Biocompatible Carbon-Coated Ferrite Nanodot-Based Magnetoliposomes for Magnetic-Induced Multimodal Theragnostic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Magnetic Carbon Dots (MNCDs)
2.2. Synthesis of Liposomes Encapsulated MNCDs (MNCDs+Lipo)
2.3. Preparation of PP Extract-Coated Liposomes Encapsulated MNCDs (MNCDs+Lipo@PPE)
2.4. Instrumentation
2.5. Colloidal Stability Measurement
2.6. Optical and MR Imaging
2.7. MTT Assay
2.8. Live/Dead Assay
2.9. Encapsulation Efficiency
2.10. Drug Release Kinetics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural and Magnetic Properties
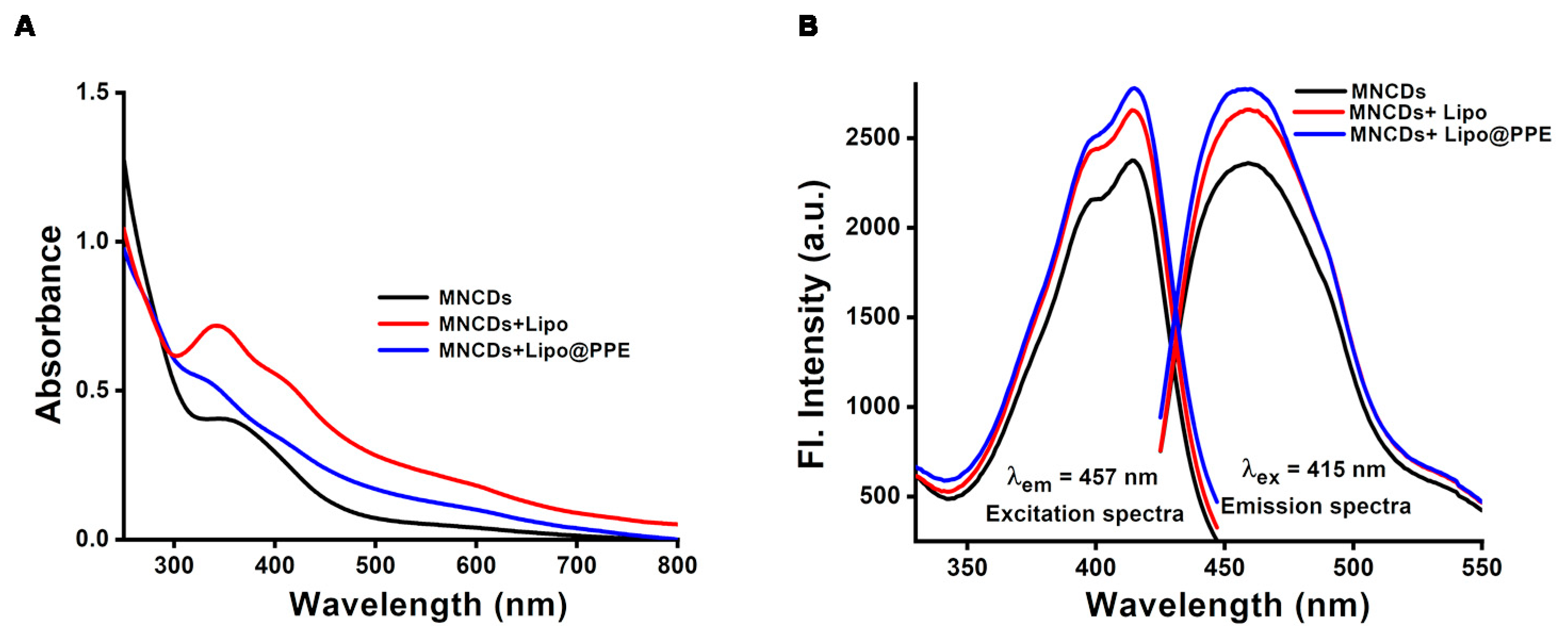
3.2. Optical Properties
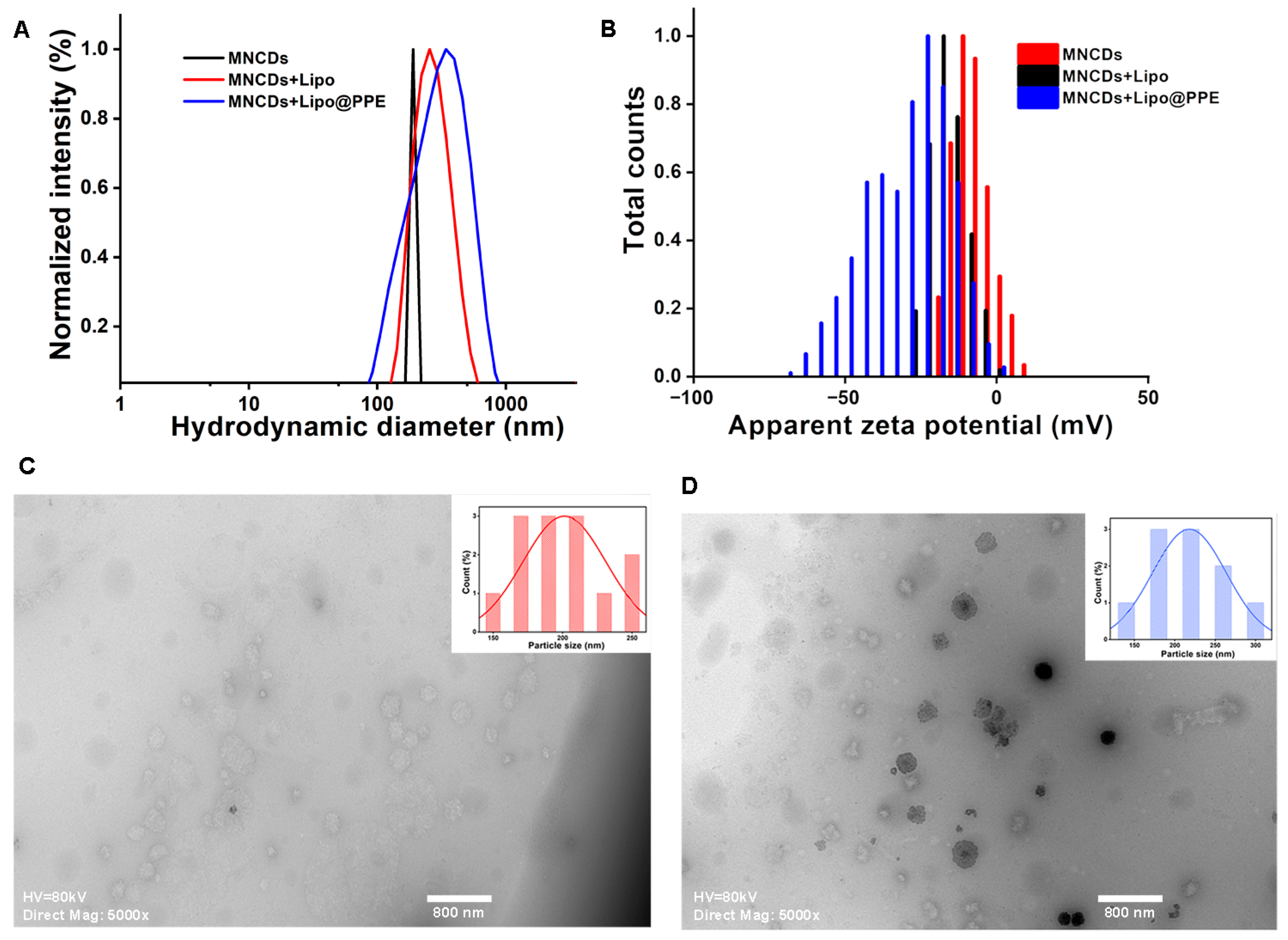
3.3. Particle Size Analysis and Zeta Potential Measurement
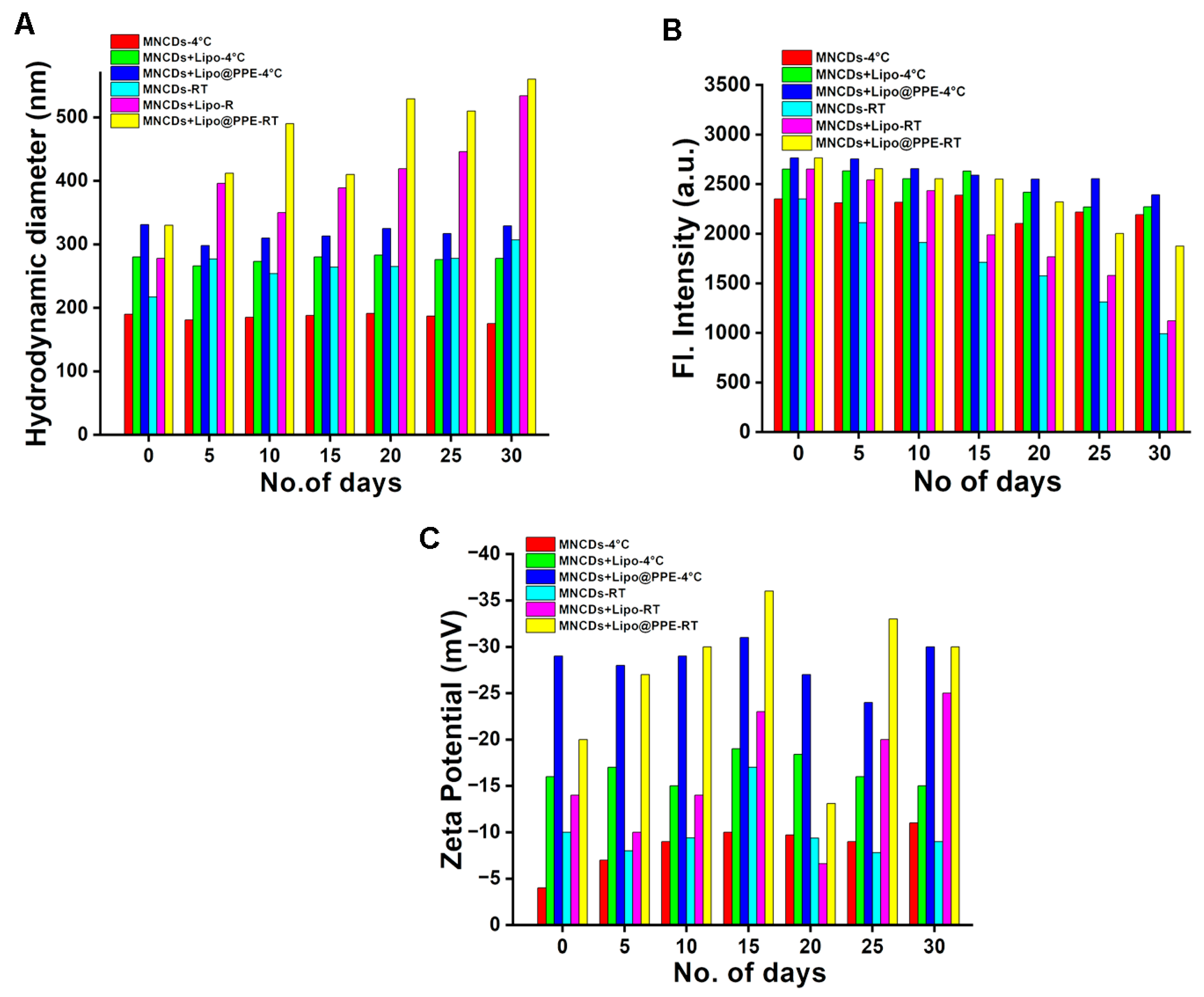
3.4. Stability Analysis
3.5. Phantom Optical Imaging
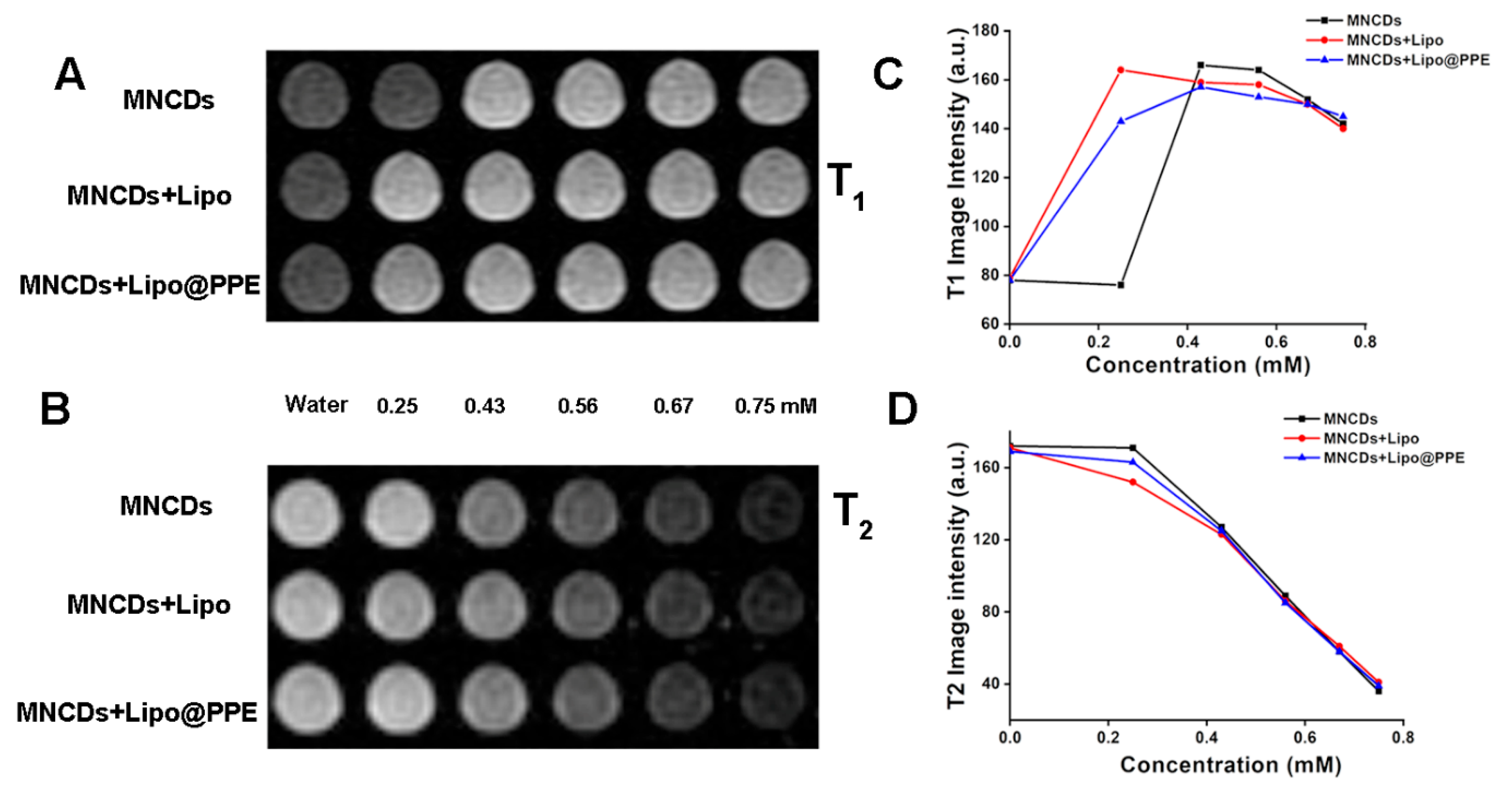
3.6. T1 and T2-Weighted MR Imaging
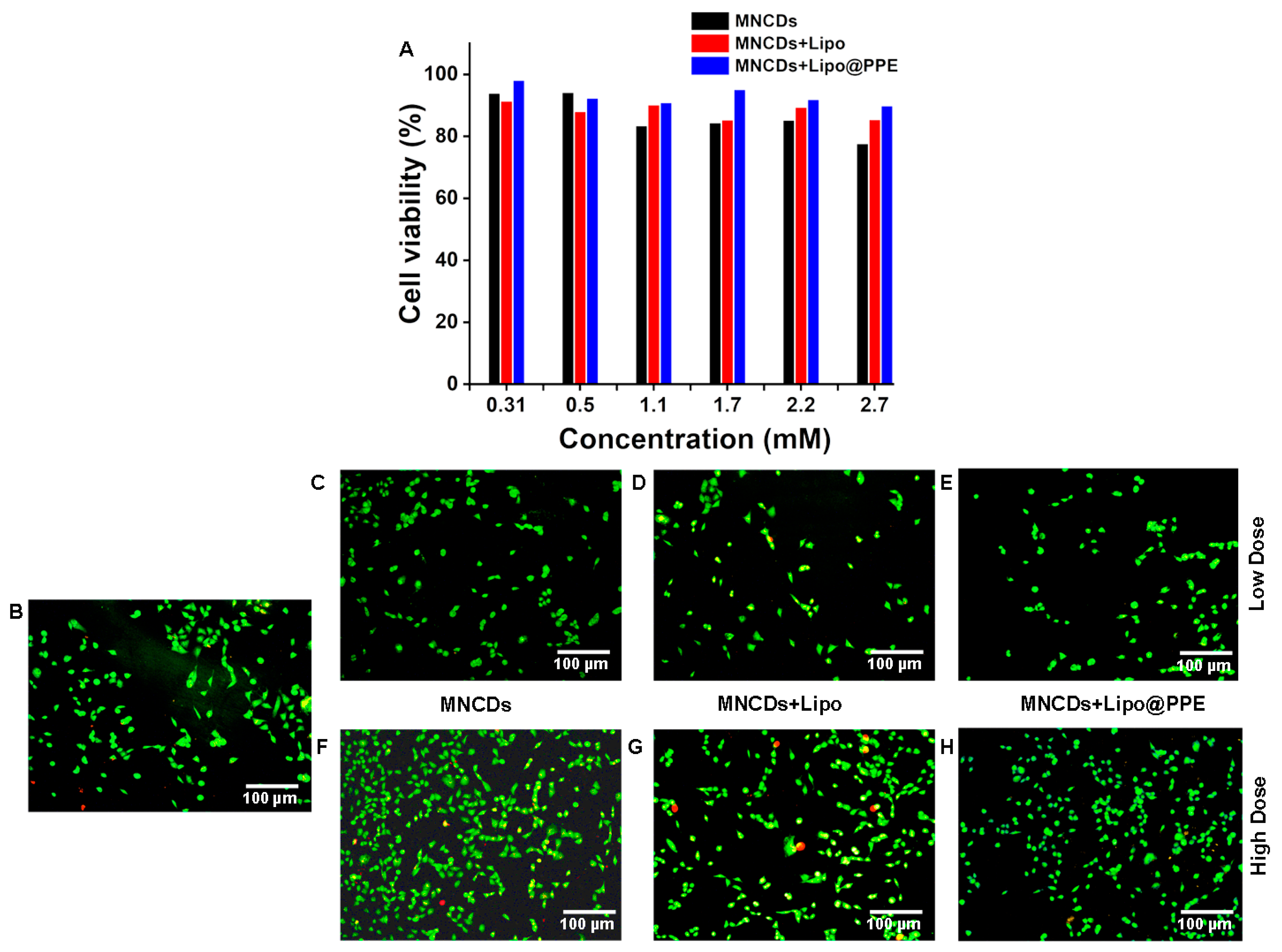
3.7. Toxicity Analysis
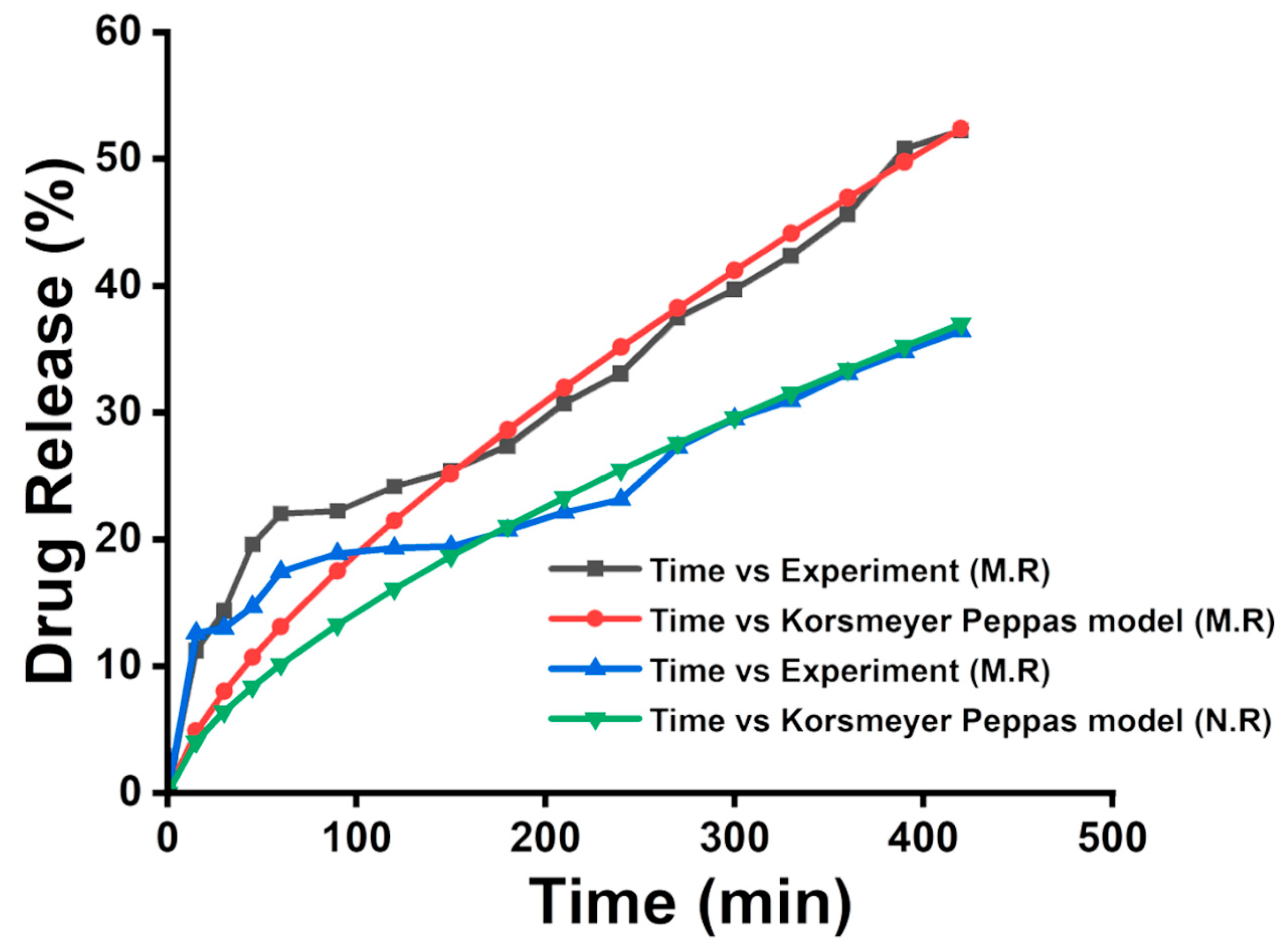
3.8. Encapsulation Efficiency and Drug Release Patterns
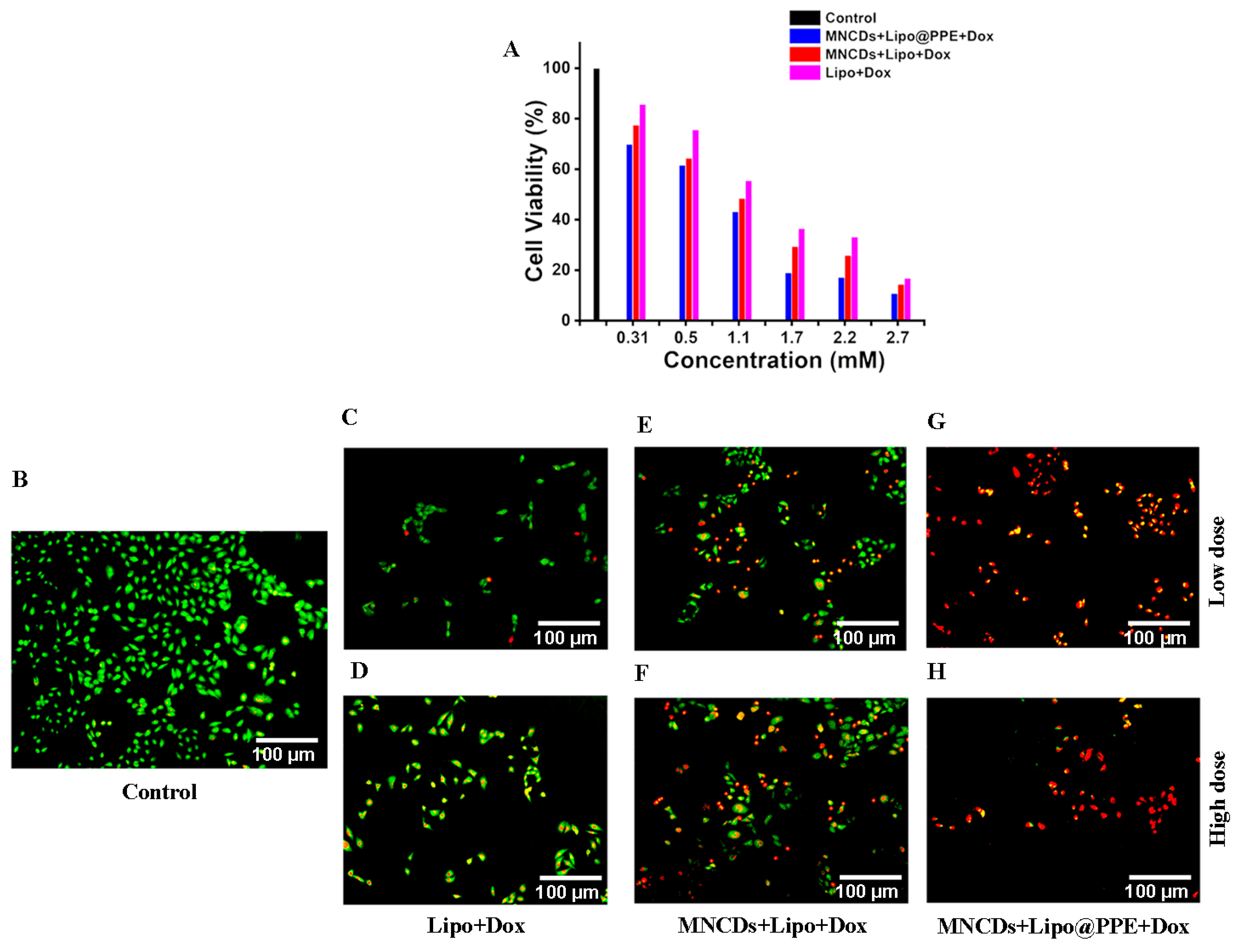
3.9. Anticancer Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Yan, L.; Xu, S.; Zhang, G.; Pei, L.; Yu, H.; Zhu, X.; Han, X. Current role of magnetic resonance imaging on assessing and monitoring the efficacy of phototherapy. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2024, 110, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, D.K.; Jagannathan, N.R. Emerging MR methods for improved diagnosis of prostate cancer by multiparametric MRI. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2022, 35, 587–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Sinha, N.; Jagannathan, N.R. Potential of in vitro nuclear magnetic resonance of biofluids and tissues in clinical research. NMR Biomed. 2023, 36, e4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haribabu, V.; Girigoswami, K.; Sharmiladevi, P.; Girigoswami, A. Water–Nanomaterial Interaction to Escalate Twin-Mode Magnetic Resonance Imaging. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 4377–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Zhang, Y.N.; Yan, M.; Xia, J.; Wang, M.; Tian, G.; Lv, H.; Liu, K.; Zhang, G. Aggregation-induced magnetic coupling nanoassemblies that effectively switched from T2 to T1 contrast imaging for highly specific MRI detection of micron sized hepatocellular carcinoma. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 506, 159882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowtham, P.; Haribabu, V.; Prabhu, A.D.; Pallavi, P.; Girigoswami, K.; Girigoswami, A. Impact of nanovectors in multimodal medical imaging. Nanomed. J. 2022, 9, 107–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailasa, S.K.; Koduru, J.R. Perspectives of magnetic nature carbon dots in analytical chemistry: From separation to detection and bioimaging. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 33, e00153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, H.; Yang, W.; Bai, Y.; Wu, Z.; Cui, T.; Bian, K.; Yi, J.; Shao, C.; Zhang, B. One-Dose Bioorthogonal Gadolinium Nanoprobes for Prolonged Radiosensitization of Tumor. Small 2025, 21, 2500504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, S.; Rocha, S.; Viana, S.D.; Rebelo, R.; Rocha-Pereira, P.; Lousa, I.; Valente, M.J.; Catarino, C.; Belo, L.; Bronze-da-Rocha, E.; et al. Gadoteric Acid and Gadolinium: Exploring Short- and Long-Term Effects on Healthy Animals. J. Xenobiot. 2025, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhoopathy, J.; Vedakumari, S.W.; Pravin, Y.R.; Prabhu, A.D. Radiopaque Silk Sericin Nanoparticles for Computed Tomography Imaging of Solid Tumors. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2025, 8, 5007–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarciglia, A.; Papi, C.; Romiti, C.; Leone, A.; Di Gregorio, E.; Ferrauto, G. Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents (GBCAs) for MRI: A Benefit–Risk Balance Analysis from a Chemical, Biomedical, and Environmental Point of View. Glob. Chall. 2025, 9, 2400269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, P.; Prabhu, A. Smart SPIONs for Multimodal Cancer Theranostics: A Review. Mol. Pharm. 2025, 22, 2372–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafabakhsh, R.; Zhang, R.; Thoröe-Boveleth, S.; Moosavifar, M.; Abergel, R.J.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T.; Pallares, R.M. Gold Nanoparticle-Enabled Fluorescence Sensing of Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents in Urine. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2025, 8, 2013–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, R.; Saha, M.; Ghosh, B.; Chauhan, N.; Mohan, H.; Kumaran, S.S.; Mukherjee, C. Folate Receptor Targeting Mn(II) Complex Encapsulated Porous Silica Nanoparticle as an MRI Contrast Agent for Early-State Detection of Cancer. Small 2025, 21, 2401787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, V.; Harini, K.; Thirumalai, A.; Girigoswami, K.; Girigoswami, A. Nanostructured Carbon Dots as Ratiometric Fluorescent Rulers for Heavy Metal Detection. Int. J. Nano Dimens. 2024, 15, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Chen, L.; Guo, R.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, S. Gadolinium Functionalized Carbon Dot Complexes for Dual-Modal Imaging: Structure, Performance, and Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2025, 11, 2037–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajipour Keyvani, A.; Mohammadnejad, P.; Pazoki-Toroudi, H.; Perez Gilabert, I.; Chu, T.; Manshian, B.B.; Soenen, S.J.; Sohrabi, B. Advancements in Cancer Treatment: Harnessing the Synergistic Potential of Graphene-Based Nanomaterials in Combination Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 2756–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Yi, X.; Xiang, D.; Zhou, L. Nanoagent-Mediated Photothermal Therapy: From Delivery System Design to Synergistic Theranostic Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2025, 20, 6891–6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, R.; Yang, B. Carbon dots: A new type of carbon-based nanomaterial with wide applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Kang, M.; Ji, S.; Ye, S.; Guo, J. Research on Red/Near-Infrared Fluorescent Carbon Dots Based on Different Carbon Sources and Solvents: Fluorescence Mechanism and Biological Applications. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, V.; Verma, R.; Gopalkrishnan, C.; Yuan, M.-H.; Batoo, K.M.; Jayavel, R.; Chauhan, A.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Balasubramani, R.; Ghotekar, S. Bio-inspired synthesis of carbon-based nanomaterials and their potential environmental applications: A state-of-the-art review. Inorganics 2022, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, R.; Prabakaran, L.; Senthil, R.; Yesudhason, B.V.; Dharmalingam, S.; Sathyaraj, W.V.; Atchudan, R. Current Innovations in Intraocular Pressure Monitoring Biosensors for Diagnosis and Treatment of Glaucoma—Novel Strategies and Future Perspectives. Biosensors 2023, 13, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojjati, S.M.; Salehi, Z.; Akrami, M. MRI-traceable multifunctional magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MMSN) capped with graphene quantum dots (GQD) as a theragnostic system in colorectal cancer treatment. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 96, 105700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanidenko, E.A.; Vedernikova, A.A.; Badrieva, Z.F.; Brui, E.A.; Ondar, S.O.; Miruschenko, M.D.; Volina, O.V.; Koroleva, A.V.; Zhizhin, E.V.; Ushakova, E.V. Manganese-Doped Carbon Dots as a Promising Nanoprobe for Luminescent and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Photonics 2023, 10, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Qing, X.; Liu, S.; Yang, D.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y. Hollow Mesoporous Manganese Oxides: Application in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Small 2022, 18, 2106511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Ma, Q.; Gong, L.; Di, S.; Gong, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, J.-J.; et al. Manganese-based multifunctional nanoplatform for dual-modal imaging and synergistic therapy of breast cancer. Acta Biomater. 2022, 141, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jin, X.; Yan, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X. Recent research progress in CDs@ MOFs composites: Fabrication, property modulation, and application. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Shi, B.; Zhu, W.; Lü, C. Temperature-responsive polymer-tethered Zr-porphyrin MOFs encapsulated carbon dot nanohybrids with boosted visible-light photodegradation for organic contaminants in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, S.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Qiu, M.; Pan, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Endoplasmic reticulum-targeted polymer dots encapsulated with ultrasonic synthesized near-infrared carbon nanodots and their application for in vivo monitoring of Cu2+. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 627, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Fei, J.; Dong, Z.; Yu, F.; Li, J. Nanoarchitectonics with a Membrane-Embedded Electron Shuttle Mimics the Bioenergy Anabolism of Mitochondria. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202319116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Fei, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Cui, Y.; Li, J. Hypocrellin-Loaded Gold Nanocages with High Two-Photon Efficiency for Photothermal/Photodynamic Cancer Therapy in Vitro. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 8030–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Fei, J.; Wang, A.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Rational assembly of a biointerfaced core@shell nanocomplex towards selective and highly efficient synergistic photothermal/photodynamic therapy. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 20197–20210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Martín, F.; D’Amelio, N. Biomembrane lipids: When physics and chemistry join to shape biological activity. Biochimie 2022, 203, 118–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, M.W.S.; Tero, R. Cholesterol-induced microdomain formation in lipid bilayer membranes consisting of completely miscible lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2021, 1863, 183626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Aranguren, L.; Anas, A.T.M.; Muhammad, U.; Parag, J.; Marwah, M.K. Mitochondrial-targeted liposome-based drug delivery—Therapeutic potential and challenges. J. Drug Target. 2025, 33, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegafaw, T.; Mulugeta, E.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Baek, A.; Kim, J.; Chang, Y.; Lee, G.H. Surface Modification, Toxicity, and Applications of Carbon Dots to Cancer Theranosis: A Review. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Chen, S.; Liao, Y.; Li, S.; Ge, J.; Tao, F.; Huo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z. Near-infrared fluorescent carbon dots encapsulated liposomes as multifunctional nano-carrier and tracer of the anticancer agent cinobufagin in vivo and in vitro. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2019, 174, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, B.; Moulahoum, H.; Ghorbanizamani, F.; Barlas, F.B.; Yesiltepe, O.; Gumus, Z.P.; Meral, K.; Odaci Demirkol, D.; Timur, S. Carbon dots and curcumin-loaded CD44-Targeted liposomes for imaging and tracking cancer chemotherapy: A multi-purpose tool for theranostics. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 62, 102363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vescovo, D.; Manetti, C.; Ruggieri, R.; Spizzirri, U.G.; Aiello, F.; Martuscelli, M.; Restuccia, D. The Valorization of Potato Peels as a Functional Ingredient in the Food Industry: A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2025, 14, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Champi, D.; Romero-Orejon, F.L.; Moran-Reyes, A.; Muñoz, A.M.; Ramos-Escudero, F. Bioactive compounds in potato peels, extraction methods, and their applications in the food industry: A review. CyTA—J. Food 2023, 21, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.P.; Saldaña, M.D.A. Subcritical water extraction of phenolic compounds from potato peel. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2452–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, B.; Gullón, B.; Yáñez, R. Identification and Recovery of Valuable Bioactive Compounds from Potato Peels: A Comprehensive Review. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, W.; Irna, S.; Hemiawati, S.M.; Ronny, L.; Ichwan, S. Pharmacological Activity of Chemical Compounds of Potato Peel Waste (Solanum tuberosum L.) in vitro: A Scoping Review. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2024, 16, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himanshu, M.; Singh, A.; Srivastava, N.; Verma, B. Comparative photocatalytic performance of iron nanoparticles biosynthesized from aqueous extracts of potato, potato peels, and leaves. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 292, 139156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumalai, A.; Girigoswami, K.; Prabhu, A.D.; Durgadevi, P.; Kiran, V.; Girigoswami, A. 8-Anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonate-Conjugated Carbon-Coated Ferrite Nanodots for Fluoromagnetic Imaging, Smart Drug Delivery, and Biomolecular Sensing. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1378. [Google Scholar]
- Janani, G.; Girigoswami, A.; Deepika, B.; Udayakumar, S.; Girigoswami, K. Unveiling the Role of Nano-Formulated Red Algae Extract in Cancer Management. Molecules 2024, 29, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessy Mercy, D.; Kiran, V.; Thirumalai, A.; Harini, K.; Girigoswami, K.; Girigoswami, A. Rice husk assisted carbon quantum dots synthesis for amoxicillin sensing. Results Chem. 2023, 6, 101219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Long, S.; Feng, R.; Yu, M.-J.; Xu, B.-C.; Tao, H. Thiolated dextrin nanoparticles for curcumin delivery: Stability, in vitro release, and binding mechanism. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika, B.; Gowtham, P.; Raghavan, V.; Isaac, J.B.; Devi, S.; Kiran, V.; Mercy, D.J.; Sofini, P.S.; Harini, A.; Girigoswami, A. Harmony in nature’s elixir: A comprehensive exploration of ethanol and nano-formulated extracts from Passiflora incarnata leaves: Unveiling in vitro cytotoxicity, acute and sub-acute toxicity profiles in Swiss albino mice. J. Mol. Histol. 2024, 55, 977–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harini, K.; Alomar, S.Y.; Vajagathali, M.; Manoharadas, S.; Thirumalai, A.; Girigoswami, K.; Girigoswami, A. Niosomal Bupropion: Exploring Therapeutic Frontiers through Behavioral Profiling. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, D.; Rajamanikandan, R.; Ilanchelian, M. Investigating the Function of Ribonucleic Acid in Suppressing the Spectral and In Vitro Cytotoxic Effects of Methylene Blue/Thionine Dyes. Luminescence 2025, 40, e70221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandekar, A.S.; Gaikar, P.S.; Angre, A.P.; Chaughule, A.M.; Pradhan, N.S. Effect of annealing on microstructure and magnetic properties of Mn ferrite powder. J. Biol. Chem. Chron. 2019, 5, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, T.-W.; Yang, C.-H.; Su, C.-J.; Huang, Y.-T.; Yeh, Y.-Q.; Liao, K.-F.; Lin, T.-C.; Shih, O.; Lee, M.-T.; Su, A.-C. Revealing cholesterol effects on PEGylated HSPC liposomes using AF4–MALS and simultaneous small-and wide-angle X-ray scattering. Appl. Crystallogr. 2023, 56, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowtham, P.; Girigoswami, K.; Pallavi, P.; Harini, K.; Gurubharath, I.; Girigoswami, A. Alginate-Derivative Encapsulated Carbon Coated Manganese-Ferrite Nanodots for Multimodal Medical Imaging. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ge, J.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L.; Cui, J.; Zeng, J.; Gao, M. Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: A next generation contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol 2022, 14, e1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momper, R.; Steinbrecher, J.; Dorn, M.; Rörich, I.; Bretschneider, S.; Tonigold, M.; Ramanan, C.; Ritz, S.; Mailänder, V.; Landfester, K.; et al. Enhanced photoluminescence properties of a carbon dot system through surface interaction with polymeric nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 518, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Fernando, K.S.; Pathak, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Harruff, B.A.; Wang, X.; Wang, H. Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7756–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiganesh, T.; Daisy Vimala Rani, J.; Girigoswami, A. Spectroscopically characterized cadmium sulfide quantum dots lengthening the lag phase of Escherichia coli growth. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 92, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.; Pérez-Andrés, E.; Thevenot, J.; Sandre, O.; Berra, E.; Lecommandoux, S. Magnetic field triggered drug release from polymersomes for cancer therapeutics. J. Control. Release 2013, 169, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Kiran, V.; Thirumalai, A.; Durgadevi, P.; Akhtar, N.; Prabhu, A.D.; Girigoswami, K.; Girigoswami, A. Biocompatible Carbon-Coated Ferrite Nanodot-Based Magnetoliposomes for Magnetic-Induced Multimodal Theragnostic. Colloids Interfaces 2026, 10, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids10010004
Kiran V, Thirumalai A, Durgadevi P, Akhtar N, Prabhu AD, Girigoswami K, Girigoswami A. Biocompatible Carbon-Coated Ferrite Nanodot-Based Magnetoliposomes for Magnetic-Induced Multimodal Theragnostic. Colloids and Interfaces. 2026; 10(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids10010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiran, Venkatakrishnan, Anbazhagan Thirumalai, Pazhani Durgadevi, Najim Akhtar, Alex Daniel Prabhu, Koyeli Girigoswami, and Agnishwar Girigoswami. 2026. "Biocompatible Carbon-Coated Ferrite Nanodot-Based Magnetoliposomes for Magnetic-Induced Multimodal Theragnostic" Colloids and Interfaces 10, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids10010004
APA StyleKiran, V., Thirumalai, A., Durgadevi, P., Akhtar, N., Prabhu, A. D., Girigoswami, K., & Girigoswami, A. (2026). Biocompatible Carbon-Coated Ferrite Nanodot-Based Magnetoliposomes for Magnetic-Induced Multimodal Theragnostic. Colloids and Interfaces, 10(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids10010004






