Safety and Efficacy of Bilateral Tubeless Supine Mini-Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy for the Management of Bilateral Renal Calculi in Renal Failure Patients
Abstract
1. Background
2. Material and Methods
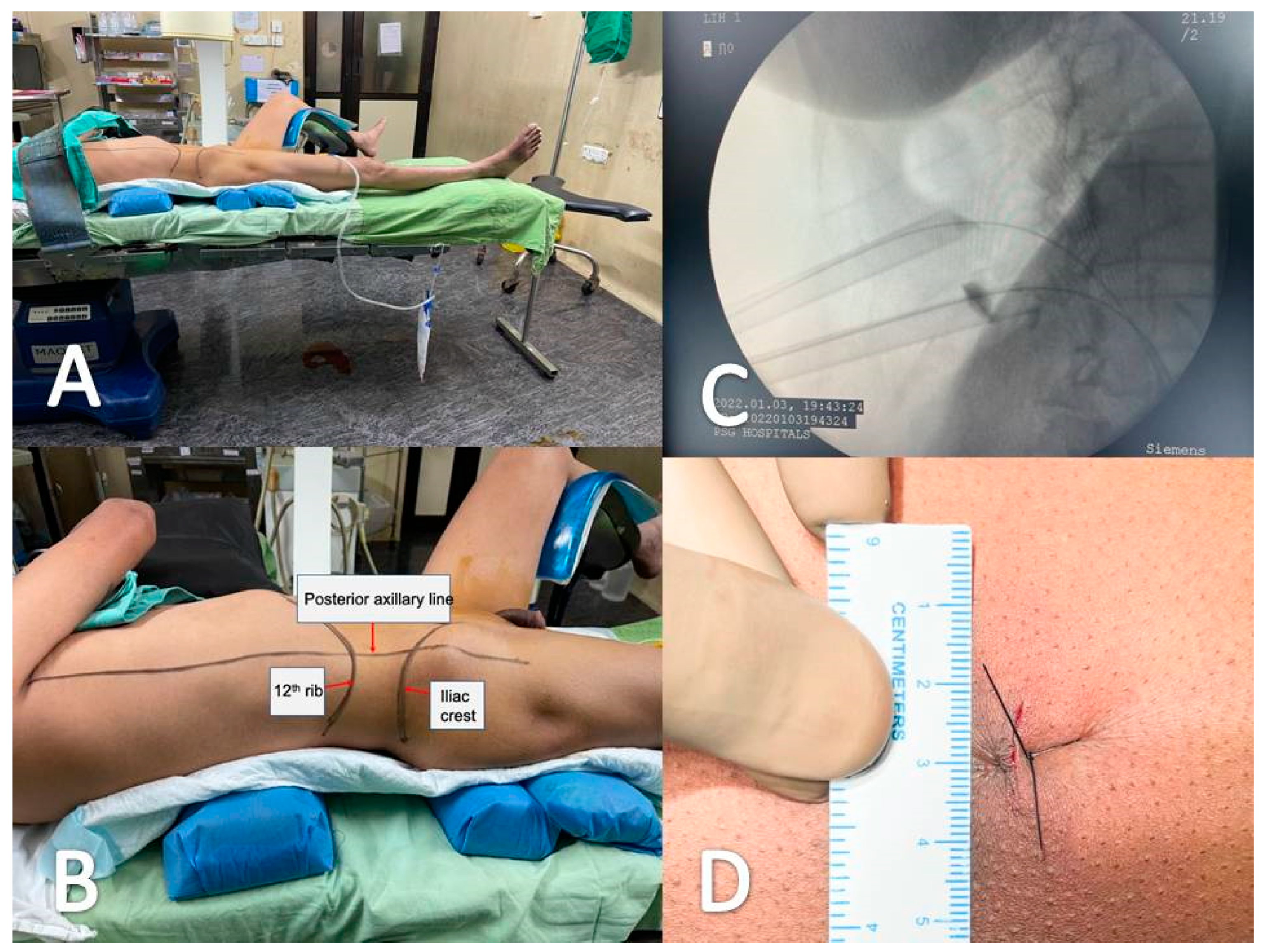
2.1. Supine Mini-PCNL Technique
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Ferraro, P.M.; Taylor, E.N.; Gambaro, G.; Curhan, G.C. Dietary and Lifestyle Risk Factors Associated with Incident Kidney Stones in Men and Women. J. Urol. 2017, 198, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez, A.; Torrecilla, C.; Colom, S.; Cuadrado, J.M.; Fernández-Concha, J.; Riera, L.; Vigués, F. Simultaneous bilateral percutaneous nephrolithotomy: Effectiveness and safety. Actas Urol. Esp. 2018, 42, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Lieske, J.C. Acute and chronic kidney injury in nephrolithiasis. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2014, 23, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pillai, S.; Mishra, D.; Sharma, P.; Venkatesh, G.; Chawla, A.; Hegde, P.; Thomas, J. Tubeless simultaneous bilateral percutaneous neph-rolithotomy: Safety, feasibility and efficacy in an Indian setting. Int. J. Urol. 2014, 21, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.; Dhliwayo, B.; Rai, B.P.; Mokete, M.; Amitharaj, R.; Aboumarzouk, O.M.; Somani, B.K. Safety, Feasibility, and Efficacy of Bilateral Synchronous Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy for Bilateral Stone Disease: Evidence from a Systematic Review. J. Endourol. 2017, 31, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackman, S.V.; Hedican, S.P.; Peters, C.A.; Docimo, S.G. Percutaneous nephrolithotomy in infants and preschool age children: Experience with a new technique. Urology 1998, 52, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabnis, R.B.; Jagtap, J.; Mishra, S.; Desai, M. Treating renal calculi 1-2 cm in diameter with minipercutaneous or retrograde intrarenal surgery: A prospective comparative study. BJU Int. 2012, 110, E346–E349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Rosette, J.J.; Opondo, D.; Daels, F.P.; Giusti, G.; Serrano, A.; Kandasami, S.V.; Wolf, J.S.; Grabe, M.; Gravas, S. Categorisation of complications and validation of the Clavien score for percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernstorm, I.; Johansson, B. Percutaneous pyelolithotomy. A new extraction technique. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 1976, 10, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.P.; Mishra, S.; Suryawanshi, M.; Seth, A.; Kumar, R. Comparison of standard with tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomy. J. Endourol. 2008, 22, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferakis, N.; Stavropoulos, M. Mini percutaneous nephrolithotomy in the treatment of renal and upper ureteral stones: Lessons learned from a review of the literature. Urol. Ann. 2015, 7, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traxer, O.; Smith, T.G., 3rd; Pearle, M.S.; Corwin, T.S.; Saboorian, H.; Cadeddu, J.A. Renal parenchymal injury after standard and mini percutaneous nephrostolithotomy. J. Urol. 2001, 165, 1693–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghamir, S.M.; Hosseini, S.R.; Gooran, S.J. Totally tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomy. J. Endourol. 2004, 18, 647–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellman, G.C.; Davidoff, R.; Candela, J.; Gerspach, J.; Kurtz, S.; Stout, L. Tubeless percutaneous renal surgery. J. Urol. 1997, 157, 1578–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Guo, X.; Niu, G.; Wang, Y. Advantages of tubeless mini-percutaneous nephrolithotomy in the treatment of preschool children under 3years old. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2015, 50, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Nahas, A.R.; Shokeir, A.A.; El-Assmy, A.M.; Mohsen, T.; Shoma, A.M.; Eraky, I.; El-Kenawy, M.R.; El-Kappany, H.A. Post-percutaneous nephrolithotomy extensive hemorrhage: A study of risk factors. J. Urol. 2007, 177, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, C.; Desai, M.; Häcker, A.; Hakenberg, O.W.; Liatsikos, E.; Nagele, U.; Tolley, D. Incidence, prevention, and management of complications following percutaneous nephrolitholapaxy. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurien, A.; Baishya, R.; Mishra, S.; Ganpule, A.; Muthu, V.; Sabnis, R.; Desai, M. The impact of percutaneous nephrolithotomy in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Endourol. 2009, 23, 1403–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Singh, U.P.; Sureka, S.K.; Madhavan, K.; Raj, A.; Ansari, M.S.; Kapoor, R. Safety and outcome of percutaneous nephrolithotomy in patients with solitary kidney: A tertiary care center experience. Indian J. Urol. 2019, 35, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proietti, S.; Sortino, G.; Giannantoni, A.; Sofer, M.; Peschechera, R.; Luciani, L.G.; Morgia, G.; Giusti, G. Single-session supine bilateral percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Urology 2015, 85, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofer, M.; Giusti, G.; Proietti, S.; Mintz, I.; Kabha, M.; Matzkin, H.; Aviram, G. Upper calyx approachability through a lower calyx access for prone versus supine percutaneous nephrolithotomy. J. Urol. 2016, 195, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontos, S.; Smyth, N.; Papatsoris, A.; Nalagatla, S.K. Upper pole infra costal access for supine percutaneous nephrolithotomy:Advantage or risk? Hell. Urol. 2020, 32, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoznek, A.; Ouzaid, I.; Gettman, M.; Rode, J.; De La Taille, A.; Salomon, L.; Abbou, C.-C. Fluorosopy-guided renal access in supine percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Urology 2011, 78, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total patients | 27 |
| Mean age (years) | 45.9 |
| Male–female ratio | 16:11 |
| Mean stone size (cm) | 2.4 ± 0.4 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 24.5 ± 2.8 |
| Comorbidities | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 16 |
| Systemic hypertension | 9 |
| Heart disease | 6 |
| COPD | 8 |
| Mean operative time | 75 min |
| Mean hospitalization time in days | 3.7 days |
| Access | |
| Single | 46 |
| Multiple | 6 |
| Auxiliary procedures | 2 |
| Stone clearance rate | 92.5% |
| Post-operative complications based on CROES validation of Clavien scores n (%) | |
| Grade 1 | 3 (11.1) |
| Grade 2 | 8 (29.6) |
| Grade 4 A | 2 (7.4) |
| Hemoglobin [Hb] Status | |
|---|---|
| Mean pre-operative Hb % (mean ± SD) | 11.95 ± 1.2 |
| Mean post-operative Hb % (mean ± SD) | 10.67 ± 1.5 |
| Mean drop in post-operative Hb % (mean ± SD) | 1.28 ± 0.77 |
| Packed red cell transfusion rate (n) | 4 |
| Mean drop in post-operative Hb % (mean ± SD) if operative time < 90 min | 2.5 ± 0.75 |
| Mean drop in post-operative Hb % (mean ± SD) if operative time > 90 min | 1.06 ± 0.55 |
| p value < 0.001 | |
| Mean serum creatinine (n = 27) | Baseline (mean ± SD) | 2.78 ± 0.57 |
| Immediately post operative (mean ± SD) | 3.20 ± 0.89 | |
| At 1 month post operative (mean ± SD) | 1.70 ± 0.41 | |
| Mean serum creatinine of patients requiring transient dialysis in post-operative period (n = 2) | Baseline (mean ± SD) | 3.40 ± 0.28 |
| Immediately post-operative (mean ± SD) | 5.60 ± 0.28 | |
| At 1 month post-operative (mean ± SD) | 1.9 ± 0.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murugan Ponnuswamy, P.; Iyyan Arumugam, B.; Siddarth Rajagopal, S.V.; Boopathy Vijayaraghavan, K.M. Safety and Efficacy of Bilateral Tubeless Supine Mini-Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy for the Management of Bilateral Renal Calculi in Renal Failure Patients. Soc. Int. Urol. J. 2024, 5, 56-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/siuj5010011
Murugan Ponnuswamy P, Iyyan Arumugam B, Siddarth Rajagopal SV, Boopathy Vijayaraghavan KM. Safety and Efficacy of Bilateral Tubeless Supine Mini-Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy for the Management of Bilateral Renal Calculi in Renal Failure Patients. Société Internationale d’Urologie Journal. 2024; 5(1):56-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/siuj5010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurugan Ponnuswamy, Puvai, Bhalaguru Iyyan Arumugam, Shree Vishnu Siddarth Rajagopal, and Krishna Mohan Boopathy Vijayaraghavan. 2024. "Safety and Efficacy of Bilateral Tubeless Supine Mini-Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy for the Management of Bilateral Renal Calculi in Renal Failure Patients" Société Internationale d’Urologie Journal 5, no. 1: 56-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/siuj5010011
APA StyleMurugan Ponnuswamy, P., Iyyan Arumugam, B., Siddarth Rajagopal, S. V., & Boopathy Vijayaraghavan, K. M. (2024). Safety and Efficacy of Bilateral Tubeless Supine Mini-Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy for the Management of Bilateral Renal Calculi in Renal Failure Patients. Société Internationale d’Urologie Journal, 5(1), 56-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/siuj5010011





