Evaluation of Drug Interactions in Hospitalized Patients with Respiratory Disorders in Greece
Abstract
:Highlights
- Patients admitted for hospitalization in Greece due to respiratory disorders are patients with multimorbidity, polypharmacy, and a high prevalence of drug–drug interactions (DDIs) in their medication regimens.
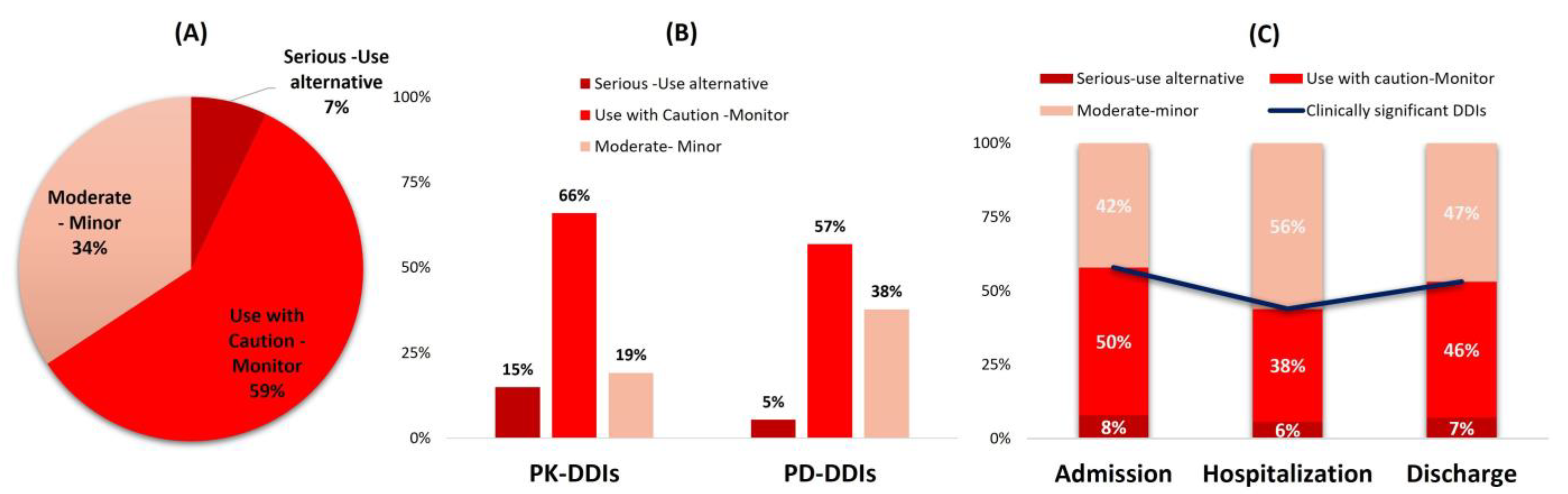
- Clinically significant DDIs that may require modulation in medical regimen or patient monitoring for side effects accounted for 58% upon admission and discharge and less during hospitalization (43%).
- The recorded DDIs mostly refer to cases requiring monitoring and caution to avoid the oc-currence of QT-prolongation, INR modulation, and CYP-mediated metabolism inhibition.
- The clinical significance of DDIs within the cohort can be considered manageable under proper patient monitoring, but clinicians should be aware and always examine if any oc-curring arrhythmias, INR modulations, and prolonged or increased drug actions are linked with DDIs.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethics Approval
2.2. DDI Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
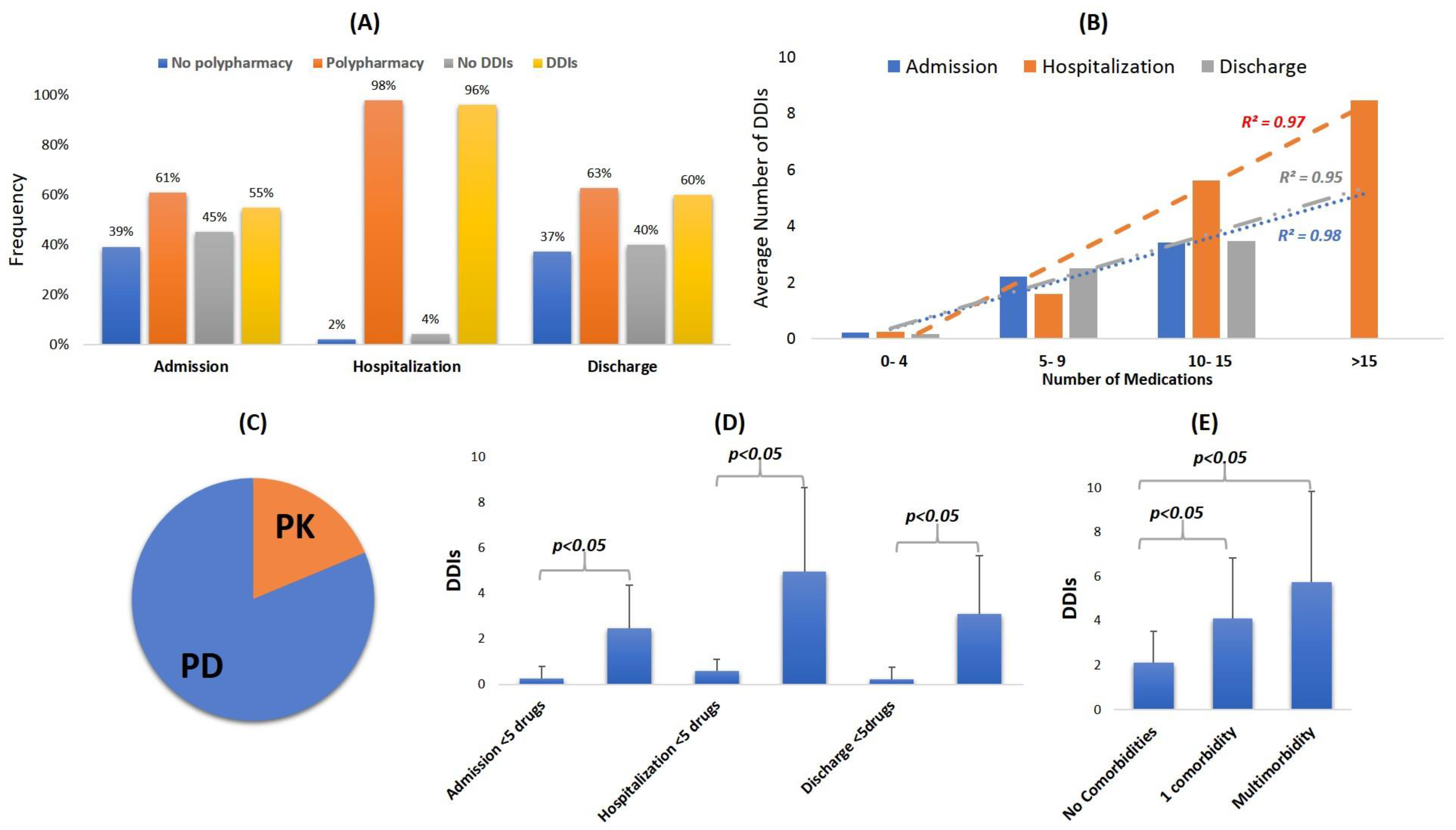
3.1. Patient Demogrpahics, Diagnosis and Comorbidities, and Clinical Status
3.2. Medications Administered
3.3. Identified DDIs and Underlying Pharmacological Mechanisms
3.4. Clinical Significance of Identified DDIs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| ATC | Drug Category | Pharmacological Subgroup |
|---|---|---|
| A02 | Drugs for acid-related disorders | Proton pump inhibitors |
| A03 | Drugs for functional gastrointestinal disorders | Propulsives |
| A04 | Antiemetics and antinauseants | Serotonin (5-HT3) antagonists |
| A05 | Bile and liver therapy | Bile acids and derivatives |
| A06 | Drugs for constipation | Softeners, emollients; Osmotically acting laxatives |
| A07 | Antidiarrheal and intestinal anti-inflammatory/anti-infective agents | Antipropulsives; Antidiarrheal micro-organisms |
| A10 | Drugs used in diabetes | Biguanides; Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors; Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors |
| A11 | Vitamins | Vitamin B-complex |
| A12 | Mineral supplements | Calcium, combinations with vitamin D; Potassium; Magnesium |
| B01 | Antithrombotic agents | Vitamin-K antagonists; Heparin group; Direct oral anticoagulants |
| B02 | Antihemorrhagics | Vitamin K and other hemostatics |
| B03 | Antianemic preparations | Ferrous supplements |
| C01 | Cardiac therapy | Cardiac glycosides; antiarrhythmics; Vasodilators |
| C02 | Antihypertensives | Imidazoline receptor agonists |
| C03 | Diuretics | Thiazides; Sulfonamides; Aldosterone antagonists |
| C07 | β-blockers | selective β-blockers; α- and β-blockers |
| C08 | Ca2+ channel blockers | CCBs with vascular effects; CCBs with direct cardiac effects |
| C09 | Agents acting on the renin–angiotensin system | ACE inhibitors; ARBs |
| C10 | Lipid modifying agents | HMG CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) |
| D03 | Preparations for treatment of wounds and ulcers | Cicatrizants |
| D08 | Antiseptics and disinfectants | Antiseptics and disinfectants |
| G04 | Urologicals | Drugs used in benign prostatic hypertrophy |
| H02 | Corticosteroids for systemic use | Glucocorticoids |
| H03 | Thyroid therapy | Thyroid hormones |
| H05 | Calcium homeostasis | Antiparathyroid agents |
| J01 | Antibacterials for systemic use | Penicillin; macrolides; quinolones |
| J02 | Antimycotics for systemic use | Imidazole and Triazole derivatives |
| J05 | Antivirals for systemic use | Direct acting antiviral drugs (remdesivir) |
| L01 | Antineoplastic agents | Protein kinase inhibitors |
| L04 | Immunosuppressant | Interleukin inhibitors; Antimetabolites |
| M01 | Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic products | Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids |
| M04 | Antigout preparations | Uric acid inhibitors |
| N02 | Analgesics | Analgesics and antipyretics |
| N03 | Antiepileptic | Carboxamide (carbamazepine) and fatty acid (valproic acid) derivatives |
| N04 | Anti-Parkinson drugs | Dopaminergic agents |
| N05 | Psycholeptic | Antipsychotics; anxiolytics; sedatives |
| N06 | Psychoanaleptics | Antidepressants |
| P01 | Antiprotozoal | Aminoquinolines |
| R03 | Drugs for obstructive airway diseases | β-2-receptor agonists; glucocorticoids |
| R05 | Cough and cold preparations | Expectorants; Mucolytics |
| R06 | Antihistamines for systemic use | Aminoalkyl ethers; Substituted alkylamines |
| S01 | Ophthalmological | Antibiotics; β-blocking agents |
| V03 | All other therapeutic products | Detoxifying agents for antineoplastic treatment |
References
- World Health Organization. Chronic Respiratory Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/chronic-respiratory-diseases#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 18 November 2022).
- Shukla, S.D.; Vanka, K.S.; Chavelier, A.; Shastri, M.D.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Bakshi, H.A.; Pabreja, K.; Mahmood, M.Q.; O’Toole, R.F. Chronic Respiratory Diseases: An Introduction and Need for Novel Drug Delivery Approaches. In Targeting Chronic Inflammatory Lung Diseases Using Advanced Drug Delivery Systems; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillas, G.; Perlikos, F.; Tsiligianni, I.; Tzanakis, N. Managing Comorbidities in COPD. Int. J. COPD 2015, 10, 95–109. [Google Scholar]
- Chatila, W.M.; Thomashow, B.M.; Minai, O.A.; Criner, G.J.; Make, B.J. Comorbidities in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, N.C.; Miravitlles, M.; Camelier, A.A.; de Almeida, V.D.C.; Tosta Maciel, R.R.B.; Rosa Camelier, F.W. Prevalence and Impact of Comorbidities in Individuals with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2022, 85, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattan Ambardar, S.; Hightower, S.L.; Huprikar, N.A.; Chung, K.K.; Singhal, A.; Collen, J.F.; Huprikar, S.L.; Chung, N.A.; Singhal, K.K.; Collen, A.; et al. Post-COVID-19 Pulmonary Fibrosis: Novel Sequelae of the Current Pandemic. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiner-Vives, E.; Cordovilla-Pérez, R.; de la Rosa-Carrillo, D.; García-Clemente, M.; Izquierdo-Alonso, J.L.; Otero-Candelera, R.; Pérez-de Llano, L.; Sellares-Torres, J.; de Granda-Orive, J.I. Short and Long-Term Impact of COVID-19 Infection on Previous Respiratory Diseases. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2022, 58, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease—GOLD. Available online: https://goldcopd.org/# (accessed on 18 November 2022).
- Rogliani, P.; Ritondo, B.L.; Zerillo, B.; Matera, M.G.; Calzetta, L. Drug Interaction and Chronic Obstructive Respiratory Disorders; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 2, p. 100009. [Google Scholar]
- Roux-Marson, C.; Baranski, J.B.; Fafin, C.; Exterman, G.; Vigneau, C.; Couchoud, C.; Moranne, O.; Investigators, P.S.P.A. Medication Burden and Inappropriate Prescription Risk among Elderly with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masnoon, N.; Shakib, S.; Kalisch-Ellett, L.; Caughey, G.E. What Is Polypharmacy? A Systematic Review of Definitions. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillot, J.; Maumus-Robert, S.; Bezin, J. Polypharmacy: A General Review of Definitions, Descriptions and Determinants. Therapies 2020, 75, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjerrum, L.; Lopez-Valcarcel, B.G.; Petersen, G. Risk Factors for Potential Drug Interactions in General Practice. Eur. J. Gen. Pract. 2008, 14, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantudo-Cuenca, M.D.; Gutiérrez-Pizarraya, A.; Pinilla-Fernández, A.; Contreras-Macías, E.; Fernández-Fuertes, M.; Lao-Domínguez, F.A.; Rincón, P.; Pineda, J.A.; Macías, J.; Morillo-Verdugo, R. Drug-Drug Interactions between Treatment Specific Pharmacotherapy and Concomitant Medication in Patients with COVID-19 in the First Wave in Spain. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, I.R.; Aronson, J.K. Adverse Drug Reactions: Definitions, Diagnosis, and Management. Lancet 2000, 356, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierodiakonou, D.; Theodorou, E.; Sifaki-Pistolla, D.; Bouloukaki, I.; Antonopoulou, M.; Poulorinakis, I.; Tsakountakis, N.; Voltiraki, F.; Chliveros, K.; Tsiligianni, I. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Polypharmacy in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study from Crete, Greece. Clin. Respir. J. 2021, 15, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charalampopoulou, E.; Kontogiorgis, C.; Nena, E.; Constantinides, T.; Kolios, G. The Complex Phenomenon of Polypharmacy in Older Age People of Greece: Data from the New Era of e-Prescribing. Drugs Ther. Perspect. 2017, 33, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgerini, M.; Schiavo, G.; Lucchetta, R.C.; de Carvalho Mastroianni, P. Drug Interactions for Elderly with Respiratory Disorders and Times of Covid-19: A Systematic Scoping Review. Vitae 2020, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanakis, M.; Patelarou, A.; Patelarou, E.; Tzanakis, N. Drug Interactions for Patients with Respiratory Diseases Receiving COVID-19 Emerged Treatments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanakis, M.; Ioannou, P.; Tzalis, S.; Papakosta, V.; Patelarou, E.; Tzanakis, N.; Patelarou, A.; Kofteridis, D.P. Drug-Drug Interactions among Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 in Greece. J. Clin. Med 2022, 11, 7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanakis, M.; Melissourgaki, M.; Lazopoulos, G.; Patelarou, A.E.; Patelarou, E. Prevalence and Clinical Significance of Drug–Drug and Drug–Dietary Supplement Interactions among Patients Admitted for Cardiothoracic Surgery in Greece. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanakis, M.; Roubedaki, M.; Tzanakis, I.; Zografakis-Sfakianakis, M.; Patelarou, E.; Patelarou, A. Impact of Adverse Drug Reactions in Patients with End Stage Renal Disease in Greece. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechanont, S.; Maphanta, S.; Butthum, B.; Kongkaew, C. Hospital Admissions/Visits Associated with Drug-Drug Interactions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2014, 23, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart-Van Rijkom, J.E.F.; Uijtendaal, E.V.; Ten Berg, M.J.; Van Solinge, W.W.; Egberts, A.C.G. Frequency and Nature of Drug-Drug Interactions in a Dutch University Hospital. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 68, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, M.; Wiebe, N.; Guthrie, B.; James, M.T.; Quan, H.; Fortin, M.; Klarenbach, S.W.; Sargious, P.; Straus, S.; Lewanczuk, R.; et al. Comorbidity as a driver of adverse outcomes in people with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palleria, C.; Di Paolo, A.; Giofrè, C.; Caglioti, C.; Leuzzi, G.; Siniscalchi, A.; De Sarro, G.; Gallelli, L. Pharmacokinetic Drug-Drug Interaction and Their Implication in Clinical Management. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2013, 18, 600–609. [Google Scholar]
- Gallelli, L.; Siniscalchi, A.; Palleria, C.; Mumoli, L.; Staltari, O.; Squillace, A.; Maida, F.; Russo, E.; Gratteri, S.; De Sarro, G.; et al. Adverse Drug Reactions Related to Drug Administration in Hospitalized Patients. Curr. Drug Saf. 2017, 12, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanlon, P.; Nicholl, B.I.; Jani, B.D.; McQueenie, R.; Lee, D.; Gallacher, K.I.; Mair, F.S. Examining Patterns of Multimorbidity, Polypharmacy and Risk of Adverse Drug Reactions in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Cross-Sectional UK Biobank Study. BMJ Open 2018, 8, 18404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez-Manglano, J.; Barquero-Romero, J.; Mena, P.A.; Recio-Iglesias, J.; Cabrera-Aguilar, J.; López-García, F.; Viu, R.B.; Soriano, J.B. Polypharmacy in Patients Hospitalised for Acute Exacerbation of COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 791–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojadinovic, D.; Zivkovic Zaric, R.; Jankovic, S.; Lazic, Z.; Cekerevac, I.; Susa, R. Risk Factors for Potential Drug-Drug Interactions in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 189, 1123–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naser, A.Y.; Mansour, M.M.; Alanazi, A.F.R.; Sabha, O.; Alwafi, H.; Jalal, Z.; Paudyal, V.; Dairi, M.S.; Salawati, E.M.; Alqahtan, J.S.; et al. Hospital Admission Trends Due to Respiratory Diseases in England and Wales between 1999 and 2019: An Ecologic Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, J.; Lucke, T.; Herrera, R.; Watz, H.; Holle, R.; Vogelmeier, C.; Ficker, J.H.; Jörres, R.A. Compatibility of Medication with PRISCUS Criteria and Identification of Drug Interactions in a Large Cohort of Patients with COPD. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 49, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, B.; Makubate, B.; Hernandez-Santiago, V.; Dreischulte, T. The rising tide of polypharmacy and drug-drug interactions: Population database analysis 1995-2010. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatsisvili, A.; Sapounidis, I.; Pavlidou, G.; Zoumpouridou, E.; Karakousis, V.-A.A.; Spanakis, M.; Teperikidis, L.; Niopas, I. Potential Drug–Drug Interactions in Prescriptions Dispensed in Community Pharmacies in Greece. Pharm. World Sci. 2010, 32, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalagkas, P.-N.; Poulentzas, G.; Tsiolis, L.; Berberoglou, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Douros, A.; Kontogiorgis, C.; Constantinides, T. Investigating Potential Drug-Drug Interactions from Greek e-Prescription Data. Curr. Drug Saf. 2022, 17, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhou, P.; He, N.; Zhai, S. Drug-Induced Torsades de Pointes: Disproportionality Analysis of the United States Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 966331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milic, M.; Bao, X.; Rizos, D.; Liu, F.; Ziegler, M.G. Literature Review and Pilot Studies of the Effect of QT Correction Formulas on Reported Beta2-Agonist-Induced QTc Prolongation. Clin. Ther. 2006, 28, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, S.R.; Kostis, W.J.; Celano, C.M.; Januzzi, J.L.; Ruskin, J.N.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Huffman, J.C. Meta-Analysis of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor-Associated QTc Prolongation. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 11731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briasoulis, A.; Agarwal, V.; Pierce, W.J. QT Prolongation and Torsade de Pointes Induced by Fluoroquinolones: Infrequent Side Effects from Commonly Used Medications. Cardiology 2011, 120, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniowska, B.; Tylutki, Z.; Wyszogrodzka, G.; Polak, S. Drug-Drug Interactions and QT Prolongation as a Commonly Assessed Cardiac Effect—Comprehensive Overview of Clinical Trials. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponte, M.; Keller, G.; Girolamo, G. Mechanisms of Drug Induced QT Interval Prolongation. Curr. Drug Saf. 2009, 5, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, R.; Sabir, F.R.N.; Omari, C.; Pepper, C.; Tayebjee, M.H. Managing Drug-Induced QT Prolongation in Clinical Practice. Postgrad. Med. J. 2021, 97, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braz-de-Melo, H.A.; Faria, S.S.; Pasquarelli-do-Nascimento, G.; de Oliveira Santos, I.; Kobinger, G.P.; Magalhães, K.G. The Use of the Anticoagulant Heparin and Corticosteroid Dexamethasone as Prominent Treatments for COVID-19. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 615333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, D.; Pasina, L.; Maggioni, A.P.; Oreni, L.; Conti, F.; Pezzati, L.; Casalini, G.; Bonazzetti, C.; Morena, V.; Ridolfo, A.; et al. Drug–Drug Interactions and Prescription Appropriateness at Hospital Discharge: Experience with COVID-19 Patients. Drugs Aging 2021, 38, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernier, M.; Lancrerot, S.L.; Parassol, N.; Lavrut, T.; Viotti, J.; Rocher, F.; Drici, M.D. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Direct Oral Anticoagulants May Increase Their Benefit-Risk Ratio. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 76, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murad, M.H.; Coto-Yglesias, F.; Wang, A.T.; Sheidaee, N.; Mullan, R.J.; Elamin, M.B.; Erwin, P.J.; Montori, V.M. Drug-Induced Hypoglycemia: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Salem, C.; Badreddine, A.; Fathallah, N.; Slim, R.; Hmouda, H. Drug-Induced Hyperkalemia. Drug Saf. 2014, 37, 677–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, D.K.; Stern, T.A. Linezolid and Serotonin Syndrome. Prim. Care Companion J. Clin. Psychiatry 2009, 11, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, A.; Van Ryn, J.; Sennewald, R.; Yamamura, N.; Stangier, J.; Feuring, M.; Härtter, S. Switching from Enoxaparin to Dabigatran Etexilate: Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Safety Profile. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 68, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, J.H.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Ravaud, P.; Cantagrel, A.; Combe, B.; Flipo, R.M.; Schaeverbeke, T.; Houvenagel, E.; Gaudin, P.; Loeuille, D.; et al. Predictive Risk Factors of Serious Infections in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Abatacept in Common Practice: Results from the Orencia and Rheumatoid Arthritis (ORA) Registry. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1108–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.L.; Sawitzke, A.D.; Doane, J. Abatacept and Serious Respiratory Infections in Patients with Previous Lung Disease. Clin. Rheumatol. 2008, 27, 1569–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjestad, C.; Westin, A.A.; Skogvoll, E.; Spigset, O. Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitors on the Serum Concentrations of the Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors Citalopram, Escitalopram, and Sertraline. Ther. Drug Monit. 2015, 37, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Prueksaritanont, T.; Lin, J.H. Drug Interactions with Calcium Channel Blockers: Possible Involvement of Metabolite-Intermediate Complexation with CYP3A. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2000, 28, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Serbin, M.A.; Guzauskas, G.F.; Veenstra, D.L. Clopidogrel-Proton Pump Inhibitor Drug-Drug Interaction and Risk of Adverse Clinical Outcomes among PCI-Treated ACS Patients: A Meta-Analysis. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2016, 22, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaźniewicz-Łada, M.; Główka, A.K.; Mikulska, A.A.; Główka, F.K. Pharmacokinetic Drug-Drug Interactions among Antiepileptic Drugs, Including CBD, Drugs Used to Treat COVID-19 and Nutrients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roblek, T.; Trobec, K.; Mrhar, A.; Lainscak, M. Potential Drug-Drug Interactions in Hospitalized Patients with Chronic Heart Failure and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Arch. Med. Sci. 2014, 10, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Petrie, I.D.; Levy, R.H.; Ragueneau-Majlessi, I. Mechanisms and Clinical Significance of Pharmacokinetic-Based Drug-Drug Interactions with Drugs Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2017 S. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2019, 47, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Straubinger, R.M.; Mager, D.E. Pharmacodynamic Drug-Drug Interactions. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 105, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.L.; Böttiger, Y.; Kockum, H.; Eiermann, B. High Prevalence of Drug–Drug Interactions in Primary Health Care Is Caused by Prescriptions from Other Healthcare Units. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 122, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manias, E.; Kusljic, S.; Wu, A. Interventions to Reduce Medication Errors in Adult Medical and Surgical Settings: A Systematic Review. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2020, 11, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Methods | |
| Study design | Observational, retrospective, and descriptive study of DDIs |
| Setting | Patients hospitalized in the Respiratory Medicine Department |
| Participants | Patients requiring inpatient treatment for respiratory disorders |
| Variables |
|
| Data sources/ measurement | DDIs based on literature search and relative databases (Medscape, Drugs.com) |
| Study size | Target population: patients admitted with respiratory disordersStudy population: signed informed consent form |
| Bias | Diligence in informing the purpose and objectives of the study Diligence in recording the medication regimens in predefined time periods Recording demographics and medication regimens Analysis of data regarding the significance |
| Results | |
| Participants | 102 patients that signed the informed consent |
| Descriptive data |
|
| Outcome data |
|
| Main results |
|
| Demographics | Mean (±S.D) | Min/Max | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 69.3 (±16.9) | 18/93 | |
| Height (m) | 1.65 (±0.2) | 1.5/1.9 | |
| Weight (kg) | 77.4 (±18.2) | 54.0/128.0 | |
| Body Mass Index (BMI, kg/m2) | 30.5 (±5.4) | 27.9/45.0 | |
| Comorbidities | 2 (2) (median; IQR) | 0/9 | |
| Hospitalization duration (d) | 7 (5) (median, IQR) | 2/74 | |
| Residence | Social Habits | ||
| Urban | 48% | Smoking | 10% |
| Semi-urban | 15% | ||
| Rural | 37 | ||
| Drug A | ATC | Drug B (Victim) | ATC | # | Significance | Pharmacological Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Furosemide | C03 | Allopurinol | M04 | 2 | Monitor | Increased metabolite concentration |
| Amiodarone | C01 | Digoxin | C01 | 1 | SUA | P-gp inhibition |
| Lovastatin | 1 | Monitor | ||||
| Dabigatran | B01 | 2 | ||||
| Atorvastatin | C10 | 1 | ||||
| Carvedilol | C07 | 1 | CYP2C9 inhibition | |||
| Carbamazepine | N03 | Amitriptyline | N06 | 1 | Monitor | Induction of CYP3A4 |
| Itraconazole | J02 | Apixaban | B01 | 1 | Monitor | CYP3A4 inhibition |
| Carbamazepine | N03 | 1 | Induction of CYP3A4 | |||
| Azithromycin | J01 | Lovastatin | C10 | 1 | Monitor | CYP3A4 inhibition |
| Dabigatran | B01 | 1 | P-gp inhibition | |||
| Carvedilol | C07 | Dabigatran | B01 | 1 | Monitor | P-gp inhibition |
| Chloramphenicol | J01 | Alfuzosin | G04 | 1 | Monitor | CYP3A4 inhibition |
| Haloperidol | N05 | 1 | ||||
| Rasagiline | N04 | 1 | CYP1A2 inhibition | |||
| Esomeprazole | A02 | Clopidogrel | B01 | 9 | SUA | CYP2C19 inhibition |
| Digoxin | C01 | 1 | Monitor | P-gp inhibition | ||
| Diltiazem | C08 | Eplerenone | C03 | 1 | SUA | CYP3A4 inhibition |
| Rivaroxaban | B01 | 1 | Monitor | |||
| Pioglitazone | A10 | 1 | ||||
| Tamsulosin | G04 | 2 | ||||
| Donepezil | N06 | 1 | ||||
| Omeprazole | A02 | Escitalopram | N06 | 1 | Monitor | CYP2C9 inhibition |
| Esomeprazole | 7 | Monitor | ||||
| Lovastatin | C10 | Dabigatran | B01 | 1 | Monitor | P-gp inhibition |
| Haloperidol | N05 | Nebivolol | C07 | 1 | Monitor | CYP2D6 inhibition |
| Paroxetine | N06 | Aripiprazole | N05 | 1 | Monitor | CYP2D6 inhibition |
| Primidone | N03 | Roflumilast | R03 | 1 | SUA | Induction of CYP3A4 |
| Sertraline | N06 | Metoprolol | C07 | 2 | Monitor | CYP2D6 inhibition |
| Amlodipine | C08 | Simvastatin | C10 | 1 | SUA | CYP3A4 inhibition |
| Sulfomathoxazole | J01 | Acenocoumarol | B01 | 1 | Monitor | CYP2C9 inhibition |
| Fluoxetine | N06 | Tamsulosin | G04 | 1 | Monitor | CYP2D6 inhibition |
| Amlodipine | C08 | Tramadol | N02 | 1 | Monitor | CYP3A4 inhibition |
| Verapamil | C08 | Simvastatin | C10 | 1 | SUA | CYP3A4 inhibition |
| Rivaroxaban | B01 | 1 | Monitor | P-gp inhibition |
| Drug A | ATC | Drug B | ATC | # | Significance | Pharmacological Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abatacept | L04 | Adalimumab | L04 | 1 | SUA | Immunosuppression |
| Alfuzosin | G04 | Haloperidol | N05 | 1 | Monitor | QT prolongation |
| Salbutamol | R03 | 2 | ||||
| Allopurinol | M04 | Acenocoumarol | B01 | 1 | Monitor | INR modulation |
| Amiodarone | C01 | Azithromycin | J01 | 1 | Monitor | QT prolongation |
| Quetiapine | N05 | 1 | ||||
| Amitriptyline | N06 | Indapamide | C03 | 1 | ||
| Aspirin | B01 | Duloxetine | N06 | 1 | Monitor | INR modulation |
| Azithromycin | J01 | Olanzapine | N05 | 2 | Monitor | QT prolongation |
| Mirtazapine | N06 | 1 | ||||
| Formoterol | R03 | 1 | ||||
| Bisoprolol | C07 | Rivastigmine | N06 | 1 | SUA | Cardiovascular ADRs |
| Tramadol | Ν02 | 1 | ||||
| Ciprofloxacin | J01 | Haloperidol | N05 | 1 | Monitor | QT prolongation |
| Salbutamol | R03 | 4 | ||||
| Alfuzosin | G04 | 1 | ||||
| Citalopram | N06 | Levofloxacin | J01 | 1 | Monitor | QT prolongation |
| Clonazepam | N03 | Bromazepam | N05 | 1 | Monitor | Sedation, respiratory depression |
| Donepezil | N06 | Escitalopram | N06 | 2 | Monitor | QT prolongation |
| Levofloxacin | J01 | 1 | ||||
| Salbutamol | R03 | 2 | ||||
| Haloperidol | N05 | 1 | ||||
| Alfuzosin | G04 | 1 | ||||
| Nintedanib | L01 | 1 | ||||
| Ceftriaxone | J01 | 9 | ||||
| Methylprednisolone | H02 | 26 | ||||
| Apixaban | B01 | 1 | Monitor | INR modulation | ||
| Escitalopram | N06 | Haloperidol | N05 | 1 | Monitor | QT prolongation |
| Salbutamol | R03 | 2 | ||||
| Levofloxacin | J01 | 4 | ||||
| Gabapentin | N03 | Fentanyl | N02 | 1 | SUA | Sedation, respiratory depression |
| Lorazepam | N05 | 1 | ||||
| Hydroxychloroquine | P01 | Citalopram | N06 | 1 | Monitor | QT prolongation |
| Hydroxyzine | N05 | Solifenacin | G04 | 1 | Monitor | |
| Leflunomide | L04 | Acenocoumarol | B01 | 1 | Monitor | INR modulation |
| Levofloxacin | J01 | Olanzapine | N05 | 1 | Monitor | QT prolongation |
| Mirtazapine | N06 | 1 | ||||
| Trimethoprim | J01 | 2 | ||||
| Salbutamol | R03 | 5 | ||||
| Alfuzosin | G04 | 1 | ||||
| Levomepromazine | N05 | Trifluoperazine | N05 | 1 | Monitor | QT prolongation |
| Linezolid | J01 | Salbutamol | R03 | 3 | Monitor | Cardiovascular ADRs |
| Fentanyl | N02 | 1 | SUA | Serotonin syndrome | ||
| Quetiapine | N05 | 1 | ||||
| Citalopram | N06 | 1 | ||||
| Insulin | A12 | 1 | Monitor | Hypoglycemia | ||
| Mirtazapine | N06 | Olanzapine | N05 | 1 | Monitor | QT prolongation |
| Venlafaxine | N06 | 3 | ||||
| Rivaroxaban | B01 | 1 | Monitor | INR modulation | ||
| Moxifloxacin | J01 | 1 | Monitor | QT prolongation | ||
| Perindopril | C09 | Allopurinol | M04 | 1 | SUA | Anaphylaxis risk, Steven Johnson’s syndrome |
| Perphenazine | N05 | Levomepromazine | N05 | 1 | Monitor | QT prolongation |
| Indapamide | C03 | 1 | ||||
| Piperacillin | J01 | Vancomycin | J01 | 1 | Monitor | Risk of nephrotoxicity |
| Potassium Chloride | A12 | Eplerenone | C03 | 1 | SUA | Hyperkalemia |
| Pregabalin | N03 | Lorazepam | N05 | 1 | Monitor | Sedation, respiratory depression |
| Quetiapine | N05 | Donepezil | N06 | 1 | Monitor | QT prolongation |
| Levodopa | N04 | 1 | ||||
| Levofloxacin | J01 | 2 | ||||
| Ramipril | C09 | Potassium Chloride | A12 | 1 | Monitor | Hyperkalemia |
| Ipratropium | R03 | Risperidone | N05 | 1 | Monitor | Hypoglycemia |
| Salbutamol | Haloperidol | N05 | 4 | Monitor | QT prolongation | |
| Propafenone | C01 | 1 | ||||
| Azithromycin | J01 | 7 | ||||
| Ondansetron | A04 | 1 | ||||
| Fluoxetine | N06 | 2 | ||||
| Sertraline | N06 | Salbutamol | R03 | 3 | Monitor | QT prolongation |
| Spironolactone | C03 | Potassium Chloride | A12 | 2 | Monitor | Hyperkalemia |
| Tocilizumab | L04 | Remdesivir | J05 | 1 | Monitor | Hepatotoxicity |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spanakis, M.; Ioannou, P.; Tzalis, S.; Chouzouri, F.; Patelarou, E.; Kofteridis, D.P.; Antoniou, K.M.; Schiza, S.E.; Patelarou, A.; Tzanakis, N. Evaluation of Drug Interactions in Hospitalized Patients with Respiratory Disorders in Greece. Adv. Respir. Med. 2023, 91, 74-92. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm91010008
Spanakis M, Ioannou P, Tzalis S, Chouzouri F, Patelarou E, Kofteridis DP, Antoniou KM, Schiza SE, Patelarou A, Tzanakis N. Evaluation of Drug Interactions in Hospitalized Patients with Respiratory Disorders in Greece. Advances in Respiratory Medicine. 2023; 91(1):74-92. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm91010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpanakis, Marios, Petros Ioannou, Sotiris Tzalis, Flora Chouzouri, Evridiki Patelarou, Diamantis P. Kofteridis, Katerina M. Antoniou, Sophia E. Schiza, Athina Patelarou, and Nikos Tzanakis. 2023. "Evaluation of Drug Interactions in Hospitalized Patients with Respiratory Disorders in Greece" Advances in Respiratory Medicine 91, no. 1: 74-92. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm91010008
APA StyleSpanakis, M., Ioannou, P., Tzalis, S., Chouzouri, F., Patelarou, E., Kofteridis, D. P., Antoniou, K. M., Schiza, S. E., Patelarou, A., & Tzanakis, N. (2023). Evaluation of Drug Interactions in Hospitalized Patients with Respiratory Disorders in Greece. Advances in Respiratory Medicine, 91(1), 74-92. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm91010008