Inspiratory–Expiratory Muscle Training Improved Respiratory Muscle Strength in Dialysis Patients: A Pilot Randomised Trial
Abstract
Highlights
- Low-intensity home-based breathing exercise improves respiratory muscle strength
- Only 4 weeks of training is required to improve maximal inspiratory–expiratory pressure
- Deconditioned dialysis patients may benefit from respiratory muscle training
- A home-based program autonomously executed is effective for preventing respiratory muscle function decline
Abstract
1. Introduction
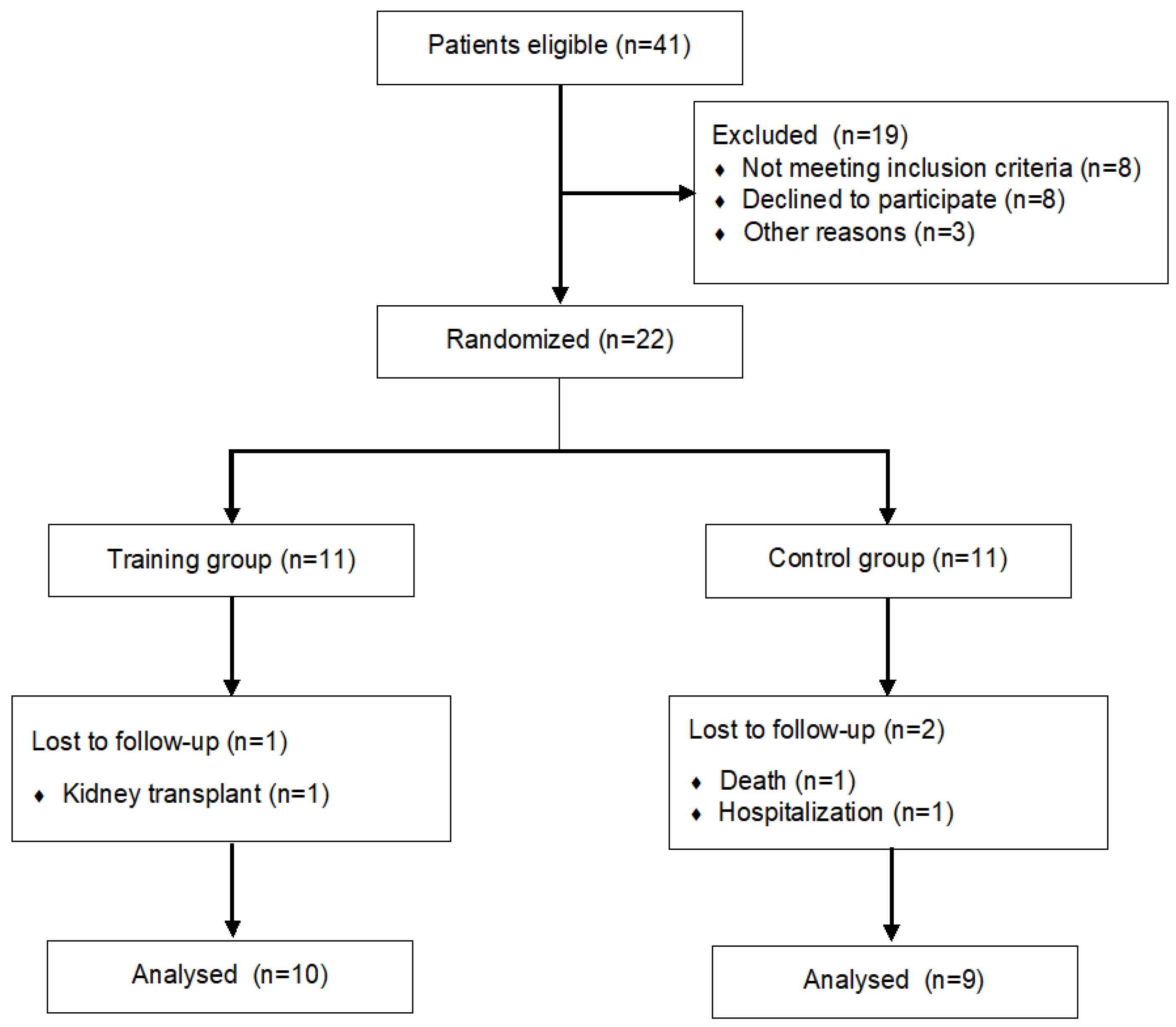
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Randomization and Blinding
2.3. Training Protocol
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Training Features
3.2. Data Stability
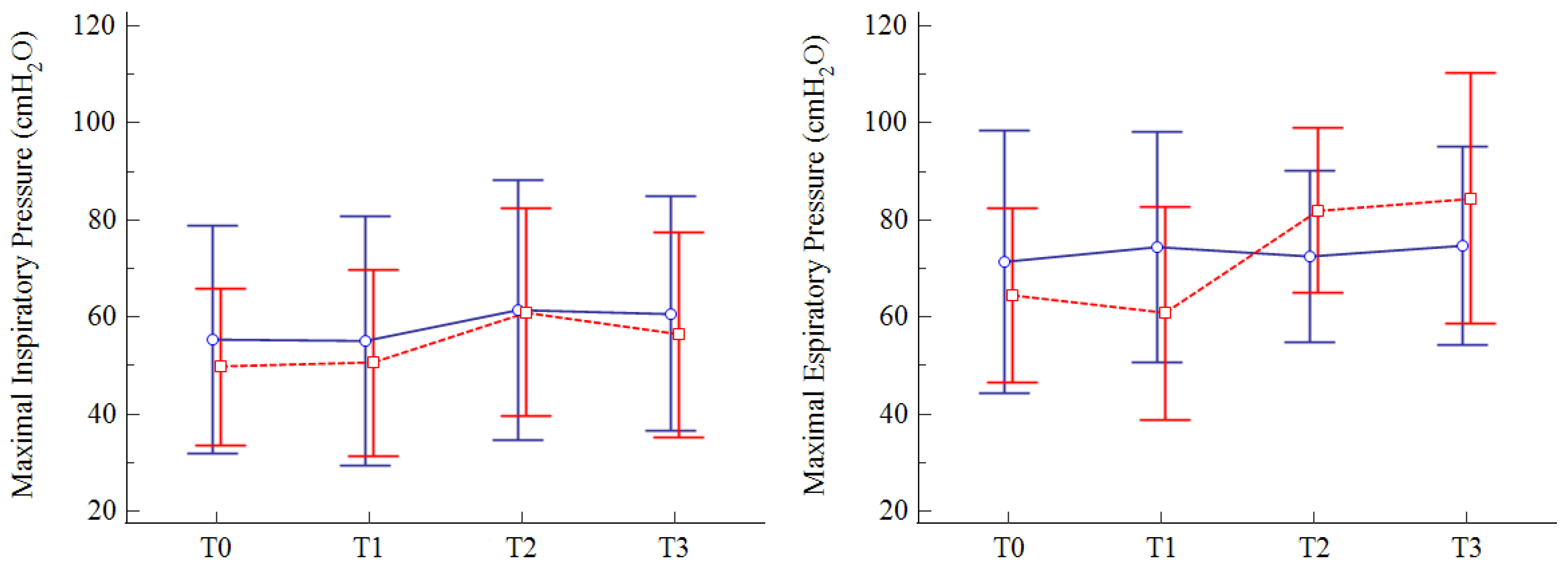
3.3. Primary Outcome
3.4. Secondary Outcomes
3.5. Maintenance of Benefits and Adherence
3.6. Post-Hoc Power Calculation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fahal, I.H. Uraemic sarcopenia: Aetiology and implications. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Medeiros, A.I.C.; Fuzari, H.K.B.; Rattesa, C.; Brandão, D.C.; de Melo Marinho, P.É. Inspiratory muscle training improves respiratory muscle strength, functional capacity and quality of life in patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review. J. Physiother. 2017, 63, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauveau, P.; Moreau, K.; Lasseur, C.; Fouque, D.; Combe, C.; Aparicio, M. Sarcopénie et myopathie urémique: Similitudes et différences [Sarcopenia or uremic myopathy in CKD patients]. Nephrol. Ther. 2016, 12, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, F.; Mallamaci, F.; D’Arrigo, G.; Baggetta, R.; Bolignano, D.; Torino, C.; Lamberti, N.; Bertoli, S.; Ciurlino, D.; Rocca-Rey, L.; et al. Exercise in Patients on Dialysis: A Multicenter, Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomidori, L.; Lamberti, N.; Malagoni, A.M.; Manfredini, F.; Pozzato, E.; Felisatti, M.; Catizone, L.; Barillà, A.; Zuccalà, A.; Tripepi, G.; et al. Respiratory muscle impairment in dialysis patients: Can minimal dose of exercise limit the damage? A Preliminary study in a sample of patients enrolled in the EXCITE trial. J. Nephrol. 2016, 29, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, V. Influência do Treinamento Muscular Inspiratório Sobre a Função Respiratória e Qualidade de Vida de Pacientes Com Doença Renal Crônica em Hemodiálisee a Relação Com a Composição Corporal e Com a Capacidade Aeróbia [Internet]. Universidade Federal de Goiás. 2014. Available online: http://repositorio.bc.ufg.br/tede/handle/tede/3987 (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Pellizzaro, C.O.; Thomé, F.S.; Veronese, F.V. Effect of peripheral and respiratory muscle training on the functional capacity of hemodialysis patients. Ren. Fail. 2013, 35, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, R.R.; Castro, A.A.; Napoleone, F.M.; Faray, L.; de Paula Júnior, A.R.; Osório, R.A. Respiratory biofeedback accuracy in chronic renal failure patients: A method comparison. Clin. Rehabil. 2012, 26, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, P.; Ganem, R.; Zamir, D.; Zonder, H. Specific inspiratory muscle training in chronic hemodialysis. Harefuah 1996, 130, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Dipp, T.; Macagnan, F.E.; Schardong, J.; Fernandes, R.O.; Lemos, L.C.; Plentz, R.D.M. Short period of high-intensity inspiratory muscle training improves inspiratory muscle strength in patients with chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis: A randomized controlled trial. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2020, 24, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.F.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D.; CONSORT Group. CONSORT 2010 statement: Updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMJ 2010, 340, c332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laveneziana, P.; Albuquerque, A.; Aliverti, A.; Babb, T.; Barreiro, E.; Dres, M.; Dubé, B.-P.; Fauroux, B.; Gea, J.; Guenette, J.A.; et al. ERS statement on respiratory muscle testing at rest and during exercise. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; van der Grinten, C.P.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, P.L. The six-minute walk test. Respir. Care 2003, 48, 783–785. [Google Scholar]
- Tarasuik, A.; Heimer, D.; Bark, H. Effect of chronic renal failure on skeletal and diaphragmatic muscle contraction. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1992, 146, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanravan, B.; Gamboa, J.; Wilund, K. Exercise and CKD: Skeletal Muscle Dysfunction and Practical Application of Exercise to Prevent and Treat Physical Impairments in CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, N.; Anding-Rost, K. Exercise training in chronic kidney disease-effects, expectations and adherence. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14 (Suppl. S2), ii3–ii14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howden, E.J.; Coombes, J.S.; Strand, H.; Douglas, B.; Campbell, K.L.; Isbel, N.M. Exercise training in CKD: Efficacy, adherence, and safety. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 65, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiwe, S.; Jacobson, S.H. Exercise training in adults with CKD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 64, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernier-Jean, A.; Beruni, N.A.; Bondonno, N.P.; Williams, G.; Teixeira-Pinto, A.; Craig, J.C.; Wong, G. Exercise training for adults undergoing maintenance dialysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 1, CD014653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, J.; Chernofsky, A.; Nayor, M.; Rahaghi, F.N.; San Jose Estepar, R.; Washko, G.; Synn, A.; Vasan, R.S.; O’Connor, G.; Larson, M.G.; et al. The association of lung function and pulmonary vasculature volume with cardiorespiratory fitness in the community. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2101821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, N.G.; Marizeiro, D.F.; Florêncio, A.C.L.; Silva, Í.C.; Meneses, G.C.; Bezerra, G.F.; Martins, A.M.C.; Libório, A.B. Effects of respiratory muscle training on endothelium and oxidative stress biomarkers in hemodialysis patients: A randomized clinical trial. Respir. Med. 2018, 134, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuenyongchaiwat, K.; Namdang, P.; Vasinsarunkul, P.; Phongsukree, P.; Chaturattanachaiyaporn, K.; Pairojkittrakul, S.; Traitanon, O. Effectiveness of inspiratory muscle training on respiratory fitness and breathlessness in chronic renal failure: A randomized control trial. Physiother. Res. Int. 2021, 26, e1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, P.H.S.; Lima, M.M.O.; Costa, H.; Martins, J.B.; Flecha, O.D.; Gonçalves, P.F.; Alves, F.L.; Rodrigues, V.G.B.; Maciel, E.H.B.; Mendonça, V.A.; et al. Effects of the inspiratory muscle training and aerobic training on respiratory and functional parameters, inflammatory biomarkers, redox status and quality of life in hemodialysis patients: A randomized clinical trial. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polla, B.; D’Antona, G.; Bottinelli, R.; Reggiani, C. Respiratory muscle fibres: Specialisation and plasticity. Thorax 2004, 59, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, A.I.C.; Brandão, D.C.; Souza, R.J.P.; Fuzari, H.K.B.; Barros, C.E.S.R.; Barbosa, J.B.N.; Leite, J.C.; Cavalcanti, F.C.B.; Dornelas de Andrade, A.; de Melo Marinho, P.É. Effects of daily inspiratory muscle training on respiratory muscle strength and chest wall regional volumes in haemodialysis patients: A randomised clinical trial. Disabil. Rehabil. 2019, 41, 3173–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, F.; Lamberti, N.; Malagoni, A.M.; Felisatti, M.; Zuccalà, A.; Torino, C.; Tripepi, G.; Catizone, L.; Mallamaci, F.; Zoccali, C. The role of deconditioning in the end-stage renal disease myopathy: Physical exercise improves altered resting muscle oxygen consumption. Am. J. Nephrol. 2015, 41, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Training (n = 11) | Control (n = 11) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 62 ± 13 | 65 ± 11 | 0.60 |
| Male sex | 6 | 7 | 0.69 |
| BMI | 27.9 ± 5.0 | 26.2 ± 6.6 | 0.51 |
| Years of dialysis | 3 ± 2 | 4 ± 3 | 0.95 |
| Smoking | 6 | 7 | 0.69 |
| Current Smoking | 0 | 1 | 1.00 |
| Hypertension | 11 | 11 | 1.00 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 8 | 9 | 0.66 |
| Diabetes | 6 | 4 | 0.67 |
| Charlson Index | 5 ± 3 | 6 ± 3 | 0.23 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dl | 11.0 ± 1.7 | 11.5 ± 0.4 | 0.41 |
| Serum creatinine, mg/dl | 9.7 ± 3.0 | 9.4 ± 2.7 | 0.83 |
| MIP (cmH2O) | 48 ± 22 | 53 ± 28 | 0.65 |
| MEP (cmH2O) | 65 ± 24 | 69 ± 32 | 0.78 |
| FEV1 (L) | 2.22 ± 0.78 | 2.29 ± 0.52 | 0.80 |
| FVC (L) | 2.76 ± 0.94 | 3.05 ± 0.78 | 0.44 |
| MVV (L) | 69 ± 24 | 82 ± 26 | 0.22 |
| 6MWT (m) | 315 ± 136 | 322 ± 69 | 0.80 |
| T0 | T1 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIP (cmH2O) | 52 (40–65) | 53 (39–67) | 0.92 |
| MEP (cmH2O) | 68 (53–82) | 67 (52–82) | 0.83 |
| FEV1 (L) | 2.24 (1.93–2.56) | 2.19 (1.89–2.48) | 0.19 |
| FVC (L) | 2.91 (2.49–3.34) | 2.81 (2.45–3.17) | 0.12 |
| MVV (L) | 73 (61–86) | 73 (60–87) | 0.90 |
| RMT Group (n = 10) | CON Group (n = 9) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | |
| MIP (cmH2O) | 50 (19–91) | 51 (17–94) | 61 * (30–112) | 56 (19–115) | 55 (16–111) | 55 (14–113) | 61 (16–124) | 63 (16–113) |
| MEP (cmH2O) | 64 (29–100) | 61 (26–112) | 82 * (55–128) | 84 * (39–136) | 71 (41–134) | 74 (45–132) | 72 (43–113) | 75 (40–113) |
| FEV1 (L) | 2.29 (1.20–3.47) | 2.23 (1.12–3.19) | 2.19 (1.12–3.28) | 2.23 (1.20–3.18) | 2.20 (1.46–2.89) | 2.14 (1.47–2.85) | 2.08 (1.40–1.74) | 2.08 (1.33–1.58) |
| FEV1% predicted | 80 (67–92) | 79 (66–90) | 76 (63–88) | 79 (66–92) | 82 (71–94) | 79 (67–90) | 78 (66–89) | 79 (67–91) |
| FVC (L) | 2.84 (1.73–4.39) | 2.81 (1.73–4.01) | 2.74 (1.73–4.06) | 2.79 (1.73–3.85) | 3.00 (1.99–4.52) | 2.81 (1.88–3.95) | 2.75 (1.77–3.92) | 2.75 (1.73–2.85) |
| FVC% predicted | 79 (69–90) | 79 (70–88) | 78 (70–86) | 79 (68–89) | 83 (73–93) | 81 (71–91) | 81 (63–96) | 80 (64–96) |
| MVV (L) | 68 (36–113) | 67 (33–111) | 68 (45–103) | 73 (46–127) | 79 (37–120) | 79 (38–122) | 82 (51–131) | 77 (49–120) |
| 6MWD (Meters) | 306 (162–449) | 296 (172–421) | 327 (229–425) | - | 322 (266–379) | 297 (251–344) | 307 (268–344) | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lamberti, N.; Piva, G.; Battaglia, Y.; Franchi, M.; Pizzolato, M.; Argentoni, A.; Gandolfi, G.; Gozzi, G.; Lembo, M.; Lavisci, P.; et al. Inspiratory–Expiratory Muscle Training Improved Respiratory Muscle Strength in Dialysis Patients: A Pilot Randomised Trial. Adv. Respir. Med. 2023, 91, 93-102. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm91010009
Lamberti N, Piva G, Battaglia Y, Franchi M, Pizzolato M, Argentoni A, Gandolfi G, Gozzi G, Lembo M, Lavisci P, et al. Inspiratory–Expiratory Muscle Training Improved Respiratory Muscle Strength in Dialysis Patients: A Pilot Randomised Trial. Advances in Respiratory Medicine. 2023; 91(1):93-102. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm91010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleLamberti, Nicola, Giovanni Piva, Yuri Battaglia, Michele Franchi, Matteo Pizzolato, Antonio Argentoni, Giorgio Gandolfi, Giulia Gozzi, Margherita Lembo, Pietro Lavisci, and et al. 2023. "Inspiratory–Expiratory Muscle Training Improved Respiratory Muscle Strength in Dialysis Patients: A Pilot Randomised Trial" Advances in Respiratory Medicine 91, no. 1: 93-102. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm91010009
APA StyleLamberti, N., Piva, G., Battaglia, Y., Franchi, M., Pizzolato, M., Argentoni, A., Gandolfi, G., Gozzi, G., Lembo, M., Lavisci, P., Storari, A., Rinaldo, N., Manfredini, F., & Cogo, A. (2023). Inspiratory–Expiratory Muscle Training Improved Respiratory Muscle Strength in Dialysis Patients: A Pilot Randomised Trial. Advances in Respiratory Medicine, 91(1), 93-102. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm91010009









