Learnable Petri Net Neural Network Using Max-Plus Algebra
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We formally establish a connection between Petri nets, their representations via max-plus-algebra, and specifically designed neural network architectures.
- We propose a learnable representation of a Petri net in the max-plus domain, allowing us to derive its parameters from available process data.
- We propose forward- and backward-propagation algorithms for the architecture, thereby enabling learnable Petri nets. Particularly, we propose a parameter-sharing approach between the date and counter representations, allowing us to learn both representations at once.
- We apply the approach to an application example from production flow shop modelling to illustrate the feasibility of the approach.
2. Related Work
2.1. Petri Net
2.2. Max-Plus Algebra and Neural Networks
2.3. System Identification Using Max-Plus Algebra
2.4. Neural Networks in Production Scheduling
3. Theoretical Background and Relation Between Petri Nets and NN
3.1. Petri Nets
- : set of places;
- : set of transitions;
- : set of arcs;
- : set of colours (data types);
- : colour function assigning a colour set to each place and transition;
- : node connectivity function defining the source and target of each arc;
- : arc expression function specifying the token expressions for each arc;
- : guard function assigning Boolean expressions controlling transition enabling;
- : initialization function specifying the initial coloured token distribution.
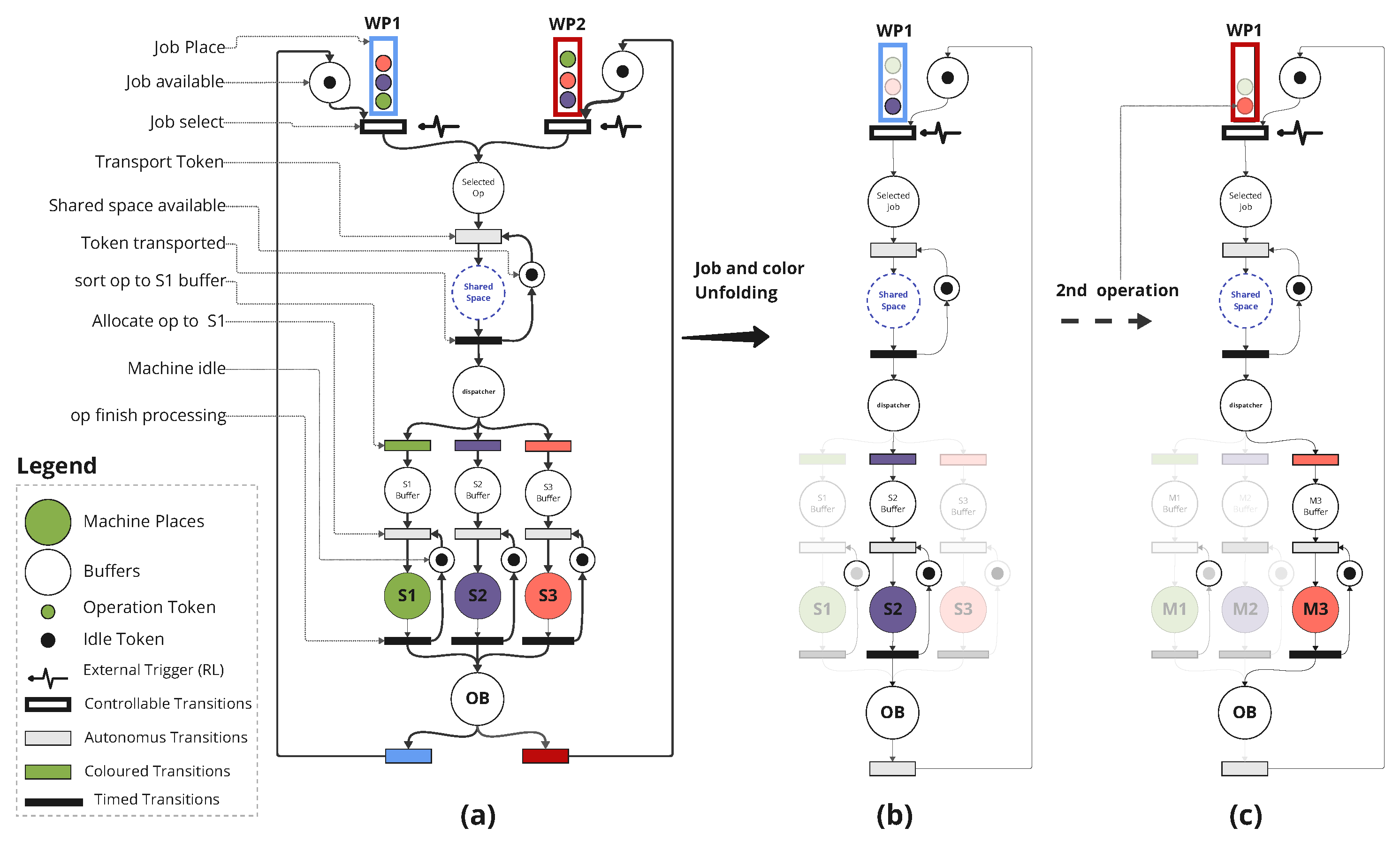
3.2. Petri Net Colour Unfolding
- : set of unfolded places, one per colour per original place.
- : set of unfolded transitions, one per binding per original transition.
- : set of unfolded arcs.
- : arc weight function defined as
- : initial marking function given by
3.3. Timed Event Graphs (TEGs)
3.4. Max-Plus Algebra and TEGs
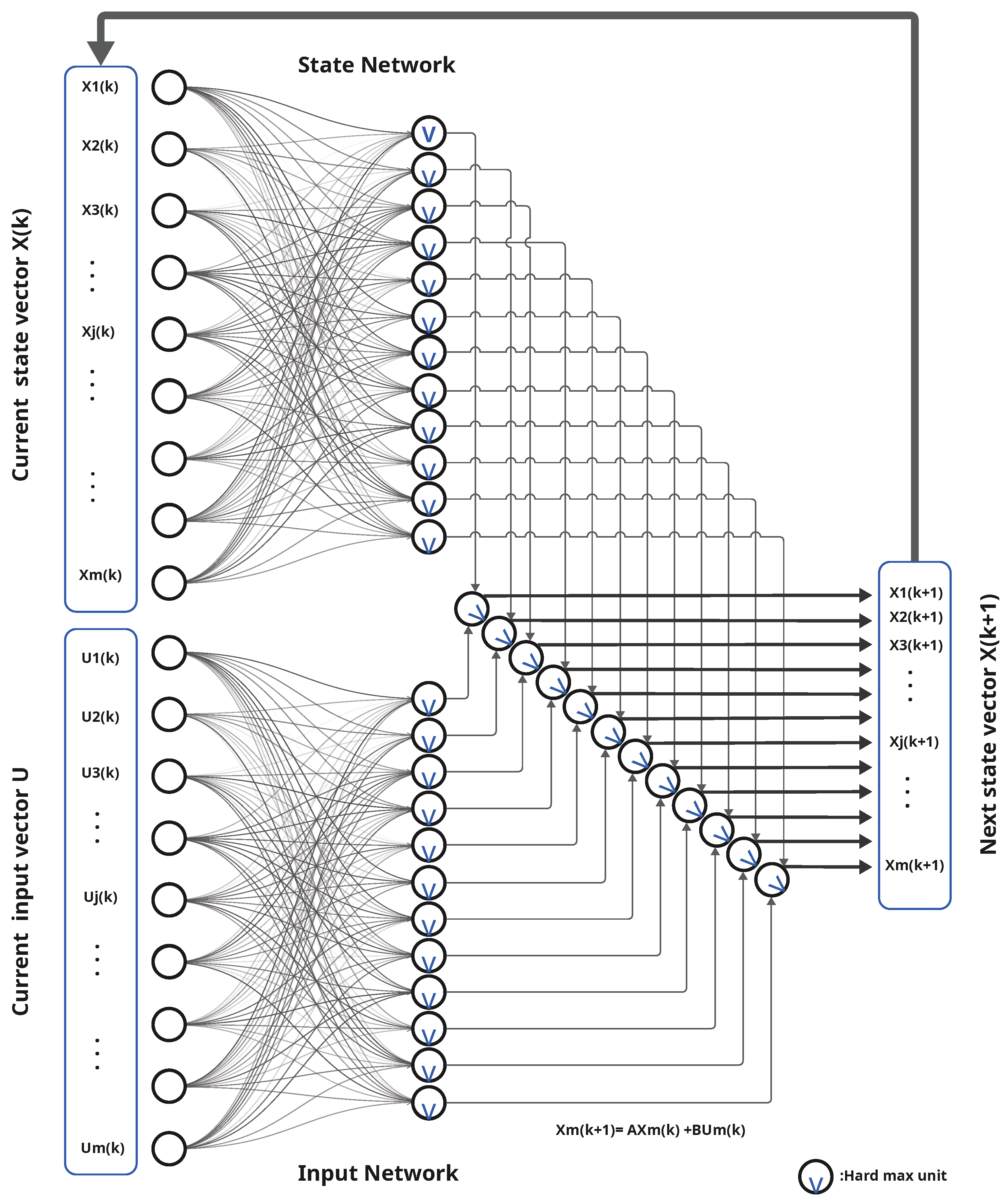
3.5. Neural Networks and TEGs
4. Learning the TEG Parameters Using Supervised Learning
4.1. Problem Statement
4.2. Learning Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 Petri net supervised learning. |
|
4.3. Network Architecture and Tracing
4.4. Back-Propagation
| Algorithm 2 Forward propagation in max-plus algebra. |
|
| Algorithm 3 Back-propagation in max-plus algebra. |
|
5. Application to Production Scheduling for a Robot Manufacturing Cell
5.1. Environment Description: Robot Manufacturing Cell
5.2. Modelling Using Coloured Petri
5.3. Unfolding Coloured Timed Petri Net into Timed Event Graph
5.4. Dater and Counter Representations of the Manufacturing Cell
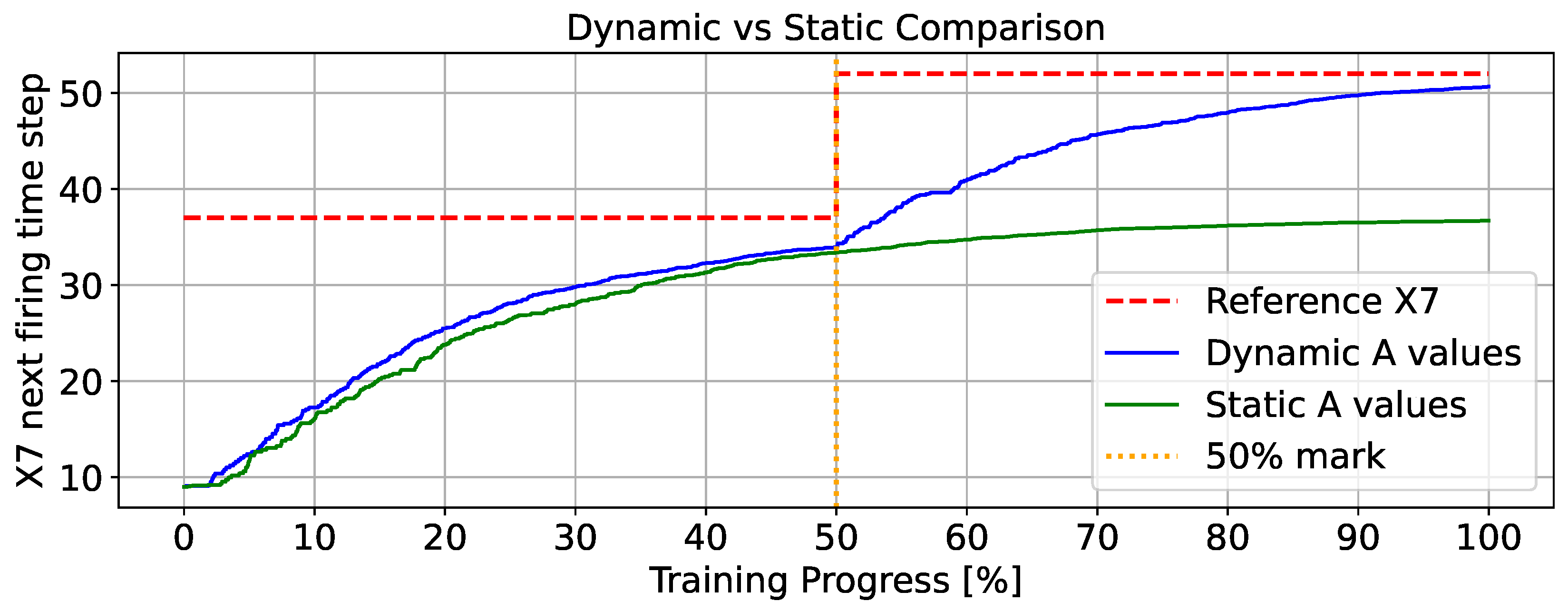
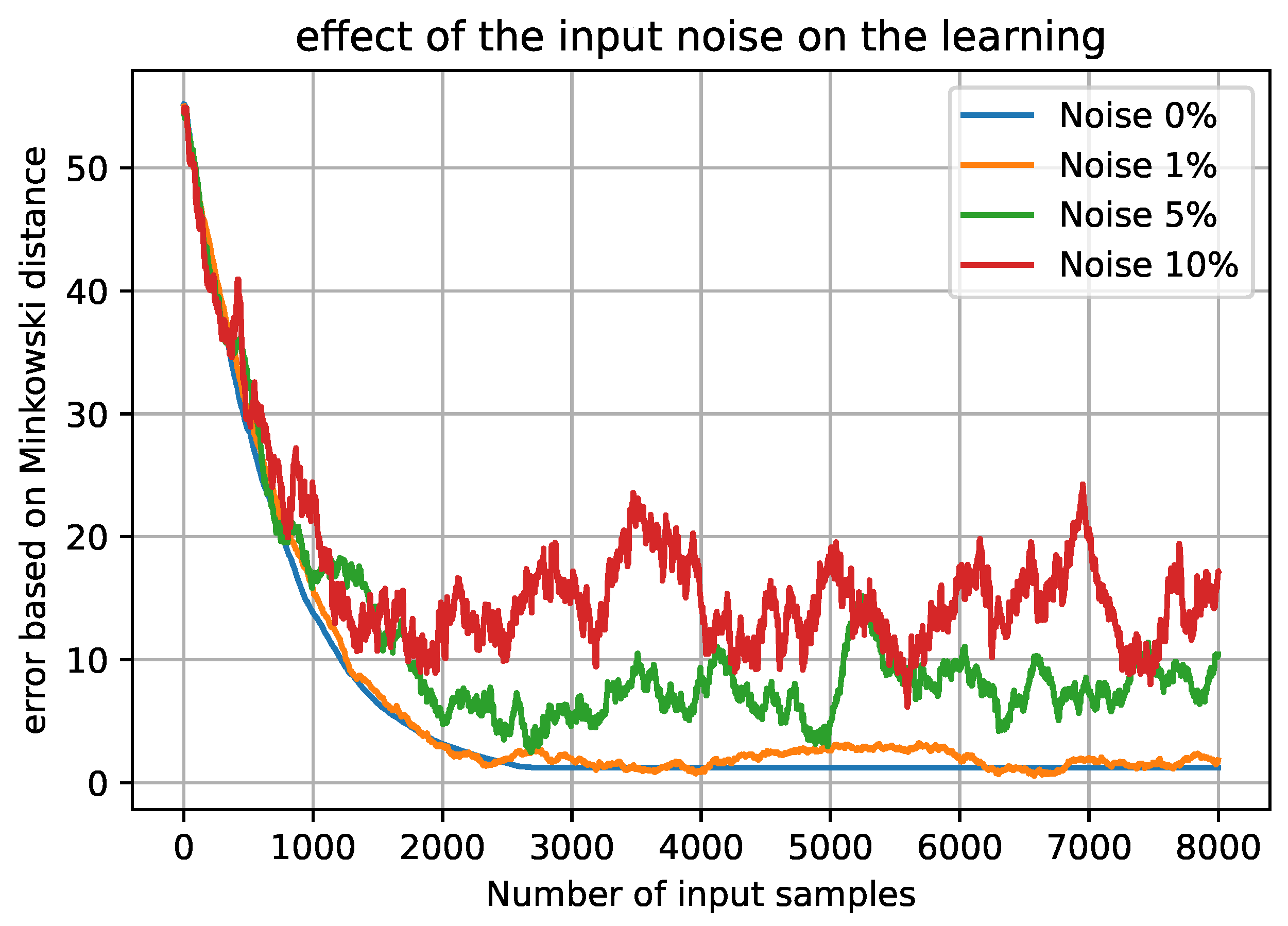
6. Results and Discussion
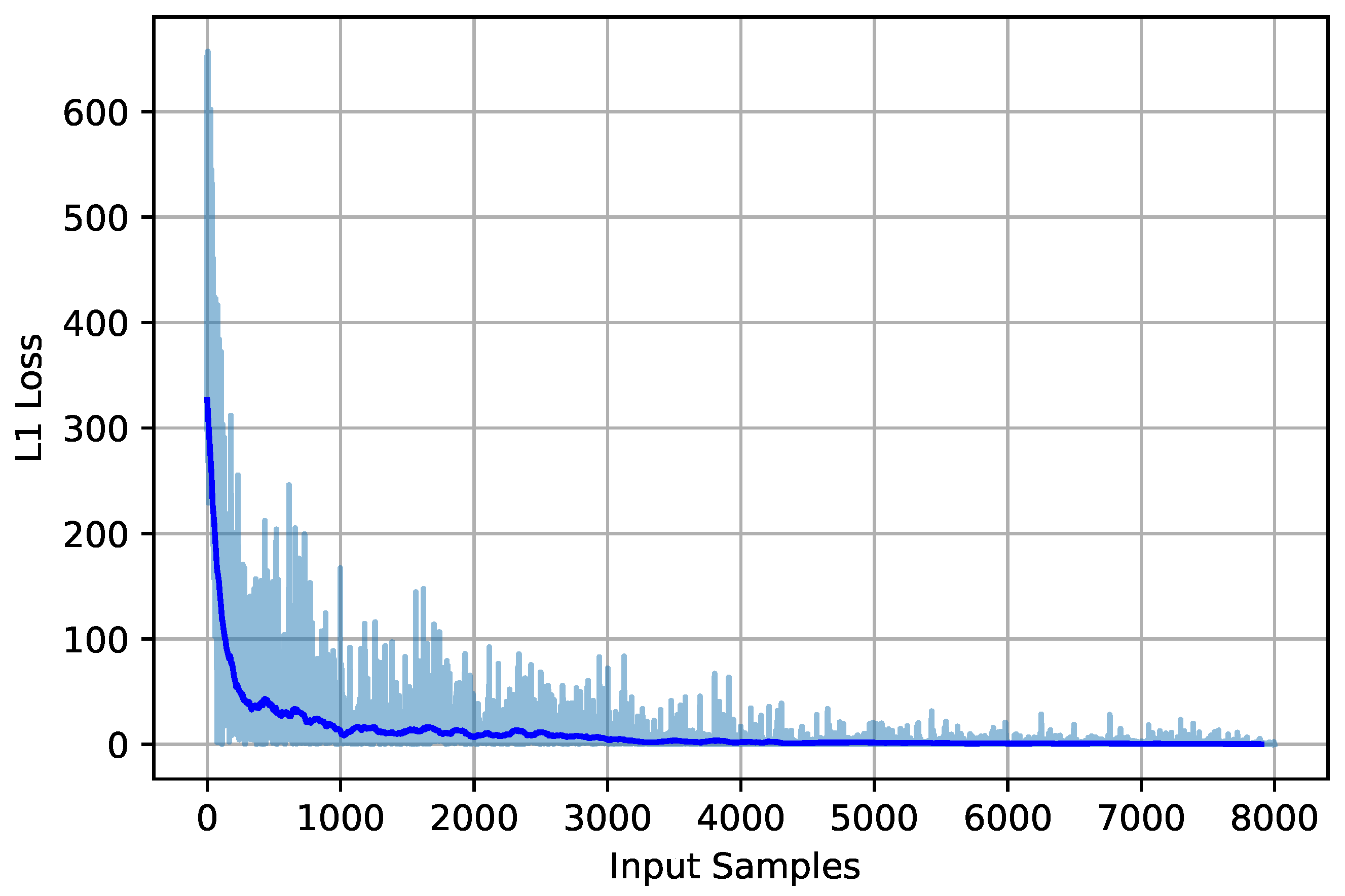
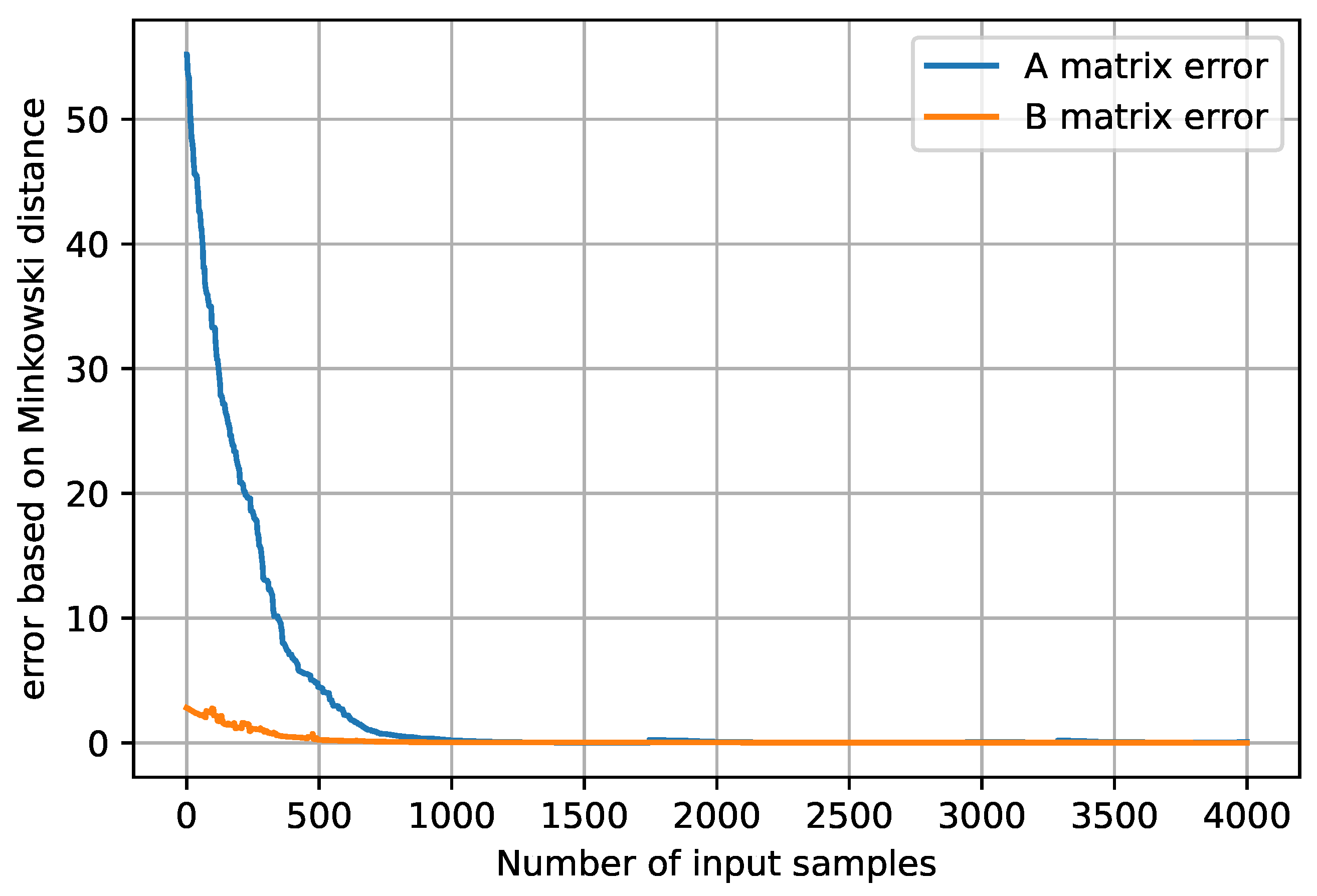
6.1. Dataset Generation and Training
6.2. Results
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lassoued, S.; Schwung, A. Introducing PetriRL: An innovative framework for JSSP resolution integrating Petri nets and event-based reinforcement learning. J. Manuf. Syst. 2024, 74, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.G.; Li, Z.L.; Chen, Y.Z. Hybrid petri net modeling of traffic flow and signal control. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Kunming, China, 12–15 July 2008; Volume 4, pp. 2304–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavone, G.; Dotoli, M.; Seatzu, C. A Survey on Petri Net Models for Freight Logistics and Transportation Systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 1795–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, H.M.; Sekiguchi, T. A timed Petri net and beam search based online FMS scheduling system with routing flexibility. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Sacramento, CA, USA, 9–11 April 1991; pp. 2548–2553. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, K.; Rozenberg, G. High-Level Petri Nets: Theory and Application; Jensen, K., Rozenberg, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Baccelli, F.; Cohen, G.; Olsder, G.J.; Quadrat, J.P. Synchronization and Linearity: An Algebra for Discrete Event Systems; Wiley series in probability and mathematical statistics; J. Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 99–151. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, G.; Moller, P.; Quadrat, J.P.; Viot, M. Algebraic tools for the performance evaluation of discrete event systems. Proc. IEEE 1989, 77, 39–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre-Biel, J.I.; Faulín, J.; Juan, A.A.; Jiménez-Macías, E. Petri Net Model of a Smart Factory in the Frame of Industry 4.0. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatono, I.; Yamagata, K.; Tamura, H. Modeling and online scheduling of flexible manufacturing systems using stochastic Petri nets. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 1991, 17, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, F.; Zeiler, P.; Bertsche, B. Modelling the production systems in industry 4.0 and their availability with high-level Petri nets. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, G.X.; Sussner, P. An introduction to morphological neural networks. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Vienna, Austria, 25–29 August 1996; IEEE: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 1996; Volume 4, pp. 709–717. [Google Scholar]
- Sussner, P.; Esmi, E.L. Morphological perceptrons with competitive learning: Lattice-theoretical framework and constructive learning algorithm. Inf. Sci. 2011, 181, 1929–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charisopoulos, V.; Maragos, P. Morphological perceptrons: Geometry and training algorithms. In Mathematical Morphology and Its Applications to Signal and Image Processing, Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium, ISMM 2017, Fontainebleau, France, 15–17 May 2017; Proceedings 13; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Maragos, P.; Charisopoulos, V.; Theodosis, E. Tropical geometry and machine learning. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 728–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charisopoulos, V.; Maragos, P. A Tropical Approach to Neural Networks with Piecewise Linear Activations. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.08749. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Naitzat, G.; Lim, L.H. Tropical Geometry of Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 5824–5832. [Google Scholar]
- De Schutter, B.; van den Boom, T.J.; Verdult, V. State space identification of max-plus-linear discrete event systems from input-output data. In Proceedings of the 41st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 10–13 December 2002; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 4, pp. 4024–4029. [Google Scholar]
- Farahani, S.S.; van den Boom, T.; De Schutter, B. Exact and approximate approaches to the identification of stochastic max-plus-linear systems. Discret. Event Dyn. Syst. 2014, 24, 447–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.S. Intelligent predictive maintenance for fault diagnosis and prognosis in machine centers: Industry 4.0 scenario. Adv. Manuf. 2017, 5, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, A.; Fraile, J.M.; Chamoso, P.; González-Briones, A.; Sittón, I.; Corchado, J.M. A predictive maintenance model using recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications (SOCO 2019), Seville, Spain, 13–15 May 2019; Proceedings 14. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Usuga Cadavid, J.P.; Lamouri, S.; Grabot, B.; Pellerin, R.; Fortin, A. Machine learning applied in production planning and control: A state-of-the-art in the era of industry 4.0. J. Intell. Manuf. 2020, 31, 1531–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Ma, Y.; Qiao, F.; Gu, X. Data mining-based dynamic scheduling approach for semiconductor manufacturing system. In Proceedings of the 2015 34th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Hangzhou, China, 28–30 July 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 2603–2608. [Google Scholar]
- Priore, P.; Ponte, B.; Puente, J.; Gómez, A. Learning-based scheduling of flexible manufacturing systems using ensemble methods. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 126, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wang, W.; Ren, S.; Zhong, R.Y.; Jiang, J. A proactive task dispatching method based on future bottleneck prediction for the smart factory. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2019, 32, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Liu, Z.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Tan, J.; Wu, F. Petri net-based dynamic scheduling of flexible manufacturing system via deep reinforcement learning with graph convolutional network. J. Manuf. Syst. 2020, 55, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.E.; Koo, J.; Chaterji, S.; Bagchi, S. Minerva: A reinforcement learning-based technique for optimal scheduling and bottleneck detection in distributed factory operations. In Proceedings of the 2018 10th International Conference On Communication Systems & Networks, Bengaluru, India, 3–7 January 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Waschneck, B.; Reichstaller, A.; Belzner, L.; Altenmüller, T.; Bauernhansl, T.; Knapp, A.; Kyek, A. Optimization of global production scheduling with deep reinforcement learning. Procedia CIRP 2018, 72, 1264–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dietterich, T.G. A reinforcement learning approach to job-shop scheduling. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–25 August 1995; Volume 95, pp. 1114–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Gabel, T.; Riedmiller, M. Adaptive reactive job-shop scheduling with reinforcement learning agents. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Intell. Comput. 2008, 24, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, M.S.A.; Schwung, A. Reinforcement learning on job shop scheduling problems using graph networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.03836. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, M.S.A.; Schwung, A. Graph neural networks-based scheduler for production planning problems using reinforcement learning. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 69, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Chun, J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.; Park, J. Learning to schedule job-shop problems: Representation and policy learning using graph neural network and reinforcement learning. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 3360–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía, G.; Caballero-Villalobos, J.P.; Montoya, C. Petri Nets and Deadlock-Free Scheduling of Open Shop Manufacturing Systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2018, 48, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisig, W. Understanding Petri Nets; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Moro, A.R.; Yu, H.; Kelleher, G. Hybrid heuristic search for the scheduling of flexible manufacturing systems using Petri nets. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 2002, 18, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K. Coloured Petri Nets: Basic Concepts, Analysis Methods and Practical Use; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Heiner, M.; Yang, M. An efficient method for unfolding colored Petri nets. In Proceedings of the 2012 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), Berlin, Germany, 9–12 December 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- DiCesare, F.; Harhalakis, G.; Proth, J.M.; Silva Suarez, M.; Vernadat, F.B. Practice of Petri Nets in Manufacturing; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Butkovič, P. Max-Linear Systems: Theory and Algorithms; Springer monographs in mathematics; Springer: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Hornik, K.; Stinchcombe, M.; White, H. Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural Netw. 1989, 2, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhi, R.; Nowak, R.D. The Role of Neural Network Activation Functions. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 1779–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.; Gu, S.; Poole, B. Categorical Reparameterization with Gumbel-Softmax. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1611.01144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwung, D.; Csaplar, F.; Schwung, A.; Ding, S.X. An application of reinforcement learning algorithms to industrial multi-robot stations for cooperative handling operation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 15th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Emden, Germany, 24–26 July 2017; pp. 194–199. [Google Scholar]
- Schwung, A.; Schwung, D.; Hameed, M.S.A. Cooperative Robot Control in Flexible Manufacturing Cells. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 17th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Helsinki-Espoo, Finland, 22–25 July 2019; Volume 1, pp. 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Trunk, J.; Cottenceau, B.; Hardouin, L.; Raisch, J. Model decomposition of timed event graphs under periodic partial synchronization: Application to output reference control. Discret. Event Dyn. Syst. 2020, 30, 605–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Station | ||
|---|---|---|
| Input station | 0 | – |
| Input station | – | 0 |
| Working station | 10 | 30 |
| Working station | 20 | 10 |
| Working station | 30 | 20 |
| Output station | 0 | 0 |
| Noise Level | Matrix Distance | State Distance |
|---|---|---|
| 2.05 | 2.82 | |
| 9.07 | 9.59 | |
| 12.98 | 29.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdul Hameed, M.S.; Lassoued, S.; Schwung, A. Learnable Petri Net Neural Network Using Max-Plus Algebra. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2025, 7, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/make7030100
Abdul Hameed MS, Lassoued S, Schwung A. Learnable Petri Net Neural Network Using Max-Plus Algebra. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction. 2025; 7(3):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/make7030100
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdul Hameed, Mohammed Sharafath, Sofiene Lassoued, and Andreas Schwung. 2025. "Learnable Petri Net Neural Network Using Max-Plus Algebra" Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction 7, no. 3: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/make7030100
APA StyleAbdul Hameed, M. S., Lassoued, S., & Schwung, A. (2025). Learnable Petri Net Neural Network Using Max-Plus Algebra. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction, 7(3), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/make7030100






