Abstract
Water scarcity is a global issue that is expected to continue increasing in importance in the coming decades. Reclaimed water is one important source available to meet future needs. The reclamation process for wastewaters, particularly from industrial sources, involves the need to remove low-level contaminants. Here we report the efficacy of an ion flotation process that uses the biosurfactant monorhamnolipid as a metal collector to recover Cs+, Cd2+, and La3+ from water. These elements were tested at collector-to-colligend ratios of 2, 5, and 10. The collector-to-colligend ratio and metal valence play a large role in determining flotation success with removal efficiencies varying widely. The maximum removal efficiency for the metals when floated individually were 46.2, 99.8, and 98.6% for Cs+, Cd2+, and La3+, respectively. When mixed together at near equimolar concentrations removal efficiencies were 39.4, 98.4, and 88.1%, respectively. Removal efficiency for Cs+, Cd2+, and La3+ were up to 49.9, 99.5, and 51.5% when mixed at a ratio of 200:10:1, whereas conditional stability constants predict a removal order of La3+ > Cd2+> Cs+. Future research should examine parameters, including pH and ionic strength, that may affect the flotation process as well as actual metal-contaminated waste streams to evaluate the usefulness of this technology.
1. Introduction
Water scarcity issues are widely recognized and described in the literature [1,2,3,4,5]. The United Nations defines water scarcity as “the point at which the aggregate impact of all users impinges on the supply or quality of water under prevailing institutional arrangements to the extent that the demand by all sectors, including the environment, cannot be satisfied fully” [1]. By 2030, demand for water is expected to reach 6900 billion m3 (40% above current accessible reliable supplies), and a third of the world population is projected to live in basins where the water deficit is greater than 50%. As a result, wastewater reclamation and re-use from industrial and residential sectors will be increasingly important [6]. In particular, the industrial sector is projected to account for 22% of water use in 2030 [7]. Reclamation of industrial wastestreams will require treatment to remove both organic and metal contaminants. Metals, in particular, pose risks to environmental and human health; they are not biodegraded and hence are subject to accumulation. Metals are commonly found in effluents from mining operations [8,9], industrial processes [10], landfills [11], and wastewater treatment facilities [12].
Many technologies have been designed to remove metals from aqueous media and their efficacy, advantages, and disadvantages are reviewed elsewhere [10,13]. Major technological approaches include chemical precipitation [14], chemical coagulation/flocculation, ion exchange, adsorption, electrochemical treatments, filtration and flotation. Flotation is a highly effective and historically significant process for the beneficiation of mineral ores [15,16,17], and it is equally suitable for the concentration of dissolved species as well. Two flotation sub-types have found extensive application in wastewater treatment for their ability to remove and concentrate dissolved metal ions from solution: precipitate and ion flotation [10]. The former utilizes chemicals to precipitate dissolved metals and air bubbles to collect the resulting precipitate at the solution surface [10]. The latter concentrates dissolved, surface-inactive ions (colligends) through complexation with surfactants (collectors) and subsequent introduction of air bubbles. The ion-surfactant complexes (sublate) attach to the bubble air/water interfaces and accumulate at the solution surface as foam that can then be collected into a metal concentrate herein called foamate [18]. The solution remaining in the column then has a reduced metal concentration and is ready for additional treatment or release. Since its first description by Sebba [19] in 1959, a large body of research has demonstrated ion flotation’s efficacy and optimal operating conditions for a wide variety of collector and colligend pairs (see Pinfold, Matis & Mavros, and Lemlich [15,18,20] for literature reviews). This body demonstrates two important advantages of ion flotation over other treatment approaches: (1) it can achieve high metal removal efficiencies even when metals are very dilute in solution and (2) selective metal recovery is possible by manipulating the collector and other flotation conditions. When developing a flotation process, the collector characteristics of collector-colligend selectivity, critical micelle concentration, solubility, toxicity, and biodegradability should be considered. The latter two points are particularly important because some collector will remain in the cleaned solution, and secondary contamination by a toxic or recalcitrant collector is undesirable.
Biosurfactants are increasingly being examined for use in remediation of aqueous media due to their metal selectivity; tolerance to variations in pH, salt concentrations, and temperature; and green characteristics when compared to chemical surfactants used during in situ remediation strategies: natural production from low-cost renewable resources, lower toxicity, and increased biodegradability [21,22]. We have recently explored the ability of the microbially-produced surfactant monorhamnolipid to bind metals including rare earth elements [23,24,25,26]. Monorhamnolipids are selective for valuable metals (e.g., rare earth elements) and metals of environmental concern (e.g., Cd, Pb, Cu) over common soil and water cations [26]. Despite demonstrated metal interactions, rhamnolipid-based metal recovery technologies for metalliferous solutions are in the early stages of investigation. Recent reports describe rhamnolipid’s use in metal remediation applications for metalliferous solutions: micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration [27,28], precipitate flotation [29], and ion flotation [30]. Building on the last report, the present research was performed to elucidate additional operational limits of ion flotation using monorhamnolipid as a collector. Monorhamnolipids were chosen for this study because they are known to strongly and selectively bind metals and a metal selectivity sequence has already been described [25,26]. This selectivity sequence guided the choice of metals used in this study, specifically to determine if target metals of value, such as lanthanum, could be recovered from a mixture of metals. Thus, the objectives of this study are to: 1) examine collector-to-colligend ratio effects on metal removal efficiency, and 2) determine ion flotation efficiencies in mixed metal systems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Monorhamnolipids
Monorhamnolipid from Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 was produced, harvested, and purified as previously described [26]. P. aeruginosa ATCC 9027 is a natural mutant previously shown to exclusively produce monorhamnolipid [31,32]. The monorhamnolipid produced is a congener mixture of up to 30 molecules in which the rhamnose headgroup is preserved but the alkyl chains can vary in chain length and, to a lesser extent, saturation (Figure 1) [33]. The production protocol used for this work generates a mixture in which the major congener rhamnosyl-β-hydroxydecanoyl-β-hydroxydecanoate typically dominates at 75–85 wt% of the mixture [33,34]. This complex assembly of congeners is referred to herein as monorhamnolipid.
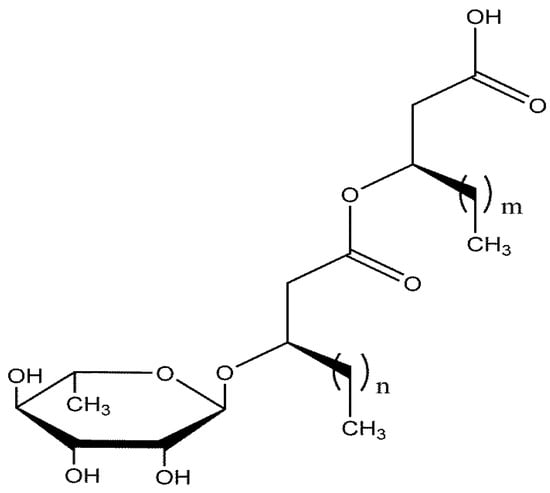
Figure 1.
Structure of monorhamnolipids utilized in this study. The varying chain lengths of the monorhamnolipid congeners are represented by ‘m’ and ‘n’ which vary from 4 to 12.
2.2. Chemicals
Cs(NO3), Cd(NO3)2•4H2O, and La(NO3)3•6H2O were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich with a purity of ≥99% and were used as received. These metals were selected because they are present as free ions at pH 7 (utilized for this study) [35] and they are representatives of the strongly binding (La3+), moderately binding (Cd2+), and weakly binding (Cs+) metals described by Hogan et al. [26] and Hogan [36]. 100% molecular-grade ethanol was purchased from Fisher Scientific and used as received.
2.3. Flotation Apparatus
Flotation columns were based on the design of Thalody and Warr [37] (Figure 2). The University of Arizona Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Glass Shop constructed each column from a glass tube (50 cm tall with a diameter of 5.5 cm) fused to a medium glass frit (Chemglass, 10–15 µm pore size) at the bottom. The column was equipped with a bulk solution sampling port 2 cm above the frit, and a removable funnel for directing foam into the foamate reservoir. The flotation gas was compressed air (breathing quality UN 1002). A gas manifold with three outlets distributed air to three flotation columns at a pressure of 20 psi and a flow rate of 50 mL min−1. Airflow to each column was controlled by an independent rotameter.
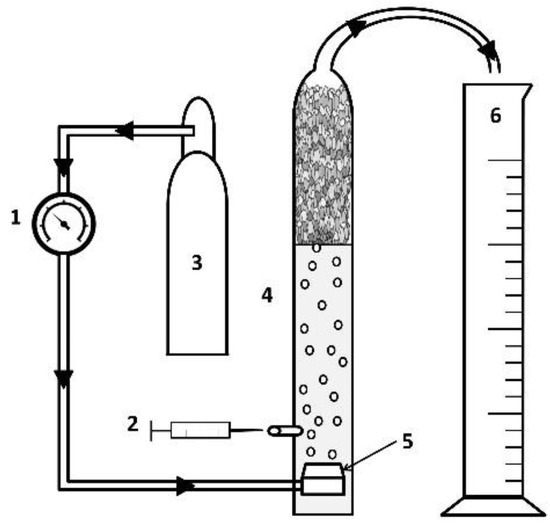
Figure 2.
Experimental apparatus schematic diagram: 1. rotameter, 2. sample syringe and port, 3. compressed air cylinder, 4. flotation column, 5. gas dispersion frit, 6. foamate reservoir.
2.4. Ion Flotation Experiments
One previous study [30] has examined ion flotation parameters using rhamnolipid as the collector to determine optimal operating parameters (Cd2+ concentration, rhamnolipid concentration, pH, aeration rate, and frother addition) for removal of Cd2+ from solution. Results from this work guided the establishment of initial operating conditions in the present study. All experiments in this study were conducted at pH 7 because Bodagh et al. [30] showed the effect of pH on the flotation efficiency of Cd2+ goes through a peak in the range of pH 6.5-7, after which the removal decreases. This decrease is attributed to the formation of metal hydrates and/or (oxy)hydroxides instead of rhamnolipid complexes. Furthermore, monorhamnolipid has a pKa of ~5.5 [31] near and below which rhamnolipids are poorly soluble and lose their frothing character. Preliminary experiments were performed to determine an air flow rate of 50 mL min−1 (see supplementary materials). Faster flow rates caused excessive entrainment of water in the foam, lowering the efficiency of flotation. Preliminary experiments were also performed to determine an ethanol frother concentration of 0.5 or 0.8% (v/v) (see supplementary materials). Finally, ion flotation has been found to be most efficient at or below the collector’s CMC [18,19,38]. This is because aggregated surfactants compete with interface-attached surfactants for colligend, hindering flotation. Monorhamnolipid has a CMC that varies from 10 to 180 µM depending on solution conditions, in particular pH [33]. Monorhamnolipid produced by P. aeruginosa ATCC 9027 has a CMC of 108 µM for experimental conditions similar to those herein [39], thus a monorhamnolipid concentration of 100 µM was selected for this study.
For all experiments, 250 mL of solution were added to the column, and air sparging was initiated immediately. Foam formation began immediately with 8–10 min required for foam to reach the top of the column for collection. Foamate was collected in acid-washed 250 mL polypropylene graduated cylinders during the experiment. The columns were sparged with air until foam ceased to exit the column; operation times are noted for each experiment. All solutions were made using ultrapure water (≥18 MΩ-cm) and were prepared in acid-washed polypropylene volumetric flasks. Ultrapure water was utilized to remove the variable of other metals native to less pure water sources, e.g., Ca and Mg. The pH was adjusted to 7.0 ± 0.1 using 1.0 M NaOH or HCl. Before each experiment, columns were prepared by rinsing with 9:1 chloroform:methanol to ensure that adsorbed rhamnolipid from previous experiments was removed, rinsing 5 times with ultrapure water, and drying by running air through the fritted glass.
Both foamate and column solutions were measured for metal concentration. Foamate samples were collected at the end of all experiments, after air sparging stopped. Foam entering the foamate reservoir was broken by initial addition of 20 mL of 2% trace metals grade nitric acid. The foamate was mixed by manual agitation, then a 10 mL sample was collected in a metal-free polypropylene 15 mL centrifuge tube (VWR, Radnor, PA). Water transfer from the column to the foamate reservoirs was measured gravimetrically. In addition, samples of approximately 2 mL were taken from the column via a syringe from the rubber septum sealed sampling port (sampling frequencies described below). Samples were collected in metal-free polypropylene 15 mL centrifuge tubes (VWR, Radnor, PA), diluted in 2% trace metals grade nitric acid (Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA), and analyzed by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in the Arizona Laboratory for Emerging Contaminants at the University of Arizona.
2.4.1. Collector-to-Colligend Ratio Effect
The collector-to-colligend ratio (φ) was varied to determine the operational limitations of monorhamnolipid collector with a monovalent cation Cs+, divalent cation Cd2+, and trivalent cation La3+. Each metal was tested independently using a single column (n = 1) at φ values of 2, 5, and 10. Column conditions were pH 7.0 ± 0.1, 100 µM monorhamnolipid, 50 mL min−1 airflow rate, 0.8% (v/v) ethanol frother, and 250 mL of solution. Solution samples were collected from the column sampling port at 0, 5, 10, 15, 25, 40, and 60 min. Airflow was stopped at 40 min and the foam remaining in the column allowed to collapse back into the column solution before the final sampling at 60 min. The foamate was sampled at the termination of the experiment as described above.
2.4.2. Metal Removal Measured by Foamate Fractions
The previous experiments measured the metal removal efficiency by sampling the column solution. Metals are not actually removed from the column, however, until the foam exits the column and is collected in the foamate reservoir. It is possible for metals to reflux in the headspace of the column which would result in differences in metal removal efficiencies measured from the column solution versus collected foamate. We therefore measured the kinetics of metal removal by sampling foamate fractions at a series of time intervals. This experiment was performed in triplicate columns (n = 3) with La3+ at φ = 10, 100 µM monorhamnolipid, pH 7.0 ± 0.1, 50 mL min−1 airflow, 0.5% (v/v) ethanol, and a solution volume of 250 mL. Foamate samples were collected from 0–2, 2–4, 4–6, 6–10, 10–15, and 15–20 min where time 0 is the beginning of foam exiting the column funnel. Samples were collected in 50 mL polypropylene metal-free centrifuge tubes (VWR, Radnor, PA) with 4 mL of 2% trace metals grade nitric acid to break the foam. The volume of solution transferred was determined gravimetrically. Sparging was ceased after 20 min of foam production. The averages of metal recovery for each time interval were compared by one-way ANOVA (α = 0.05) using the Tukey-Kramer HSD test to compare means.
2.4.3. Flotation in Mixed Metal Systems
The flotability of a mixed Cs+, Cd2+, and La3+ solution was tested with the metals at near equimolar and order of magnitude different concentrations. In both experiments, the total metal concentration was targeted to be 10 µM (φ = 10). In the former experiment, the target concentration for each metal was 3.3 µM. In the latter, the target concentrations for the metals were 9, 0.9, and 0.09 µM for Cs+, Cd2+, and La3+, respectively. In both experiments, triplicate columns (n = 3) were tested. Column conditions were 100 µM monorhamnolipid, pH 7.0 ± 0.1, 50 mL min−1 airflow, 0.5% (v/v) ethanol, and a solution volume of 250 mL. Column solution samples were collected at 0, 2.5, 5, 10, 15, 25, and 40 min. Airflow was stopped at 25 min, and column solution was collected at 40 min after all column foam had collapsed. The foamate was sampled to determine metal recovery.
2.4.4. Low Concentration La3+
Due to unexpected results from the mixed metal system experiments, flotation of La3+ was tested at a low concentration. This experiment was performed in triplicate columns (n = 3) with La3+ at 0.1 µM, 100 µM monorhamnolipid, pH 7.0 ± 0.1, 50 mL min−1 airflow, 0.5% (v/v) ethanol, and a solution volume of 250 mL. Column solution samples were collected at 0, 2.5, 5, 10, 15, 25, and 40 min. Airflow was stopped at 25 min, and column solution was collected at 40 min after all column foam had collapsed. The foamate was sampled to determine metal recovery.
2.5. Calculations
Metal removal efficiency (R) was calculated using Equation (1)
where C is the column solution concentration of metal at time t and Co is the column solution concentration at time t = 0 [20,30,40]. This measure is a traditional method of reporting metal removal during ion flotation, but it does not take into account the transfer of water from the column to the foamate. Water removal from the column impacts the efficiency of the flotation processes because it reduces the mass of treated solution and dilutes the metal concentrate. To take into account water transfer, an enrichment factor is also reported. The enrichment factor (E) is calculated using Equation (2)
where Cf represents the metal concentration in the foamate [38]. If E < 1 the colligend is concentrating in the column as bulk water is removed in the foam. If E = 1, there is no retarding or concentrating effect occurring during flotation. If E > 1, the colligend is being concentrated in the foamate—the larger the E value, the more concentrated the colligend and the more effective the concentration process.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Collector-to-colligend Ratio Effect
The effect of collector-to-colligend ratio (φ) on ion flotation was examined for Cs+, Cd2+, and La3+ individually at φ ratios of 2, 5, and 10 (Table 1). All three metals were successfully floated and concentrated at φ ratios 5 and 10, but only Cs+ and Cd2+ were collected at φ = 2 (La3+ collection at φ = 2 is discussed below). The rate of removal from solution followed the order of Cd2+ > La3+ > Cs+ for each φ tested (data not shown), which contrasts with the order of La3+ > Cd2+ > Cs+ predicted by the conditional stability constants of these metals with monorhamnolipid (further discussion in Section 3.3). The efficacy of flotation was assessed using multiple parameters. Metal removal efficiency for La3+ and Cd2+ ranged from 90.1 to 99.8% while Cs+ had lower removal efficiencies ranging from 37.1 to 46.2%. Removal efficiencies were lower for φ = 2 than φ = 5 or 10. These values exceeded the maximum removal percentages of 57% or less for Cd2+, Zn2+, and Cu2+ reported by Bodagh et al. [30]. The differences in rhamnolipid ion flotation performance between the two studies could be the result of different rhamnolipid mixtures since Bodagh et al. use a crude mono- and dirhamnolipid mixture from P. aeruginosa MA01, while this study uses a pure monorhamnolipid from P. aeruginosa 9027. Also likely, the differences could be the result of different flotation conditions.

Table 1.
Results of ion flotation for Cs+, Cd2+, and La3+ at varying collector-to-colligend ratios in single columns (n = 1). Column conditions: 250 mL volume, pH 7.0 ± 0.1, 50 mL min−1 airflow, 100 µM monorhamnolipid, 0.8% (v/v) ethanol.
The removal efficiencies reported in Table 1 are based on column solution concentration without regard to water transferred into the foamate. To account for transfer of water, an enrichment factor—the ratio of foamate concentration to initial solution concentration—is also reported. All the treatments showed enrichment of the metals in the foamate, indicating successful flotation, but the degree of enrichment varied greatly. Cd2+ had an enrichment factors of 27.2 and 15.4 at φ = 2 and 5, respectively. La3+ and Cs+ had lower enrichment factors with maximums of 6 at φ = 5 and 1.9 at φ = 2, respectively. All the treatments exhibited decreasing enrichment factors with increasing φ. The decrease in enrichment is not surprising because as φ increased, so did the entrainment and transfer of water. Water transfer was 42, 42, and 30% for Cs+, Cd2+, and La3+ at φ = 10 versus 33, 34, and 18% for φ = 5, respectively. Metals are sometimes used for foam inhibition because they counteract effects of electrostatic stabilization and reduce the solubility of ionic surfactants [41]. Thus, at higher φ, there are relatively fewer metals for foam inhibition and a richer, more stable foam is produced which entrains more water. For all three metals, coarser foam with larger bubbles was observed for φ values of 2 compared to 10.
No foam was produced for La3+ at φ = 2, but a white scum formed and concentrated at the solution surface with some adsorbing onto the glass (Figure 3). The concentration of La3+ in the column solution was reduced from 34.4 to 13.6 µM within 25 min despite the lack of foam (data not shown). Though no metal was actually removed from the column, the final apparent metal removal efficiency from the column solution was 61.2%, thus the metal was likely sequestered in the scum as the La-rhamnolipid precipitate—the design of the columns used in this study excluded the possibility of collecting the scum for analysis to perform a mass balance or speciation analysis. Scum formation in the presence of multivalent metals is typical for carboxylic acid-based surfactants such as the “natural” alkali soaps [42] and suggests that the solubility limit of the La-rhamnolipid association was exceeded at a φ = 2. The formation of scum with La3+ but not Cd2+ or Cs+ at equal stoichiometries is consistent with observations of decreasing solubility of transition metal cation complexes with anionic surfactants as metal valence increases [43].

Figure 3.
Scum concentrating on the solution surface and adsorbing to the column while floating La3+ at φ = 2.
Scum formation in lieu of foam during ion flotation is perfectly acceptable [19] and perhaps preferable because it provides highly concentrated material that is easily removed from the surface. The lack of foam formation suggests there were insufficient monomers available to produce a foam. When the metal-surfactant complex precipitates, the metals can still be recovered though a related process called precipitate flotation wherein the collector carries the precipitate to the surface and into the foam [20,44]. In this case, the addition of more monorhamnolipid likely would have allowed the collection of the ~60% of La present as a precipitate and the remaining 40% present as a dissolved species. Alternatively, a second neutral surfactant could be added as a frother to collect the precipitate from the solution.
Overall, the results of the colligend to collector ratio experiments show that the efficacy and efficiency of ion flotation is reliant on φ and metal valence. When φ is small, the metals are better enriched, but foam quality decreases. At larger φ, removal efficiencies increase, but at the cost of greater water transfer and lower metal enrichment. Because the metal sublates are colligend and collector complexes, flotation requires a specific stoichiometric φ for optimal sublate formation. In all ion flotation systems there is an ideal φ ratio which is almost always greater than the stoichiometric ratio of the sublate, but which varies widely with values ranging from 1 to 44 in early ion flotation studies [18]. The ideal φ ratio for monorhamnolipids appears to lie between 2 and 5 for the metals and conditions tested herein.
3.2. Metal Removal Measured by Foamate Fractions
During initial experiments, it was observed that metal concentrations in the column solution dropped rapidly in the first 5–10 min. This rapid initial rate of removal is desirable because it reduces the time required to complete the flotation process during batch operations. Due to column design, however, metal removed from solution is not actually removed from the column until the foam reaches the top of the column, passes through the funnel, and is collected in the foamate reservoir. As foam progresses through the column headspace, it is possible for metals to reflux as the foam coalesces and entrained water drains towards the column solution. Thus, we examined the temporal metal content of foam fractions in triplicate La3+ columns at specified intervals over a 20 min time period (Figure 4). Metal concentrations were significantly higher in the 4–6 and 6–10 min fractions than in the 0–2, 10–15, and 15–20 min fractions. The majority (90.4 ± 6.7%) of the La3+ was collected in the first 10 min of foam production.
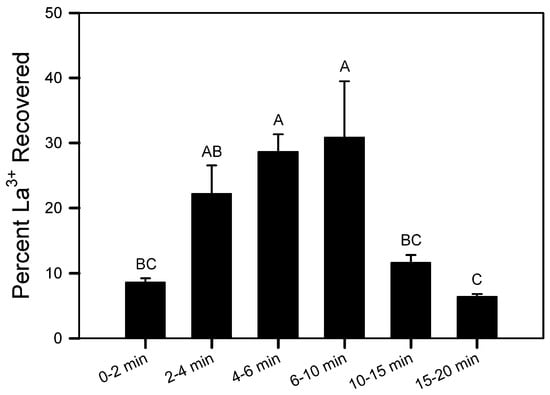
Figure 4.
Metal recovery during ion flotation of La3+ at φ = 10 measured by foam collected during different time frames of foam production. Bars represent averages and standard deviations of triplicate columns (n = 3). Bars not connected by the same letter indicate significant differences in removal percentage.
In the previous section, the 10 min removal of La3+ (φ = 10) as measured from column solution was 94%. In this experiment, 90.4% of La3+ was recovered in 10 min as measured in the foam collected. The similar percentages among these experiments suggests that metals are not being refluxed inside the column under these experimental conditions. Thus under these conditions, the concentration of metal removed from a solution in a given time frame can be considered approximately the same as the concentration of metals removed from the column as foam in an equivalent time frame, i.e., the metal removed from the column solution in the first 10 min of flotation will be present in the first 10 min of foam collected. These results provide important information necessary to determine ion flotation process parameters such as foam recovery time required to achieve specified treatment levels of contaminated solutions.
3.3. Flotation in Mixed Metal Systems
Metals are rarely present as single element solutions, and interest in using ion flotation to selectively concentrate target metals dates back to Sebba’s original description of the methodology [19]. The ability of monorhamnolipid to selectively remove specific metals was tested using mixed metal solutions of Cs+, Cd2+, and La3+ at near equimolar concentrations and concentrations differing by orders of magnitude. Given that monorhamnolipid is selective for rare earth elements and elements of environmental concern over common soil and water cations [26], it was hypothesized that in a mixed system the order of removal would be La3+ > Cd2+ > Cs+.
Flotation results of mixed metal solutions with Cs+, Cd2+, and La3+ at near equimolar concentrations (total φ = 10) are summarized in Table 2 and Figure 5. The order of removal was Cd2+ > La3+ >> Cs+ with removal efficiencies of 98.4, 88.1, and 39.4%, respectively. The enrichment factor was greatest for Cd2+ at 5.1. Cd+2 was almost completely removed from solution by 10 min, while La3+ reached a near maximal removal at 15 min. Comparison of these result to those for φ = 10 in Section 3.1 shows that the metals’ removal efficiency percentages were the same whether floated individually or as a mixture. This result is congruent with a system containing excess monorhamnolipid as there should be no competition of metals for collector.

Table 2.
Results of ion flotation for mixed metal solutions of Cs+, Cd2+, and La3+ in triplicate columns (n = 3). Column conditions: 250 mL volume, pH 7.0 ± 0.1, 50 mL min−1 airflow, 100 µM monorhamnolipid, 0.5% (v/v) ethanol.
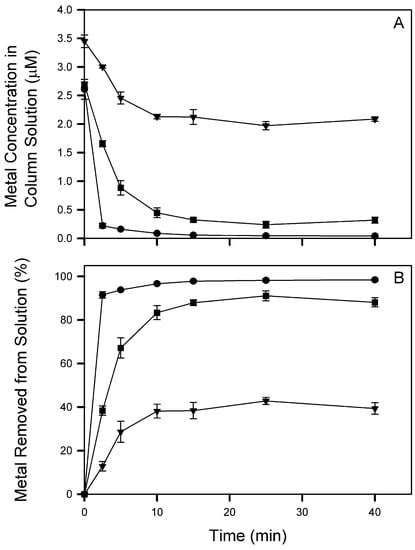
Figure 5.
Column solution concentration (A) and percent metal removed from solution (B) during flotation (φ = 10) of Cs+ (▼), Cd2+ (●), and La3+ (■). The 40 min data were collected after sparging ceased and column foam collapsed. Symbols represent mean and standard deviation values from triplicate columns (n = 3).
The metal removal order observed in this mixed metal experiment was Cd2+ > La3+ >> Cs+. This order is different from that predicted by conditional stability constants for these metals with monorhamnolipid, log β = 9.29, 7.17, and 3.43 for La3+, Cd2+, and Cs+, respectively [26,36]. Similarly, Bodagh et al. [30] report a selectivity sequence of Cd2+ > Zn2+ > Cu2+ during ion flotation with rhamnolipid collectors, and this sequence is also different from what is predicted based on conditional stability constants (log β = 7.17, 5.62, and 9.27, respectively). These results disprove the hypothesis that stability constants are good predictors of flotation selectivity when rhamnolipid is in excess. However, under conditions where rhamnolipid is limiting, metals compete for rhamnolipid collector, and conditional stability constants should predict which metals are removed during flotation. However, as demonstrated by the precipitation of La3+ in Section 3.1, other factors may still reduce the utility of stability constants in this application.
The efficacy of ion flotation of mixed metal solutions with Cs+, Cd2+, and La3+ at order-of-magnitude different concentrations (total φ = 10) was tested (Table 3, Figure 6) to determine the efficacy of target-metal flotation when non-target-metals are at much higher concentrations. Removal efficiency for Cs+, Cd2+, and La3+ were up to 49.9, 99.5, and 51.5%. Interestingly, the final removal efficiency of La3+ was much less than the maximum observed removal; Figure 6B shows La3+ reaching a maximum removal of 51.5% at 10 min which then decreases to 11.7% at the end of the experiment. These results indicate that although La3+ was removed from the bulk solution initially, it was not removed from the column and returned to the bulk solution as the column foam was allowed to collapse. A possible explanation is La3+ refluxing in the column, which contradicts the results of Section 3.2 and exemplifies the sensitivity of flotation systems to changes in operational conditions.

Table 3.
Results of ion flotation for mixed metal solutions of Cs+, Cd2+, and La3+ in triplicate columns (n = 3). Column conditions: 250 mL volume, pH 7.0 ± 0.1, 50 mL min−1 airflow, 100 µM monorhamnolipid, 0.5% (v/v) ethanol.
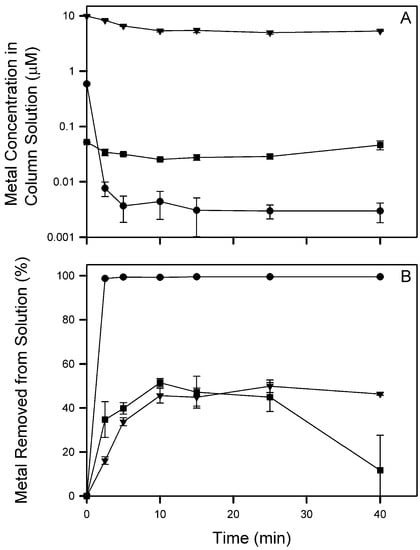
Figure 6.
Column solution concentration (A) and percent metal removed from solution (B) during flotation (φ = 10) of Cs+ (▼), Cd2+ (●), and La3+ (■). The 40 min data were collected after sparging ceased and column foam collapsed. Symbols represent mean and standard deviation values from triplicate columns (n = 3).
In this experiment, the Cs+ and Cd2+ removal efficiencies were the same during both the φ = 10 individual and mixed metal studies. La3+, however, exhibited a large decrease from a maximum of 98.1 when floated individually to 51.5% when floated at a low concentration (0.05 µM) in a mixed system. In a follow-up experiment, flotation of 0.1 µM La3+ individually reached a maximum removal efficiency of 40.7% (Figure 7). This result indicates the observed difference between La3+ when floated individually and in a mixture at low concentration is a concentration effect, not an effect of metal competition. Figure 7 also shows the removal percentage increased to a maximum of 40.7% at 25 min then decreased to 32.5% at 40 min. Sparging ceased after 25 min, and the increase in La3+ is due to the collapse of column foam back into the bulk solution.
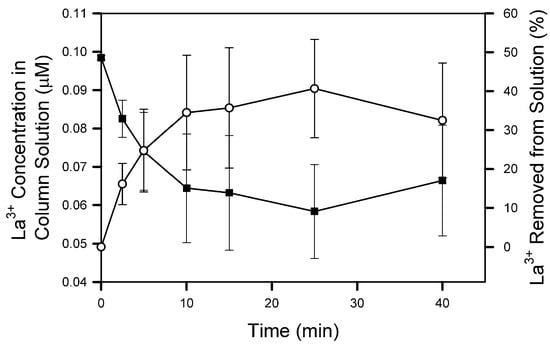
Figure 7.
La3+ column solution concentration (■) and percent metal removed from solution (○) during flotation of La3+. The 40 min data were collected after sparging ceased and column foam collapsed. Symbols represent mean and standard deviation values from triplicate columns (n = 3).
The determinants of selectivity during ion flotation has long been of interest. It is generally agreed that selectivity in ion flotation is controlled by the valence of the metal with higher valence metals being removed preferentially [45], but other determinants are important as well. Among metals of the same valence, selectivity correlates with hydrated radius [43,46,47,48], the absolute partial molal entropy of cations in aqueous solution [49], the crystalline radius [30,50], stability constant of collector-cation complexes [47], and a combination of these [51]. The relative importance of these determinants likely depends on the interactions of the collector and colligend. Two possible mechanisms may help explain the flotation process. The first mechanism is adsorption wherein the collectors adsorb to the air-water interface and then complex with colligends through electrostatic or other associations. The second mechanism is conglutination wherein the collector and colligend form a complex in solution before adsorbing to the interface [52,53]. Studies have found evidence to support both the former [47,48,52] and latter [53] mechanisms. Previous work clearly demonstrates rhamnolipid associates with metals in solution [25,26,54], thus it is reasonable to assume the rhamnolipid flotation system operates under the conglutination mechanism. The faster removal kinetics (Figure 5) of Cd2+ over La3+ in the presence of excess rhamnolipid suggest the Cd-monorhamnolipid association formed in the bulk solution may have a higher affinity for the air-water interface than that for the La; the underlying cause of this observation is difficult to determine without additional information, e.g., the nature of the metal associations and speciation of the metals in the experimental conditions. Liu and Doyle [51] describe a model where the sublate stability constants may be predictors of selectivity, but their model is based on the assumption that flotation occurs through the adsorption mechanism.
4. Conclusions
Monorhamnolipids were examined for their utility as ion flotation collectors for Cs+, Cd2+, and La3+. Monorhamnolipids form stable foam during the aeration process, but the stability of the system is highly dependent on the metal and on the stoichiometric ratio of monorhamnolipid to metal. A stoichiometric ratio 2-5 maximized recovery without reducing enrichment of the metals tested. Examination of the foamate fraction shows that metals are rapidly removed, with removal concentrations nearing maximum within 10-15 min. When present as both individual and mixed metals solutions, metals were not removed as predicted by their stability constants, indicating the affinity of the metal associations for the air-water interface should be investigated. Overall, this study shows that monorhamnolipids have potential for use in ion flotation technologies but determining the optimal operating conditions for efficient flotation processes is a significant challenge subject to perturbation by even modest changes to single process parameters. Research efforts should be directed towards finding a specific application for monorhamnolipid-based ion flotation and developing application-specific processes for optimal flotation performance. Such process development should especially focus on increasing scale of operations to make treatment of metalliferous solutions at industrially-relevant volumes feasible. Large volume flotation operations have been proven in mineral processing and wastewater treatment, and lessons can be drawn from these applications for ion flotation. In lieu of costly trial-and-error operations, factorial design experiments in conjunction with system modeling should be used to establish optimal conditions statistically [20,55]. Flotation column design and operation should focus on continuous flow systems with consideration given to multi-stage treatment and counter current operation. Closer examination of the system kinetics will be important for scaled-up operations as they will dictate parameters such as aeration rate, bubble size, column height/diameter, solution volume, draining time, etc. [20,45,55,56]. Finally, because the production of both biologically synthesized and chemically synthesized [57] rhamnolipids have not been adequately evaluated at industrial scales, the economics of large-scale production should be studied to elucidate the long-term potential of rhamnolipid applications.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2504-5377/2/4/43/s1, Discussions of preliminary aeration rate and frother concentration experiments, Figure S1: Percent La3+ removed from solution during flotation with 0.0, 0.5, and 1.0% (v/v) ethanol frother.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.E.H.; Methodology, D.E.H. and R.M.M.; Validation, D.E.H. and J.E.C.; Formal Analysis, D.E.H. and J.E.C.; Investigation, D.E.H.; Resources, D.E.H. and R.M.M.; Data Curation, D.E.H.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, D.E.H.; Writing-Review & Editing, D.E.H., J.E.C., and R.M.M.; Visualization, D.E.H.; Supervision, J.E.C. and R.M.M; Project Administration, R.M.M.; Funding Acquisition, D.E.H. and R.M.M.
Funding
This research was funded by a National Science Foundation (NSF) Graduate Research Fellowship Grant (DGE-1143953) to DEH; a University of Arizona Technology and Research Initiative Fund 2015/2016, Water Sustainability Student Fellowship Grant to DEH; and a NSF Networks for Sustainable Molecular Design and Synthesis Grant (CHE-1339597) co-funded with the Environmental Protection Agency.
Acknowledgments
Glass blowing services were provided by the University of Arizona Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Glass Shop. The metal analyses for this study were performed by the Arizona Laboratory for Emerging Contaminants (ALEC) at the University of Arizona.
Conflicts of Interest
One author of this paper (R.M.M.) has equity ownership in GlycoSurf, which is developing products related to the research being reported. D.E.H. also has a dual appointment at the University of Arizona and GlycoSurf, though the research reported is wholly a product of the university. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by the University of Arizona in accordance with its policy on objectivity in research.
References
- United Nations Water. Coping with Water Scarcity: A Strategic Issue and Priority for System-Wide Action. 2006. Available online: http://www.unwater.org/publications/coping-water-scarcity/ (accessed on 27 August 2018).
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Mekonnen, M.M.; Chapagain, A.K.; Mathews, R.E.; Richter, B.D. Global monthly water scarcity: Blue water footprints versus blue water availability. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Global Water Scarcity: Monthly Blue Water Footprint Compared to Blue Water Availability for the World’s Major River Basins. Value of Water Research Report Series No 53. 2011. Available online: http://waterfootprint.org/media/downloads/Report53-GlobalBlueWaterScarcity.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2018).
- Fuller, A.C.; Harhay, M.O. Population growth, climate change and water scarcity in the southwestern United States. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 6, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerten, D.; Lucht, W.; Ostberg, S.; Heinke, J.; Kowarsch, M.; Kreft, H.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Rastgooy, J.; Warren, R.; Schellnhuber, H.J. Asynchronous exposure to global warming: Freshwater resources and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 034032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, C.; McLain, J.E.; Gerrity, D. Water Recycling FAQs; The University of Arizona Cooperative Extension: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2012; Available online: https://extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1568.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2018).
- Addams, L.; Boccaletti, G.; Kerlin, M.; Stuchtey, M. Charting Our Water Future: Economic Framework to Inform Decision-Making. 2030 Water Resources Group, 2009. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/mckinsey/dotcom/client_service/sustainability/pdfs/charting%20our%20water%20future/charting_our_water_future_full_report_.ashx (accessed on 27 August 2018).
- Merten, D.; Buchel, G. Determination of rare earth elements in acid mine drainage by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Microchim. Acta 2004, 148, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravotta, C.A. Dissolved metals and associated constituents in abandoned coal-mine discharges, Pennsylvania, USA. Part 1: Constituent quantities and correlations. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 166–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiddee, P.; Naidu, R.; Wong, M.H.; Hearn, L.; Muller, J.F. Field investigation of the quality of fresh and aged leachates from selected landfills receiving e-waste in an arid climate. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2292–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verplanck, P.L.; Furlong, E.T.; Gray, J.L.; Phillips, P.J.; Wolf, R.E.; Esposito, K. Evaluating the behavior of gadolinium and other rare earth elements through large metropolitan sewage treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3876–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, M.A. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Honaker, R.Q. Rare earth elements recovery using staged precipitation from a leachate generated from coarse coal refuse. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 195, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemlich, R. Adsorptive Bubble Separation Techniques; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972; ISBN 9780124433502. [Google Scholar]
- Klassen, V.I.; Mokrousov, V.A. An Introduction to the Theory of Flotation; Butterworths: London, UK, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Wen, S. Surface modification of malachite with ethanediamine and its effect on sulfidization flotation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebba, F. Concentration by ion flotation. Nature 1959, 184, 1062–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinfold, T.A. Ion flotation. In Adsorptive Bubble Separation Techniques; Lemlich, R., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972; pp. 53–73. ISBN 9780124433502. [Google Scholar]
- Matis, K.; Mavros, P. Recovery of metals by ion flotation from dilute aqueous solutions. Sep. Purif. Methods 1991, 20, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, D.E.; Veres-Schalnat, T.A.; Pemberton, J.E.; Maier, R.M. Biosurfactant Complexation of Metals and Applications for Remediation. In Biosurfactants: Research Trends and Applications; Mulligan, C.N., Mudhoo, A., Sharma, S.K., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2014; pp. 277–308. ISBN 9781466518230. [Google Scholar]
- Franzetti, A.; Gandolfi, I.; Fracchia, L.; Van Hamme, J.; Gkorezis, P.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Biosurfactant use in heavy metal removal from industrial effluents and contaminated sites. In Biosurfactants: Production and Utilization—Processes, Technologies, and Economics; Kosaric, N., Vardar-Sukan, F., Eds.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 159, pp. 361–369. ISBN 9781466596696. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.; Champion, J.T.; Artiola, J.F.; Brusseau, M.L.; Miller, R.M. Complexation of cadmium by a rhamnolipid biosurfactant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 2402–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, D.C.; Artiola, J.F.; Miller, R.M. Removal of cadmium, lead, and zinc from soil by a rhamnolipid biosurfactant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 2280–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa-Loza, F.J.; Artiola, J.F.; Maier, R.M. Stability constants for the complexation of various metals with a rhamnolipid biosurfactant. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, D.E.; Curry, J.E.; Pemberton, J.E.; Maier, R.M. Rhamnolipid biosurfactant complexation of rare earth elements. J. Hazard Mater. 2017, 340, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Zeftawy, M.A.M.; Mulligan, C.N. Use of rhamnolipid to remove heavy metals from wastewater by micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration (MEUF). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 77, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.P.; Sarkar, B. Simultaneous removal of Cd (II) and p-cresol from wastewater by micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration using rhamnolipid: Flux decline, adsorption kinetics and isotherm studies. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 213, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abyaneh, A.S.; Fazaelipoor, M.H. Evaluation of rhamnolipid (RL) as a biosurfactant for the removal of chromium from aqueous solutions by precipitate flotation. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 165, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodagh, A.; Khoshdast, H.; Sharafi, H.; Zahiri, H.S.; Noghabi, K.A. Removal of cadmium(II) from aqueous solution by ion flotation using rhamnolipid biosurfactant as an ion collector. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 3910–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebron-Paler, A.; Pemberton, J.E.; Becker, B.A.; Otto, W.H.; Larive, C.K.; Maier, R.M. Determination of the acid dissociation constant of the biosurfactant monorhamnolipid in aqueous solution by potentiometric and spectroscopic methods. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 7649–7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Miller, R. Effect of a Pseudomonas rhamnolipid biosurfactant on cell hydrophobicity and biodegradation of octadecane. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 2101–2106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lebron-Paler, A. Solution and Interfacial Characterization of Rhamnolipid Biosurfactant from P. aeruginosa ATCC 9027. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Pemberton, J.E.; Maier, R.M. Effect of fatty acid substrate chain length on Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 monorhamnolipid yield and congener distribution. Process. Biochem. 2014, 49, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geological Survey of Japan. Atlas of Eh-pH diagrams: intercomparison of thermodynamic databases. Report 419. 2005. Available online: http://www.eosremediation.com/download/Chemistry/Chemical%20Properties/Eh_pH_Diagrams.pdf (accessed on 27 September 2018).
- Hogan, D.E. Biosurfactant (Monorhamnolipid) Complexation of Metals and Applications for Aqueous Metalliferous Waste Remediation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Thalody, B.; Warr, G.G. Ion flotation: A laboratory experiment linking fundamental and applied chemistry. J. Chem. Educ. 1999, 76, 956–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobelli-Turi, C.; Maracci, F.; Margani, A.; Palmera, M. Separation of metallic ions by foaming: Studies in Italy. In Adsorptive Bubble Separation Techniques; Lemlich, R., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972; pp. 265–272. ISBN 9780124433502. [Google Scholar]
- Eismin, R.J.; Munusamy, E.; Kegel, L.L.; Hogan, D.E.; Maier, R.M.; Schwartz, S.D.; Pemberton, J.E. Evolution of aggregate structure in solutions of anionic monorhamnolipids: Experimental and computational results. Langmuir 2017, 33, 7412–7424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmani, M.H.; Davoodi, M.; Ehrampoush, M.H.; Ghaneian, M.T.; Fallahzadah, M.H. Removal of cadmium (II) from simulated wastewater by ion flotation technique. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2013, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, D. Foams. In Surfactant Science and Technology, 2nd ed.; VCH Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 249–265. ISBN 1560815868. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, D. Surfactants in solution: Micellization and related association phenomena. In Surfactant Science and Technology, 2nd ed.; VCH Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 81–131. ISBN 1560815868. [Google Scholar]
- Walkowiak, W. Mechanism of selective ion flotation. 1. Selective flotation of transition metal cations. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1991, 26, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, A.I.; Matis, K.A.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Golyshin, P.N. The use of biosurfactants in flotation: Application for the removal of metal ions. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, F.M. Ion flotation—Its potential for hydrometallurgical operations. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2003, 72, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorné, J.; Rubin, E. Ion fractionation by foam. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1969, 4, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.C.; Talbot, F.D. The removal of copper, cadmium, and lead ions from dilute aqueous solutions using foam fractionation. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1973, 51, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, K.; Hayashi, S. The removal of sodium, cadmium and chromium ions from dilute aqueous solutions using foam fractionation. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1977, 55, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieves, R.B.; Burton, K.E.; Craigmyle, J.A. Experimental foam fractionation selectivity coefficients for the alkali (Group IA) metals. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1987, 22, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrampoush, M.H.; Salmani, M.H.; Ghaneian, M.T.; Davoudi, M.; Fallahzadeh, M.H. Selectivity in removal of cadmium (II) from mixed metal effluents using ion flotation. World Appl. Sci. J. 2011, 13, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Doyle, F.M. A thermodynamic approach to ion flotation. II. Metal ion selectivity in the SDS–Cu–Ca and SDS–Cu–Pb systems. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 178, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieves, R.B.; Kyle, R.N. Models for interactions between ionic surfactants and nonsurface-active ions in foam fractionation processes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1982, 17, 465–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.Z.; Meng, Y.T.; Zeng, G.M.; Fang, Y.Y.; Shi, J.G. Evaluation of tea-derived biosurfactant on removing heavy metal ions from dilute wastewater by ion flotation. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 317, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalnat, T.A. Metal Complexation and Interfacial Behavior of the Microbially-Produced Surfactant Monorhamnolipid by Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Doyle, F.M. A thermodynamic approach to ion flotation. I. Kinetics of cupric ion flotation with alkylsulfates. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 178, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wace, P.F.; Banfield, D.L. Foam separation. Chem. Process. Eng. 1966, 47, 70–76, 90. [Google Scholar]
- Palos Pacheco, R.; Eismin, R.J.; Coss, C.S.; Wang, H.; Maier, R.M.; Polt, R.; Pemberton, J.E. Synthesis and characterization of four diastereomers of monorhamnolipids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 5125–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).