Prostate Cancer Detection by Novice Micro-Ultrasound Users Enrolled in a Training Program
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Micro-Ultrasound Guided Biopsy
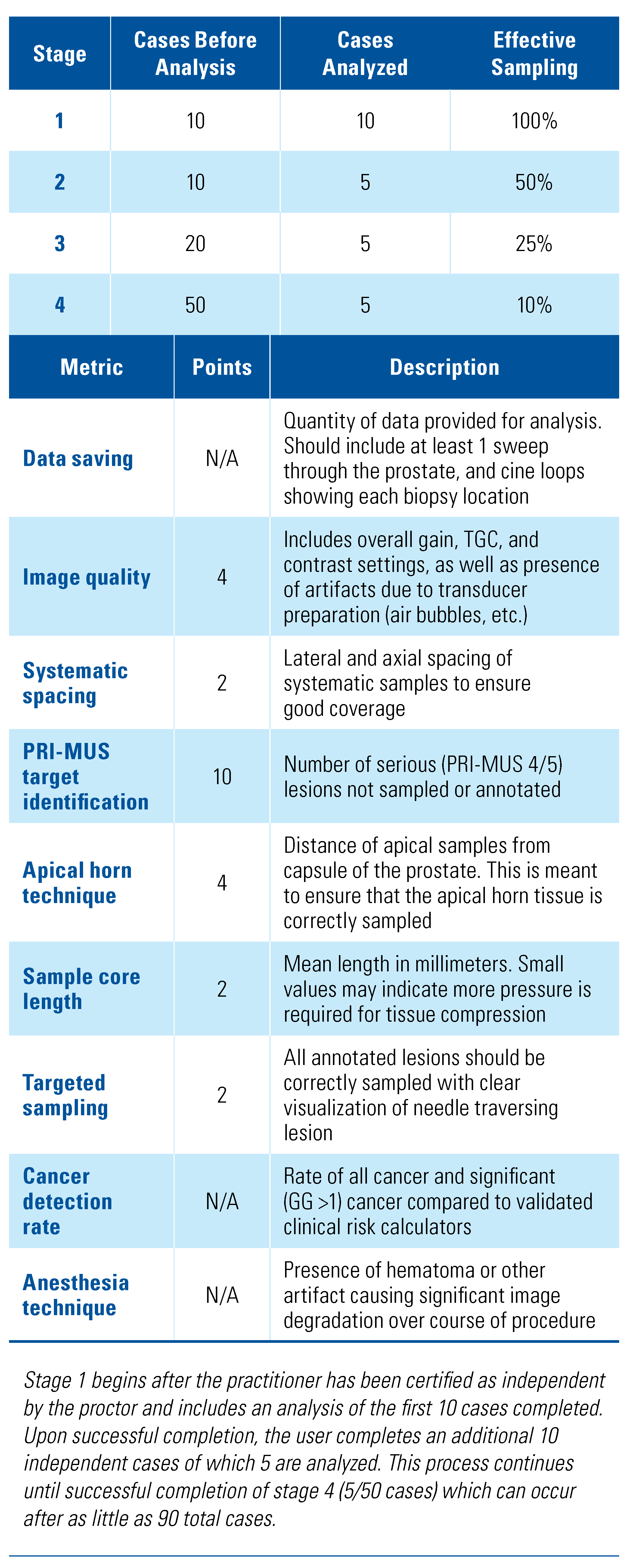
2.2. Training Program
2.3. Feedback Metrics
2.4. Statistical Analysis
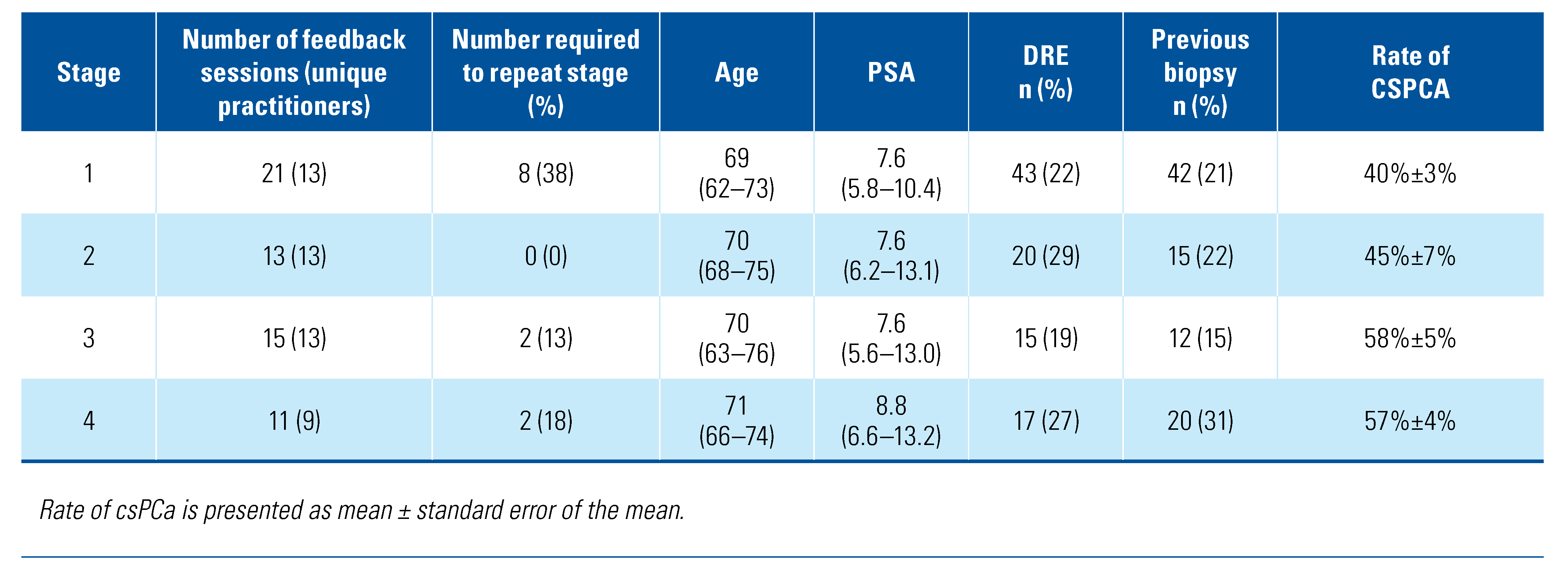
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roehl, A.K.; Antenor, J.A.V.; Catalona, W.J. Serial biopsy results in prostate cancer screening study. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 2435–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriole, G.L.; Catalona, W.J. The diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer. Annu. Rev. Med. 1991, 42, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovich, C.; Hyndman, M.E.; Eure, G.; Ghai, S.; Fradet, V. A Multi-institutional randomized controlled trial comparing novel first generation high-resolution micro-ultrasound with conventional frequency ultrasound for transrectal prostate biopsy. J. Urol. 2019, 201 (Supplement 4), e394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghai, S.; Eure, G.; Fradet, V.; Hyndman, M.E.; McGrath, T.; Wodlinger, B.; et al. Assessing cancer risk on novel 29 mhz micro-ultrasound images of the prostate: Creation of the micro-ultrasound protocol for prostate risk identification. J. Urol. 2016, 196, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovich, C.P.; Hyndman, M.E.; Eure, G.; Ghai, S.; Caumartin, Y.; Herget, E.; et al. A multi-institutional randomized controlled trial comparing first-generation transrectal high-resolution micro-ultrasound with conventional frequency transrectal ultrasound for prostate biopsy. BJUI Compass. 2021, 2, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luger, F.; Gusenleitner, A.; Kaar, J.; Mayr, C.; Loidl, W. Does 29Mhz micro-ultrasound provide uniform diagnostic accuracy within and beyond the peripheral zone? Ann. Urol. Nephrol. 2019, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 7Lughezzani, G.; Saita, A.; Lazzeri, M.; Paciotti, M.; Maffei, D.; Lista, G.; et al. Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of micro-ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging/ultrasound fusion targeted biopsies for the diagnosis of clinically significant prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 2, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouassaly, R.; Klein, E.A.; El-Shefai, A.; Stephenson, A. Impact of using 29 MHz high-resolution micro-ultrasound in real-time targeting of transrectal prostate biopsies: Initial experience. World J. Urol. 2019, 0123456789, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovich, C.P.; Cornish, T.C.; Mullins, J.K.; Fradin, J.; Mettee, L.Z.; Connor, J.T.; et al. High-resolution transrectal ultrasound: Pilot study of a novel technique for imaging clinically localized prostate cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2014, 32, 34–e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Socarrás, M.E.; Gomez Rivas, J.; Cuadros Rivera, V.; Reinoso Elbers, J.; Llanes González, L.; Mercado, I.M.; et al. Prostate mapping for cancer diagnosis: The Madrid Protocol. Transperineal prostate biopsies using mpMRI fusion and micro-ultrasound guided biopsies. J. Urol. 2020, 204, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornud, F.; Lefevre, A.; Flam, T.; Dumonceau, O.; Galiano, M.; Soyer, P.; et al. MRI-directed high-frequency (29MhZ) TRUS-guided biopsies: Initial results of a single-center study. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4838–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claros, O.R.; Tourinho-Barbosa, R.R.; Fregeville, A.; Gallardo, A.C.; Muttin, F.; Carneiro, A.; et al. Comparison of initial experience with transrectal magnetic resonance imaging cognitive guided micro-ultrasound biopsies versus established transperineal robotic ultrasound magnetic resonance imaging fusion biopsies for prostate cancer. J. Urol. 2020, 203, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, M.; Pavlovich, C.; Eure, G.; Fradet, V.; Ghai, S. Prospective validation of PRI-MUSTM, the Prostate Risk Identification using Micro-Ultrasound protocol for real-time detection of prostate cancer using high-resolution micro-ultrasound imaging. J. Urol. 2018, 199 (Suppl. S4), e733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasivisvanathan, V.; Rannikko, A.S.; Borghi, M.; Panebianco, V.; Mynderse, L.A.; Vaarala, M.H.; et al. MRI-targeted or standard biopsy for prostate-cancer diagnosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankerst, D.P.; Straubinger, J.; Selig, K.; Guerrios, L.; De Hoedt, A.; Hernandez, J.; et al. A contemporary prostate biopsy risk calculator based on multiple heterogeneous cohorts. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjørve, K.M.C.; Tjørve, E. The use of Gompertz models in growth analyses, and new Gompertz-model approach: An addition to the Unified-Richards family. Merks RMH, ed. PLoS ONE. 2017, 12, e0178691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rooij, M.; Israël, B.; Tummers, M.; Ahmed, H.U.; Barrett, T.; Giganti, F.; et al. ESUR/ESUI consensus statements on multi-parametric MRI for the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer: Quality requirements for image acquisition, interpretation and radiologists’ training. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 5404–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, O.; Riedl, C.C.; Ishill, N.M.; Moskowitz, C.S.; Zhang, J.; Hricak, H. Interactive dedicated training curriculum improves accuracy in the interpretation of MR imaging of prostate cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2010, 20, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Ayoola, A.; Hoffman, D.; Khasgiwala, A.; Prabhu, V.; Smereka, P.; et al. The learning curve in prostate MRI interpretation: Self-directed learning versus continual reader feedback. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 208, W92–W100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Huang, R.; Deng, F.-M.; Wysock, J.S.; Bjurlin, M.A.; et al. The institutional learning curve of magnetic resonance imaging-ultrasound fusion targeted prostate biopsy: Temporal improvements in cancer detection in 4 years. J. Urol. 2018, 200, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calio, B.; Sidana, A.; Sugano, D.; Gaur, S.; Jain, A.; Maruf, M.; et al. Changes in prostate cancer detection rate of MRI-TRUS fusion vs. systematic biopsy over time: Evidence of a learning curve. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2017, 20, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasabwala, K.; Patel, N.; Cricco-Lizza, E.; Shimpi, A.A.; Weng, S.; Buchmann, R.M.; et al. The learning curve for magnetic resonance imaging/ultrasound fusion-guided prostate biopsy. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 2, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porpiglia, F.; Cossu, M.; De Luca, S.; Manfredi, M.; Mele, F.; Bertolo, R.; et al. MP77-04 The role of the operator in the cancer detection with mri/trus fusion transrectal prostate biopsy. J. Urol. 2018, 199 (Suppl. 4), e1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]


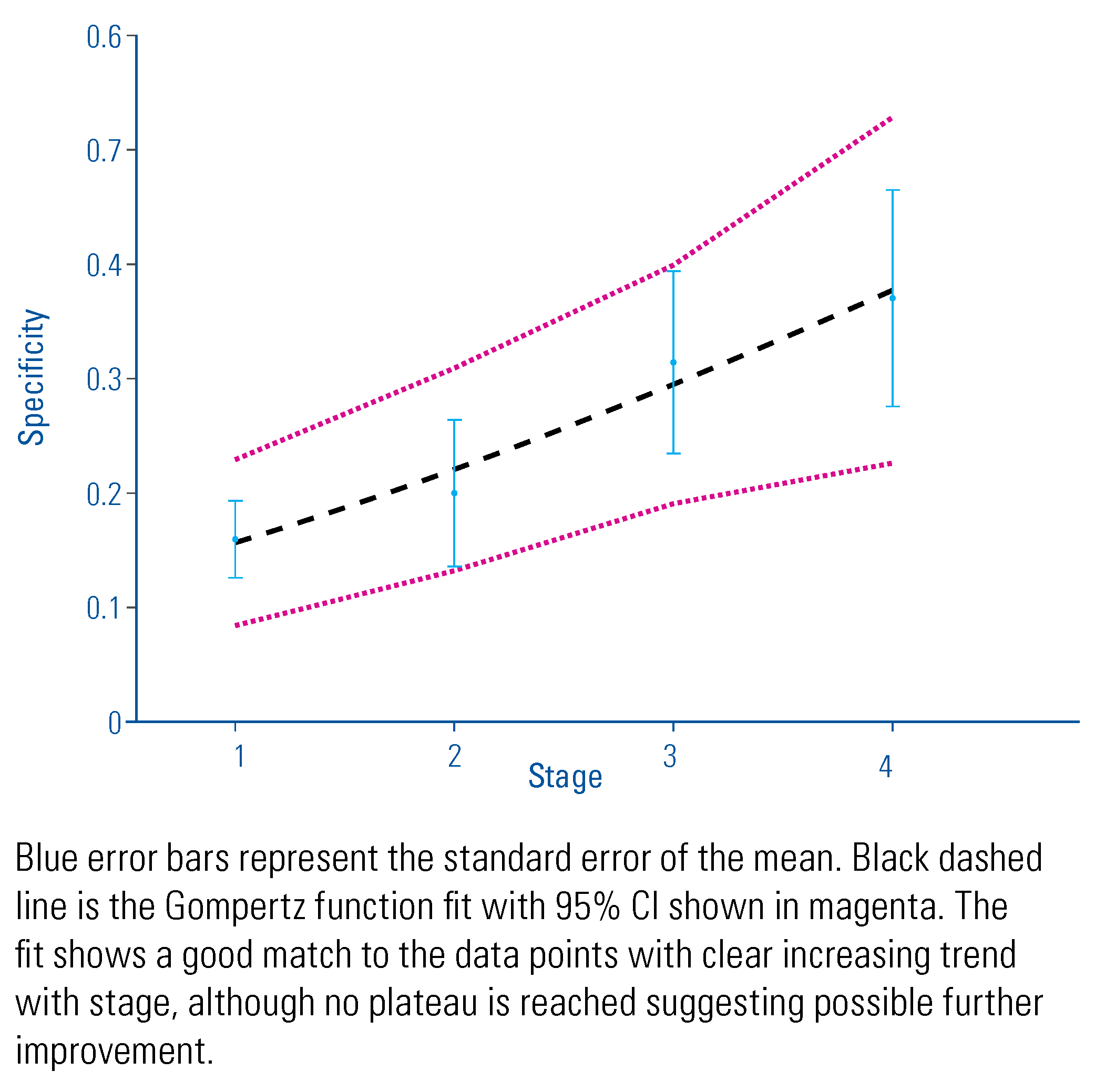

This is an open access article under the terms of a license that permits non-commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. © 2022 The Authors. Société Internationale d'Urologie Journal, published by the Société Internationale d'Urologie, Canada.
Share and Cite
Cash, H.; Hofbauer, S.L.; Shore, N.; Pavlovich, C.P.; Bulang, S.; Schostak, M.; Planken, E.; Jaspars, J.J.; Luger, F.; Klotz, L.; et al. Prostate Cancer Detection by Novice Micro-Ultrasound Users Enrolled in a Training Program. Soc. Int. Urol. J. 2022, 3, 62-68. https://doi.org/10.48083/KKVJ7280
Cash H, Hofbauer SL, Shore N, Pavlovich CP, Bulang S, Schostak M, Planken E, Jaspars JJ, Luger F, Klotz L, et al. Prostate Cancer Detection by Novice Micro-Ultrasound Users Enrolled in a Training Program. Société Internationale d’Urologie Journal. 2022; 3(2):62-68. https://doi.org/10.48083/KKVJ7280
Chicago/Turabian StyleCash, Hannes, Sebastian L. Hofbauer, Neal Shore, Christian P. Pavlovich, Stephan Bulang, Martin Schostak, Erik Planken, Joris J. Jaspars, Ferdinand Luger, Laurence Klotz, and et al. 2022. "Prostate Cancer Detection by Novice Micro-Ultrasound Users Enrolled in a Training Program" Société Internationale d’Urologie Journal 3, no. 2: 62-68. https://doi.org/10.48083/KKVJ7280
APA StyleCash, H., Hofbauer, S. L., Shore, N., Pavlovich, C. P., Bulang, S., Schostak, M., Planken, E., Jaspars, J. J., Luger, F., Klotz, L., & Salomon, G. (2022). Prostate Cancer Detection by Novice Micro-Ultrasound Users Enrolled in a Training Program. Société Internationale d’Urologie Journal, 3(2), 62-68. https://doi.org/10.48083/KKVJ7280




