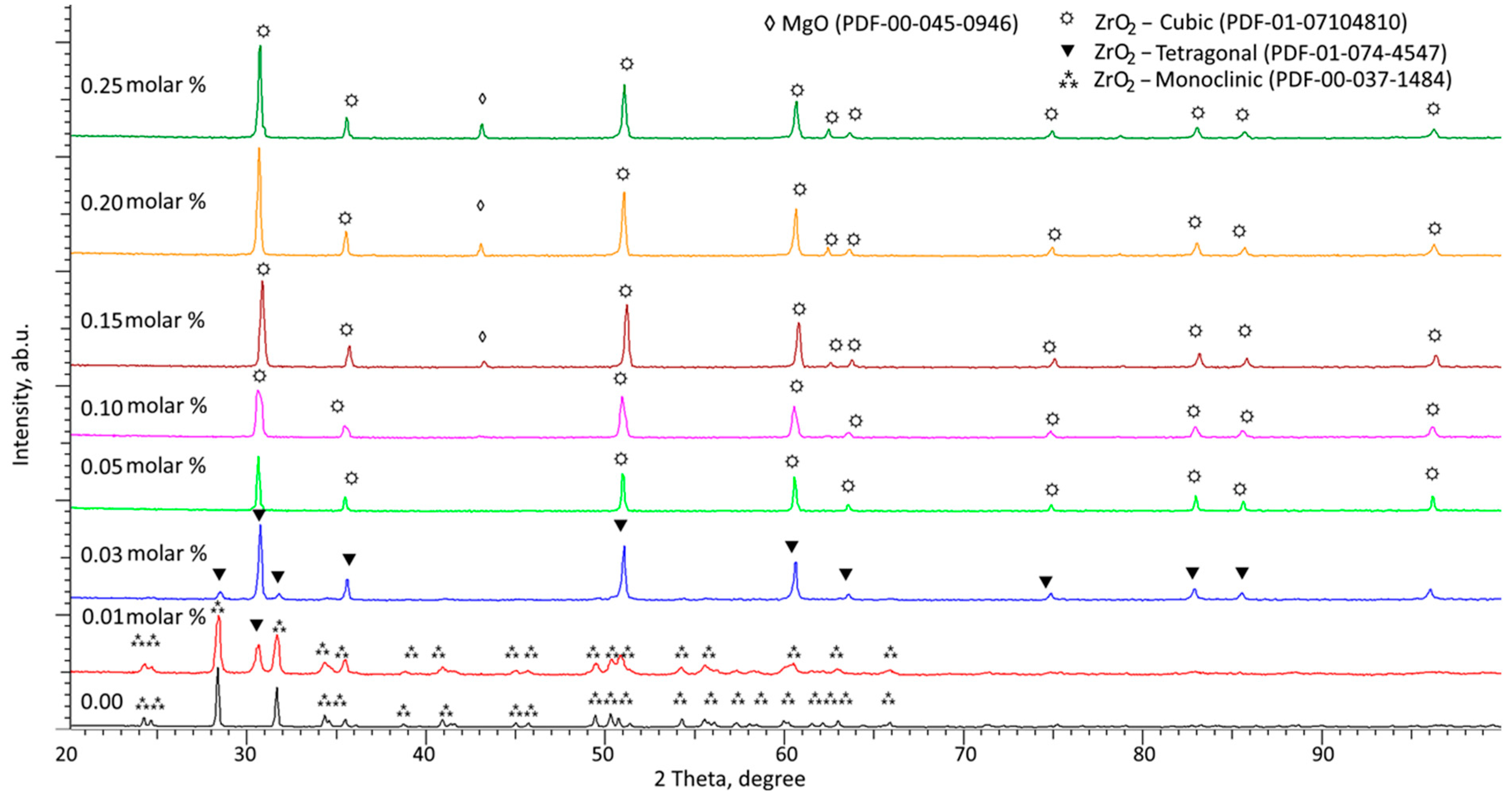
Figure 4 shows the results of X-ray phase analysis of the studied samples of ZrO
2 ceramics depending on the MgO dopant concentration. The general view of the presented X-ray diffraction patterns indicates the polycrystalline structure of the studied samples, which have a fairly high structural ordering degree, the change of which is due to the processes of polymorphic phase transformations, which are clearly manifested in the form of a change in the position of diffraction reflections with a variation in the MgO dopant concentration.
According to the presented X-ray diffraction data, thermal annealing of ZrO2 ceramics without the addition of an MgO dopant at an annealing temperature of 1500 °C does not lead to polymorphic transformations in the form of monoclinic phase → tetragonal phase (m—ZrO2 → t—ZrO2) or monoclinic phase → cubic phase (m—ZrO2 → c—ZrO2), which consist in changing the type of crystal lattice, as well as changing the spatial syngony. Analysis of the obtained X-ray diffraction pattern for an undoped sample showed that the samples subjected to mechanochemical synthesis and subsequent thermal annealing are characterized by a monoclinic phase with a spatial syngony of P21/a(14) and crystal lattice parameters of a = 5.28894 Å, b = 5.17469 Å, c = 5.12792 Å, and β = 99.043°. In this case, the difference between the obtained parameters of the crystal lattice from the reference values (PDF-00-037-1484, a = 5.31290 Å, b = 5.21250 Å, c = 5.14710 Å, and β = 99.043°) is due to the deformation processes of compression (for parameters a and c) and tension (for parameter b) during mechanochemical synthesis, the presence of which is also evidenced by the distorted shape of the diffraction reflections presented in the diffraction pattern.
The addition of 0.01 molar% of the MgO dopant to the composition of ceramics during mechanochemical grinding and subsequent thermal annealing leads to the formation of the tetragonal phase t—ZrO2 in the composition of ceramics, the presence of which is confirmed by X-ray phase analysis data. The appearance of reflections characteristic of the tetragonal phase t—ZrO2 on the diffraction pattern indicates that in the composition of ceramics during thermal annealing, the processes of polymorphic transformations of the type m—ZrO2 → t—ZrO2 are initialized. At the same time, comparing the results of X-ray diffraction patterns of annealed ceramic samples in the initial (without the addition of MgO) state and doped ceramics, we can conclude that the presence of MgO in the powder composition leads to the initialization of polymorphic transformation processes. However, a low concentration of MgO does not allow the completion of these polymorphic transformations. According to the assessment of the weight contributions of each phase, it was found that the content of the tetragonal phase t—ZrO2 is no more than 34%.
An increase in the MgO concentration to 0.03 molar% leads to the almost complete displacement of the m—ZrO
2 monoclinic phase, the contribution of which is estimated to be less than 10%. Such a displacement is due to the acceleration of the processes of polymorphic transformations of the m—ZrO
2 → t—ZrO
2 type, which can lead to the densification of ceramics due to a decrease in the volume of the crystal lattice and rearrangement of the crystal lattice with a change in the spatial syngony from P21/a(14) (monoclinic type of structure) to P42/mmc(137) (tetragonal type of structure). The dominant phase in this case is the tetragonal phase t—ZrO
2. At the same time, the analysis of the structural parameters indicates its densification and a decrease in deformation distortions of the crystal lattice [
29,
30].
At an MgO dopant concentration of 0.05 molar%, according to the presented X-ray diffraction data, a second-type polymorphic transformation t—ZrO2 → c—ZrO2 occurs during thermal annealing, with the complete displacement of the monoclinic phases and tetragonal phases. Such a structural transformation can be explained by the processes of thermal expansion with an increase in the MgO dopant concentration, which leads to an acceleration of the polymorphic transformation processes, as well as a decrease in the temperature of their initialization.
An increase in the MgO concentration to 0.10 molar% leads to a densification of the crystal lattice, which is expressed in a decrease in the volume of the crystal lattice for the c—ZrO2 cubic phase, from 132.65 Å3 (for a concentration of 0.05 molar%) to 128.79 Å3. This densification indicates the structural densification of ceramics due to the displacement of the monoclinic and tetragonal phases, as well as a decrease in the grain size. However, the distorted form of diffraction reflections due to structural compaction may be due to the effect of reducing the size of crystallites, the average value of which for a MgO concentration of 0.10 molar% is no more than 28–33 nm. Moreover, a full-profile analysis of the obtained diffraction patterns made it possible to establish the presence of low-intensity diffraction reflections at 2θ = 43–44°, characteristic of the cubic MgO phase of the Fm-3m(225) spatial system, the content of which is no more than 3.5%.
With an increase in the MgO concentration to 0.15 molar%, the main structural changes are associated with densification of the crystal structure, as well as an increase in the impurity cubic MgO phase from 3.5% to 7%. This indicates that at high concentrations of magnesium oxide (above 0.05 molar%), not only are the processes of polymorphic transformations of the monoclinic phase into the cubic phase completed with the formation of a transitional tetragonal phase, but also structural inclusions in the form of a cubic MgO phase are formed. The formation of which, according to the data of morphological features, occurs in the intergranular space at the grain boundary.
An increase in the MgO concentration above 0.15 molar% leads to thermal expansion of the c—ZrO
2 cubic phase, which is due to the processes of changing the values of the coefficients of linear and volume expansion of the crystal lattice, as well as an increase in the concentration of the MgO cubic phase in the composition of ceramics. At the same time, the analysis of deformation distortions of the crystal structure indicates a decrease in the concentration of deformation stresses in the structure of ceramics [
29,
30].
In the case of dopant concentrations of MgO equal to 0.25 molar%, the broadening of the main reflections can be due to the formation of inclusions of the cubic substitution phase MgxZr1−xO2, the appearance of which is due to the effects of partial replacement of zirconium ions by magnesium ions at the sites of the crystal lattice. The differences in the crystal lattice parameters can also be explained by differences in the ionic radii of zirconium (79 pm) and magnesium (66 nm).
Table 1 presents the data of structural parameters determined by the analysis of the obtained diffraction patterns. The dynamics of changes in structural parameters reflect the processes associated with structural ordering as a result of thermal annealing, polymorphic transformation processes, and thermal broadening of the crystal lattice and its volume.
An analysis of the change in the structural parameters of the crystal lattice depending on the MgO dopant concentration showed the following. At low concentrations, the main changes in the parameters of the crystal lattice are associated with the processes of structural ordering, as well as compaction of the crystal lattice due to the reduction in deformation distortions and stresses in the structure. At the same time, polymorphic transformations of the m—ZrO
2 → t—ZrO
2 and t—ZrO
2 → c—ZrO
2 type occurring with a change in the dopant concentration are accompanied by compaction of the samples, as evidenced by a decrease in the crystal lattice parameters. However, in the case of high MgO dopant concentrations equal to 0.20–0.25 molar%, a broadening of the parameters is observed, which is due to the processes of thermal broadening of the crystal structure and its volume as a result of a change in the magnitude of thermal vibrations. Such a difference in the change in the parameters of the crystal lattice and its volume with variation in the MgO dopant concentration can be due to the fact that at high concentrations of the dopant, the processes of polymorphic transformations of the t—ZrO
2 → c—ZrO
2 type reach the limit by displacement of the tetragonal phase and its complete transformation into a cubic one. However, the processes of structural changes associated with the addition of a dopant during thermal heating at high concentrations can lead to thermal broadening processes while maintaining the structural ordering degree, as evidenced by the data presented in
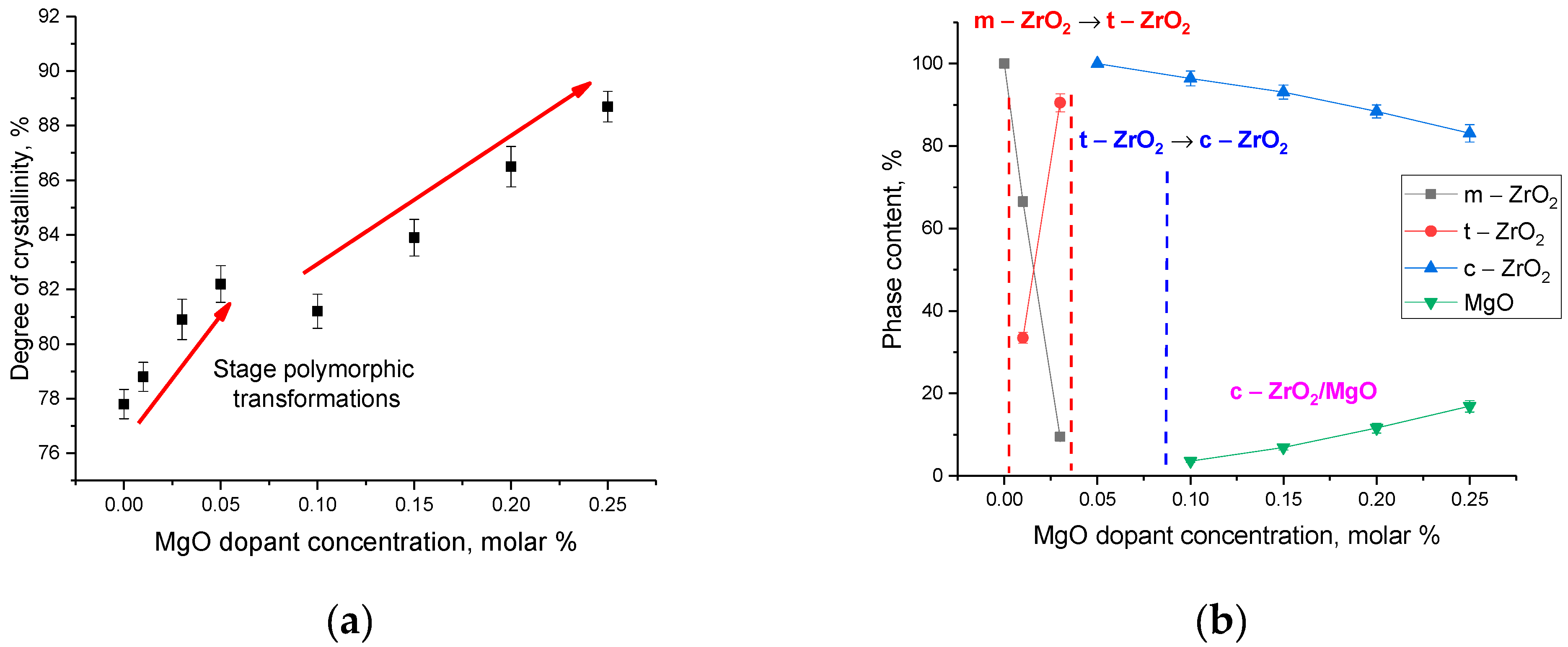
Figure 5a. The structural ordering degree (crystallinity degree) was calculated by comparative analysis of the weight contributions of diffraction reflections and the area of background radiation on diffraction patterns, which is characteristic of amorphous or disordered inclusions.
The general view of the presented changes in the degree of structural ordering has a general trend towards an increase, indicating a decrease in amorphous inclusions or regions of disorder, and also confirms the above assumption about the processes of thermal broadening of the crystal lattice at MgO dopant concentrations of 0.20–0.25 molar%. The presence of a turning point at a MgO concentration of 0.10 molar% is characteristic of the formation of a cubic MgO phase in the structure of inclusions, the appearance of which at a low concentration can lead to partial disordering of the structure.
On the basis of the obtained data from the X-ray phase analysis, a phase diagram of polymorphic transformations in ZrO
2 ceramics was constructed depending on the MgO dopant concentration. The diagram is shown in
Figure 5b.
The general view of the presented polymorphic transformations in ZrO2 ceramics with a change in the concentration of the MgO dopant can be divided into three characteristic stages, accompanied by a change in the phase composition of the ceramics. The first stage is characteristic of m—ZrO2 → t—ZrO2 polymorphic transformations, accompanied by an increase in the concentration of the tetragonal phase with an increase in the content of the MgO dopant. The second stage is typical for polymorphic transformations of the t—ZrO2 → c—ZrO2 type, followed by displacement of the tetragonal and monoclinic phases, with their conversion to the cubic phase. The third stage is typical for the formation of interstitial solid solutions of the c—ZrO2/MgO type. At the same time, the change in the dopant concentration, which leads to an increase in the contribution of the MgO phase, is in good agreement with the data of morphological studies, which reflect the filling of the interboundary space with MgO grains followed by the formation of an interstitial solid solution.
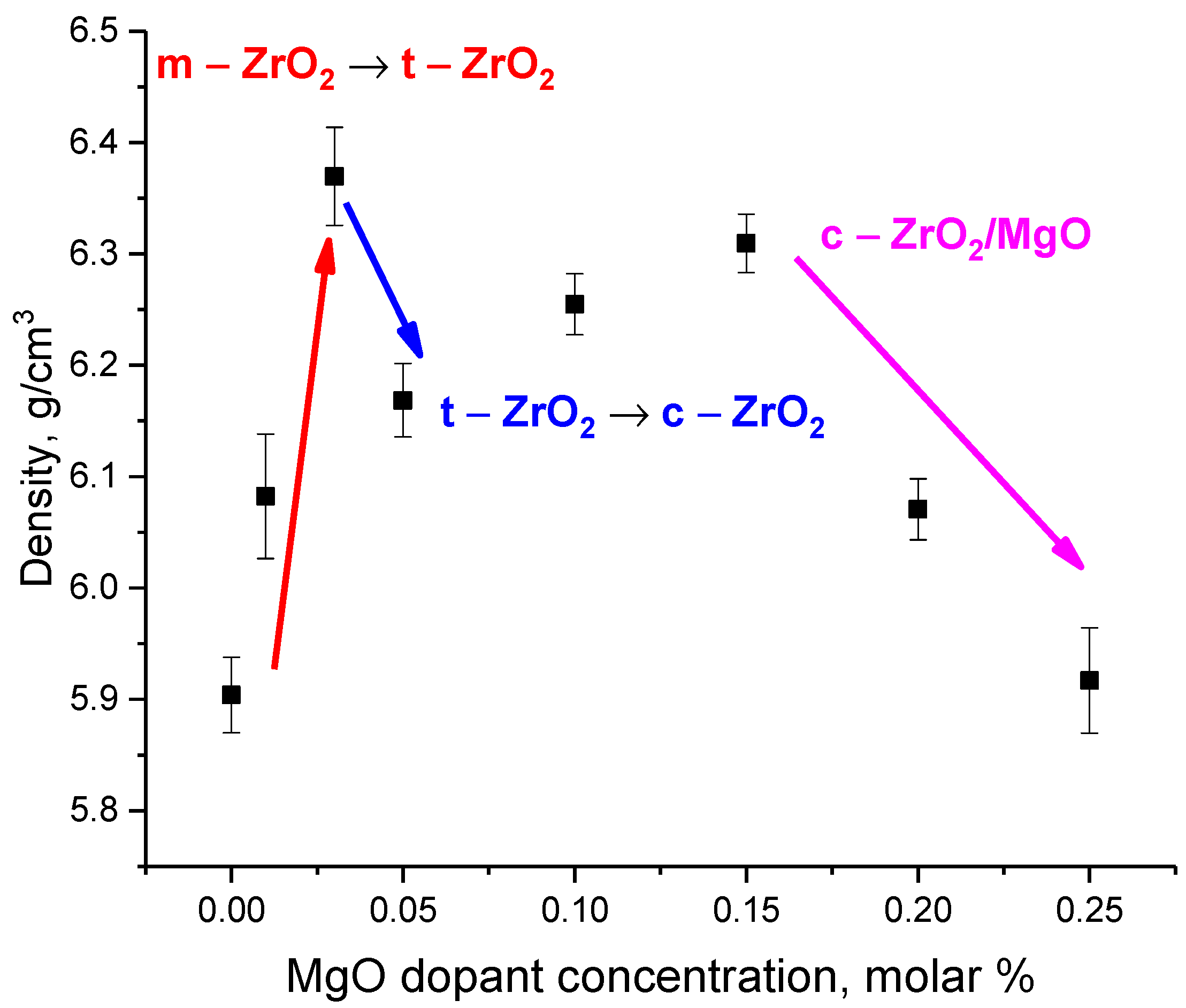
Figure 6 shows the results of changes in the density of ceramics with a variation in dopant concentration, calculated on the basis of X-ray phase analysis data, taking into account the data on changes in the parameters and volume of the crystal lattice. The density was refined taking into account the contributions of each phase, as well as changes in their structural parameters.
As can be seen from the data presented, the general form of changes in density indicates a strong influence of the processes of polymorphic transformations and densification of ceramics with variation in MgO dopant concentrations. In the case of polymorphic transformations of the m—ZrO2 → t—ZrO2 type, the displacement of the m—ZrO2 monoclinic phase leads to an increase in the density of ceramics, as well as a decrease in porosity. At the same time, the dominance of the tetragonal phase in the composition leads to an increase in density to 6.36 g/cm3. The second type of polymorphic transformations of the type t—ZrO2 → c—ZrO2 leads to a slight decrease in density, which is associated with the presence of impurity inclusions, as well as deformation distortions caused by phase transformations. An increase in the dopant concentration from 0.05 to 0.15 molar% leads to densification of ceramics with the dominant cubic phase in the structure, which indicates the densification and structural ordering of the crystal lattice, as well as a decrease in its volume. At the same time, the formation of inclusions in the ceramic structure in the form of a cubic MgO phase, which has a rather low density (3.56 g/cm3), leads to a decrease in density values from 6.3 to 5.9 g/cm3.
An important factor in the change in polymorphic transformations in ceramics is the change in their strength and thermophysical characteristics, the change in which regulates the area of applicability of ceramics, as well as the range of possibilities for their application. Moreover, in most cases, the addition of dopants in the form of magnesium oxide or yttrium oxide is used not only to stabilize phase polymorphic transformations in ceramics, but also to increase resistance to external influences [
31,
32,
33].
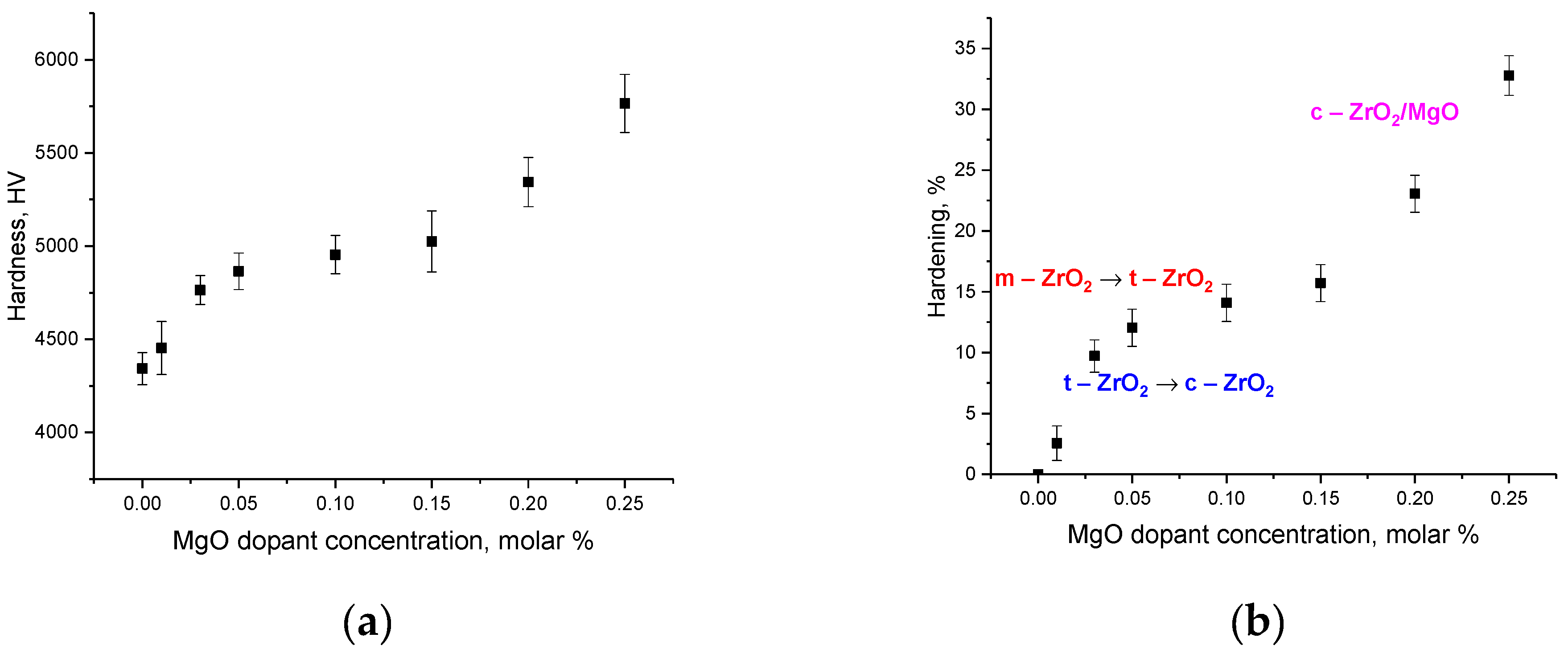
Figure 7a shows the results of estimating the change in the hardness of ZrO
2 ceramics depending on the concentration of the MgO dopant. The hardness was determined using the indentation method using a microhardness tester, and the measurement error was determined by collecting statistical data during serial tests.
As can be seen from the presented data, the most pronounced changes in hardness are observed for samples that are interstitial solid solution c—ZrO
2/MgO, for which the hardness value is more than 5300 HV. At the same time, phase transformations of the m—ZrO
2 → t—ZrO
2 type lead to greater changes in hardness, and as a result, greater hardening than subsequent phase polymorphic transformations t—ZrO
2 → c—ZrO
2, for which the change in hardness is minimal (no more than 1–2%).
Figure 7b shows the results of the change in hardening value calculated from these changes in hardness values compared with an undoped ZrO
2 ceramic sample obtained under the same conditions.
As can be seen from the presented data, polymorphic transformations of the m—ZrO
2 → t—ZrO
2 type lead to hardening with ceramics by 3–10% with the displacement of the monoclinic phase from the composition of ceramics and the dominance of the tetragonal phase. In this case, polymorphic transformations of the t—ZrO
2 → c—ZrO
2 type lead to an increase in the hardening value from 9.7% to 12%, and further structural ordering of the cubic phase leads to an insignificant change in the hardening value (no more than 1.5–3%). At the same time, the maximum increase in strength above 15% is observed for samples in which the formation of intergranular inclusions occurs in the form of a cubic MgO phase, as well as a decrease in grain size (see
Figure 2). Such a difference in the effects of hardening may be due to differences in the effects caused by a change in the concentration of the dopant in the composition of ceramics, as well as the processes associated with them. The reduction in grain sizes during recrystallization leads to an increase in the number of boundary effects, as well as dislocation density, which has a direct relationship with the change in grain sizes. As is known, the value of the dislocation density is inversely proportional to the square of the average value of the grain sizes, from which it follows that a decrease in the grain size leads to an increase in the dislocation density. At the same time, variation in dislocation density at its increase can lead to the occurrence of hardening effects due to the creation of additional obstacles to the propagation of microcracks and cleavages under external actions, including indentation, which is an effect of the indenter on the sample surface at constant pressure during certain time intervals [
32,
33].
Figure 8a shows the results of estimating the change in the dislocation density depending on the MgO dopant concentration. The dislocation density was estimated using the grain size estimate presented in the SEM images of
Figure 2.
As can be seen from the presented data, the largest change in the dislocation density is observed for MgO dopant concentrations of 0.20–0.25 molar%, which is more than a 1.5–2-fold increase in the dislocation density. In this case, the variation in the concentration of the MgO dopant from 0.01 to 0.15 molar% does not lead to significant changes in the dislocation density. This behavior of the change in dislocation density is primarily due to size effects caused by recrystallization processes and a decrease in grain sizes associated with polymorphic transformations.
Figure 8b shows the results of the evaluation of the effect of the change in dislocation density on the hardening effect calculated based on the change in ceramic hardness values.
As can be seen from the data presented, an increase in the dislocation density above 0.1 × 109 cm−2 leads to an increase in hardening by more than 15%, while an increase in the dislocation density by more than five times (up to a value of 0.5 × 109 cm−2) at dopant concentrations leads to an increase in hardening by no more than two times. This effect indicates that with a decrease in the grain size, the so-called dislocation hardening appears, which is associated with the creation of additional obstacles for the propagation of microcracks and chips under external influences.
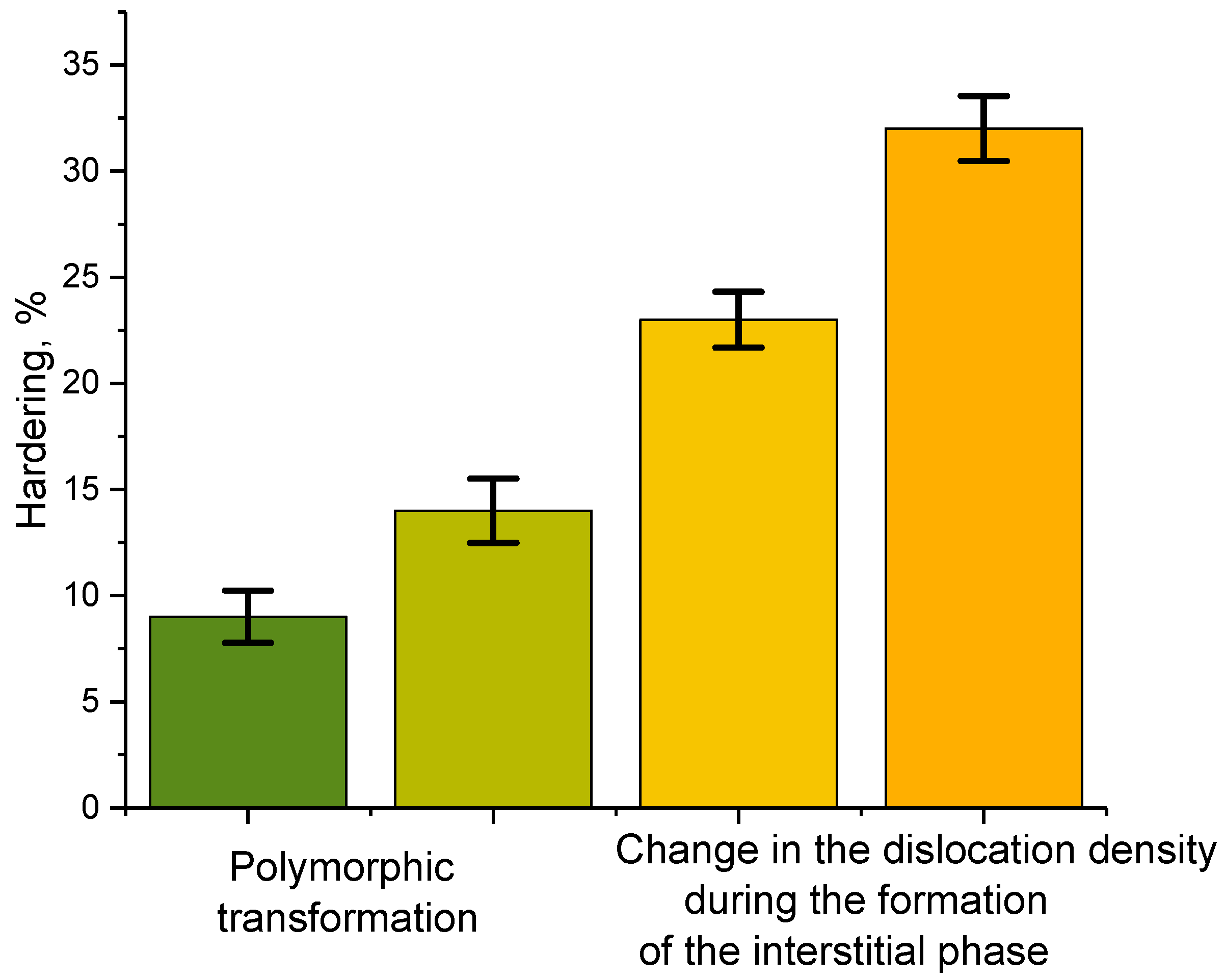
Figure 9 shows the results of evaluating the effects of various types of structural changes in ZrO
2 ceramics resulting from variation in the MgO dopant concentration on the hardening and change in strength properties of ceramics.
As can be seen from the presented data, polymorphic transformations of the first and the second type result in the hardening of ceramics by 10–15%, while an increase in dislocation density as a result of recrystallization processes at high MgO dopant concentrations leads to a hardening of ceramics by 25–30% in comparison with the strength properties of underperformed ceramics. Thus, it can be concluded from the obtained data that ceramic hardening is more affected by dislocation hardening than phase polymorphic transformations caused by the variation in the MgO dopant concentration. The obtained results of the influence of dopants on the resistance of ceramics to polymorphic transformations, as well as the assessment of the effects of hardening of materials, are in good agreement with several experimental studies related to the study of structural ceramics [
34,
35]. At the same time, in the case of composite ceramics, much attention is paid to corrosion resistance [
34,
36], as well as thermal resistance to sudden temperature changes [
37,
38], which will be the focus of the next stages of research. It should also be noted that the efficiency of ceramic hardening is associated with two factors: polymorphic transformations and dislocation hardening, of which the latter is one of the important factors used as an effective method for modifying ceramics and steels [
39,
40].