Abstract
Recent findings of archaeological research in the Vathy gulf area, Astypalaia Island, indicate its continuous habitation since prehistoric times, most importantly in the transitional period from the Final Neolithic to the Early Bronze Age (late 4th/early 3rd millennium BC). The evaluation of the prehistoric stone artefacts from Vathy using non-invasive analytical methods (Near Infrared Spectroscopy—NIR), in combination with the mineral-petrographic characterization of the main lithological formations of the island, is expected to provide important information about raw material procurement and possible exchange networks. The geological study of the island combined with the analytical methods applied to the archaeological artefacts and the geological samples led to the identification of both local and allogenic materials. The possible locations of raw material sources were established and the origin of allogenic materials was estimated. The stone artefacts made of local geo-materials consist mainly of calcitic sandstone, shale, marl, and limestone/marble, comprising the largest part of the lithological formations of the island, as well as pumice and volcanic rocks of varying chemical composition. By means of a portable microscope and NIR spectroscopy, we were further able to identify allogenic geo-materials including chalcedony, mica schist, bauxite and meta-bauxite, steatite, and paragonite. Based on the mineralogical and petrographic characterization of the stone artefacts, a first attempt is made to evaluate the possible raw material sources and to identify potential intra-island modes of stone exploitation.
1. Introduction
Archaeometry focuses on the application of analytical techniques in archaeological finds to provide information about dating, prospecting, analysis of technology and provenance, as well as reconstruction of a coeval environment [1], thus providing another scope for the interpretation of cultural and archaeological growth and evolution [2,3,4,5]. Many researchers [6,7,8,9,10,11,12] have used analytical techniques in a variety of archaeological findings to acquire knowledge about the source rock material (including volcanic rocks, chert, clayey raw materials, sandstones, etc.), their provenance, or even their utility.
For this reason, the use of non-invasive techniques is a matter of great importance, contributing significantly to the archaeological desiderata arising, while keeping the findings intact. The study of archaeomaterials include fundamental techniques widely used for their chemical identification (i.e., X-ray Fluorescence analysis—XRF, RAMAN Spectroscopy) or their textural analysis (i.e., Scanning Electron Microscope—SEM).
According to Hunt [13], reflectance spectroscopy can be defined as the technique that uses the energy in certain wavelength regions of the electromagnetic spectrum to analyze minerals. The operating principle of this methodology is based on the process of energy absorption in the near infrared region (350–2500 nm) to describe changes in molecular level, measuring the energy of the bond vibrations between the cations and the molecules. Molecular vibrations are in fact internal movements of atoms related to changes of the length and the angle of their bonds.
The bonds vibrate differently, at discrete wavelengths, as a function of their length, representing consequently the presence of certain NIR-active chemical compounds, leading to specific mineralogical components. Vibration modes are generally distinguished in stretching and bending vibrations because the relative positions of the atoms are not absolutely fixed and are, on the contrary, constantly fluctuating. The stretching vibrations are caused by changes in the distance between atoms along their bond axis. The bending vibrations are related to the change in the angle between two bonds, and characterized by scissoring, rocking, wagging and twisting motions. When a molecule absorbs infrared radiation, the molecular vibrations trigger a net change in the dipole moment, depending on the value of the charge difference and the distance between the two charged centers. Even though the study of molecular vibrations was originally based on Hook’s Law, describing a simple harmonic oscillator in quantum physics can be considered only approximately simple harmonic due to the inelastic nature of the molecular bonds. Normal, or fundamental absorptions occur when a molecule is excited from ground to the lowest-energy excited state (v = 1). Overtones occur when fundamental mode is excited with two or more quanta of energy (2 v, 3 v etc.), resulting in a higher energy state. Finally, combination bands result from two or more fundamental vibrations that are excited simultaneously.
This methodology is based on diffuse reflectance spectroscopy and is considered a non-invasive method as it can be applied in-situ, directly to any material and is appropriate when no sample preparation is needed, retrieving characteristic spectra from the visible to the near infrared region, thus providing information about its chemical composition. When infrared light penetrates the sample, it can be reflected, or scattered, following a chain path until finally exiting the sample. This whole process will cause the initial energy to be lost, since part of it will be absorbed by the material. The detector will collect the new infrared radiation, now containing some new information. Diffuse reflection occurs since the light penetrates the surface layer of the particles, excites the vibrational regions of the target molecule, and then scatters in all directions. Thus, the reflection spectrum produced, depends on the composition of the sample.
In the field of archaeometry, only few researchers have applied NIR spectroscopic analysis to a variety of materials, including ceramics [14], ancient wood [15], paper [16], or even with the use of imaging spectroscopy in paintings [17] etc. Tanyaş et al. [18], studied the spectral properties of chlorite stone bowls to explore the regional locations of the source rocks, incorporating ASTER satellite data, and also emphasizing in petrographic and geochemical analysis, that critically supplement the spectroscopic analysis.
Although NIR spectroscopy has numerous advantages, being economical and a direct method without any necessary sample preparation, its non-invasive nature, as in most methodologies, necessitates the contribution of other methodologies as well, to provide a reliable evaluation of the material. Spectral signatures can be affected by many factors, causing the problematic interpretation of spectral signatures. These factors mainly deal with the presence of multiple mineral phases resulting in the presence of overlapping spectral absorptions, as well as the textural characteristics of the material (i.e., the presence of porosity, the grain size of the minerals) that may affect the spectra. In this study, we attempt to thoroughly examine a variety of archaeological artefacts, regarding the use of non-invasive techniques, such as NIR spectroscopy, in the identification of the source materials to draw conclusions about their provenance. The study of the archaeological artefacts was also based on microscopic observation, providing further information about the microstructure of the stone tools and their mineralogical composition in order to eliminate the above concerns.
Astypalaia is one of the Dodecanese islands in Southern Aegean (Figure 1). Although important finds from historical times have been located on the island, its prehistory was until recently overlooked. Chance finds at the Pyrgos peninsula overlooking the Vathy gulf (“Vathy”) in the Northeastern part of the island in 2008 and extensive surveys and excavations since 2011 [19,20] led to the location of archaeological remains from prehistoric to modern times, indicating almost unceasing habitation. The prehistoric occupation is as early as the Final Neolithic/Early Bronze Age (4th–3rd millennia BC); the location and subsequent excavation of infant jar burials and the discovery of a prehistoric fortified acropolis with important petroglyphs [19,20,21] constitute Vathy a diachronic palimpsest and place Astypalaia within the broader frame of insular prehistory as known from the other Dodecanese islands and mostly the Cyclades.
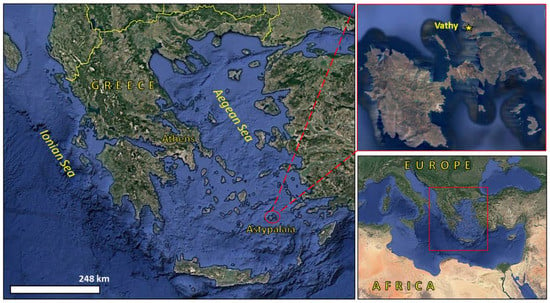
Figure 1.
Oblique satellite view (Google Earth Pro) of Greece and Astypalaia Island in the Aegean Sea.
During the surveys, a total of 117 ground-stone implements [22,23] were recovered (Table 1); the collection includes mostly utilitarian items (suggesting fishing and processing activities, e.g., grinding and pounding of edibles or other materials), along with two stone beads. A retouched geometric artefact, originally thought to be of flint is also included in the analyzed sample (a final total of 118 artefacts).

Table 1.
Typology of the assemblage recovered during the surveys.
Contacts with other Aegean islands are to be found in the chipped stone assemblage made from obsidian of mostly Melian origin (macroscopic identification [24]) as well as in pottery imported from the Cyclades [25]. With that in mind, it was of interest to investigate the provenance of the raw materials employed in the manufacture of the ground tools and implements that were also recovered at the site [26].
The evaluation of the stone artefacts using non-invasive analytical methods (Near Infrared Spectroscopy—NIRS), combined with the mineral-petrographic characterization of the main lithological formations of the island, is expected to provide important information about the commercial transactions of that time and the expertise of the islanders on stone exploitation. Information about the geologic structure of the island in combination with the evaluation of the archaeological and geological materials led to the identification of local and non-local materials.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Archaeological Artefacts
The collection of artefacts retrieved during archaeological fieldwork at Vathy comprises lids, grindstones, pounders, rubbers, polishing pebbles, floaters, two beads, a chisel, and a single bifacial geometric tool (Figure 2). Numerous obsidian tools [24] and marble [25] are also included in the lithic finds, constituting other subjects of research. During our research, 118 stone artefacts were studied through the in-situ application of non-invasive, non-destructive methods since rapid technological development provide important information without interfering in the archaeological artefacts.
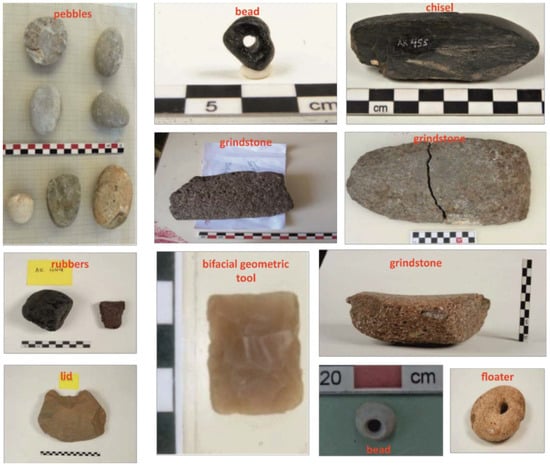

Figure 2.
Representative photographs of the stone artefacts analyzed in the present study.
The artefacts were studied macroscopically with the aid of a portable microscope (Wifi ProScope mobile, Bodelin Technologies, Oregon City, OR, USA) and the capture of micro-photographs (Figure 3a). The mineralogical identification was determined through the application of Near Infrared Spectroscopy (NIR) using an SM-3500 specTERRA (Spectral Evolution Inc., Lawrence, MA, USA) portable apparatus, with a field of view (FOV) 2 × 1.5 cm, in contact with the surface of the samples, and a total number of 1200 of spectra were evaluated (Figure 3b). The data acquired ranges from 0.35 to 2.5 μm with a spectral resolution according to the software, between 3.5 and 8 nm. The spectra were finally produced by the instrument at 1 nm intervals, using the DARWin SP Data Acquisition software (Spectral Evolution Inc., Lawrence, MA, USA), which is accompanied by the United States Geological Survey (USGS spectral library) mineral standards database. Sample spectra were first calibrated relative to a (5 × 5 cm in size standard panel (Spectral Evolution, Inc. Lawrence, MA, USA).
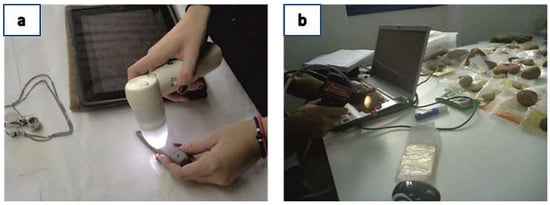
Figure 3.
Non-destructive analytical techniques employed for the evaluation of the stone artefacts studied: (a) use of the WiFi ProScope mobile microscope paired with iPad; (b) use of Near Infrared (NIR) portable spectrometer SM-3500 specTERRA.
The spectra are characterized by absorption features, due to energy-matter interactions at this region caused by molecular vibrations at specific frequencies. Consequently, the absorption features allow us to determine which functional molecular group participates in the structure of the mineral. The major spectral features in the NIR region are a result mostly of the water content and the vibrations of the hydroxyl groups, such as Al-OH, Fe-OH, Mg-OH [27]. Therefore, it is easy to identify hydrous minerals, such as amphiboles, mica, clay minerals, etc. Minerals, such as quartz and feldspars, do not include hydroxyl or water in their structure, thus they cannot be identified through NIRS. The main characteristic absorption features imprinted through NIR spectroscopy are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Major absorption features [27] of the minerals identified in the present study.
2.2. Raw Materials
Destructive methods were used in the lithologic specimens, including petrographic study and mineralogical identification. Through the petrographic observation, the lithologic samples of Astypalaia Island were studied in detail, providing further information about the texture of the samples as well as the grain size of the minerals and the mineral evaluation was verified through the XRPD.
Petrographic thin sections were prepared and studied by means of transmitted light microscopy (Zeiss AxioScope A.1, Carl Zeiss Microscopy Deutschland GmbH, Oberkochen, Deutschland) in order to determine the rock type and mineral mode. The mineralogy of the samples was further verified in the Mineral and Rocks Research Laboratory, Department of Geology, University of Patras, Greece, by means of X-ray Powder Diffraction (BRUKER D8 Advance, Bruker AXS, Karlsruhe, Germany) using Ni filtered Cu-Kα radiation, operating at 40 kV and 40 mA and employing a Bruker Lynx Eye fast detector. Samples were step-scanned from 2° to 70° 2θ and a time/step of 0.2 s. Samples were powdered (<10 μm) in a vibration disc mill using an agate grinding set and randomly mounted in a sample holder. The crystalline phases were identified using the DIFFRACplus EVA software (Bruker-AXS, Bruker-AXS, Madison, WI, USA), based on the ICDD Powder Diffraction File (2006 Version).
3. Geologic Setting of Astypalaia and Field Observations
To answer the question about the provenance of the raw materials present at Vathy, a detailed bibliographic review was carried out for the in-depth study of the local lithologies. Field observations through extensive sampling and GPS recording provided valuable information for the petrographic study and the determination of the mineralogical composition of the rocks. For this reason, we tried to perform as much as possible a representative sampling (41 samples in total) at Pyrgos-Vathy, Analipsi, and Livadi peninsulas (Figure 4).
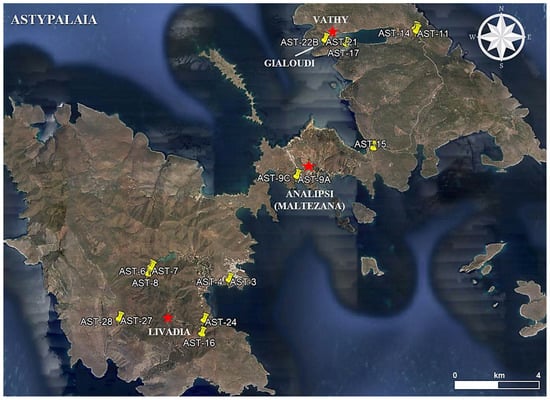
Figure 4.
Oblique satellite view (Google Earth Pro) of Astypalaia Island showing the sampling sites.
The geologic structure of Astypalaia has been studied by many researchers [28,29,30,31,32,33] and consists of sedimentary rocks, i.e., Upper Jurassic to Upper Eocene Alpine geologic formations, as well as meta-Alpine lithologies. According to the geologic map (Figure 5) of [32,34], the lithology of the island consists mostly of limestones, whilst the larger part of the Western region of the island consists of Flysch (Upper Eocene–Oligocene), including sandstones, mudstones, and conglomerates (Figure 6a). In Western Astypalaia, Upper Jurassic neritic medium-bedded limestones, approximately 250 m thick, are overthrusted on flysch. Τhe Eastern part of the island comprises Senonian–Maastrichtian, thick-bedded to massive, rudist limestones and Paleocene–Middle Eocene, thick-bedded to massive, black, nummulitic limestones (Figure 6b). Quaternary sedimentary rocks characterize meta-Alpine lithologies. At several sampling sites, dynamic deformation characteristics were also observed (Figure 6c). Finally, in many sites in the Central part of the island Poros occurred, of aeolian origin, consisting of calcarenites as well as marine and continental fauna (Figure 6d).
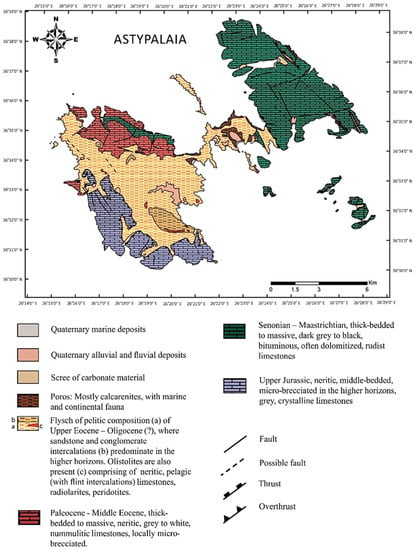
Figure 5.
The geological map of Astypalaia (digitized and modified from [34]).
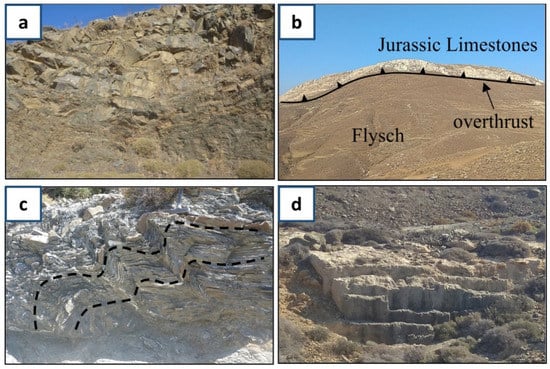
Figure 6.
Representative photographs during our field work: (a) Sandstone and mudstone intercalations; (b) of the Jurassic limestones over thrusting Eocene flysch; (c) characteristics of dynamic deformation through the presence of folded sandstones; (d) Calcarenite quarry.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Microscopic Observation and Spectroscopic Characteristics of the Prehistoric Artefacts
The evaluation of the raw material of the prehistoric artefacts was conducted through microscopic observation and the application of NIRS (Figure 7). The archaeological sample includes: sandstone, shale, marl, limestone and marble, pumice and volcanic rocks of varying chemical composition, steatite, mica schist, obsidian, chalcedony, and bauxite and meta-bauxite. It is important however to study the provenance of the raw materials in order to characterize them as either local, if they belong to the local lithology, or as non-local. This information will clarify the systems of raw material procurement on Astypalaia during the period under study.
As concluded from the application of NIR spectroscopy, the majority of the studied stone implements (grindstones, polishing pebbles, and pounders) are comprised of calcite (CaCO3) (Figure 7a). Calcite has diagnostic features in the near infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum, displaying a characteristic doublet feature at 1880 nm and 1990 nm approximately, as well as a deep major absorption feature near 2340 nm, shifted to lower wavelength position for more dolomitic (MgCO3) compositions [35,36]. Even if the major absorption feature is distinguishable in all studied spectra indicating the presence of calcite, we observed differences in the reflectance values, the depth and the intensity of the absorption features. The differences are attributed to the textural characteristics of the lithotypes that were used as raw, i.e., the grain size of calcite, the cohesion of the grains, internal grain defects, the presence of impurities, or the presence of inclusions and, if so, the inclusion size [37]. According to [36], powdered carbonate materials have nearly flat spectral characteristics for wavelengths lower than 1600 nm. This parameter seems to be critical for the stone artefacts that display this characteristic, indicating the use of micritic limestone as raw material, i.e., limestone with a grain size of calcite of <4 μm. Other spectra display a negative slope toward higher wavelengths, and even if the major absorption features at 2340 nm approximately are distinguishable, the characteristic doublet is hardly seen and is not clearly developed. As described by [37], even small amounts of organic matter in the mineralogical composition can suppress the spectral bands. Broad, rounded features at 1400 nm and 1900 nm indicate the presence of molecular water either due to hydration or trapping water in the crystal lattice. Furthermore, small absorption features at 1900 nm region are often observed and are attributed to very small water polymers forming inclusions, adhered to the inclusion walls [37,38].
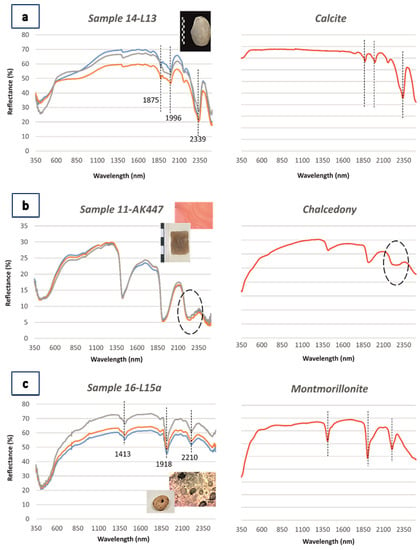
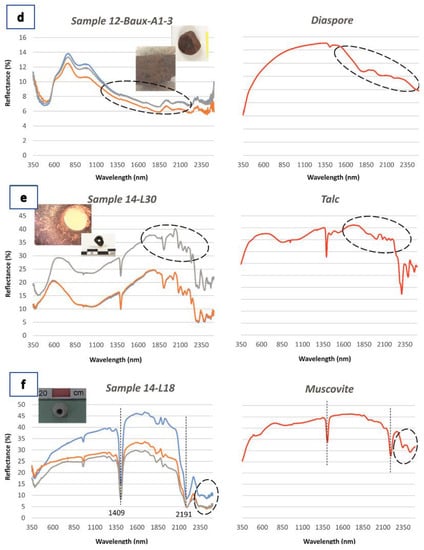
Figure 7.
Representative reflectance spectra of the studied stone artefacts (left column), in comparison to the associated laboratory reference, spectra of the USGS spectral library (right column) that were used in the present study [39]: (a) pebble; (b) bifacial geometric tool; (c) floater; (d) rubber; (e) and (f) bead.
We also identified spectra that are characterized by absorption features at approximately 2200 nm and at 2290 nm, except for the absorption bands of calcite, which indicate the presence of more mineralogical components in the raw material. The specific wavelength position of the absorption features is attributed to Al-OH and Mg, Fe-OH molecular vibrations, respectively. The spectral signature of the raw materials, in accordance with the microscopic evaluation of the samples, are related to calcite, as well as clay minerals, i.e., kaolinite, smectite, nontronite, and chlorite. The overlapping features of these minerals make them difficult to identify, and according to the abundance of each mineral, the spectral properties of the raw materials are influenced, i.e., the reflectance values and the depth parameters of the absorption.
Spectra that are characterized by absorption features at 1400 nm and 1900 nm and a rounded absorption feature near 2240 nm due to molecular vibrations of the Si-OH group (Figure 7b) are typical for chalcedony [27]. The impurities observed through the microscopic study, which are responsible for the color of the artefact varying from brown to white, characterize the spectral properties in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. Sometimes, the spectra are differentiated displaying absorption features near 1000 nm attributed to spin-allowed crystal-field transitions due to the presence of metal cations, with a positive slope toward longer wavelengths. Some samples are not characterized by the rounded absorption feature at 2240 nm, implying the presence of a more crystalline variety of silica, i.e., quartz, rather than chalcedony. The absorption features at 1400 nm and 1900 nm correspond to molecular water H2O absorbed in crystal grains or incorporated into the silica framework [40].
Pumice artefacts have a light yellowish to beige color, rounded surfaces and high porosity. They comprise amorphous SiO2, and minor crystals of biotite which were observed through the microscopic study (Figure 7c). The spectral characteristics of some pumice artefacts have a nearly flat reflectance, displaying absorption features at 1900 nm as well as in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum at 400 nm. On the contrary, intense, distinguishable absorption features at 1900 and 2200 nm, indicating the presence of hydrous Al-rich minerals, characterize other pumice artefacts. The microscopic study verified the presence locally of altered areas, related to clay minerals, as indicated by the NIRS.
Furthermore, among the lithic artefacts, pebbles of volcanic origin were also studied, whose lithologic characteristics differ from one another, indicating their different chemical composition. Their color, sometimes reddish, while other times a light beige to dark gray color, in combination with their textural characteristics (presence or absence of porosity, shape and network of pores, mineral composition of phenocrysts and fine-grained groundmass, and the presence or absence of amorphous material) indicate different physicochemical conditions for the raw material, raising questions regarding their origin. The phenocrysts identified through microscopic observation are mainly minerals, including feldspars, especially plagioclase, as well as biotite, while the fine-grained groundmass consists of quartz, feldspars, and volcanic glass (amorphous SiO2).
Some artefacts are comprised of compact material, with a reddish to dark greyish color, indicating a geo-material that stands out from the local lithology of the island. Through microscopic analysis, we observed dark grey color areas forming spots locally, in the reddish material, whereas rarely, some artefacts had a dark gray color uniformly. The spectral characteristics of these samples displayed absorption features at 480 nm and 840 nm, as well as a steep, negative slope from 740 nm toward higher wavelengths. A not intense but broad absorption feature is also identified at 1830 nm (Figure 7d). The microscopic study as well as the spectroscopic analysis of the artefacts indicate the presence of hematite and diaspore in the mineralogy of the raw material, which are indicative mineralogical components of bauxite and meta-bauxite. Hematite (Fe2O3) is an iron oxide, common in many geologic environments, indicating oxidizing conditions. Diaspore is an Al-rich mineral (α-AlO(OH)), comprising the major component of bauxite, along with gibbsite and boehmite.
The absorption features observed through the application of NIRS, at the spectra of the green bead at 1390 nm, 1900 nm, 2080 nm, 2134 nm, 2174 nm, 2232 nm, 2320 nm, 2384 nm, and 2465 nm indicate the presence of talc in the raw material (Figure 7e). Talc is a hydrated magnesium silicate (Mg3Si4O10(OH)2), occurring as an alteration product of Mg-rich silicate minerals, e.g., olivine, pyroxene, and amphiboles. The broad absorption feature at 830 nm, as well as the positive slope of the reflectance spectra from approximately 1400 nm to 2000 nm, also indicate the presence of a Fe-rich mineral phase, the absorption features of which are probably overlapped from the absorption features of talc, hence it is difficult to be determined. However, a small absorption feature at 2290 nm is attributed to chlorite. The spectroscopic characteristics of the green bead, in contribution with the textural characteristics of the samples, indicate steatite as a raw material.
The other studied bead, similar in size with the aforementioned, has a nearly light grey color and the spectral characteristics of the sample indicate the presence of Al-rich minerals, due to the characteristic absorption features at 2190 nm, indicative of Al-OH molecular vibrations (Figure 7f). These spectral characteristics, in combination with the double absorption feature at 2343 nm and 2431 nm, are typical spectral signatures for mica minerals [27,41], i.e., muscovite, paragonite, lepidolite, phengite, etc. [42]. The wavelength position of the absorption feature at ~2200 nm is used to evaluate the compositional differentiation of these minerals. Paragonite and Al-rich white mica have absorption features smaller than 2195 nm [43], whereas muscovite’s absorption feature is located at approximately 2200 nm and phengite’s is at up to 2235 nm [44]. Due to the white color of this artefact as well as the diagnostic feature at 2190 nm, we can limit the composition of the raw material to paragonite or Al-rich white mica.
4.2. Petrographic and Mineralogical Analysis of Astypalaian Lithotypes
The rock samples considered in the present study were characterized through petrographic examination (Figure 8) and the mineralogical composition was determined through mineralogical analysis (Figure 9, Table 3).

Figure 8.
Representative photomicrographs of the studied samples: (a,b) sandstone specimens (samples AST6, AST7); (c) coarse-grained calcite crystals filling micro-veins in micritic limestone (sample AST25); (d) micritic limestone with the characteristic grumeleuse texture (sample AST13); (e) brecciated zones in coarse-grained limestone (sample AST26); (f) biomicrite comprising a variety of fossils and clastic fragments (sample AST9A2); (g) biosparite, comprising fossils and sparitic calcite (sample AST4B); (h) breccia lithotype characterized by subangular fragments, in fine-grained groundmass of quartz and feldspars (sample AST4A). Mineral abbreviations are according to [44]: calcite (cal); dolomite (dol); feldspars (fs); quartz (qz).
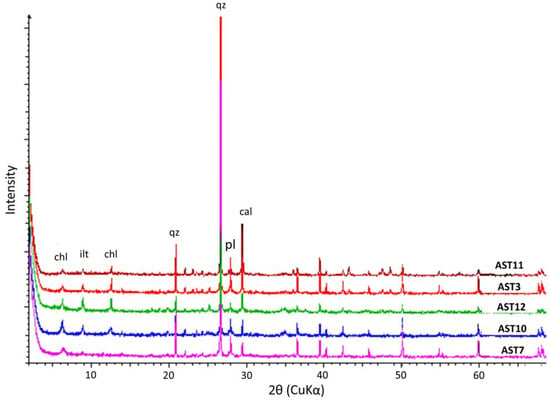
Figure 9.
Representative X-ray powder diffractograms of sandstones.Mineral abbreviations are according to [44]: calcite (cal); chlorite (chl); plagioclase (pl); illite (ilt); quartz (qz).

Table 3.
The mineralogy of the samples as resulted from the evaluation of the X-ray powder diffractograms. Mineral abbreviations are according to [44]: alkali-feldspars (afs); aragonite (arg); calcite (cal); chlorite (chl); dolomite (dol); illite (ilt); muscovite (ms); plagioclase (pl); quartz (qz).
The petrographic investigation of the sandstone specimens (samples AST3, AST5, AST6, AST7, AST10, AST24, AST28) obtained from Astypalaia revealed that they are moderate to poorly sorted, often characterized by a cataclastic texture. The samples include medium- to fine-grained particles, comprising sub-angular to sub-rounded grains of quartz and in less abundance feldspars (Figure 8a). Subhedral to anhedral calcite, as well as chlorite and illite, comprise the cementing material. Opaque minerals as well as clay minerals are rarely identified displaying higher abundance, observed even macroscopically through light to dark reddish areas (Figure 8b). Quartz is the most abundant minerals, forming either monocrystalline or polycrystalline constituents. The presence of polycrystalline grains, which are not fully separated, indicate small transportation, thus the immature nature of the specimens. The feldspars often display characteristic twinning and are altered to calcite or sericite, i.e., fine-grained mica. Tectonic processes due to diagenesis are imprinted in the textural characteristics of the samples, i.e., the undulose extinction of quartz, the fragmentation of the crystals, and the presence of foliation. Sometimes, the samples are also characterized by a net of micro-veins, filled with fine- to coarse-grained calcite. Patches of yellowish areas that were observed through the petrographic study are attributed to small cavities that are filled by clay minerals. Minor rock fragments that were also identified in some samples include sub-rounded and sub-angular mica schist and chert.
The textural characteristics of the samples, AST8, AST13, AST14, AST22A and AST25 indicate the abundance of calcite, varying in grain size. The samples are often characterized by the presence of micro-veins, filled with more coarse-grained calcite (200–750 μm), showing in general a specific orientation but irregularity in their thickness (Figure 8c). Samples AST8 and AST13 are characterized by the presence of a grumeleuse texture, i.e., micritic clots that are surrounded by microsparitic calcite (Figure 8d). A grumeleuse texture is typical for recrystallization processes, where coarser calcite crystals are developed against smaller crystals. Samples AST21 and AST27 have an orange-beige color and comprise large calcite grains (2–4 mm). As concluded from the mineralogical analysis, the sample AST26 consists of dolomite (Figure 8e), with calcite in trace amounts. Calcite and dolomite differentiation cannot be achieved only through petrographic study, thus the mineralogical analysis by means of XRPD made a decisive contribution. The sample consist of inequigranural polygonal calcite grains, with an almost isometric growth in size, indicating a well-crystallized, more cohesive geologic formation compared to the aforementioned. Furthermore, micro-brecciated zones are observed, imprinting the tectonic processes involved in the formation of the lithotype, where the fragmentation of calcite occur.
Samples AST9A1, AST9A2, and AST9B display channel-like porous, typical characteristic for loose, non-cohesive lithologies and comprise micritic calcite, bioclasts, and endoclasts (Figure 8f). The textural characteristics of the samples are indicative to biomicrites, coinciding to deposition in shallow hot water environments. The clastic fragments are in agreement with the lithologic formations of Astypalaia, comprising mostly mudstone and sandstone. In the mineralogical analysis of the samples, aragonite was also identified.
On the other hand, samples AST4B and AST15 comprise microsparitic calcite and bioclasts, indicating a fossiliferous origin typical for biosparites, differing though in the grain size of the carbonate constituents (Figure 8g). The structure of the lithotype is more cohesive and no porosity was observed macroscopically, or even microscopically. Furthermore, we also observed micro-zones filled with brecciated calcite, coinciding with the tectonic processes involved.
Sample AST16B represents a calcitic olistholith, abundant in euhedral to subhedral coarse-grained calcite crystals (250 μm–2 mm), in a fine-grained quartzitic groundmass. Samples AST4A and AST4C comprises fragments of carbonate rocks, sandstone and mudstone, quartzitic matrix, as well as calcite and minor clay mineral as cementing material, indicative for breccias (Figure 8h). The samples are moderate to poorly sorted, with sub-angular to sub-rounded constituents. The fragments are usually cracked and cut by micro-veins, rich in calcite and silicic material. Minor opaque minerals also occur alongside the cracks and the micro-veins. Quartz and feldspars are usually characterized by undulose extinction and fragmentation.
4.3. Preliminary Results on the Provenance of the Raw Materials
Our preliminary results for the main mineral raw materials are summarized in Table 4. The stone artefacts characterized as local are related to geo-materials whose lithological characteristics are consistent with the lithology of Astypalaia Island. These include sandstone, limestone/marble, marl, and shale.

Table 4.
Classification of the stone artefacts according to lithological characteristics of the raw material, in local and non-local.
Geo-materials characterized as non-local include chalcedony, bauxite/meta-bauxite, steatite, and mica (paragonite most probably), the closest to Astypalaia occurrences of which are illustrated in Figure 10.
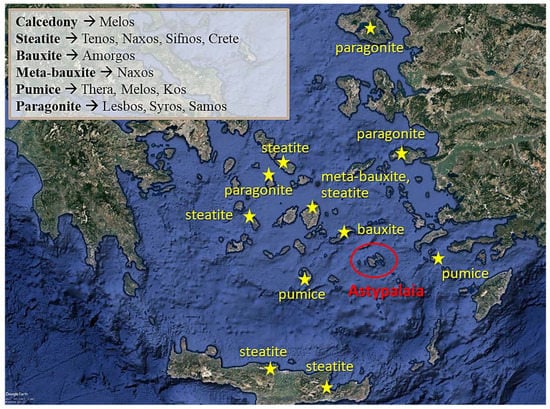
Figure 10.
Oblique satellite image (Google Earth Pro) of the islands in the Aegean Sea, with the main occurrences of chalcedony, steatite, bauxite, meta-bauxite, pumice, and paragonite.
Steatite, the so-called ‘soapstone’ due to its texture, is a magnesium-rich rock comprising mostly talc and to a lesser extent other minerals including amphiboles, chlorite and serpentine. The application of the NIRS at the steatite beads indicated the presence of talc, displaying the related characteristic absorption features at the spectra. In the Aegean Sea, steatite occurs at Tenos, Naxos, Sifnos, and Crete. According to [45], the mineralogical composition of steatite in Crete varies, exhibiting mineralogical heterogeneity, related to the complex geologic structure of the island and the associated host rocks. The main mineral phase comprises mostly of antigorite or tremolite, and other minerals related to the protolith. We can conclude that the origin of the steatite beads is not connected with the occurrences from Crete, due to the presence of talc, identified through the NIRS, thus most possibly the provenance of steatite is to be linked with Tenos, Naxos, or Sifnos.
Bauxites are sedimentary rocks which are characterized by the presence of Al-rich minerals, i.e., gibbsite [Al(OH)3], boehmite [γ-AlO(OH)], and diaspore [α-AlO(OH)], thus their high Al content. Bauxites that have undergone metamorphic processes, processes related to changes in the pressure and temperature that contribute to differentiation in the mineralogy and the textural characteristics of the rock, are called ‘meta-bauxites’, and such occurrences are extremely rare. In the Aegean Sea islands, bauxite occur at Amorgos, whereas meta-bauxites occur at Naxos [46].
On the other hand, chalcedony is a cryptocrystalline variety of silica, mainly consisting of quartz and moganite, i.e., fine-grained crystalline aggregates undiscernible even through microscopic study. Moganite is also a silica mineral comprised of SiO2, differing though in its crystalline structure, which is trigonal for quartz and monoclinic for moganite. The nearest to Astypalaia occurrence of chalcedony is located at Melos island [47].
Paragonite and white mica are typical minerals occurring in medium to low grade metamorphic environments. Even though these minerals participate in a variety of geologic formations in many islands of the Aegean Sea, the most known occurrences, especially of paragonite are located in the Lesbos [48], Syros [49], and Samos [50] islands.
Regarding the artefacts that are made of pumice, they are an interesting case since although pumice does not belong to the local lithology of the island, abundant cobbles of pumice along with volcanic rocks of varying chemical composition were found in large quantities in Gialoudi Bay (Figure 11) during surface research. In general, the eruptive products are highly influenced by the physicochemical properties of the erupting magma, concerning the chemical composition, viscosity, and gas contents, etc. Furthermore, their detailed study provides valuable information about the eruptive conditions of pre-existing volcanic activities or even contributes to addressing a possible future volcanic danger. The nearest to Astypalaia locations, known for their volcanic activity, are Thera, Melos, and Kos. The conditions of transportation of pyroclastic material at extremely long distances (tens of km) are studied by various researchers [51,52,53] and is still controversial.

Figure 11.
(a) View of Gialoudi bay towards the southeast; (b) Abundant pumice cobbles in the area of Gialoudi bay; (c) representative cobble of volcanic rock in the same area.
5. Conclusions
Non-invasive techniques, including use of a portable microscope and NIR spectroscopy, successfully helped us to evaluate the kind of the raw material that was used for the archaeological artefacts. The geochemical composition in the majority of the stone tools was compared to the available spectral library and successfully identified by the interpretation of the retrieved spectra. The local geo-materials include limestone, marl, sandstone, and shale. The variation on the spectral properties of the raw material, which consists of limestone, indicate the exploitation and extensive usage of similar lithologies relative to their mineralogical component from many and different sites in the island. Diagnostic absorption features in specific wavelength positions of the electromagnetic spectrum helped us to distinguish materials that indicate an allochonous nature, not compatible with the local lithologic formations of Astypalaia, including chalcedony, bauxite/meta-bauxite, steatite, and paragonite.
The materials of volcanic provenance pose a more intricate challenge: although they do not belong to the geological “profile” of Astypalaia, they are in a sense “local”, having been deposited in the area tens of thousands of years before the arrival of the people who used them. The study of volcanic pebbles from Gialoudi Bay and the search for similar locations of occurrences in other coastal areas of the island is still under research.
The majority of the artefacts collected during the 2011–2015 surveys at Vathy are made of locally available rocks. The larger and more numerous artefacts—discs, grinding slabs, the pebbles used for grinding/pounding—are of local origin, while the adze, beads (personal items), artefacts with geometric shape, and some of the sturdier pounders are of exogenous provenance. The inhabitants of Vathy in the FNL/EBA exploited both local (including the intrusive volcanic deposits at Gialoudi) and non-local raw materials, taking advantage of their properties according to the task at hand and following long-established practices. These initial results are indications that Astypalaia, although distanced, was not isolated even at these early times, and they encourage us to apply the process of geological recognition and NIRS analysis on the assemblage from the excavations as well.
It cannot be deduced, by surface finds alone, whether the exogenous materials were brought to Vathy as personal items of people from the Cyclades or whether they formed part of an exchange network that included obsidian and pottery as well. Nor can the affinities of a past society with specific areas be pin-pointed through laboratory analyses and scientific models alone, including the study of the quantitative and qualitative characteristics of the larger assemblage (to date some 750 artefacts and utensils have been recovered (E.A. personal communication). of ground tools and implements as it emerges from the on-going excavations at Vathy, and their comparison with similar assemblages from neighboring islands (E.A. has undertaken a comparative study from similar artefacts from Leros, Nissyros, and Rhodes.) will determine any similarities and/or differences.
Due to our interdisciplinary synergy, we are better prepared to understand the activities of the inhabitants of Vathy in the Early Bronze Age as these emerge from the ongoing excavations. The complexity of the features and structures that are being located (infant jar burials, petroglyphs, defensive structures [23], and the increasing number of ground stone artefacts [24] made on various materials) completely justify the analysis undertaken and described in the course of this paper.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.I. and M.K.; methodology, I.I. and M.K.; software, M.K.; validation, I.I., A.V., M.K. and E.A.; formal analysis, M.K.; investigation, I.I. and M.K.; resources, M.K.; data curation, M.K.; writing—original draft preparation, M.K.; writing—review and editing, M.K., I.I., A.V. and E.A.; visualization, M.K.; supervision, I.I. and A.V.; project administration, A.V. and I.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Biró, K.T. Non-destructive research in archaeology. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2005, 265, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.; Törnberg, A.; Törnberg, P. An Evolutionary Developmental Approach to Cultural Evolution. Curr. Anthropol. 2014, 55, 154–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintigh, K.; Altschul, J.; Beaudry, M.; Drennan, R.; Kinzig, A.; Kohler, T.; Limp, W.F.; Maschner, H.; Michener, W.; Pauketat, T.; et al. Grand Challenges for Archaeology. Am. Antiq. 2014, 79, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liritzis, I. Twelve thousand years of non-linear cultural evolution: The physics of chaos in Archaeology. Synesis J. Sci. Technol. Ethics Policy 2013, 4, G19–G31. [Google Scholar]
- Liritzis, I.; Laskaris, N.; Vafiadou, A.; Karapanagiotis, I.; Volonakis, P.; Papageorgopoulou, C.; Bratitsi, M. Archaeometry: An overview. Sci. Cult. 2020, 6, 49–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philokyprou, M. The initial appearance of ashlar stone in Cyprus. Issues of provenance and use. Mediterr. Archaeol. Archaeom. 2011, 2011, 37–53. [Google Scholar]
- Columbu, S.; Piras, G.; Sitzia, F.; Pagnotta, S.; Raneri, S.; Legnaioli, S.; Palleschi, V.; Lezzerini, M.; Giamello, M. Petrographic and mineralogical characterization of volcanic rocks and surface-depositions on Romanesque Monuments. Mediterr. Archaeol. Archaeom. 2018, 18, 37–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cau Ontiveros, M.A.; Martinez Farreras, V.; Pecci, A.; Mas Florit, C.; Fantuzzi, L. Archaeometric analysis for provenance and content of roman amphorae from the site of Sa Mesquida (Mallorca, Spain). Mediterr. Archaeol. Archaeom. 2018, 18, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glascock, M.D. A systematic approach to geochemical sourcing of obsidian artifacts. Sci. Cult. 2020, 6, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, C.; Iliopoulos, I. Ceramic technology, ethnic identification and multiethnic contacts: The archaeological example of the Cuyes river valley (Southeastern Ecuadorian highlands). J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2020, 33, 102557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulou, V.; Iliopoulos, I.; Liritzis, I. Characterizations techniques of clays for the archaeometric study of ancient ceramics: A review. Sci. Cult. 2020, 6, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarpelis, N. Silcrete and chert as source rocks of early prehistoric artifacts: The case of central Evia (Greece). Mediterr. Archaeol. Archaeom. 2021, 21, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, G.R. Spectral Signatures of Particulate Minerals in the Visible and near Infrared. Geophysics 1977, 42, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, S. Etruscan Fine Ware Pottery: Near-Infrared (NIR) Spectroscopy as a Tool for the Investigation of Clay Firing Temperature and Atmosphere. Minerals 2022, 12, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, T.; Yonenobu, H.; Tsuchikawa, S. Near-Infrared Spectroscopic Investigation of the Hydrothermal Degradation Mechanism ofWood as an Analogue of Archaeological Objects. Part I: Softwood. Appl. Spectrosc. 2008, 62, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtblau, D.; Strlič, M.; Trafela, T.; Kolar, J.; Ander, M. Determination of mechanical properties of historical paper based on NIR spectroscopy and chemometrics—A new instrument. Appl. Phys. 2008, 29, 19872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, J.K.; Thoury, M.; Zeibel, J.G.; Ricciardi, P.; Morales, K.M.; Dooley, K.A. Visible and infrared imaging spectroscopy of paintings and improved reflectography. Herit. Sci. 2016, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyaş, H.; Dirican, Μ.; Lütfi Süzen, Μ.; Türkmenoğlu, A.G.; Kolat, Ç.; Atakuman, Ç. Identification of possible source areas of stone raw materials combining remote sensing and petrography. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 3923–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachopoulos, A. Archaeological fieldwork at Vathy, Astypalaia, Dodona. History—Archaeology. MΓ-MΔ 2017, 2014, 371–411. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Vlachopoulos, A. Vathy, Astypalaia. Research and material studies in a diachronic palimpsest of Aegean Archaeology. Dodekan. Chron. Kθ Rhodes 2021, 2021, 83–131. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Tsigkas, G.; Sfikas, G.; Pasialis, A.; Vlachopoulos, A. Nikou, C. Markerless detection of ancient rock carvings in the wild: Rock art in Vathy, Astypalaia. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 135, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, Ε. Ground stone tools and utensils from the Vathy peninsula. The surface finds. In Vathy, Astypalaia. Ten Years of Research in a Diachronic Palimpsest of the Aegean (2011–2020); Vlachopoulos, A., Ed.; Hellenic Ministry of Culture: Athens, Greece; University of Ioannina: Ioannina, Greece; Melissa Publishing House: Athens, Greece, 2022; (In Greek; abstracts in English). [Google Scholar]
- Adam, E. Ground stone tools and utensils, finds. In Vathy, Astypalaia. Ten Years of Research in a Diachronic Palimpsest of the Aegean (2011–2022); Vlachopoulos, A., Ed.; Hellenic Ministry of Culture: Athens, Greece; University of Ioannina: Ioannina, Greece; Melissa Publishing House: Athens, Greece, 2022; (In Greek; abstracts in English). [Google Scholar]
- Metaxas, O. The chipped stone assemblage from the field survey of Vathy, Astypalaia. In Vathy, Astypalaia. Ten Years of Research in a Diachronic Palimpsest of the Aegean (2011–2022); Vlachopoulos, A., Ed.; Hellenic Ministry of Culture: Athens, Greece; University of Ioannina: Ioannina, Greece; Melissa Publishing House: Athens, Greece, 2022; (In Greek; abstracts in English). [Google Scholar]
- Vlachopoulos, A.; Angelopoulou, A. Early Cycladic Figurines from Vathy, Astypalaia. In Early Cycladic Sculpture in Context from Beyond the Cyclades: Mainland Greece, the North and East Aegean; Marthari, M., Renfrew, C., Boyd, M., Eds.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 202–226. [Google Scholar]
- Iliopoulos, I.; Kokkaliari, M. Accessing provenance issues of prehistoric stone artefacts from Vathy (Astypalaia, Greece) through the minero-petrographic characterization of local lithologies. In Vathy, Astypalaia. Ten Years of Research in a Diachronic Palimpsest of the Aegean, (2011–2022); Vlachopoulos, A., Ed.; Hellenic Ministry of Culture: Athens, Greece; University of Ioannina: Ioannina, Greece; Melissa Publishing House: Athens, Greece, 2022; (In Greek; abstracts in English). [Google Scholar]
- Clark, R.N.; King, T.V.; Klejwa, M.; Swayze, G.A.; Vergo, N. High spectral resolution reflectance spectroscopy of minerals. J. Geophys. Res. 1990, 95, 12653–12680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, G. About the geology of Astypalaia Island. Sci. Yearb. Issued Fac. Nat. Math. Sci. 1966, 10, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Marnelis, P.; Bonneau, M. Stratigraphie et structure de l’Île d’Astypalea (Dodécanèse, Grèce). In VI. Colloquium on the Geology of the Aegean Region; Kallergis, G., Ed.; 6th Aegeiscollathens; Institute of Geological and Mining Research: Yaoundé, Cameroon, 1977; Volume 1, pp. 323–332. [Google Scholar]
- Ring, U. Structure and deformation history of Astypalea island, Aegean Sea. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2001, 34, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouga, A. The Effect of Volcanic Ash Sedimentation and Dispersion at the Present and Modern Marine Sediments of Kos, Nissyros and Astypalea Islands (SE Volcanic Arc), Aegean Sea, Greece. Ph.D. Dissertation, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chatzaras, V. Geotraverse across the Hellenides between Western Crete and the Cycladic Islands. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Patras, Patras, Greece, 2010; 206p. [Google Scholar]
- Papoulia, M.; Karymbalis, E.; Gaki-Papanastassiou, K.; Maroukian, H. Assessment of the susceptibility of the coast of Astypalea Island (SE Aegean Sea) to sea-level rise. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2013, 47, 305–314. [Google Scholar]
- IGME. Geological Map of Greece 1986, 1:50000; Astipalaia Sheet; IGME: Athens, Greece, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, R.N. Spectroscopy of rocks and minerals, and principles of spectroscopy. In Remote Sensing for Earth Sciences—Manual of Remote Sensing, 3rd ed.; Renz, A.N., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 3–58. [Google Scholar]
- Gaffey, S.J. Spectral reflectance of carbonate minerals in the visible and near infra-red (0.35–2.55 microns): Calcite, aragonite, and dolomite. Am. Mineral. 1986, 71, 151–162. [Google Scholar]
- Crowley, J.K. Visible and near-infrared spectra of carbonate rocks-reflectance variations related to petrographic texture and impurities. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 5001–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aines, R.D.; Rossman, G.R. Water in minerals? A peak in the infrared. J. Geophys. Res. 1984, 89, 4059–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.N.; Swayze, G.A.; Wise, R.; Livo, E.; Hoefen, T.; Kokaly, R.; Sutley, S.J. USGS Digital Spectral Library splib06a; Digital Data Series; U.S. Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 2007; p. 231.
- Rice, M.S.; Cloutis, E.A.; Bell, J.F., III; Bish, D.L.; Horgan, B.H.; Mertzman, S.A.; Craig, M.A.; Renaut, R.W.; Gautason, B. Mountain, B. Reflectance spectra diversity of silica-rich materials: Sensitivity to environment and implications for detections on Mars. Icarus 2013, 223, 499–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doublier, M.P.; Roache, A.; Potel, S. Application of SWIR Spectroscopy in very low-grade metamorphic environments: A comparison with XRD methods. Geol. Surv. West. Aust. 2010, 61, 2992. [Google Scholar]
- Fleet, M.E.; Deer, W.A.; Howie, R.A.; Zussman, J. Rock-Forming Minerals: Micas, 2nd ed.; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Doublier, M.P.; Roache, T.; Potel, S. Short-wavelength infrared spectroscopy: A new petrological tool in low-grade to very low-grade pelites. Geology 2010, 38, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, L.; Evans, W. Abbreviations for names of rock forming minerals. Am. Mineral. 2010, 3, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.E.; Kilikoglou, V.; Olive, V.; Bassiakos, Y.; Ellam, R.; Bray, I.S.J.; Sanderson, D.C.W. A new protocol for the chemical characterisation of steatite—Two case studies in Europe: The Shetland Islands and Crete. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2007, 34, 626–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, H.; Mondillo, N.; Boni, M.; Thorne, R.; Tavlan, M. Bauxite and nickel-cobalt lateritic deposits of the Tethyan belt. Bauxite. Soc. Econ. Geol. 2016, 19, 349–387. [Google Scholar]
- Papavasiliou, K.; Voudouris, P.; Kanellopoulos, C.; Alfieris, D.; Xydous, S. Mineralogy and Geochemistry of the Triades-Galana Pb-Zn-Ag-Au intermediate-high sulfidation epithermal deposit, Milos island, Greece. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2016, 50, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzipanagiotou, K.; Tsikouras, B.; Migiros, G.; Gartzos, E.; Serelis, K. Origin of rodingites in ultramafic rocks from Lesvos island (NE Aegean, Greece). Ofioliti 2003, 28, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Seck, H.A.; Koetz, J.; Okrusch, M.; Seidel, E.; Stosch, H.G. Geochemistry of a meta-ophiolite suite; an associated metagabbros, eclogites and glaucophanites on the island of Syros, Greece. Eur. J. Mineral. 1996, 8, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ockenga, E.; Yalçin, Ü.; Medenbach, O.; Schreyer, W. Zincohögbomite, a new mineral from eastern Aegean metabauxites. Eur. J. Mineral. 1998, 10, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.R.; Cas, R.A.F. Transport of pyroclastic flows across the sea during the explosive, rhyolitic eruption of the Kos Plateau Tuff, Greece. Bull. Volcanol. 2001, 62, 41–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufek, J.; Bergantz, G.W. Dynamics and deposits generated by the Kos Plateau Tuff eruption: Controls of basal particle loss on pyroclastic flow transport. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2007, 8, Q12007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufek, J.; Manga, M.; Staedter, M. Littoral blasts: Pumice-water heat transfer and the conditions for steam explosions when pyroclastic flows enter the ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earths 2007, 112, B11201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).