Abstract
Highly cross-linked polymers are commonly used in purification and separation techniques because of their many useful features. In order to better adjust their porosity to adsorption of specific compounds, methods like surface functionalization or imprinting are used. In this work, a series of highly cross-linked polydivinylbenzenes (pDVB) were prepared using a suspension method. Toluene was applied as a pore-forming diluent. Some part of toluene (1 mL) was replaced with phenol (F), 2,4,6-trichlorophenol (T) or their mixture (M) to prepare polymers with porosity more suitable for phenols sorption. Another approach was an introduction of sulfone groups onto the polymer surface (pDVB-SO3H). The physicochemical characteristics of the synthetized adsorbents included CHN, FTIR, DSC and porosimetric analyses. Afterwards, to evaluate sorption properties of the prepared adsorbents towards phenols, ibuprofen and salicylic acid the solid phase extraction (SPE) experiments were performed. The polymers had the specific surface areas of about 440–560 m2/g created mainly by mesopores with widths ca. 3.75 and 4.75–7.15 nm. Materials obtained with the addition of porosity modifiers (phenol, trichlorophenol, mixture) had more uniform porous structure and their sorption capacity toward phenols increased ca. 5%. Similar sorption capacities were obtained for ibuprofen. Salicylic acid had low affinity to the surface of the tested polymers.
1. Introduction
The highly cross-linked polymers have many useful features, such as their well-developed porous structure, high thermal resistance, and low ability to swelling. This makes them very useful materials as adsorbents for purification and separation techniques [1,2,3,4,5]. In order to make their porous structure more suitable to adsorb a specific group of compounds, methods like surface sensitization or imprinting are used [6]. Additionally, functionalization reactions can be carried out to modify the chemical nature of their surface [7,8]. Other methods allow for the design of surface properties of the polymer (e.g., polarity, acidity) while already at the stage of synthesis [9,10]. These methods rely on the usage of monomers with functional groups, which give the polymer a specific character and are able to interact with an analyte. Their presence also helps to improve the wettability of the polymer, which is advantageous when uptake is carried out from the aqueous solutions.
The chemistry of polymeric sorbent is particularly important in the case of analysis of polar analytes like phenols or pharmaceuticals that exhibit biological activity. Although their concentration in natural waters or sewage is on a low level, they pose a serious threat to the environment. All living organisms are exposed to the harmful effects of these substances and products of their decomposition. A lot of such compounds are not biodegradable, and remain in the environment for a very long time. This type of pollution may lead to contamination of drinking water. For this reason, governments around the world introduced directives on maximum limit values for the most toxic compounds and the requirement for constant monitoring of their presence [11,12,13,14].
Moreover, if pollutants are very diluted, it is an additional difficulty from an analytical point of view, as a stage of quantitative isolation and concentration should be included in the determination procedure [1,15]. For many years analytical methods for extraction of phenolic compounds based on liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) and Soxhlet extraction, for liquid and solid samples, respectively [16]. These methods are expensive and time consuming therefore SPE (solid phase extraction) as more convenient, cheap, fast and environmentally friendly method was proposed [1]. Due to differentiated chemical character of pollutants there is no one universal adsorbent suitable “for all purposes”. Depending on the properties and molecular size of an analyte, the right adsorbent should be selected. The most important features of the adsorbent are: Porosity, surface chemistry and stability, both chemical and thermal. Porosity affects sorption capacity. Chemical structure determines its usefulness for a particular type of analytes. Chemical and thermal stability influences the regime of working conditions, especially in the stage of recyclability.
Many studies were performed to evaluate the usefulness of commercially available sorbents like Isolute ENV, PLRP-S, PGC, LiChrolut EN, Bond Elut Env, OASIS HLB [17,18,19] also newly prepared materials are examined [20,21,22,23]. Researchers used stationary and dynamic methods, different experimental conditions and sample matrices. In addition, the way of presentation of the data is not unified. For this reason, it is difficult to compare results obtained by various groups.
In order to model the sorption process usually one-component solutions are used, but from the practical applications point of view, studies performed for multicomponent mixtures are more useful.
In this work we present the series of highly cross-linked porous polydivinylbenzenes (pDVB). The aim of our study was the evaluation if the addition of a potential adsorbate to pore forming agents in the stage of polymerization will have an influence on a porous structure and sorption properties of the synthesized polymer towards the added adsorbate. Moreover, the influence of the sulphonation reaction on the porous structure of the chemically modified polymer, as well as its sorption properties towards phenols and pharmaceuticals was evaluated. All the polymers were synthesized via a suspension method using toluene as a basic pore-forming diluent. To prepare polymers with modified porous structure, 1 mL of toluene was replaced with an appropriate amount of phenol (P), 2,4,6-trichlorophenol (T) or their mixture (M). Moreover, the chemical modification of pDVB was performed in order to introduce sulfonic groups onto the polymer surface. The prepared materials were tested in the sorption processes of phenolic compounds (a multicomponent mixture consisted of phenol, 2-chlorophenol, 2,4-dichlorophenol and 2,4,6-trichlorophenol), salicylic acid and ibuprofen using dynamic method—solid phase extraction (SPE). The elemental and ATR-FTIR analyses confirmed the chemical structure of the tested materials and the correct course of the modification process. The polymers possessed well developed porous structure with specific surface areas of 440 to 560m2/g and bimodal pore size distribution. It was shown that the type of the porogen, as well as the sulphonation reaction influenced the porosity of pDVB polymers. SPE experiments revealed that changes in the porous structure of the polymers had an impact on their sorption properties. In the case of 2,4-dichlorophenol and 2,4,6-trichlorophenol, pDVB-T and pDVB-M had higher sorption capacity than pDVB, pointing out the positive role of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in the formation of pores suitable for the sorption of these compounds. The similar effect was observed for ibuprofen uptake. The opposite effect was obtained for salicylic acid.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Divinylbenzene (DVB), α,α’-Azoiso-bis-butyronitrile (AIBN), poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA), methanol (MeOH), 2-chlorophenol (ChP), 2,4-dichlorophenol (DChP) and 2,4,6-trichlorophenol (TChP), 1,4-dioxane and (S)-(+)-2-(4-Isobutylphenyl)propionic acid (ibuprofen), 2-hydroxybenzoic acid (salicylic acid) were purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). 98% H2SO4, 36% HCl, NaOH, hexane, acetone, toluene and phenol (P) were from POCh (Gliwice, Poland).
2.2. Synthesis of Polymeric Microspheres
In a three-necked flask equipped with a stirrer, a thermometer and a water condenser 5 g of PVA and 175 of distilled water was dissolved. Next, the mixture of the monomer (DVB), pore forming agent (toluene, P, T) and the initiator (AIBN) was prepared and poured into the dispersion medium, all details are collected in Table 1. The reaction mixture was stirred at 250 rpm at 80 °C for 18 h. After the reaction the obtained polymers were washed in an ultrasonic bath successively with distilled water (150 mL), methanol (150 mL), hexane (150 mL) and again methanol (150 mL) (each solvent for half an hour). After the washing the solvent was filtered off and the polymers were dried in the open air for 10 days.

Table 1.
Details of the syntheses.
2.3. Sulphonation
The sulphonation process was carried out in a two-neck flask equipped with a thermometer and a water condenser. A mixture of 13 g pDVB and 120 mL H2SO4 (98%) was gradually heated from 35 to 100 °C for 4 h. After the reaction was completed the mixture was poured into distilled water, the polymer was filtered off, washed with water to remove the acid (neutral pH) and dried in the open air for 10 days.
2.4. Characterization
Elemental analyses (CHN) were performed on a Perkin Elmer CHN 2400 analyzer (Palo Alto, CA, USA).
The acid number was determined by standard titration method.
Attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectra were collected using a Bruker FTIR spectrophotometer TENSOR 27 in the frequency range of 4000 to 600 cm−1, the resolution of the apparatus was 4 cm−1.
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analyses were carried out on a Netzsch DSC 204 calorimeter (Netzsch, Germany). Samples of about 7 mg weight were placed in an aluminum pan with a pierced lid and heated to 500 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C·min−1. The measurements were conducted under argon atmosphere. An empty pan was used as a reference. The samples were analyzed as received. Additionally, pDVB-SO3H was dried at 100 °C for 30 min. to remove adsorbed moisture.
The porous structure parameters of the studied sorbents were determined by nitrogen sorption experiments, the isotherms were measured at −196 °C with adsorption analyzer ASAP 2405 (Micrometrics Inc., USA). Before analyses, the samples were outgassed at 140 °C for 1 h. The specific surface area was calculated using the standard BET method while the total pore volume was calculated as the volume of liquid adsorbate at a relative pressure of 0.99.
To investigate the sorption properties of the prepared materials, laboratory cartridges were filled with 100 mg of the studied polymer. Next, the aqueous solution of ibuprofen (100 mg·L−1), salicylic acid (100 mg·L−1) and a standard methanolic mixture of phenols (phenol (P), 2-chlorophenol (ChP), 2,4-dichlorophenol (DChP), and 2,4,6-trichlorophenol (TChP)—100 mg·L−1 of each compound) were prepared. The procedures of the sorption experiments and HPLC analyses for phenolic compounds were the same as in our previous works [7,10]. The aqueous solution of the phenolic compounds (2 mg·L−1) was prepared by dilution (1:50 v/v) of the standard methanolic solution. Different volumes of the aqueous solution were sucked through the cartridge connected to the water aspirator. Next, the phenolic compounds were eluted from cartridge with adequate volume of methanol (2 mL of MeOH for each 100 mL of sucked aqueous solution). The obtained eluates were analyzed using HPLC system - Waters 2690 Alliance (Waters, USA) equipped with an automatic sampler, UV detector Waters 2487 and μ-BondapakTMC18 (3.9 × 300 mm) column. As a mobile phase methanol: Water (60:40, v/v) at a flow rate of 1 mL/min−1 was applied. Detection was performed at λ = 210 nm.
The sorption of pharmaceuticals (ibuprofen and salicylic acid) was performed in the same way as phenols. The only difference regarded the parameters of HPLC analysis: A mobile phase methanol: Water (80:20, v/v), a flow rate of 1 mL·min−1, detection of ibuprofen was performed at 222 nm, and salicylic acid at 200.5 nm, respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Morphology of the Research Materials and Their Chemical Properties
Table 2 presents the data of the elemental analysis for the studied materials. Theoretical values for pDVB are 92.2% of carbon and 7.8% of hydrogen. As one can see the results obtained for pDVB, pDVB-P and pDVB-T are very close to the theoretical ones. Some differences are due to the manner of conducting the polymerization process. The presence of nitrogen in the structure of polymers is a consequence of using the AIBN as the polymerization initiator. In the case of pDVB-M the differences are bigger pointing to the fact that a little amount of added porogens (T and /or P) were entrapped in the polymeric structure.

Table 2.
The results of elemental analysis and acid number (AN).
The analysis of the results obtained for pDVB-SO3H proved that sulphonation was successful. It was also calculated that for every three aromatic rings of the polymer, two sulphonic groups are attached. The exact number of acidic groups can be quantified by determining the acid number (AN) using a standard titration method. In the case of pDVB-SO3H it was ca 18 mg/g.
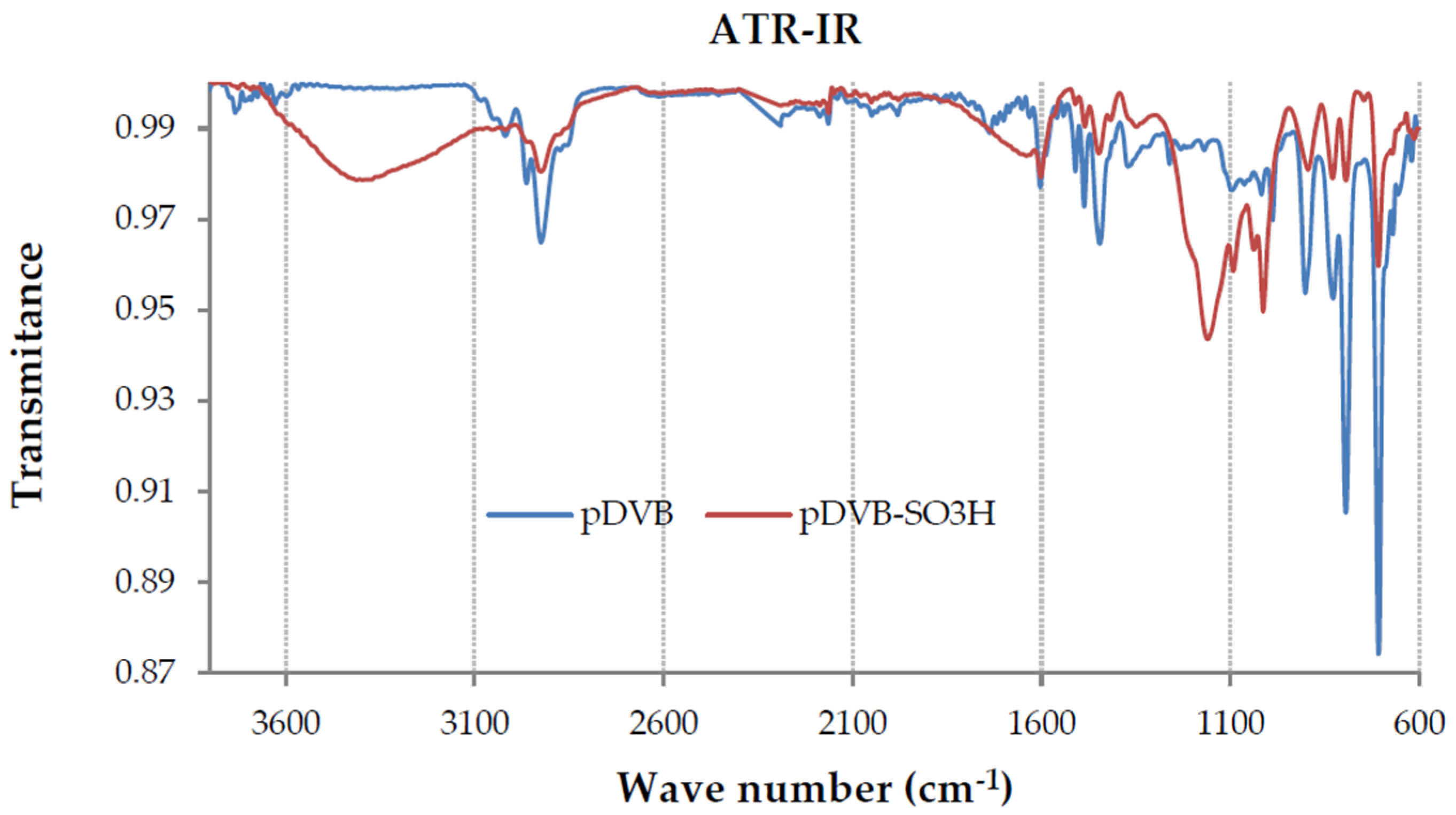
ATR-FTIR spectroscopy gives additional confirmation of the chemical structure of the studied polymers. The spectra of pDVB and pDVB-SO3H are presented in Figure 1. The spectra of pDVB-P pDVB-T and pDVB-M were omitted as they were identical with that for pDVB.
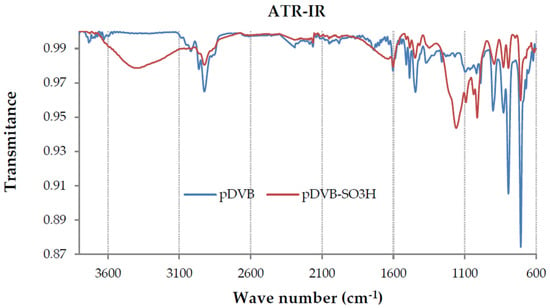
Figure 1.
The ATR-FTIR spectra of pDVB and pDVB-SO3H polymers.
In the spectrum of pDVB four absorption bands in the range 1430–1600 cm−1 are signals characteristic for aromatic system (ρ =C-H and ν C=C) and that at 707 cm−1 is due to ring out-of-plane deformation vibrations. Symmetric and asymmetric out-of-plane deformation vibrations of two neighboring H atoms observed at 792 and 830 cm−1 inform that the benzene rings are di-substituted. Moreover, quite intense signals of out-of-plane deformation vibrations of vinyl groups at 995 and 902 cm−1 are also observed, indicating the presence of residual carbon-carbon double bonds, which is also confirmed by DSC analysis. The characteristic absorption bands derived from the deformation vibrations of aliphatic groups are visible at ~1375 and stretching ones at 2850–3000 cm−1.
The spectrum of pDVB-SO3H, obtained after the sulphonation reaction, reveals new absorption bands at 1160 and 1091 cm−1 due to the asymmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations of SO3H group. Moreover, bands characteristic for sulphonic acids are visible at 2700–3600 cm−1 (ν-OH) and 990–1090 cm−1 (ν S=O).
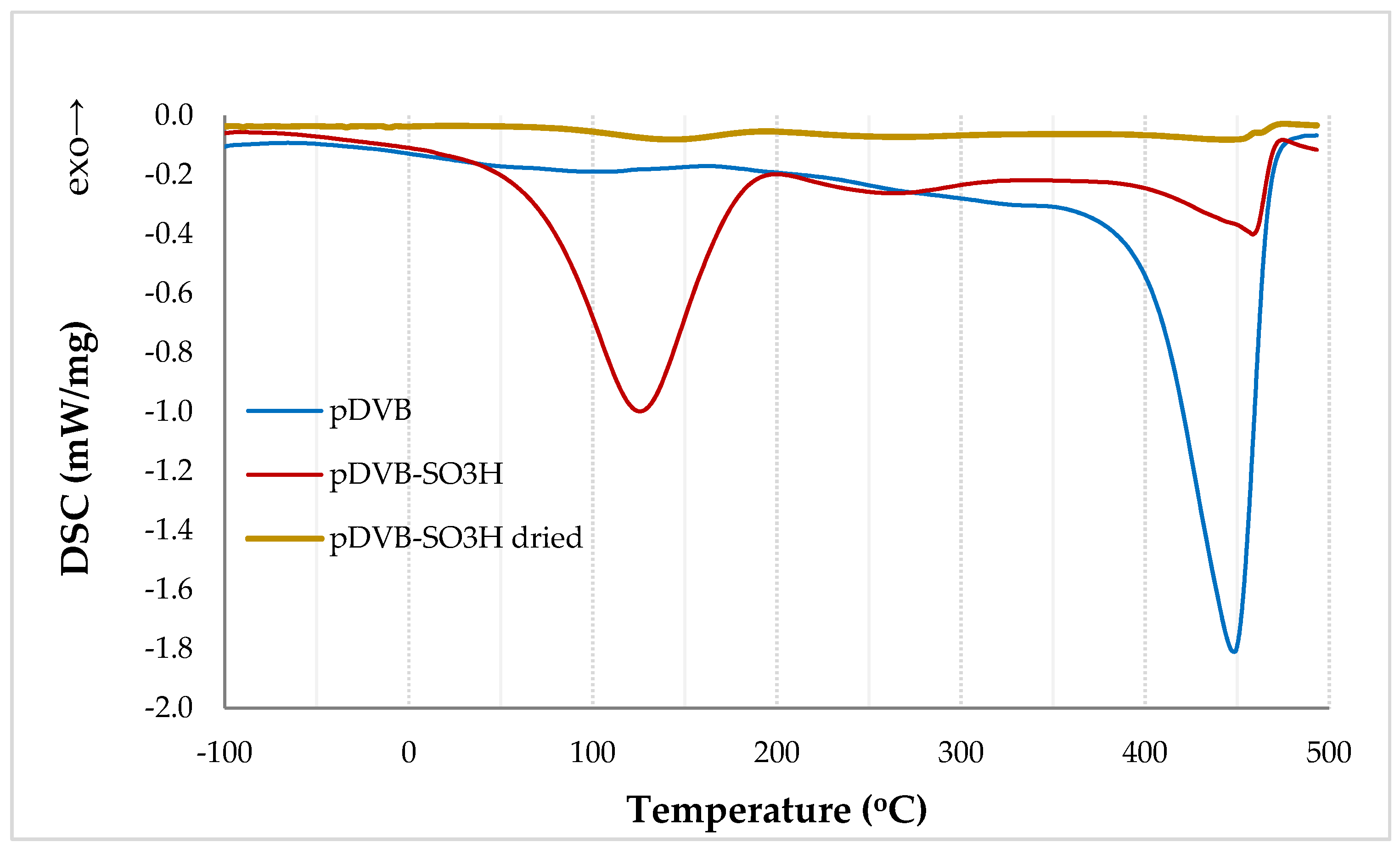
The DSC results of the studied polymers are presented in Figure 2. Due to the fact, that pDVB is a highly cross-linked aromatic polymer, it has good thermal stability. Its decomposition takes place in the range of 350 to 490 °C. The flat and broad exothermic peak (120–300 °C) is the effect of the post-curing process. This process is characteristic for highly crosslinked polymers synthesized via suspension polymerization [24,25]. The shape and low energetic effect (27 J/g) of the peak prove that only an insignificant number of vinyl groups did not react during the polymerization.
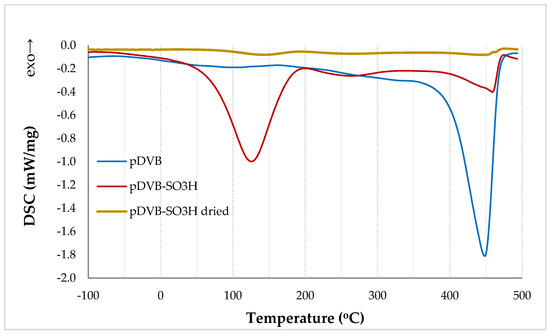
Figure 2.
The DSC results for pDVB and pDVB-SO3H polymers.
The sulphonic group just like sulphuric acid possesses hygroscopic properties. Moreover, sulphonated polymer (pDVB-SO3H) presents such property, for this reason in the DSC curve in the range of 50–200 °C a big endothermic peak originated from desorption of water is visible. The process takes place in a wide range of temperatures because the studied material is porous. Initially, at a lower temperature, water is removed from the outer surface of the polymer, then from the pores of smaller and smaller widths. To remove water molecules adsorbed in micropores temperature up to 200 °C is needed. The thermal decomposition of this material starts above 400 °C. After thorough drying (pDVB-SO3H dried), the peak of water desorption practically disappears and the completely dried material becomes more thermally resistant, its decomposition starts above 450 °C. This increase of thermal stability can be a result of the formation of pyrosulphuric and sulphonyl bridges [26,27].
3.2. Characteristics of the Porous Structure
Table 3 presents porous structure parameters of the prepared polymers. The highest values of the specific surface area (SBET) and total pore volume (Vtot) were obtained for pDVB. The materials whose porosity was regulated by the presence of phenol, trichlorophenol or their mixture had the specific surface areas 2–5% lower and pore volumes 5–18% lower than unmodified pDVB.

Table 3.
The porous structure parameters.
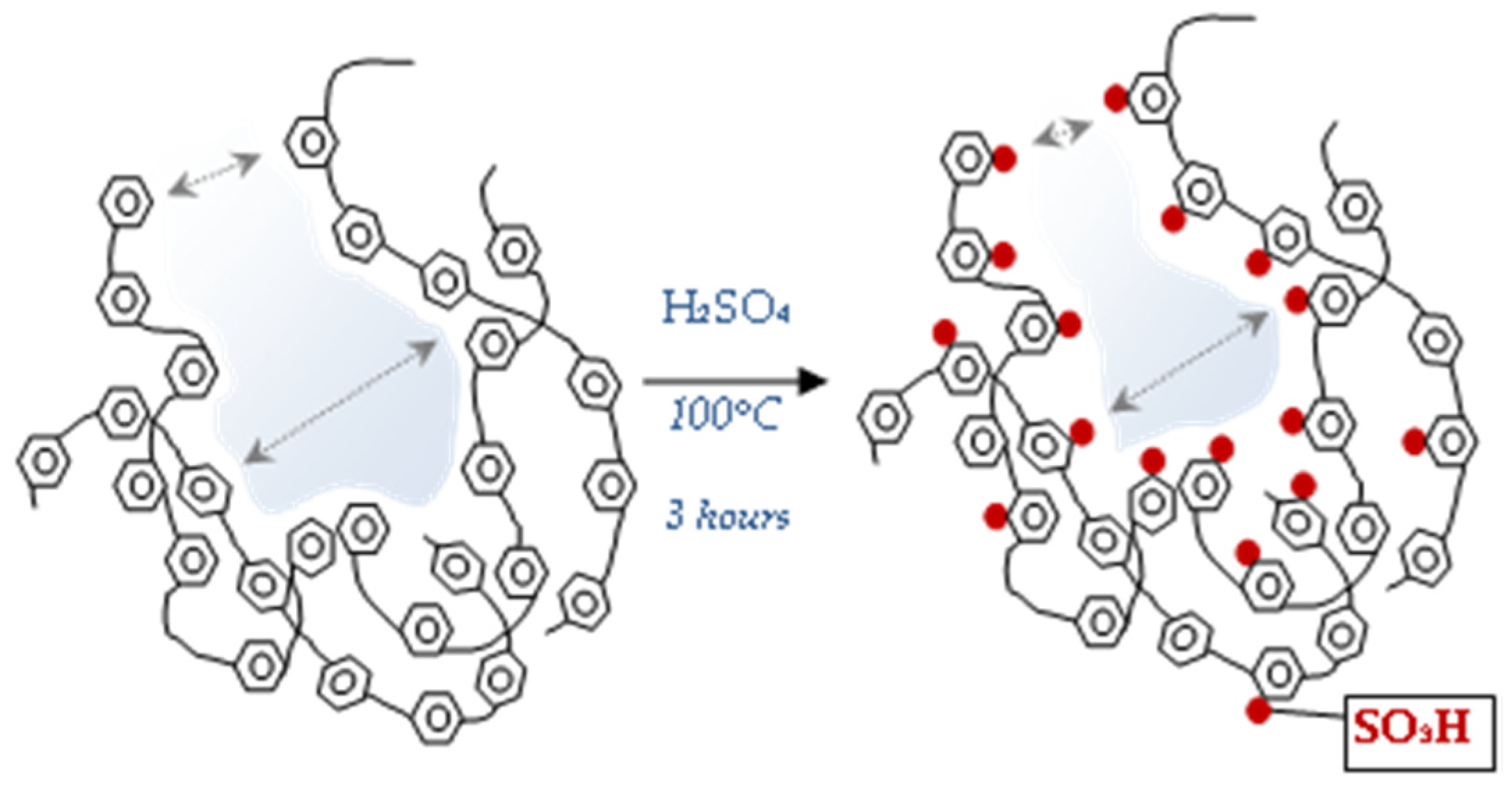
The lowest values were observed for pDVB-SO3H. Due to a steric effect caused by bulky sulphonic groups some pores become not available for nitrogen molecules. If -SO3H group is placed inside mesopore, its width apparently decreases that is observed as the narrowing of pores and formation of micropores. The scheme of the described process is shown in Figure 3.
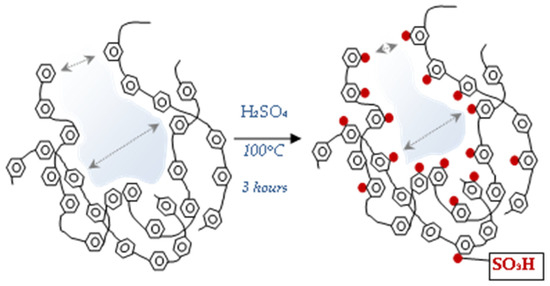
Figure 3.
The process of narrowing of pores and micropore formation during the pDVB sulphonation.
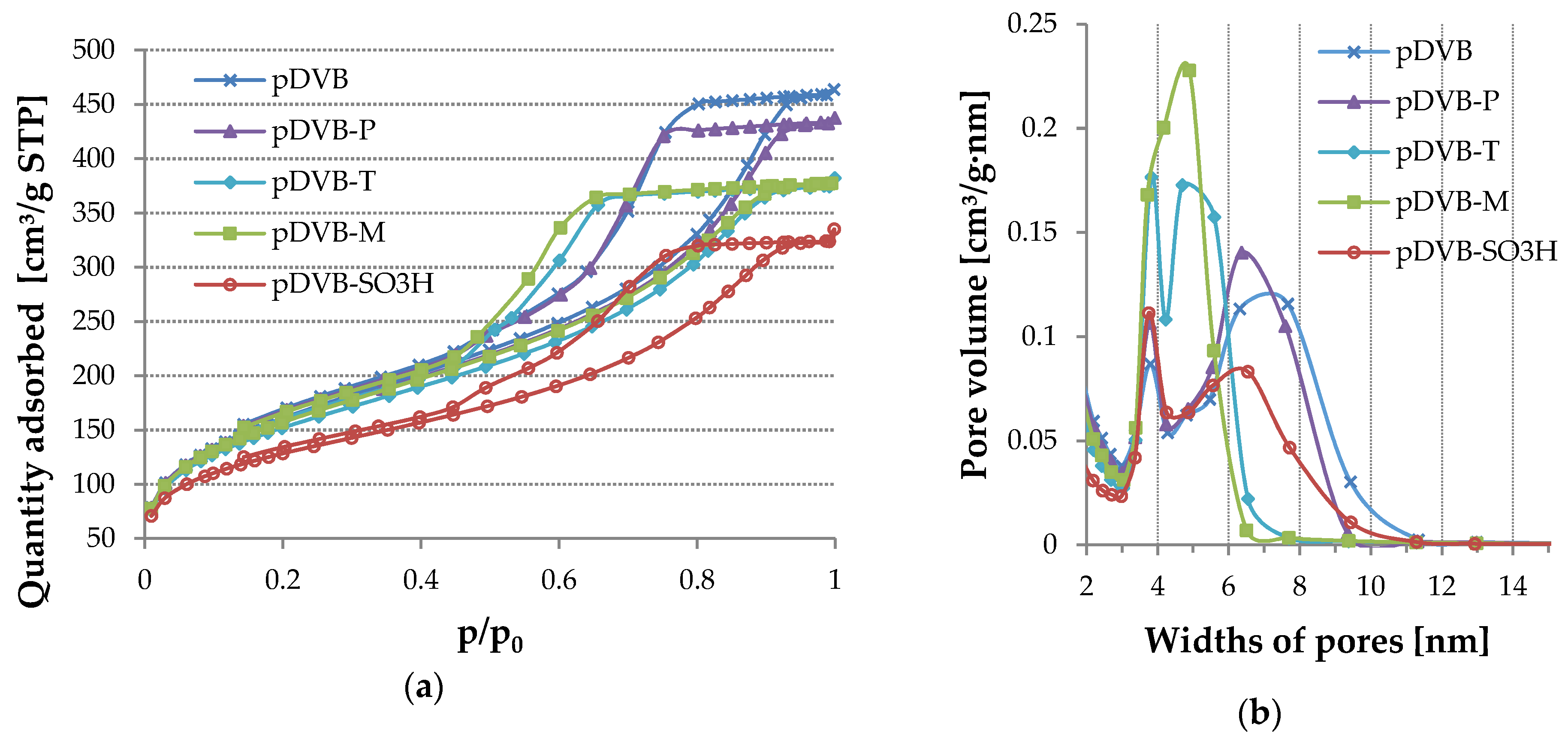
The confirmation of this explanation can also be found in Figure 4 where nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms and pore size distributions (PSD) are shown. The location of pDVB-SO3H isotherm indicates the decrease of porous structure parameters values. It is evident when the PSD plots of pDVB-SO3H and pDVB are compared. A peak at 3.75 nm is a little higher for pDVB-SO3H than that for pDVB, proving increase in the number of narrow mesopores. Next peak corresponding to broader mesopores in the case of pDVB-SO3H has it apex at 6.5 nm and half-height width in the range of 4.8–7.7 nm, while that for pDVB has the top at ca 7 nm and its half-height width is 4.2–9 nm. Moreover, the heights of both peaks are different demonstrating loss of pore volume as a consequence of sulphonation taking place inside wider mesopores.
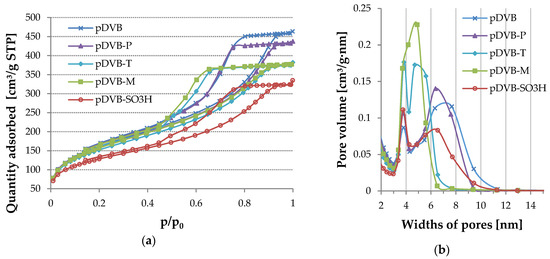
Figure 4.
The results of the nitrogen sorption experiments for the studied polymers. (a) N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms; (b) Pore size distribution.
Equally interesting is the comparison of the isotherms obtained for other materials. According to IUPAC classification, isotherms of type IV-H2 are characteristic for materials with complex pore system, in which pores are interconnected, have irregular shapes and narrow entrances [28]. Such structure is typical of polymeric networks, therefore the shapes of hysteresis loops are very similar in all cases. The differences in porous structure can be discussed on the basis of PSDs.
Replacement of 1 mL of toluene with phenol (pDVB-P) results in not only increase in the number of narrow pores (3.75 nm), but also wider mesopores. However, the latter are more homogeneous in comparison to those in pDVB. Even greater uniformity of wider mesopores was obtained by replacing 1 mL of toluene with trichlorophenol (pDVB-T). In the case of this material both peaks (3.75 and 4.75 nm) are high and narrow and the maximum pore width does not exceed 7 nm. The hardest to explain seems to be the result obtained for pDVB-M. The usage of the mixture of phenol and trichlorophenol instead of 1 mL of toluene resulted in the polymer with the most uniform porosity. PSD in this case has only one narrow peak with apex at 4.9 nm and half-height width in the range of 3.5–5.7 nm. The observed changes in the formation of porous structure can be explained by the fact that trichlorophenol is better soluble in toluene than phenol and the latter has a tendency to create dimers and more complex systems in solution due to strong hydrogen interactions [29].
3.3. The Sorption Abilities of the Studied Materials
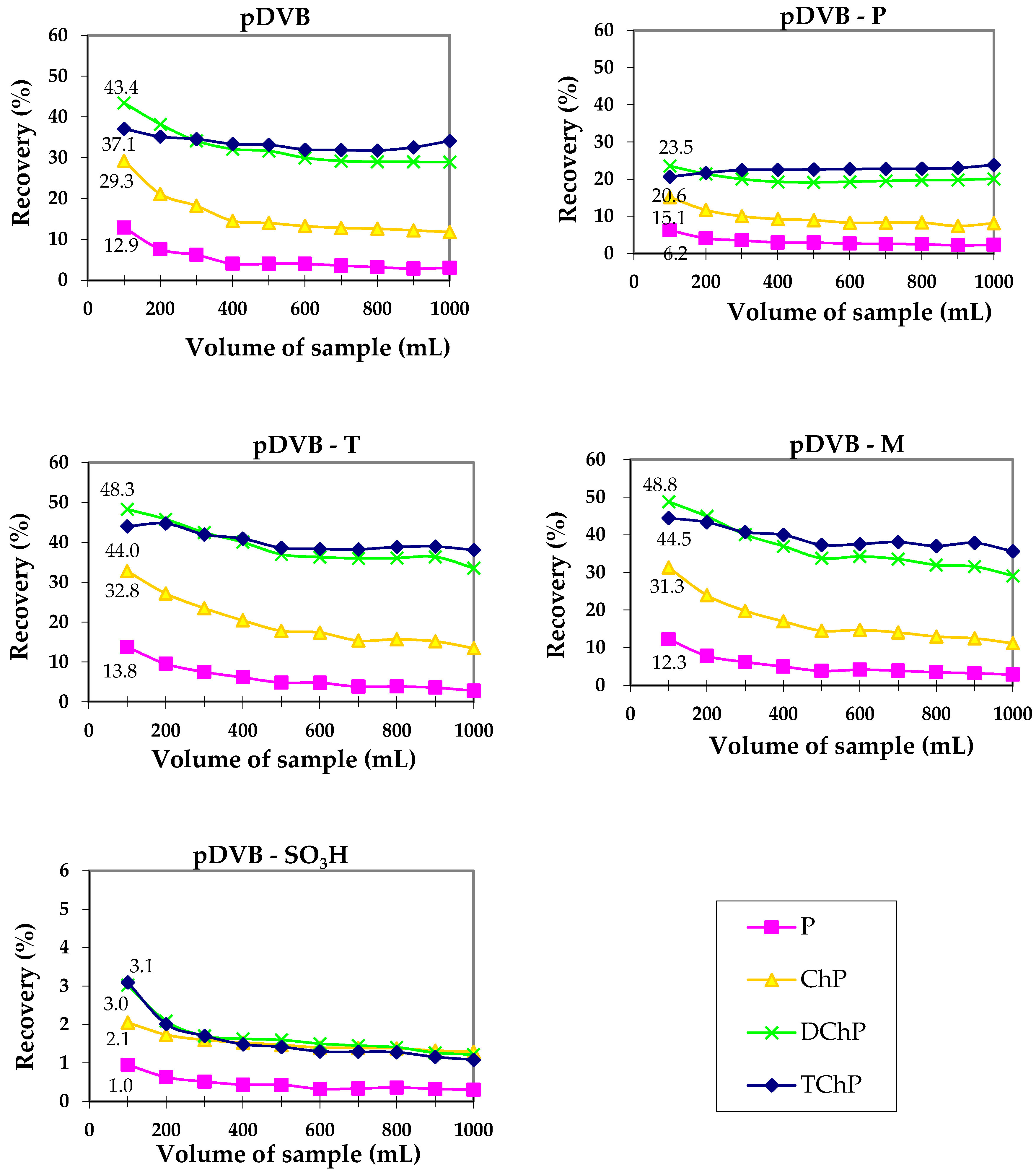
Although the strong effect of phenol and trichlorophenol on the creation of pDVB porosity was observed, their molecular imprint was not reflected by the more selective or significantly better sorption properties. Figure 5 presents the results of the dynamic sorption studies performed using SPE method for phenolic compounds.
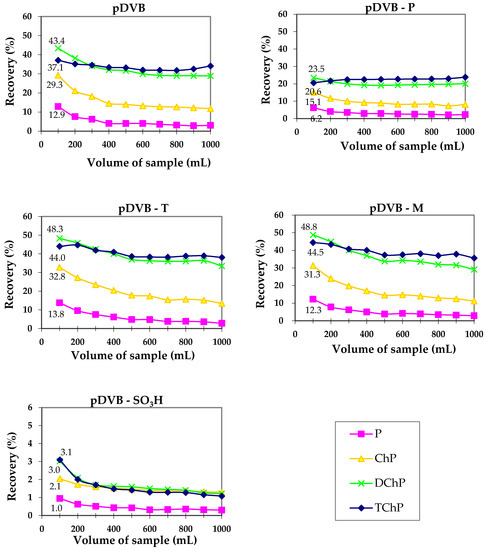
Figure 5.
Results of solid phase extraction (SPE) experiments obtained for the mixture of phenols.
The performed studies revealed the sorption abilities of pDVB, pDVB-T and pDVB-M are comparable, however some differences are observed. In the case of 2,4-dichlorophenol and 2,4,6-trichlorophenol pDVB-T and pDVB-M sorbents had higher sorption capacity than pDVB, pointing out the positive role of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in the formation of pores suitable for the sorption of these compounds. Maximal recoveries for 2,4-dichlorophenol are in the range of 43 to 49%. The interactions of the other phenols with the polymer surface is not so strong, therefore their recoveries are lower. As our previous studies proved [30], the adsorbents possessing pores with width 3–4 nm were the most effective in the sorption of phenols. The materials presented in this work have also pores in this range, but their contents in the structure is probably insufficient to provide higher sorption capacity. In the case of pDVB-P uptake of phenols is almost twice lower than for pDVB. Both materials have almost identical porous structure parameters. Therefore, it should be assumed that during SPE experiment the flow of the solution through the bed of polymeric sorbent was not the same (channeling effect). On the other hand, for pDVB-SO3H, drastic decrease in sorption capacity is observed, due to repulsive character of the acidic surface of the polymer, caused by the presence of sulphonic groups.
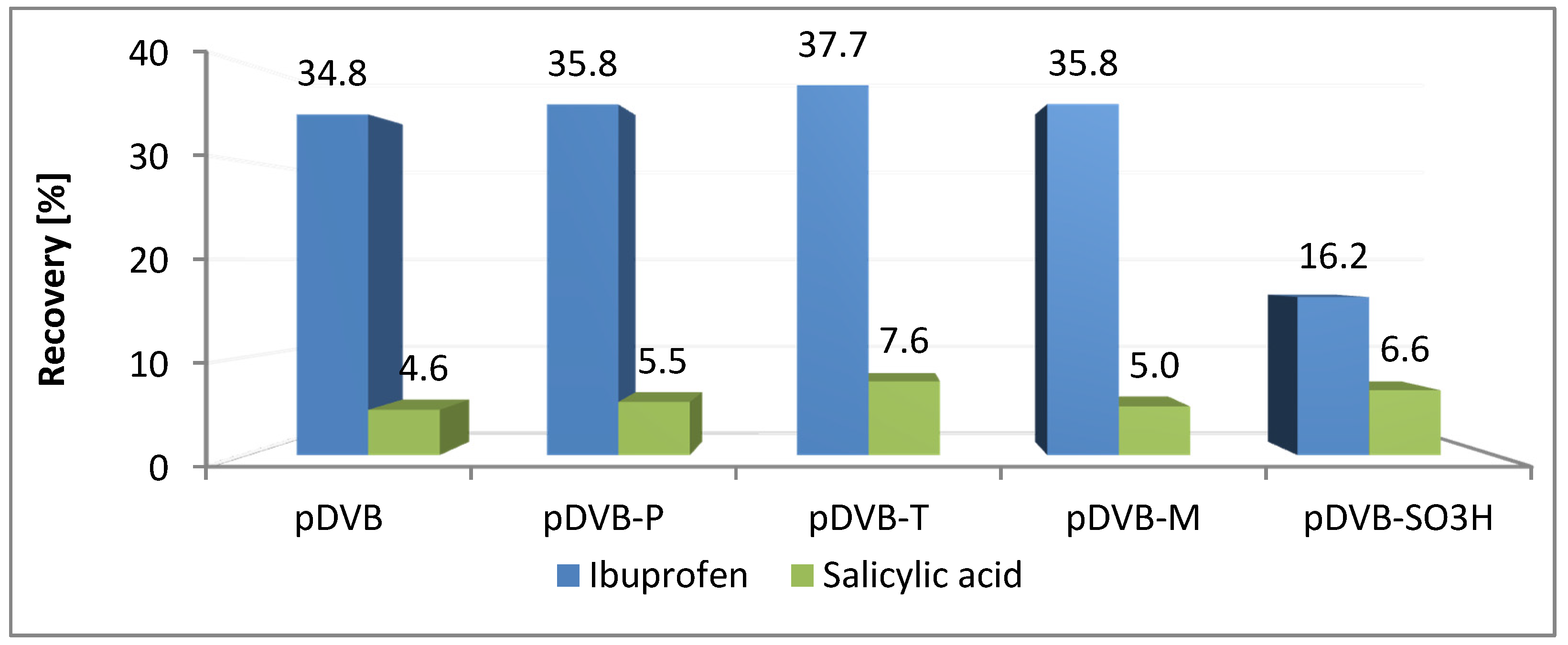
The sorption of ibuprofen on the studied materials (Figure 6) is very similar to that of trichlorophenol. Both compounds have slightly acidic chemical character and their solubility in water is poor. The recoveries are in the range of 35–38% excluding pDVB-SO3H with twice lower value. In the case of salicylic acid recoveries are in the range of 4.5 to 7.6% for all the materials, even for the sulphonated one. Although uptake was not high, it is obvious that the acidic character of the polymer did not interfere with the process and the main factor influencing it was porosity.
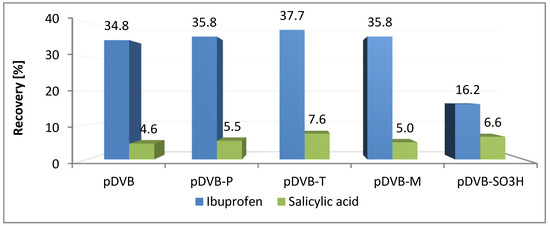
Figure 6.
Results of SPE experiments received for the pharmaceuticals.
4. Conclusions
This work presents the way of synthesis and characterization of the porous polymers obtained by suspension polymerization of divinylbenzene. In order to modify porosity of this materials, in the procedure of synthesis, 1 mL of porogenic solvent was replaced with an adequate quantity of phenol, 2,4,6-trichlorophenol or their mixture (1:1 molar ratio). The chemical modification of pDVB was performed using the sulphonation reaction. The successful course of polymerization and modification reactions was confirmed by the elemental and FTIR analyses.
The DSC analysis proved that all the studied highly cross-linked polymers were thermally stable up to 350 °C (pDVB) and after sulphonation even to 450 °C. Moreover, the DSC data indicated that pDVB-SO3H polymer has hygroscopic properties.
The polymers possessed specific surface areas in the range of 440 to 560 m2/g and they were mainly mesoporous with bimodal pore size distribution in the range up to 12 nm. Mean pore widths were ca. 3.75 and 4.75–7.15 nm. It is worth noticing that, although the materials with porosity regulated by the addition of phenol, trichlorophenol or their mixture had specific surface areas 2–5% lower and pore volumes 5–18% lower than for pDVB obtained in the presence of toluene, their porous structures were more uniform. It was also proved that the process of chemical modification with sulphuric acid took place in wider mesopores resulting in a decrease of porous structure parameters.
The studies on phenols sorption with the use of the SPE method showed that the best sorption properties possessed pDVB (unmodified), pDVB-T and pDVB-M. In the case of the two latter polymers positive influence of the compounds modifying porosity was observed by a ca 5% increase in the recoveries in comparison to pDVB. The similar relationship was observed for SPE of ibuprofen. The highest recovery 37.7% was obtained in the case of pDVB-T. Salicylic acid had very low affinity to the surface of the tested polymers. The highest recoveries in SPE experiments were received for pDVB-T and pDVB-SO3H: 7.6 and 6.6%, respectively.
Studies of the sorption properties of the tested polymers towards phenols and ibuprofen revealed that the process of uptake is affected by both porosity and chemical character of the adsorbent, while sorption of strongly acidic molecules like salicylic acid only depends on the sorbent porosity.
The performed studies showed that it is possible to improve the sorption properties of the prepared polymeric materials by changing the chemical composition of the polymerization mixture. Even if the increase is not so significant, the method of the synthesis is really simple and worth considering. The proposed procedure can be optimized to get better results.
After the sulphonation, the sorption properties of pDVB-SO3H were worse, in comparison, to unmodified pDVB, in the case of adsorbates possessing acidic character. However, due to the presence of a sulphonic group in the structure of adsorbent it can be presumed that sorption of compounds with basic functionalities or those in ionic forms (e.g. paracetamol, tramadol or sodium ibuprofen) could be more effective.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S.; methodology, M.S.; software, M.S.; investigation, M.S. and J.O.T.; resources, M.G., writing—original draft preparation, M.S.; writing—review and editing M.S and M.G.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Simpson, N.K.J. Solid-Phase Extraction: Principles, Techniques and Applications; Nigel, J.K.S., (Varian Associates), Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 0-8247-09021-X. [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Mendoza-Castillo, D.I.; Reynel-Ávila, H.E. (Eds.) Adsorption Processes for Water Treatment and Purification; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-58135-4. [Google Scholar]
- Fathy, M.; Moghny, T.A.; Awadallah, A.E.; El-Bellihi, A.-H.A.-A. Study the adsorption of sulfates by high cross-linked polystyrene divinylbenzene anion-exchange resin. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekici, S.; Güntekin, G.; Saraydın, D. The Removal of Textile Dyes with Cross-Linked Chitosan-Poly(acrylamide) Adsorbent Hydrogels. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2011, 50, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobiesiak, M.; Podkoscielna, B. Preparation and characterization of porous DVB copolymers and their applicability for adsorption (solid-phase extraction) of phenol compounds. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasapollo, G.; Del Sole, R.; Mergola, L.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Scardino, A.; Scorrano, S.; Mele, G. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Present and Future Prospective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5908–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobiesiak, M.; Podkościelna, B.; Podkościelny, P. New functionalised polymeric microspheres for multicomponent solid phase extraction of phenolic compounds. Adsorption 2016, 22, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podkościelna, B.; Sobiesiak, M.; Zhao, Y.; Gawdzik, B.; Sevastyanova, O. Preparation of lignin-containing porous microspheres through the copolymerization of lignin acrylate derivatives with styrene and divinylbenzene. Holzforschung 2015, 69, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, M.; Gawdzik, J. Preparation and characterization of sorption properties of porous microspheres of 1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone-divinylbenzene. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2008, 31, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobiesiak, M. Bead-shaped porous polymers containing bismaleimide—their physico-chemical characteristics and sorption properties towards chlorophenols. Polish J. Appl. Chem. 2011, LV, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, L.; Telliard, W. ES&T Special Report: Priority pollutants: I-a perspective view. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1979, 13, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawell, J.K.; Hunt, S. Environmental Toxicology: Organic Pollutants; John Wiley & Sons LTD: New York, NY, USA, 1988; ISBN 0745801943. [Google Scholar]
- The European Parliament. DIRECTIVE 2006/118/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 12 December 2006. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2006, L 372, 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- The European Parliament. DECISION No 2455/2001/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 20 November 2001. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2001, L 331, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, D.; Castellet-Rovira, F.; Villagrasa, M.; Badia-Fabregat, M.; Barceló, D.; Vicent, T.; Caminal, G.; Sarrà, M.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S. The role of sorption processes in the removal of pharmaceuticals by fungal treatment of wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, C.M.; Ferrera, Z.S.; Padrón, M.E.T.; Rodríguez, J.J.S. Methodologies for the extraction of phenolic compounds from environmental samples: New approaches. Molecules 2009, 14, 298–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, D.; Barceló, D. different sorbent materials for on-line liquid-solid extraction followed by liquid chromatographic determination of priority phenolic compounds in environmental waters. J. Chromatogr. A 1996, 733, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Hassine, S.; Hammami, B.; Touil, S.; Driss, M.R. Determination of Chlorophenols in Water Samples Using Solid-Phase Extraction Enrichment Procedure and Gas Chromatography Analysis. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 95, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insa, S.; Salvadó, V.; Anticó, E. Development of solid-phase extraction and solid-phase microextraction methods for the determination of chlorophenols in cork macerate and wine samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1047, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.-Z.; Zhao, L.-X.; Yan, W.; Lin, J.-M.; Zheng, Z.-X. Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography for analysis of phenolic compounds from environmental water samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.; Du, R.; Wang, X.; Wan, M.; Dai, X.; Gao, J. Adsorption of phenolic compounds from aqueous solution using salicylic acid type adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 201–202, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Cai, Y.; Mou, S.; Lu, Y. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes as a solid-phase extraction adsorbent for the determination of chlorophenols in environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1081, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Kostoglou, M. Green adsorbents for wastewaters: A critical review. Materials (Basel) 2014, 7, 333–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grochowicz, M. Investigation of the thermal behavior of 4-vinylpyridine-trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate copolymeric microspheres. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 118, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, M. Thermal properties of TRIM–GMA copolymers with pendant amine groups. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 126, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyler, C.L.; Hirschler, M.M. Section One—Fundamentals, Chapter 7: Thermal Decomposition of Polymers; 2002; ISBN 0877653542 9780877653547. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, M.; Funabashi, K.; Yusa, H.; Kikuchi, M. Influence of functional sulfonic acid group on pyrolysis characteristics for cation exchange resin. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 1987, 24, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobiesiak, M. Chemical Structure of Phenols and Its Consequence for Sorption Processes. In Phenolic Compounds—Natural Sources, Importance and Applications; Soto-Hernandez, M., Palma-Tenango, M., García-Mateos, R., Eds.; InTech: London, UK, 2017; pp. 3–26. ISBN 978-953-51-2958-5. [Google Scholar]
- Podkościelna, B.; Sobiesiak, M. Synthesis and characterization of organic–inorganic hybrid microspheres. Adsorption 2016, 22, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).