Test–Retest Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change of the 6-Minute Step Test and 1-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test in Post-COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
Highlights
- The 6-minute step test (6MST) and 1-minute sit-to-stand test (1-min-STST) demonstrated excellent test–retest reliability in post-COVID-19 patients, comparable to the 6-minute walk test (6MWT).
- Minimal detectable change (MDC95) values were 5.57% for the 6MWT, 12.21% for the 6MST, and 3.61% for the 1-min-STST, supporting their clinical applicability in monitoring functional improvement.
- The 6MST and 1-min-STST were valid and acceptable for the evaluation of functional capacity in post-COVID-19 patients.
- Our results confirm that the 6MST and 1-min-STST are useful tools for assessing significant clinical improvements in post-COVID-19 patients.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adil, M.T.; Rahman, R.; Whitelaw, D.; Jain, V.; Al-Taan, O.; Rashid, F.; Munasinghe, A.; Jambulingam, P. SARS-CoV-2 and the pandemic of COVID-19. Postgrad. Med. J. 2021, 97, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alandijany, T.A.; Faizo, A.A.; Azhar, E.I. Coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries: Current status and management practices. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, C.H.; Cianci, R.G.; Malaguti, C.; Corso, S.D. The use of step tests for the assessment of exercise capacity in healthy subjects and in patients with chronic lung disease. J. Bras. De Pneumol. 2012, 38, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcuri, J.F.; Borghi-Silva, A.; Labadessa, I.G.; Sentanin, A.C.; Candolo, C.; Pires Di Lorenzo, V.A. Validity and Reliability of the 6-Minute Step Test in Healthy Individuals: A Cross-sectional Study. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2016, 26, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ATS Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories. ATS statement: Guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Crouch, R. 1-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test: Systematic Review Of Procedures, Performance, And Clinimetric Properties. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2019, 39, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Corso, S.; Duarte, S.R.; Neder, J.A.; Malaguti, C.; de Fuccio, M.B.; de Castro Pereira, C.A.; Nery, L.E. A step test to assess exercise-related oxygen desaturation in interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 29, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriatopoulou, M.; Korompoki, E.; Fotiou, D.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Kastritis, E.; Terpos, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Organ-specific manifestations of COVID-19 infection. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 20, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, T.; Knight, M.; A’Court, C.; Buxton, M.; Husain, L. Management of post-acute COVID-19 in primary care. BMJ 2020, 370, m3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosbois, J.M.; Riquier, C.; Chehere, B.; Coquart, J.; Béhal, H.; Bart, F.; Wallaert, B.; Chenivesse, C. Six-minute stepper test: A valid clinical exercise tolerance test for COPD patients. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2016, 11, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, M.M.; Stevenson, P.J.; Charette, S.L.; Pyka, G.; Marcus, R. Effect of muscle strength and movement speed on the biomechanics of rising from a chair in healthy elderly and young women. Gait Posture 1998, 8, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haley, S.M.; Fragala-Pinkham, M.A. Interpreting change scores of tests and measures used in physical therapy. Phys. Ther. 2006, 86, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H.; Beyer, N.; Frølich, A.; Godtfredsen, N.; Bieler, T. Intra- and inter-rater reproducibility of the 6-minute walk test and the 30-second sit-to-stand test in patients with severe and very severe COPD. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2018, 13, 3447–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandes, N.A.; Wouters, E.F.; Meijer, K.; Annegarn, J.; Pitta, F.; Spruit, M.A. Reproducibility of 6-minute walking test in patients with COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, A.E.; Rasekaba, T.; Fiore, J.F.; Burge, A.T., Jr.; Lee, A.L. The 6-minute walk distance cannot be accurately assessed at home in people with COPD. Disabil. Rehabil. 2015, 37, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jette, A.M.; Tao, W.; Norweg, A.; Haley, S. Interpreting rehabilitation outcome measurements. J. Rehabil. Med. 2007, 39, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Liu, C.H.; Fan, C.W.; Lu, C.P.; Lu, W.S.; Hsieh, C.L. The test-retest reliability and the minimal detectable change of the Purdue pegboard test in schizophrenia. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2013, 112, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, R.S.; Jürgensen, S.P.; Arcuri, J.F.; Goulart, C.L.; Santos, P.B.D.; Roscani, M.G.; Mendes, R.G.; Oliveira, C.R.; Caruso, F.R.; Borghi-Silva, A. Reliability and validity of six-minute step test in patients with heart failure. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2021, 54, e10514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Americano, C.V.; Oliveira, C.C.; Sousa Miranda, Y.A.D.; Cabral, L.F.; Reboredo, M.M.; Malaguti, C.; José, A. Respiratory and functional outcomes in post-hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Fisioter. Mov. 2025, 38, e38101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.; Ferreira, A.S.; Hegazy, F.A.; Alaparthi, G.K. Cardiorespiratory Response to Six-Minute Step Test in Post COVID-19 Patients-A Cross Sectional Study. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozalevli, S.; Ozden, A.; Itil, O.; Akkoclu, A. Comparison of the Sit-to-Stand Test with 6 min walk test in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir. Med. 2007, 101, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Castro, R.; Núñez-Cortés, R.; Larrateguy, S.; Alsina-Restoy, X.; Barberà, J.A.; Gimeno-Santos, E.; García, A.R.; Sibila, O.; Blanco, I. Assessment of Exercise Capacity in Post-COVID-19 Patients: How Is the Appropriate Test Chosen? Life 2023, 13, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, F.R.; Marques, J.M.; Brasiliano da Paz, M.; Uchôa Cavalcanti, E.B.; Gomes Costa, R.R. Sit-to-stand test and handgrip strength in men and women with post-COVID-19 syndrome without invasive ventilator support: Insights from a Brazilian observational study. Monaldi. Arch. Chest Dis. 2024, 94, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, B.V.; Arcuri, J.F.; Labadessa, I.G.; Costa, J.N.; Sentanin, A.C.; Di Lorenzo, V.A. Validity of the six-minute step test of free cadence in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2014, 18, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, J. The SARS-CoV-2, a new pandemic zoonosis that threatens the world. Vacunas 2020, 21, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi Neto, J.M.; Tebexreni, A.S.; Alves, A.N.F.; Smanio, P.E.P.; de Abreu, F.B.; Thomazi, M.C.; Nishio, P.A.; Cuninghant, I.A. Cardiorespiratory fitness data from 18,189 participants who underwent treadmill cardiopulmonary exercise testing in a Brazilian population. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevillano-Castaño, A.; Peroy-Badal, R.; Torres-Castro, R.; Gimeno-Santos, E.; García Fernández, P.; Garcia Vila, C.; Ariza Alfaro, A.; De Dios Álvarez, R.; Vilaró, J.; Blanco, I. Is there a learning effect on 1-min sit-to-stand test in post-COVID-19 patients? ERJ Open Res. 2022, 8, 00189–02022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevillano-Castaño, A.I.; Peroy-Badal, R.; Torres-Castro, R.; Cañuelo-Márquez, A.M.; Rozalén-Bustín, M.; Modrego-Navarro, Á.; De Sousa-De Sousa, L.; Ramos-Álvarez, J.J.; Maté-Muñoz, J.L.; García-Fernández, P. Test–Retest Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change in Chester Step Test and 1-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test in Long COVID Patients. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, M.K.P.; Chu, A.M.Y.; Tiwari, A. Persistent symptoms after SARS-CoV-2 infection: Long-term implications for health and quality of life. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2022, 17, 100373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spruit, M.A.; Singh, S.J.; Garvey, C.; ZuWallack, R.; Nici, L.; Rochester, C.; Hill, K.; Holland, A.E.; Lareau, S.C.; Man, W.D.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Key concepts and advances in pulmonary rehabilitation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, e13–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strassmann, A.; Steurer-Stey, C.; Lana, K.D.; Zoller, M.; Turk, A.J.; Suter, P.; Puhan, M.A. Population-based reference values for the 1-min sit-to-stand test. Int. J. Public Health 2013, 58, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenforde, M.W.; Kim, S.S.; Lindsell, C.J.; Billig Rose, E.; Shapiro, N.I.; Files, D.C.; Gibbs, K.W.; Erickson, H.L.; Steingrub, J.S.; Smithline, H.A.; et al. Symptom Duration and Risk Factors for Delayed Return to Usual Health Among Outpatients with COVID-19 in a Multistate Health Care Systems Network-United States, March–June 2020. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travensolo, C.F.; Arcuri, J.F.; Polito, M.D. Validity and reliability of the 6-min step test in individuals with coronary artery disease. Physiother. Res. Int. 2020, 25, e1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kessel, S.A.M.; Olde Hartman, T.C.; Lucassen, P.; van Jaarsveld, C.H.M. Post-acute and long-COVID-19 symptoms in patients with mild diseases: A systematic review. Fam. Pract. 2022, 39, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, S.D.; Eliasziw, M.; Donner, A. Sample size and optimal designs for reliability studies. Stat. Med. 1998, 17, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
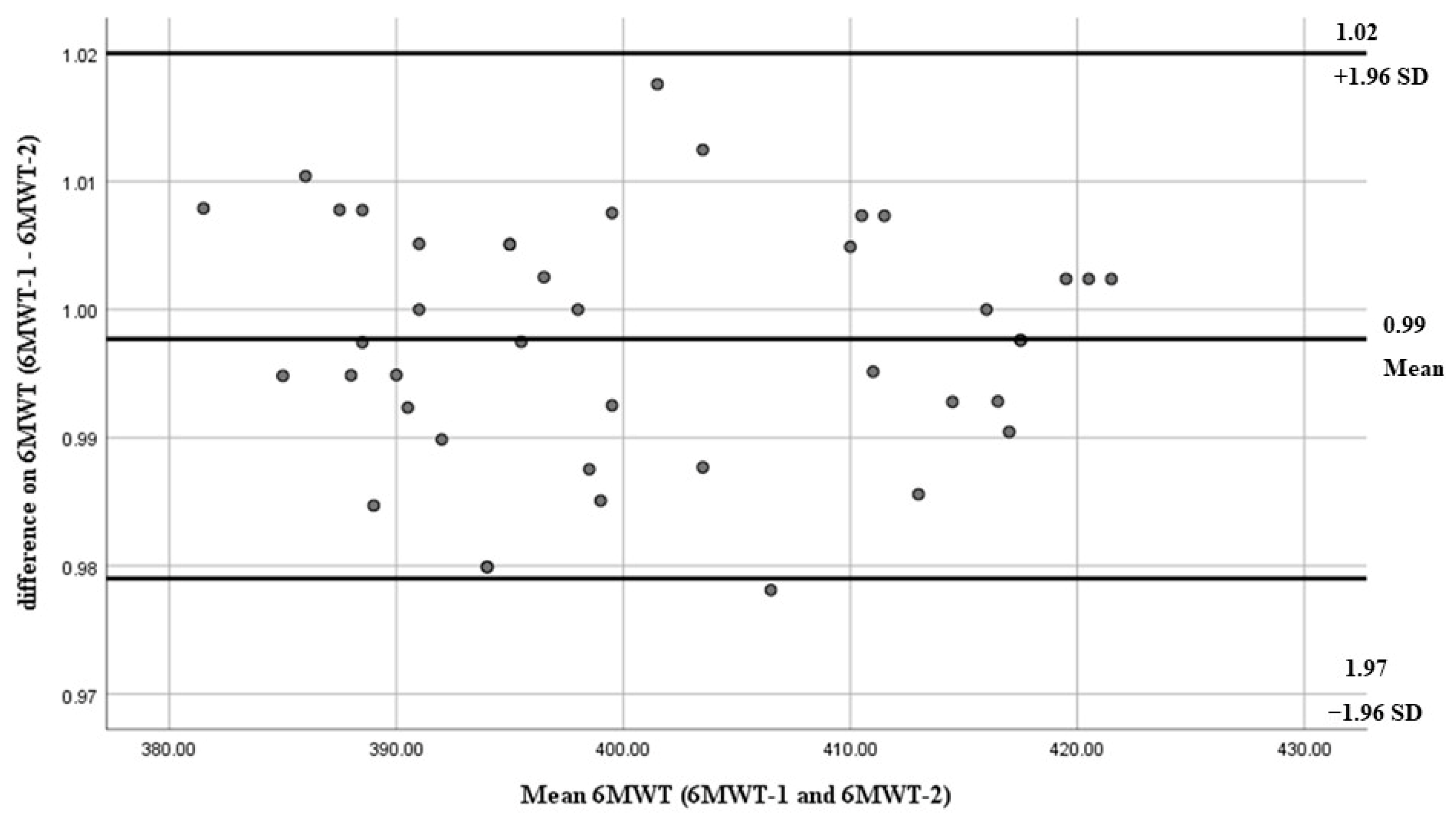
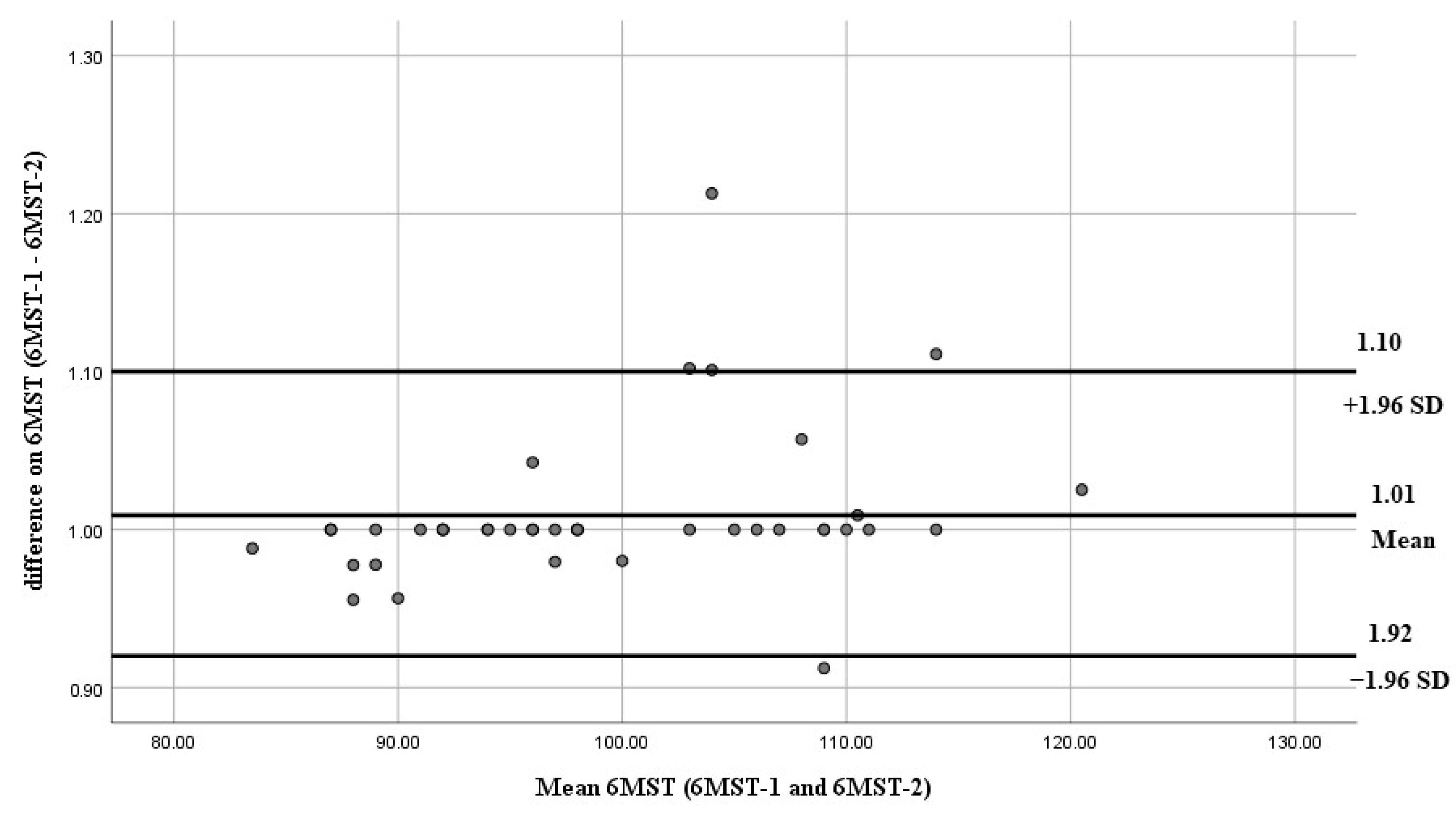
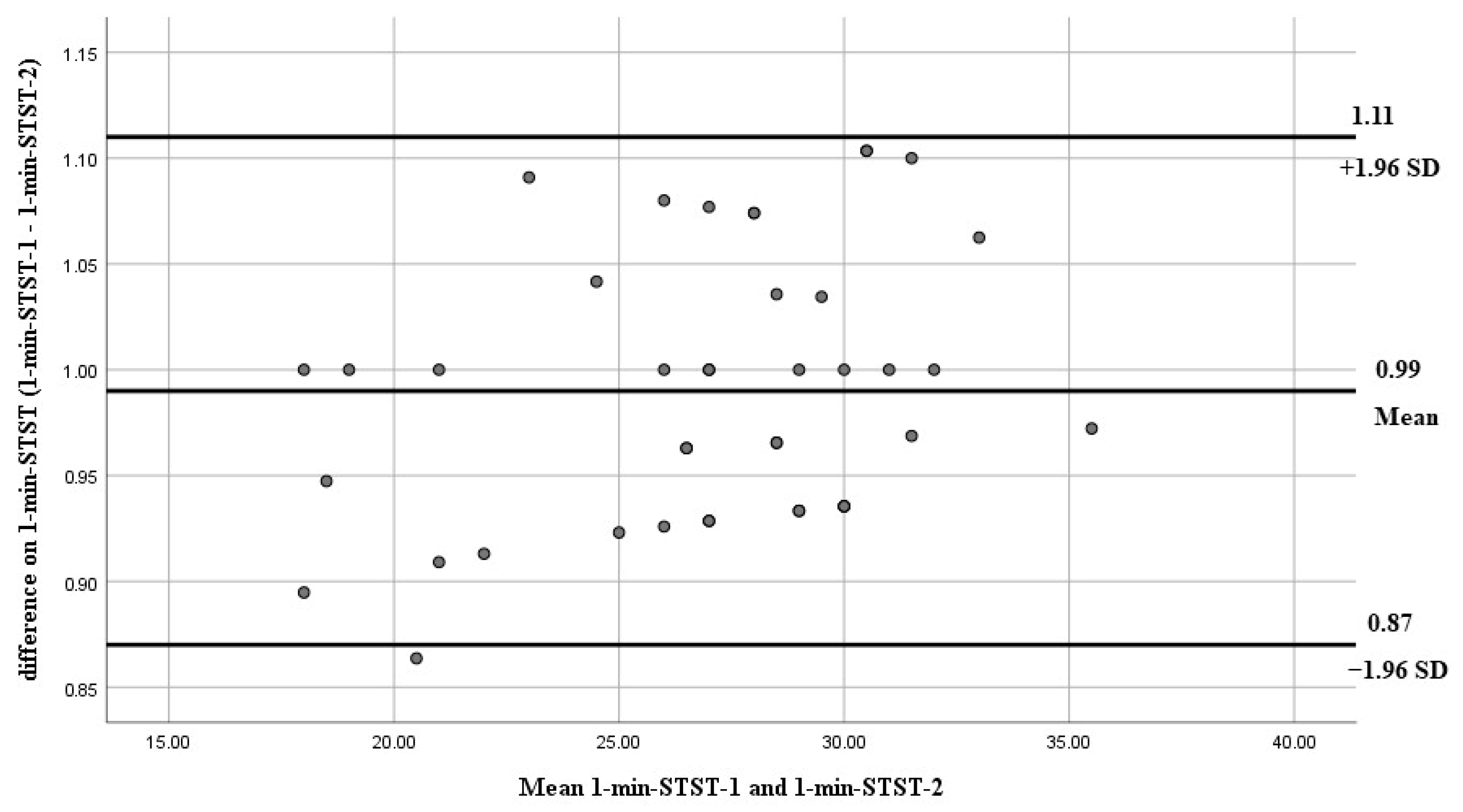
| Variables | Mean ± SD | (95% CI) Min–Max |
|---|---|---|
| Gender: Male (n, %) Female (n, %) | 20 (47.62) 22 (52.38) | |
| Age (years) | 54.62 ± 6.90 | (52.47 to 56.77) 40–66 |
| Weight (kg) | 54.74 ± 5.89 | (52.90 to 56.57) 45–68 |
| High (m) | 1.62 ± 0.06 | (1.60 to 1.64) 1.52–1.76 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 20.87 ± 2.02 | (20.24 to 21.50) 16.30–25.39 |
| 6MWT | 6MST | 1-min-STST | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trail 1 | Trail 2 | p-Value | Trail 1 | Trail 2 | p-Value | Trail 1 | Trail 2 | p-Value | |
| Original is left HR (bpm) | 88.64 ± 7.70 | 88.69 ± 6.91 | 0.915 | 92.90 ± 6.48 | 92.88 ± 5.97 | 0.955 | 92.40 ± 5.99 | 91.90 ± 6.17 | 0.166 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 141.14 ± 6.35 | 140.19 ± 4.79 | 0.111 | 144.24 ± 4.55 | 143.64 ± 4.51 | 0.263 | 142.52 ± 3.96 | 141.88 ± 4.25 | 0.261 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 79.74 ± 7.16 | 80.31 ± 6.58 | 0.181 | 82.57 ± 6.26 | 82.90 ± 5.64 | 0.432 | 83.02 ± 5.63 | 83.03 ± 5.51 | 1.000 |
| O2 sat (%) | 96.64 ± 0.76 | 96.74 ± 0.63 | 0.400 | 96.67 ± 0.52 | 96.64 ± 0.48 | 0.710 | 97.00 ± 0.62 | 97.02 ± 0.68 | 0.785 |
| RPE | 10.79 ± 1.30 | 10.95 ± 0.94 | 0.181 | 11.26 ± 1.08 | 11.36 ± 0.91 | 0.400 | 9.69 ± 1.22 | 9.62 ± 1.08 | 0.628 |
| leg fatigue | 1.51 ± 0.61 | 1.61 ± 0.60 | 0.400 | 2.81 ± 0.63 | 2.64 ± 0.66 | 0.109 | 1.93 ± 0.68 | 1.92 ± 0.75 | 1.000 |
| 6MWT | ||||
| Trail 1 | Trail 2 | ICC(3,k) | SEM | MDC95 |
| 400.60 ± 11.77 | 401.52 ± 11.88 | 0.97 | 4.04 | 5.57 |
| 6MST | ||||
| Trail 1 | Trail 2 | ICC(3,k) | SEM | MDC95 |
| 99.55 ± 10.10 | 98.62 ± 8.75 | 0.93 | 19.41 | 12.21 |
| 1-min-STST | ||||
| Trail 1 | Trail 2 | ICC(3,k) | SEM | MDC95 |
| 26.79 ± 4.55 | 27.02 ± 4.13 | 0.96 | 1.70 | 3.61 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Polish Respiratory Society. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amput, P.; Tapanya, W.; Wongphon, S.; Naravejsakul, K.; Sritiyot, T. Test–Retest Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change of the 6-Minute Step Test and 1-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test in Post-COVID-19 Patients. Adv. Respir. Med. 2025, 93, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93050033
Amput P, Tapanya W, Wongphon S, Naravejsakul K, Sritiyot T. Test–Retest Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change of the 6-Minute Step Test and 1-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test in Post-COVID-19 Patients. Advances in Respiratory Medicine. 2025; 93(5):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93050033
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmput, Patchareeya, Weerasak Tapanya, Sirima Wongphon, Krittin Naravejsakul, and Thanakorn Sritiyot. 2025. "Test–Retest Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change of the 6-Minute Step Test and 1-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test in Post-COVID-19 Patients" Advances in Respiratory Medicine 93, no. 5: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93050033
APA StyleAmput, P., Tapanya, W., Wongphon, S., Naravejsakul, K., & Sritiyot, T. (2025). Test–Retest Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change of the 6-Minute Step Test and 1-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test in Post-COVID-19 Patients. Advances in Respiratory Medicine, 93(5), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93050033






