Abstract
This work is devoted to the influence of NaCl salt concentration on the formation and stability of colloidal gas aphrons (CGA) produced by the anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and zwitterionic surfactant coco amido propyl betaine (CAPB) in the presence of xanthan gum (XG) as a stabilizer. Dynamic surface tension measurements as well as volume and half-life time of the produced foams are considered for stability analysis. A sharp decrease of the half-life time and volume of the CGAs at NaCl concentrations larger than 20,000 ppm was observed, which was attributed to the precipitation of SDS in the solution. The mentioned SDS precipitation altered the dynamic surface tension behavior, dilational surface elasticity, and turbidity of the solution. The main reason for the precipitation of SDS is the increased Krafft point caused by the addition of salt. However, for the zwitterionic surfactant CAPB, the effects of added NaCl on the interfacial properties required for CGAs production was negligible due to the simultaneous effects on the cationic and anionic head groups in the CAPB leading to negligible changes in the net repulsion forces. Yet, an overall reduction in the half-life time of CGAs with increasing salt concentration, even when we have no precipitation, was observed for both surfactants, which could be explained by the reduction in the ability of XG to increase the viscosity with increasing salt concentration.
1. Introduction
Colloidal gas aphrons (CGAs) were introduced by Sebba, and refer to a colloidal system of bubbles in the micron-range size. According to Sebba, each CGA comprises of a gas core encapsulated in a viscous shell formed by two layers of surfactants. The hydrophilic heads of the first layer are inside the shell and the tails are in the core. The second layer has heads in the shell while the tails are oriented outward. There is also a third layer of surfactant which is called the compatibility layer and has tails inward and heads in the aqueous medium [1,2]. CGAs have been frequently used as drilling fluid for depleted fractured formations. Their ability to survive longer at higher pressures in comparison to regular foams as well as easy production and easy handling have made them a suitable choice for drilling engineering [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. From the review article [10], it can be seen that many papers have studied the effect of different parameters, including stirring time and speed, surfactant and polymer type, and concentration, etc., on the formation, stability, and performance of CGAs. However, the influence of salts has not been sufficiently investigated. This is while the presence of salts significantly changes both the surface activity of ionic surfactants [12] and rheological properties of polymers [13,14,15]. In addition, many water sources used for making CGAs contain various amounts of salts and specifically during offshore drilling when using sea water, the salinity level may be even higher than 30,000 ppm.
Let us mention a few works published in this framework. Longe evaluated the effect of added 200 ppm NaCl to the solution of 0.5 g/L NaDBS for a CGA production and observed that the presence of NaCl lowers the minimum and maximum bubble size [16]. He argued that, in the presence of electrolyte, one of the ions is adsorbed at the surface along with the surfactant and increases the effective concentration of the ionic surfactant. Kommalapati et al. [17] also changed the salinity of a CGA system from 0 to 400 ppm and observed that the increased salt concentration enhances the stability. Save et al. [18] evaluated CGAs made by 0.85 mM of Cetyl Trimethyl Ammonium Chloride surfactant in the presence of 10,000, 40,000 and 80,000 ppm of NaCl and observed that the added salt increased the volume of CGAs but the value of half-life time was reduced. The half-life time describes the time needed for half of the liquid content of CGA solution to drain down and be collected at the bottom of the vessel. It should be noted that their work was in the category of water purification systems and their stability was of the order of 100–300 s, which is much lower than the needed stability for the cases of CGAs as drilling fluid. They concluded that the addition of salt compresses the electrical double layer leading to the reduction of their mutual repulsion and finally decreasing the thickness of the liquid films and the stability of the foam. They related the observed increase in the CGA volume to the reduction in CMC which increases foamability. Almost the same results were obtained by Juregi et al. who examined the stability of CGAs made by anionic surfactant sodium bis-(2-ethyl hexyl) sulfosuccinate) at NaCl concentrations of 0, 0.07, and 0.14 mM and observed that the stability of CGAs decreases with increasing salt concentration [19]. The authors stated that increasing salt concentration suppresses the repulsive electrostatic interactions between bubbles leading to less stability. Chaphalkar et al. also reported that adding 200 ppm of NaCl to the solution increases the volume of CGAs for the ionic surfactants used [20].
Despite the mentioned works on the influence of salts on CGA properties, none of these works have considered the presence of polymer although it is frequently used as viscosifier in CGA based drilling fluids. It also affects the surface behavior of surfactants [21] and enhances the stability of produced CGA systems [10,22]. Moreover, the reported salinities are mostly in the low range and the given results cannot be used for regular saline water systems.
The formation and stability of the CGAs mostly depend on the surface behavior of the surfactant in the solution which is strongly affected by the presence of salt. Therefore, in this work, we performed a systematic study to understand the main influences of added salt on the surfactant behavior and justify the changes of the volume and half-life time of CGAs. We specifically deal with the influence of NaCl salt on the performance of the anionic SDS and the zwitterionic CAPB surfactants for generating CGAs. This is done by studying the dynamic surface tension behavior of aqueous solutions of these surfactants in presence of XG as viscosifier and salt concentrations up to 40,000 ppm as well as performing tests for calculating the volume and half-life time of CGAs. It should be noted that both SDS and CAPB surfactants are utilized in the CGA formation and are proven to produce CGAs with good stability [22].
2. Experimental Setup and Procedure
The drop profile analysis Tensiometer (PAT) [23] manufactured by SINTERFACE Technologies, Germany, was employed for dynamic surface tension measurements. For performing each experiment, a drop was formed in a closed cuvette and the surface tension was recorded versus time by keeping the drop size constant until 600 s. Then, the drop surface area oscillation experiments with frequencies of 0.02, 0.05 and 0.08 Hz were performed. We also used the ODBA capillary pressure based apparatus (oscillating drop and bubble analyzer tensiometry) produced by SINTERFACE Technologies, Germany) for the fast dynamic surface tension measurements in time-scales lower than 1 s. The capillary pressure method uses the pressure difference between inside and outside of the drop/bubble as well as the radius of curvature, to calculate the surface tension. The high-accuracy pressure sensor of the device is able to measure the pressure with a resolution of 1 Pascal and is sufficiently sensitive to record the pressure changes in the drop/bubble in the range of milliseconds during fast adsorption of the surfactants at interface [24].
For producing CGAs, a specific amount of polymer was dissolved in water using a disperser (IKA T25), then pre-weighted amounts of surfactant and salt were added consecutively to the fluid and were gently mixed until a homogeneous mixture was achieved. 200 mL of the prepared solution was poured into a 500 mL beaker, placed under the disperser and CGAs were generated at a specific stirring time and speed. When CGAs were produced, they were immediately poured in a 500 mL graduated cylinder and the total volume was recorded. Afterwards, the height of the clear liquid gathered at the bottom of the graduated cylinder was recorded versus time and the half-life time of the CGA was determined as the time needed to collect 100 mL of liquid at the bottom of the cylinder.
XG was purchased from Sigma Aldrich, SDS was provided from AppliChem and CAPB was provided from Behdash Chemical Co., Iran. The CAPB surfactant came as a 30 wt.% solution in water. NaCl was also purchased from Mojallali Chemical Co., Iran. All the experiments were performed at constant temperature of 20 °C using deionized water.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of NaCl on SDS made CGAs
SDS is a frequently used surfactant for making CGAs [10,25]. But its anionic nature is a reason to be affected by the presence of ions in the system. Figure 1 depicts volume and half-life time of CGAs made by aqueous solutions of 16.6 mM (2 CMC) SDS and 0.1 wt.% XG for different NaCl concentrations. Two trends are seen in the figure. Below 10,000 ppm NaCl, an approximately constant value for the CGA volume could be observed while the half-life time decreases slightly. However, both CGA volume and half-life time diminish for NaCl concentrations above 10,000 ppm with a steep slope.
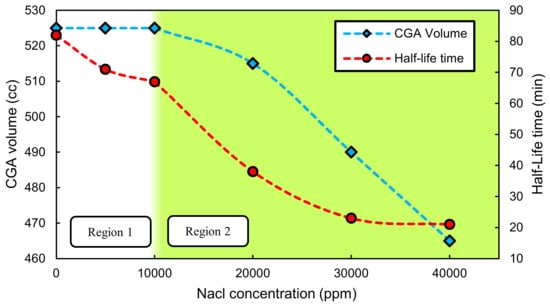
Figure 1.
Volume and half-life time for CGAs made by 0.1 wt.% XG and 16.6 mM SDS vs. NaCl concentration.
Both the stability and volume of CGAs depend on the solution surface properties. In that regard, dynamic surface tension measurements were carried out for different NaCl concentrations using PAT experimental setup. Moreover, to have a better resolution on the dynamic surface tension at short times, which is an important parameter for foam formation as result of bubble formation in sub-seconds, ODBA capillary pressure based method was used for fast dynamic measurements [24]. According to Figure 2, a fast dynamic surface tension behavior is detected for 0, 5000, and 10,000 ppm of NaCl, while an overall reduction in the surface tension could be observed with increasing the salt concentration. This reduction is due to the decreased repulsion between the surfactant head groups which leads also to a reduction of the CMC of the ionic surfactants and an increase in surface activity [26]. But, for 20,000 ppm NaCl, although the equilibrium surface tension is further reduced, the dynamic surface behavior has changed and a further increase of surface tension at concentrations of 30,000 and 40,000 ppm indicates that a precipitation of SDS has occurred in the solution. The fast dynamic results in Figure 2-left also support this argument as the surface tension starts at a higher value for 20,000 ppm than 10,000 ppm which reveals the lower concentration of surfactants in the 20,000 ppm case. The turbidity changes of the solutions as shown in Figure 3 and surface elasticity increments for concentrations larger than 20,000 ppm as depicted in Supplementary Information confirm this statement as well.
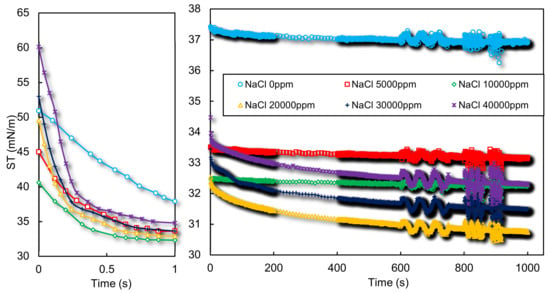
Figure 2.
Dynamic surface tension of aqueous solutions of 0.1 wt.% XG, 16.6 mM SDS and various concentrations of NaCl. The left picture shows the fast dynamic tensions measured by ODBA capillary pressure based setup and the right picture shows the PAT results.
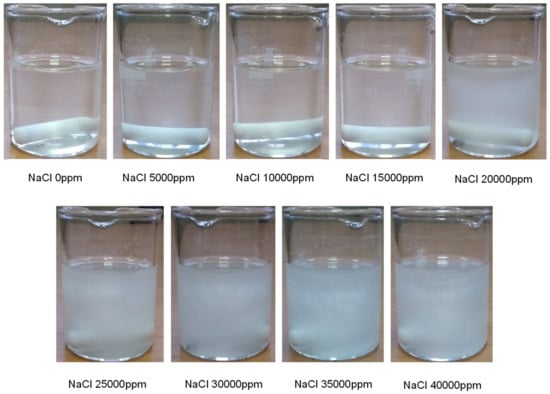
Figure 3.
Aqueous solutions of 0.1 wt.% XG, 16.6 mM SDS and various concentrations of NaCl.
At lower concentrations than CMC, the solubility of SDS is controlled by the solubility product of sodium and dodecyl sulfate ions as well as the non-idealities induced by the presence of other ions [27,28]. But the behavior is much different above the CMC and large concentrations of SDS can be dissolved in water by micelle formation [29,30,31]. In this regard, The Krafft point plays an important role in the solubility as well since surfactant micelles can be formed above this temperature. Below the Krafft temperature, the individually dispersed surfactants are in equilibrium with the hydrated solid surfactants while above, hydrated solid surfactants melt and micelles also participate in the equilibrium [32]. Iyota and Krastev measured the surface tension of aqueous SDS-NaCl solution for different concentrations of NaCl at constant SDS mole fraction and observed a reduction of surface tension followed by an increase upon the NaCl concentration increment [33]. At the point of reversal of the surface tension trend, the solution became turbid as a sign of SDS precipitation. According to their work, ionic surfactants are salted out at high salt concentrations and hydrated crystalline particles are formed in solution. This is in accordance with the increment of the SDS Krafft temperature by addition of NaCl as reported by others [32,34,35,36]. For instance, Chundru observed that changing the NaCl concentration from 0 to 0.02 M at a constant SDS concentration of 0.1 M, increases the Krafft temperature from 15.7 to 17.5 °C [34]. Shinoda et al. also reported that the Krafft temperature of SDS increases significantly by the addition of NaNO3 [32]. In another work, Nakayama and Shinoda measured an increase in the Krafft point followed by a reduction in the solubility of SDS by adding salt [35]. Sharker also observed that the SDS Krafft temperature increases with the addition of NaCl, CsCl, and KCl while it decreases when LiCl is added [36]. This is because the type of the counterion is determinative in Krafft point changes and the Krafft point lowers in the presence of strongly hydrated ions such as Li+ [32].
As a result, when the Krafft point increases to above the solution temperature, surfactant micelles break down and hydrated solid surfactants are formed as precipitates. Consequently, the surfactant concentration in the medium diminishes and a slower dynamic of adsorption (reduction of surface tension versus time) is observed. This phenomenon could be observed in Figure 2 for concentrations of 20,000-40,000 ppm of NaCl. It should be noted that NaCl does not precipitate in our experiments since according to the literature at the temperature of 20 °C, an amount around 260,000 ppm of NaCl is soluble in water [37] which is much more than the NaCl content for our case studies.
Despite the mentioned points about the solubility changes by addition of single salts, it should be noted that when miscellaneous ions such as Ca2+ and Mg2+ are present in the solution, the problem becomes more complex [27].
As discussed above, the SDS precipitation is responsible for a lower stability in region 2, as depicted in Figure 1. However, this is not the case in region 1 in which no precipitation occurs. The little decrease in the half-life time in region 1 is due to viscosity reduction of the XG solution in presence of ions that directly influences the CGAs stability [22]. XG is an anionic polymer in which the viscosity is created as the result of repulsion forces between different molecules. The presence of an ionic field weakens this repulsion force leading to a lower viscosity of the solution, which affects the stability of the system. Different studies have illustrated the influence of ions on the rheological properties of XG solutions [13,14,15].
3.2. Influence of NaCl on CAPB made CGAs
CAPB is a zwitterionic surfactant having both anionic and cationic charges at medium and high pH levels [38,39]. Figure 4 depicts the dynamic surface tension behavior of aqueous 10 mM CAPB in presence of 0.1 wt.% XG and various NaCl concentrations. No considerable dependency on the NaCl concentration can be observed. All measured equilibrium surface tension values are between 28.5–29.5 mN/m. This observation, which is in contrast to the results for SDS, originates from the surfactant’s nature. According to Rosen, the effect of electrolytes on the surface behavior and CMC is larger for anionic and cationic rather than zwitterionic surfactants [31]. The strong dependency of the surface behavior of anionic and cationic surfactants on the ionic strength is because the electrostatic repulsion forces between the ionic head groups is weakened in the presence of counterions and surfactant molecules can get closer to each other at the interface. However, for zwitterionic surfactants, both electrostatic repulsion and attraction forces are present and a balance among them is responsible for the arrangement of surfactant molecules in micelles and at surfaces. In this case, the electric field generated by ions weakens both the repulsion and attraction forces leading to little alteration in the balance, so that the surface activity is not considerably influenced by added salt. In this regard, Kamenka et al. have also reported very little variations in the micellar aggregation number upon the addition of electrolyte for betaine type zwitterionic surfactants [40].
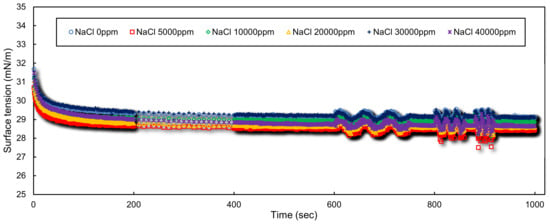
Figure 4.
Dynamic surface tension of aqueous solutions of 0.1 wt.% XG, 10 mM CAPB and various concentrations of NaCl.
Since CAPB is not influenced by the presence of high amounts of ions, its ability to produce CGAs is not damaged. Figure 5 shows the values of CGA volume and half-life time for aqueous solutions of 0.1 wt.% XG, 10 mM CAPB and different NaCl concentrations. A little decrease in the stability is observed by increasing NaCl concentration which, as stated previously, is the result of weakened ability of XG to build up viscosity of the solution. It should be noted that this decrease in stability could be compensated for by adding more XG to the solution. However, for the case of SDS, the precipitation at high salinities makes it impossible to utilize this surfactant in offshore drillings where large concentrations of different ions are present.
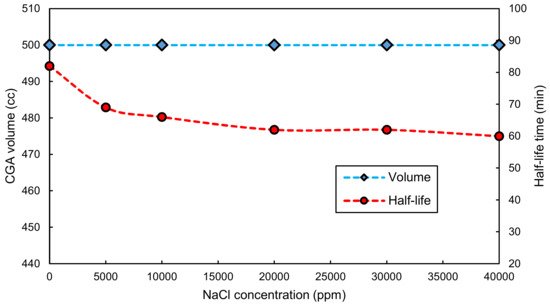
Figure 5.
Volume and half-life time for CGAs made by 0.1 wt.% XG and 10mM CAPB vs. NaCl concentrations.
4. Conclusions
The influence of NaCl on formation and stability of CGAs made by the anionic SDS and zwitterionic CAPB surfactants in the presence of XG was investigated and the following conclusions can be drawn:
- A significant reduction in the half-life time of produced CGAs by SDS was observed for NaCl concentrations above 20,000 ppm which can be attributed to the precipitation of SDS in the solution.
- Increasing the Krafft temperature of SDS solutions by the addition of NaCl was the reason for SDS precipitation in solution.
- Fast dynamic surface tension measurements using bubble pressure tensiometry supported this observation, i.e., lower effective surfactant concentration due to the precipitation process.
- NaCl did not have considerable influence the surface behavior of the zwitterionic surfactant CAPB and its ability for CGAs production was not reduced. This is because of the presence of both cationic and anionic head groups at the surfactant inducing both attraction and repulsion forces. In this case, the presence of salt simultaneously weakens both attraction and repulsion forces leading to negligible changes in the net forces.
- NaCl decreased the overall ability of XG to build up the viscosity, leading to a considerable decrease in the half-life time of CGAs for both surfactants.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2504-5377/4/1/9/s1, Figure S1: Surface elasticity values of aqueous solutions of 0.1 wt.% XG, 16.6 mM SDS for various concentrations of NaCl at a fixed frequency of 0.05 Hz.
Author Contributions
The authors has been involved in: B.K. for “conceptualization, methodology, performing experiments, data analysis and writing the original manuscript”, M.M. for “experiments and measurements”, A.J. for “conceptualization, methodology, resources, experimental setup and protocols development, data analysis and writing the original manuscript”, A.B. has been involved in “conceptualization, resources and data analysis”, R.M. has been involved in “conceptualization, data analysis, and review and editing”, K.E. has been involved in “conceptual analysis, resources, review and editing”. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The supports of MPIKG and TU-Berlin for some of the chemicals and tools are appreciated
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sebba, F. Microfoams—an unexploited colloid system. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1971, 35, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebba, F. Foams and biliquid foams, aphrons; Chichester; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Kinchen, D.; Peavy, M.A.; Brookey, T.; Rhodes, D. Case history: Drilling techniques used in successful redevelopment of low pressure H2S gas carbonate formation. In Proceedings of the SPE/IADC drilling conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 27 February–1 March 2001; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA. [Google Scholar]
- White, C.C.; Chesters, A.P.; Ivan, C.D.; Maikranz, S.; Nouris, R. Aphron-based drilling fluid: Novel technology for drilling depleted formations in the North Sea. In Proceedings of the SPE/IADC Drilling Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 19–21 February 2003; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Gregoire, M.; Hilbig, N.; Stansbury, M.; Al-Yemeni, S.; Growcock, F.B. Drilling Fractured Granite in Yemen with Solids-Free Aphron Fluid. In Proceedings of the IADC World Drilling, Rome, Italy, 9–10 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Xu, B. Application of micro-foam drilling fluid technology in Haita area. Nat. Sci. 2012, 4, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Leleux, J.; Delvaux, A. Novell Drilling Fluid Design Enables Successful Drilling of Depleted Carbonate Reservoirs Offshore Republic of Congo. In Proceedings of the SPE/IADC Drilling Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 5–7 March 2013; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Oyatomari, C.; Orellan, S.; Alvarez, R.; Bojani, R. Application of Drilling Fluid System Based on Air Microbubbles as an Alternative to Underbalance Drilling Technique in Reservoir B-6-X.10- Tia Juana, Lake Maracaibo. In Proceedings of the IADC Global Leadership for the Drilling Industry Conference, Madrid, Spain, 5–6 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Montilva, J.; Ivan, C.D.; Friedheim, J.; Bayter, R. Aphron drilling fluid: Field lessons from successful application in drilling depleted reservoirs in Lake Maracaibo. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 6–9 May 2002; Offshore Technology Conference: Richardson, TX, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Molaei, A.; Waters, K.E. Aphron applications—A review of recent and current research. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 216, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rea, A.B.; Alvis, E.C.; Paiuk, B.P.; Climaco, J.M.; Vallejo, M.; Leon, E.; Inojosa, J. Application of aphrons technology in drilling depleted mature fields. In Proceedings of the SPE Latin American and Caribbean Petroleum Engineering Conference, Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago, 27–30 April 2003; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Kralchevsky, P.A.; Danov, K.D.; Broze, G.; Mehreteab, A. Thermodynamics of ionic surfactant adsorption with account for the counterion binding: Effect of salts of various valency. Langmuir 1999, 15, 2351–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higiro, J.; Herald, T.J.; Alavi, S. Rheological study of xanthan and locust bean gum interaction in dilute solution. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.Y.; Zhang, K.; Chon, B.H.; Choi, H.J. Enhanced oil recovery performance and viscosity characteristics of polysaccharide xanthan gum solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Oostrom, M.; Truex, M.J.; Vermeul, V.R.; Szecsody, J.E. Rheological behavior of xanthan gum solution related to shear thinning fluid delivery for subsurface remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longe, T.A. Colloidal gas aphrons: Generation, flow characterization and application in soil and groundwater decontamination. Ph.D. Thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA, April 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kommalapati, R.R.; Roy, D.; Valsaraj, K.T.; Constant, W.D. Characterization of colloidal gas aphron suspensions generated from plant-based natural surfactant solutions. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1996, 31, 2317–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Save, S.V.; Pangarkar, V.G. Characterisation of colloidal gas aphrons. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1994, 127, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauregi, P.; Gilmour, S.; Varley, J. Characterisation of colloidal gas aphrons for subsequent use for protein recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 1997, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaphalkar, P.G.; Valsaraj, K.T.; Roy, D. A study of the size distribution and stability of colloidal gas aphrons using a particle size analyzer. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1993, 28, 1287–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzi, B.; Javadi, A.; Bahramian, A.; Miller, R. Thixotropic bulk elasticity versus interfacial elasticity in xanthan gum surfactant mixed solutions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 557, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzi, B.; Javadi, A.; Bahramian, A.; Miller, R. Formation and stability of colloidal gas aphron based drilling fluid considering dynamic surface properties. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 174, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbaschi, M.; Bastani, D.; Javadi, A.; Kovalchuk, V.I.; Kovalchuk, N.M.; Makievski, A.V.; Bonaccurso, E.; Miller, R. Drop profile analysis tensiometry under highly dynamic conditions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 413, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, A.; Krägel, J.; Makievski, A.V.; Kovalchuk, V.I.; Kovalchuk, N.M.; Mucic, N.; Loglio, G.; Pandolfini, P.; Karbaschi, M.; Miller, R. Fast dynamic interfacial tension measurements and dilational rheology of interfacial layers by using the capillary pressure technique. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 407, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasdar, M.; Kazemzadeh, E.; Kamari, E.; Ghazanfari, M.H.; Soleymani, M. Insight into the behavior of colloidal gas aphron (CGA) fluids at elevated pressures: An experimental study. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 537, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, A.J.; Franses, E.I. Adsorption and surface tension of ionic surfactants at the air–water interface: Review and evaluation of equilibrium models. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 178, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baviere, M.; Bazin, B.; Aude, R. Calcium effect on the solubility of sodium dodecyl sulfate in sodium chloride solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1983, 92, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, A.; Henley, H.; Thomas, E. Multiphase equilibrium flash with salt precipitation in systems with multiple salts. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 93, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, H.; Shinoda, K.; Hutchinson, E. The effect of added alcohols on the solubility and the Krafft point of sodium dodecyl sulfate. J. Phys. Chem. 1966, 70, 3502–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.M.; Tjeerdema, R.S. Fate and effects of the surfactant sodium dodecyl sulfate. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1993, 95–149. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, M.J.; Kunjappu, J.T. Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda, K.; Yamaguchi, N.; Carlsson, A. Physical meaning of the Krafft point: Observation of melting phenomenon of hydrated solid surfactant at the Krafft point. J. Phys. Chem. 1989, 93, 7216–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyota, H.; Krastev, R. Miscibility of sodium chloride and sodium dodecyl sulfate in the adsorbed film and aggregate. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chundru, S.K.C. Effect of Counter Ion Concentration Added with Mixture of Water and Ethylene Glycol on Krafft Temperature of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate. Master’s Thesis, Eastern Michigan University, Ypsilanti, MI, USA, December 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama, H.; Shinoda, K.O.Z.O. The effect of added salts on the solubilities and Krafft points of sodium dodecyl sulfate and potassium perfluoro-octanoate. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1967, 40, 1797–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharker, K.K. Counter-ion effects on the krafft temperature and micelle formation of ionic surfactants in aqueous solution. Ph.D. Thesis, Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh, September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pinho, S.P. and Macedo, E.A. Solubility of NaCl, NaBr, and KCl in water, methanol, ethanol, and their mixed solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2005, 50, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.E.; Amini, S. Cocamidopropyl betaine. Dermatitis 2008, 19, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danov, K.D.; Kralchevska, S.D.; Kralchevsky, P.A.; Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P.; Lips, A. Mixed solutions of anionic and zwitterionic surfactant (betaine): Surface-tension isotherms, adsorption, and relaxation kinetics. Langmuir 2004, 20, 5445–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenka, N.; Chevalier, Y.; Zana, R. Aqueous solutions of zwitterionic surfactants with varying carbon number of the intercharge group. 1. Micelle aggregation numbers. Langmuir 1995, 11, 3351–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).