Abstract
This research explores the integration of the Dry Sensor Interface-24 (DSI-24) EEG headset with a ChatGPT-enabled Furhat robot to monitor cognitive stress in video gaming environments. The DSI-24, a cutting-edge, wireless EEG device, is adept at rapidly capturing brainwave activity, making it particularly suitable for dynamic settings such as gaming. Our study leverages this technology to detect cognitive stress indicators in players by analyzing EEG data. The collected data are then interfaced with a ChatGPT-powered Furhat robot, which performs dual roles: guiding players through the data collection process and prompting breaks when elevated stress levels are detected. The core of our methodology is the real-time processing of EEG signals to determine players’ focus levels, using a mental focusing feature extracted from the EEG data. The work presented here discusses how technology, data analysis methods and their combined effects can improve player satisfaction and enhance gaming experiences. It also explores the obstacles and future possibilities of using EEG for monitoring video gaming environments.
1. Introduction
The rapid evolution of video gaming technology and its widespread popularity have opened new frontiers in the study of cognitive processes and stress management. Recent research indicates that video gaming can have both positive and negative effects on various cognitive domains. For instance, studies have shown that action video games can enhance attentional control, spatial skills, and mental flexibility [1,2]. However, concerns have also been raised about potential adverse effects, such as increased aggression and addiction [3].
Human bio-signal sensing allowed relies on electrodes that can be wet or dry, and research is performed to propose other types of electrodes aiming to improve the quality of measures and ease of use [4,5,6]. In this field, Electroencephalography (EEG), a non-invasive method that records electrical activity of the brain, has emerged as a vital tool in understanding the cognitive impact of video gaming [7]. EEG’s ability to provide real-time brain activity data makes it particularly suitable for studying the dynamic cognitive processes involved in gaming. The intersection of EEG and video gaming research offers exciting opportunities for deeper insights into cognitive responses during gaming. This includes understanding how gaming can influence cognitive skills like attention, memory, and problem-solving, and investigating the neural correlates of gaming-induced cognitive changes [8,9]. The trends in scholarly publications on video gaming and EEG are determined through a comparative analysis of Scopus-indexed conference and journal publications, as shown in Figure 1. The base layer of the graph represents the total number of publications on the topic of Video Gaming. Superimposed on this, in a contrasting color, is the stacked count of publications specifically focused on EEG and Video Gaming [10,11]. This visualization highlights the growth and research interest in both fields, with a particular emphasis on the intersection of EEG technology and video gaming studies.
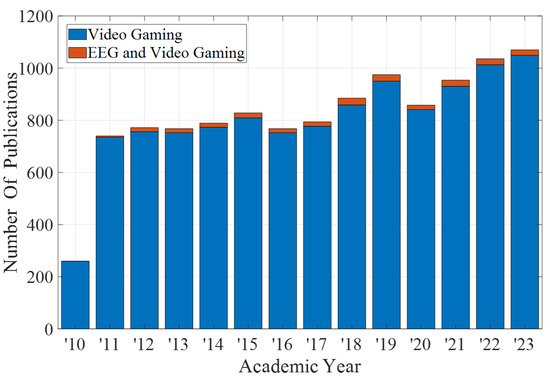
Figure 1.
Number of Scopus-indexed conference and journal papers on ‘Video Gaming’ compared to those specifically on ‘EEG and Video Gaming’ over the academic years 2010–2023.
Social robots, being developed and conceived for different applications [12], have been used in different studies related to human cognition and mental activity. Stress management interventions [13], social anxiety interventions [14], and social cognition studies [15] are examples of such applications. To be used in such tasks, a social robot can benefit from capabilities in sound and image acquisition and processing, sound emission and expression display, Additionally, the ability to make conversations is important in contexts of assistive social robotics for realistic and engaging interactions with humans, and the usage of generative artificial intelligence tools for this task can be of high benefit. In this context, Furhat has been used in conjunction with language models in studies related to different areas of human–robot interaction [16,17].
At the intersection of the aforementioned technologies, this paper presents a novel integration of the Dry Sensor Interface-24 (DSI-24) [18] EEG headset with a ChatGPT-enabled Furhat robot, aimed at monitoring and analyzing cognitive stress in video gaming environments. The main components of the system have been combined as follows:
- The DSI-24 is a state-of-the-art wireless EEG device, highly efficient in capturing brainwave activity in real-time, making it an ideal tool for dynamic and interactive settings such as video gaming.
- The Furhat [19] social robot (available: https://furhatrobotics.com/furhat-robot/, accessed on 29 May 2024) is one of the emerging platforms that can be employed in human–robot interaction with a variety of applications.
- ChatGPT (available: https://openai.com/chatgpt/, accessed on 29 May 2024) has been seen as a flexible tool for text generation, which can be adapted to different context through user prompts. While it is mainly accessed through a web browser, it can be accessed through an API embedded in a program serving a specific application.
While these components have already existed and have been used in different research areas, their combination in the context of stress monitoring and video gaming is a novel usage that has been tailored in this work to make use of their capabilities efficiently. The primary objective of this work is to identify and analyze indicators of cognitive stress among video game players. By analyzing EEG data, we aim to gain insights into the mental states of players during gaming sessions, particularly focusing on stress levels and cognitive load. The integration with a ChatGPT-powered Furhat robot is a crucial aspect of our study, as this AI-driven interface assists in both guiding players through the data collection process and providing timely interventions, such as suggesting breaks, when high stress levels are detected.
This article is organized as follows: Section 2, describes the system level design, detailing the integration of the Dry Sensor Interface-24 (DSI-24) EEG headset with the ChatGPT-enabled Furhat robot. Section 3, presents the findings of the conducted experiments and their implications. Section 4, outlines the limitations of the proposed system and potential avenues for further research and exploration. Finally, a conclusion in given in Section 5.
2. System-Level Design
2.1. System Components
The main components of the system are a DSI-24 EEG headset and Furhat. In this section, these components are first presented, then the experimental setup relying on them is depicted.
2.1.1. DSI-24
The centerpiece of this work is the DSI-24 [18], which is a high-performance wireless EEG headset, designed for advanced neurophysiological research and brain–computer interface (BCI) applications [20,21,22,23]. This high-end instrumentation features 21 scalp electrodes, plus three additional sensors for reference and ground, ensuring high-quality data acquisition with minimal noise interference. The captured EEG waveforms are sampled at 300 Hz, providing precise temporal resolution of 3.3 milliseconds necessary for capturing rapid neural dynamics. A 16-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC) dictates the amplitude resolution of the captured EEG traces. Furthermore, the DSI-24 is notable for its user-friendly design, allowing for quick setup and real-time monitoring, which is essential for both laboratory and clinical environments. It is compatible with various software platforms, facilitating seamless integration with existing research workflows [24,25,26].
2.1.2. Furhat
Furhat consists of a motorized robotic head that can change its orientation and display different faces through a back projection system and a replaceable physical mask. It can emit speech sounds with customizable voices and use human-like facial expressions. It can also detect humans visually and auditively and interact with them. Its interactions benefit from its conversational capabilities, its customizability and programmability to achieve ad hoc tasks. Furhat has been used in studies related to different aspects of human–robot interaction [27,28].
2.2. Experimental Set-Up
The general outline of the experimental configuration is shown in Figure 2. A dry sensor interface-24 (DSI-24) EEG headset is used to capture brainwave activities through 24 electrodes positioned on the subject’s scalp. The subject participates in a video gaming environment, where they are exposed to both visual and auditory stimuli. Their interaction with this environment is enabled through the use of a gaming controller or a car simulator driving wheel, which allows for active engagement in the video games.
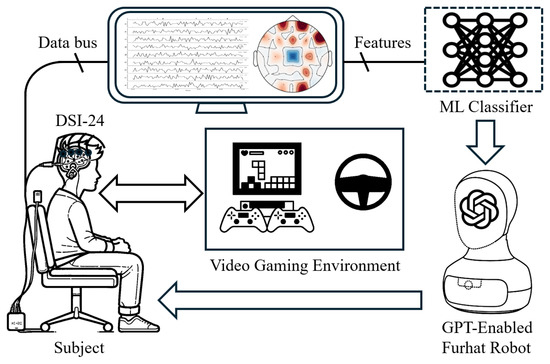
Figure 2.
Experimental setup for EEG-based cognitive stress monitoring in video gaming environments.
While the subject is deeply engaged in the game, the DSI-24 EEG headset continuously records the brain’s electrical activity. The captured raw EEG data are subsequently transformed into a two-dimensional brain heatmap. This heatmap offers a visual depiction of the brain’s electrical dynamics, effectively illustrating the variations in activity across different regions of the brain in a clear, easily interpretable format. This representation, known as brain topology, provides crucial insights into the spatial distribution and connectivity of brain activity. In this work, the EEG device adheres to the internationally recognized 10–20 system for electrode placement on the scalp. This system delineates specific regions for electrode placement with the following labels: Fp (frontopolar), F (frontal), C (central), P (parietal), O (occipital), T (temporal), and A (auricular, near the ear). Odd-numbered electrodes are positioned on the left side of the scalp, while even-numbered electrodes are located on the right side [29]. The DSI-24 Dry EEG device, featuring 24 channels, is employed, including 21 sensor electrodes at positions Fp1, Fp2, Fz, F3, F4, F7, F8, Cz, C3, C4, T7/T3, T8/T4, Pz, P3, P4, P7/T5, P8/T6, O1, O2, A1, and A2, with an additional Fpz electrode serving as the ground. The electrode placement of the DSI-24 ensures standardized and reproducible measurements of brain activity, as illustrated in Figure 3. Figure 4 shows one of the sensor electrodes of the DSI-24 device, which has a diameter of around 2.5 cm for the outer circle of black pins and a diameter of around 1.5 cm for the inner circle of gray pins. Overall, the electrodes are distributed on the device to fit a wide range of head sizes: from 54 to 62 cm circumference for adults (available: https://wearablesensing.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/Wearable-Sensing-DSI-24-Specification-Sheet_s.pdf, accessed on 17 July 2024).
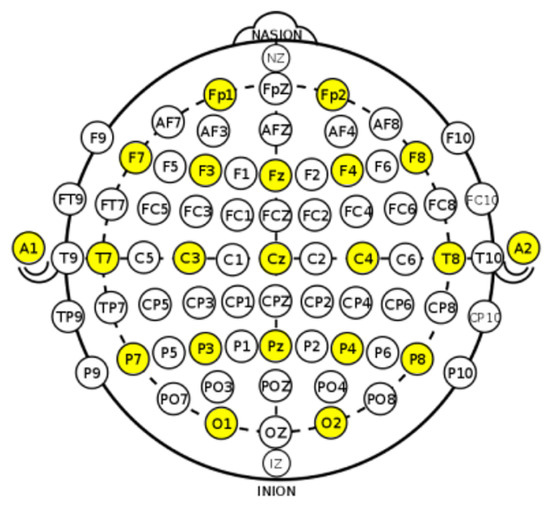
Figure 3.
The 10-20 electrode placement system with the DSI-24 electrodes highlighted.
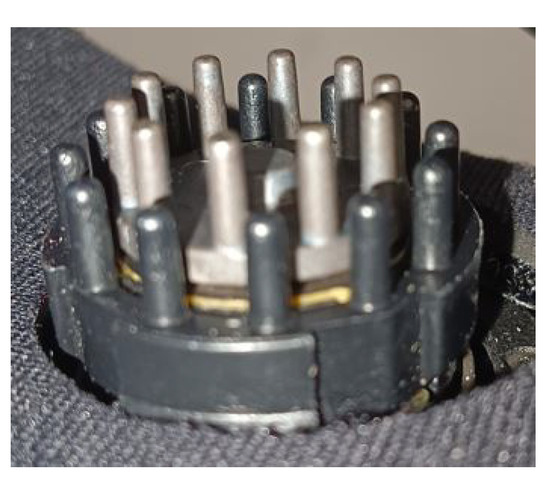

Figure 4.
A sensor electrode from the DSI-24 EEG device.
Subsequently, a Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier [30] is utilized to analyze the EEG heatmap data. This classifier is specifically designed to determine the subject’s cognitive stress level during the gaming experience. Employing sophisticated algorithms, the classifier categorizes stress levels, quantifying the cognitive load experienced by the subject. Concurrently, a large language model (LLM)-enabled Furhat Robot is integrated into the experimental setup. The specific LLM utilized in this work is the Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), known for its advanced natural language processing and generation capabilities. This robot plays a crucial role in guiding the subject through the data acquisition protocol, and also in providing real-time feedback. Based on the machine learning model’s classification outcomes, the Furhat Robot interacts with the subject. It is programmed to issue alerts regarding elevated cognitive stress levels, thus offering immediate monitoring and potential intervention.
2.3. Data Acquisition Procedure
The process of acquiring EEG data in the system level design involves crucial steps to guarantee the precision and dependability of the recorded brain signals. Initially a thorough cleaning of each electrode is carried out to eliminate any dust or impurities, which is essential for obtaining precise EEG readings. Following this, the EEG electrodes are strategically positioned on the participants head following the recognized DSI 10-20 standardized system to ensure comprehensive coverage of all brain regions. These electrodes capture the impulses of the brain, which are then amplified and converted into digital format by an EEG amplifier in-tandem with a analog-to-digital converter. The use of the amplifier does not only improve signal quality, but also reduces noise due to interference and cross-talk. Once digitized, the EEG signals are sent to a computer system equipped with software for pre-processing and analysis. This configuration enables the real time visualization and recording of the EEG data.
In EEG experiments, adhering to a systematic and standardized method is key to ensure smooth data collection and accurate EEG signal acquisition. This study employs varied stimuli to evoke cognitive stress and test cognitive-motor functions, providing a thorough understanding of brain responses under diverse conditions. This approach enhances the richness of the dataset and deepens insights into brain activity dynamics.
The first stimulus involves a virtual car simulator that is designed to engage participants, in both the learning process and in competitive gaming activities simultaneously. This simulation activates areas in the brain related to motor skills and mental challenges, offering a mix of fun and skill improvement. The second stimulus involves playing PlayStation games like FIFA and Fortnite, selected for their competitive nature. This competitiveness is expected to trigger responses linked to cognitive stress during fast decision making. The third activity is an educational game that tests players with tasks involving information processing, critical thinking, and decision making. This activity aims to engage higher level thinking skills and observe how the brain reacts.
Recruiting volunteers is a part of gathering data. Despite obstacles and the spontaneous nature of volunteer involvement, having a diverse and extensive dataset is crucial. A larger dataset with information significantly boosts the training of machine learning algorithms leading to better accuracy. To that end, in this research work, a total of 43 volunteers were utilized with roles between students, teachers and professors, with an age range from 23 to 45, were recruited. Each volunteer consented to using their brain EEG data in this study. A total of around 10 min were needed to place the DSI 24 EEG headset on each volunteers head for data collection purposes. The recording session utilized a total of 5 to 7 min per volunteer with a duration of 60 s before and after each stimulus. This additional time serves as guard bands and is used to establish a baseline of brain activity, prior-to and immediately proceeding the stimulus activity.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Implementation and EEG Measurements
An example of the implemented set-up is shown in Figure 5a, which displays a representative example of a player engaging in the FIFA video game using a controller, with the DSI-24 EEG headset securely positioned on their head. This image captures the typical setup of the gaming environment, highlighting how players interact with the game while their brainwave activity is being monitored. The DSI-24 headset is shown in use, illustrating its fit and placement on the player’s scalp, crucial for accurate EEG data collection. The ChatGPT-enabled Furhat Robot, characterized by its ability to exhibit various facial expressions, is shown in Figure 5b. The robot, designed for interactive communication, is shown in the process of conversing with a participant. This image emphasizes the robot’s advanced features, including its expressive capabilities and integration with the GPT language model, which enables it to provide feedback and guidance based on the EEG data.

Figure 5.
Experimental setup: (a) Player interaction in FIFA gaming environment, (b) ChatGPT-enabled Furhat robot with expressive capabilities.
The results in Figure 6, presents two distinct brain heatmaps, offering a visual comparison of brain activity under different cognitive states. A heatmap of normal brain activity, characterized by a balanced and uniform distribution of neural activity across various regions of the brain is depicted in Figure 6a. This image serves as a baseline representation of brain function in a relaxed state, with no specific areas showing heightened activity. In contrast, Figure 6b illustrates brain activity under cognitive stress, with a noticeable increase in activity in the frontal lobe. This heatmap highlights the intensified neural activity in the frontal regions, indicative of the brain’s response to stress. The active frontal lobe is clearly demarcated by warmer colors on the heatmap, signifying higher levels of brain activity in this area. This comparison between the two states visually demonstrates the brain’s dynamic response to stress and the significant role of the frontal lobe in managing cognitive load and stress responses.
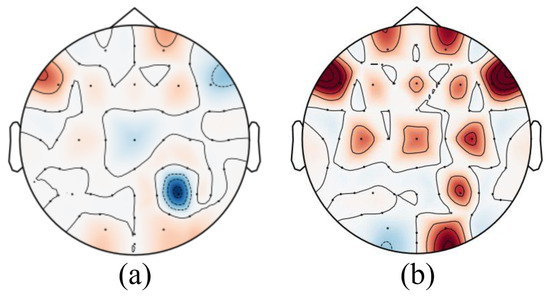
Figure 6.
Comparative brain heatmaps: (a) normal brain activity, (b) brain activity under stress with active frontal lobe. The generated heatmaps were calculated from the time domain root mean square (RMS) value of the EEG signal over a 1 s window.
The results obtained in this study indicate that cognition and emotional responses can be effectively measured using psychophysiological techniques, particularly EEG, as suggested in the research [31]. The utilization of Fp1 and Fp2 electrodes in this context has revealed a correlation between the complexity and difficulty levels of various video games and the increase in gamma band activity, while changes in the alpha band were not significantly evident. This observation confirms that with heightened visual challenges and difficulty in games, there is an associated increase in gamma band activity, providing valuable insights for game designers aiming to create more engaging experiences.
In accordance with the findings documented in [32], the importance of the prefrontal lobe, especially the F3 and F4 regions, in controlling consciousness and emotional responses has been reaffirmed. The study also acknowledges the presence of potential artifacts, such as muscle tension, eye movements, and ambient noise in EEG data. To address these issues, the EEG data in this research were decimated to 128 Hz and subjected to filtering processes, including a notch filter to remove power-line noise in the 49 to 51 Hz range and a high-pass filter for frequencies below 0.2 Hz. Consequently, the processing facilitated the extraction of the five band power features across Delta, Theta, Alpha, Beta, and Gamma frequency bands from the EEG data spanning one-second intervals from each channel.
In light of the importance of the prefrontal lobe in emotion recognition and cognitive processing, future studies could benefit from an advanced electrode setup focused on this region. Utilizing smaller, higher-count electrodes would allow for more precise mapping of brain activity, leading to a better understanding of the neural dynamics associated with cognitive stress. Previous research has highlighted the prefrontal lobe’s critical role in emotion recognition, further emphasizing the need for targeted electrode placement in this area [33]. By optimizing electrode placement and count, we can improve the resolution of our data and gain more detailed insights into the specific neural mechanisms at play.
3.2. Machine Learning Classification
3.2.1. Pre-Processing
The EEG data are collected using a DSI-24 EEG headset. These data are then transformed into a two-dimensional brain heatmap, offering a visual representation of the subject’s brain activity. To optimize the heatmap for real-time analysis, the resolution is adjusted, and the color palette is standardized. Data augmentation techniques are applied to the heatmaps to simulate varying brain states, including different levels of cognitive stress and relaxation. This process results in a comprehensive dataset suitable for training machine learning models, with each heatmap undergoing normalization to a uniform size for consistency in feature extraction.
3.2.2. Baseline Model
The baseline model for EEG data interpretation does not focus on intricate practical applications, but serves as a foundation for comparing more complex models. The dataset for training this model, as shown in Figure 6, consists of flattened vector representations of the brain heatmaps. Each vector, representing a unique pattern of brain activity, is labeled with the corresponding cognitive state. A machine learning classifier, such as a Support Vector Machine (SVM), is trained to categorize these vectors, distinguishing between different cognitive states based on the heatmap patterns. SVMs have been used in different works for EEG signal classification [34,35].
3.2.3. Feature Extraction Using Local Binary Pattern
In contrast to the baseline model, a more advanced approach involves extracting features from the brain heatmaps using the Local Binary Pattern (LBP) technique, as depicted in Figure 7. LBP is efficient for summarizing texture information in images, including EEG heatmaps and has been used in EEG classification in different applications [36,37]. The method involves dividing each heatmap into regions and computing the LBP for each pixel, creating a binary code that captures the relative intensities in a local area. These binary patterns are then aggregated into histograms, each serving as a distinct signature of the activity in a specific brain region. The LBP histograms, with their reduced dimensionality yet rich information content, serve as input fora SVM model designed to classify different states of brain activity.
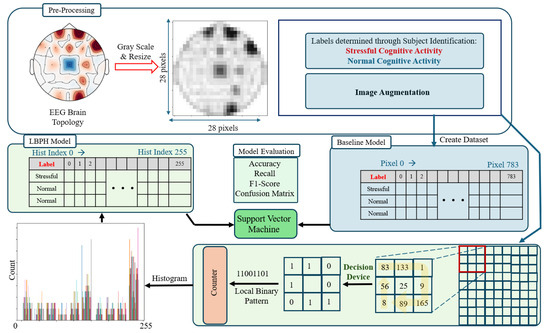
Figure 7.
The baseline model and the Local Binary Pattern Histogram (LBPH) approach are exemplified using a sample brain topology measurement.
3.2.4. Model Evaluation
Model performance, encompassing both the baseline and LBP-based SVM classifiers, is assessed using real-time EEG data. This evaluation, detailed in Table 1, includes metrics computed post-training and testing phases, ensuring the models’ effectiveness in classifying brain states from live EEG readings. The evaluation criteria focus on accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity, providing a comprehensive understanding of each model’s capabilities.

Table 1.
Classification metrics for Baseline and LBPH Machine Learning Models *.
4. Limitations and Future Work
One limitation of this study is the reliance on the DSI-24 EEG headset, which, while advanced, may not capture the full spectrum of neurophysiological responses associated with cognitive stress due to its limited number of electrodes. In relation to the previous literature, a review was made in [38], addressing methods of assessing mental stress with EEG. It showed that most of the reported studies addressed the prefrontal cortex, pre-frontal and frontal lobes as brain regions with a number of channels that did not exceed 9 in 15 studies out of 33 reported ones. The reported accuracies of these methods were between 50% and 99.94%, and they relied on a variety of classifiers like linear discriminant analysis (LDA), SVM, K-nearest neighbors (KNN), random forest (RF), artificial neural network (ANN) and convolutional neural network (CNN). It is important yo highlight that each study was made on a separate set of conditions, using different features and classifiers, which could be more or less complex. While the accuracy reported in this work competes with many of the ones reported in [38], many have been reported to be more accurate. However, this work relies on features and a classification scheme that are computationally competitive and adds an important feature, which is the interaction with the social robot that can help to make the level of stress evolve with time, affecting the accuracy results. We add that the interaction dynamics between the player and the Furhat robot were not extensively explored, particularly in terms of the robot’s influence on player behavior and stress levels. Future research could expand on these aspects by integrating more comprehensive EEG systems with a higher number of channels for finer brain activity mapping and conducting in-depth analyses of player-robot interactions. Exploring the use of advanced machine learning algorithms for more nuanced interpretation of EEG data and extending this research to diverse gaming genres and settings would also be beneficial in understanding the broader applications of this technology in cognitive stress monitoring. However, the combination of an EEG-based stress monitoring system in conjunction with a social robot interacting with the use of a language model is a new way of using these technologies which can be built on for a better exploitation of their abilities. This can help in the enhancement of user experiences not only in video gaming, but also in other domains where stress can be managed through social interaction and conversation.
5. Conclusions
The work presented in this study successfully integrates the DSI-24 EEG headset with a ChatGPT-enabled Furhat robot to monitor cognitive stress in video gaming environments, showcasing a novel approach to understanding and managing player well-being. The study capitalizes on the DSI-24’s ability to rapidly capture brainwave activity and utilizes real-time EEG signal processing, which, coupled with the interactive capabilities of the Furhat robot, enhances both the gaming experience and stress monitoring. While acknowledging limitations like the headset’s electrode count and the depth of player-robot interaction analysis, the study opens pathways for future research. These include employing advanced EEG systems and machine learning techniques, as well as expanding the scope to various gaming genres and settings. Overall, this work marks a significant contribution to EEG-based cognitive monitoring and highlights the potential of integrating advanced technology and AI in interactive and dynamic environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.K.; methodology, A.S.K., A.A.A., A.Z.A., F.J.A., N.M.Y.A., S.N.A. and K.Y.; software, A.S.K. and N.M.Y.A.; validation, A.A.A., A.Z.A., F.J.A., N.M.Y.A., S.N.A., A.S.K., S.S., S.A.K. and K.Y.; formal analysis, A.A.A., A.Z.A., F.J.A., N.M.Y.A., S.N.A., A.S.K., S.A.K. and K.Y.; investigation, S.S., S.A.K. and K.Y.; resources, S.A.K., A.S.K. and K.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.K.; writing—review and editing, A.S.K.; supervision A.S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of American University of the Middle East (code: SP000-0403-2023 date: 3 April 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. No patient-identifying information or images were used or published in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the AUM Robotics Center for their support specifically Albert Potams, Ahmed Rashid and Nadhira Khezami for valuable discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Brilliant, T.D.; Nouchi, R.; Kawashima, R. Does Video Gaming Have Impacts on the Brain: Evidence from a Systematic Review. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavelier, D.; Green, C.S.; Pouget, A.; Schrater, P. Brain Plasticity Through the Life Span: Learning to Learn and Action Video Games. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 35, 391–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.A.; Shibuya, A.; Ihori, N.; Swing, E.L.; Bushman, B.J.; Sakamoto, A.; Rothstein, H.R.; Saleem, M. Violent Video Game Effects on Aggression, Empathy, and Prosocial Behavior in Eastern and Western Countries: A Meta-Analytic Review. Psychol. Bull. 2010, 136, 151–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Fan, Y.; Wang, M.; Ji, B.; Li, L.; Jin, M.; Shang, S.; Ni, C.; Cheng, Y.; Dong, L.; et al. Microneedle Array Electrode With Ag-PPS Modification for Superior Bio-Signal Recording on Skin. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 24196–24204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Wu, N.; Ji, B.; Liu, J. A Film Electrode upon Nanoarchitectonics of Bacterial Cellulose and Conductive Fabric for Forehead Electroencephalogram Measurement. Sensors 2023, 23, 7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Kwon, J.; Kim, J.; Ryu, H.; Ok, J.; Kwon, S.; Park, H.; Kim, T.i. Wearable EEG electronics for a Brain–AI Closed-Loop System to enhance autonomous machine decision-making. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2022, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappenman, E.S.; Luck, S.J. The Oxford Handbook of Event-Related Potential Components; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Palaus, M.; Marrón, E.M.; Viejo-Sobera, R.; Redolar-Ripoll, D. Neurobiological Consequences of Playing Video Games. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, S.; Gleich, T.; Lorenz, R.C.; Lindenberger, U.; Gallinat, J. Playing Super Mario induces structural brain plasticity: Gray matter changes resulting from training with a commercial video game. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, T.; Saeed, U.; Arsalan, A.; Anwar, S.M.; Ashraf, M.U.; Alsubhi, K. EEG in game user analysis: A framework for expertise classification during gameplay. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, C.; Yuan, H.; He, E.J.; Bai, X.; Yang, L.; He, B. A high resolution EEG study of dynamic brain activity during video game play. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 22–26 August 2007; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 2489–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, K.; Said, S.; Alkork, S.; Beyrouthy, T. A Survey on Recent Advances in Social Robotics. Robotics 2022, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, A.; Klęczek, K.; Alimardani, M. The Effectiveness of Social Robots in Stress Management Interventions for University Students. In Social Robotics; Ali, A.A., Cabibihan, J.J., Meskin, N., Rossi, S., Jiang, W., He, H., Ge, S.S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 181–190. [Google Scholar]
- Rasouli, S.; Gupta, G.; Nilsen, E.; Dautenhahn, K. Potential Applications of Social Robots in Robot-Assisted Interventions for Social Anxiety. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2022, 14, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wykowska, A. Social Robots to Test Flexibility of Human Social Cognition. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2020, 12, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabo, R.; Beňuš, S.; Kevická, V.; Trnka, M.; Rusko, M.; Darjaa, S.; Kejriwal, J. Towards the Use of Social Robot Furhat and Generative AI in Testing Cognitive Abilities. Hum. Aff. 2024, 34, 224–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galatolo, A.; Leite, I.; Winkle, K. Personality-Adapted Language Generation for Social Robots. In Proceedings of the 2023 32nd IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Busan, Republic of Korea, 28–31 August 2023; pp. 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DSI-24-Wearable Sensing|Dry EEG. Available online: https://wearablesensing.com/dsi-24/ (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Al Moubayed, S.; Beskow, J.; Skantze, G.; Granström, B. Furhat: A Back-Projected Human-Like Robot Head for Multiparty Human-Machine Interaction. In Cognitive Behavioural Systems, Proceedings of the COST 2102 International, Dresden, Germany, 21–26 February 2011; Esposito, A., Esposito, A.M., Vinciarelli, A., Hoffmann, R., Müller, V.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 114–130. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Masullo, M.; Maffei, L.; Pascale, A.; Chau, C.k.; Lin, M. Improving informational-attentional masking of water sound on traffic noise by spatial variation settings: An in situ study with brain activity measurements. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 218, 109904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ryu, J.; Lee, Y.; Park, H.; Lee, K. Methods for Selecting Design Alternatives through Integrated Analysis of Energy Performance of Buildings and the Physiological Responses of Occupants. Buildings 2024, 14, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Wang, S.; Lee, S.; Seo, S.; Lee, N.; Kim, S. Viewer Emotional Response to Webtoon-Based Drama: An EEG Analysis. Int. J. Human–Computer Interact. 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yang, P.; Shu, Y.; Liu, N.; Sheng, J.; Luo, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Emotion Recognition from Few-Channel EEG Signals by Integrating Deep Feature Aggregation and Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.M.; Choi, C.X.; Tsoi, T.C.; Shea, C.K.; Yiu, K.W.; Han, Y.M. Effects of multisession cathodal transcranial direct current stimulation with cognitive training on sociocognitive functioning and brain dynamics in ASD: A double-blind, sham-controlled, randomized EEG study. Brain Stimul. 2023, 16, 1604–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, D.; Laufer, I.; Zuckerman, I. Modulation of Beta Power as a Function of Attachment Style and Feedback Valence. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Brain Informatics, Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1–3 August 2023; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, K.; Kalaganis, F.P.; Oikonomou, V.P.; Nikolopoulos, S.; Laskaris, N.A.; Kompatsiaris, I. Harnessing the Potential of EEG in Neuromarketing with Deep Learning and Riemannian Geometry. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Brain Informatics, Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1–3 August 2023; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robb, D.A.; Lopes, J.; Ahmad, M.I.; McKenna, P.E.; Liu, X.; Lohan, K.; Hastie, H. Seeing eye to eye: Trustworthy embodiment for task-based conversational agents. Front. Robot. AI 2023, 10, 1234767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaccia, S.; Revel, G.M.; Scalise, L.; Bevilacqua, R.; Rossi, L.; Paauwe, R.A.; Karkowsky, I.; Ercoli, I.; Artur Serrano, J.; Suijkerbuijk, S.; et al. Social Robot and Sensor Network in Support of Activity of Daily Living for People with Dementia. In Proceedings of the Dementia Lab 2019. Making Design Work: Engaging with Dementia in Context, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 21–22 October 2019; Brankaert, R., IJsselsteijn, W., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 128–135. [Google Scholar]
- Jasper, H.H. The ten-twenty electrode system of the International Federation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1958, 10, 371–375. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, M.; Khanna, R. Support Vector Machines for Classification. In Efficient Learning Machines: Theories, Concepts, and Applications for Engineers and System Designers; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 39–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegedues, C.; Constantino, J.; Dixen, L.; Burelli, P. Investigating Perceived and Mechanical Challenge in Games Through Cognitive Activity. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Game, Boston, MA, USA, 21–24 August 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Zhou, W.; Li, C.; Li, D.; Liu, P.X. An Emotion Recognition Method for Game Evaluation Based on Electroencephalogram. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2023, 14, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshdy, A.; Al Kork, S.; Beyrouthy, T.; Nait-ali, A. Simplicial Homology Global Optimization of EEG Signal Extraction for Emotion Recognition. Robotics 2023, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.; Mohanty, M.N. Classification of EEG Signal Using SVM. In Advances in Electrical Control and Signal Systems; Pradhan, G., Morris, S., Nayak, N., Eds.; Singapore: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 859–869. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam, S.; Dharmar, S. Implementation of a non-linear SVM classification for seizure EEG signal analysis on FPGA. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 131, 107826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.A.; Shanir, P.P.; Khan, Y.U.; Farooq, O. A hybrid Local Binary Pattern and wavelets based approach for EEG classification for diagnosing epilepsy. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 140, 112895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.S.; Kanhangad, V.; Pachori, R.B. Classification of seizure and seizure-free EEG signals using local binary patterns. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2015, 15, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katmah, R.; Al-Shargie, F.; Tariq, U.; Babiloni, F.; Al-Mughairbi, F.; Al-Nashash, H. A Review on Mental Stress Assessment Methods Using EEG Signals. Sensors 2021, 21, 5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).