Fabrication and Fractality of Fe2O3-CeO2/ZSM-5 Composites for High-Temperature Desulfurization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
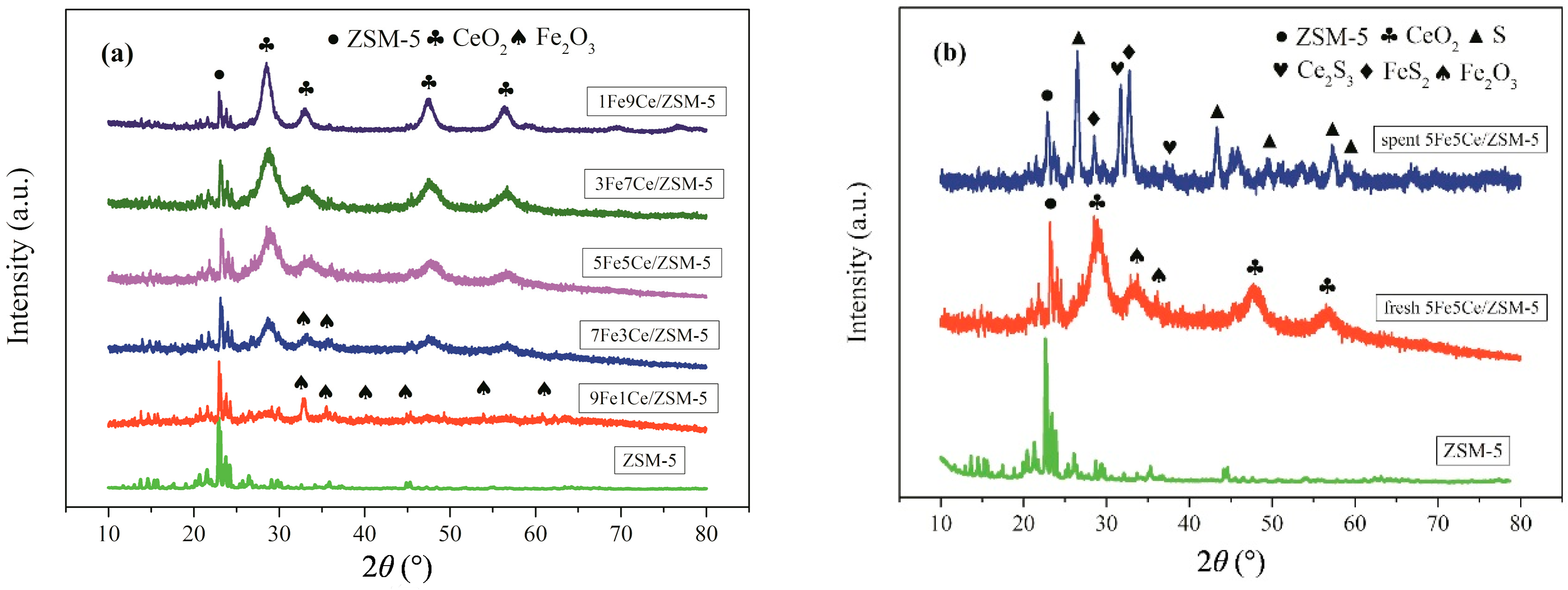
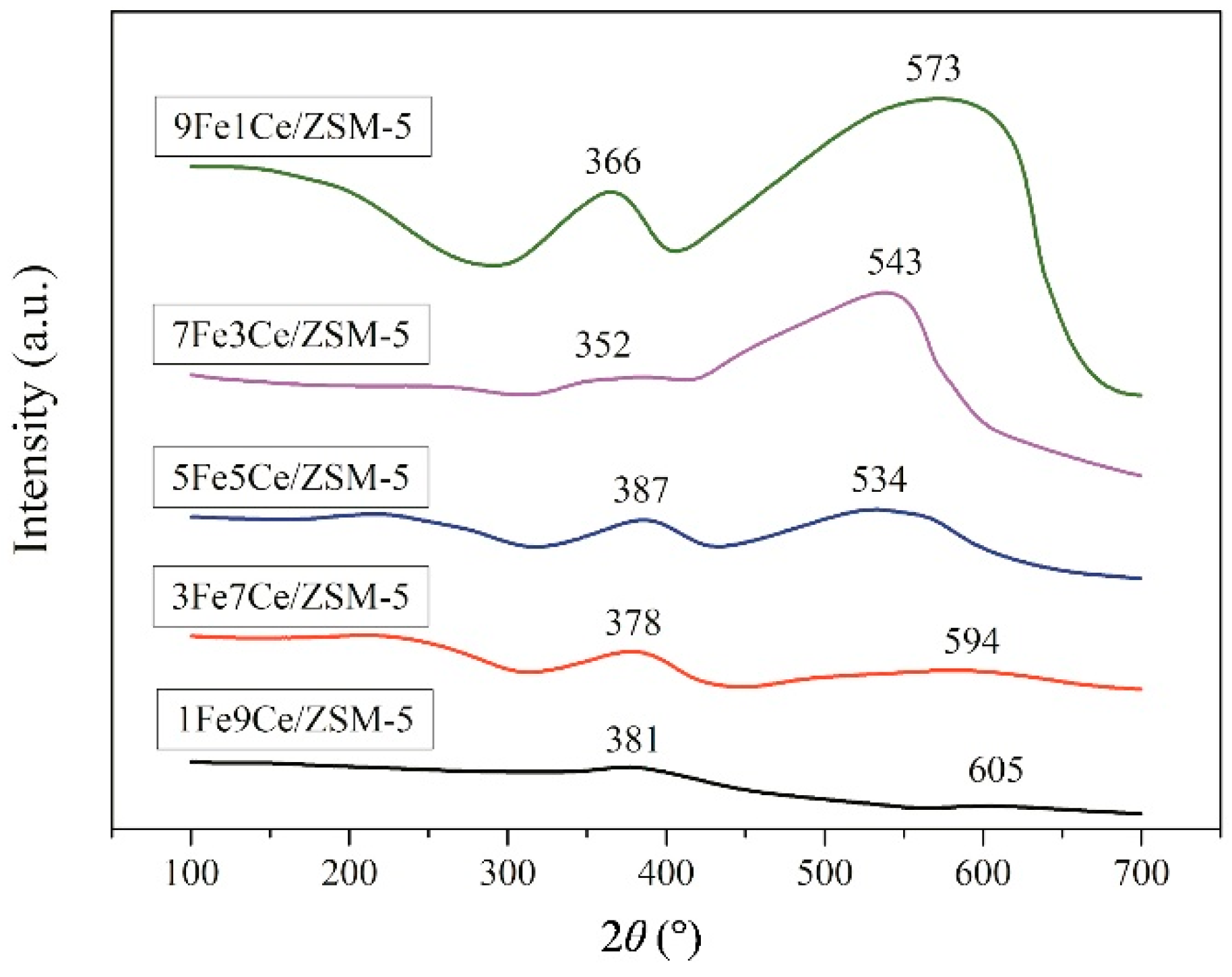
2.1. Characterization Analysis
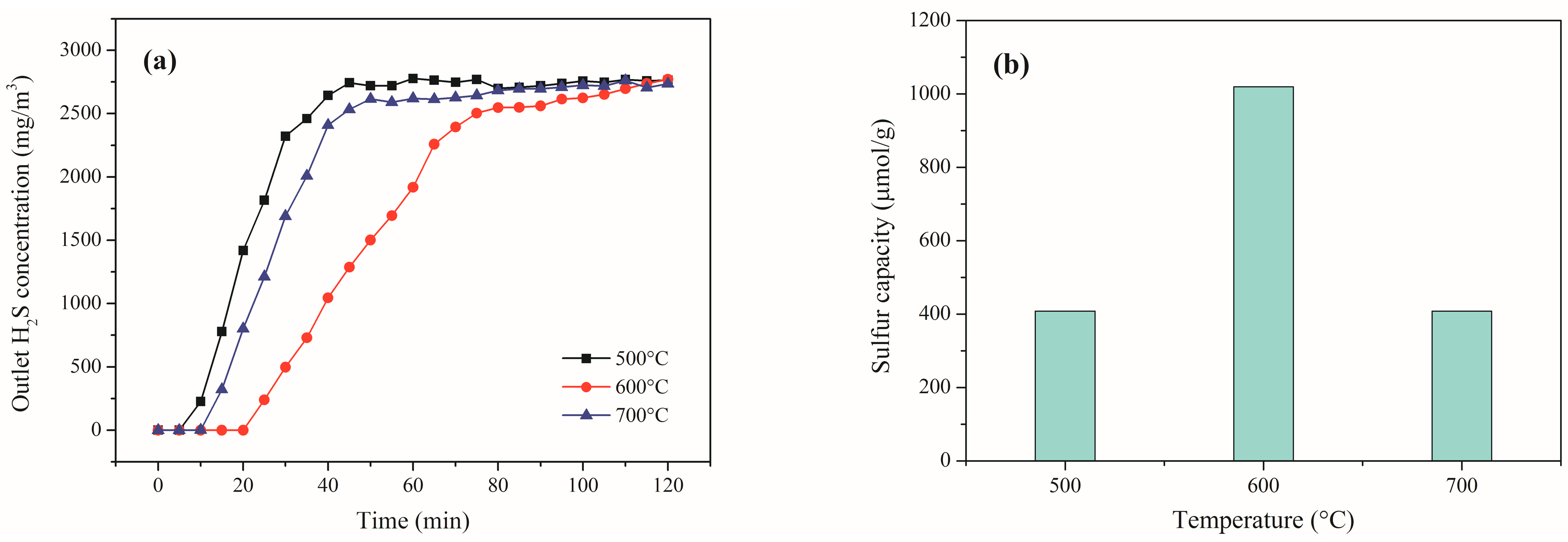
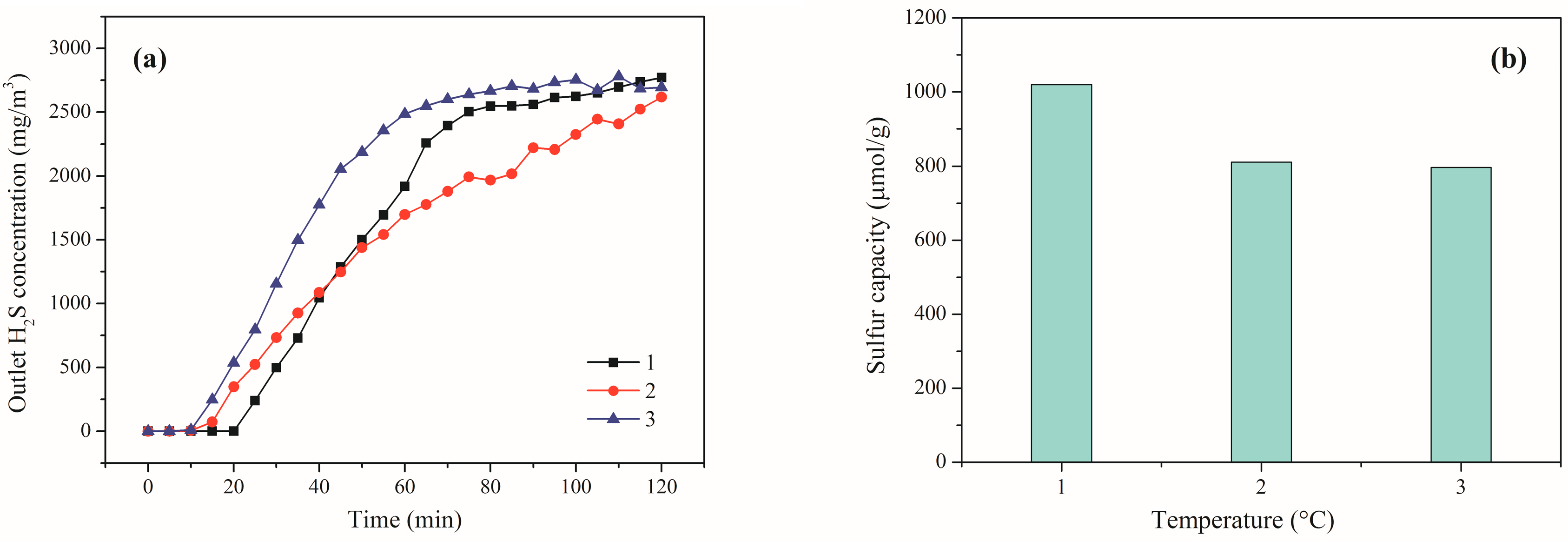
2.2. Effect of Reaction Temperature
2.3. Effect of CeO2 Content
2.4. Reusability
3. Experimental
3.1. Sorbent Preparation
3.2. Sorbent Characterization
3.3. Adsorption
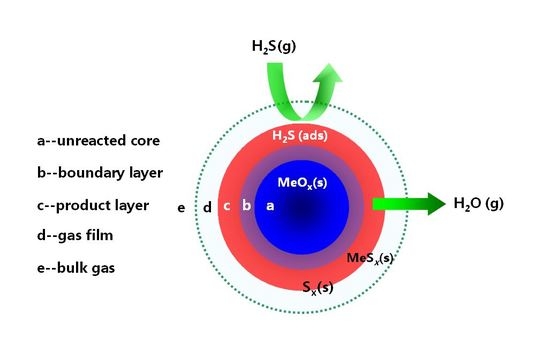
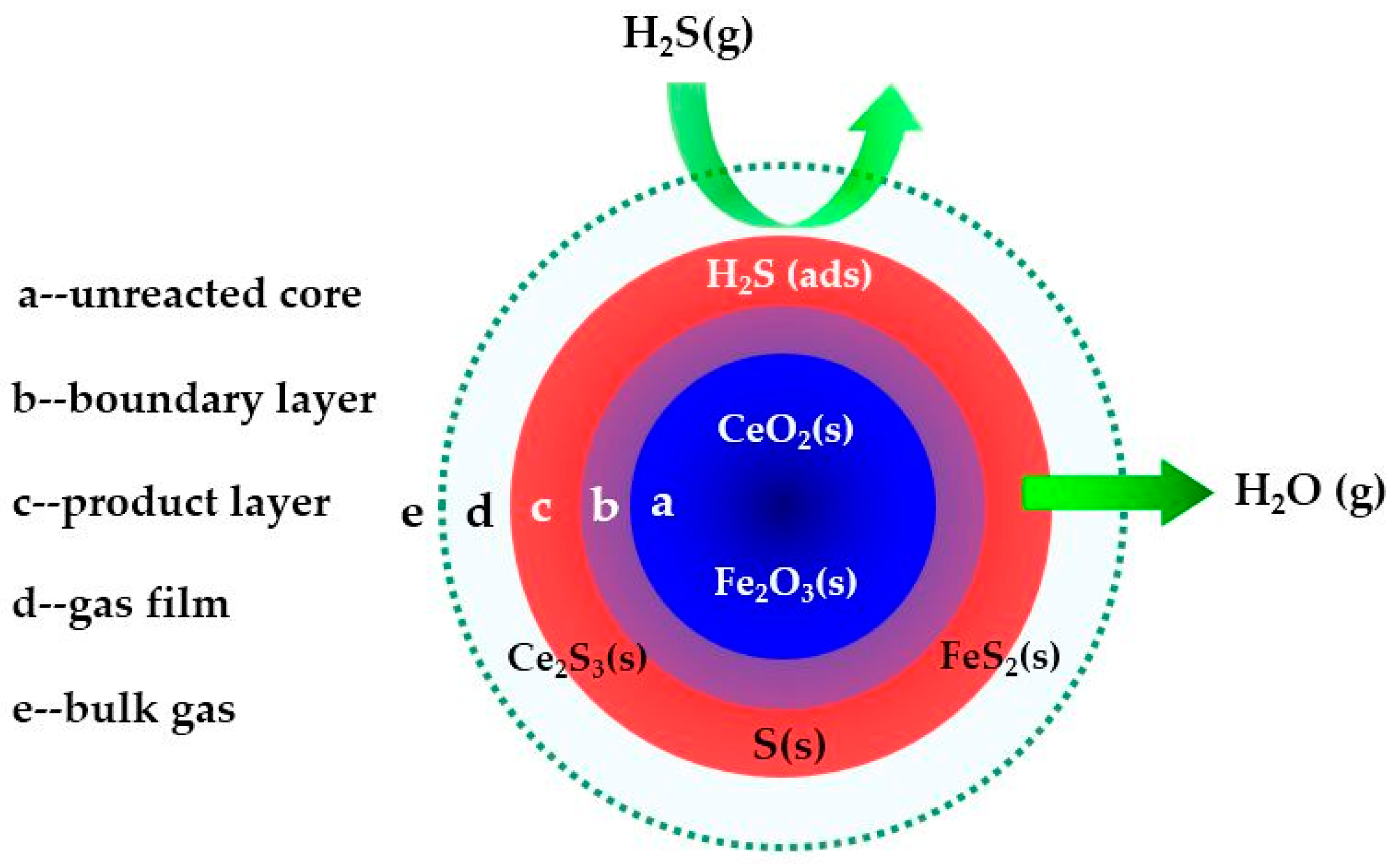
4. Desulfurization Process
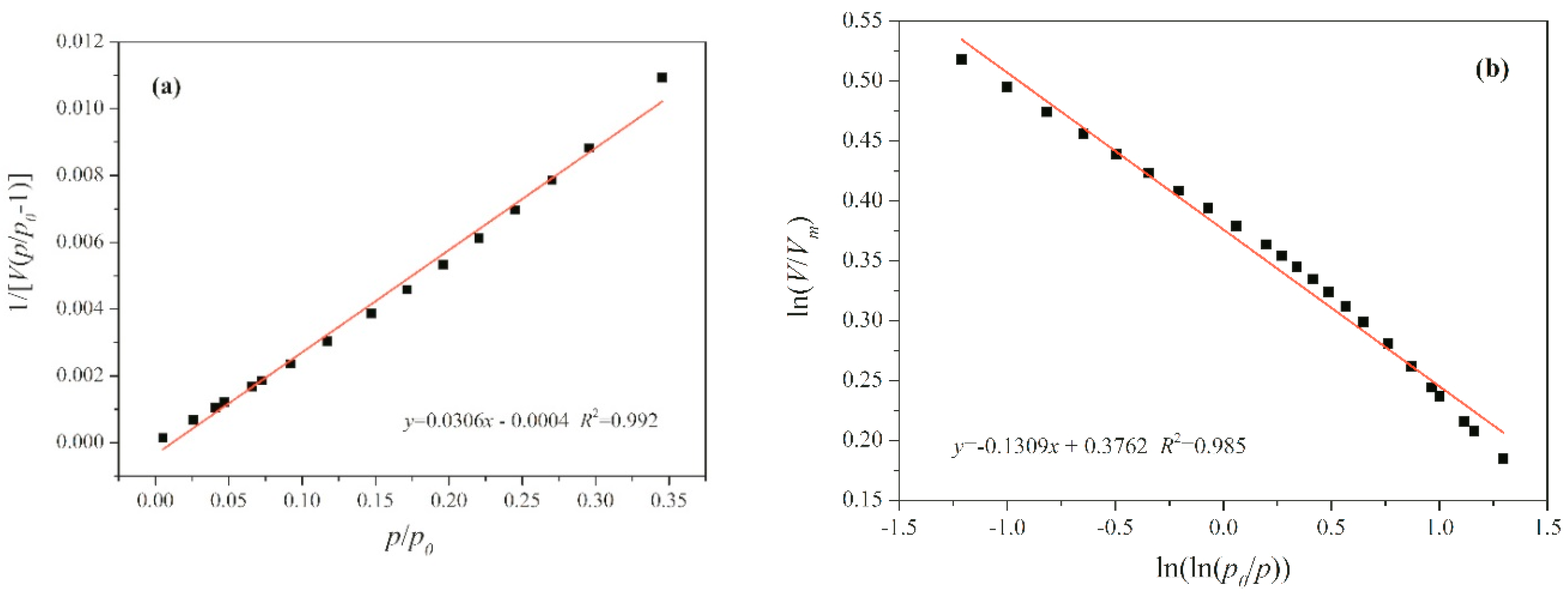
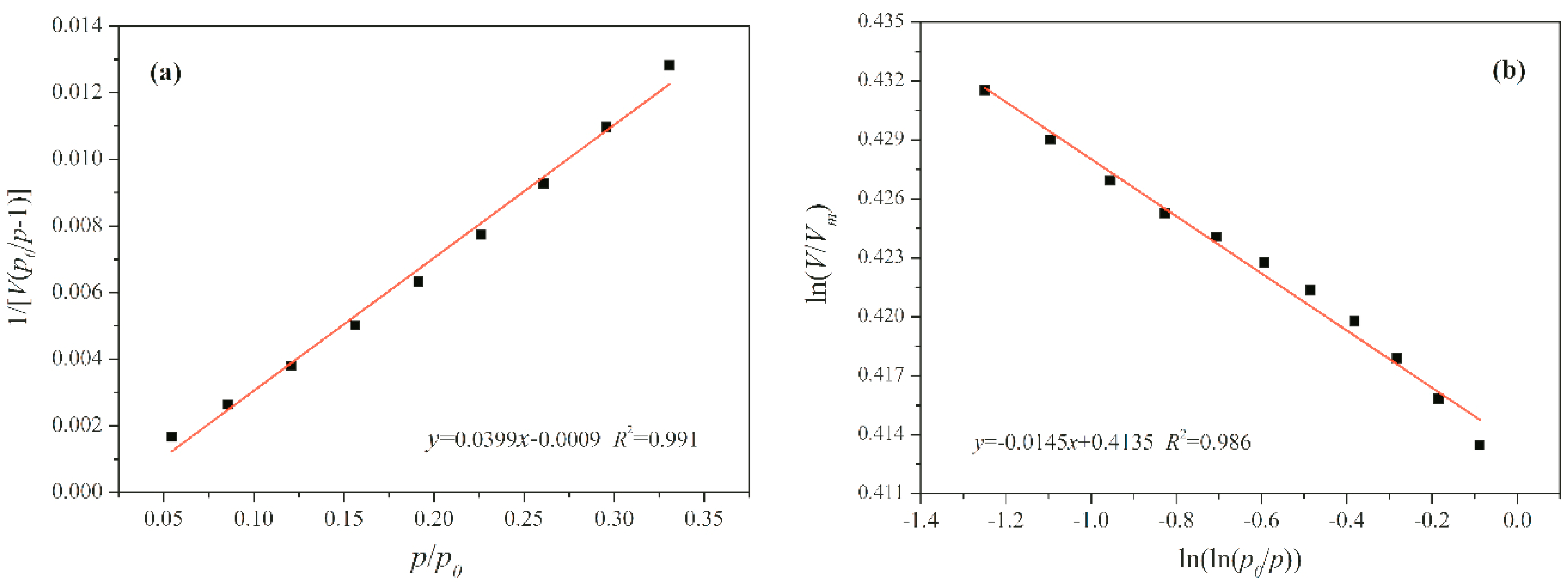
5. Fractal Analysis
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Y.; Rezvani, S.; McIlveen-Wright, D.; Minchener, A.; Hewitt, N. Techno-economic study of CO2 capture and storage in coal fired oxygen fed entrained flow IGCC power plants. Fuel Process. Technol. 2008, 89, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Cheah, S.; Bain, R.; Feik, C.; Magrini-Bar, K.; Phillips, S. Integrated process configuration for high-temperature sulfur mitigation during biomass conversion via indirect gasification. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 8326–8333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higman, C.; Tam, S. Advances in coal gasification, hydrogenation, and gas treating for the production of chemicals and fuels. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1673–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.W.; Ni, W.D.; Li, Z.; Ma, L.W. Strategic thinking on IGCC development in China. Energy Policy 2008, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrida, A.; Romano, M.C.; Lozza, G.C. Thermodynamic assessment of IGCC power plants with hot fuel gas desulfurization. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 3374–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.P.; Ying, Y.J.; Zhang, C.Q.; Peng, W.W. Research improvement in Zn-based sorbent for hot gas desulfurization. Powder Technol. 2008, 180, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, M.; Palaciosa, J.M.; Alonsoa, L.; García, E.; Moliner, R. Performance of zinc oxide based sorbents for hot coal gas desulfurization in multicycle tests in a fixed-bed reactor. Fuel 2000, 79, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvana, O.; Atakül, H. Investigation of CuO/mesoporous SBA-15 sorbents for hot gas desulfurization. Fuel Process. Technol. 2008, 89, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvana, O.; Sirkecioğlu, A.; Atakül, H. Investigation of nano-CuO/mesoporous SiO2 materials as hot gas desulphurization sorbents. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liang, B.; Parnas, R. Manganese-based regenerable sorbents for high temperature H2S removal. Fuel 2013, 107, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, W.J.W.; Kapteijn, F.; Moulijin, J.A. A high capacity manganese-based sorbent for regenerative high temperature desulfurization with direct sulfur production conceptual process application to coal gas cleaning. Chem. Eng. J. 2003, 96, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, K.M.; Kalakota, V.; Adusumilli, S. High-temperature desulfurization of gasifier effluents with rare earth and rare earth transition metal oxides. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Krcha, M.D.; Janik, M.J.; Roy, A.D.; Dooley, K.M. Ce-Mn oxides for high-temperature gasifier effluent desulfurization. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 6765–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasyerli, S.; Dogu, G.; Dogu, T. Selective oxidation of H2S to elemental sulfur over Ce-V mixed oxide and CeO2 catalysts prepared by the complexation technique. Catal. Today 2006, 1–3, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.G.; Perales, J.F.; Velo, E.; Puigjaner, L. Kinetic behaviour of iron oxide sorbent in hot gas desulfurization. Fuel 2005, 84, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Chang, L.P.; Wang, D.H.; Xie, K.C.; Wall, T.; Yu, J.L. Removal of sulfur at high temperatures using iron-based sorbents supported on fine coal ash. Fuel 2010, 89, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.D.; Groves, F.R., Jr.; Harrison, D.P. Elemental sulfur production during the regeneration of iron oxide high-temperature desulfurization sorbent. Catal. Today 1998, 40, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.L.; Sun, T.; Zhao, Y.P.; Shangguan, J.; Lin, J.Y. Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous iron oxide for removal of H2S at medium temperatures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4859–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Xin, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, Z.P.; Zhang, Z.L.; Zheng, L.R. Ce-Ti amorphous oxides for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: Confirmation of Ce-O-Ti active sites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 17, 9600–9605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Li, C.; Fan, H. Effect of binder on the properties of iron oxide sorbent for hot gas desulfurization. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2010, 19, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Fan, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yan, Q. Study on the Reduction Behavior of zirconia supported iron oxide catalysts by temperature-programmed reduction combined with in situ mössbauer spectroscopy. J. Solid State Chem. 1996, 121, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Liu, B.S.; Wang, F.; Li, J.F. Fabrication and performance of xMnyCe/hexagonal mesoporous silica sorbents with wormhole-like framework for hot coal gas desulfurization. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 7754–7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.J.; Zhou, W.G.; Wu, J. CuO-CeO2/ZSM-5 composites for reactive adsorption of hydrogen sulfide at high temperature. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 94, 2276–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.J.; Zhou, W.G.; Wu, J. CeO2-MnOx/ZSM-5 sorbents for H2S removal at high temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.J.; Zhou, W.G.; Wu, J. CeO2-La2O3/ZSM-5 sorbents for high-temperature H2S removal. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.S.; Wan, Z.Y.; Zhan, Y.P.; Au, C.T. Desulfurization of hot coal gas over high-surface-area LaMeOx/MCM-41 sorbents. Fuel 2012, 98, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.J.; Zhou, W.G.; Wu, J. Perovskite LaMnO3/ZSM-5 composites for H2S reactive adsorption at high temperature. Adsorption 2016, 22, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.J.; Zhou, W.G.; Wu, J. La2CuO4/ZSM-5 sorbents for high-temperature desulphurization. Fuel 2016, 177, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neveux, L.; Chiche, D.; Pérez-Pellitero, J.; Favergeon, L.; Gay, A.S.; Pijolat, M. New insight into the ZnO sulfidation reaction: Mechanism and kinetics modeling of the ZnS outward growth. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 1532–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiche, D.; Bazer, D. New insight on the ZnO sulfidation reaction: Evidences for an outward growth process of the ZnS phase. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 181–182, 508–515. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.J.; Zhou, W.G.; Wu, J. Effect of Ce and La on the activity of CuO/ZSM-5 and MnOx/ZSM-5 composites for elemental mercury removal at low temperature. Fuel 2017, 194, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, D.J.; Zhou, W.G.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Y. High-Temperature H2S Removal from IGCC Coarse Gas; Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer, P.; Avnir, D. Chemistry in noninteger dimensions between two and three. I. Fractal theory of heterogeneous surfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 3558–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnir, D.; Farin, D.; Pfeifer, P. Chemistry in noninteger dimensions between two and three. II. Fractal surface of adsorbents. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 78, 3566–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.; Cherkashinin, Y.G.; Korili, S.A. Fractal Dimension of a Pillared Montmorillonite from Nitrogen Adsorption at 77 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2004, 49, 639–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowski, A.; Podkościelny, P.; Hubicki, Z.; Barczak, M. Adsorption of phenolic compounds by activated carbon-a critical review. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1049–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahouli, B.; Blacher, S.; Brouers, F. Applicability of the Fractal FHH Equation. Langmuir 1997, 13, 4391–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.K. The roughness of aerosol particles: Surface fractal dimension measured using nitrogen adsorption. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1996, 25, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Long, C.; Tao, W.; Li, A.; Zhang, Q. Fractal dimensions of macroporous and hypercrosslinked polymeric adsorbents from nitrogen adsorption data. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 3147–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | SBET | Vtotal | Vmicro | Vmeso | Daver |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m2/g | mm3/g | mm3/g | mm3/g | nm | |
| ZSM-5 | 320 | 255 | 108 | 147 | 3.19 |
| fresh 5Fe5Ce/ZSM-5 | 170 | 119 | 59 | 60 | 2.79 |
| spent 5Fe5Ce/ZSM-5 | 116 | 78 | 43 | 35 | 2.69 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Zhou, W.; Wu, J. Fabrication and Fractality of Fe2O3-CeO2/ZSM-5 Composites for High-Temperature Desulfurization. Colloids Interfaces 2017, 1, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids1010010
Liu D, Zhou W, Wu J. Fabrication and Fractality of Fe2O3-CeO2/ZSM-5 Composites for High-Temperature Desulfurization. Colloids and Interfaces. 2017; 1(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids1010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Dongjing, Weiguo Zhou, and Jiang Wu. 2017. "Fabrication and Fractality of Fe2O3-CeO2/ZSM-5 Composites for High-Temperature Desulfurization" Colloids and Interfaces 1, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids1010010
APA StyleLiu, D., Zhou, W., & Wu, J. (2017). Fabrication and Fractality of Fe2O3-CeO2/ZSM-5 Composites for High-Temperature Desulfurization. Colloids and Interfaces, 1(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids1010010