Exploring the Feasibility of a Microchip Laser Ablation Method for the Preparation of Biopolymer-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles: Case Studies with Gelatin and Collagen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kogan, M.J.; Olmedo, I.; Hosta, L.; Guerrero, A.R.; Cruz, L.J.; Albericio, F. Peptides and Metallic Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Nanomedicine 2007, 2, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khlebtsov, N.G.; Dykman, L.A. Optical Properties and Biomedical Applications of Plasmonic Nanoparticles. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2010, 111, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, N.; Kamali, M.; Baghersad, M.H. Recent Biomedical Applications of Gold Nanoparticles: A Review. Talanta 2018, 184, 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Lou, X.Y.; Liang, F.; Yang, Y.W. Surface-Functionalized Gold and Silver Nanoparticles for Colorimetric and Fluorescent Sensing of Metal Ions and Biomolecules. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 459, 214461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, Z.; Saleem, R.; Khan, R.R.M.; Liaqat, M.; Pervaiz, M.; Saeed, Z.; Muhammad, G.; Amin, M.; Rasheed, S. Green Synthesis, Properties, and Biomedical Potential of Gold Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2024, 59, 103271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Xu, C. Gold Nanoparticle-Mediated Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer for Analytical Applications in the Fields of Life Health and Safety. Talanta 2025, 282, 127023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Osone, S.; Kim, T.; Higashi, H.; Seto, T. Synthesis of Nanoparticles by Laser Ablation: A Review. KONA Powder Part. J. 2017, 2017, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandran, A.; Sreenilayam, S.P.; Madanan, K.; Thomas, S.; Brabazon, D. Nanoparticle Production via Laser Ablation Synthesis in Solution Method and Printed Electronic Application—A Brief Review. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, T.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yin, K. Facile Fabrication of Hierarchical Textures for Substrate-Independent and Durable Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 9392–9400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Wang, L.; Deng, Q.; Huang, Q.; Jiang, J.; Li, G.; He, J. Femtosecond Laser Thermal Accumulation-Triggered Micro-/Nanostructures with Patternable and Controllable Wettability Towards Liquid Manipulating. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darroudi, M.; Khorsand Zak, A.; Muhamad, M.R.; Zamiri, R. Preparation of Gelatinous Gold Nanoparticles by Pulsed Laser Ablation. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2015, 41, 4587–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, H.; He, W.; Ming, W. Progress in Laser Ablation and Biological Synthesis Processes: “Top-Down” and “Bottom-Up” Approaches for the Green Synthesis of Au/Ag Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.H.; Taira, T. Sub-Nanosecond Laser Induced Air-Breakdown with Giant-Pulse Duration Tuned Nd:YAG Ceramic Micro-Laser by Cavity-Length Control. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettiarachchi, B.S.; Takaoka, Y.; Uetake, Y.; Yakiyama, Y.; Lim, H.H.; Taira, T.; Maruyama, M.; Mori, Y.; Yoshikawa, H.Y.; Sakurai, H. Uncovering gold nanoparticle synthesis using a microchip laser system through pulsed laser ablation in aqueous solution. Ind. Chem. Mater. 2024, 2, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, B.S.; Takaoka, Y.; Uetake, Y.; Yakiyama, Y.; Yoshikawa, H.Y.; Maruyama, M.; Sakurai, H. Mechanistic Study in Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis through Microchip Laser Ablation in Organic Solvents. Metals 2024, 14, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, B.S.; Yakiyama, Y.; Sakurai, H. Tailoring Carbon-Encapsulated Gold Nanoclusters via Microchip Laser Ablation in Polystyrene Solution: Controlling Size, Structure, and Photoluminescent Properties. RSC Appl. Interfaces 2025, 2, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, M.P.; Lee, S.J.; Park, I.S.; Lee, M.H.; Bae, T.S.; Kuboki, Y.; Uo, M.; Watari, F. Synthesis of Gelatin-Capped Gold Nanoparticles with Variable Gelatin Concentration. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, A.J.; Janes, R.W.; Wallace, B.A. Tools and methods for circular dichroism spectroscopy of proteins: A tutorial review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8400–8413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, R.; Park, J.S.; Seo, C.H.; Park, Y. Applications of Circular Dichroism for Structural Analysis of Gelatin and Antimicrobial Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 3229–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rub, M.A.; Asiri, A.M.; Khan, J.M.; Khan, R.H.; Din, K.-U. Interaction of Gelatin with Promethazine Hydrochloride: Conductimetry, Tensiometry and Circular Dichroism Studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1050, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asil, S.M.; Narayan, M. Molecular Interactions between Gelatin-Derived Carbon Quantum Dots and Apo-Myoglobin: Implications for Carbon Nanomaterial Frameworks. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264, 130416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Jo, K.; Kim, S.; Woo, M.; Choi, Y.; Jung, S. Food Hydrocolloids. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 160, 110739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correard, F.; Maximova, K.; Estève, M.A.; Villard, C.; Roy, M.; Al-Kattan, A.; Sentis, M.; Gingras, M.; Kabashin, A.V.; Braguer, D. Gold Nanoparticles Prepared by Laser Ablation in Aqueous Biocompatible Solutions: Assessment of Safety and Biological Identity for Nanomedicine Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 5415–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévy, A.; De Anda Villa, M.; Laurens, G.; Blanchet, V.; Bozek, J.; Gaudin, J.; Lamour, E.; Macé, S.; Mignon, P.; Milosavljević, A.R.; et al. Surface Chemistry of Gold Nanoparticles Produced by Laser Ablation in Pure and Saline Water. Langmuir 2021, 37, 5783–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Kim, K.K.; Song, J.K.; Park, S.M. The Effects of Ambient Ions on the Growth of Gold Nanoparticles by Laser Ablation in Liquid. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2014, 35, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costela, A.; Garcia-Moreno, I.; Barroso, J.; Sastre, R. Laser Performance of Coumarin 540A Dye Molecules in Polymeric Host Media with Different Viscosities: From Liquid Solution to Solid Polymer Matrix. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, T.; Enoki, M.; Chivavibul, P.; Matsui, A.; Kobayashi, Y. Effect of Confinement Layer on Laser Ablation and Cavitation Bubble during Laser Shock Peening. Mater. Trans. 2016, 57, 1776–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupfeld, T.; Laurens, G.; Merabia, S.; Barcikowski, S.; Gökce, B.; Amans, D. Dynamics of Laser-Induced Cavitation Bubbles at a Solid-Liquid Interface in High Viscosity and High Capillary Number Regimes. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 044306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

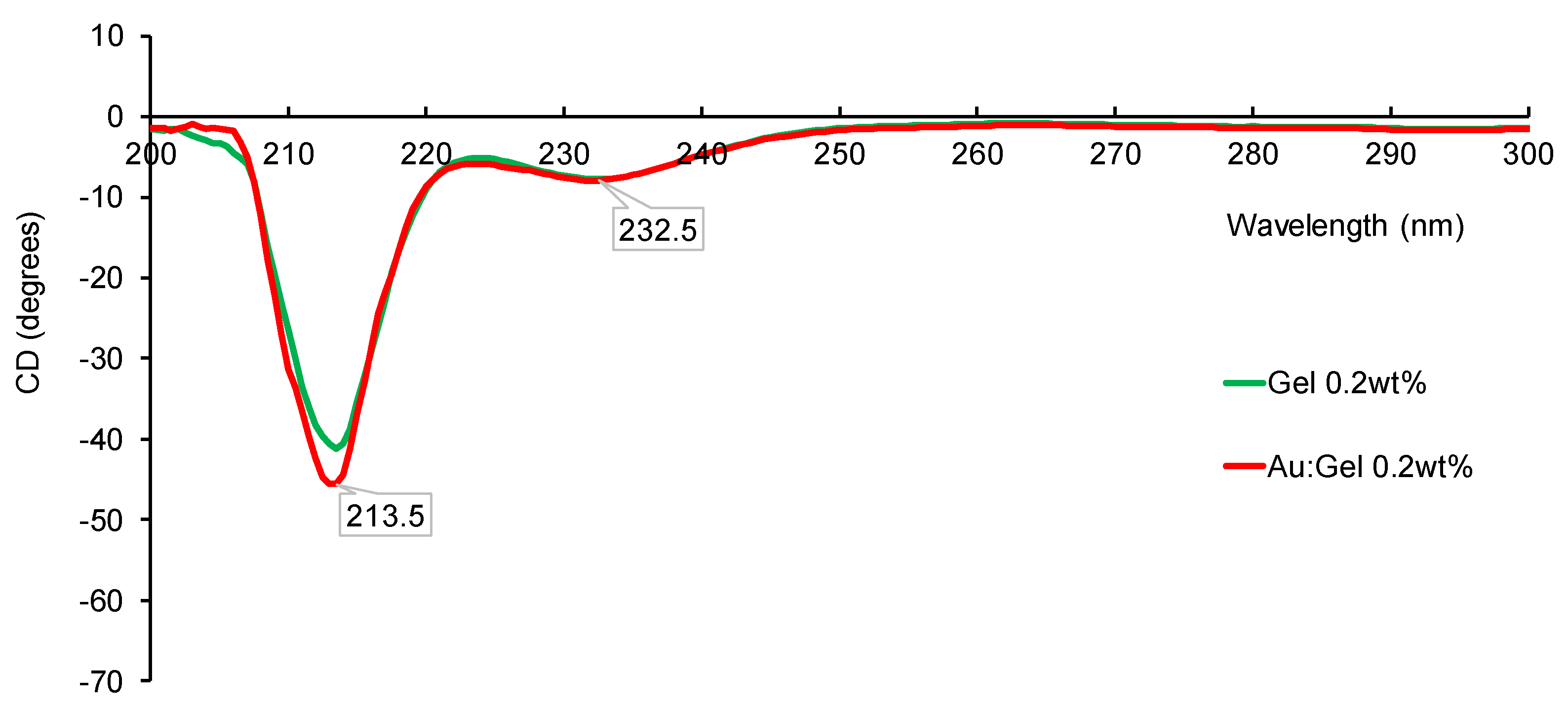
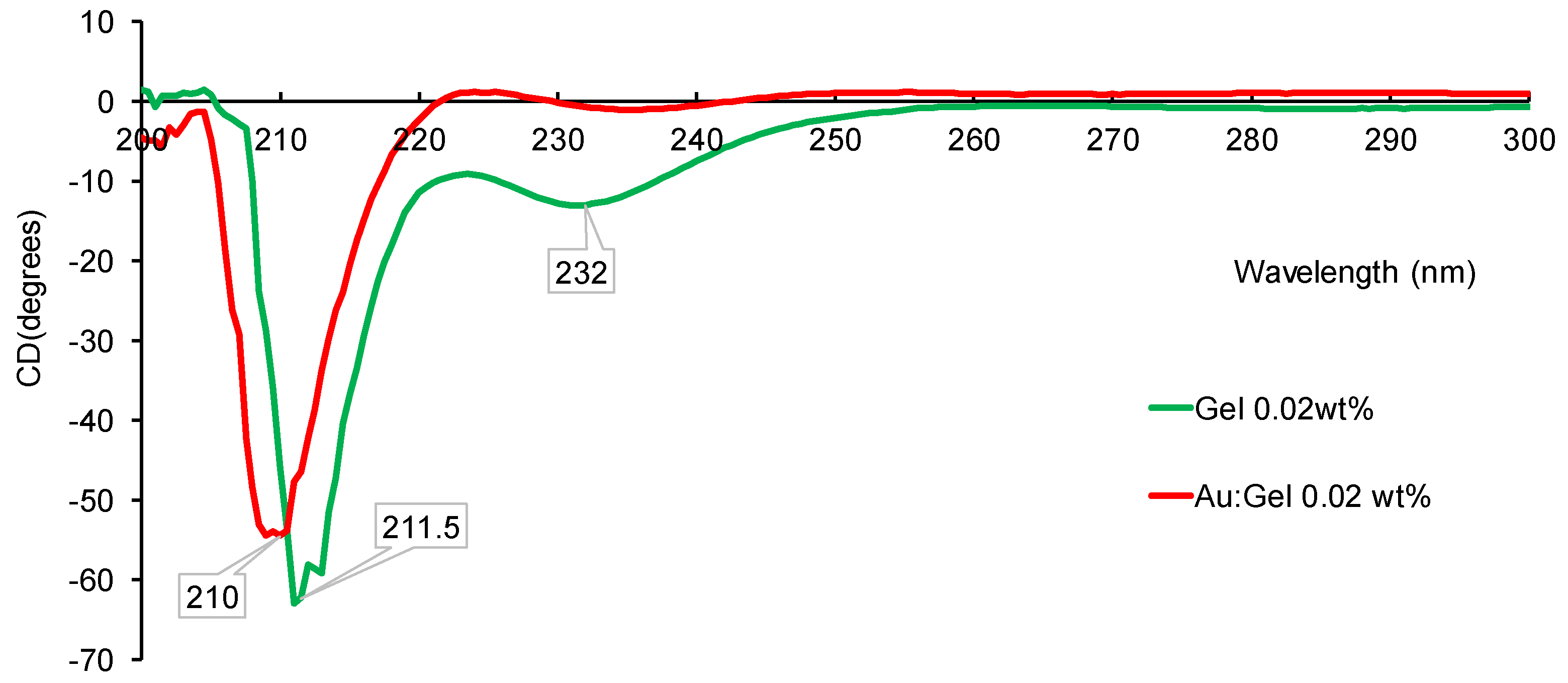
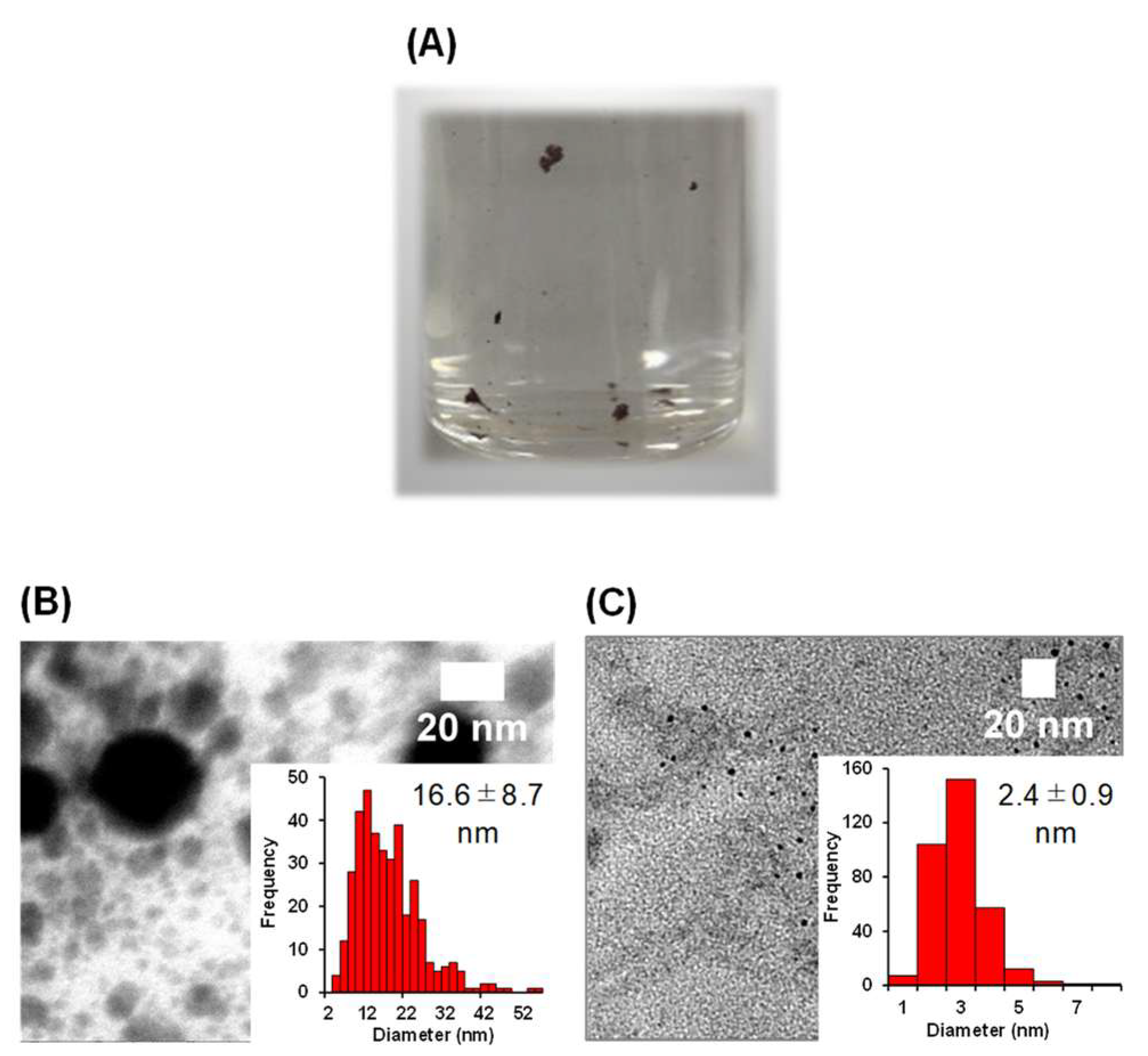
| Entry | Gel Concentration (wt%) | Au–Gel NPs (nm) a | Yield of Au (mmol) b | Au–Gel Colloid Size (nm) c | Gel Colloid Size (nm) c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.02 | 4.2 ± 2.1 | 4.4 × 10−5 | 23 ± 4 | 11 ± 4 |
| 2 | 0.05 | 3.9 ± 2.0 | 5.7 × 10−5 | 30 ± 4 | 7 ± 2 |
| 3 | 0.1 | 4.5 ± 2.3 | 2.2 × 10−5 | 10 ± 4 | 7 ± 2 |
| 4 | 0.2 | 4.3 ± 0.9 | 4.4 × 10−5 | 31 ± 2 | 7 ± 1 |
| 5 | 0.5 | 4.4 ± 2.5 | 7.5 × 10−5 | 25 ± 3 | 4 ± 2 |
| Entry | Matrix | Concentration (wt%) | Solvent | pH Before PLAL | pH After PLAL | Color After PLAL | ICP (mmol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gel | 0.2 | water | 6.57 | 6.81 | Clear red | 4.4 × 10−5 |
| 2 | Gel | 0.2 | PBS | 7.16 | 8.33 | Cloudy red | 3.8 × 10−6 |
| 3 | ColI | 0.2 | PBS | 6.57 | 6.81 | Clear red | 4.4 × 10−5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Assan, N.; Suezawa, T.; Uetake, Y.; Yakiyama, Y.; Matsusaki, M.; Sakurai, H. Exploring the Feasibility of a Microchip Laser Ablation Method for the Preparation of Biopolymer-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles: Case Studies with Gelatin and Collagen. Colloids Interfaces 2025, 9, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9040042
Assan N, Suezawa T, Uetake Y, Yakiyama Y, Matsusaki M, Sakurai H. Exploring the Feasibility of a Microchip Laser Ablation Method for the Preparation of Biopolymer-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles: Case Studies with Gelatin and Collagen. Colloids and Interfaces. 2025; 9(4):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9040042
Chicago/Turabian StyleAssan, Nazgul, Tomoyuki Suezawa, Yuta Uetake, Yumi Yakiyama, Michiya Matsusaki, and Hidehiro Sakurai. 2025. "Exploring the Feasibility of a Microchip Laser Ablation Method for the Preparation of Biopolymer-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles: Case Studies with Gelatin and Collagen" Colloids and Interfaces 9, no. 4: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9040042
APA StyleAssan, N., Suezawa, T., Uetake, Y., Yakiyama, Y., Matsusaki, M., & Sakurai, H. (2025). Exploring the Feasibility of a Microchip Laser Ablation Method for the Preparation of Biopolymer-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles: Case Studies with Gelatin and Collagen. Colloids and Interfaces, 9(4), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9040042







