Electrode Material Effect on the Flash Ignition in Soda-Lime Silicate Glass
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- Stage I (or incubation): the material is resistive, a limited current flows, and the power source works in current control;
- -
- Stage II (or flash event): the material becomes electrically conductive, the electric current increases until it reaches the set limit, and most of the densification takes place; such a phenomenon is observed at an onset combination of an electric field and furnace temperature;
- -
- Stage III (or steady stage): the power source works in current control, marginal densification is observed, and the grains coarsen.
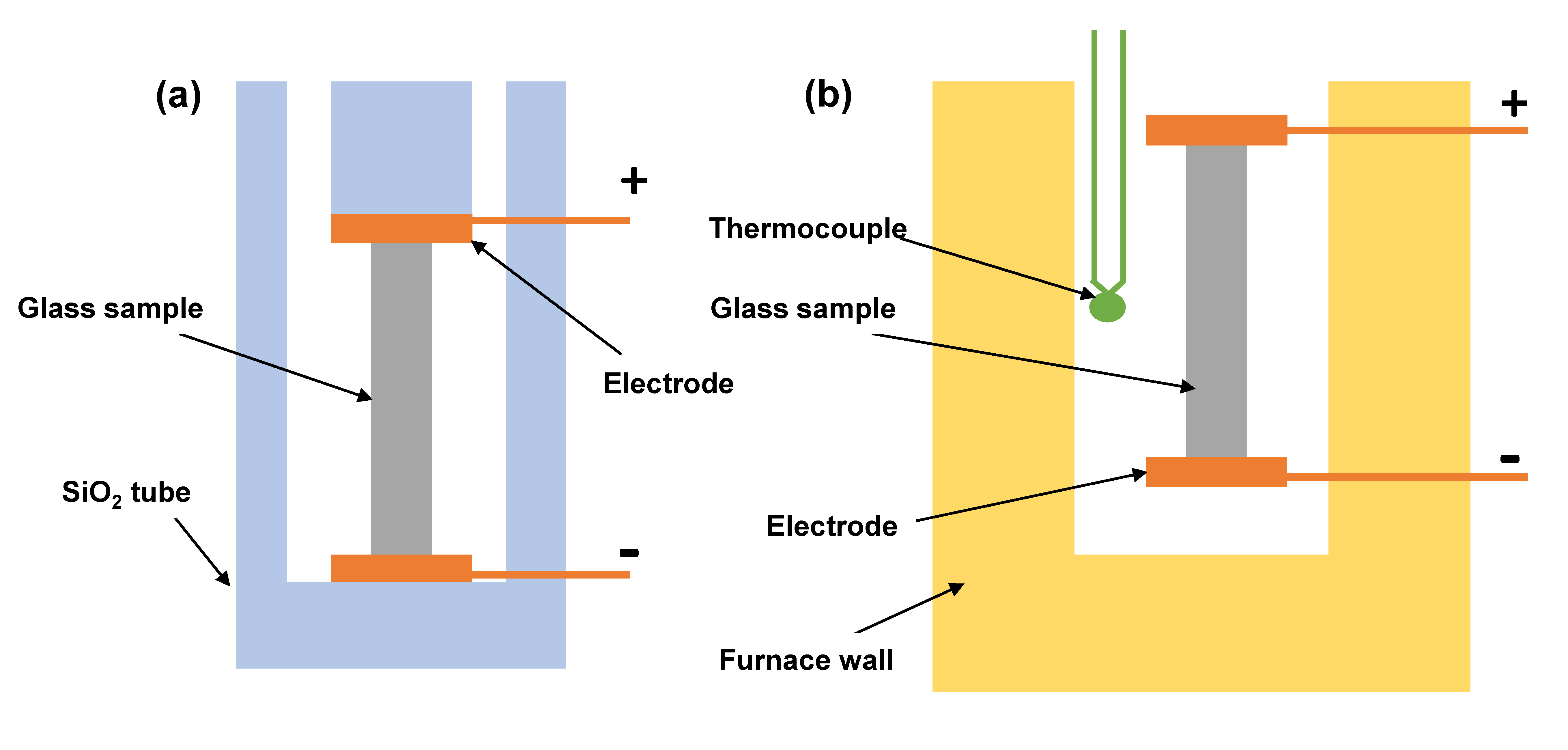
2. Materials and Methods
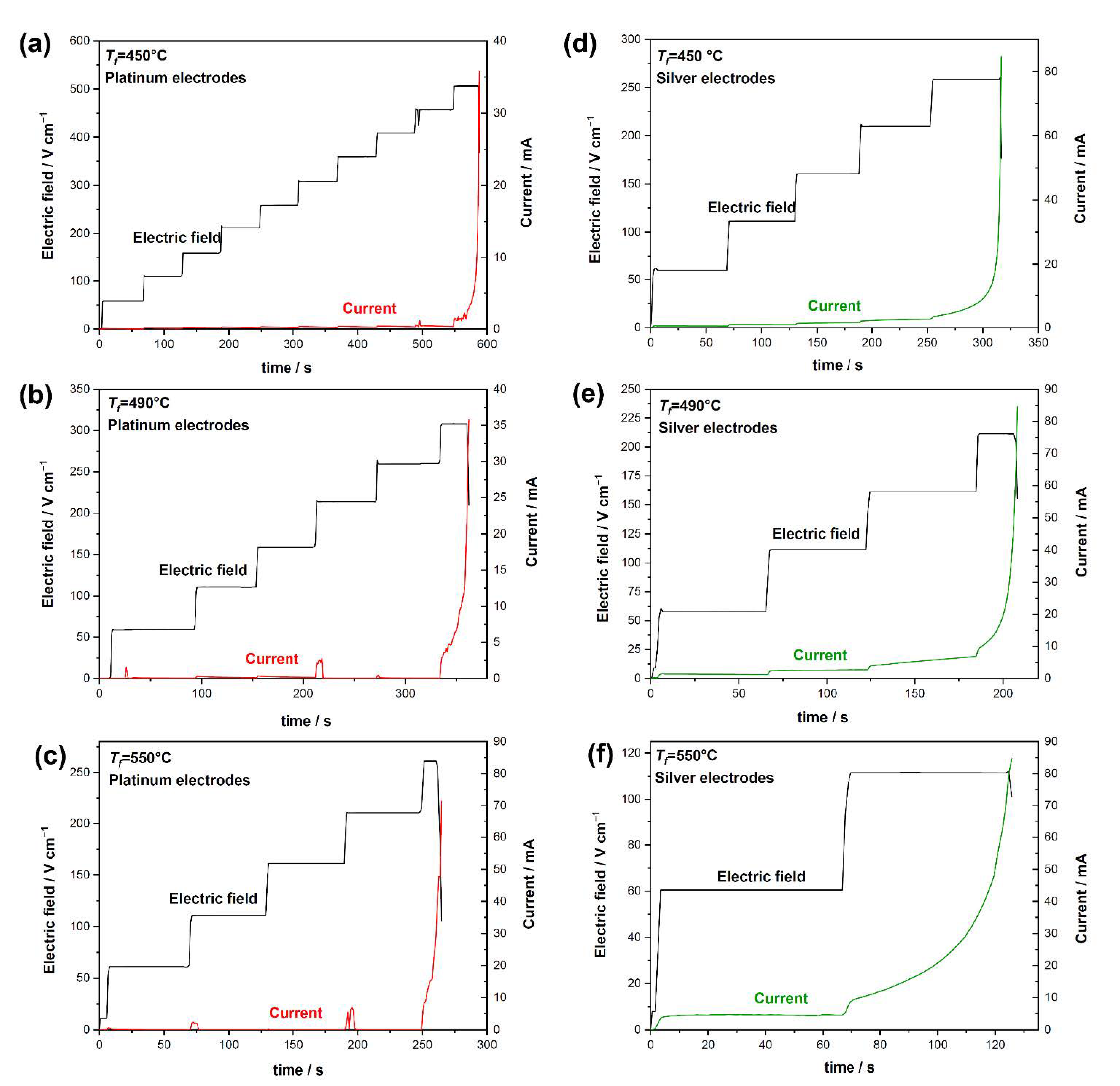
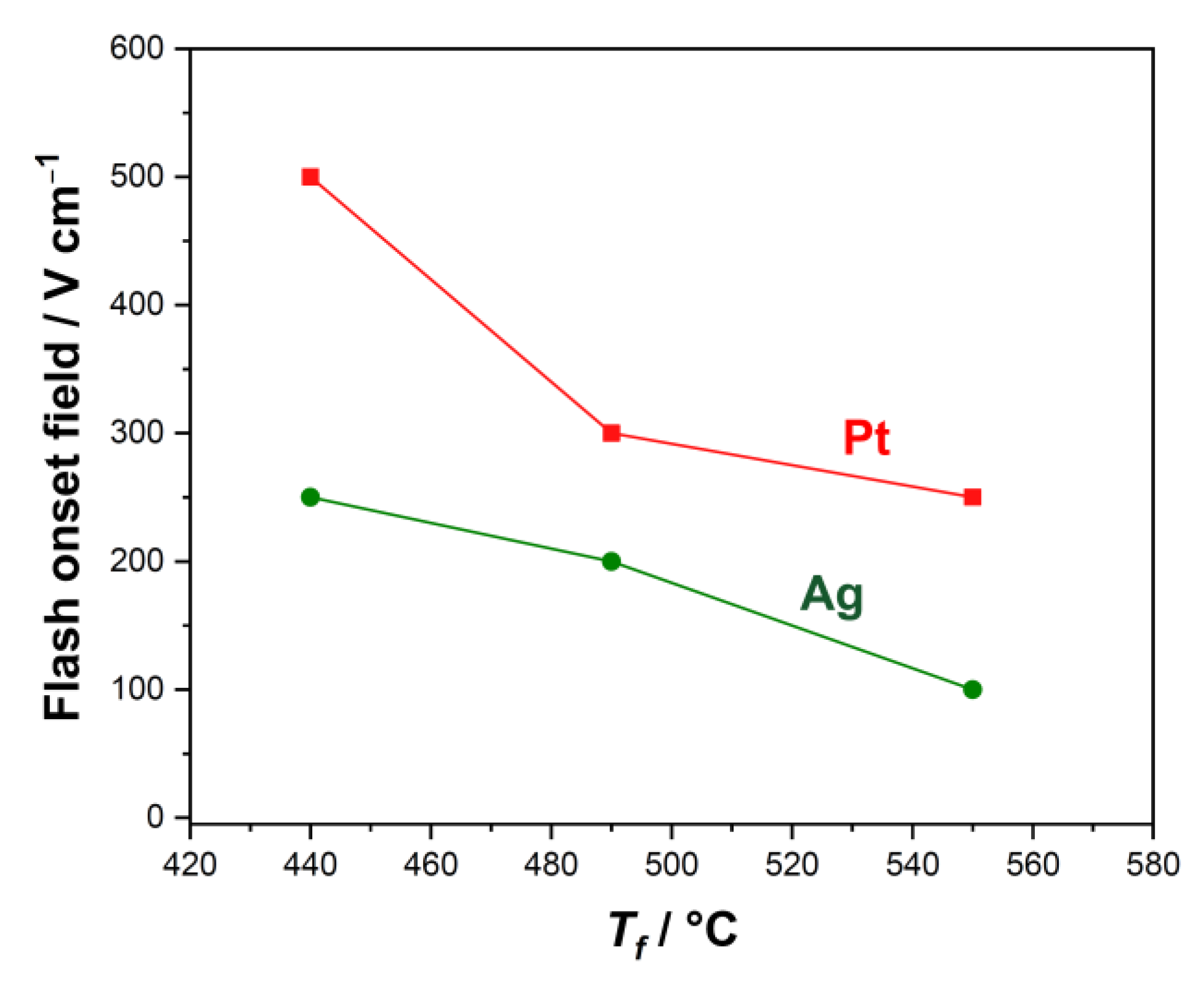
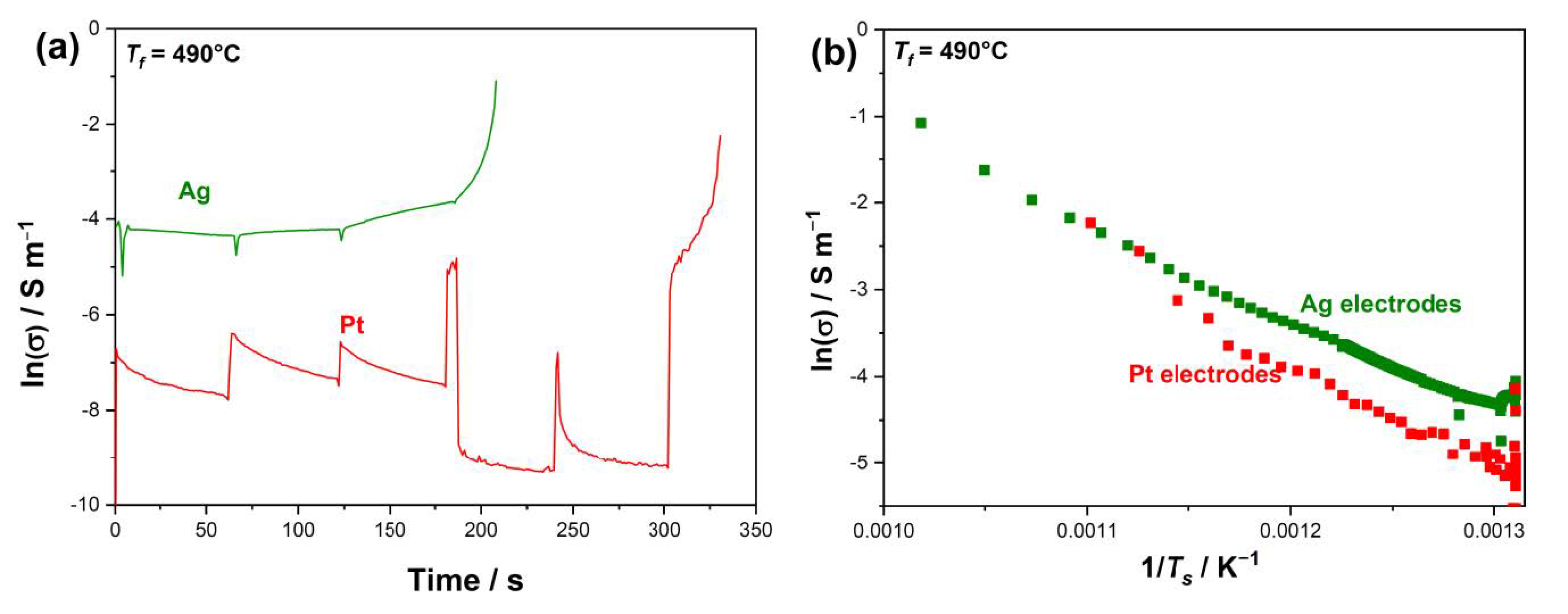
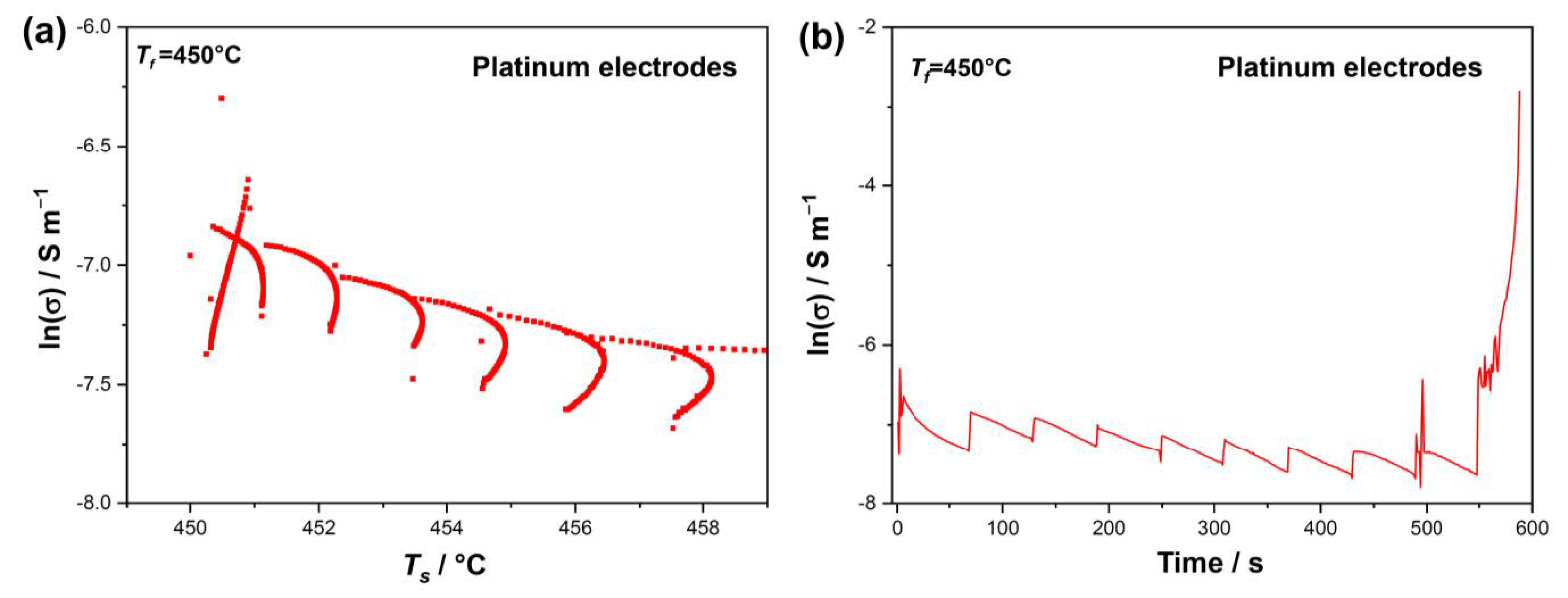
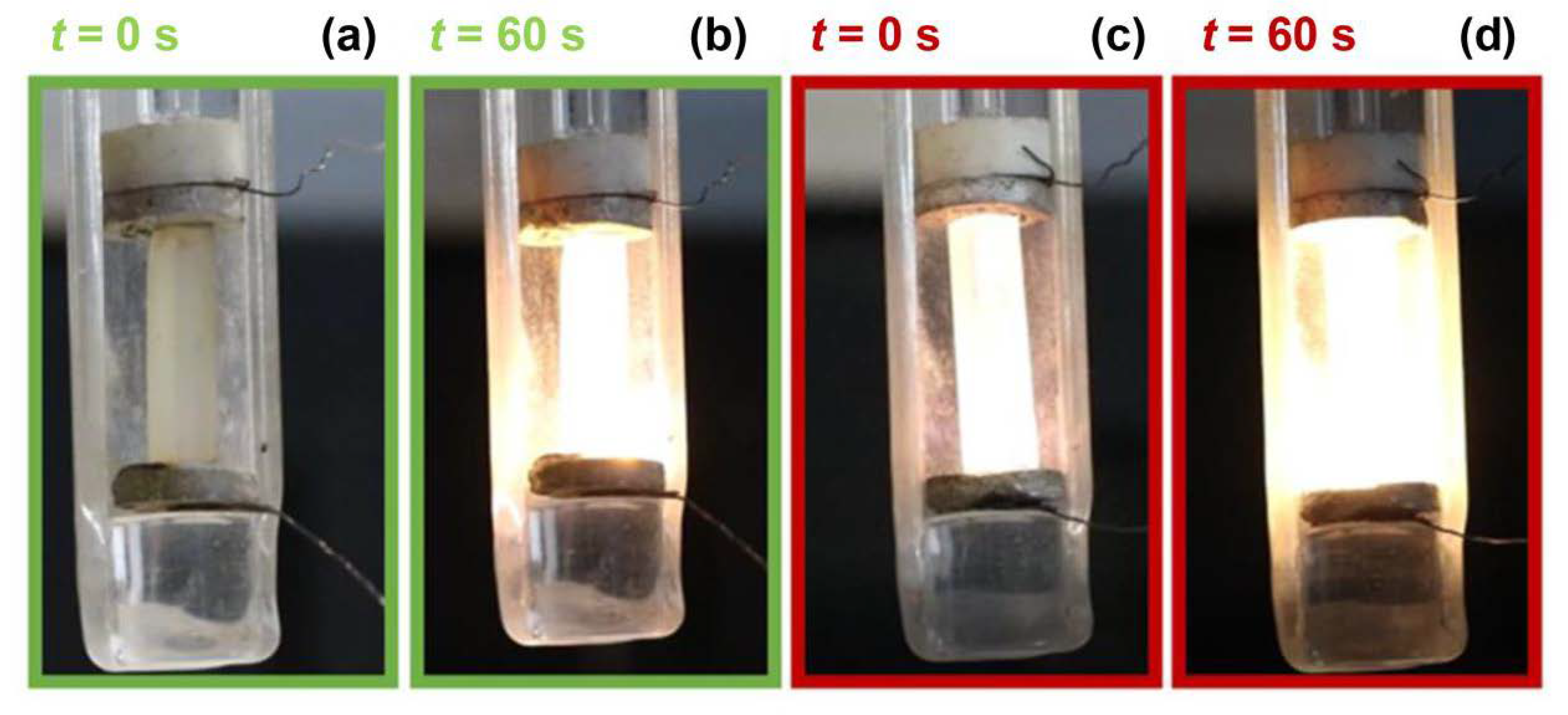
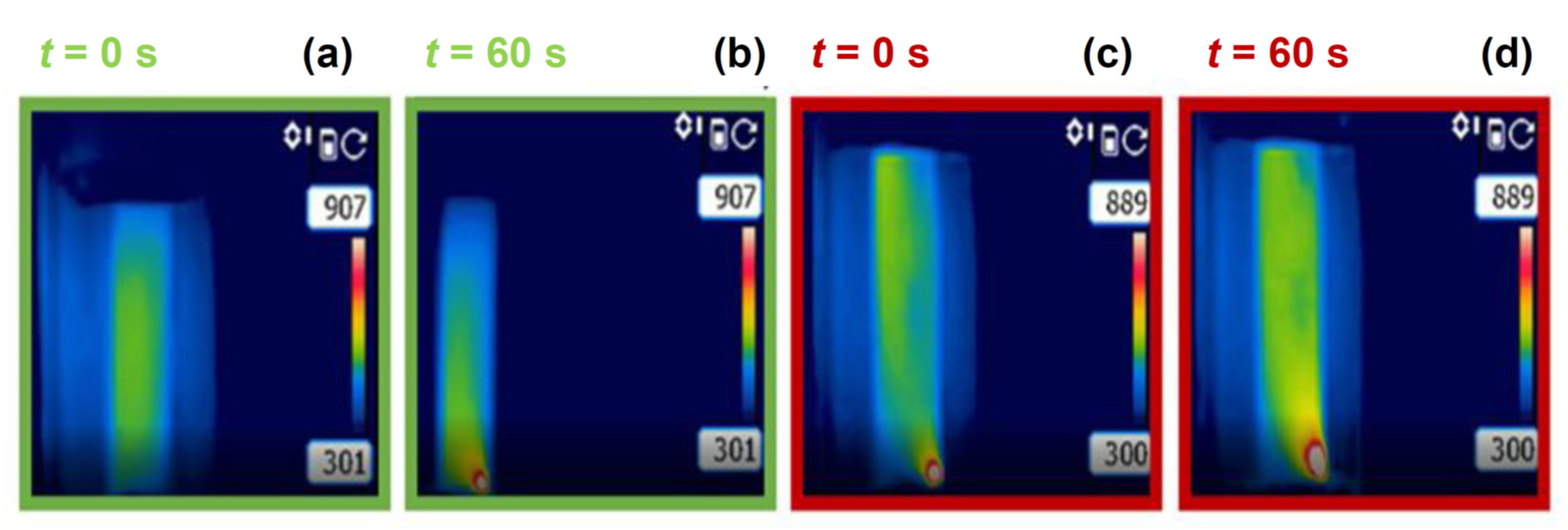
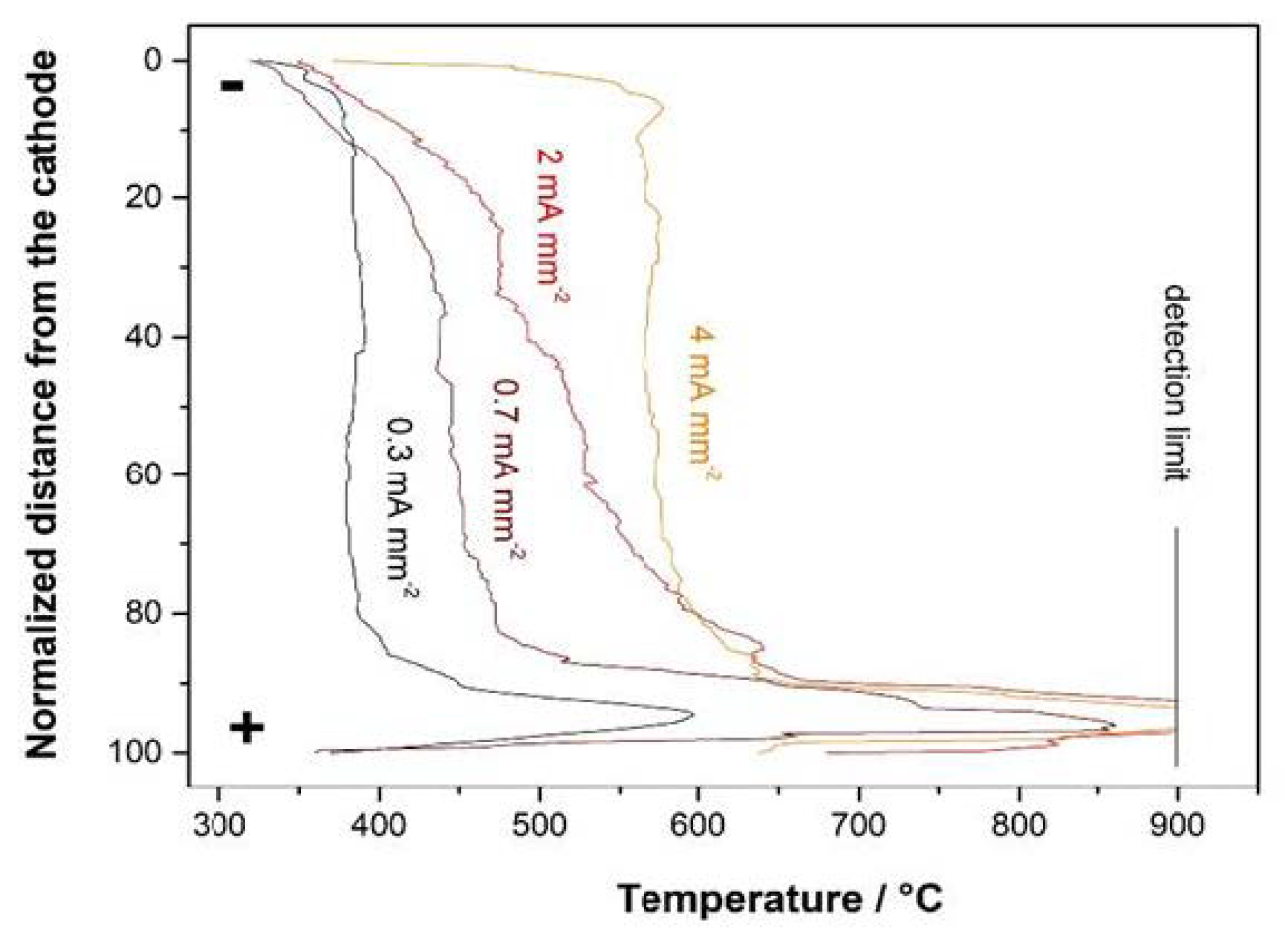
3. Results
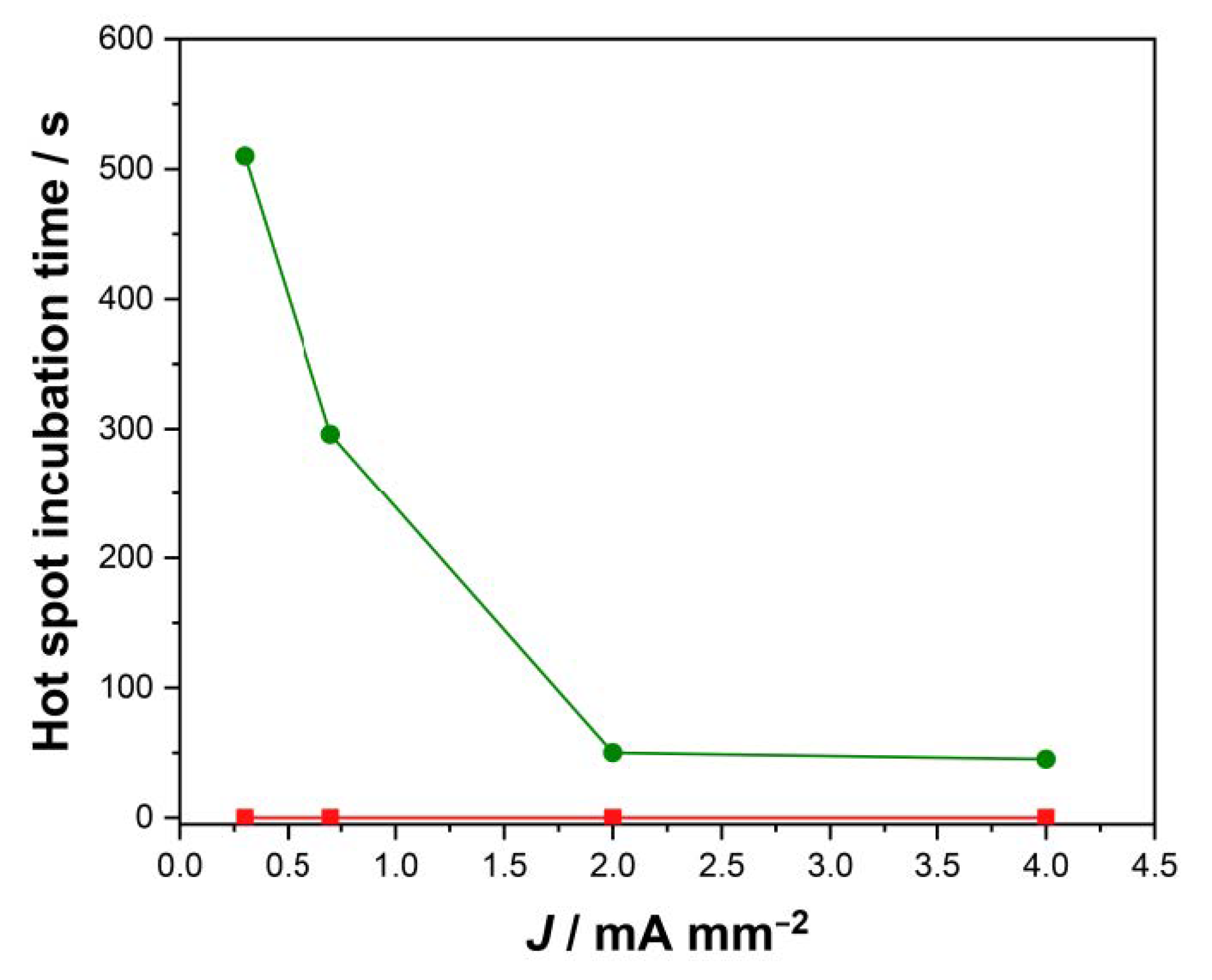
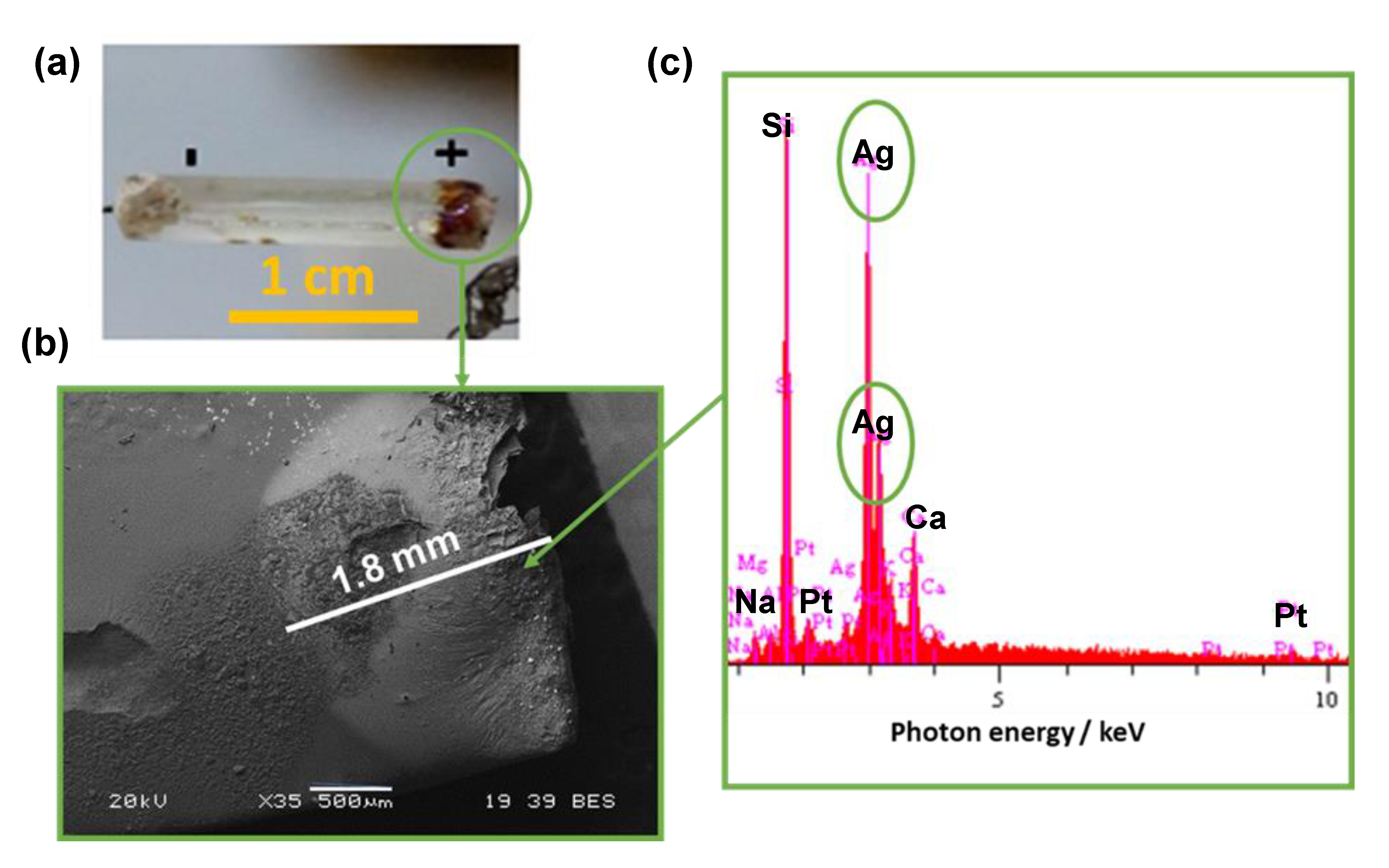
- The flash onset field is doubled when Pt electrodes are used;
- At the same temperature, samples with Ag electrodes are characterized by a higher conductivity (i.e., the electric current in Ag-plated samples is much larger than that in Pt-plated ones before the flash);
- A nonlinear conductivity trend is detected: the electric current sharply increases when an onset electric field is applied (Figure 2), this rise in the electric current being sharper when Pt electrodes are considered.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joule, J.P. On the Heat evolved by Metallic Conductors of Electricity, and in the Cells of a Battery during Electrolysis. London, Edinburgh, Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1841, 19, 260–277. [Google Scholar]
- Asai, S. Electromagnetic Processing of Materials. In Fluid Mechanics and Its Applications; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 99, ISBN 978-94-007-2644-4. [Google Scholar]
- Biesuz, M.; Sauders, T.; Ke, D.; Reece, M.J.; Hu, C.; Grasso, S. A review of electromagnetic processing of materials (EPM): Heating, sintering, joining and forming. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.T.; Parker, J.D. Review of resistance spot welding of steel sheets Part 1 Modelling and control of weld nugget formation. Int. Mater. Rev. 2004, 49, 45–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesuz, M.; Grasso, S.; Sglavo, V.M. What’s new in ceramics sintering? A short report on the latest trends and future prospects. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2020, 24, 100868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrù, R.; Licheri, R.; Locci, A.M.; Cincotti, A.; Cao, G. Consolidation/synthesis of materials by electric current activated/assisted sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2009, 63, 127–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bram, M.; Laptev, A.; Prasad Mishra, T.; Nur, K.; Kindelmann, M.; Ihrig, M.; Pereira da Silva, J.; Steinert, R.; Peter Buchkremer, H.; Litnovsky, A.; et al. Application of Electric Current Assisted Sintering Techniques for the Processing of Advanced Materials. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattan Ze’ev, B.; Shomrat, N.; Tsur, Y. Recent Advances in Mechanism Research and Methods for Electric-Field-Assisted Sintering of Ceramics. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dancer, C.E.J. Flash sintering of ceramic materials. Mater. Res. Express 2016, 3, 102001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.S.C. A Study on the Phenomena of Flash Sintering with Tetragonal Zirconia. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Colorado Boulder, Boulder, CO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Grasso, S.; Mckinnon, R.; Saunders, T.; Reece, M.J. Review of flash sintering: Materials, mechanisms and modelling. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2017, 116, 24–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesuz, M.; Sglavo, V.M. Flash sintering of ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 115–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cologna, M.; Rashkova, B.; Raj, R. Flash sintering of nanograin zirconia in <5 s at 850 °C. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 3556–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muccillo, R.; Kleitz, M.; Muccillo, E.N.S. Flash grain welding in yttria stabilized zirconia. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 1517–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, R.I.; Zapata-Solvas, E.; Bonilla, R.S.; Sneddon, T.; Wilshaw, P.R. Electrical characteristics of flash sintering: Thermal runaway of Joule heating. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 1865–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jung, J.-I.; Luo, J. Thermal runaway, flash sintering and asymmetrical microstructural development of ZnO and ZnO–Bi2O3 under direct currents. Acta Mater. 2015, 94, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun, J.M.; Raj, R. A first report of photoemission in experiments related to flash sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 2427–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, K.; Jha, S.K.; Raj, R. Correlations between conductivity, electroluminescence and flash sintering. Scr. Mater. 2016, 118, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesuz, M.; Luchi, P.; Quaranta, A.; Martucci, A.; Sglavo, V.M. Photoemission during flash sintering: An interpretation based on thermal radiation. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 3125–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, K.S.; Sglavo, V.M.; Raj, R. Flash sintering as a nucleation phenomenon and a model thereof. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34, 4063–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nie, J.; Chan, J.M.; Luo, J. Probing the densification mechanisms during flash sintering of ZnO. Acta Mater. 2017, 125, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Parker, B.; Falco, S.; Zhang, J.Y.; Fu, Z.Y.; Todd, R.I. Ultra-fast firing: Effect of heating rate on sintering of 3YSZ, with and without an electric field. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 2547–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaim, R. On the kinetics of liquid-assisted densification during flash sintering of ceramic nanoparticles. Scr. Mater. 2019, 158, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Wang, Q.; Lian, Y.; Wang, Y. Densification kinetics of flash sintered 3mol% Y2O3stabilized zirconia. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 747, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaim, R. Liquid Film Capillary Mechanism for Densification of Ceramic Powders during Flash Sintering. Materials 2016, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, T.P.; Avila, V.; Neto, R.R.I.; Bram, M.; Guillon, O.; Raj, R. On the role of Debye temperature in the onset of flash in three oxides. Scr. Mater. 2019, 170, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Cao, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y. Effect of oxygen partial pressure on temperature for onset of flash sintering 3YSZ. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasylkiv, O.; Borodianska, H.; Sakka, Y.; Demirskyi, D. Flash spark plasma sintering of ultrafine yttria-stabilized zirconia ceramics. Scr. Mater. 2016, 121, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, S.; Saunders, T.; Porwal, H.; Milsom, B.; Tudball, A.; Reece, M.; Chen, I.W. Flash Spark Plasma Sintering (FSPS) of α and β SiC. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 99, 1534–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manière, C.; Lee, G.; Olevsky, E.A. All-Materials-Inclusive Flash Spark Plasma Sintering. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manière, C.; Lee, G.; Torresani, E.; Gerling, J.F.; Yakovlev, V.V.; Martin, D.; Olevsky, E.A. Flash microwave pressing of zirconia. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Gucci, F.; Porwal, H.; Grasso, S.; Mahajan, A.; Reece, M.J. Flash spark plasma sintering of magnesium silicide stannide with improved thermoelectric properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, A. Flash-Sintering of MnCo2O4 and (La, Sr) (Co, Fe) O3 Ceramics for Potential Application in SOFC. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Trento, Trento, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Akbari-Fakhrabadi, A.; Mangalaraja, R.V.; Sanhueza, F.A.; Avila, R.E.; Ananthakumar, S.; Chan, S.H. Nanostructured Gd-CeO2 electrolyte for solid oxide fuel cell by aqueous tape casting. J. Power Sources 2012, 218, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiridigliozzi, L.; Biesuz, M.; Dell’Agli, G.; Di Bartolomeo, E.; Zurlo, F.; Sglavo, V.M.; Dell’Agli, G.; Di Bartolomeo, E.; Zurlo, F.; Sglavo, V.M.; et al. Microstructural and electrical investigation of flash-sintered Gd/Sm-doped ceria. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 7479–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojaimi, C.L.; Ferreira, J.A.; Chinelatto, A.L.; Chinelatto, A.S.A.; Pallone, E.M.d.J.A. Microstructural analysis of ZrO2/Al2O3 composite: Flash and conventional sintering. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 2473–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata-Solvas, E.; Bonilla, S.; Wilshaw, P.R.; Todd, R.I. Preliminary investigation of flash sintering of SiC. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 33, 2811–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chan, J.M.; Huang, R.; Luo, J. Water-assisted flash sintering: Flashing ZnO at room temperature to achieve ~98% density in seconds. Scr. Mater. 2018, 142, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, C.; Heffner, W.; Tessarollo, R.; Raj, R.; Jain, H. Electric field-induced softening of alkali silicate glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, C.T.; Heffner, W.R.; Raj, R.; Jain, H. AC electric field-induced softening of alkali silicate glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 101, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, C.T.; Kopatz, C.; Smith, N.J.; Jain, H. Development of highly inhomogeneous temperature profile within electrically heated alkali silicate glasses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, C.; Roling, B.; Raj, R.; Jain, H. Mechanism of electric field-induced softening (EFIS) of alkali silicate glasses. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2017, 471, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, L.; Biesuz, M.; Sglavo, V.M.; Saunders, T.; Binner, J.; Reece, M.; Grasso, S. DC-electro softening in soda lime silicate glass: An electro-thermal analysis. Scr. Mater. 2018, 151, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesuz, M.; Pinter, L.; Saunders, T.; Reece, M.; Binner, J.; Sglavo, V.; Grasso, S. Investigation of Electrochemical, Optical and Thermal Effects during Flash Sintering of 8YSZ. Materials 2018, 11, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliman, L.B.; Bouchet, R.; Gouvea, D.; Soudant, P.; Steil, M.C. Flash sintering of ionic conductors: The need of a reversible electrochemical reaction. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimley, C.A.; Prette, A.L.G.; Dickey, E.C. Effect of boundary conditions on reduction during early stage flash sintering of YSZ. Acta Mater. 2019, 174, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesuz, M.; Cipriani, M.; Sglavo, V.M.; Sorarù, G.D. Electrode-dependent Joule heating in soda lime silicate glass during flash processes. Scr. Mater. 2020, 182, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.W.; Perry, R.H. Perry’s Chemical Engineers’ Handbook; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 0071593136. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, O.L.; Stuart, D.A. Calculation of Activation Energy of Ionic Conductivity in Silica Glasses by Classical Methods. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1954, 37, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amma, S.; Lanagan, M.T.; Kim, S.H.; Pantano, C.G. Ionic Conductivity in Sodium-Alkaline Earth-Aluminosilicate Glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 99, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldin, F.M.E.; El Alaily, N.A. Electrical conductivity of some alkali silicate glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1998, 52, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, J. On pre-breakdown phenomena in insulators and electronic semi-conductors. Phys. Rev. 1938, 54, 647–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Mathpal, M.C.; Tripathi, A.K.; Prakash, J.; Agarwal, A.; Ahmad, M.M.; Swart, H.C. Plasmonic resonance of Ag nanoclusters diffused in soda-lime glasses. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 8596–8603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cipriani, M.; Sglavo, V.M.; Sorarù, G.D.; Biesuz, M. Electrode Material Effect on the Flash Ignition in Soda-Lime Silicate Glass. Ceramics 2021, 4, 70-82. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics4010007
Cipriani M, Sglavo VM, Sorarù GD, Biesuz M. Electrode Material Effect on the Flash Ignition in Soda-Lime Silicate Glass. Ceramics. 2021; 4(1):70-82. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics4010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleCipriani, Mattia, Vincenzo M. Sglavo, Gian Domenico Sorarù, and Mattia Biesuz. 2021. "Electrode Material Effect on the Flash Ignition in Soda-Lime Silicate Glass" Ceramics 4, no. 1: 70-82. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics4010007
APA StyleCipriani, M., Sglavo, V. M., Sorarù, G. D., & Biesuz, M. (2021). Electrode Material Effect on the Flash Ignition in Soda-Lime Silicate Glass. Ceramics, 4(1), 70-82. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics4010007







