Adaptive Multi-View Hypergraph Learning for Cross-Condition Bearing Fault Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose an adaptive hyperedge construction mechanism that learns condition-aware, high-order relations via reconstruction-driven selection and weighting, enabling the hypergraph to capture stable cross-condition structure beyond pairwise links.
- We develop a view-level attention fusion module that aggregates time-, frequency-, and time–frequency-domain embeddings into a unified representation, assigning data-driven importance to each view to improve cross-condition generalization.
- Comprehensive experiments on the Case Western Reserve University (CWRU) and Ottawa bearing datasets validate the proposed framework, with results indicating that AMH delivers superior diagnostic performance, robustness, and cross-condition generalization compared with current state-of-the-art baseline.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Methods
2.2. Graph-Based Methods
3. Methodology
3.1. Problem Definition
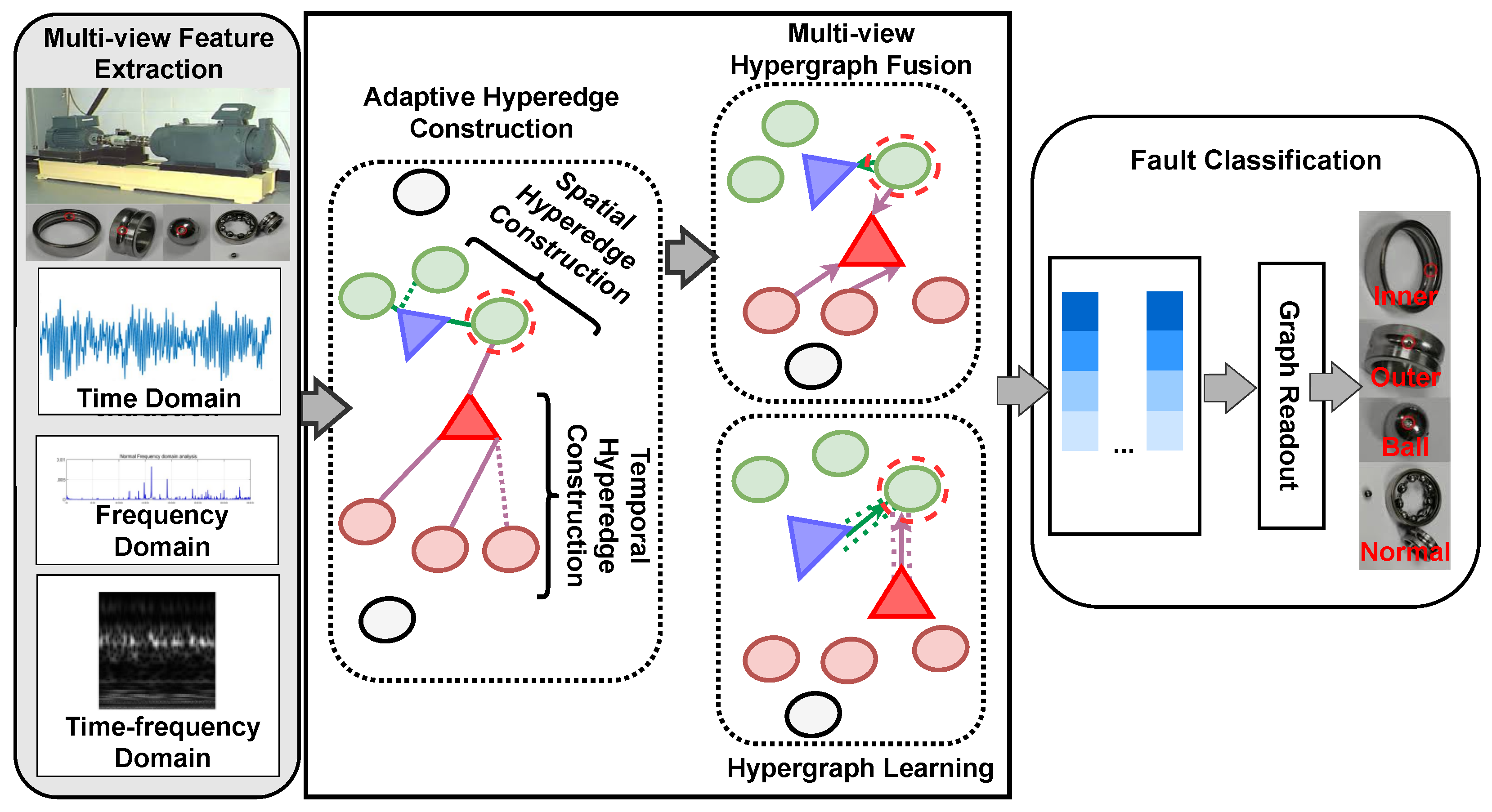
3.2. Multi-View Feature Extraction
- Time-domain view (): statistical features such as Root Mean Square (RMS);
- Frequency-domain view (): Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) spectral energy;
- Time–frequency view (): short-time Fourier transform (STFT).
3.3. Adaptive Hyperedge Construction
3.4. Multi-View Hypergraph Fusion
3.5. Hypergraph Learning with Attention
3.6. Loss Function
4. Experiments
- RQ1: How effectively does the proposed AMH framework perform in comparison with baseline approaches regarding diagnostic performance, model robustness, and generalization across different operating conditions?
- RQ2: How well can various models differentiate among distinct fault types, and what typical patterns of misclassifications can be observed?
- RQ3: What is the specific impact of each major component of AMH, including adaptive hyperedge construction, multi-view feature integration, and attention-guided hypergraph learning, on the overall diagnostic performance?
4.1. Benchmarks
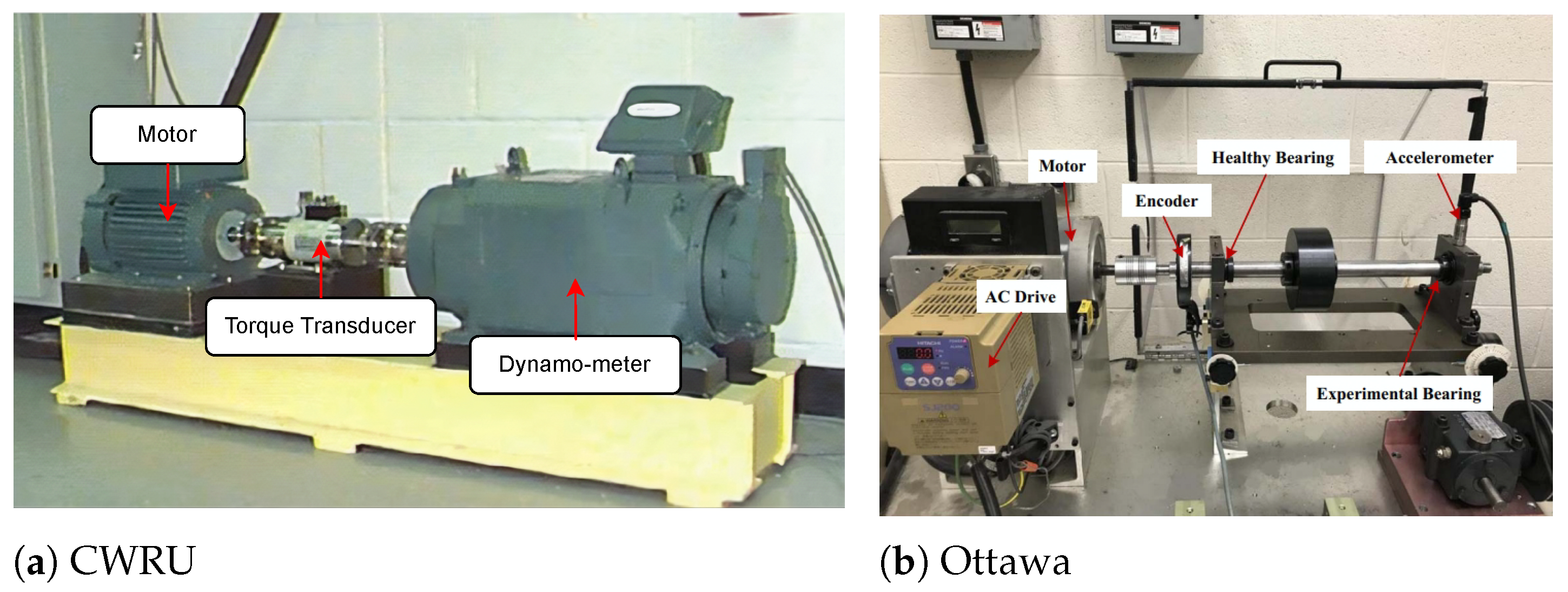
4.1.1. CWRU Bearing Dataset
4.1.2. Ottawa Bearing Dataset
4.2. Model Configuration
4.3. Baseline Models
- (1) CNN [28]: A convolutional neural network that learns localized temporal and spectral representations directly from raw vibration inputs.
- (2) LSTM [46]: A recurrent network based on Long Short-Term Memory units, designed to capture long-range temporal correlations and dynamic behaviors in sequential vibration data.
- (3) GRU [47]: A Gated Recurrent Unit model that simplifies the gating mechanism of LSTM while maintaining the ability to capture temporal dependencies with reduced computational complexity.
- (4) GCN [48]: A Graph Convolutional Network that learns spatial relationships among nodes based on pairwise graph structures, effectively capturing inter-sample or inter-sensor correlations.
- (5) HGCN [49]: A Hypergraph Convolutional Network that extends GCNs by introducing hyperedges to represent high-order relationships among multiple nodes simultaneously.
4.4. Computational Cost
4.5. Metrics for Evaluation
4.6. Main Results
4.6.1. Performance Comparison (RQ1)
4.6.2. Confusion Pattern Analysis (RQ2)
4.6.3. Ablation Study (RQ3)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruan, D.; Wang, J.; Yan, J.; Gühmann, C. CNN parameter design based on fault signal analysis and its application in bearing fault diagnosis. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2023, 55, 101877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, B.; Eisenbart, B.; Nikzad, M.; Fox, B.; Blythe, A.; Bwar, K.H.; Wang, J.; Du, Y.; Shevtsov, S. Application of KNN and ANN Metamodeling for RTM filling process prediction. Materials 2023, 16, 6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, P.; Yi, W.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Chai, B.X. STHFD: Spatial–Temporal Hypergraph-Based Model for Aero-Engine Bearing Fault Diagnosis. Aerospace 2025, 12, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, X.; Zhao, S.; Lu, X. A novel fault diagnosis method based on CNN and LSTM and its application in fault diagnosis for complex systems. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 1289–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jin, J.; Zhang, T.; Chai, B.X.; Di Pietro, A.; Georgakopoulos, D. Leveraging auxiliary task relevance for enhanced bearing fault diagnosis through curriculum meta-learning. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 22467–22478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Deng, C. An improved GNN using dynamic graph embedding mechanism: A novel end-to-end framework for rolling bearing fault diagnosis under variable working conditions. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 200, 110534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Li, J.; Deng, K. The footprint of factorization models and their applications in collaborative filtering. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. (TOIS) 2021, 40, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Shi, P. Improved GNN based on Graph-Transformer: A new framework for rolling mill bearing fault diagnosis. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2024, 46, 2804–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.; Bai, Y.; Li, X.; Jin, J. HyperMAN: Hypergraph-enhanced Meta-learning Adaptive Network for Next POI Recommendation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.22049. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Bwar, K.; Eisenbart, B.; Lu, G.; Belaadi, A.; Fox, B.; Chai, B. Application of machine learning for composite moulding process modelling. Compos. Commun. 2024, 48, 101960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, B.X.; Gunaratne, M.; Ravandi, M.; Wang, J.; Dharmawickrema, T.; Di Pietro, A.; Jin, J.; Georgakopoulos, D. Smart industrial internet of things framework for composites manufacturing. Sensors 2024, 24, 4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tong, H.; Xu, J.; Maciejewski, R. Graph convolutional networks: A comprehensive review. Comput. Soc. Netw. 2019, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Shi, H.; Tan, S.; Song, B.; Tao, Y. A knowledge-driven spatial-temporal graph neural network for quality-related fault detection. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 184, 1512–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jin, J.; Zhang, L.; Dai, H.N.; Di-Pietro, A.; Zhang, T. Towards spatial-temporal meta-hypergraph learning for multimodal few-shot fault diagnosis. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2025, 48, 100924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhou, K.; Liu, J. SuperGraph: Spatial-temporal graph-based feature extraction for rotating machinery diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 4167–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xie, F.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, L.; Huang, B. Spatial-temporal graph feature learning driven by time–frequency similarity assessment for robust fault diagnosis of rotating machinery. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2024, 62, 102711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Shao, D.; Cui, L. CTNet: A data-driven time-frequency technique for wind turbines fault diagnosis under time-varying speeds. ISA Trans. 2024, 154, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zhou, S. Maximum L-Kurtosis deconvolution and frequency-domain filtering algorithm for bearing fault diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 223, 111916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tian, J.; Liang, P.; Xu, X.; Yu, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, D. Single and simultaneous fault diagnosis of gearbox via wavelet transform and improved deep residual network under imbalanced data. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaleshtori, A.E.; Aghaie, A. A novel bearing fault diagnosis approach using the Gaussian mixture model and the weighted principal component analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 242, 109720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Anand, R. Bearing fault diagnosis using multiple feature selection algorithms with SVM. Prog. Artif. Intell. 2024, 13, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matania, O.; Cohen, R.; Bechhoefer, E.; Bortman, J. Zero-fault-shot learning for bearing spall type classification by hybrid approach. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 224, 112117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobie, C.; Freitas, C.; Nicolai, M. Simulation-driven machine learning: Bearing fault classification. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 99, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, D.; Wang, H. A novel adaptive generalized domain data fusion-driven kernel sparse representation classification method for intelligent bearing fault diagnosis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 247, 123225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saufi, M.S.R.M.; Isham, M.F.; Talib, M.H.A.; Zain, M.Z.M. Extremely low-speed bearing fault diagnosis based on raw signal fusion and DE-1D-CNN network. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2024, 12, 5935–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Liu, Y.; Fang, J.; Liu, W.; Zhong, M.; Liu, X. An optimized CNN-BiLSTM network for bearing fault diagnosis under multiple working conditions with limited training samples. Neurocomputing 2024, 574, 127284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Shi, C.; Sheng, H.; Li, X.; Yang, T. Lightweight CNN architecture design for rolling bearing fault diagnosis. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 126142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, O.; Slavkovikj, V.; Vervisch, B.; Stockman, K.; Loccufier, M.; Verstockt, S.; Van de Walle, R.; Van Hoecke, S. Convolutional neural network based fault detection for rotating machinery. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 377, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, B.; Gao, D. Bearing fault diagnosis base on multi-scale CNN and LSTM model. J. Intell. Manuf. 2021, 32, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Chen, D.; He, D.; Sun, Y.; Yin, X. Bearing fault diagnosis based on VMD and improved CNN. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2023, 23, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Q.; Chai, Y.; Huang, X. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method base on periodic sparse attention and LSTM. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 12044–12053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Lai, P.; Li, T.; Teng, F.; Jin, Z. Mt-ConvFormer: A multi-task bearing fault diagnosis method using a combination of CNN and transformer. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 74, 3501816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaeibonehkhater, M.; Labbaf-Khaniki, M.A.; Manthouri, M. Transformer-based bearing fault detection using temporal decomposition attention mechanism. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.11245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chai, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Q. Gaussian mixture variational-based transformer domain adaptation fault diagnosis method and its application in bearing fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 20, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; An, J.; Liu, H.; Xiang, J.; Zhao, B.; Dunkin, F. A lightweight transformer with strong robustness application in portable bearing fault diagnosis. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 9649–9657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Cai, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Shi, K.; Zhong, X.; Liao, Z.; Li, Q. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method using time-frequency information integration and multi-scale TransFusion network. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 284, 111344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Tang, C.; Sun, J.; Shi, Z.; Xu, J.; Ji, X.; Yu, J. LSTM-based node-gated graph neural network for cross-condition few-shot bearing fault diagnosis. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 3445–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Yang, X.; Yang, X. A graph neural network-based bearing fault detection method. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, D.; Andrade, E.; Rativa, D.; Maciel, A.M. Fault detection and diagnosis in industry 4.0: A review on challenges and opportunities. Sensors 2024, 25, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lu, Y.; Jiu, S.; Huang, H.; Yang, G.; Yu, J. Prototype-oriented hypergraph representation learning for anomaly detection in tabular data. Inf. Process. Manag. 2025, 62, 103877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, L. Graph neural network-based bearing fault diagnosis using Granger causality test. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 242, 122827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Bai, J.; Yang, J.; Lee, J.J. Crash risk prediction using sparse collision data: Granger causal inference and graph convolutional network approaches. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 259, 125315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.T.; Prasad, R.K.; Michael, G.R.; Singh, N.H.; Kaphungkui, N. Spatial-Temporal Bearing Fault Detection Using Graph Attention Networks and LSTM. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.11923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Zhu, J.; Cao, S.; Li, P.; Xu, C. Bearing fault diagnosis under multisensor fusion based on modal analysis and graph attention network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 3526510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Baddour, N. Bearing vibration data collected under time-varying rotational speed conditions. Data Brief 2018, 21, 1745–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, P.; Hou, B.; Lei, J.; Zhang, Z. Bearing fault diagnosis method based on EEMD and LSTM. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Tang, Y.; Wang, T.; Lei, N. An improved MSCNN and GRU model for rolling bearing fault diagnosis. Stroj. Vestn.-J. Mech. Eng. 2023, 69, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mo, L.; Yan, R. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on WHVG and GCN. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 3519811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, P.; Huang, X. Residual-hypergraph convolution network: A model-based and data-driven integrated approach for fault diagnosis in complex equipment. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 72, 3501811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Yin, A.; He, Q.; Lu, S.; Wei, Y. A feature cross-fusion HGCN based on feature distillation denoising for fault diagnosis of helicopter tail drive system. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 270, 126587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Ma, X.; Qi, P.; Ding, Z.; Jin, J. Learning from heterogeneity: A dynamic learning framework for hypergraphs. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2025, 6, 1513–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CWRU Datasets | ||||
| Condition | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Bearing Type | SKF6205-2RS | SKF6205-2RS | SKF6205-2RS | SKF6205-2RS |
| Load (hp) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Speed (rpm) | 1797 | 1772 | 1750 | 1730 |
| Ottawa Datasets | ||||
| Condition | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Bearing Type | ER16K | ER16K | ER16K | ER16K |
| Speed profile | IS | DS | IDS | DIS |
| Condition | Metric | CNN | LSTM | GRU | GCN | HGCN | AMH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Precision | 0.8500 | 0.8136 | 0.8814 | 0.9273 | 0.8644 | 1.0000 |
| Recall | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| F1-score | 0.9189 | 0.8972 | 0.9369 | 0.9623 | 0.9273 | 1.0000 | |
| 2 | Precision | 0.0000 | 0.6250 | 0.8438 | 0.9298 | 0.9639 | 0.9883 |
| Recall | 0.0000 | 0.0806 | 0.4286 | 0.8833 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| F1-score | 0.0000 | 0.1429 | 0.5684 | 0.9060 | 0.9719 | 0.9839 | |
| 3 | Precision | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| Recall | 0.6000 | 0.7627 | 0.7857 | 0.8596 | 0.8393 | 0.9643 | |
| F1-score | 0.7500 | 0.8654 | 0.8800 | 0.9245 | 0.9126 | 0.9818 | |
| 4 | Precision | 0.4661 | 0.4911 | 0.5955 | 0.8889 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| Recall | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| F1-score | 0.6358 | 0.6587 | 0.7465 | 0.9412 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Bwar, K.H.; Chai, R.; Tse, K.M.; Chai, B.X. Adaptive Multi-View Hypergraph Learning for Cross-Condition Bearing Fault Diagnosis. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2025, 7, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/make7040147
Li Y, Bwar KH, Chai R, Tse KM, Chai BX. Adaptive Multi-View Hypergraph Learning for Cross-Condition Bearing Fault Diagnosis. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction. 2025; 7(4):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/make7040147
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yangyi, Kyaw Hlaing Bwar, Rifai Chai, Kwong Ming Tse, and Boon Xian Chai. 2025. "Adaptive Multi-View Hypergraph Learning for Cross-Condition Bearing Fault Diagnosis" Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction 7, no. 4: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/make7040147
APA StyleLi, Y., Bwar, K. H., Chai, R., Tse, K. M., & Chai, B. X. (2025). Adaptive Multi-View Hypergraph Learning for Cross-Condition Bearing Fault Diagnosis. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction, 7(4), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/make7040147











