Abstract
The accelerated development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) capabilities and systems is driving a paradigm shift in productivity, innovation and growth. Despite this generational opportunity, AI is fraught with significant challenges and risks. To address these challenges, responsible AI has emerged as a modus operandi that ensures protections while not stifling innovations. Responsible AI minimizes risks to people, society, and the environment. However, responsible AI principles and practice are impacted by ‘principle proliferation’ as they are diverse and distributed across the applications, stakeholders, risks, and downstream impact of AI systems. This article presents a systematic review of responsible AI principles and practice with the objectives of discovering the current state, the foundations and the need for responsible AI, followed by the principles of responsible AI, and translation of these principles into the responsible practice of AI. Starting with 22,711 relevant peer-reviewed articles from comprehensive bibliographic databases, the review filters through to 9700 at de-duplication, 5205 at abstract screening, 1230 at semantic screening and 553 at final full-text screening. The analysis of this final corpus is presented as six findings that contribute towards the increased understanding and informed implementation of responsible AI.
1. Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is driving a surge of innovations across all industries and domains, unseen since the Industrial Revolution. Recent AI achievements include Nobel prizes in physics and chemistry [1,2], billion-dollar valuations of frontier AI models [3], and projected trillion-dollar productivity gains for the global economy [4,5,6]. Despite these advances, AI is fundamentally challenged by its inherent design limitations [7,8], risk-prone applications [9], and emerging threat scenarios of technological displacement, large-scale cyberattacks, and existential risks [10,11]. These challenges are being collectively recognized, studied and evaluated as “Responsible AI (RAI)” [12,13]. Responsible AI refers to the design, development, deployment, and adoption of AI systems that minimize risks to people, society, and the environment while ensuring alignment with human values and societal norms. The somewhat irresponsible release and general availability of foundational AI models further signify the importance of responsible AI as an active field of study. For instance, the AI Incident Database [14,15] records cases of AI risks and misuse, and 2024 records a high number of cases, 233, which is more than a 50% increase from 2023, indicating the increasing use of AI, as well as the increased public awareness of AI and its impact. In response to these challenges, national AI policies are becoming increasingly visible. The year 2024 marked a shift toward global coordination on responsible AI governance and policymaking. For instance, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) presented a revised AI principles [16] and governance framework, the Council of Europe adopted a legally binding AI treaty and passed the European Union AI Act [17], the world’s first comprehensive regulatory framework, as well as the Continental AI Strategy [18] in the African Union, the Governing AI for Humanity report by the United Nations and formation of the first International Network of AI Safety Institutes for global AI safety cooperation [19,20]. Narrowing down to AI systems and the design, development, deployment lifecycle associated with these systems, it is somewhat challenging to determine what responsibility means within the system and operational setting as they are artifacts or tools built using training datasets. However, the technology, or the tool that holds that technology, is inseparable from the socio-technical system. This system involves people and organizations in various roles, such as developers, manufacturers, users, bystanders, or policymakers, and the interactions and processes that organize these roles. The responsibility is shared between the AI technology and this socio-technical system within which it exists.
Given the nature of this challenge, it is important to establish a chain of responsibility that links the interaction and disposition of AI systems to the diverse stakeholders of the AI supply chain, starting with training data right up to larger/legacy systems that integrate or embed AI modules. This chain includes ethical principles and practices, which are fundamental in guiding the development and operation of AI systems. Ethics, as a branch of philosophy, explores what is morally right and wrong [21], offering a foundation for establishing principles that can guide responsible AI practices.However, ethics itself is subjective and can vary from person to person, culture to culture, and society to society [22]. What is considered ethical for one individual may not align with the ethics of another. AI systems are complex socio-technical entities and they are shaped by the social context in which they are developed, used, and interacted with. This involves multiple stakeholders, institutions, and cultural norms [23]. Therefore, stepping beyond subjective ethics and into responsibility in AI ensures that individuals and organizations are aware of the impact of their AI-driven actions and are actively taking steps to safeguard the choices, liberties, and preferences of individuals and groups from risk, harm and damage. In this context, the importance of AI responsibility has become paramount, demanding greater responsibility and accountability from individuals and organizations involved in AI development and usage. Therefore, aligning AI with broadly accepted social norms and considering its impact on individuals, communities, and the environment is essential [24].
Organizations recognize that responsible AI practices are essential for building trust, minimizing privacy invasion, and ensuring an acceptably low risk of harm to users and society [25]. The adoption of responsible AI practices is influenced by market dynamics, liability laws, external regulations, and internal motivations. Key aspects of responsible AI development include testing the safety and security of systems during development, evaluating potential social impacts prior to release, being willing to abandon projects that do not meet high safety standards, and delaying system release until risks are mitigated [26]. The increasing reliance on AI systems to perform critical tasks related to user health and well-being has also brought forth serious safety and security concerns [26]. Instances of biased decision making in credit markets and criminal justice systems, privacy concerns stemming from facial recognition technologies, and the potential disruption of employment due to automation highlight the urgent need for responsible AI development. The implications of irresponsible AI extend to potential risks, such as the escalation of military conflicts involving autonomous weapons and large-scale job displacement.
This article aims to address these challenges by conducting a systematic review of responsible AI principles and practice. The following six research questions direct this review: (1) What is the current state of responsible AI principles and practice? (2) What are the foundations of responsibility? (3) How do these foundations define responsibility in AI? (4) What factors drive the need for responsible AI? (5) What are the principles of Responsible AI? and (6) How do these principles translate into the practice of responsible AI? The rest of the article is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the systematic review methodology adopted in this study, consisting of search strategy, data sources, and a four-stage study selection process. Section 3, Section 4, Section 5, Section 6, Section 7 and Section 8 present the findings of the systematic review corresponding to the six research questions outlined above, and Section 9 concludes the paper.
2. Systematic Review Methodology
Originating as Cochrane Reviews in healthcare and health policy, a systematic review collects, analyzes and evaluates research in a systematic, transparent, and reproducible manner and contributes towards new, aggregated knowledge that informs policy and practice [27]. A systematic review considers all pre-existing evidence related to the research questions and provides both conceptual and practical foundations for future research directions [28]. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [29,30] were followed throughout this review, with the primary objectives of summarizing existing evidence, identifying gaps in the research, and establishing a framework to guide future research efforts. On the topic of Responsible AI, several reviews and broad-based studies have already been reported in recent literature [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. As the first step, these reviews were evaluated to ensure the novelty and validity of the contribution of this work. This evaluation confirmed gaps in the literature for the research questions noted above, i.e., the lack of a systematic review on responsible AI principles and practice that is informed by a deep thematic analysis of related literature. Table 1 presents the review protocol of this study, containing research questions, databases, search query, search strategy, inclusion and exclusion criteria, quality assessment and analysis method.

Table 1.
Systematic review protocol.
2.1. Search Strategy
The search strategy was designed to identify literature specifically focused on “responsibility” in the design, development, deployment, use and management of AI systems. This would distinguish it from the broader focus on ethical AI and AI ethics. Terms such as “ethical AI” and “trustworthy AI” were excluded because they represent different research directions to the principles and practice of responsible AI. Ethical AI has been a prominent topic in AI research for several years, and the focus has been to identify what the term “responsibility” specifically means in AI literature, separate from these broader ethical considerations. The search was further qualified by adding contextual terms that capture the various ways in which the word or phrase “responsible” was used in the literature, including frameworks, guidelines, implementations, challenges, assessment, and governance structures.
2.2. Data Sources
Scopus, Web of Science, Semantic Scholar, and CrossRef were selected as the data sources due to the wide coverage of singular discipline, multi-disciplinary and interdisciplinary research relevant to responsible AI. These databases collectively index the major journals, conferences, and publication venues where responsible AI research is published within the academic community. All articles were sourced from reputable publishers, including Elsevier, MDPI, Springer Link, Science Direct, IEEE Xplore, Wiley Online Library, Nature Publishing Group, Taylor and Francis Online, World Scientific Publishing, Oxford Academic, and the ACM Digital Library.
2.3. Study Selection
This section presents the study selection process across the stages of initial search and de-duplication, abstract search and screening, LLM-assisted semantic screening and full-text screening.
2.3.1. Stage 1: Initial Search and De-Duplication
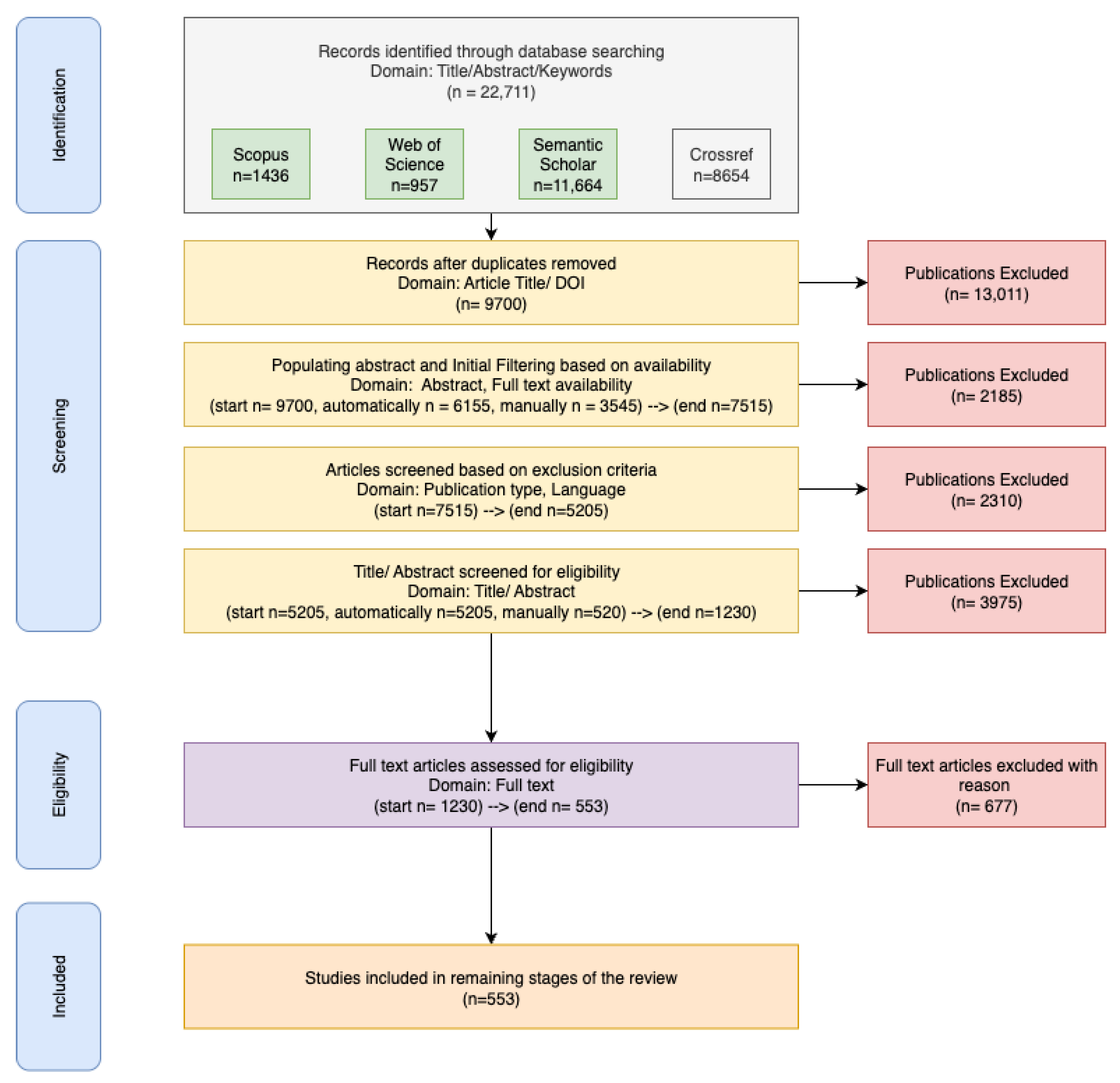
Multiple iterations of the search process were conducted, with each iteration involving comparison of results and refinement of the search procedure to ensure inclusion of a comprehensive set of relevant work. In the final iteration, publications were retrieved from the three databases from 2020 to 2025. This process retrieved 22,711 initial results (Scopus: 1436; Web of Science: 957; Semantic Scholar: 11,664; CrossRef: 8664). Database searches were conducted in March 2025 to ensure consistency in the temporal scope of retrieved publications and citation metrics across all databases. The outcomes of these searches were merged and duplicate entries were eliminated based on Digital Object Identifier (DOI) and title similarity. This de-duplication process reduced the total number of publications from 23,668 to 9700.
2.3.2. Stage 2: Abstract Search and Screening
Some abstracts were missing in the original database search, and this was addressed by using the Elsevier abstract retrieval API to programmatically populate missing abstracts. The abstract retrieval API returned abstracts only from journals and conference proceedings, and the Document Object Identifier (DOI) was used for each entry to retrieve accurate data. Abstracts were successfully populated for 6155 entries (63.5% of the deduplicated set) using this automated pipeline. The remaining 3545 records were manually reviewed by two reviewers, and abstracts were populated for an additional 1360 articles for which the Elsevier API did not have data. However, the remaining 2185 records had to be excluded after a manual search due to a lack of abstracts or full-text availability. The third reviewer inspected these missing records and found out that most of these were article summaries, talks, thesis submissions, and other types of content that also aligned with the exclusion criteria. While some abstracts may have been missed, given that both automated and manual retrieval of abstracts was conducted, this percentage is relatively low compared to what was gathered. When retrieving abstracts, publication type, publisher, and language information were also populated programmatically (using the API) and manually for missing entries. Based on the exclusion criteria, non-peer-reviewed publications such as book chapters, preprints, and non-English publications were excluded. This stage concluded with 5205 articles.
2.3.3. Stage 3: LLM-Assisted Semantic Screening
A large language model (LLM)-based semantic screening approach was applied to these 5205 articles in order to ensure contextually relevant filtering over traditional keyword matching. Unlike conventional search engines that rely on exact keyword matching, this approach assessed semantic and contextual relevance. The filtering process employed two primary criteria and five secondary criteria. Primary criteria: Articles were required to have clear evidence of both keywords “responsible” and “artificial intelligence” with specific focus towards the design, development, deployment, use and management of AI systems. Secondary criteria: Articles were further evaluated for relevance to the research question noted in Section 1: principles, practices, frameworks and guidelines for responsible AI, practical implementation and organizational challenges, evaluation metrics and assessment frameworks, governance and regulatory compliance considerations.
The LLM filtering process identified approximately 1230 publications meeting the thematic criteria. To validate this automated approach, manual review of a random sample (30% of filtered results, n = 369) was conducted, achieving 87% agreement between LLM classifications and human reviewers. Manual review of a random sample (10% of excluded results, n = 397) was also conducted and achieved 97% agreement between LLM classification and human reviewers. This higher agreement rate for exclusions demonstrates greater accuracy in excluding irrelevant articles using the LLM-assisted screening approach. The prompt used for this LLM-based filtering is available in the Supplementary Section.
2.3.4. Stage 4: Full-Text Screening
For the final screening stage, two independent reviewers conducted a comprehensive full-text review of all eligible publications (n = 1230). The full-text review process applied specific screening criteria relevant to the research questions with substantive content focused on the design, development, deployment, use and management of AI systems. Articles that merely referenced “responsible” terminology without meaningful engagement with responsible principles or practice were excluded. Responsible AI themes needed to constitute a central focus of the publication, requiring that responsibility occupy a substantial portion (minimum one-third) of the study’s content and analysis. The responsibility discourse had to be directly connected to artificial intelligence systems, machine learning applications, or AI governance structures. Publications addressing only broader organizational responsibility or sustainability issues without AI-specific context were excluded. All publications were required to satisfy the comprehensive inclusion and exclusion parameters established in the research design. An additional reviewer served as adjudicator for comparing and validating the screening outcomes. Inter-rater reliability reached 78% agreement between the primary reviewers. Conflicts in assessment were addressed through collaborative discussion involving both primary reviewers and the adjudicating researcher until consensus was achieved.
The final corpus comprised 553 peer-reviewed publications that satisfied all methodological requirements and criteria defined across these four stages.
The PRISMA flow diagram in Figure 1 illustrates the systematic study selection process across four stages.
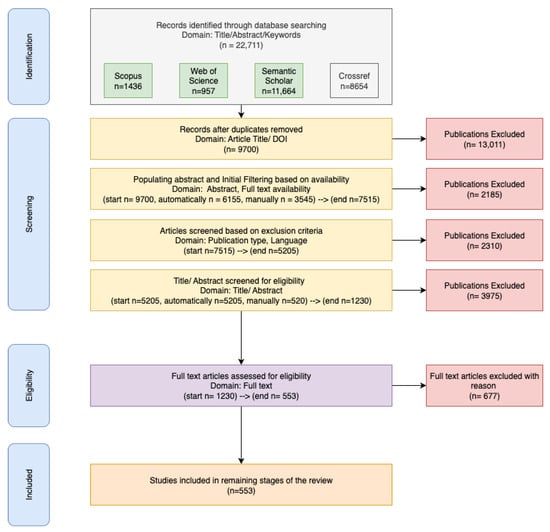
Figure 1.
The PRISMA flow diagram for the phases of the systematic review.
2.4. Data Extraction and Analysis
The systematic content analysis of the final selected publications was executed through a dual-stage review process. An initial reviewer performed a detailed examination of all publications to extract relevant information addressing the research questions concerning responsible AI conceptualization, frameworks, principles, and applications. Following this extraction phase, a secondary reviewer validated the extracted data to confirm accuracy and adherence to the established inclusion/exclusion criteria for responsible AI research.
The information systematically extracted from each publication encompassed:
- Publication details: Title, authorship, publication year, and source venue;
- Study characteristics: Publication format (journal article or conference proceeding), publishing house, and bibliometric data;
- Terminology and definitions: Explicit definitions of “responsible AI,” “AI responsibility,” and associated concepts where available;
- Framework identification: Recognition of responsible AI frameworks, principles, guidelines, or regulatory standards examined;
- Principle mapping: Identification of specific responsible AI principles discussed;
- Application context: Practical implementations, organizational barriers, evaluation methodologies, or governance mechanisms;
- Sectoral focus: Particular industries or application domains where responsible AI concepts are implemented.
Funding sources and authors’ financial disclosures were not extracted because they were judged immaterial to the conceptual focus of this review.
The following subsections unpack and discuss findings from this final corpus in alignment to the six research questions, Finding 1 corresponds to research question 1, “What is the current state of responsible AI principles and practice?”, and similarly up to Finding 6 and research question 6.
3. Finding 1: Topics and Themes in Review Results
The final corpus was subject to a deep analysis and synthesis of concepts, relationships, summary findings and conclusions in order to develop a broad appreciation of the current state of responsible AI principles and practice. To systematically analyze the content of the selected publications, semantic grouping based on content similarity was applied. BERTopic [44], a state-of-the-art topic modeling technique that combines transformer-based embeddings with traditional clustering approaches, was employed. The BERTopic pipeline consists of several key steps: first, documents are embedded using OpenAI’s text-embedding-3-large model, followed by dimensionality reduction using Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) [45] to prepare the data for clustering. The reduced embeddings are then clustered using Hierarchical Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (HDBSCAN) [46], a density-based clustering algorithm that can identify clusters of varying shapes and sizes while effectively handling outliers. BERTopic generated 40 initial distinct topics. These topics were derived by combining titles, abstracts, and keywords from each publication into a unified text corpus. The documents within each group were then processed using a class-based TF-IDF transformation to identify the most representative terms. Through a systematic consolidation process based on four techniques (semantic similarity, thematic overlap, topic frequency, and coherence of grouped topics), 40 initial distinct topic clusters were identified. These 40 clusters were refined into 15 major themes. Of the initial 553 articles, BERTopic classified 60 as outliers (11%). One reviewer went through all the outliers after the thematic analysis and assigned 21 documents to relevant topics. This resulted in a final analyzed corpus of 514 (94%) articles. These outlier documents either represented intersections between multiple topics or did not align clearly with any of the identified themes, indicating potential emerging or cross-cutting research areas in the responsible AI domain. Once the initial topic analysis was done, three independent runs were again executed with different random initialization seeds. Each run produced between 38 and 46 initial clusters, these were further evaluated to determine the presence of the same 15 major themes.
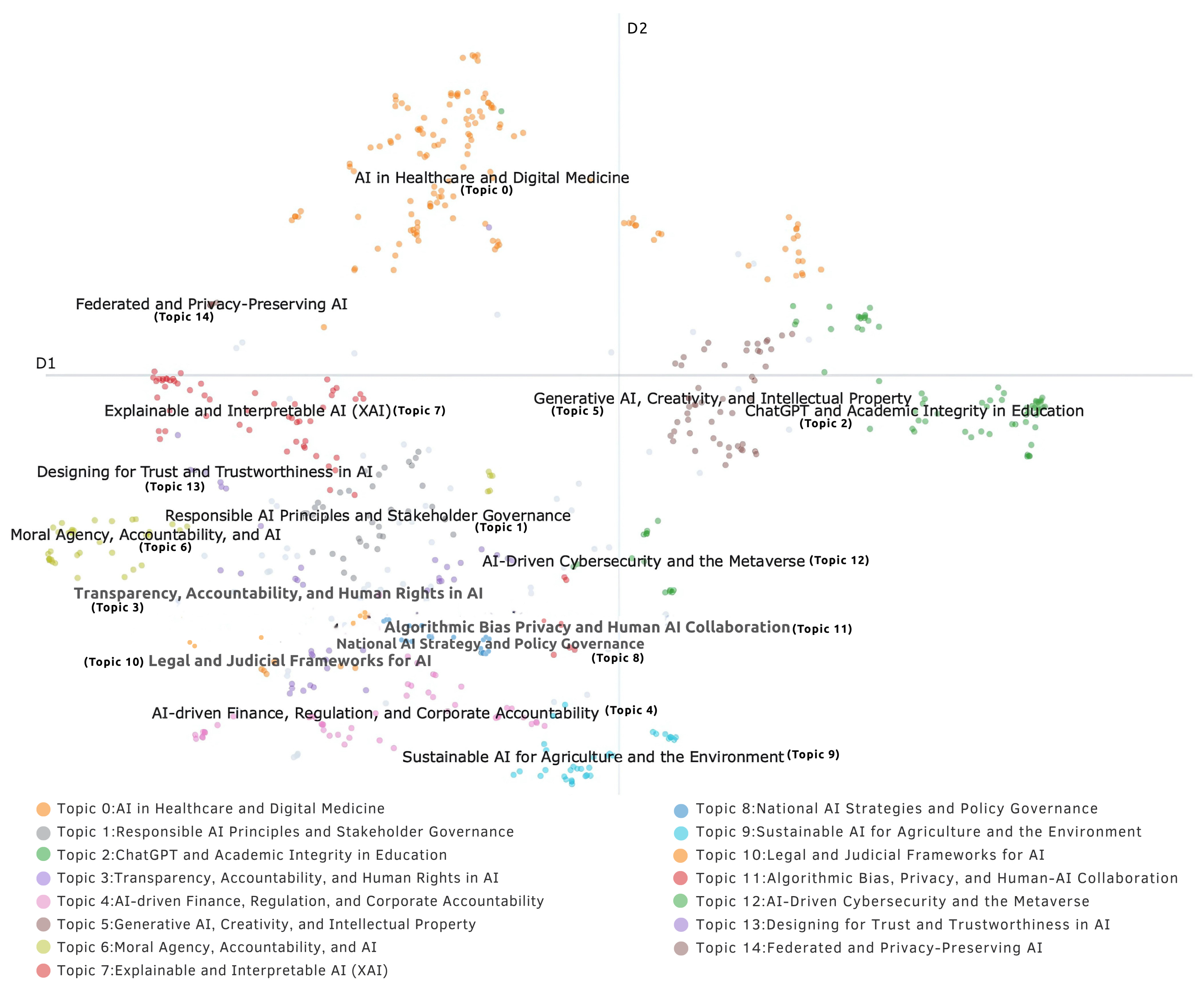
The visualization of topic embeddings in two-dimensional space, as per Figure 2, reveals patterns in the responsible AI research landscape. The 15 identified topics show distinct positioning that illustrates their relationships and boundaries.
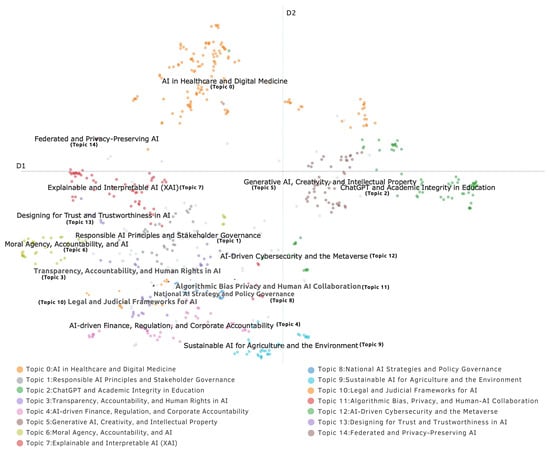
Figure 2.
Visualization of topic embeddings generated by the BERTopic approach.
Domain-specific applications of responsible AI principles appear toward the periphery of the embedding space. Topic 0 (AI in Healthcare and Digital Medicine) occupies a distinct region due to its specialized vocabulary and unique regulatory considerations. Topic 2 (ChatGPT and Academic Integrity in Education) forms a separate cluster with its focus on educational contexts. Topics 5 (Generative AI, Creativity, and Intellectual Property) and 4 (AI-driven Finance, Regulation, and Corporate Accountability) maintain peripheral positions with their specialized terminology and regulatory frameworks. Topic 9 (Sustainable AI for Agriculture and Environment) combines environmental concepts with technical approaches, creating a distinct profile. Topic 14 (Federated and Privacy Preserving AI) forms a defined cluster due to its technical methodological focus. The central region contains topics related to fundamental responsible AI principles in a nuanced arrangement. Topic 7 (Explainable and Interpretable AI) and Topic 13 (Designing for Trust and Trustworthiness in AI) appear in close proximity, suggesting a relationship between explainability and trust in AI systems. Topic 6 (Moral Agency, Accountability, and AI) forms its own region, representing philosophical foundations of machine ethics, while Topic 1 (Responsible AI Principles and Stakeholder Governance), a broad research area, occupies a middle position. Topics 12 (AI-Driven Cybersecurity and the Metaverse), 3 (Transparency, Accountability, and Human Rights), and 11 (Algorithmic Bias, Privacy, and Human–AI Collaboration) form a vertical arrangement suggesting a progression from technical security considerations to broader human rights and fairness issues. Topics 8 (National AI Strategies and Policy Governance) and 10 (Legal and Judicial Frameworks for AI) intersect with Topics 3 (Transparency, Accountability, and Human Rights in AI) and 11 (Algorithmic Bias, Privacy, and Human–AI Collaboration), showing how governance and legal frameworks address issues of transparency, accountability, and algorithmic bias. These 15 topics recognize a distinction between principles and practices, with governance approaches connecting foundational concepts and applications. Final topics and article distributions can be found in Table 2.

Table 2.
Topics from Finding 1—by theme, article count and percentage.
4. Finding 2: Foundations of Responsibility
The concept of “responsibility” is foundational across ethics, law, governance, professional practice, and increasingly, as it relates to our development and use of technology. However, it is not a singular or uniform idea. Rather, responsibility takes on different forms depending on context, each with its own philosophical, legal, or organizational implications. This section presents key types of responsibility that are formally recognized in academic and institutional discourse, and in doing so, develops context for the subsequent sections focusing on the responsible principles and practice of AI.
Moral Responsibility: Moral responsibility refers to the ethical duty of individuals or groups to act according to moral norms, such as fairness, compassion, and justice. It is grounded in the assumption that actors are capable of rational decision-making and are thus accountable for their actions, particularly when those actions affect others [47,48]. Moral responsibility often underpins debates about blame, praise, and ethical obligation, especially in relation to harm or wrongdoing.
Legal Responsibility: Legal responsibility pertains to obligations codified in laws and regulations. It involves liability for one’s actions and the consequences thereof, as determined by judicial systems. Legal responsibility can be civil (e.g., breach of contract) or criminal (e.g., violating statutory laws), and it includes principles such as due process, negligence, and restitution [49]. Unlike moral responsibility, legal responsibility does not necessarily require intent; it may be assigned based on causation or strict liability.
Social Responsibility: Social responsibility is the duty of individuals and organizations to act in ways that benefit society at large. This includes avoiding actions that could harm communities, the environment, or vulnerable populations. The concept has grown in prominence in discussions of environmental ethics, social equity, and sustainability [50]. Social responsibility often overlaps with civic ethics and global justice concerns, emphasising collective well-being.
Professional Responsibility: Professional responsibility refers to the ethical and procedural duties associated with membership in a specific profession. It includes maintaining competence, following industry standards, respecting confidentiality, and acting with integrity. Professional bodies often articulate these responsibilities in codes of conduct or ethics [51]. Breaches can result in disciplinary action, including loss of licensure or reputation.
Organizational Responsibility: Organizational or corporate responsibility reflects the idea that businesses and institutions are accountable not only to shareholders but also to employees, consumers, and society. This includes fulfilling economic goals while also attending to ethical labor practices, environmental impacts, and stakeholder interests [52,53]. Corporate social responsibility frameworks, such as open standards for ethical AI deployment (environmental, social and governance (ESG) criteria), formalize these expectations.
Civic Responsibility: Civic responsibility encompasses the obligations of individuals and groups to contribute to the functioning and well-being of a democratic society. This includes voting, obeying laws, participating in civil discourse, and upholding public institutions [54]. Civic responsibility is rooted in the social contract and reflects the duties required for sustaining collective governance and shared rights.
Economic Responsibility: Economic responsibility refers to the obligation of entities—individuals, businesses, or governments—to support economic stability, efficiency, and fairness. It includes duties like ensuring sustainable growth, fair competition, equitable labor practices, and responsible consumption [55]. In institutional contexts, economic responsibility often intersects with other domains, such as legal and corporate responsibility.
Technological Responsibility: Technological responsibility involves the obligation to ensure that technological development and use are safe, secure, and aligned with societal values. This includes foreseeing potential risks, preventing misuse, and designing systems with care and foresight [56]. It emphasises both the creators’ and users’ responsibility to mitigate harm and ensure that innovation serves the public good. Technological responsibility is the first step towards responsible AI practice, but it works in combination with other categories given its ubiquitous nature and impact.
These categories of responsibility apply to diverse societal contexts and institutional frameworks by defining obligations, assigning accountability, and shaping behavior at various levels. Each type of responsibility carries its own implications depending on the context in which it is applied. These different categories of responsibility are not mutually exclusive and often overlap and interact within various societal contexts and institutional frameworks. The specific ways they function are shaped by cultural norms, legal systems, professional standards, organizational structures, civic values, economic priorities, and the evolving landscape of technology.
5. Finding 3: Responsibility in AI
Responsibility in the context of AI is a complex and multifaceted concept that requires a human-centered approach focused on well-being and alignment with societal values [22]. It involves the practical application of ethical, legal, economic, and cultural concerns to benefit society. To achieve this, responsible AI emphasizes the development and use of AI systems that benefit humans, society, and the environment while minimizing the risk of negative consequences [57].
The implementation of responsible AI depends on several fundamental principles that guide the design, development, and deployment of AI systems. These principles include transparency and explainability, fairness and algorithmic bias prevention, privacy and data protection, robustness and reliability, accountability, and social benefit [58]. Each principle addresses different aspects of responsible AI practice, together forming a comprehensive framework for ethical AI development. The ART principles—accountability, responsibility, and transparency—emerge as essential foundational elements [22,23]. Here, responsibility relates to the role of people in relation to AI systems. This highlights that AI systems are socio-technical, and responsibility fundamentally lies with the people and organizations that create, develop, or use these systems [23]. As noted in [59], “those who develop, create, and integrate AI into society should not be allowed to rescind their responsibility, simply because their creations act differently to how they were designed”. Responsible AI requires the systematic adoption of these principles for AI models to be of practical use. It involves designing ethical, transparent, and accountable solutions [22] that operate responsibly and meet stakeholder expectations and applicable regulations [42]. This necessitates Accountability-by-Design, where AI systems are designed to facilitate end-to-end answerability and auditability, establishing a continuous chain of human responsibility [60].
From an organizational perspective, responsible AI involves the integration of ethical and responsible use of AI into strategic implementation and planning processes [25]. It requires alignment of stakeholders’ expectations and implementation of risk mitigation strategies. Ultimately, responsible AI aims to create systems that align with user expectations and prevalent societal laws, rules, and regulations [61], ensuring that AI technologies remain beneficial while minimizing potential harm.
The terms “Responsible AI”, “Ethical AI” and “Trustworthy AI” are often used interchangeably [62]; however, there are important differences between these terms. Ethical AI aims to align AI strictly in terms of human beings and their behavior, although this optimal and ideal alignment cannot be expected to be practically implemented [63]. Trustworthy AI refers to the dependability and subjectivity of what is perceived to be “trust”, which can be misleading depending on the individuals or groups concerned [63]. Due to these ambiguities of the two prior terms, a new term was coined, “Responsible AI” as a more effective representation of the expectations of “Ethical AI” and “Trustworthy AI” with other broader concepts [63].
Governments, recognizing the growing importance of AI, are positioning themselves as leaders in shaping policies and regulations to govern its ethical and responsible use. This competition for leadership provides an impetus for countries to invest in developing robust frameworks that protect against the negative impacts of AI while promoting its beneficial applications. Similarly, organizations are capitalizing on the current focus on responsible AI practices. The heightened attention serves as an incentive for businesses to adopt ethical AI frameworks, not only to mitigate risks but also to align with societal expectations. Positive feedback from the public and stakeholders regarding responsible AI practices can improve a company’s reputation and contribute to its competitive advantage.
There are several leading national and international groups that have been formed with experts in AI and legal domains to provide guidelines to build AI systems while minimizing the risks from these systems. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Artificial Intelligence Group, United Kingdom AI Council, and the High Level Expert Group (HLEG) on Artificial Intelligence established by the European Commission, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO) in Australia and the UNESCO Ad Hoc Expert Group (AHEG) for the Recommendation on the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence are some of these leading organizations [64]. The increasing interest and efforts in developing responsible AI definitions and policies show the significance of adopting responsible AI strategies in implementing AI systems. However, the involvement of the private sector along with leading companies in defining responsible AI policies and principles raises several concerns, as they can develop and adopt soft policies to minimize the impact of adhering to strict responsible AI policies, which can hinder their revenue streams [64,65].
6. Finding 4: The Need for Responsible AI
The need for responsible AI is driven primarily by the severity of challenges, risks, and harms posed by AI systems [26]. The physical harms of malfunctioning system operations due to excess AI automation, the psychological harms due to decision-making by biased or erroneous AI systems, the lack of human-in-the-loop processes for managing and supervising AI systems, hallucinations and inaccuracies as well as social issues of technological job displacement, AI-driven misinformation, and deepfakes are some of the widely recognized and publicly experienced risks of AI. As the reliance on black box machine learning models increases for making sensitive predictions, stakeholders within the AI community are increasingly advocating for greater transparency to understand the inner workings of these algorithms [26]. The demand for transparency is driven by the need to ensure ethical AI practices and to address concerns related to biases, fairness, and potential discrimination. The reluctance to adopt techniques that lack direct interpretability, tractability, and trustworthiness stems from the recognition of the importance of responsible AI implementation [26]. Stakeholders, including organizations, policymakers, and the public, increasingly emphasize the need for AI systems to be understandable and explainable. Interpretable AI systems are seen as important for public acceptance, building trust, and enabling effective oversight and regulation. Identifying the implicit assumptions of AI algorithms poses a significant challenge [40,66]. Implicit biases and contextual influences can impact the accuracy and reliability of AI systems, making it essential to unravel and comprehend the underlying assumptions to address potential limitations and biases. The opacity of AI results further complicates decision-making processes that rely on deliberative rationality [67]. When AI results are difficult to understand and interpret, it becomes challenging for human decision makers to assess the validity, reliability, and potential biases associated with the outcomes. This opacity can hinder effective decision-making, especially in contexts where human judgment and reasoning are crucial.
The development and training processes of AI systems rely heavily on human inputs, which introduces the potential for inherent biases of programmers to manifest within algorithms [13]. This raises concerns about the replication and perpetuation of biases present in training data, resulting in biased results and decision-making. The presence of biased AI systems poses significant ethical challenges as it has the capacity to reinforce and perpetuate existing societal inequalities and discrimination. In the current context of AI research, privacy issues arising from AI-powered technologies have become a significant concern. One of the prominent risks is the potential compromise of privacy due to sensitive, granular, and in-depth data collection practices [24]. As AI systems collect vast amounts of personal information, there is an increased risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and misuse of personal data, which can lead to privacy violations. Moreover, the use of customer data for marketing purposes poses privacy challenges [42]. AI-powered systems can analyze customer data to generate hyper-personalized targeting strategies, raising questions about the transparency and consent surrounding data usage. The extensive profiling and targeting capabilities of AI algorithms can result in privacy invasion and the potential manipulation of individuals’ preferences and behaviors.
AI errors can cause risks and harms to individuals, businesses, and society as a whole. One of the key factors contributing to AI errors is when an algorithm is tasked with making predictions beyond the scope of its training data [40]. AI models are trained on specific datasets, and their accuracy and reliability are optimized for the tasks for which they were originally designed. When asked to perform tasks or make predictions outside their training data boundaries, the algorithms may lack the necessary context or knowledge to produce accurate results. This can lead to erroneous outcomes and decisions. The consequences of AI errors can be significant, particularly in critical domains such as healthcare, finance, or autonomous systems. In healthcare, for example, if an AI model fails to detect a medical condition or provides incorrect treatment recommendations, it can jeopardise patient safety and well-being. Similarly, in financial systems, AI errors can lead to incorrect risk assessments or faulty predictions, resulting in financial losses for individuals or businesses.
Organizations must also carefully assess the potential benefits and drawbacks associated with the adoption of AI. This evaluation involves weighing factors such as the accuracy, reliability, and fairness of AI systems against the costs of implementation, management, and potential risks. Justifying the investment and management costs to citizens and taxpayers becomes a requirement to ensure transparency and accountability [24]. The misuse and underuse of AI technology can have far-reaching implications. Misuse can lead to negative social impacts, violations of privacy, or exacerbation of existing biases and discrimination. On the other hand, underuse may result in missed opportunities for advancements in various sectors, such as healthcare, transportation or education, where AI has the potential to drive significant positive change.
The use of AI-powered systems has the potential to create significant social issues within society. These issues encompass a range of concerns that arise from the impact of AI on various aspects of our lives. One notable issue is behavior manipulation, where AI-powered systems have the ability to influence and manipulate individuals’ behaviors and choices [68]. This raises concerns regarding the potential exploitation of people’s vulnerabilities and the erosion of personal autonomy. The customization of content, advertisements, and recommendations based on individual preferences can lead to the formation of filter bubbles and echo chambers, limiting exposure to diverse perspectives and posing a threat to democratic values [68].
Another important concern is the economic risks associated with AI. While AI systems can offer automation and efficiency improvements, they also pose a risk of job displacement and unemployment [68]. As AI technology advances, certain tasks and roles traditionally performed by humans may be replaced, potentially leading to adverse social and economic consequences. Furthermore, the use of AI in weapons and military systems raises ethical dilemmas [68]. The development of autonomous weapons raises concerns about accountability, adherence to international laws and norms, and the potential for unintended consequences or escalation. Ensuring the responsible use of AI technologies in military contexts is essential for upholding ethical standards and preserving human lives. AI can be exploited for generating fake materials, spreading misinformation, and facilitating scams [24]. These actions can undermine trust, manipulate individuals, and cause significant societal damage.
Developing socially beneficial AI systems is a further challenge due to the usual market incentives that prioritize high and rapid return on investment, often neglecting the significant needs of socially beneficial developments, especially during their initial and risky phases [68]. Additionally, the traditional organization and granularity of academic research, including in the field of AI, tend to favour focused analytical methods and disciplinary targets [68]. While this approach contributes to in depth knowledge within specific domains, it can limit the exploration of broader societal implications and hinder the development of Responsible AI practices [68]. To address these limitations, there is a need to address heterogeneous tasks and involve non-academic contributors, social actors, and stakeholders in research and development processes [68].
AI systems in healthcare, transportation, network management, surveillance, and defence systems, require special attention [68,69]. The security and privacy of individual users must be prioritized, considering factors such as security in digital interactions, confidentiality, intelligibility, and transparency [68]. Responsible AI practices should also address social risks, including social acceptability, long-term impacts on future generations, social cohesion in terms of employment, resource sharing, inclusion, social recognition, and the integration of human rights, historical, social, cultural, and ethical values [68].
7. Finding 5: Principles of Responsible AI
Responsible AI frameworks and definitions provide guidelines based on a set of core principles that should be included in the responsible practice of AI systems. As discussed in the previous section, these definitions and frameworks also contain significant overlap, leading to diverse directions of practice and policy. This unanticipated challenge is further described as “principle proliferation” [64,65]. Through the systematic review process, this study addresses this challenge by identifying seven primary principles in (1) transparency and explainability, (2) fairness and algorithmic bias, (3) privacy and data protection, (4) robustness and reliability, (5) accountability, (6) human agency and oversight and (7) socially beneficial practice of AI. This study also identified several other secondary principles, the following subsections present each of the primary principles and a collective of the secondary principles.
7.1. Transparency and Explainability
Transparency and explainability represent the importance of the decision making processes and reasoning in AI systems [58,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78]. Explainability and interpretability aims to build trust among users [79] while transparency ensures that decision making processes are understandable and accessible to stakeholders affected by AI outcomes [74]. Explainability focuses on the ability of AI systems to provide clear justifications for their decisions [80,81] and helps stakeholders understand how AI systems operate. They enable the assessment of system reliability and support informed decisions about AI deployment. Explainability also provides insights into the decision making process [31,82]. This includes the reasons for decisions, influencing factors, and available alternatives. Transparency requires information disclosure to ensure individuals know when they interact with AI systems [79,83] and helps users understand how their personal information is used. For example, transparent biometric identification systems should inform users about the purpose and usage of collected biometric data [79]. Transparency and explainability contribute to responsible AI through multiple mechanisms [73,77]. They enable the identification and mitigation of potential biases in AI systems [58,76]. These principles support regulatory compliance and ethical governance by providing clear documentation of AI system behavior [74,75]. They also enhance user autonomy by giving individuals meaningful control over their interactions with AI systems [70,78]. In any system, proper documentation is essential for maintaining transparency [70,71,72,78]. It requires clear content about system design, data sources, intended purposes, and operational requirements [79]. In business contexts, transparent AI systems should disclose their accuracy and robustness against potential risks, enabling organizations to implement appropriate safeguards [79]. Organizations developing AI systems must balance the level of transparency with security considerations [73,81]. This includes protecting sensitive intellectual property while providing sufficient information for stakeholder trust and system accountability. The implementation of these principles requires standardized approaches across the AI development lifecycle [72,74]. This includes clear documentation practices, consistent evaluation metrics, and established procedures for explaining AI decisions to different stakeholder groups [31,80]. The integration of transparency and explainability in AI systems supports responsible innovation while maintaining public trust in AI technologies [75,77].
7.2. Fairness and Algorithmic Bias
Fairness ensures that AI systems do not discriminate against individuals or groups based on personal attributes, such as race, religion, gender, sexual orientation, disability, or ethnic origin [58]. The criticality and impact of unfair outcomes from AI systems vary based on the type of application [79]. For example, biased outcomes in applications such as hiring, facial recognition, and loan applications can cause significant negative social ramifications [79]. AI systems are susceptible to biases present in the training data, which can lead to unfair outcomes [71,80]. Addressing algorithmic bias requires careful examination of training data, algorithmic design, and ongoing monitoring [74]. Using diverse and representative datasets is essential to mitigate bias and ensure that AI models do not discriminate against underrepresented groups [73,80]. The biased and discriminative behavior of AI systems not only undermines trust but also hinders the adoption of AI technologies that have potential societal benefits [79]. To evaluate fairness, quantitative measures such as disparate impact, equalized odds, and demographic parity help assess the distribution of outcomes across different demographic groups [80]. Continuous monitoring of AI systems through feedback loops, regular assessments, and audits is necessary to identify and rectify emerging biases [80]. The principle of fairness aims to prevent discriminatory impacts and promote equity in AI decision-making processes [37,84]. Real-world implications of algorithmic bias are evident across domains. Predictive policing algorithms can reinforce existing biases in law enforcement practices [80]. Credit scoring algorithms may exhibit bias in financial services, while recruitment systems have shown bias against certain demographic groups [81]. These examples demonstrate why responsible AI frameworks emphasize addressing biases and ensuring equitable outcomes. The challenge of defining fairness persists as it remains a subjective concept that changes across social contexts [58]. Transparency in AI decision making processes, including disclosure of data sources and model logic, becomes essential for external scrutiny and accountability [74]. By adhering to fairness principles, AI systems can better serve society by promoting equity and ensuring that AI benefits are distributed justly [71].
7.3. Privacy and Data Protection
Privacy and data protection by design are critical principles, especially when AI systems rely on data. This principle ensures the protection of individuals’ personal information and promotes secure data practices, addressing privacy concerns and mitigating potential data breaches or unauthorized access [83]. Ethical AI guidelines highlight the need for privacy to build trust in AI systems [31,65]. The increasing reliance on AI systems that utilize vast amounts of personal data raises significant ethical concerns [71]. Organizations take extra precautions, including adding roles specific to data privacy, such as data privacy officers, to mitigate privacy risks, which can severely damage a company’s reputation [31]. Not only that, there are role-level accountability contracts in place by some organizations where they define boundaries for responsibility and identify who should be held accountable when an AI system misbehaves [75]. Complying with policies and standards is considered the best approach to reduce privacy risks [31]. Application domains involving highly sensitive data, such as healthcare innovations, must align with legislation, rules, and privacy standards to ensure privacy while benefiting the public [31]. With the growing number of data breaches, governments are actively working on forming policies to regulate data privacy [72]. The European Union (EU) led the policy-making process with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which includes strict measures and hefty fines to protect user privacy [79]. The data protection impact assessment (DPIA) is a mandate for any application that poses a risk to data privacy in many privacy policies, including GDPR [79]. Privacy risks exist across multiple phases of the AI lifecycle [76,85]. Data-hungry deep neural networks require continuous data collection processes to capture massive amounts of training data. For example, [86] discussed the privacy leakages and vulnerabilities in ChatGPT, which was trained on massive amounts of data scraped from the internet. Even though organizations such as OpenAI adopt privacy policies, perfect compliance with these policies remains a significant challenge [86]. Key privacy protection measures include data anonymization and encryption [74], stringent data protection protocols [71], and robust data governance practices [74]. Privacy-preserving machine learning techniques like federated learning enable AI models to be trained across multiple decentralized data sources while maintaining security and privacy guarantees [76]. Organizations must ensure informed consent about data usage [71,74] and implement data minimization practices to collect only necessary information [70]. By embracing privacy by design and implementing comprehensive data protection measures, responsible AI frameworks uphold individuals’ rights and contribute to the establishment of a secure and trustworthy AI ecosystem [71]. Beyond privacy preserving, it allows users to have absolute control over how their data is being used, and they are paid accordingly, achieving data dignity [58]. This approach helps maintain public trust while ensuring compliance with evolving privacy regulations and ethical standards.
7.4. Robustness and Reliability
The robustness and reliability of AI refer to the capability to withstand attacks, erroneous inputs, execution errors and unforeseen behaviors without causing harmful or unintended outcomes. This ensures the safety, security and reliability of AI under malicious or uncertain real-world conditions coming from external inputs. Robustness extends beyond security against external attacks to encompass the overall safety of AI systems [58,71] and can be helpful for maintaining trust and preventing harm when AI is deployed in critical domains. AI systems must perform reliably and accurately, even when facing harsh conditions like adversarial attacks, perturbations, or implementation errors [58,71]. For example, AI in self-driving applications uses extensive training data from different scenarios. However, when training data does not reflect the entire distribution, such as using daytime data for nighttime operations, it can cause severe problems in critical applications [87]. Hence, it is important to verify and guarantee the reliability of AI under different conditions, even for scenarios not present in the training data. Real-world environments are characterized by uncertainty, volatility, and constant change [58]. Corrupted inputs can interrupt the normal behavior of an AI system and make it unavailable for external users. This is particularly important in domains such as healthcare and autonomous vehicles, where failures can endanger human lives [71]. Society is unlikely to accept AI integration in critical sectors unless these systems demonstrate reliable and fault-tolerant performance [88]. It is evident that AI systems can be subjected to attacks and security vulnerabilities during the entire lifecycle. Therefore, ensuring robustness requires proper strategies, including defense mechanisms. Development of AI systems should go through strict quality assurance processes with rigorous testing to guarantee robustness and reliability [79]. This includes implementing security measures to protect information integrity, confidentiality, and continuous functionality for users [58]. Key approaches to achieve robustness include uncertainty quantification to measure, communicate, and utilize uncertainty to improve transparency [58]. Resilience ensuring mechanisms integrate backup measures so that a failure in one part of the system does not lead to significant damage in the performance of the whole system [88], and responsibility distribution increases system resilience by ensuring agents share responsibility for completing a task. This means that no single agent has full responsibility and if one fails, others can correct the problem [88]. Causal learning and formal verification methods help develop AI systems that are stable and robust across environments [58,88]. The energy footprint of training and inference of foundational models is a further concern for low levels of robustness and reliability, where AI models can underperform where energy resources are lacking. In this case, further investment is required in energy-efficient AI and hardware-based AI models [89,90].
7.5. Accountability
Accountability ensures that the people or organizations who developed the AI system hold responsibility for actions and decisions made from it throughout the lifecycle [31]. The lack of accountability can lead to the misuse of AI to go against human values. Explainability, which provides explanations and reasons for the decisions made by AI systems, and transparency are major requirements to establish accountability within the system [31,79]. Without accountability, people who design and develop AI systems will be careless and blame algorithms instead of taking responsibility for the outcomes [31]. For example, people who engage in developing an AI model resulting in bias for a certain group because of selected features should take responsibility without passing the blame to the algorithm [31]. This addresses the “responsibility gap” that emerges as AI systems become more autonomous [71,72,91,92,93]. An accountability flowchart is presented in [93], which maps the conceptual decision points that determine whether an AI responsibility gap exists. It demonstrates different answers to fundamental questions, such as whether responsibility requires control or whether AI can possess moral agency, and how that leads toward either accepting or resolving the responsibility gap.
Governments develop standards and policies to provide pathways to the safe, secure and privacy-preserved development of AI systems. However, accountability ensures that organizations adhere to these standards and policies during the design and development process of the AI system [31,79]. Key approaches include establishing role-level accountability through formal contracts to define responsibility boundaries [75], creating open standards for ethical AI deployment [94], and implementing comprehensive legal frameworks [80]. Accountability guides the development of AI systems to meet human values by enforcing considerate product design, dependable technical architecture, rigorous evaluation of potential impacts, and transparent disclosure of information regarding these aspects [60]. Auditability of an AI system is also considered as a part of the accountability, which validates the compliance of the system according to policy, industry standards or regulations through a reviewing, assessing and auditing process [79,95]. Ref. [95] proposed an end-to-end algorithmic auditing framework to close the accountability gap in the development of AI systems that cover the entire AI lifecycle. This framework audits the engineering processes involved in designing and developing AI systems to ensure that the organization’s AI principles and guidelines, along with ethical expectations, are met during the entire AI lifecycle [95]. Human oversight in critical decision-making processes [70,80] and continuous monitoring for biases and unintended consequences [74,80] further strengthen accountability mechanisms in AI systems.
7.6. Human Agency and Oversight
Human agency and oversight focus on the importance of maintaining human autonomy and control over AI systems throughout their lifecycle [83]. This principle ensures that AI systems augment human capabilities rather than replace them entirely [71,75,76], while protecting human decision-making power and agency in AI-driven environments. Different levels of human oversight can be implemented to maintain control over AI systems [70]. Human in the Loop (HITL) requires direct human intervention in every decision cycle of the AI system. Human on the Loop (HOTL) enables human intervention during AI system design and monitoring phases. Human in Command (HIC) provides oversight of the AI system’s activity and decision making about when and how to use the AI system [70]. These mechanisms ensure that humans maintain meaningful control over their digital experiences and make informed choices [71]. Human oversight becomes particularly decisive in scenarios where AI decisions have significant societal impact, such as healthcare, criminal justice, and autonomous systems [80]. In these contexts, human judgment is essential for addressing complex ethical considerations and contextual understanding that AI systems may lack [80]. The integration of human oversight helps prevent unchecked automation and ensures alignment with ethical and societal norms. The implementation of this principle faces several challenges. AI technologies can potentially influence human autonomy through recommendation systems and personalized marketing [71]. Therefore, striking a balance between automation and human agency becomes significant in the design and deployment of AI systems [71]. Organizations must establish clear protocols for human intervention, especially when AI systems encounter ambiguous situations or scenarios outside their trained domains [80]. To protect human agency effectively, policymakers and technologists must consider the ethical implications of AI-driven persuasion and implement appropriate safeguards [71]. This includes developing skills in AI oversight, promoting accountability, and ensuring transparency in human AI interactions [77]. By prioritizing human agency and oversight, responsible AI frameworks ensure that AI technologies remain under meaningful human control while serving human values and societal goals [83].
7.7. Socially Beneficial
The socially beneficial principle highlights the requirement of AI systems to have advantages for society, which should significantly outweigh the anticipated risks and disadvantages [96]. This means that AI should not only avoid causing harm or negative consequences but should positively contribute to the well-being of individuals and communities in society [71,74].
Cheng et al. [58] present the social responsibility of AI through a hierarchical pyramid with four layers of responsibilities. At the foundation lies functional responsibilities, where AI must perform in a manner consistent with operating efficiency and key performance indicators. The second layer consists of legal responsibilities, requiring AI to operate within regulatory frameworks. Ethical responsibilities form the third layer, obligating AI to do what is right, fair, and just while preventing harm. At the top are philanthropic responsibilities, where AI should act as a good citizen by addressing broader societal challenges such as climate change and public health. This framework helps reconcile different obligations while emphasizing that AI should fulfill all components in the pyramid simultaneously.
AI systems should be developed and deployed to address critical societal challenges such as poverty, hunger, inequality, climate change, and public health [58]. The equitable distribution of AI benefits across society becomes significant [71], ensuring that technological advancements do not exacerbate existing social disparities. This includes proactive measures to mitigate negative consequences, such as economic disparities and job displacement [74,80]. The implementation of socially beneficial AI requires various strategies. Organizations must develop and implement ethical AI frameworks that prioritize fairness, transparency, accountability, and human autonomy [71,74,80]. Collaboration among technologists, policymakers, ethicists, and the public helps incorporate diverse perspectives and ensure AI aligns with societal values [74,80]. Investment in reskilling and upskilling initiatives becomes necessary to support individuals in the AI-driven economy [71,80]. AI applications can help discover and correct biases, minimize discrimination, and enhance outcomes for underrepresented people [71]. Data-driven insights from AI can assist governments and institutions in creating evidence-based policies that promote inclusivity and fairness [71]. By analyzing multiple perspectives and prioritizing representation in decision-making processes, AI can promote fairer policies and a more inclusive society [71]. The socially beneficial principle plays an important role in promoting AI applications that provide fair and positive outcomes for diverse groups within society, ensuring that technological advancements in AI contribute to social development and address societal challenges responsibly. This aspect of responsible AI is vital to align AI developments with human values, inclusivity, and the betterment of society as a whole while maintaining public trust and acceptance of AI technologies [74].
7.8. Other Principles
In addition to the core principles discussed above, responsible AI encompasses several other important principles. Ethical AI ensures AI systems operate within established moral frameworks and contribute to the betterment of society. AI safety focuses on deployment methods that do not harm humanity [58], incorporating testing and validation procedures to prevent dangerous outcomes. AI literacy and education emphasize that individuals interacting with AI systems should have a basic understanding of the technology, its capabilities, limitations, and risks [74,97]. For instance, in healthcare settings, structured education programs help professionals understand the probabilistic nature of AI outputs and their limitations [98]. Healthcare providers need to understand both the capabilities and constraints of AI systems to make informed decisions about their integration into clinical workflows. The AI literacy principle extends beyond technical knowledge to include critical thinking skills, enabling users to identify biases or errors in AI outputs, make decisions about when and how to use AI systems, understand the limitations of AI predictions, evaluate the ethical implications of AI applications, and maintain skepticism and verification. This understanding helps ensure that AI systems are used effectively and safely across different domains [80]. Beneficence and non-maleficence ensure that AI aims to do good [67] and avoids inflicting harm [67,73]. These principles guide the development of AI systems that contribute to human welfare while implementing safeguards against negative impacts. Justice [67] and inclusiveness [58,67] promote fair and equitable AI development and deployment, ensuring that AI benefits are distributed across society and that diverse perspectives are considered in AI development. Data governance [72] and compliance with laws and regulations [58,61,72] ensure responsible data management and legal adherence. These principles involve establishing protocols for data collection, storage, and usage while maintaining compliance with evolving regulatory frameworks. Societal and environmental well-being principles [72,85] guide AI’s contribution to society and the environment, considering both immediate and long-term impacts of AI deployment. Human dignity [78] ensures that AI development respects human rights and values. Principles of solidarity and sustainability [78] focus on promoting collective well-being and ensuring AI contributes to long-term societal goals. Governance [67] principles guide the development of global governance structures. These include establishing mechanisms for oversight, verification, and improvement of AI systems. Awareness and mitigation of negative impacts [67] focus on ensuring data security and reducing discrimination, requiring monitoring and adjustment of AI systems.
8. Finding 6: Responsible AI in Practice
This section translates the principles of responsible AI into two critical domains that are fast adopters of AI, healthcare and education. The scale of adoption in healthcare can range from personal wearable devices to hospital patient management systems, while in education, the AI system typically takes the form of teaching or learning assistants.
8.1. Responsible AI in Healthcare
The integration of artificial intelligence in healthcare necessitates a careful balance between technological advancement and responsible implementation. Healthcare AI applications span diagnostic support, personalized treatment planning, clinical decision support systems, and virtual healthcare assistance [99]. AI applications in healthcare include clinical documentation improvement [100], population health management [99], and mental health support [99]. These applications demonstrate the potential for AI to enhance healthcare delivery while highlighting the need for responsible implementation. However, the critical nature of healthcare activities and the sensitivity of patient data demand rigorous adherence to responsible AI principles [41]. Healthcare organizations must establish robust frameworks for data privacy and security, ensuring compliance with regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR [99]. The interpretability and explainability of AI systems are essential, as healthcare professionals need to understand and validate AI-generated recommendations [41]. This transparency enables healthcare providers to maintain appropriate oversight and integrate AI-driven insights with clinical judgment [100]. Fairness and equality in healthcare AI systems need extra attention. AI algorithms must be designed and validated to avoid discriminatory effects on minority ethnic communities [41]. This includes careful consideration of training data representation and regular monitoring of system outputs for potential biases. Healthcare organizations implementing AI systems must establish clear accountability frameworks, defining responsibilities for AI development companies, healthcare professionals, and administrative staff [41]. The implementation of AI in clinical settings requires structured education programs for healthcare professionals. These programs should address the probabilistic nature of AI outputs and their limitations [98]. Healthcare providers need to understand both the capabilities and constraints of AI systems to make informed decisions about their integration into clinical workflows [98]. Security considerations extend beyond data protection to encompass the entire AI system lifecycle. Healthcare organizations must protect against potential misuse of development and validation data, software vulnerabilities, and unauthorized access [98]. This comprehensive security approach helps maintain the integrity of AI-driven healthcare services while protecting patient privacy. The successful integration of AI in healthcare depends on maintaining human oversight throughout the implementation process. Healthcare professionals must retain the ability to validate and override AI-generated recommendations when clinical judgment indicates alternative approaches [100]. This human-in-the-loop approach ensures that AI systems augment rather than replace clinical expertise while maintaining patient safety and care quality [98].
8.2. Responsible AI in Education
The integration of artificial intelligence in education requires a balanced approach between technological innovation and responsible implementation. Educational AI applications encompass personalized learning, administrative efficiency, and academic support systems [101,102]. Recent developments have shown a significant shift towards generative AI technologies like ChatGPT, evolving the landscape of educational technology [103,104,105,106]. These applications include adaptive learning systems that customize educational content [101], intelligent tutoring systems providing automated feedback [107,108], and learning analytics for identifying at-risk students [107]. Administrative functions extend to chatbot-driven process automation [101] and enhanced data security management [104].
The sensitive nature of student data and educational activities requires strict adherence to responsible AI principles. Educational institutions must establish comprehensive frameworks for data privacy and security [101,103]. Similar to the healthcare sector, the transparency and explainability of AI systems are required, as educators need to understand and validate AI-generated recommendations and assessments. This transparency enables educational providers to maintain appropriate oversight and integrate AI-driven insights with pedagogical judgment [101,103]. Fairness and equality in educational AI systems require particular attention. AI algorithms must be designed and validated to avoid discriminatory outcomes, especially for disadvantaged student groups. This includes careful consideration of training data representation and regular monitoring of system outputs for potential biases. Educational institutions implementing AI systems must establish clear accountability frameworks [103,107], defining responsibilities for AI developers, educators, and administrative staff. The emergence of generative AI tools has introduced new complexities in academic integrity [103]. Educational institutions must develop robust strategies to prevent misuse while harnessing these tools’ educational potential. This includes implementing new assessment approaches that emphasize critical thinking and original analysis over content reproduction. Technical infrastructure requirements extend to expertise development and sustainable funding mechanisms [101], while security considerations must encompass the entire AI system lifecycle. The successful integration of AI in education depends on maintaining human oversight throughout the implementation process. Educators must retain the ability to validate and override AI-generated recommendations when pedagogical judgment indicates alternative approaches. This human-centric approach ensures that AI systems augment rather than replace educational expertise while maintaining academic quality and student development [102]. The focus on ethical principles, student rights, and human AI collaboration continues to shape the responsible implementation of AI in educational practices [101,109].
9. Discussion
This article has followed a rigorous systematic review methodology in investigating the current state of responsible AI principles and practices. The findings of this study start with the current state of responsible AI principles and practice, followed by the foundations of responsibility and the definitions of responsibility in AI. The need for responsible AI is explicated in the lead-up to the principles of responsible AI, concluding with the translation of these principles into the practice of responsible AI specifically for the two sectors of healthcare and education.
Despite a rigorous systematic review methodology, the following limitations of this study must be noted. This review adopts a descriptive synthesis rather than a quantitative meta-analysis, which omits the application of formal study-level risk-of-bias tools. To reduce methodological heterogeneity, the study restricted inclusion to peer-reviewed journal and conference articles, reasoning that the editorial process offers a substantial quality screen. This filter does not guarantee internal validity and may inadvertently privilege research from well-resourced institutions. The search strategy omitted gray literature and non-English publications. While these exclusions simplified screening and ensured linguistic consistency for the topic modeling pipeline, they could introduce publication and language bias. From the articles reviewed, more than 75% of the 535 included studies were published after 2020 in venues located predominantly in high-income countries. Representation from low and middle-income regions was limited, which constrains the generalizability of emergent themes to global practice. In addition, the LLM classifier that assisted title-and-abstract screening could have produced false negatives despite subsequent manual checks of borderline cases. All database queries were executed in March 2025; literature published after this date was not captured.
Future work on the topic of responsible AI is anticipated to be complex, given multiple expert predictions now placing Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) within 5–10 years rather than decades ahead as AI systems surpass human performance on key benchmarks [110,111]. This demands immediate advancements in governance and safety mechanisms for AI systems operating in human-centric environments [112]. The emergence of human-equivalent intelligence introduces novel considerations, including potential AI consciousness and moral status [113], with one of the notable issues being the potential for moral hazards as AGI systems could act autonomously in ways that could contravene human interests [114]. AI robotics and physical AI systems are projected to produce eight million working humanoid robots by 2040 [115], which further emphasizes the urgent need for comprehensive safety regulations and liability frameworks that can effectively govern human–robot interactions. Despite advances in predictive and generative AI, robotic AI systems face unique challenges in dynamic environments, sensory processing, and mechanical movements that require novel computational approaches to ensure safe and efficient operation [116]. These complexities underscore the necessity for innovative computational methods to ensure that robotic AI operates safely and efficiently within human spaces.
10. Conclusions
Across all industry sectors, organizations are rapidly exploring how AI can deliver applied system innovations that drive productivity and growth objectives. The adoption of responsible AI principles and practices is an equally important organizational priority to that of AI-led innovations. It is mandated in the design, development, deployment and adoption of AI systems and models to minimise the risks posed to people, society, and the environment. This article follows a rigorous systematic review methodology in investigating the current state of responsible AI principles and practice, the foundational notions of responsibility, the need for responsible AI, definitions, principles and the translation of these principles into the responsible practice of AI.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/asi8040097/s1, Supplementary Document S1: PRISMA 2020 checklist for systematic reviews, Complete search methodology, LLM prompts, BERTopic analysis, and bibliography of all 553 research papers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M., and D.D.S.; data curation, N.E.-H., S.N., and H.M.; formal analysis, L.G.; investigation, L.G., N.E.-H., S.N., H.M., Z.I., M.M., and D.D.S.; methodology, L.G., S.N., H.M., Z.I., and D.D.S.; resources, Z.I.; software, N.E.-H., and S.N.; supervision, M.M., and D.D.S.; validation, H.M., Z.I., and M.M.; visualization, L.G., and N.E.-H.; writing—original draft, L.G., N.E.-H., H.M., Z.I., M.M., and D.D.S. and S.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Review data available by request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kitano, H. Artificial intelligence to win the nobel prize and beyond: Creating the engine for scientific discovery. AI Mag. 2016, 37, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burki, T. Nobel Prizes honour AI pioneers and pioneering AI. Lancet Digit. Health 2025, 7, e11–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottier, B.; Rahman, R.; Fattorini, L.; Maslej, N.; Besiroglu, T.; Owen, D. The rising costs of training frontier AI models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.21015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, M.; Hazan, E.; Roberts, R.; Singla, A.; Smaje, K. The Economic Potential of Generative AI: The Next Productivity Frontier. McKinsey & Company. 2023. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/the-economic-potential-of-generative-ai-the-next-productivity-frontier (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Cuéllar, M.F.; Dean, J.; Doshi-Velez, F.; Hennessy, J.; Konwinski, A.; Koyejo, S.; Moiloa, P.; Pierson, E.; Patterson, D. Shaping AI’s Impact on Billions of Lives. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.02730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acemoglu, D. The simple macroeconomics of AI. Econ. Policy 2025, 40, 13–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaee, P.; Mirzadeh, I.; Alizadeh, K.; Horton, M.; Bengio, S.; Farajtabar, M. The illusion of thinking: Understanding the strengths and limitations of reasoning models via the lens of problem complexity. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.06941. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Dai, Y.; Yu, P.S.; Sun, L. A comprehensive survey of ai-generated content (aigc): A history of generative ai from gan to chatgpt. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.04226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, P.; Saeri, A.K.; Grundy, E.A.; Graham, J.; Noetel, M.; Uuk, R.; Dao, J.; Pour, S.; Casper, S.; Thompson, N. The ai risk repository: A comprehensive meta-review, database, and taxonomy of risks from artificial intelligence. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.12622. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G.; Yao, A.; Song, D.; Abbeel, P.; Darrell, T.; Harari, Y.N.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Xue, L.; Shalev-Shwartz, S.; et al. Managing extreme AI risks amid rapid progress. Science 2024, 384, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrycks, D.; Mazeika, M.; Woodside, T. An overview of catastrophic AI risks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.12001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenthapadi, K.; Lakkaraju, H.; Rajani, N. Generative ai meets responsible ai: Practical challenges and opportunities. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Long Beach, CA, USA, 6–10 August 2023; pp. 5805–5806. [Google Scholar]
- Mikalef, P.; Conboy, K.; Lundström, J.E.; Popoviˇc, A. Thinking responsibly about responsible AI and ‘the dark side’ of AI. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2022, 31, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, S. Preventing repeated real world AI failures by cataloging incidents: The AI incident database. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual Event, 2–9 May 2021; Volume 35, pp. 15458–15463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welcome to the Artificial Intelligence Incident Database— Incidentdatabase.ai. Available online: https://incidentdatabase.ai (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- OECD AI Policy Observatory Portal—oecd.ai. Available online: https://oecd.ai/en/ai-principles (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- Smuha, N.A. Regulation 2024/1689 of the Eur. Parl. & Council of June 13, 2024 (Eu Artificial Intelligence Act). Int. Leg. Mater. 2025, 1–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Continental Artificial Intelligence Strategy | African Union — au.int. Available online: https://au.int/en/documents/20240809/continental-artificial-intelligence-strategy (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- Roberts, H.; Hine, E.; Taddeo, M.; Floridi, L. Global AI governance: Barriers and pathways forward. Int. Aff. 2024, 100, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidan, E.; Ibrahim, I.A. AI governance in a complex and rapidly changing regulatory landscape: A global perspective. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pojman, L.; Fieser, J. Cengage Advantage Books: Ethics: Discovering Right and Wrong; Nelson Education: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dignum, V. Responsible Artificial Intelligence: How to Develop and Use AI in a Responsible Way; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dignum, V. The role and challenges of education for responsible AI. Lond. Rev. Educ. 2021, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Corchado, J.M.; Mehmood, R.; Li, R.Y.M.; Mossberger, K.; Desouza, K. Responsible Urban Innovation with Local Government Artificial Intelligence (AI): A Conceptual Framework and Research Agenda. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2021, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Anand, A. Responsible Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Value Formation and Market Performance in Healthcare: The Mediating Role of Patient’s Cognitive Engagement. Inf. Syst. Front. 2021, 25, 2197–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askell, A.; Brundage, M.; Hadfield, G. The role of cooperation in responsible AI development. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.04534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, D.; Thomas, J.; Oliver, S. An introduction to systematic reviews (2nd Edition). Psychol. Teach. Rev. 2017, 23, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranfield, D.; Denyer, D.; Smart, P. Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br. J. Manag. 2003, 14, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PRISMA Statement—Prisma-Statement.org. Available online: www.prisma-statement.org (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Anagnostou, M.; Karvounidou, O.; Katritzidaki, C.; Kechagia, C.; Melidou, K.; Mpeza, E.; Konstantinidis, I.; Kapantai, E.; Berberidis, C.; Magnisalis, I.; et al. Characteristics and Challenges in the Industries towards Responsible AI: A Systematic Literature Review. Ethics Inf. Technol. 2022, 24, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, M.; Kallina, E.; Bohné, T.; Mougenot, C.; Calvo, R.A.; Cave, S. Challenges of responsible AI in practice: Scoping review and recommended actions. AI Soc. 2025, 40, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radanliev, P.; Santos, O.; Brandon-Jones, A.; Joinson, A. Ethics and responsible AI deployment. Front. Artif. Intell. 2024, 7, 1377011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siala, H.; Wang, Y. SHIFTing artificial intelligence to be responsible in healthcare: A systematic review. Soc. Sci. Med. 2022, 296, 114782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukkien, D.R.M.; Nap, H.H.; Buimer, H.P.; Peine, A.; Boon, W.P.C.; Ket, J.C.F.; Minkman, M.M.N.; Moors, E.H.M. Toward Responsible Artificial Intelligence in Long-Term Care: A Scoping Review on Practical Approaches. Gerontologist 2021, 63, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakova, B.; Yang, J.; Cramer, H.; Chowdhury, R. Where Responsible AI Meets Reality: Practitioner Perspectives on Enablers for Shifting Organizational Practices. Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2021, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, D.; Vold, K.; Robinson, D.; Calvo, R.A. Responsible AI—Two Frameworks for Ethical Design Practice. IEEE Trans. Technol. Soc. 2020, 1, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R. Principles and business processes for responsible AI. Comput. Law Secur. Rev. 2019, 35, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, D. Tackling COVID-19 Through Responsible AI Innovation: Five Steps in the Right Direction. Harv. Data Sci. Rev. 2020. Available online: https://hdsr.mitpress.mit.edu/pub/as1p81um (accessed on 18 April 2025). [CrossRef]
- Wearn, O.R.; Freeman, R.; Jacoby, D.M.P. Responsible AI for conservation. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019, 1, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trocin, C.; Mikalef, P.; Papamitsiou, Z.; Conboy, K. Responsible AI for Digital Health: A Synthesis and a Research Agenda. Inf. Syst. Front. 2021, 25, 2139–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiong, M.; Olya, H. Toward an Understanding of Responsible Artificial Intelligence Practices. In Proceedings of the Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, 7–10 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fosso Wamba, S.; Queiroz, M.M. Responsible Artificial Intelligence as a Secret Ingredient for Digital Health: Bibliometric Analysis, Insights, and Research Directions. Inf. Syst. Front. 2023, 25, 2123–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grootendorst, M. BERTopic: Neural topic modeling with a class-based TF-IDF procedure. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.05794. [Google Scholar]
- Becht, E.; McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Dutertre, C.A.; Kwok, I.W.H.; Ng, L.G.; Ginhoux, F.; Newell, E.W. Dimensionality reduction for visualizing single-cell data using UMAP. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Astels, S. hdbscan: Hierarchical density based clustering. J. Open Source Softw. 2017, 2, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punishment and Responsibility: Essays in the Philosophy of Law; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1968.
- Strawson, P.F. Freedom and Resentment and Other Essays; Routledge: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.S. Causation and Responsibility: An Essay in Law, Morals, and Metaphysics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Van Norren, D.E. The ethics of artificial intelligence, UNESCO and the African Ubuntu perspective. J. Inf. Commun. Ethics Soc. 2023, 21, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, S. Ethics and Values in Social Work; Bloomsbury Publishing: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, A.B. The pyramid of corporate social responsibility: Toward the moral management of organizational stakeholders. Bus. Horizons 1991, 34, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmans, A. Grow the Pie: How Great Companies Deliver Both Purpose and Profit–Updated and Revised; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Galston, W.A. Liberal Purposes: Goods, Virtues, and Diversity in the Liberal State; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, M.S.; Carroll, A.B. Corporate social responsibility: A three-domain approach. Bus. Ethics Q. 2003, 13, 503–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, H. The Imperative of Responsibility: In Search of an Ethics for the Technological Age; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, B.; Lu, Q.; Perera, H.; Zhu, L.; Xing, Z.; Liu, Y.; Whittle, J. Towards Concrete and Connected AI Risk Assessment (C2AIRA): A Systematic Mapping Study. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/ACM 2nd International Conference on AI Engineering–Software Engineering for AI (CAIN), Los Alamitos, CA, USA, 15–16 May 2023; pp. 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Varshney, K.R.; Liu, H. Socially Responsible AI Algorithms: Issues, Purposes, and Challenges. J. Artif. Int. Res. 2021, 71, 1137–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M. In AI We Trust: Ethics, Artificial Intelligence, and Reliability. Sci. Eng. Ethics 2020, 26, 2749–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, D. Understanding Artificial Intelligence Ethics and Safety: A Guide for the Responsible Design and Implementation of AI Systems in the Public Sector. SSRN Electron. J. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.; Sharp, H. Responsible AI Systems: Who are the Stakeholders? In Proceedings of the 2022 AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society, Oxford, UK, 1–3 August 2022; AIES ’22. pp. 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumen, B.; Göllner, S.; Tropmann-Frick, M. Aspects and Views on Responsible Artificial Intelligence. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning, Optimization, and Data Science; Nicosia, G., Ojha, V., La Malfa, E., La Malfa, G., Pardalos, P., Di Fatta, G., Giuffrida, G., Umeton, R., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 384–398. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, T.W. What Is the Difference Between AI Ethics, Responsible AI, and Trustworthy AI? We ask our Responsible AI Leads - Institute for Experiential AI — ai.northeastern.edu. 2023. Available online: https://ai.northeastern.edu/what-is-the-difference-between-ai-ethics-responsible-ai-and-trustworthy-ai-we-ask-our-responsible-ai-leads/ (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Barletta, V.S.; Caivano, D.; Gigante, D.; Ragone, A. A Rapid Review of Responsible AI Frameworks: How to Guide the Development of Ethical AI. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering, Oulu, Finland, 14–16 June 2023; EASE ’23. pp. 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobin, A.; Ienca, M.; Vayena, E. The global landscape of AI ethics guidelines. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019, 1, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavi, I.; Chamishka, S.; Nawaratne, R.; Nanayakkara, V.; Alahakoon, D.; De Silva, D. A deep learning approach for work related stress detection from audio streams in cyber physical environments. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA), IEEE. Vienna, Austria, 8–11 September 2020; Volume 1, pp. 929–936. [Google Scholar]
- Buhmann, A.; Fieseler, C. Towards a deliberative framework for responsible innovation in artificial intelligence. Technol. Soc. 2021, 64, 101475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghallab, M. Responsible AI: Requirements and challenges. AI Perspect. 2019, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandaragoda, T.; Ranasinghe, W.; Adikari, A.; de Silva, D.; Lawrentschuk, N.; Alahakoon, D.; Persad, R.; Bolton, D. The Patient-Reported Information Multidimensional Exploration (PRIME) framework for investigating emotions and other factors of prostate cancer patients with low intermediate risk based on online cancer support group discussions. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 1737–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buruk, B.; Ekmekci, P.E.; Arda, B. A Critical Perspective on Guidelines for Responsible and Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence. Med. Health Care Philos. 2020, 23, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawas, S. AI: The Future of Humanity. Discov. Artif. Intell. 2024, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merhi, M.I. An Assessment of the Barriers Impacting Responsible Artificial Intelligence. Inf. Syst. Front. 2023, 25, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachat-Rosset, G.; Klarsfeld, A. Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion in Artificial Intelligence: An Evaluation of Guidelines. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 2176618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osasona, F.; Amoo, O.O.; Atadoga, A.; Abrahams, T.O.; Farayola, O.A.; Ayinla, B.S. Reviewing the Ethical Implications of AI in Decision-Making Processes. Int. J. Manag. Entrep. Res. 2024, 6, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zhu, L.; Xu, X.; Whittle, J.; Zowghi, D.; Jacquet, A. Responsible AI Pattern Catalogue: A Collection of Best Practices for AI Governance and Engineering. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 56, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q. Toward Responsible AI: An Overview of Federated Learning for User-centered Privacy-preserving Computing. ACM Trans. Interact. Intell. Syst. 2021, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, H. What’s next for responsible artificial intelligence: A way forward through responsible innovation. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibáñez, J.C.; Olmeda, M.V. Operationalising AI Ethics: How Are Companies Bridging the Gap Between Practice and Principles? An Exploratory Study. AI & SOCIETY 2022, 37, 1663–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Qi, P.; Liu, B.; Di, S.; Liu, J.; Pei, J.; Yi, J.; Zhou, B. Trustworthy AI: From Principles to Practices. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinrinola, O.; Okoye, C.C.; Ofodile, O.C.; Ugochukwu, C.E. Navigating and Reviewing Ethical Dilemmas in AI Development: Strategies for Transparency, Fairness, and Accountability. GSC Adv. Res. Rev. 2024, 18, 050–058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Biswas, K.; Michael, K.; Bandara, R.; Sajib, S. Addressing Algorithmic Bias in AI-Driven Customer Management. J. Glob. Inf. Manag. 2021, 29, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, M.; Toreini, E.; Carmichael, P.; Coopamootoo, K.; Elliott, K.; van Moorsel, A. Establishing a social license for Financial Technology: Reflections on the role of the private sector in pursuing ethical data practices. Big Data Society 2020, 7, 2053951720908892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barredo Arrieta, A.; Díaz-Rodríguez, N.; Del Ser, J.; Bennetot, A.; Tabik, S.; Barbado, A.; Garcia, S.; Gil-Lopez, S.; Molina, D.; Benjamins, R.; et al. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. Inf. Fusion 2020, 58, 82–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdowski, P.; Rathgeb, C.; Dantcheva, A.; Damer, N.; Busch, C. Demographic bias in biometrics: A survey on an emerging challenge. IEEE Trans. Technol. Soc. 2020, 1, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsha, P.S. How can we manage biases in artificial intelligence systems—A systematic literature review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2023, 3, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Duan, R.; Ni, J. Unveiling Security, Privacy, and Ethical Concerns of ChatGPT. J. Inf. Intell. 2023, 2, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Khurshid, S. DeepRoad: GAN-Based Metamorphic Testing and Input Validation Framework for Autonomous Driving Systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 33rd IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE), Montpellier, France, 3–7 September 2018; pp. 132–142. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdanpanah, V.; Gerding, E.; Stein, S.; Dastani, M.; Jonker, C.M.; Norman, T.J.; Ramchurn, S.D. Reasoning About Responsibility in Autonomous Systems: Challenges and Opportunities. AI & Society 2022, 38, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, E.; Kahawala, S.; Haputhanthri, D.; Kempitiya, T.; De Silva, D.; Alahakoon, D.; Kleyko, D. Hyperseed: Unsupervised learning with vector symbolic architectures. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 35, 6583–6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleyko, D.; Osipov, E.; De Silva, D.; Wiklund, U.; Alahakoon, D. Integer self-organizing maps for digital hardware. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), IEEE. Budapest, Hungary, 14–19 July 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Demirtas, H. AI Responsibility Gap: Not New, Inevitable, Unproblematic. Ethics Inf. Technol. 2024, 27, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, M.; Vică, C.; Uszkai, R.; Voinea, C. Blame It on the AI? On the Moral Responsibility of Artificial Moral Advisors. Philos. Technol. 2022, 35, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelreich, J.; Köhler, S. Responsible AI Through Conceptual Engineering. Philos. Technol. 2022, 35, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, M.; Voinea, C.; Uszkai, R.; Vică, C. Understanding Responsibility in Responsible AI: Dianoetic Virtues and the Hard Problem of Context. Ethics Inf. Technol. 2021, 23, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, I.D.; Smart, A.; White, R.N.; Mitchell, M.; Gebru, T.; Hutchinson, B.; Smith-Loud, J.; Theron, D.; Barnes, P. Closing the AI Accountability Gap: Defining an End-to-End Framework for Internal Algorithmic Auditing. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, Barcelona, Spain, 27–30 January 2020; FAT* ’20. pp. 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, K. A Shared Agenda for Responsible AI Progress—blog.google. 2023. Available online: https://blog.google/technology/ai/a-shared-agenda-for-responsible-ai-progress (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Brauner, P.; Hick, A.; Philipsen, R.; Ziefle, M. What Does the Public Think About Artificial Intelligence?—A Criticality Map to Understand Bias in the Public Perception of AI. Front. Comput. Sci. 2023, 5, 1113903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Hond, A.A.H.; Leeuwenberg, A.M.; Hooft, L.; Kant, I.M.J.; Nijman, S.W.J.; van Os, H.J.A.; Aardoom, J.J.; Debray, T.P.A.; Schuit, E.; van Smeden, M.; et al. Guidelines and quality criteria for artificial intelligence-based prediction models in healthcare: A scoping review. NPJ Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alowais, S.A.; Alghamdi, S.S.; Alsuhebany, N.; Alqahtani, T.; Alshaya, A.I.; Almohareb, S.N.; Aldairem, A.; Alrashed, M.; Bin Saleh, K.; Badreldin, H.A.; et al. Revolutionizing healthcare: The role of artificial intelligence in clinical practice. BMC Med. Educ. 2023, 23, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, A.; Talukdar, W. Intelligent Clinical Documentation: Harnessing Generative AI for Patient-Centric Clinical Note Generation. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. Technol. 2024, 9, 994–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarisayi, K.S. Strategic leadership for responsible artificial intelligence adoption in higher education. CTE Workshop Proc. 2024, 11, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksuti, E.; Erbas, I. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Education. Int. J. Innov. Res. Multidiscip. Educ. 2024, 2, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- García-López, I.M.; González González, C.S.; Ramírez-Montoya, M.S.; Molina-Espinosa, J.M. Challenges of implementing ChatGPT on education: Systematic literature review. Int. J. Educ. Res. Open 2025, 8, 100401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, J.; Mohamed Ismail, M.F.b.; Popenici, S. Higher Education’s Generative Artificial Intelligence Paradox: The Meaning of Chatbot Mania. J. Univ. Teach. Learn. Pract. 2024, 21, 14–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, T.; Nair, S.; Kalendra, D.; Robin, M.; De Oliveira Santini, F.; Junior Ladeira, W.; Sun, M.; Day, I.; Rather, R.A.; Heathcote, L. The Role of ChatGPT in Higher Education: Benefits, Challenges, and Future Research Directions. J. Appl. Learn. Teach. 2023, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiguzel, T.; Kaya, H.; Cansu, F. Revolutionizing education with AI: Exploring the transformative potential of ChatGPT. Contemp. Educ. Technol. 2023, 15, ep429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zahrani, A.M.; Alasmari, T.M. Exploring the impact of artificial intelligence on higher education: The dynamics of ethical, social, and educational implications. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Weng, Z. Navigating the ethical terrain of AI in education: A systematic review on framing responsible human-centered AI practices. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2024, 7, 100306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, V. The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Personalizing Online Learning. J. Online Distance Learn. 2024, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Introducing OpenAI o3 and o4-mini — openai.com. Available online: https://openai.com/index/introducing-o3-and-o4-mini/ (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- OpenAI o3 Breakthrough High Score on ARC-AGI-Pub — arcprize.org. Available online: https://arcprize.org/blog/oai-o3-pub-breakthrough (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- Damar, M.; Özen, A.; Çakmak, Ü.E.; Özoğuz, E.; Erenay, F.S. Super AI, Generative AI, Narrow AI and Chatbots: An Assessment of Artificial Intelligence Technologies for The Public Sector and Public Administration. J. AI 2024, 8, 83–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebo, J.; Long, R. Moral consideration for AI systems by 2030. AI Ethics 2025, 5, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B. Potential safety issues and moral hazard posed by artificial general intelligence. Appl. Comput. Eng. 2024, 106, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan Stanley. Could AI Robots Help Fill the Labor Gap? 2024. Available online: https://www.morganstanley.com/ideas/humanoid-robot-market-outlook-2024 (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- De Silva, D.; Withanage, S.; Sumanasena, V.; Gunasekara, L.; Moraliyage, H.; Mills, N.; Manic, M. Robotic Motion Intelligence Using Vector Symbolic Architectures and Blockchain-Based Smart Contracts. Robotics 2025, 14, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Institute of Knowledge Innovation and Invention. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).