Abstract
Manganese oxide forms prepared by different methods differ by their compositions, phase ratios in polyphase samples, and crystallite sizes (XRD and TEM characterization). Among the phases, tunnel-structured β-MnO2 (pyrolusite), α-MnO2 (cryptomelane), ε-MnO2 (akhtenskite), and β-Mn2O3 (bixbyite) have been identified. Water vapor sorption isotherms showed substantial differences in the affinities of water molecules to oxide surfaces of the manganese oxide forms under study. The parameters of the BET equation and pore size distribution curves have been calculated. The manganese oxide forms have mesoporous structures characterized by uniform and non-uniform pore sizes as well as by moderate hydrophilic behavior.
1. Introduction
Polymorphic forms of manganese dioxide are widely used as catalysts for such gaseous reactions as ozone decomposition [1,2,3], CO oxidation [4,5], NO reduction [6,7], and volatile organic compound oxidation [8,9]. The activity and stable action of such catalysts significantly depend on a relative humidity of gaseous mixtures. In most cases, water vapor adsorption causes complete loss of catalytic activity of manganese oxides towards the above-mentioned reactions [2,3,6]. Therefore, besides nitrogen adsorption required for determination of textural properties of manganese oxides and used in many works [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9], water vapor adsorption is also topical. Water vapor sorption isotherms are able to provide significant information about hydrophilic/hydrophobic behavior of these materials. For this purpose, values of water vapor adsorption at low P/PS would be compared [10,11,12,13,14]. When Type I, II, IV, or VI (according to the well-known classification [15]) water vapor adsorption isotherms are observed, it means that the surface under study is hydrophilic, while hydrophobic surfaces are characterized by Type III or V adsorption isotherms [11]. By the appearances of Type III or V adsorption isotherms, one can judge about a change in the affinity of water molecules to the surface under investigation over the course of increasing coverage by water and about transition from hydrophobic to hydrophilic surface behavior at P/PS > 0.5–0.6. In our opinion, as a result of water vapor adsorption, the change in physicochemical properties of oxide surfaces takes place, which, in turn, leads to the change in activity of oxide catalysts in the redox reactions. From available published work, it can be concluded that hydrophilic/hydrophobic properties of manganese dioxide polymorphic forms depend on their structures and compositions [14,16,17], the nature of cations and degrees of surface hydration [18], as well as on methods of surface modification [19]. For instance, as was reported [14], values of the maximum water vapor adsorption (a∞, mmol/g) decrease roughly tenfold for manganese oxides of different structures in the following order: OL > OMS-1 > OMS-2, i.e., tunnel-structured cryptomelane (OMS-2) is hydrophobic. In the case of protonated hollandite, its affinity to water molecules rises sharply [18]. Water vapor adsorption also depends on such important factors as sizes and morphologies of adsorbent nanoparticles [20,21]. In the case of manganese oxide forms, systematic investigations of the influence of synthesis methods and conditions on their structures (phase compositions) and crystallite sizes as well as on their water vapor adsorption properties are absent.
The aim of the work was to study the influence of some methods for preparing manganese oxide forms on their phase compositions and structural-adsorption parameters determined with the help of water vapor adsorption.
2. Materials and Methods
In the study, eight samples of manganese oxide forms were used. They were prepared by different methods and denoted as 1S-Mn–8S-Mn.
1S-Mn. Commercial manganese oxide (analytical grade, GOST 4470-79, “Krasnyy Khimik”, Leningrad, USSR).
2S-Mn. This fine-dispersed manganese oxide sample was synthesized by reduction of water-dissolved potassium permanganate with formic acid at 70 °C. The formed precipitate was filtered, washed with cold water until neutral pH, first air-dried at room temperature and then further dried in a drying oven at 80 °C for 1 h [22].
3S-Mn. 5% KMnO4 aqueous solution (60.8 mL) was added dropwise to 5% MnSO4 aqueous solution (77 mL) heated in a water bath up to 50–60 °C under vigorous stirring for 2 h. The obtained mixture was kept in a water bath at 60 °C for two more hours and then was kept overnight at room temperature. The formed precipitate was filtered, washed with distilled water and dried at 110 °C for 8 h [23].
4S-Mn. Its typical synthesis [24] was as follows: 5.89 g of KMnO4 in 100 mL of water was added to a solution of 8.8 g of MnSO4·H2O in 30 mL of water and 3 mL concentrated HNO3. The solution was refluxed at 100 °C for 24 h, and the product was filtered, washed, and dried at 120 °C.
5S-Mn. This MnO2 sample was synthesized by using KMnO4 and Mn(CH3COO)2·4H2O as reactants. KMnO4 and Mn(CH3COO)2·4H2O were mechanically mixed in the molar ratio of 2:3 in an agate mortar and an appropriate amount of water was added to the mixture to obtain a rheological phase. The rheological phase mixture was heated at 100 °C for 12 h. The mixture was cooled down to room temperature and washed with distilled water several times. Thus, a precursor was obtained. The precursor was heated at 400 °C for 4 h in air [25].
6S-Mn. This MnO2 sample was synthesized via a sol-gel reaction and its typical synthesis was as follows [26]: maleic acid (0.78 g, 6.7 mmol) and KMnO4 (3.16 g, 20 mmol) were dissolved in deionized water (200 mL) at predetermined temperatures 40 °C. After stirring for 30 min, the mixture was allowed to settle for 60 min. The sample obtained after this step was then filtered, washed with deionized water, and dried at 120 °C for 12 h. Then calcination was carried out at 450 °C for 2 h. The product was pulverized, washed with 0.1 M HCl and deionized water, and then dried at 120 °C for 12 h.
7S-Mn. This sample was synthesized via KNO3 and MnSO4 melting together [27]. KNO3 was put into a crucible and heated to 380 °C under stirring to form a molten solution; MnSO4 was added into it and the weight ratio of KNO3 to MnSO4 was 15. After being maintained at 380 °C for 3 h, the crucible was cooled to room temperature under ambient conditions, and the product was obtained by washing with deionized water, centrifugation, and drying at 90 °C for 12 h.
8S-Mn. This sample was obtained by a modernized method [24]. A typical preparation was as follows: a solution of 35 g of KOH in cold water (200 mL) was added to a MnSO4·H2O solution (30 g in 200 mL of water). Ozone contained in ozone-air mixture (OAM) at CO3 of 100 mg/m3 was bubbled vigorously (about 1 L/min) through the solution for 4 h. The black product was washed with water and kept in air overnight. Then it was calcined at 600 °C for 4 h.
The samples were investigated on a Siemens D500 powder diffractometer (CuKα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å) with a secondary beam graphite monochromator (Siemens AG, Munich, Germany). After thorough grinding with a pestle, each sample was placed into a glass cell with an enclosed volume of 2 × 1 × 0.1 cm3 for XRD pattern recording in the 2θ range from 0° to 90° with a step of 0.03° and an accumulation time at every point of 60 s.
The morphologies of the prepared materials were studied by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The images of the materials were obtained in TEM-125K microscope (Selmi, Sumy, Ukraine) operating at voltage of 100 kV. The samples were prepared by dispersing in ethanol and sonicated for 1–2 min. For TEM observations, the suspension was dropped on a carbon-coated copper grid.
Water vapor sorption was studied using a temperature-controlled at 21 °C vacuum setup with a conventional McBain-Bakr silica-spring balance (Odessa I.I. Mechnikov National University, Odessa, Ukraine). Previously, the samples were de-gassed at 110 °C for 2 h [28]. Their specific surface areas were estimated by the BET method, their pore size distribution curves were determined using desorption branches of their isotherms, and their pore radii were estimated using the Kelvin equation [15].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Composition
The XRD data show that both the commercial 1S-Mn sample and the 4S-Mn, 5S-Mn, 6S-Mn, 7S-Mn, and 8S-Mn samples synthesized by us are crystalline (Figure 1) and the 2S-Mn and 3S-Mn samples are semicrystalline. All XRD patterns were treated by the Rietveld method. The results of phase identification, phase contents and crystallite sizes are summarized in Table 1.
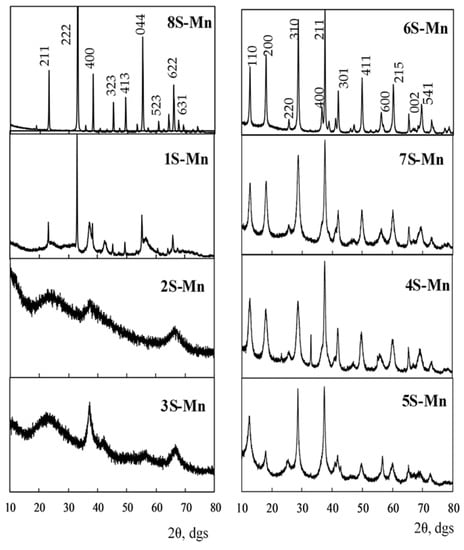
Figure 1.
X-ray diffraction patterns of the manganese oxide samples under study.

Table 1.
Phase compositions and phase parameters for the manganese oxide samples under study.
Judging from the presented data, commercial 1S-Mn is polyphase and consists of β-Mn2O3 (bixbyite) (JCPDS 24-0508), β-MnO2 (pyrolusite) (JCPDS 24-0735), and ε-MnO2 (akhtenskite) (JCPDS 30-0820) with the highest content of β-MnO2. The crystalline 4S-Mn–7S-Mn samples contain α-MnO2 (cryptomelane K1.33Mn8O16) (JCPDS 34-0168). In addition to cryptomelane, ca. 10% of β-Mn2O3 and β-MnO2 impurity phases are observed in the 4S-Mn and 5S-Mn samples, respectively. Bixbyite (JCPDS 24-0508) content in the 8S-Mn sample is 100%. Despite the fact that the 2S-Mn and 3S-Mn samples are semicrystalline, the peak near 39° in their XRD patterns permit to identify the ε-MnO2 phase. The corresponding h k l values are marked on the peaks in Figure 1 for the α-MnO2 (samples 4S-Mn, 5S-Mn, 6S-Mn, 7S-Mn) and β-Mn2O3 (samples 1S-Mn, 8S-Mn) phases. For the 4S-Mn sample, β-Mn2O3 peaks at 2θ = 23.186°, 33.022°, 45.263°, and 55.303° were assigned to the (2 1 1), (2 2 2), (3 3 2), (4 4 0) planes, respectively. As to other phases, β-MnO2 phase peaks in the 1S-Mn and 5S-Mn samples at 2θ = 37.328°, 42.823°, 46.185°, and 56.652° were assigned to the (1 0 1), (1 1 1), (2 1 0), (2 2 1) planes, respectively. Thus, the 1S-Mn sample is polyphase, the 2S-Mn, 3S-Mn, 6S-Mn, 7S-Mn, and 8S-Mn samples are monophase whereas the 4S-Mn and 5S-Mn samples, besides the main phase, contain the impurity phases. All the samples, except for 8S-Mn, are tunnel-structured with various tunnel sizes: β-MnO2 (2.3 × 2.3 Å), ε-MnO2 (2.3 × 4.6 Å), and α-MnO2 (4.6 × 4.6 Å) [29]. Crystallite sizes of the samples differ considerably (Table 1). The largest crystallite sizes (87 nm for 1S-Mn and 66 nm for 4S-Mn and 8S-Mn) were determined for bixbyite, crystallite sizes for cryptomelane in the 4S-Mn, 5S-Mn, and 7S-Mn samples were similar (14–16 nm) but for the 6S-Mn sample, the crystallite size of cryptomelane increased up to 36 nm. The smallest crystallite sizes, approx. 3 nm, were observed for akhtenskite in the semicrystalline 2S-Mn and 3S-Mn samples.
3.2. Morphology
Microimages for some manganese oxide forms distinguished from each other by their morphologies are shown in Figure 2a–d.
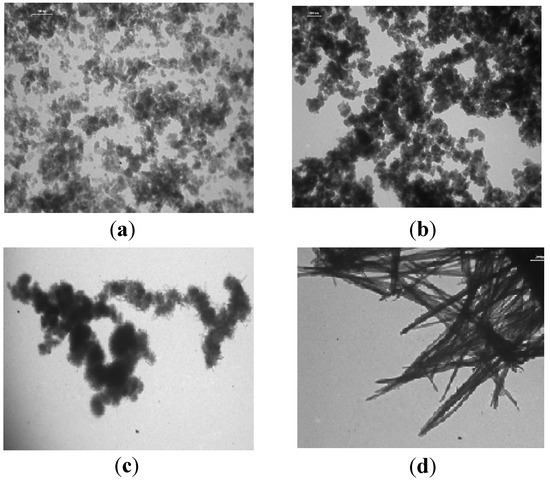
Figure 2.
TEM images for the 1S-Mn (a); 2S-Mn (b); 3S-Mn (c); and 6S-Mn (d) samples.
The polymorphous 1S-Mn sample (Figure 2a) consists of non-uniform particles. Particle forms for the semicrystalline ε-MnO2 phase (2S-Mn and 3S-Mn) depend on the method of their preparation. The TEM image for 2S-Mn indicates the formation of grain-like aggregates of nanoparticles with a rod-like morphology. The 3S-Mn sample consists of spherical nanoparticle aggregates with an urchin-like morphology. TEM image for nano-sized particles for cryptomelane shows that 6S-Mn (Figure 2d) has non-uniform needle-like nanorod morphology.
3.3. Water Vapor Sorption
Isotherms of water vapor adsorption-desorption by all manganese oxide samples are shown in Figure 3. According to the well-known classification [15], adsorption isotherms for all manganese oxide samples, except for 6S-Mn (cryptomelane) and 8S-Mn (bixbyite), are assigned to Type IV with Type H3 hysteresis loops. Since the phase compositions and crystallinity of the samples differ (Table 1), their affinity to water molecules would be different.
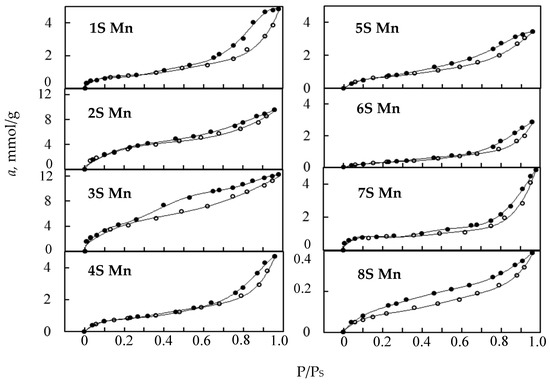
Figure 3.
Water vapor adsorption-desorption isotherms for the manganese oxide samples under study.
The adsorption isotherm of the polyphase (β-Mn2O3, β-MnO2, and ε-MnO2) 1S-Mn sample and the adsorption isotherms for the 4S-Mn, 5S-Mn, and 7S-Mn samples predominantly consisted of the cryptomelane phase, were characterized by similar crystallite sizes, and practically overlapped. Semicrystalline 2S-Mn and 3S-Mn samples consisting of ε-MnO2 had higher adsorption magnitudes. ε-MnO2 crystallites with very small particles (3 nm) of urchin-like morphology (Figure 2c) resulted in the highest adsorption and Ssp values.
Water vapor adsorption is significantly lower for the 6S-Mn sample characterized by large cryptomelane crystallites (36 nm) and disorderly stacked needle-like nanorod morphology. The 8S-Mn sample comprising single β-Mn2O3 phase with large crystallites has a very weak affinity to water molecules and is characterized by Type III isotherm with H3 Type hysteresis loop. As can be concluded from bixbyite contents in the 1S-Mn and 4S-Mn samples (30% and 9.5%, respectively), bixbyite contribution to water vapor adsorption is minimal. Poor water vapor adsorption by β-Mn2O3 has been also reported elsewhere [30].
The adsorption and desorption branches of the isotherms for all samples under study, except for 4S-Mn and 6S-Mn, overlap below P/Ps = 0.3 and that is characteristic of metal oxides [31]. Different widths of the hysteresis loops indicate different abilities of the samples to interact with water molecules. The water vapor adsorption isotherms were analyzed using the linearized BET equation. Figure 4 shows that initial linear portions of all isotherms are observed over P/PS ranges from 0.03 to 0.22 with the correlation coefficient, R2, of 0.98–0.99.
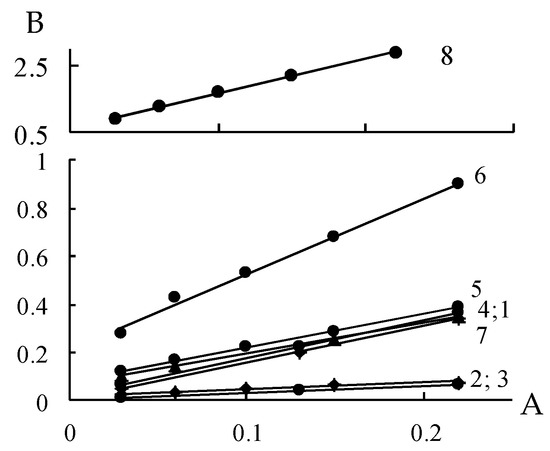
Figure 4.
Initial linear portions of the BET adsorption isotherms for the manganese oxide samples under study A = P/Ps; B = A/a (1 − A). Indexation 1–8 corresponds to Arabic numerals in the sample designations.
Parameters of water vapor adsorption by the manganese oxide forms under study, i.e., the water monolayer capacities, аm, the BET constants, С, characterizing the heat of adsorption for the first layer of water molecules, and the specific surface areas, Ssp, are summarized in Table 2. Ssp were calculated based on two values of a water molecule cross section 10.6 Å2 and 14.8 Å2, corresponding to two different types of water molecule packing on oxide surfaces [30].

Table 2.
Structural-adsorption parameters for manganese oxide samples under study.
Based on the desorption branches of their water vapor isotherms, pore diameter distribution curves were obtained for each sample under study. Some examples of the curves are shown in Figure 5, while all their maximum values are presented in Table 2.
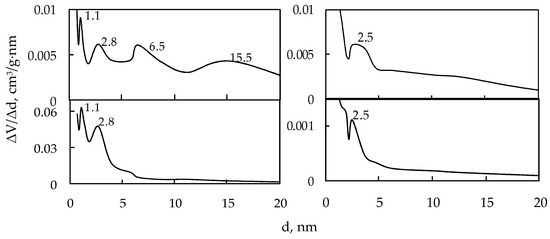
Figure 5.
Pore diameter distribution curves for the manganese oxide samples under study.
Analyzing our results shown in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5 and in Table 2, we can draw the following conclusions: the tunnel-structured 5S-Mn and 6S-Mn samples as well as the 8S-Mn sample not characterized by a tunnel structure have highly uniform mesoporous structure, whereas the 2S-Mn, 4S-Mn, and 7S-Mn samples have non-uniform mesoporous structure; 1S-Mn and 3S-Mn have mixed micro-mesoporous structure with a micropore diameter of 1.1 nm.
Since available information [14,18,32] about water vapor adsorption by manganese oxides is limited and incommensurable, we tried to compare the reported data with our results using values of maximum adsorption, a∞, in mmol/g characterizing hydrophilicity of materials. The reported data can be presented as the following order: manganese oxide of an unknown structure (15.3) > birnessite (9.72) > todorokite (7.7) > protonated hollandite (6.1) > cryptomelane (1.1) >> cryptomelane treated with NaOH (0) (I). For manganese oxide forms under study a∞ decreases in the order: 3S-Mn, akhtenskite (12.2) > 2S-Mn, akhtenskite (9.54) > 1S-Mn, mixture of pyrolusite, bixbyite and akhtenskite (4.85) ≈ 7S-Mn, cryptomelane (4.85) ≈ 4S-Mn, mixture of cryptomelane and bixbyite (4.7) > 5S-Mn, mixture of cryptomelane and pyrolusite (3.44) > 6S-Mn, cryptomelane (2.86) >> 8S-Mn, bixbyite (0.39) (II). Order I shows that a∞ depends on structural types of manganese oxides and chemical properties of their surface. For instance, NaOH treatment of cryptomelane completely suppresses its adsorptive capacity. Distinct hydrophobic behavior of cryptomelane [14] was independently confirmed [33] by a hydrophilicity index (0.91), determined as a molar ratio of adsorbed toluene to adsorbed water. Comparing order I and order II, we can assert that the hydrophobic behavior of the cryptomelane samples synthesized in the current work is different and 6S-Mn is the most hydrophobic cryptomelane sample. Manganese oxide of an unknown structure has the highest a∞ value close to the a∞ value of our semicrystalline akhtenskite (3S-Mn).
4. Conclusions
Manganese oxide forms were synthesized by different methods. Phase composition and contents as well as crystallite sizes of the manganese oxide forms were determined from the XRD data treated by the Rietveld method. All samples, except for those obtained by potassium permanganate reduction with formic acid (2S-Mn) and MnSO4 (3S-Mn), are crystalline. The synthesized manganese oxide forms can be classified as monophase samples (2S-Mn, 3S-Mn, 6S-Mn, 7S-Mn, and 8S-Mn) and impure cryptomelane mixed with bixbyite C (4S-Mn) or pyrolusite (5S-Mn). The commercial 1S-Mn is polyphase. Bixbyite phase is characterized by the largest crystallites of 66 and 87 nm. Cryptomelane crystallite sizes can vary from 14 to 36 nm.
A method by which the manganese oxide forms were synthesized influences not only phase composition and crystallite sizes but also particle morphology.
The water vapor adsorption isotherms for the manganese oxide forms under study were analyzed using the BET method and it can be concluded that the semicrystalline 2S-Mn and 3S-Mn samples have much higher monolayer capacities than the crystalline samples.
The desorption branches were used for the calculation of pore diameter distribution curves and the conclusion has been drawn that manganese oxide forms can be classified as those of the highly uniform mesoporous structure (5S-Mn, 6S-Mn, and 8S-Mn), of non-uniform mesoporous structure (2S-Mn, 4S-Mn, and 7S-Mn), and mixed micro-mesoporous structure (1S-Mn and 3S-Mn).
For manganese oxide forms synthesized by us, hydrophobicity increases in the following order: 3S-Mn < 2S-Mn < 1S-Mn < 7S-Mn ≈ 4S-Mn < 5S-Mn < 6S-Mn < 8S-Mn. It is reasonable to expect that the negative effect of adsorbed water on catalytic properties of manganese oxide forms, e.g., in the reaction of ozone decomposition, decreases in the same order.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.R.; Investigation, A.N. and G.D.; Data Curation, A.T. and G.D.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, T.R., A.T. and V.V.; Writing—Review & Editing, T.R. and A.T.; Project Administration, T.R.
Funding
The study was carried out with the support of the Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Kolotilov S.V. (L.V. Pisarzhevskii Institute of Physical Chemistry of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine) for his help with electron microscopy studies of the samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jia, J.; Zhang, P.; Chen, L. Catalytic decomposition of gaseous ozone over manganese dioxides with different crystal structures. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 189, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Liu, F.; He, H.; Zhang, R. The Effects of Mn2+ Precursors on the Structure and Ozone Decomposition Activity of Cryptomelane-Type Manganese Oxide (OMS-2) Catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 23119–23126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, C.; He, H. Transition metal doped cryptomelane-type manganese oxide catalysts for ozone decomposition. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 201, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Hu, H.; Zhang, J. Cobalt-Doped K-OMS-2 Nanofibers: A Novel and Efficient Water-Tolerant Catalyst for the Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabineiro, S.A.; Santos, V.P.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Órfão, J.J.; Figueiredo, J.L. CO oxidation over gold supported on Cs, Li and Ti-doped cryptomelane materials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 480, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Shi, J.W.; Fan, Z.; Gao, G.; Niu, C. Sulfur and Water Resistance of Mn-Based Catalysts for Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx: A Review. Catalysts 2018, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Shi, J. Water-promoted low-concentration NO removal at room temperature by Mg-doped manganese oxides OMS-2. Appl. Catal. A 2015, 507, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, S.; Nuns, N.; Trentesaux, M.; Batra, V.S.; Giraudon, J.-M.; Lamonier, J.-F. Reaction of formaldehyde over birnessite catalyst: A combined XPS and ToF-SIMS study. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 223, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, A.; Suib, S.L. Total oxidation of volatile organic compounds with hydrophobic cryptomelane-type octahedral molecular sieves. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2000, 35, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtch, N.C.; Jasuja, H.; Walton, K.S. Water stability and adsorption in metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10575–10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, E.P.; Mintova, S. Nanoporous materials with enhanced hydrophilicity and high water sorption capacity. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2008, 114, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naono, H.; Hakuman, M. Analysis of adsorption isotherms of water vapor for nonporous and porous adsorbents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1991, 145, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttakin, M.; Mitra, S.; Thu, K.; Ito, K.; Saha, B.B. Theoretical framework to evaluate minimum desorption temperature for IUPAC classified adsorption isotherms. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2018, 122, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Garcia-Martinez, J.; Suib, S.L. Adsorptive and acidic properties, reversible lattice oxygen evolution, and catalytic mechanism of cryptomelane-type manganese oxides as oxidation catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 3198–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregg, S.J.; Sing, K.S.W. Adsorption, Surface Area and Porosity; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982; ISBN 0-12-300956-1. [Google Scholar]
- Suib, S.L. Structure, porosity, and redox in porous manganese oxide octahedral layer and molecular sieve materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gac, W. The influence of silver on the structural, redox and catalytic properties of the cryptomelane-type manganese oxides in the low-temperature CO oxidation reaction. Appl. Catal. B 2007, 75, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Tezuka, S.; Kanoh, H. Gaseous molecular sieving property of a microporous hollandite-type hydrous manganese oxide. Chem. Lett. 2000, 29, 560–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.G.; Yang, C.M.; Kim, B.H. Enhanced electrochemical properties of boron functional groups on porous carbon nanofiber/MnO2 materials. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 788, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatlier, M.; Munz, G.; Henninger, S.K. Relation of water adsorption capacities of zeolites with their structural properties. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2018, 788, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Xu, Z.; Wang, C.; Gao, Y. Shape evolution of metal nanoparticles in water vapor environment. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 2628–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakitskaya, T.L.; Khitrich, V.F.; Raskola, L.A.; Makordey, F.V.; Sirovetnik, O.V. Decomposition of ozone microconcentrations by fine-dispersed MnO2 catalyst. Herald ONU(Ukr). Chemistry 2004, 9, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Karyakin, Y.V.; Angelov, I.I. Pure Chemical Substances. M. Chem. 1974, 407. [Google Scholar]
- DeGuzman, R.N.; Shen, Y.F.; Neth, E.J.; Suib, S.L.; O’Young, C.L.; Levine, S.; Newsam, J.M. Synthesis and characterization of octahedral molecular sieves (OMS-2) having the hollandite structure. Chem. Mater. 1994, 6, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Feng, C.; Kim, S.-J.; Yin, S.; Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Li, S. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of KMn8O16 nanorods for Lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 88, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; He, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, D. Effects of textural parameters and noble metal loading on the catalytic activity of cryptomelane-type manganese oxides for formaldehyde oxidation. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sul, N.; Duan, Y.; Jiao, X.; Chen, D. Large-scale preparation and catalytic properties of one-dimensional α/β-MnO2 nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. 2009, 113, 8560–8565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakitskaya, T.L.; Truba, A.S.; Ennan, A.A.; Dlubovskii, R.M.; Volkova, V.Y. Water vapour adsorption by nanostructured polyphase compositions based on the solid component of welding aerosol. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musil, M.; Choi, B.; Tsutsumi, A. Morphology and Electrochemical Properties of α-, β-, γ-, and δ-MnO2 Synthesized by Redox Method. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A2058–A2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prélot, B.; Villiéras, F.; Pelletier, M.; Razafitianamaharavo, A.; Thomas, F.; Poinsignon, C. Structural–chemical disorder of manganese dioxides: II. Influence on textural properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 264, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombácz, E.; Hajdú, A.; Illés, E.; László, K.; Garberoglio, G.; Jedlovszky, P. Water in contact with magnetite nanoparticles, as seen from experiments and computer simulations. Langmuir 2009, 25, 13007–13014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foote, H.W.; Dixon, J.K. The adsorption of water and benzene vapors by manganese dioxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1930, 52, 2170–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuino, H.C.; Dharmarathna, S.; Njagi, E.C.; Mei, M.C.; Suib, S.L. Gas-phase total oxidation of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylenes using shape-selective manganese oxide and copper manganese oxide catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. 2012, 116, 12066–12078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not Available. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).