Abstract
Macroporous composite foams consisting of β-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP) and titanium nitride (TiN) have been prepared by a facile emulsion route involving sintering at elevated temperatures after shaping. Commercially available hydroxyapatite and titanium particles are used as the starting material; to which, the surface of the particles has been modified by preferential adsorption of hexadecylamine to change from hydrophilic to hydrophobic character in water. This renders stable air-in-water emulsions from the particle-filled suspensions by simple mechanical frothing. Sintered β-TCP/TiN foams with a porosity of 65–70%, pore size of 20–2000 nm, and three-point rupture strength of 25–43 kPa have been obtained. Electrical resistance has been found to reduce pronouncedly when the initial titanium loading exceeds 15 vol.% for the composite foams sintered at 1000 °C under reducing nitrogen-hydrogen atmosphere.
1. Introduction
Calcium phosphates are calcium salts of phosphoric acid, and constitute the inorganic component of hard tissues such as bones and teeth [1]. Use of the calcium phosphates in biomedical applications, e.g., bone-graft substitute, targeted delivery vehicle, biomineralization, etc., has attracted intense interest over recent decades [1,2,3,4,5], due mainly to the growing healthcare needs for aged populations. The calcium phosphates, especially hydroxyapatite and tricalcium phosphate (TCP), and their composites are often shaped into various morphologies, including nanoparticle, film, and porous scaffold, in order to meet biological properties required for specific applications in a cost-effective manner [6,7,8,9]. Biocompatible TCP foams or scaffolds with designed hierarchical pore structures similar to the natural hard tissues, in particular, are highly desirable and have been prepared by various process schemes from either natural resources or synthetic products [10]. In view of the literature, Li et al. [11] mixed biphasic calcium phosphate powders with polymer resins to form fluid suspensions before being shaped and polymerized in molds. Porous and permeable scaffolds were obtained by subsequent sintering at elevated temperatures after removal of the polymeric template. Similarly, Ramay and Zhang [12] fabricated biphasic calcium phosphate scaffolds by combining gel casting with polymeric sponge template, so that use of monomers of low viscosity in the gel casting would facilitate the ease of shaping into complex geometries together with an increased powder loading. Instead of the use of synthetic polymeric template, Salin et al. [13] employed cuttlefish bone as a natural template for the preparation of biphasic calcium phosphate scaffolds with a hierarchical pore structure. Xu and Simon Jr. [14] used water-soluble mannitol as a porogen, i.e., pore-forming agent, in their biocompatible calcium phosphate cements for fast-setting porous scaffolds used in load-bearing situations. In addition, various rapid prototyping techniques have been used to fabricate three-dimensional scaffolds with designed pore structures [15,16,17,18]. Scaffolds with aligned and interconnected pore channels have also been prepared by extrusion [19,20] and freeze casting [21].
Even though substantial advancements have been made for the fabrication of porous calcium phosphate scaffolds by the above processes, use of air bubbles or liquid droplets as the template without needs of extensive tooling and expensive capital investment is highly desirable for the macroporous foam shaping. In this regard, Pickering emulsions involving preferential adsorption of solid particles at the oil-water or air-water interface provide an alternative route to prepare porous microcapsules and scaffolds facilely with tailored porosity and pore architecture [22]. For example, Liu et al. [23] prepared hydroxyapatite/poly(L-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) composite microparticles as injectable scaffolds via the emulsion route. Hu et al. [24] fabricated porous hydroxyapatite/poly(lactide-co-glycolide) scaffolds by solvent evaporation from Pickering emulsion templates. Yang et al. [25] recently combined Pickering emulsion templates with three-dimensional printing for preparing hierarchically macroporous scaffolds. In our recent studies [26,27,28], binary composite foams involving inorganic metals and oxides have been developed from the particle-filled stable emulsions; in which, hodrophobicity of the particles has been modified to attain the desired compositional distribution from the composite emulsions. Enlightening from these findings, macroporous composite foams consisting of biocompatible TCP and electrically conductive titanium nitride (TiN) functional particles have been prepared in this study by tuning the hydrophobicity of the dissimilar functional particles for emulsion shaping. Pore structures of the sintered composite foams have been examined together with their flexural strength and electrical conductance. The electrically conductive phosphate scaffolds have been reported to be beneficial to bone healing, including cellular in-growth, maturation, adhesion, and orientation of tissues, when electrical stimuli of different forms were applied near the injured region [29]. Narkevica et al. [30], for example, have recently reported that cytocompatible and electrically conductive TiO2−x scaffolds with three-dimensional open structures facilitated fibroblast and osteblast cell line spreading on the scaffold surface under externally applied electrical stimuli in their in vitro studies.
2. Materials and Methods
Commercially available hydroxyapatite (Ca5(PO4)3(OH), purity > 90%, Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and titanium (Ti, Yong-Zhen Technomaterial Co., Ltd., Taiwan) powders were used as the starting material. De-ionized (D.I.) water with an electrical resistivity of 18.2 MΩ⋅cm at 25 °C was from Millipore Super-Q Plus (USA). Reagent-grade hexadecylamine (HDA, CH3(CH2)15NH2, purity > 98%, Sigma Aldrich, USA) was used without further purification for the surface modification of the hydroxyapatite and Ti particles in water [27].
As shown in Figure 1, the as-received hydroxyapatite powders of 12.6 g were first mixed with 0.5 g HDA in water before addition of the Ti powders for a total ball-mixing time of 21 h. The Ti weight varied from 2.0 to 11.4 g, corresponding to a volumetric Ti fraction (fTi) from 0.1 to 0.5 in the hydroxyapatite/titanium mixtures. Note that solids fraction of the suspensions, consisting both of hydroxyapatite and Ti, was held at 10 vol.%. Some of the suspensions after ball-mixing were centrifuged at 7000 rpm and the powder mixtures were washed by D.I. water ultrasonically before being dried and die-pressed under 120 MPa to form pellets for contact-angle measurement [31,32]. The rest of the powdered suspensions were agitated vigorously by a mechanical blender with a maximum rotational speed of 1200 rpm. Air-in-water foams were produced by the mechanical frothing (as illustrated in Figure 1, in which an air bubble is preferentially adsorbed by the HDA-modified particles during the emulsion process) and were packed into non-porous molds followed by drying in an oven (80 °C for 24 h). The wet foams can be easily shaped into molds of different geometries, and the dried foams were then sintered at 1000 and 1200 °C, respectively, in a reducing atmosphere comprising 95 vol.% nitrogen and 5 vol.% hydrogen with an isothermal holding of 2 h.
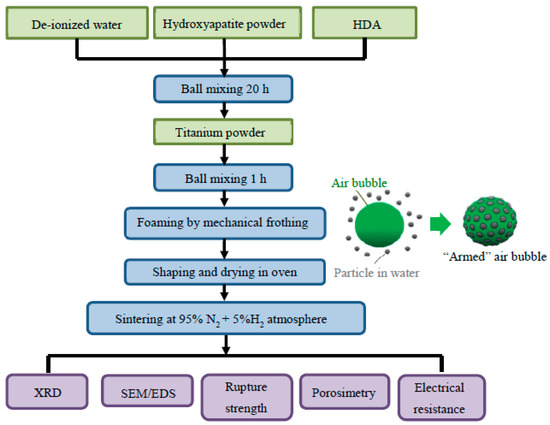
Figure 1.
Experimental flowchart.
Microstructure of the starting powders and cellular foams were examined by field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM, JSM-6700F, JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with an energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS). Phase composition was determined by X-ray diffractometry (XRD, MAC MXP III, Japan) using Cu K 1 radiation with a characteristic wavelength of 0.15405 nm. A sessile drop-shape analyzer (FTA 2000, First Ten Angstroms Inc., USA) was used for the apparent contact-angle measurement which dispenses water drops from a syringe pointed vertically down onto the surface-smooth powder compacts at 25 °C and captures the water profile on the samples by an optical system [31,32]. An average of at least five measurements was carried out for the hydroxyapatite and Ti particles. Mercury porosimetry (Autopore 9520, Micromeritics, USA) was used to measure the pore volume and pore-size distribution of the sintered foams. A maximum pressure of 414 MPa was used for the measurement. Three-point flexural strength of the sintered foams was determined by an Instron (USA) with a spanning distance of 30 mm and a cross-head speed of 0.5 mm·min−1.
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 2 shows morphology of the as-received hydroxyapatite and Ti particles. Both particles appear to be highly agglomerated. The hydroxyapatite particles show a needle-like structure with an elongated length about 200 nm. The atomic Ca/P ratio determined from the EDS is about 1.27, which is indicative of Ca deficiency in the starting powder. This is in good agreement with XRD results in Figure 3; to which, the hydroxyapatite particles have been found consisting of some dicalcium phosphate (CaHPO4, JCPDS no. 70359) with a Ca/P ratio of 1 as a minor phase, in addition to the major hydroxyapatite (JCPDS no. 9–432) with a theoretical Ca/P ratio of 1.67. The Ti particles, on the other hand, are of an almost spherical shape with size less than 200 nm. The as-received Ti powders yet comprise some TiN (JCPDS no. 38–1420), presumably on the Ti surface for avoiding oxidation of the metallic Ti particles during the powder production.
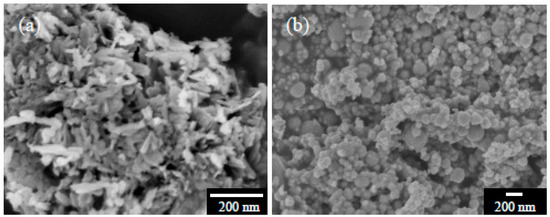
Figure 2.
SEM micrographs of the as-received (a) hydroxyapatite and (b) titanium particles.
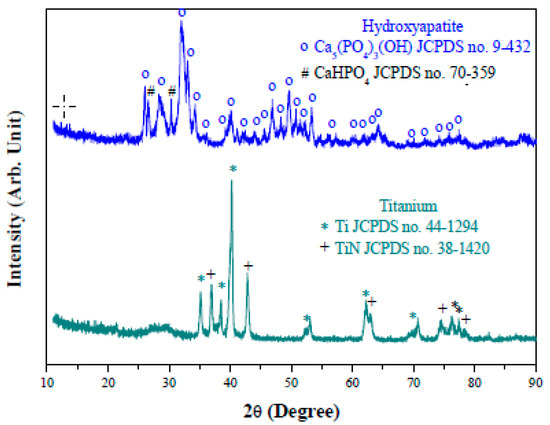
Figure 3.
XRD patterns of the as-received hydroxyapatite and titanium particles.
The as-received hydroxyapatite and Ti particles are both water-loving, i.e., hydrophilic in character, as shown in Figure 4. The contact angles were both below 10° when HDA was absent. The particle surface has been modified by preferential adsorption of HDA molecules so that the initially hydrophilic surface is changed to hydrophobic in water, resulted in a pronounced increase on the contact angle when the HDA concentration was firstly added. Affinity of the HDA molecules to the particles may be determined from the slope of the contact-angle gradient over given HDA concentrations. This indicates that the affinity of HDA molecules to the Ti surface appears to be a bit stronger when compared to that of the hydroxyapatite counterpart. In Figure 4, the initially hydrophilic surface of both the hydroxyapatite and Ti particles with the contact angle <10° was changed to hydrophobic with the contact angle approaching nearly 90° for the hydroxyapatite and even greater than 90° for the Ti, respectively. This stems from monolayer Langmuir adsorption of the nonionic HDA molecules on the particle surface so that a more complete coverage of the HDA molecules on the particle surface results in a more hydrophobic character [27]; to which, the non-polar hydrophobic tail of the HDA molecules is brought in direct contact with the water medium in replacement of the water-loving hydroxide on both particles’ surfaces. To obtain stable air-in-water emulsions, a contact angle close to 90° is desirable. Therefore, a HDA concentration of 4 wt.% (with respect to the hydroxyapatite weight) was chosen deliberately for the subsequent emulsification process. This renders sufficiently stable air-in-water emulsions from the particle-filled suspensions by a simple mechanical frothing.
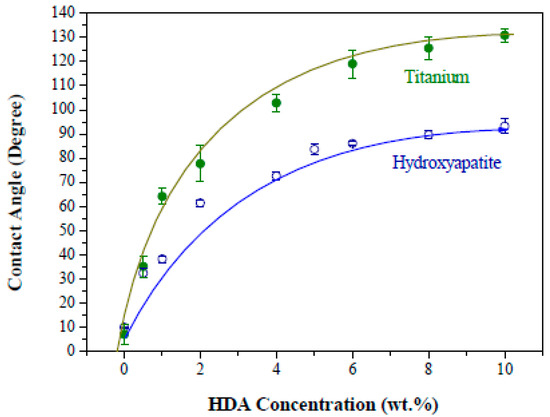
Figure 4.
Effect of HDA concentration on the contact angle of hydroxyapatite and titanium particles, respectively.
Figure 5 shows composite foams with fTi of 0.1 to 0.25 after sintering at 1000 °C at the reducing atmosphere. Spherical voids with a size ranging from μm to even mm are apparent. This reveals that the hydrophobic particles resided preferentially at the air-water interface around the air bubbles during the emulsification process. The “armed” emulsions were hence protected by the adsorbed particles with a sufficient mechanical strength to withstand stresses involved during the subsequent shaping and drying in molds. It may also be interesting to note that only the voids were left behind after the calcination since no porogen/template was used. A closer examination at each spherical void, in the insets of Figure 5, shows that the curved interface is indeed composed of dense packing of uniform grains/particles. The packing structure of the particles is considered critically important to the emulsion stability and the resulted pore structure as well. At the sintering temperature of 1000 °C, particles in the strut between the voids are only partially sintered and form interconnected pore channels between the voids. As shown in Figure 6, the composite foams present a porosity around 65 to 70 vol.% over the fTi fractions used. This, together with the void structure examined in Figure 5, suggests that the HDA concentration chosen in this study provides a sufficiently stable hydrophobic surface for the composite particles in the emulsion, so that “armed” emulsion bubbles can be produced facilely via the simple mechanical frothing. Pore size of the composite foams falls in a broad range from 20 to 2000 nm in Figure 7; to which, the pores are primarily from the interparticle packing structure in the strut of the foams. In addition, the composite foams exhibit three-point rupture strengths of 25 to 43 kPa that appear to increase with the initial Ti loading fraction.
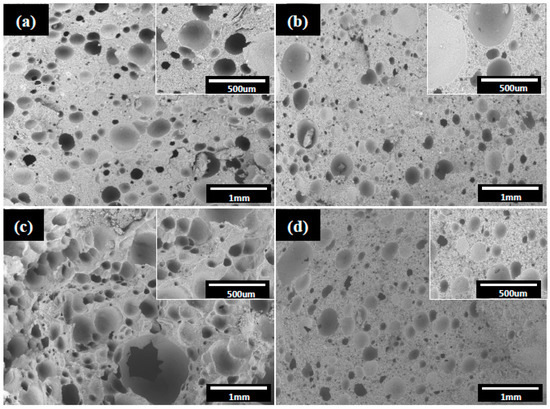
Figure 5.
SEM micrographs of the macroporous composite foams with volumetric titanium fraction of (a) 0.1, (b) 0.15, (c) 0.2, and (d) 0.25 after sintering at 1000 °C at 95 N2/5H2 atmosphere for 2 h.
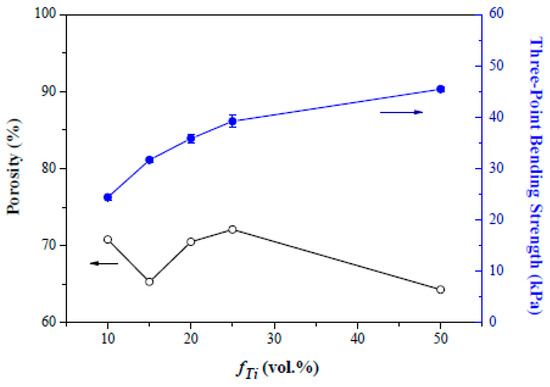
Figure 6.
Porosity and rupture strength of the sintered composite foams with volumetric titanium fraction ranging from 0.1 to 0.5. The foams were sintered at 1000 °C at 95 N2/5H2 atmosphere for 2 h.
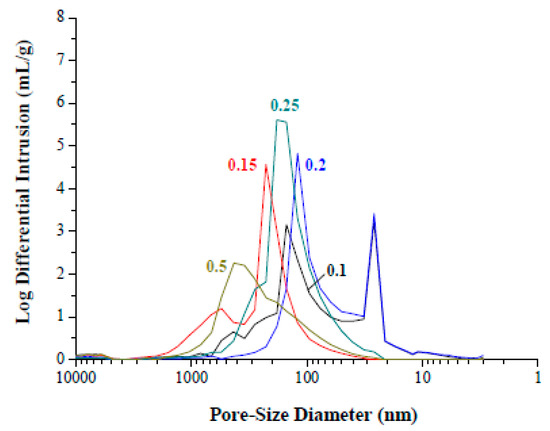
Figure 7.
Pore-size distribution of the sintered composite foams with volumetric titanium fraction from 0.1 to 0.5. The foams were sintered at 1000 °C at 95 N2/5H2 atmosphere for 2 h.
The composite foams sintered at 1000 °C consist of TCP (rhombohedral β-form, JCPDS no. 9–169) and TiN phases in Figure 8. The Ti metal in the starting powder appears to form TiN after sintering, presumably due to the reducing atmosphere used. An additional experiment (not shown here) reveals that the Ti metal remains up to a sintering temperature of 700 °C. In addition, formation of CaTiO3 perovskite also occurs after sintering at 1000 °C, resulting from reactions between the hydroxyapatite and titanium (or titanium oxide) at the elevated temperature employed. Note that the titanium oxide might come from the hydrolyzed titanium nitride on the surface of the titanium particles when brought in contact with water during the suspension preparation. This hence facilitates the formation of CaTiO3 at the elevated temperatures. In Figure 8, the formation of CaTiO3 perovskite becomes more apparent as the sintering temperature was further increased to 1200 °C; to which, the CaTiO3 perovskite appeared to become the predominant phase in the composite. Despite the presence of CaTiO3 perovskite, the electrical resistance of the composite foams reduces from 64 to 0.17 kohm when the fTi was increased from 0.1 to 0.5 in Figure 9. A marked reduction occurs when the fTi exceeds (possibly) the percolation threshold of ca. 0.15 so that formation of a long-range connective network of TiN is formed in three-dimensional porous β-TCP foams for the electrical conductance.
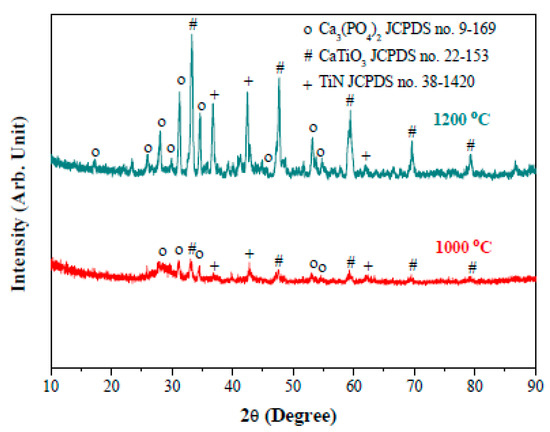
Figure 8.
XRD patterns of the sintered composite foams with volumetric titanium fraction of 0.25. The foams were sintered at 1000 and 1200 °C at 95 N2/5H2 atmosphere for 2 h.
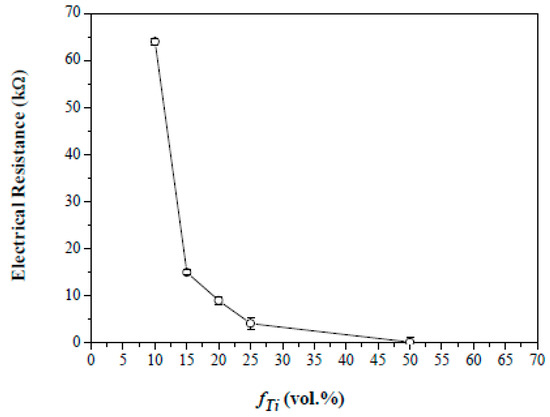
Figure 9.
Effect of Ti fraction on the electrical resistance of the sintered composite foams with volumetric titanium fraction from 0.1 to 0.5. The foams were sintered at 1000 °C at 95 N2/5H2 atmosphere for 2 h.
4. Conclusions
Electrically-conductive and porous β-TCP/TiN foams with some residual CaTiO3 perovskite have been prepared by a facile emulsion route followed by subsequent sintering at elevated temperatures. Hexadecylamine was used to preferentially adsorb on the starting hydroxyapatite and titanium particles so that the initially hydrophilic surface could be changed to partially hydrophobic in water for the stable creation of air-in-water emulsions. Sintered β-TCP/TiN foams with a porosity of 65 to 70%, a broad pore-size distribution from 20 to 2000 nm, and three-point rupture strength of 25 to 43 kPa have been obtained. Electrical resistance reduces pronouncedly when the initial titanium loading exceeds 15 vol.% for the composite foams.
Author Contributions
W.-H.K. carried out all the experimental works. W.J.T. was in charge of conceptualization, analysis, and paper writing.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministry of Science and Technology (Taiwan) under grant numbers MOST 104-2221-E-005-016-MY3 and 105-2221-E005-006-MY2.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Ministry of Science and Technology (Taiwan) for the financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Habraken, W.; Habibovic, P.; Epple, M.; Bohner, M. Calcium phosphates in biomedical applications: Materials for the future? Mater. Today 2016, 19, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Gauthier, O.; Sourice, S.; Pilet, P.; Rethore, G.; Khairoun, K.; Bouler, J.-M.; Tancret, F.; Weiss, P. A simple and effective approach to prepare injectable macroporous calcium phosphate cement for bone repair: Syringe-foaming using a viscous hydrophilic polymeric solution. Acta Biomater. 2016, 31, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paital, S.R.; Dahotre, N.B. Calcium phosphate coatings for bio-implant applications: Materials, performance factors, and methodologies. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2009, 66, 1–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginebra, M.-P.; Traykova, T.; Planell, J.A. Calcium phosphate cements: Competitive drug carriers for the musculoskeletal system? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2171–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorozhkin, S.V.; Epple, M. Biological and medical significance of calcium phosphates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 3130–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Tarafder, S. Calcium phosphate ceramic systems in growth factor and drug delivery for bone tissue engineering: A review. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1401–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanchenko, L.A.; Pinchuk, N.D. Making calcium phosphate biomaterials. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 2003, 42, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, H.K.; Yokogawa, Y.; Espinosa, F.F.; Kawamoto, Y.; Nishizawa, K.; Nagata, F.; Kameyama, T. Porous calcium phosphate coating over phosphorylated chitosan film by a biomimetic method. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kim, K.-H.; Ong, J.L. A review on calcium phosphate coatings produced using a sputtering process—An alternative to plasma spraying. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginebra, M.P.; Espanol, M.; Montufar, E.B.; Perez, R.A.; Mestres, G. New processing approaches in calcium phosphate cements and their applications in regenerative medicine. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2863–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; De Wijn, J.R.; Li, J.; Layrolle, P.; De Groot, K. Macroporous biphasic calcium phosphate scaffold with high permeability/porosity ratio. Tissue Eng. 2003, 9, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramay, H.R.R.; Zhang, M. Biphasic calcium phosphate nanocomposite porous scaffolds for load-bearing bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5171–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarin, P.; Lee, S.-J.; Apostolov, Z.D.; Kriven, W.M. Porous biphasic calcium phosphate scaffolds from cuttlefish bone. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 94, 2362–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.H.K.; Simon, C.G., Jr. Fast setting calcium phosphate–chitosan scaffold: Mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Li, D.; Lu, B.; Tang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. Fabrication of a calcium phosphate scaffold with a three dimensional channel network and its application to perfusion culture of stem cells. Rapid Prototyping J. 2007, 13, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.E.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Verbout, A.J.; Dhert, W.J.A.; de Bruijn, J.D. Scaffolds with a standardized macro-architecture fabricated from several calcium phosphate ceramics using an indirect rapid prototyping technique. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inzana, J.A.; Olvera, E.; Fuller, S.M.; Kelly, J.P.; Graeve, O.A.; Schwarz, E.M.; Kates, S.L.; Awad, H.A. 3D printing of composite calcium phosphate and collagen scaffolds for bone regeneration. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4026–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, C.F.; Perera, F.H.; Marote, A.; Ferreira, S.; Vieira, S.I.; Olhero, S.; Miranda, P.; Ferreira, J.M.F. Biphasic calcium phosphate scaffolds fabricated by direct write assembly: Mechanical, anti-microbial and osteoblastic properties. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.-Y.; Kim, H.-E.; Moon, Y.-W.; Shin, K.-H.; Koh, Y.-H. Production of porous calcium phosphate (CaP) ceramics with aligned pores using ceramic/camphene-based co-extrusion. Biomater. Res. 2015, 19, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, M.-K.; Moon, Y.-W.; Maeng, W.-Y.; Koh, Y.-H.; Kim, H.-E. Design and production of continuously gradient macro/microporous calcium phosphate (CaP) scaffolds using ceramic/camphene-based 3D extrusion. Materials 2017, 10, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deville, S.; Saiz, E.; Tomsia, A.P. Freeze casting of hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5480–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aveyard, R.; Binks, B.P.; Clint, J.H. Emulsions stabilised solely by colloidal particles. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2003, 100–102, 503–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Okada, M.; Maeda, H.; Fujii, S.; Furuzono, T. Hydroxyapatite/biodegradable poly(L-lactide–co-e-caprolactone) composite microparticles as injectable scaffolds by a Pickering emulsion route. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Gu, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Hu, M.; Chen, W.; Tong, Z.; Wang, C. Facile fabrication of poly(L-lactic acid)-grafted hydroxyapatite/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffolds by Pickering high internal phase emulsion templates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2014, 6, 17166–17175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Hu, Y.; Wang, C.; Binks, B.P. Fabrication of hierarchical macroporous biocompatible scaffolds by combining Pickering high internal phase emulsion templates with three-dimensional printing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2017, 9, 22950–22958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, W.J.; Hsu, K.-T. Macroporous ZrO2/Ti composite foams by aqueous gelcasting of particle-stabilized emulsions. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-W.; Chen, C.-W.; Hsieh, J.-H.; Tseng, W.J. Preparation of Ag/TiO2 composite foams via Pickering emulsion for bactericide and photocatalysis. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, S797–S801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, W.J.; Lin, P.-T. Effect of solids concentration on TiO2/Ni composite foams prepared by aqueous gelcasting of particle-stabilized emulsions. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 5265–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balint, R.; Cassidy, N.J.; Cartmell, S.H. Electrical stimulation: A novel tool for tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2013, 19, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narkevica, I.; Stipniece, L.; Jakobsons, E.; Cakstina, I.; Ozolins, J. Electrically active and 3D porous TiO2-x ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhao, J.-J.; Yang, M.-H.; Tseng, W.J. Effect of solids concentration on pore structure of ZnO-foams prepared by particle-stabilized foaming route. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 4649–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, W.J.; Wu, P.-S. Effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate on stability of gibbsite platelet stabilized emulsion foams. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 2711–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).