Abstract
Prostate cancer (PCa) can be highly heterogeneous and multifocal, and accurate assessment of the volume, grade, and stage of PCa in situ is not a simple task. Urine has been investigated as a source of PCa biomarkers for over 70 years, and there is now strong evidence that analysis of urine could provide more accurate diagnosis and a better risk stratification that could aid clinical decisions regarding disease surveillance and treatment. Urine diagnostics is a developing area, moving towards multi-omic biomarker integration for improved diagnostic performance. Urine tests developed by strong collaborations between scientists and clinicians have the potential to provide targeted and meaningful data that can guide treatment and improve men’s lives.
1. Introduction: Urine as a Source of Prostate Cancer Biomarkers
Prostate cancers (PCa) can be highly heterogeneous[1,2] and multifocal[2,3]. Accurate assessment of the volume, grade, and stage of prostate cancer in situ is not a simple task. Significant amounts of biopsy results can be upgraded or downgraded on prostatectomy analysis[4,5]. Multi-parametric MRI has improved enormously but has inter-operator inconsistencies[6], can miss significant cancers (Gleason > 4), and has a false positive rate of around 50%[7]. Urine has been investigated as a source of PCa biomarkers for over 70 years[8,9,10], and there is now strong evidence that urine analysis could provide a better assessment of disease diagnosis and prognosis that could aid clinical decisions regarding disease surveillance and treatment.
Prostatic secretions make up 30% of the volume of semen, and its composition can reflect pre-neoplastic or malignant changes[11]. The prostate is continually secreting, and these secretions flow from all areas of the prostate where PCa is found[12,13]. These secretions flow into the urethra whence they are flushed out of the body on urination[12]. When a cancer is present, tiny bits of tumour (cells, extracellular vesicles, and molecules) can also be carried in the secretions and these can be detected in urine[8,9]. Urine is advantageous as a source for liquid biopsy because it can be collected at low cost, is completely non-invasively, and has the potential to sample all secretory areas of the prostate at the same time.
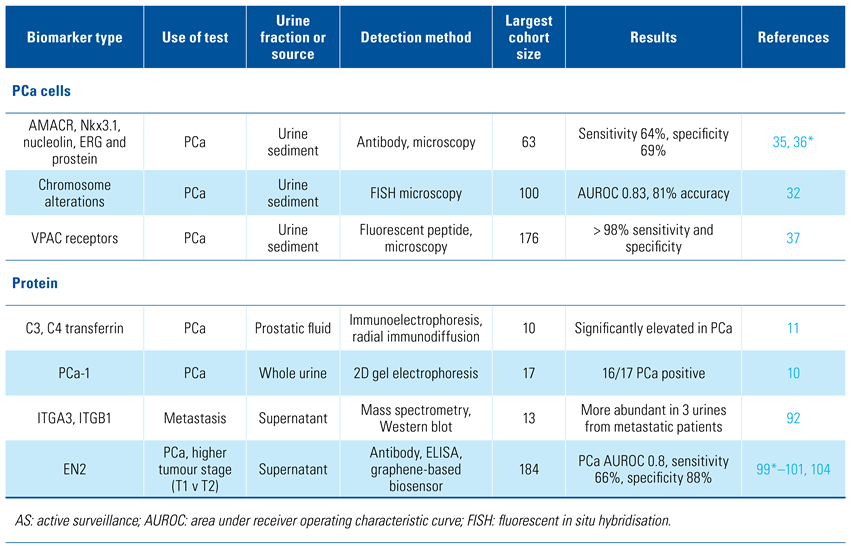
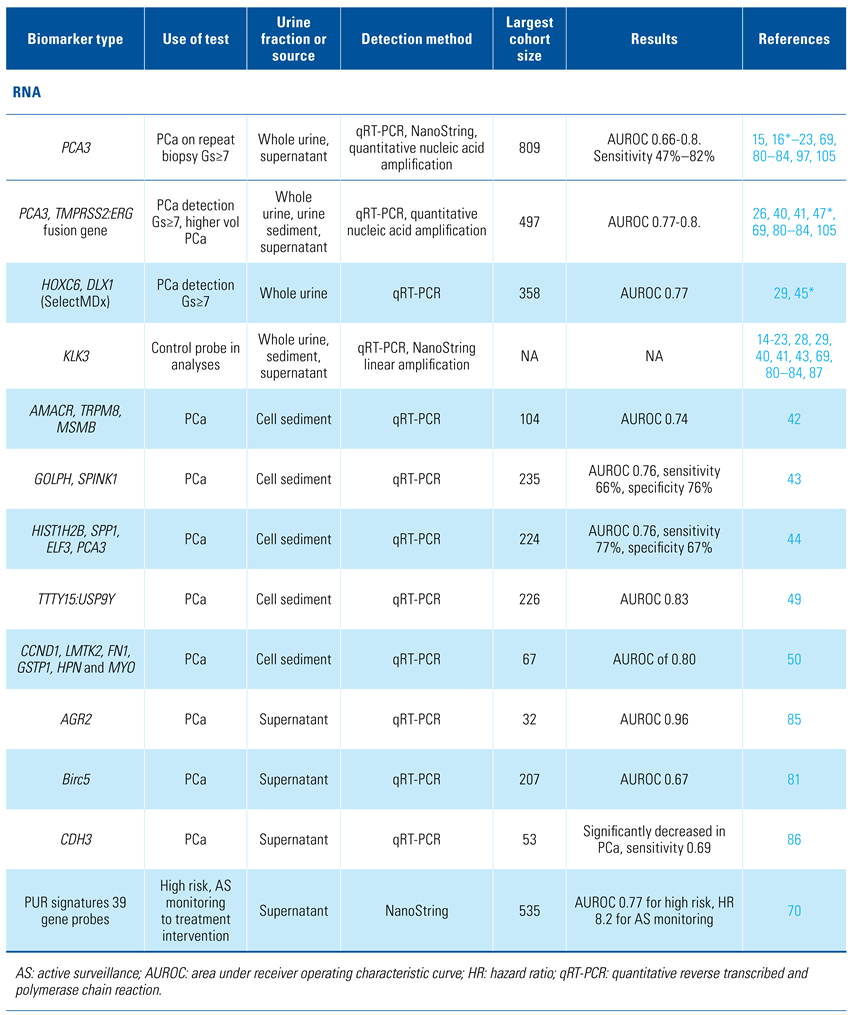
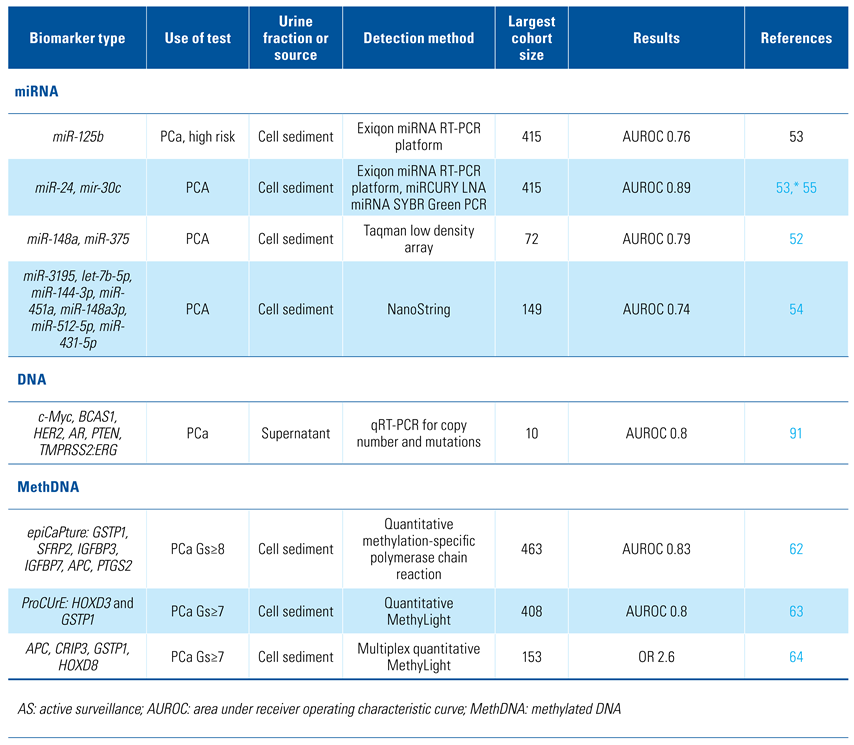
Urine samples have been analysed for promising cancer biomarkers in the form of cells, DNA, RNA, proteins, and metabolites. The relative proportions of biomarkers vary between whole urine, cell sediment, and supernatant which will be discussed separately. The majority of the research presented here has been performed on small cohorts from which limited conclusions can be made. The current state and future directions of urine analysis for prostate cancer diagnosis and prognosis are described herein. Table 1 provides an overview of the biomarkers discussed in this review.

Table 1.
Overview of relevant biomarkers.
2. Analysis of Whole Unfractionated Urine
Elevated levels of C3, C4, and transferrin proteins were found in prostatic fluid from PCa patients by Greyhack et al. in 1979[11], and in 1982 PCA-1 (prostate cancer antigen-1) protein was detected in urine from PCa patients but not in urine from age-matched non-PCa men[10]. However, it was not until 2002, when PCA3 (prostate cancer antigen 3) RNA transcripts in urine were found that the potential for urine molecular diagnostics in clinical urological practice was realised.
PCA3 is a prostate-specific long non-coding RNA overexpressed in ≥ 95% of prostate cancers that was first investigated as a urinary PCa marker by de Kok et al. in 2002[14]. In a multicentre validation study[15,16] it was shown to predict Gleason score ≥ 7 cancer with an 80% negative predictive value.
The FDA-approved Progensa PCA3 urine test was approved in 2012. Whole urine for this test is collected after prostate massage with the intent of predicting the likelihood of detecting PCa on repeat prostate biopsy[17,18]. The PCA3 score is calculated as the ratio of 2 mRNAs: PCA3/KLK3 x1000[17]. A threshold score of 35 provided a sensitivity and specificity of 58% and 72%, respectively for presence of significant PCa on rebiopsy[19,20]. Investigations into a direct relationship between the PCA3 test and PCa volume or Gleason pattern have been unclear, yielding opposing results in different studies[14,21,22]. Metanalysis by Luo et al. found great heterogeneity among published data sets with PCA3 test sensitivity ranging from 47% to 82%[23]. The reasons for this were unknown, and they may underlie the poor uptake of the PCA3 test in the clinic. However, the PCA3 test is important as it was first to demonstrate that collection, transport, and centralised laboratory analysis of urine was a viable means of PCa biomarker analysis.
The TMPRSS2:ERG fusion gene is found in ~50% of PCa foci; however, as TMPRSS2:ERG-positive and negative tumour foci can be found in individual prostates[24], a TMPRSS2:ERG may be present in ~70% of PCa-radical prostatectomies[25], making its detection more useful than was initially apparent. Urine transcript levels of TMPRSS2:ERG correlated with ERG expression in PCa tissue and aided prediction of PCa by PCA3. The Mi-Prostate score (MiPS) combined detection of PCA3, TMPRSS2:ERG and serum PSA levels[26], providing significantly improved detection of any PCa and Gleason score (Gs) ≥ 7 on biopsy compared with PSA or the prostate cancer prevention trial risk calculator (PCPT-RC)[27].
Further gene transcripts have been investigated for additional improvements. van Neste et al. combined RT-PCR data from HOXC4, HOXC6, TDRD1, DLX1, KLK3, and PCA3 with clinical information from 2 independent multicentre prospective collections (n = 906)[28].An optimal model (SelectMDX) required only a combination of PSAD, DRE result, HOXC6 and DLX1, with KLK3 used for relative biomarker quantitation[28]. SelectMDX had a strong net benefit, potentially reducing unnecessary biopsies over the PCA3 test, PSA and the PCPT-RC with a validation cohort AUROC of 0.9 for detection of Gs ≥ 7 cancer. SelectMDX has been reported to be able to reduce diagnostic costs in a study covering 5 European countries, the degree of benefit varying with the amount of overtreatment in each country’s clinical procedures[29].
3. Analysis of Urine Cell Sediment
3.1. PCa cells in urine
Urine can contain many different cell types, including bladder urothelial cells, squamous cells, seminal vesicle cells, prostate cells, red blood cells, and white blood cells[30], up to 80% of which can originate from the prostate[31,32]. Prostate cancer cells were first detected in urine samples by microscopy in 1947[9] and are associated with higher risk and advanced cancers[31]. The relative proportions of the different cell types in urine can alter with a DRE[31,33] or disease state such as prostatitis[34], prostate/urinary tract problems, or PCa[30,35].
Urine cell pellet staining for AMACR, Nkx3.1, nucleolin, ERG, and prostein[35,36] can detect prostate cancer cells but overall lacked sensitivity compared with biopsy[36]. Two fluorescent approaches have shown promise: OligoFISH probes to detect alterations in chromosomes 7, 16, 18, and 20 has been shown to have an 80% specificity compared with biopsy data[32], while a fluorescent peptide detected VPAC receptors with > 98% sensitivity and specificity[37]—VPAC receptors bind VIP, a neuropeptide linked to development, growth, immune system and cancer.
3.2. RNA in urine sediment
A disadvantage with urine sediment analysis is that the cell transcriptome is likely to alter on becoming detached and/or on contact with urine[38,39]. However, urine cell sediment has been found to be useful for PCa diagnosis.
PCA3 has a reported sensitivity of detection of PCa in urinary sediment of 62%, boosted to 73% by codetection of TMPRSS2:ERG[40,41]. Other combination markers used with PCA3 have been found to aid PCa detection in cell sediment: (1) AMACR, TRPM8, MSMB[42], (2) TMPRSS2:ERG, GOLPH, SPINK1[43], and (3) HIST1H2B, SPP1, ELF3[44]. However, Leyten et al. found that PCA3 was unnecessary when HOXC6, DLX1, and TDRD1 were used[45], TDRD1 being a direct target of ERG and co-expressed with ERG in PCa[46]. In combination with the European Randomised Study of Screening for PCa (ERSPC) risk calculator[47], Leyten et al. noted that TMPRSS2:ERG added significant predictive value to the ERSPC calculator to predict biopsy Gleason whereas PCA3 did not. TMPRSS2:ERG has been reported to be less common in Chinese populations[48], and detection of TTTY15:USP9Y gene fusion transcripts found in 35% of Chinese patients PCa[48] has improved PCa detection in urine sediments in that population (n = 226, AUROC 0.83)[49]. Other probe combinations excluding PCA3 include a panel of 6 genes overexpressed in PCa tissue (CCND1, LMTK2, FN1, GSTP1, HPN, and MYO6), used in the analysis of 156 PCa patients’ urine sediments (n = 67), which had a sensitivity of 80.6% and specificity of 62.9% for PCa detection (AUROC of 0.80)[50].
3.3. miRNA in urine sediment
miRNA dysregulation is frequently observed in cancer[51], and a number of diagnostically useful miRNAs are detectable in urine[52,53,54,55]. miR-21 and miR-125b are controlled by the androgen receptor (AR), and are overexpressed in PCa and associated with apoptotic resistance[53,54]. In contrast, miR-205 is a tumour suppressor miRNA, promoting apoptosis, and its loss is associated with the early stages of PCa development[56]. Despite miR-205 being down-regulated in PCa, it is a constituent of several miRNA urinary biomarker panels. AUROCs vary from 0.6 to 0.85 for detection of PCa using multiple combinations of miRNAs[52,53], and 0.74 for distinguishing low-risk from high-risk disease[54].
3.4. DNA-methylation in urine sediment
Epigenetic alterations are heritable changes in gene expression with no change to the DNA code. In cancer, DNA-hypermethylation silences tumour suppressors and other important regulatory genes[57]. It is easily detectable by PCR and it occurs early in tumorigenesis making it an ideal biomarker for early detection as well as disease progression monitoring and risk stratification of patients[58,59].
Pioneering work in the detection of PCa and significant PCa (Gs ≥ 7) was performed by Cairns et al. in 2001, who showed that methylation of the GSTP1 gene was detectable in urine of men with PCa but at a low sensitivity (27%)[60]. GSTP1 is hypermethylated in > 90% of PCa[60] and is relatively PCa-specific, it typically being overexpressed in most other cancers. For these reasons, it is a stalwart of PCa-methylation analysis. Gene panels improved performance, and a combination of APC, RARbeta, RASSF1A, PTGS2, ABCB1 methylation was detectable in > 85% of cases[61]. Notable examples include epiCaPture, a 6-gene DNA-methylation panel (GSTP1, SFRP2, IGFBP3, IGFBP7, APC, PTGS2) that can detect 85% of aggressive PCa (Gs ≥ 8) with a 70% improvement in the specificity of PSA[62] and ProCUrE, a 2-gene DNA-methylation panel (HOXD3 and GSTP1) with a sensitivity of 57.1% and specificity of 97% for significant PCa[63]. Zhao et al. established a 4-gene panel (APC, CRIP3, GSTP1, HOXD8) with some ability to predict cancer progression in patients on active surveillance (OR 2.559; 95% CI 1.257 to 5.212) from post-DRE urine[64]. They subsequently incorporated microRNAs and reported that miR-24, miR-30c and CRIP3 methylation could predict reclassification of AS patients[55].
Currently, no commercially available standardised DNA-methylation-based urine tests for PCa are available[60], which presents an obstacle to clinical uptake[65]. Sample storage conditions affect results as methylated-DNA is only stable for up to 28 days in urine stored at −20/−80⁰C and a preservative is required at room temperature[66]. Most urine assays use bisulfite conversion of unmethylated cytosines to uracil, leaving hypermethylated cytosines preserved for detection. However, a study of 12 different bisulfite kits discovered that conversion efficiency varied greatly[67], and storage of the less stable single-stranded bisulfite converted DNA may also be an issue[68]. Target sequence choice is critical, proximity to the transcription start site, transcription factor binding motifs, and DNase-hypersensitivity are all factors that can affect sensitivity and specificity[59]. Large, multicentre, standardised urine collections and clinical follow-up are needed to reduce the unknowns and bring PCa methylation biomarkers to fruition.
4. Urine Supernatant
4.1. RNA in urine extracellular vesicles
Large numbers of extracellular vesicles (EVs) can be found in urine[69], the majority of which in first-catch adult male urine originate from the prostate[69,70]. EVs are lipid-bound vesicles produced by a wide range of cell types[71]. EVs function as inter-cellular messengers that can bind to and influence the phenotype of cells they come into contact with[72,73]. Cancer cells produce EVs, which can enhance vasculature[74], increase metastasis[75], and influence the immune system[76] and can contain PCa-specific mRNAs such as TMPRSS2:ERG fusion gene transcripts[40]. EVs contain lipids, RNA, DNA, and proteins including membrane receptors[72,77,78] which are protected from degradation by, for example, RNAses by the EV lipid membrane[79].
The majority of publications refer to analysis of only small numbers of gene transcripts in EVs, namely PCA3, ERG, TMPRSS2:ERG, KLK3, which have been found to be useful in PCa diagnosis and detection of Gleason ≥ 4 cancer[69,80,81,82,83,84]. Additional genes with diagnostic potential are AGR2 splice variants[85], Birc5[81], and decreased expression of CDH3[86]. In contrast, Connell et al. used a NanoString panel of 167 gene probes, mostly selected from published evidence of over-expression in PCa tissue[70]. Analysis of 535 urine EV samples from patients with and without PCa led to the prostate urine risk (PUR) signatures constructed from a subgroup of 39 gene probes. In contrast to all other urine analyses, instead of a single cancer signature they constructed 4 PUR signatures, which were built around samples categorised as non-cancer (PUR-1), plus the 3 D’Amico risk groups for cancer aggression, namely low-risk (PUR-2), intermediate-risk (PUR-3), and high-risk (PUR-4). Each sample could have representation from all 4 signatures and the sum of the 4 PUR signatures in each sample was ‘1’. Connell et al. found that PUR-4 could predict the presence of significant cancer on TRUS biopsy (AUROC 0.77). On examination of an active surveillance cohort (n = 87) PUR-4 could be used to divide patients into 2 groups with rates of progression to treatment intervention of 10% and 60% up to 5 years after urine collection (HR 8.23). A strong PUR-1 signature correlated with stability of low-grade disease that did not progress in the 5-year follow-up. The PUR-2 and PUR-3 signatures had less utility but were hypothesised as integral to the creation of a clearer signature for higher grade Gleason cancer detectable by PUR-4.
A few studies have compared PCa mRNA transcripts in both cell and EV urine fractions. Prostatic transcripts appear to be higher in EV fractions[69,80,87], but may have better diagnostic utility in the cell sediment[88] with a caveat that ~10% of cell sediments may not be analysable. Hendriks et al. reported that PCA3 transcripts were expressed significantly higher in PCa patients than in non-PCa patients in both the whole-urine and cell-sediment fractions but not in the EV fraction[87]. Webb et al. compared RNA yields from cell sediment and EVs in 200 patients and found them to be highly variable with no apparent correlation. This observation suggests that examination of RNA biomarkers in whole urine could be obfuscated by the unknown relative contribution of transcripts from the different urine fractions and suggests that separate analysis of the 2 fractions is to be recommended[80].
4.2. Cell-free DNA in urine
Cell-free urine DNA (cfDNA) has been found both inside EVs and bound outside EV membranes[79], the source of which has been hypothesised to be from apoptotic cells[79] and mitochondria[89]. cf DNA yields from EVs are low (18pg/mL urine[90]) but have been used to detect methylated GSTP1 in men with PCa that was not present in urine from men with BPH[78]. Casadio et al. used copy number analysis of c-Myc, BCAS1, and HER2 by qRTPCR to distinguish PCa from non-PCa men with an AUROC of 0.8, while copy number gains of AR, genomic deletions including PTEN, and TMPRSS2:ERG fusion sequences have been detected in a small cohort of men with castrate-resistant cancer (n = 10)[91].
4.3. Supernatant proteins
Thousands of proteins on or encapsulated within EVs have been identified by mass spectrometry analysis, with for example ITGA3 and ITGB1 being linked to metastasis[92]. For a thorough review see recent papers by Pang et al.[93] and Wu et al.[94].
Possibly the most thoroughly investigated urine protein biomarker is the transcriptional repressor EN2[95]. Unusually for a transcription factor, EN2 can be secreted from normal and PCa cells and then be internalised by other cells to effect transcriptional changes in, for example, stroma[96]. EN2 is involved with embryonic brain development and is inappropriately expressed in a range of cancers including bladder and prostate where EN2 may regulate androgen-receptor activity in androgen-sensitive prostate cancer cells[97,98]. In a 2011 study by Morgan et al., men with prostate cancer had a 10-fold higher level of EN2 in their urine versus non-cancer controls, and EN2 was identified in 66% of urine samples from biopsy-proven PCa patients, some of whom had undetectable levels of serum PSA[99]. This was in contrast to < 15% positivity in control groups (some of whom would have been expected to harbour occult prostate cancer), giving a specificity of 88.2% (AUROC 0.8; P < 0.001). Higher EN2 levels correlated with advancing tumour stage, eg, pT3a versus pT2b (P = 0.027), positive margins (P = 0.008), increasing tumour volume[100,101], and subsequent diagnosis of PCa in BRCA1/2 mutation carriers[102].
There have, however, been no large-scale EN2 trials because there is no robust commercially available test for EN2 protein in urine, which may be due to its very high net-charge causing non-specific attachment to some plastic surfaces (personal communication from H. Pandha [co-author], 2019). Indeed, a recent study looking at commercially available ELISA kits for EN2 found no significant diagnostic value for urinary EN2 in PCa patients[103]. Novel approaches are in development, such as a graphene-based biosensor[104] and examining urine cfRNA EN2 transcripts[70].
5. Urine Biomarkers and the DRE
A problem with urine is the inconsistency in the amounts of prostatic material between samples. The digital rectal examination (DRE) of the prostate is one source of variation. When men present at a hospital, nerves very often mean that they would urinate before seeing the doctor and flush out all the prostatic secretions from the urethra. To replenish the prostatic biomarkers in the urethra, urine has usually been collected after a DRE whereby the doctor would stroke the prostate with a finger pushing prostate secretions into the urethra shortly before urination. However, urine cfRNA yields correlate with the clinician performing the DRE, with 10-fold differences being found between clinicians, differences which were hypothesised as being linked to the clinician’s DRE technique, finger length and prostate position[80].
A number of studies indicate that RNA yields from urine collected in the clinic without a DRE are less than a tenth of post-DRE samples[69,80] and levels of prostate markers such as KLK3 were also reduced approximately 10-fold[87]. However, studies by Donovan et al. and McKiernan et al., using non-DRE urine found AUROCs of 0.8 and 0.77, respectively for detection of Gs >7 using PCA3 and ERG combined with clinical parameters[82,83,105], strongly suggesting that non-DRE urine has utility. Webb et al. took this one step further[80]: their hypothesis centred on the finding by Huggins et al. in 1945 that the prostate was constantly secreting[12], indicating that time since previous urination was key. Urine samples collected at home from the first urination of the day were found to have RNA yields comparable to samples collected post-DRE from the same patients in the clinic a week earlier. Significantly, Webb et al. found that detection of PCA3 and TMPRSS2:ERG by RT-PCR proved to be much more sensitive in these morning samples than in the post-DRE samples. While this study was limited by the low number of men (n = 14) it does suggest that urine collections could be performed by mail, could enable mass screening, and could simplify disease monitoring of, for example, active surveillance cohorts. Webb et al. also suggested that inter-sample consistency could be further improved by collecting a second urine sample at a fixed interval of 1-hour later.
Conclusions
The extensive interconnecting luminal structures of the prostate that carry prostatic secretions to the urethra make urine a valuable non-invasive resource to examine all parts of the prostate where PCa arises. Urine has proven utility in predicting disease load and monitoring disease progression, and its use could result in the development of a PCa screening test. However, the translation of biomarkers from research to clinical practice is littered with failure[106]. The heterogeneity of PCa and analysis of cohorts with different ranges of disease severity make data difficult to inter-compare. A further layer of obfuscation is provided by variabilities in sample collection, extraction and specifics of analysis compounded by inaccurate estimates of PCa disease status by standard clinical means. However, urine diagnostics is a developing area, moving towards multi-omic biomarker integration for improved diagnostic performance. Urine tests developed by strong collaborations between scientists and clinicians have the potential to provide targeted and meaningful data that can guide treatment and truly improve men’s lives.
Conflicts of Interest
Dr Clark and Professor Cooper have a patent GB1905111.9 issued in relation to the PUR (prostate urine risk) signatures discussed in this review. Professor Pandha and Professor Morgan have a patent issued for EN2 as a diagnostic marker. Dr Perry reports grants from Enterprise Ireland, Movember, Prostate Cancer Foundation, and Science Foundation Ireland during the conduct of the study. Dr Perry has a patent EP15831140.7 issued, and a patent 15/538928 pending. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Abbreviations
| DRE digital rectal examination |
| EVs extracellular vesicles |
| Gs Gleason score |
| MiPS Mi-Prostate score |
| PCa prostate cancer |
| PCA3 prostate cancer antigen 3 |
| PCPT-RC prostate cancer prevention trial risk calculator |
| PUR prostate urine risk |
| VIP vasoactive intestinal peptide |
References
- Arora, R.; Koch, M.O.; Eble, J.N.; Ulbright, T.M.; Li, L.; Cheng, L. Heterogeneity of Gleason grade in multifocal adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Cancer 2004, 100, 2362–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.S.; Eeles, R.; Wedge, D.C.; Van Loo, P.; Gundem, G.; Alexandrov, L.B.; et al. Analysis of the genetic phylogeny of multifocal prostate cancer identifies multiple independent clonal expansions in neoplastic and morphologically normal prostate tissue. Nat. Genet. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, D.R.; Wheeler, T.M.; Egawa, S.; Weaver, R.P.; Scardino, P.T. Relationship between clinical stage and histological zone of origin in early prostate cancer: morphometric analysis. Br. J. Urol. 1991, 68, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussa, A.S.; Li, J.; Soriano, M.; Klein, E.A.; Dong, F.; Jones, J.S. Prostate biopsy clinical and pathological variables that predict significant grading changes in patients with intermediate and high grade prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2009, 103, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, J.I.; Feng, Z.; Trock, B.J.; Pierorazio, P.M. Upgrading and downgrading of prostate cancer from biopsy to radical prostatectomy: incidence and predictive factors using the modified Gleason grading system and factoring in tertiary grades. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walz, J. The “PROMIS” of magnetic resonance imaging cost effectiveness in prostate cancer diagnosis? Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 31–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.U.; El-Shater Bosaily, A.; Brown, L.C.; Gabe, R.; Kaplan, R.; Parmar, M.K.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of multi-parametric MRI and TRUS biopsy in prostate cancer (PROMIS): a paired validating confirmatory study. Lancet, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- PAPANICOLAOUGN Diagnostic value of exfoliated cells from cancerous tissues. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1946, 131, 372–378. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbut, P.A.; Lubin, E.N. Cancer cells in prostatic secretions. J. Urol. 1947, 57, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, J.J.; Anderson, N.G.; Tollaksen, S.L.; Eschenbach von, A.C.; Guevara JJr Proteins of human urine, I.I. Identification by two-dimensional electrophoresis of a new candidate marker for prostatic cancer. Clin. Chem. 1982, 28, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayhack, J.T.; Wendel, E.F.; Oliver, L.; Lee, C. Analysis of specific proteins in prostatic fluid for detecting prostatic malignancy. J. Urol. 1979, 121, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, C. The Physiology of the Prostate Gland. Physiological Reviews. 1945, 25, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeal, J.E.; Redwine, E.A.; Freiha, F.S.; Stamey, T.A. Zonal distribution of prostatic adenocarcinoma. Correlation with histologic pattern and direction of spread. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1988, 12, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kok, J.B.; Verhaegh, G.W.; Roelofs, R.W.; Hessels, D.; Kiemeney, L.A.; Aalders, T.W.; et al. DD3(PCA3), a very sensitive and specific marker to detect prostate tumors. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2695–2698. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van Gils, M.P.M.Q.; Hessels, D.; van Hooij, O.; Jannink, S.A.; Peelen, W.P.; Hanssen, S.L.J.; et al. The time-resolved fluorescence-based PCA3 test on urinary sediments after digital rectal examination; a Dutch multicenter validation of the diagnostic performance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, F.; la Taille de, A.; Van Poppel, H.; Marberger, M.; Stenzl, A.; Mulders, P.; et al. Prostate cancer gene 3 (PCA3): development and internal validation of a novel biopsy nomogram. Eur. Urol. 2009, 56, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groskopf, J.; Aubin, S.M.J.; Deras, I.L.; Blase, A.; Bodrug, S.; Clark, C.; et al. APTIMA PCA3 molecular urine test: development of a method to aid in the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessels, D.; Schalken, J.A. The use of PCA3 in the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2009, 6, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, L.S.; Fradet, Y.; Deras, I.L.; Blase, A.; Mathis, J.; Aubin, S.M.J.; et al. PCA3 molecular urine assay for prostate cancer in men undergoing repeat biopsy. Urology 2007, 69, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haese, A.; la Taille de, A.; van Poppel, H.; Marberger, M.; Stenzl, A.; Mulders, P.F.A.; et al. Clinical utility of the PCA3 urine assay in European men scheduled for repeat biopsy. Eur. Urol. 2008, 54, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostwick, D.G.; Gould, V.E.; Qian, J.; Susani, M.; Marberger, M. Prostate cancer detected by uPM3: radical prostatectomy findings. Mod. Pathol. 2006, 19, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, X.; Foj, L.; Milà, M.; Augé, J.M.; Molina, R.; Jiménez, W. PCA3 in the detection and management of early prostate cancer. Tumour Biol. 2013, 34, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Gou, X.; Huang, P.; Mou, C. The PCA3 test for guiding repeat biopsy of prostate cancer and its cut-off score: a systematic review and meta- analysis. Asian J. Androl. 2014, 16, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.; Attard, G.; Jhavar, S.; Flohr, P.; Reid, A.; de Bono, J.; et al. Complex patterns of ETS gene alteration arise during cancer development in the human prostate. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1993–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehra, R.; Han, B.; Tomlins, S.A.; Wang, L.; Menon, A.; Wasco, M.J.; et al. Heterogeneity of TMPRSS2 gene rearrangements in multifocal prostate adenocarcinoma: molecular evidence for an independent group of diseases. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7991–7995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlins, S.A.; Groskopf, J.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Reply to Carsten Stephan, Henning Cammann, and Klaus Jung’s Letter to the Editor re: Scott A. Tomlins, John R. Day, Robert J. Lonigro, et al. Urine TMPRSS2:ERG Plus PCA3 for Individualized Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.; Palanisamy, N.; Siddiqui, J.; Wood, D.P.; Wei, J.T.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; et al. Correlation of urine TMPRSS2:ERG and PCA3 to ERG+ and total prostate cancer burden. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 138, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Neste, L.; Partin, A.W.; Stewart, G.D.; Epstein, J.I.; Harrison, D.J.; Van Criekinge, W. Risk score predicts high-grade prostate cancer in DNA-methylation positive, histopathologically negative biopsies. Prostate 2016, 76, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govers, T.M.; Hessels, D.; Vlaeminck-Guillem, V.; Schmitz-Dräger, B.J.; Stief, C.G.; Martinez-Ballesteros, C.; et al. Cost-effectiveness of SelectMDx for prostate cancer in four European countries: a comparative modeling study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2019, 22, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, P.S.; Chan, J.B.; Levin, M.R.; Rao, J. Urine cytology and adjunct markers for detection and surveillance of bladder cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2010, 2, 412–440. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, M.; Yang, B.; Jarrard, D. Towards the detection of prostate cancer in urine: a critical analysis. J. Urol. 2013, 189, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinawi-Aljundi, R.; Knuth, S.T.; Gildea, M.; Khal, J.; Hafron, J.; Kernen, K.; et al. Minimally invasive prostate cancer detection test using FISH probes. Res. Rep. Urol. 2016, 8, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foot, N.C.; Papanicolaou, G.N.; Holmquist, N.D.; Seybolt, J.F. Exfoliative cytology of urinary sediments; a review of 2,829 cases. Cancer 1958, 11, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thin, R.N. The diagnosis of prostatitis: a review. Genitourin Med.3rd ed. The Medical Society for the Study of Venereal Disease; 1991, 67, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fujita, K.; Pavlovich, C.P.; Netto, G.J.; Konishi, Y.; Isaacs, W.B.; Ali, S.; et al. Specific detection of prostate cancer cells in urine by multiplex immunofluorescence cytology. Hum. Pathol. 2009, 40, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickens, K.P.; Ali, A.; Scoggin, T.; Tan, S.-H.; Ravindranath, L.; Mcleod, D.G.; et al. Prostate cancer marker panel with single cell sensitivity in urine. Prostate 2015, 75, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabulsi, E.J.; Tripathi, S.K.; Gomella, L.; Solomides, C.; Wickstrom, E.; Thakur, M.L. Development of a voided urine assay for detecting prostate cancer non-invasively: a pilot study. BJU Int. 2017, 119, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, S.M.; Screaton, R.A. Anoikis mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2001, 13, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bella Della, E.; Stoddart, M.J. Cell detachment rapidly induces changes in noncoding RNA expression in human mesenchymal stromal cells. BioTechniques 2019, 67, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessels, D.; Smit, F.P.; Verhaegh, G.W.; Alfred Witjes, J.; Cornel, E.B.; Schalken, J.A. Detection of TMPRSS2-ERG fusion transcripts and prostate cancer antigen 3 in urinary sediments may improve diagnosis of prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 5103–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, S.S.; Schmidt, F.; Laxman, B.; Regan, M.M.; Rickman, D.S.; Scherr, D.; et al. Combining urinary detection of TMPRSS2:ERG and PCA3 with serum PSA to predict diagnosis of prostate cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2013, 31, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaspishvili, T.; Kral, M.; Khomeriki, I.; Vyhnankova, V.; Mgebrishvili, G.; Student, V.; et al. Quadriplex model enhances urine-based detection of prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2011, 14, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxman, B.; Morris, D.S.; Yu, J.; Siddiqui, J.; Cao, J.; Mehra, R.; et al. A first-generation multiplex biomarker analysis of urine for the early detection of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengual, L.; Lozano, J.J.; Ingelmo-Torres, M.; Izquierdo, L.; Musquera, M.; Ribal, M.J.; et al. Using gene expression from urine sediment to diagnose prostate cancer: development of a new multiplex mRNA urine test and validation of current biomarkers. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Leyten, G.H.J.M.; Hessels, D.; Smit, F.P.; Jannink, S.A.; de Jong, H.; Melchers, W.J.G.; et al. Identification of a candidate gene panel for the early diagnosis of prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3061–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boormans, J.L.; Korsten, H.; Ziel-van der Made, A.J.C.; van Leenders, G.J.L.H.; de Vos, C.V.; Jenster, G.; et al. Identification of TDRD1as a direct target gene of ERGin primary prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyten, G.H.J.M.; Hessels, D.; Jannink, S.A.; Smit, F.P.; de Jong, H.; Cornel, E.B.; et al. Prospective multicentre evaluation of PCA3 and TMPRSS2- ERG gene fusions as diagnostic and prognostic urinary biomarkers for prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Peng, Z.; Mao, J.-H.; Yu, Y.; Yin, C.; Gao, X.; et al. RNA-seq analysis of prostate cancer in the Chinese population identifies recurrent gene fusions, cancer-associated long noncoding RNAs and aberrant alternative splicings. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 806–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Ren, S.; Jing, T.; Cai, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; et al. Clinical utility of a novel urine-based gene fusion TTTY15-USP9Y in predicting prostate biopsy outcome. Urol. Oncol. 2015, 33, 384.e9–384.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; et al. A panel of biomarkers for diagnosis of prostate cancer using urine samples. Anticancer. Res. 2018, 38, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar]
- Hata, A.; Lieberman, J. Dysregulation of microRNA biogenesis and gene silencing in cancer. Sci. Signal 2015, 8, re3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuopelyte˙, K.; Daniu¯naite˙, K.; Bakavicius, A.; Lazutka, J.R.; Jankevicius, F.; Jarmalaite, S. The utility of urine-circulating miRNAs for detection of prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredsøe, J.; Rasmussen, A.K.I.; Thomsen, A.R.; Mouritzen, P.; Høyer, S.; Borre, M.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic microRNA biomarkers for prostate cancer in cell-free urine. Eur. Urol. Focus. 2018, 4, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.; Olkhov-Mitsel, E.; Xie, H.; Yao, C.Q.; Zhao, F.; Jahangiri, S.; et al. temporal stability and prognostic biomarker potential of the prostate cancer urine miRNA transcriptome. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2020, 112, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Vesprini, D.; Liu, R.S.C.; Olkhov-Mitsel, E.; Klotz, L.H.; Loblaw, A.; et al. Combining urinary DNA methylation and cell-free microRNA biomarkers for improved monitoring of prostate cancer patients on active surveillance. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 297.e9–297.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boll, K.; Reiche, K.; Kasack, K.; Mörbt, N.; Kretzschmar, A.K.; Tomm, J.M.; et al. MiR-130a, miR-203 and miR-205 jointly repress key oncogenic pathways and are downregulated in prostate carcinoma. Oncogene 2013, 32, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.O. DNA methylation changes in prostate cancer: current developments and future clinical implementation. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2009, 9, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, S.R.; Serth, J.; Schostak, M.; Kamradt, J.; Strauss, A.; Thelen, P.; et al. DNA methylation biomarkers of prostate cancer: confirmation of candidates and evidence urine is the most sensitive body fluid for non-invasive detection. Prostate 2009, 69, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, L.K.; Lind, G.E.; Guldberg, P.; Dahl, C. DNA-methylation-based detection of urological cancer in urine: overview of biomarkers and considerations on biomarker design, source of DNA, and detection technologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, P.; Esteller, M.; Herman, J.G.; Schoenberg, M.; Jeronimo, C.; Sanchez- Cespedes, M.; et al. Molecular detection of prostate cancer in urine by GSTP1 hypermethylation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 2727–2730. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, P.G.; Wessel, T.; Kawashima, A.; Okello, J.B.A.; Jamaspishvili, T.; Guérard, K.-P.; et al. A three-gene DNA methylation biomarker accurately classifies early stage prostate cancer. Prostate 2019, 79, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, E.; Tuzova, A.V.; Walsh, A.L.; Russell, N.M.; O’Brien, O.; Kelly, S.; et al. epiCaPture: A urine DNA methylation test for early detection of aggressive prostate cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Olkhov-Mitsel, E.; Kamdar, S.; Jeyapala, R.; Garcia, J.; Hurst, R.; et al. A urine-based DNA methylation assay, ProCUrE, to identify clinically significant prostate cancer. Clin. Epigenet 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Olkhov-Mitsel, E.; van der Kwast, T.; Sykes, J.; Zdravic, D.; Venkateswaran, V.; et al. Urinary DNA Methylation Biomarkers for Noninvasive Prediction of Aggressive Disease in Patients with Prostate Cancer on Active Surveillance. J. Urol. 2017, 197, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikeska, T.; Bock, C.; Do, H.; Dobrovic, A. DNA methylation biomarkers in cancer: progress towards clinical implementation. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 12, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosschieter, J.; Bach, S.; Bijnsdorp, I.V.; Segerink, L.I.; Rurup, W.F.; van Splunter, A.P.; et al. A protocol for urine collection and storage prior to DNA methylation analysis. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0200906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worm Ørntoft, M.-B.; Jensen, S.Ø.; Hansen, T.B.; Bramsen, J.B.; Andersen, C.L. Comparative analysis of 12 different kits for bisulfite conversion of circulating cell-free DNA. Epigenetics 2017, 12, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pharo, H.D.; Honne, H.; Vedeld, H.M.; Dahl, C.; Andresen, K.; Liestøl, K.; et al. Experimental factors affecting the robustness of DNA methylation analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrini, K.L.; Patil, D.; Douglas, K.J.S.; Lee, G.; Wehrmeyer, K.; Torlak, M.; et al. Detection of prostate cancer-specific transcripts in extracellular vesicles isolated from post-DRE urine. Prostate 2017, 77, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connell, S.P.; Hanna, M.; McCarthy, F.; Hurst, R.; Webb, M.; Curley, H.; et al. A four-group urine risk classifier for predicting outcome in prostate cancer patients. BJU Int. Online ahead of print. 2019, 124, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.T.; Johnstone, R.M. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: selective externalization of the receptor. Cell 1983, 33, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborowski, M.P.; Balaj, L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Lai, C.P. Extracellular Vesicles: Composition, Biological Relevance, and Methods of Study. Bioscience 2015, 65, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, L.; Wang, M. Overview of extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and methods for exosome isolation and analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, M.; Kubota, S.; Sato, K.; Monzen, S. Exosomes released from pancreatic cancer cells enhance angiogenic activities via dynamin- dependent endocytosis in endothelial cells in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11972–11979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grange, C.; Tapparo, M.; Collino, F.; Vitillo, L.; Damasco, C.; Deregibus, M.C.; et al. Microvesicles released from human renal cancer stem cells stimulate angiogenesis and formation of lung premetastatic niche. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5346–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greening, D.W.; Gopal, S.K.; Xu, R.; Simpson, R.J.; Chen, W. Exosomes and their roles in immune regulation and cancer. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol.
- Pisitkun, T.; Shen, R.-F.; Knepper, M.A. Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human urine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13368–13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryzgunova, O.E.; Morozkin, E.S.; Yarmoschuk, S.V.; Vlassov, V.V.; Laktionov, P.P. Methylation-specific sequencing of GSTP1 gene promoter in circulating/extracellular DNA from blood and urine of healthy donors and prostate cancer patients. Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci. 2008, 1137, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, K.C.; Bond, D.T.; McKee, M.; Skog, J.; Pa˘unescu, T.G.; Da Silva, N.; et al. Nucleic acids within urinary exosomes/microvesicles are potential biomarkers for renal disease. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, M.; Manley, K.; Olivan, M.; Guldvik, I.; Palczynska, M.; Hurst, R.; et al. Methodology for the at-home collection of urine samples for prostate cancer detection. BioTechniques 2020, 68, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motamedinia, P.; Scott, A.N.; Bate, K.L.; Sadeghi, N.; Salazar, G.; Shapiro, E.; et al. Urine exosomes for non-invasive assessment of gene expression and mutations of prostate cancer. Kyprianou N, editor. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154507–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKiernan, J.; Donovan, M.J.; O’Neill, V.; Bentink, S.; Noerholm, M.; Belzer, S.; et al. A novel urine exosome gene expression assay to predict high-grade prostate cancer at initial biopsy. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, M.J.; Noerholm, M.; Bentink, S.; Belzer, S.; Skog, J.; Neill, V.O.A.; et al. A molecular signature of PCA3 and ERG exosomal RNA from non-DRE urine is predictive of initial prostate biopsy result. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2015, 18, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.W.; Newcomb, L.F.; Brown, E.C.; Brooks, J.D.; Carroll, P.R.; Feng, Z.; et al. Urinary TMPRSS2:ERG and PCA3 in an active surveillance cohort: results from a baseline analysis in the canary prostate active surveillance study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2442–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neeb, A.; Hefele, S.; Bormann, S.; Parson, W.; Adams, F.; Wolf, P.; et al. Splice variant transcripts of the anterior gradient 2 gene as a marker of prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 8681–8689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royo, F.; Zuñiga-Garcia, P.; Torrano, V.; Loizaga, A.; Sanchez-Mosquera, P.; Ugalde-Olano, A.; et al. Transcriptomic profiling of urine extracellular vesicles reveals alterations of CDH3 in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 6835–6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriks, R.J.; Dijkstra, S.; Jannink, S.A.; Steffens, M.G.; van Oort, I.M.; Mulders, P.F.A.; et al. Comparative analysis of prostate cancer specific biomarkers PCA3 and ERG in whole urine, urinary sediments and exosomes. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkstra, S.; Birker, I.L.; Smit, F.P.; Leyten, G.H.J.M.; de Reijke, T.M.; van Oort, I.M.; et al. Prostate cancer biomarker profiles in urinary sediments and exosomes. J. Urol. 2014, 191, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guescini, M.; Genedani, S.; Stocchi, V.; Agnati, L.F. Astrocytes and glioblastoma cells release exosomes carrying mtDNA. J. Neural Transm. 2010, 117, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryzgunova, O.E.; Zaripov, M.M.; Skvortsova, T.E.; Lekchnov, E.A.; Grigor’eva, A.E.; Zaporozhchenko, I.A.; et al. Comparative study of extracellular vesicles from the urine of healthy individuals and prostate cancer patients. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0157566–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Dittmar, R.; Du, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. Copy number variations in urine cell free DNA as biomarkers in advanced prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 35818–35831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijnsdorp, I.V.; Geldof, A.A.; Lavaei, M.; Piersma, S.R.; van Moorselaar, R.J.A.; Jimenez, C.R. Exosomal ITGA3 interferes with non-cancerous prostate cell functions and is increased in urine exosomes of metastatic prostate cancer patients. J. Extracell. Vesicles, eCollection 2013. 2013; 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Zhu, Y.; Ni, J.; Thompson, J.; Malouf, D.; Bucci, J.; et al. Extracellular vesicles: the next generation of biomarkers for liquid biopsy-based prostate cancer diagnosis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 2309–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, W.; Cai, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, S. Extracellular vesicles in urologic malignancies-Implementations for future cancer care. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, e12659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkunova, E.N.; Fujioka, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Deka, D.; Jaynes, J.B. Two distinct types of repression domain in Engrailed: one interacts with the groucho corepressor and is preferentially active on integrated target genes. Mol. Cell Biol. 1998, 18, 2804–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punia, N.; Primon, M.; Simpson, G.R.; Pandha, H.S.; Morgan, R. Membrane insertion and secretion of the Engrailed-2 (EN2) transcription factor by prostate cancer cells may induce antiviral activity in the stroma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, C.A.; Bei, L.; Wang, H.; Altman, J.K.; Platanias, L.C.; Eklund, E.A. Cooperation between AlphavBeta3 integrin and the fibroblast growth factor receptor enhances proliferation of Hox-overexpressing acute myeloid leukemia cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 54782–54794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Gómez, E.; Jiménez-Vacas, J.M.; Pedraza-Arévalo, S.; López-López, F.; Herrero-Aguayo, V.; Hormaechea-Agulla, D.; et al. Oncogenic role of secreted Engrailed homeobox 2 (EN2) in prostate cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, R.; Boxall, A.; Bhatt, A.; Bailey, M.; Hindley, R.; Langley, S.; et al. Engrailed-2 (EN2): a tumor specific urinary biomarker for the early diagnosis of prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandha, H.; Sorensen, K.D.; Orntoft, T.F.; Langley, S.; Høyer, S.; Borre, M.; et al. Urinary Engrailed-2 (EN2) levels predict tumour volume in men undergoing radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2012, 110, E287–E292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandha, H.; Javed, S.; Sooriakumaran, P.; Bott, S.; Montgomery, B.; Hutton, A.; et al. Correlation of urinary Engrailed-2 levels to tumour volume and pathological stage in men undergoing radical prostatectomy. J. Cancer Ther. 2013, 04, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mitra, A.V.; Bancroft, E.K.; Barbachano, Y.; Page, E.C.; Foster, C.S.; Jameson, C.; et al. Targeted prostate cancer screening in men with mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 detects aggressive prostate cancer: preliminary analysis of the results of the IMPACT study. BJU Int. 2011, 107, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Carmo Silva, J.; Vesely, S.; Novak, V.; Luksanova, H.; Prusa, R.; Babjuk, M. Is Engrailed-2 (EN2) a truly promising biomarker in prostate cancer detection? Biomarkers 2020, 25, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settu, K.; Liu, J.-T.; Chen, C.-J.; Tsai, J.-Z. Development of carbon- graphene-based aptamer biosensor for EN2 protein detection. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 534, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKiernan, J.; Donovan, M.J.; Margolis, E.; Partin, A.; Carter, B.; Brown, G.; et al. A Prospective adaptive utility trial to validate performance of a novel urine exosome gene expression assay to predict high-grade prostate cancer in patients with prostate-specific antigen 2–10 ng/ml at initial biopsy. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, W.J.; Guanzon, D.; Ma, C.; Liew, Y.J.; Duesing, K.R.; Fung, K.Y.C.; et al. DNA Methylation Cancer Biomarkers: Translation to the Clinic. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
This is an open access article under the terms of a license that permits non-commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. © 2021 The Authors. Société Internationale d'Urologie Journal, published by the Société Internationale d'Urologie, Canada.