Influence of Surface Roughness on Interfacial Properties of Particle Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Silica Particles
2.2. Contact Angle Measurements
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.4. Dynamic Light Scattering and Zeta Potential Measurements
2.5. Langmuir Trough Measurements
2.6. Interparticle Interactions
2.7. Hysteresis Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Surface Characterization of Particles
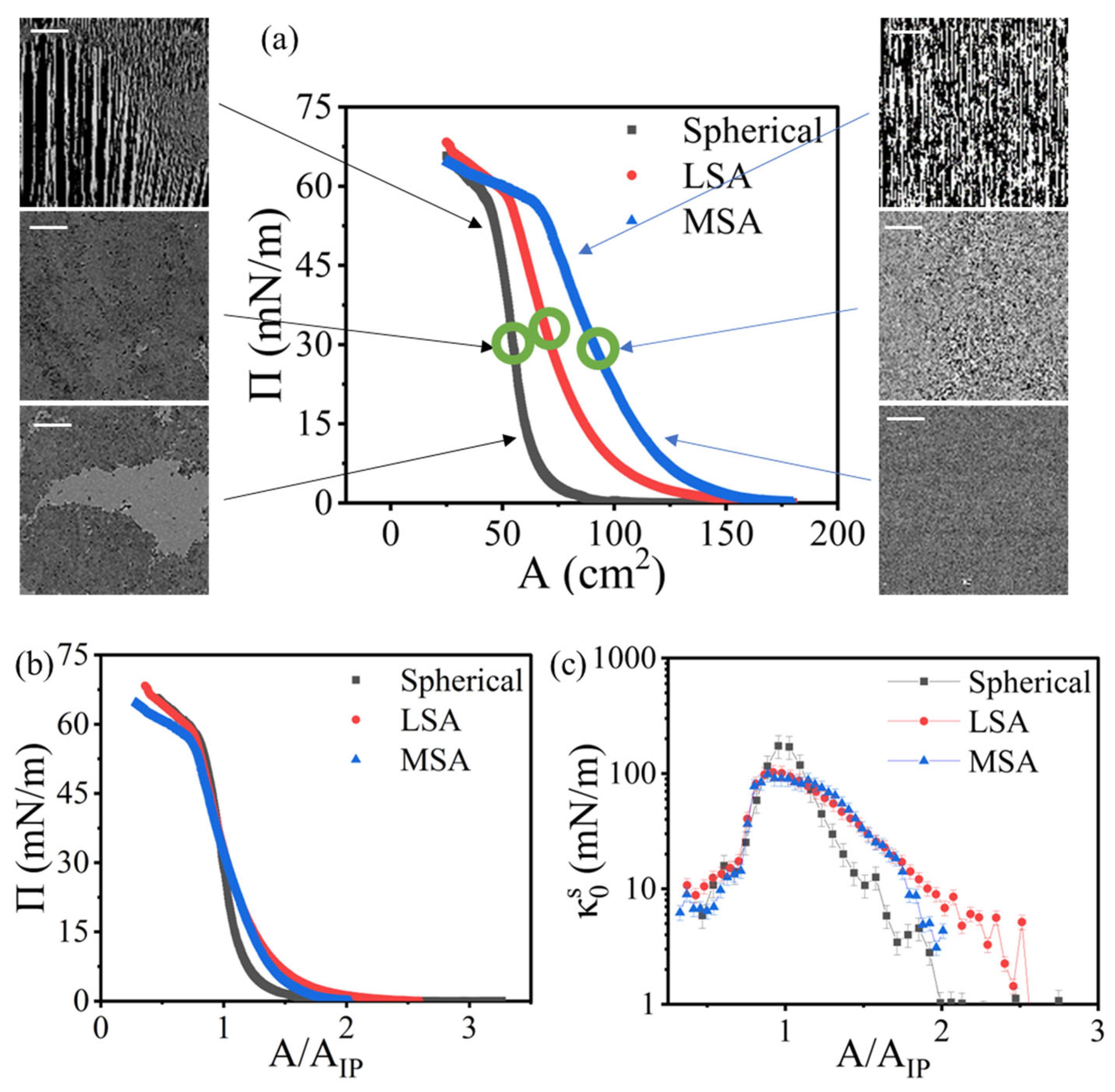
3.2. Monolayer Formation and Response to Compression
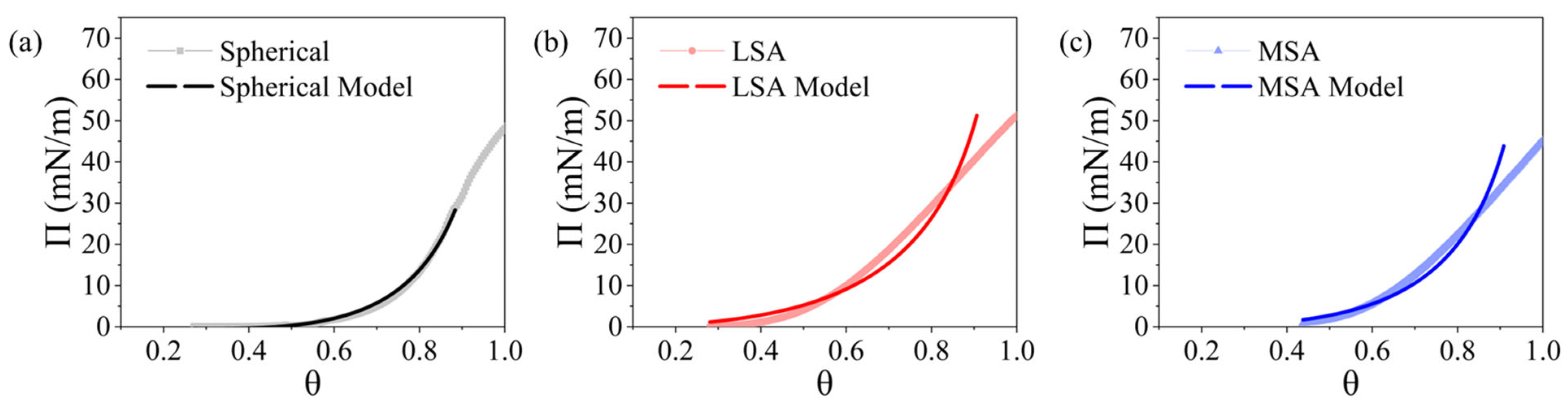
3.3. Thermodynamic Model Fit to the Measured Surface Pressure Isotherms
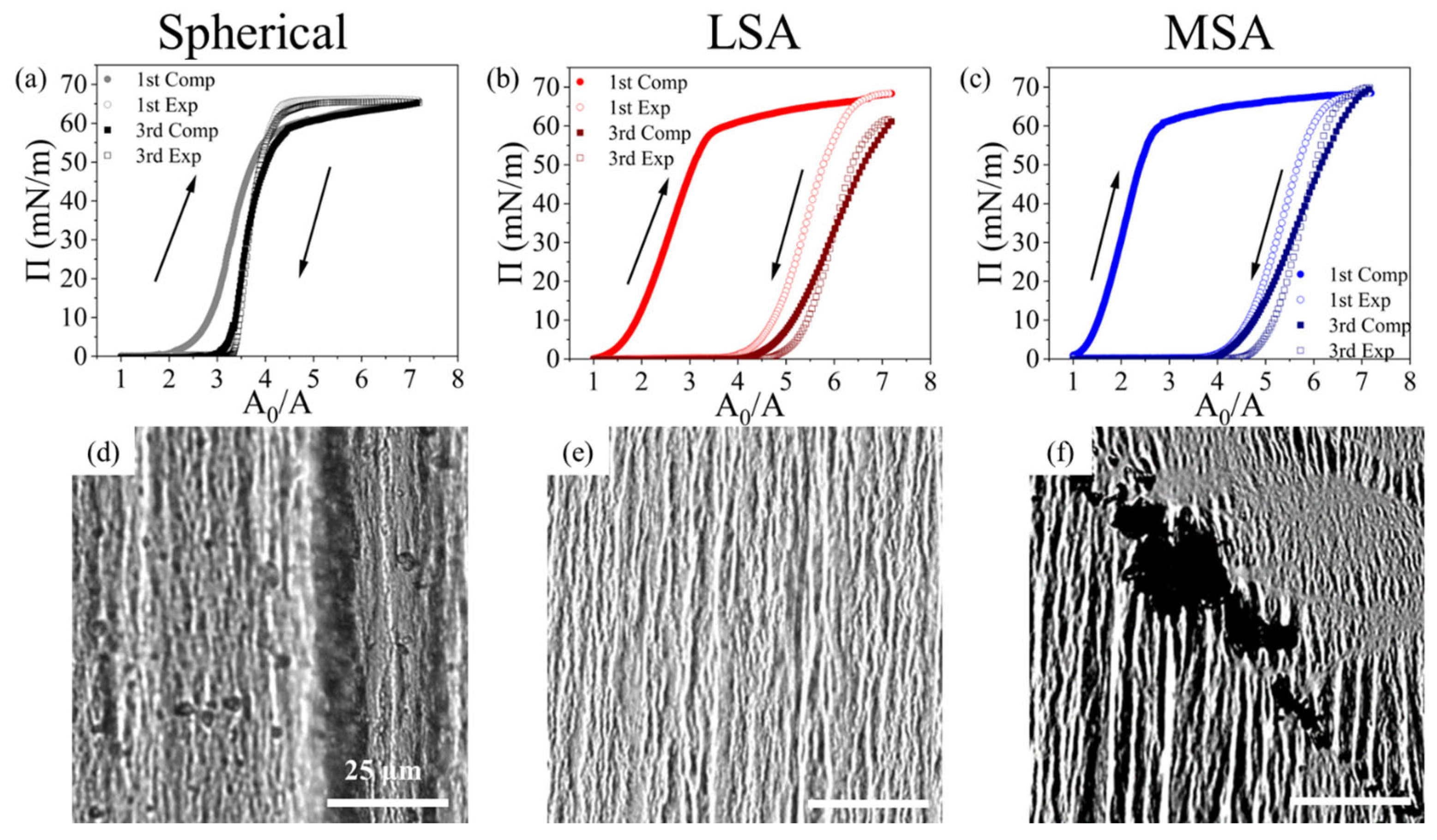
3.4. Collapse and Hysteresis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramsden, W. Separation of solids in the surface-layers of solutions and ‘suspensions’ (observations on surface-membranes, bubbles, emulsions, and mechanical coagulation)—Preliminary account. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1904, 72, 156–164. [Google Scholar]
- Pickering, S.U. CXCVI—Emulsions. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1907, 91, 2001–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, B.P.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Frith, W.J. Synergistic interaction in emulsions stabilized by a mixture of silica nanoparticles and cationic surfactant. Langmuir 2007, 23, 3626–3636. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.J.; Lee, D. Particles at fluid–fluid interfaces: From single-particle behavior to hierarchical assembly of materials. MRS Bull. 2014, 39, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaz, D.M. Colloidal Particles and Liquid Interfaces: A Spectrum of Interactions; Department of Physics, Harvard University: Cambridge, MA, USA; Manoharan Lab Publications: Stanford, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, D.Y.; Rio, E.; Langevin, D.; Wei, B.; Binks, B.P. Viscoelastic properties of silica nanoparticle monolayers at the air-water interface. Eur. Phys. J. E 2010, 31, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Böker, A.; He, J.; Emrick, T.; Russell, T.P. Self-assembly of nanoparticles at interfaces. Soft Matter 2007, 3, 1231–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Furst, E.M. Directing colloidal assembly at fluid interfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20853. [Google Scholar]
- Komura, S.; Hirose, Y.; Nonomura, Y. Adsorption of colloidal particles to curved interfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 241104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresme, F.; Oettel, M. Nanoparticles at fluid interfaces. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 413101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Da, C.; Hatchell, D.C.; Daigle, H.; Ordonez-Varela, J.-R.; Blondeau, C.; Johnston, K.P. Ultra-stable CO2-in-water foam by generating switchable Janus nanoparticles in-situ. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 630, 828–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Choi, J.; Li, H.; Jia, Y.; Huang, R.; Stebe, K.J.; Lee, D. Janus particles with varying configurations for emulsion stabilization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 20961–20968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishal, B.; Ghosh, P. The effect of silica nanoparticles on the stability of aqueous foams. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2019, 40, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lu, K.; Huang, D.; Liu, W. Foams stabilization by silica nanoparticle with cationic and anionic surfactants in column flotation: Effects of particle size. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 88, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, J.S.; Jentoft, R.E.; Grady, B.P.; Resasco, D.E.; Harwell, J.H. Silica Nanoparticle Wettability: Characterization and Effects on the Emulsion Properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 4274–4284. [Google Scholar]
- McGorty, R.; Fung, J.; Kaz, D.; Manoharan, V.N. Colloidal self-assembly at an interface. Mater. Today 2010, 13, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Qiao, X.; Binks, B.P.; Sun, K.; Bai, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Magnetic Pickering emulsions stabilized by Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 3308–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owoseni, O.; Nyankson, E.; Zhang, Y.; Adams, D.J.; He, J.; Spinu, L.; McPherson, G.L.; Bose, A.; Gupta, R.B.; John, V.T. Interfacial adsorption and surfactant release characteristics of magnetically functionalized halloysite nanotubes for responsive emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 463, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abkarian, M.; Subramaniam, A.B.; Kim, S.-H.; Larsen, R.J.; Yang, S.-M.; Stone, H.A. Dissolution Arrest and Stability of Particle-Covered Bubbles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 188301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, M.D.; Telmadarreie, A.; Xu, L.; Dong, M.; Bryant, S.L. Insight on Methane Foam Stability and Texture via Adsorption of Surfactants on Oppositely Charged Nanoparticles. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2018, 34, 14274–14285. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Z.; Worthen, A.; Qajar, A.; Robert, I.; Bryant, S.L.; Huh, C.; Prodanović, M.; Johnston, K.P. Viscosity and stability of ultra-high internal phase CO2-in-water foams stabilized with surfactants and nanoparticles with or without polyelectrolytes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 461, 383–395. [Google Scholar]
- Arab, D.; Kantzas, A.; Bryant, S.L. Nanoparticle stabilized oil in water emulsions: A critical review. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 163, 217–242. [Google Scholar]
- Katepalli, H.; Bose, A. Response of surfactant stabilized oil-in-water emulsions to the addition of particles in an aqueous suspension. Langmuir 2014, 30, 12736–12742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katepalli, H.; Bose, A.; Hatton, T.A.; Blankschtein, D. Destabilization of Oil-in-Water Emulsions Stabilized by Non-ionic Surfactants: Effect of Particle Hydrophilicity. Langmuir 2016, 32, 10694–10698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Striolo, A. Mechanistic study of droplets coalescence in Pickering emulsions. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 9533–9538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, T.N.; Pugh, R.J.; Franks, G.V.; Jameson, G.J. The role of particles in stabilising foams and emulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 137, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Skaff, H.; Emrick, T.; Dinsmore, A.D.; Russell, T.P. Nanoparticle assembly and transport at liquid-liquid interfaces. Science 2003, 299, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, A.K.Y.; Aichele, C.P. Influence of non-ionic surfactant addition on the stability and rheology of particle-stabilized emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 585, 124084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hooghten, R.; Imperiali, L.; Boeckx, V.; Sharma, R.; Vermant, J. Rough nanoparticles at the oil–water interfaces: Their structure, rheology and applications. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 10791–10798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Jia, W.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, S. Demulsification of Crude Oil-in-Water Emulsions Driven by Graphene Oxide Nanosheets. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 4644–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, A.B.; Caggioni, M.; Hartel, R.W.; Spicer, P.T. Arrested coalescence of viscoelastic droplets with internal microstructure. Faraday Discuss. 2012, 158, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madivala, B.; Vandebril, S.; Fransaer, J.; Vermant, J. Exploiting particle shape in solid stabilized emulsions. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacanna, S.; Korpics, M.; Rodriguez, K.; Colón-Meléndez, L.; Kim, S.-H.; Pine, D.J.; Yi, G.-R. Shaping colloids for self-assembly. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.V.; Papavassiliou, D.V. Modification of Oil–Water Interfaces by Surfactant-Stabilized Carbon Nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 27734–27744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Yu, D.; Tian, Q.; Hu, G. Preparation, Characterization, and Properties of Hollow Janus Particles with Tailored Shapes. Langmuir 2014, 30, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltramo, P.J.; Gupta, M.; Alicke, A.; Liascukiene, I.; Gunes, D.Z.; Baroud, C.N.; Vermant, J. Arresting dissolution by interfacial rheology design. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10373–10378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katepalli, H.; John, V.T.; Tripathi, A.; Bose, A. Microstructure and rheology of particle stabilized emulsions: Effects of particle shape and inter-particle interactions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 485, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.; de la Pena, A.; Razavi, S. Interfacial rheology insights: Particle texture and Pickering foam stability. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2023, 35, 384002. [Google Scholar]
- Botto, L.; Lewandowski, E.P.; Cavallaro, M.; Stebe, K.J. Capillary interactions between anisotropic particles. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 9957–9971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danov, K.D.; Kralchevsky, P.A.; Naydenov, B.N.; Brenn, G. Interactions between particles with an undulated contact line at a fluid interface: Capillary multipoles of arbitrary order. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 287, 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- Stamou, D.; Duschl, C.; Johannsmann, D. Long-range attraction between colloidal spheres at the air-water interface: The consequence of an irregular meniscus. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Botto, L.; Cavallaro, J.M.; Bleier, B.J.; Garbin, V.; Stebe, K.J. Near field capillary repulsion. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, S.; Cao, K.D.; Lin, B.; Lee, K.Y.C.; Tu, R.S.; Kretzschmar, I. Collapse of Particle-Laden Interfaces under Compression: Buckling vs. Particle Expulsion. Langmuir 2015, 31, 7764–7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenis, J.; Razavi, S.; Cao, K.D.; Lin, B.; Lee, K.Y.C.; Tu, R.S.; Kretzschmar, I. Mechanical stability of polystyrene and janus particle monolayers at the air/water interface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15370–15373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aveyard, R.; Clint, J.H.; Nees, D.; Quirke, N. Structure and collapse of particle monolayers under lateral pressure at the octane/aqueous surfactant solution interface. Langmuir 2000, 16, 8820–8828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordács, S.; Agod, A.; Hórvölgyi, Z. Compression of Langmuir films composed of fine particles: Collapse mechanism and wettability. Langmuir 2006, 22, 6944–6950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horozov, T.S.; Binks, B.P.; Aveyard, R.; Clint, J.H. Effect of particle hydrophobicity on the formation and collapse of fumed silica particle monolayers at the oil–water interface. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 282, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavaraj, M.G.; Fuller, G.G.; Fransaer, J.; Vermant, J. Packing, flipping, and buckling transitions in compressed monolayers of ellipsoidal latex particles. Langmuir 2006, 22, 6605–6612. [Google Scholar]
- Horozov, T.S.; Aveyard, R.; Clint, J.H.; Binks, B.P. Order−disorder transition in monolayers of modified monodisperse silica particles at the octane−water interface. Langmuir 2003, 19, 2822–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevo, B.G.; Velev, O.D. Controlled, rapid deposition of structured coatings from micro-and nanoparticle suspensions. Langmuir 2004, 20, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwijlen, T.; Imperiali, L.; Vermant, J. Separating viscoelastic and compressibility contributions in pressure-area isotherm measurements. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 206, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Hakim, M.; Oblak, L.; Vermant, J. Facile and Robust Production of Ultrastable Micrometer-Sized Foams. ACS Eng. Au 2023, 3, 235–248. [Google Scholar]
- Pepicelli, M.; Verwijlen, T.; Tervoort, T.A.; Vermant, J. Characterization and modelling of Langmuir interfaces with finite elasticity. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 5977–5990. [Google Scholar]
- Barthel, H.; Heinemann, M.; Stintz, M.; Wessely, B. Particle sizes of fumed silica. In Particle & Particle Systems Characterization: Measurement and Description of Particle Properties and Behavior in Powders and Other Disperse Systems; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; Volume 16, pp. 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Alicke, A.; Simon, S.; Sjöblom, J.; Vermant, J. Assessing the interfacial activity of insoluble asphaltene layers: Interfacial rheology versus interfacial tension. Langmuir 2020, 36, 14942–14959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainerman, V.B.; Kovalchuk, V.I.; Lucassen-Reynders, E.H.; Grigoriev, D.O.; Ferri, J.K.; Leser, M.E.; Michel, M.; Miller, R.; Möhwald, H. Surface-pressure isotherms of monolayers formed by microsize and nanosize particles. Langmuir 2006, 22, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar]
- Gun’Ko, V.; Mironyuk, I.; Zarko, V.; Voronin, E.; Turov, V.; Pakhlov, E.; Goncharuk, E.; Nychiporuk, Y.; Vlasova, N.; Gorbik, P.; et al. Morphology and surface properties of fumed silicas. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 289, 427–445. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, S.; Razavi, S. Particle Size and Rheology of Silica Particle Networks at the Air–Water Interface. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, E.L.; Brown, N.; Razavi, S. Janus particles at fluid interfaces: Stability and interfacial rheology. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, E.L.; Razavi, S. Janus particle amphiphilicity and capillary interactions at a fluid interface. AIChE J. 2023, 69, e18241. [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowski, E.P.; Cavallaro, M.; Botto, L.; Bernate, J.C.; Garbin, V.; Stebe, K.J. Orientation and Self-Assembly of Cylindrical Particles by Anisotropic Capillary Interactions. Langmuir 2010, 26, 15142–15154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.W.; Choi, K.H.; Lee, S.J.; Park, B.J. Mapping Anisotropic and Heterogeneous Colloidal Interactions via Optical Laser Tweezers. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, I.B.; Sharifi-Mood, N.; Stebe, K.J. Capillary Assembly of Colloids: Interactions on Planar and Curved Interfaces. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 2018, 9, 283–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevenen, S.; Rahman, A.; Hamilton, H.S.; Ribbe, A.E.; Bradley, L.C.; Beltramo, P.J. Nanoscale porosity in microellipsoids cloaks interparticle capillary attraction at fluid interfaces. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 11892–11904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, D. The Penguin Dictionary of Curious and Interesting Geometry; Penguin: London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]

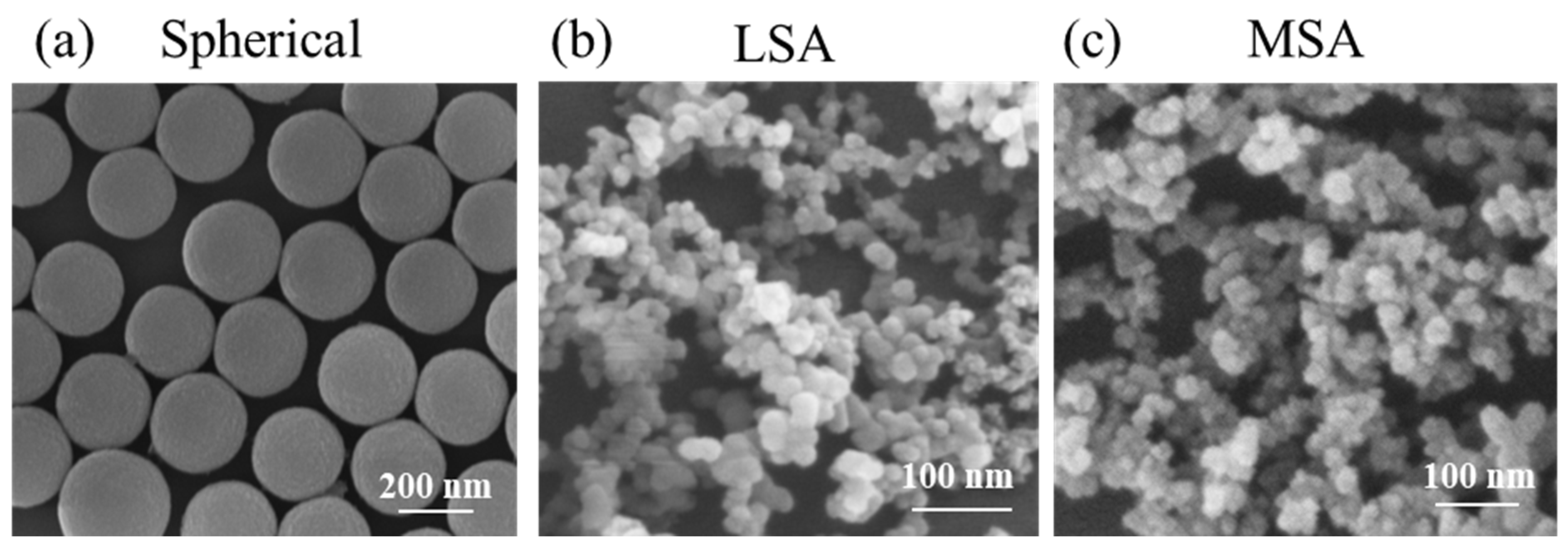

| Sample | DSEM (nm) | DH (nm) | ζ (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spherical | 283 ± 30 | 322 ± 100 | −31 ± 2 |
| LSA | - | 189 ± 16 | −23 ± 2 |
| MSA | - | 196 ± 70 | −26 ± 1 |
| Particle | (mN/m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Spherical | 160 ± 12 | 88.5% | 0.74 |
| LSA Fumed | 105 ± 5 | 90.7% | 0.26 |
| MSA Fumed | 105 ± 5 | 90.7% | 0.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Correia, E.L.; Brown, N.; Papavassiliou, D.V.; Razavi, S. Influence of Surface Roughness on Interfacial Properties of Particle Networks. Colloids Interfaces 2024, 8, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids8020017
Correia EL, Brown N, Papavassiliou DV, Razavi S. Influence of Surface Roughness on Interfacial Properties of Particle Networks. Colloids and Interfaces. 2024; 8(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids8020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorreia, Elton L., Nick Brown, Dimitrios V. Papavassiliou, and Sepideh Razavi. 2024. "Influence of Surface Roughness on Interfacial Properties of Particle Networks" Colloids and Interfaces 8, no. 2: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids8020017
APA StyleCorreia, E. L., Brown, N., Papavassiliou, D. V., & Razavi, S. (2024). Influence of Surface Roughness on Interfacial Properties of Particle Networks. Colloids and Interfaces, 8(2), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids8020017









