The Human-Centred Design of a Universal Module for Artificial Intelligence Literacy in Tertiary Education Institutions
Abstract
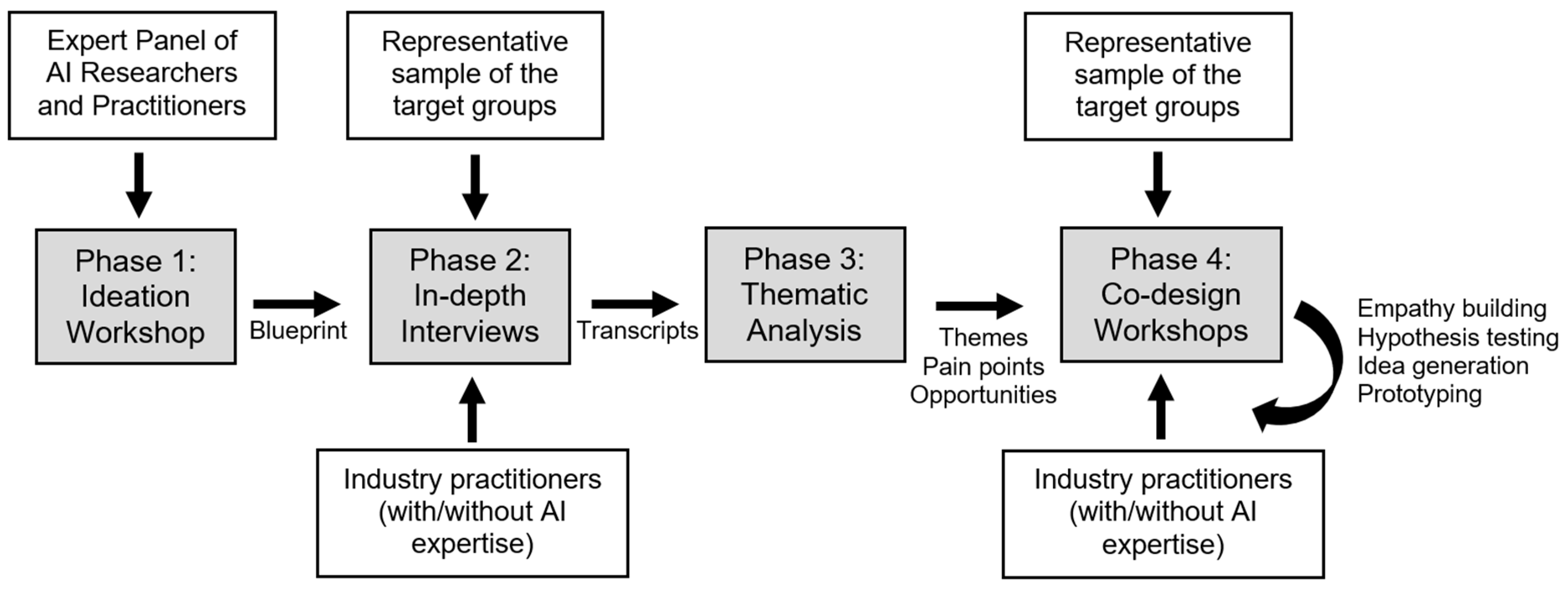
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. The Universal AI Literacy Module
3.1. Foundational AI Knowledge
3.2. Solving Problems Using AI
3.3. Ethical and Responsible Practice of AI
3.4. Entrepreneurship and Innovation with AI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Silva, D.; Kaynak, O.; El-Ayoubi, M.; Mills, N.; Alahakoon, D.; Manic, M. Opportunities and Challenges of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Research, Education, Industry Engagement and Social Impact. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2024, in press.
- Gilster, P.; Glister, P. Digital Literacy; Wiley Computer Pub: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, P.; Sharma, B.; Chaudhary, K. Digital literacy: A review of literature. Int. J. Technoethics 2020, 11, 65–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Yu, Z. A literature review of digital literacy over two decades. Educ. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 2533413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejaković, P.; Mrnjavac, Ž. The importance of digital literacy on the labour market. Empl. Relat. Int. J. 2020, 42, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D.T.K.; Leung, J.K.L.; Chu, S.K.W.; Qiao, M.S. Conceptualizing AI literacy: An exploratory review. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2021, 2, 4221–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Blunt, T.; Magerko, B. Co-Designing AI Literacy Exhibits for Informal Learning Spaces. Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2021, 5, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Megerko, B. What is AI literacy? Competencies and design considerations. In Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 April 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zou, X.H.D.a.; Cheng, G.; Liu, C. Two decades of artificial intelligence in education. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2022, 25, 28–47. [Google Scholar]
- Kandlhofer; Steinbauer, M.; Hirschmugl-Gaisch, G.; Huber, S.; Huber, P. Artificial intelligence and computer science in education: From kindergarten to university. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), Erie, PA, USA, 12–15 October 2016; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zawacki-Richter, O.; Marín, I.V.; Bond, M.; Gouverneur, F. Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence applications in higher education–where are the educators? Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2019, 16, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuka, L.; Hörmann, C.; Sabitzer, B. Teaching and Learning with AI in Higher Education: A Scoping Review. Learn. Technol. Technol. Learn. Exp. 2022, 551, 551–571. [Google Scholar]
- Eloundou, T.; Manning, S.; Mishkin, P.; Rock, D. Gpts are gpts: An early look at the labor market impact potential of large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.10130. [Google Scholar]
- Laupichler, C.M.; Aster, A.; Schirch, J.; Raupach, T. Artificial intelligence literacy in higher and adult education: A scoping literature review. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2022, 3, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, B.S.; Krathwohl, D.R. Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: The Classification of Educational Goals. Book 1, Cognitive Domain; Longman: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Ng, K.D.T.; Chu, W.S.K. Artificial intelligence (AI) literacy in early childhood education: The challenges and opportunities. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2023, 4, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lee, I.; Ali, S.; DiPaola, D.; Cheng, Y.; Breazeal, C. Integrating ethics and career futures with technical learning to promote AI literacy for middle school students: An exploratory study. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2022, 33, 290–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casal-Otero, L.; Catala, A.; Fernández-Morante, C.; Taboada, M.; Cebreiro, B.; Barro, S. AI literacy in K-12: A systematic literature review. Int. J. STEM Educ. 2023, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassignol, M.; Khoroshavin, A.; Klimova, A.; Bilyatdinova, A. Artificial Intelligence trends in education: A narrative overview. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 136, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Mou, J.; Jiang, Z. Artificial intelligence innovation in education: A Twenty-year data-driven historical analysis. Int. J. Innov. Stud. 2020, 4, 34–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, D.; Alahakoon, D. An artificial intelligence life cycle: From conception to production. Patterns 2022, 3, 100489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallaperuma, D.; De Silva, D.; Alahakoon, D.; Yu, X. Intelligent detection of driver behavior changes for effective coordination between autonomous and human driven vehicles. In Proceedings of the IECON 2018-44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Washington, DC, USA, 21–23 October 2018; pp. 3120–3125. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaratne, R.; Alahakoon, D.; De Silva, D.; Kumara, H.; Yu, X. Hierarchical two-stream growing self-organizing maps with transience for human activity recognition. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 7756–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, D.; Burstein, F.; Jelinek, H.F.; Stranieri, A. Addressing the complexities of big data analytics in healthcare: The diabetes screening case. Australas. J. Inf. Syst. 2015, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamishka, S.; Madhavi, I.; Nawaratne, R.; Alahakoon, D.; De Silva, D.; Chilamkurti, N.; Nanayakkara, V. A voice-based real-time emotion detection technique using recurrent neural network empowered feature modelling. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 35173–35194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, D.; Yu, X.; Alahakoon, D.; Holmes, G. Semi-supervised classification of characterized patterns for demand forecasting using smart electricity meters. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Beijing, China, 20–23 August 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, W.; Liu, J. Artificial Intelligence and emerging digital technologies in the energy sector. Appl. Energy 2021, 303, 117615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, D.; Mills, N.; El-Ayoubi, M.; Manic, M.; Alahakoon, D. ChatGPT and Generative AI Guidelines for Addressing Academic Integrity and Augmenting Pre-Existing Chatbots. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Orlando, FL, USA, 4–6 April 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kleyko, D.; Osipov, E.; De Silva, D.; Wiklund, U.; Alahakoon, D. Integer self-organizing maps for digital hardware. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Budapest, Hungary, 14–19 July 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaratne, R.; Bandaragoda, T.; Adikari, A.; Alahakoon, D.; De Silva, D.; Yu, X. Incremental knowledge acquisition and self-learning for autonomous video surveillance. In Proceedings of the IECON 2017-43rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Beijing, China, 29 October–1 November 2017; pp. 4790–4795. [Google Scholar]
- Matharaarachchi, A.; Mendis, W.; Randunu, K.; De Silva, D.; Gamage, G.; Moraliyage, H.; Mills, N.; Jennings, A. Optimizing Generative AI Chatbots for Net-Zero Emissions Energy Internet-of-Things Infrastructure. Energies 2024, 17, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Dai, Y.; Yu, S.P.; Sun, L. A comprehensive survey of ai-generated content (aigc): A history of generative ai from gan to chatgpt. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.04226. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Bosma, M.; Zhao, Y.V.; Guu, K.; Yu, W.A.; Lester, B.; Le, V.Q. Finetuned language models are zero-shot learners. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.01652. [Google Scholar]
- Maguire, M. Methods to support human-centred design. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 2001, 55, 587–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTaggart, R. Principles for participatory action research. Adult Educ. Q. 1991, 41, 168–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askeroth, H.J.; Richardson, C.J. Instructor perceptions of quality learning in MOOCs they teach. Online Learn. 2019, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašević, D.; Siemens, G.; Sadiq, S. Empowering learners for the age of artificial intelligence. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2023, 4, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brophy, E.J.; Freibergand, J.H. Beyond behaviorism: Changing the classroom management paradigm. Allyn Bacon 1999, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honebein, C.P. Seven goals for the design of constructivist learning environments. Constr. Learn. Environ. Case Stud. Instr. Des. 1996, 11, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, B.; Christensen, B.L. Educational Research: Quantitative, Qualitative, and Mixed Approaches; SAGE Publications: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hmelo-Silver, E.C.; Duncan, G.R.; Chinn, A.C. Scaffolding and achievement in problembased and inquiry learning: A response to Kirschner, Sweller, and Clark (2006). Educ. Psychol. 2007, 42, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espey, M. Enhancing critical thinking using team-based learning. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2018, 37, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styers, L.M.; Zandt, V.A.P.; Hayden, L.K. Active learning in flipped life science courses promotes development of critical thinking skills. CBE—Life Sci. Educ. 2018, 17, ar39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanarajan, G. Sustaining knowledge societies through distance learning: The nature of the challenge. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual Conference of the Association of Asian Open Universities, Jakarta, Indonesia, 23–26 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers, U.D.; Pawlowski, M.J. Quality in European e-learning: An introduction. In Handbook on Quality and Standardisation in e-Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.C.; Tsai, J.R.; Finger, G.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yeh, D. What drives a successful e-learning? An empirical investigation of the critical factors influencing learner satisfaction. Comput. Educ. 2008, 50, 1183–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.; Bolliger, U.D. Engagement matters: Student perceptions on the importance of engagement strategies in the online learning environment. Online Learn. 2018, 22, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H. Online learning: The meanings of student engagement. Educ. J. 2020, 9, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, R.D.; Cleveland-Innes, M. Facilitating cognitive presence in online learning: Interaction is not enough. Am. J. Distance Educ. 2005, 19, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roddy, C.; Amietr, D.; Chung, J.; Holt, C.; Shaw, L.; McKenzie, S.; Garivaldis, F.; Lodge, M.J.; Mund, E.M. Applying best practice online learning, teaching, and support to intensive online environments: An integrative review. Front. Educ. 2017, 2, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veale, M.; Borgesius, Z.F. Demystifying the Draft EU Artificial Intelligence Act—Analysing the good, the bad, and the unclear elements of the proposed approach. Comput. Law Rev. Int. 2021, 22, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagendorff, T. The ethics of AI ethics: An evaluation of guidelines. Minds Mach. 2020, 30, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K. CHATGPT Sets Record for Fastest-Growing User Base—Analyst Note. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/technology/chatgpt-sets-record-fastest-growing-user-base-analyst-note-2023-02-01/ (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Lee, A.J. Algorithmic bias and the New Chicago School. Law 2022, 14, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government, A. Australian Universities Accord, Interim Report; Australian Government Department of Education: Canberra, Australia, 2023.
| Constructs (With Levels of Learning from Bloom’s Taxonomy) | Topics |
|---|---|
| Foundational AI Knowledge (Remember, Understand) | Applications of AI across diverse disciplines and industries |
| The lifecycle of an AI application, from design to deployment | |
| Datasets and attributes used for AI model building | |
| Algorithms used for learning, reasoning, optimisation | |
| AI models and hyper-parameters | |
| AI model evaluation methods and metrics | |
| AI model deployment and scalability of AI solutions | |
| Management of AI systems and solutions | |
| Solving Problems using AI (Understand, Analyse, Apply) | Basic to advanced skills in prompt engineering |
| Using AI to produce creative work | |
| Identification and design of an AI solution | |
| Fit for purpose comparison of existing AI solutions | |
| AI model interpretation and explainability | |
| Insights generation using AI solutions | |
| Building Human-in-the-Loop AI systems | |
| Evaluation of AI-based decision-making, methods and metrics | |
| Ethical and Responsible Practice of AI (Analyse, Apply, Evaluate) | AI Regulations, local and international |
| AI ethics guidelines, codes of conduct, best practices | |
| Responsible approaches to prompt engineering | |
| Responsible approaches to AI creativity | |
| Bias detection, reporting and remediation methods | |
| Responsible use and referencing of all AI-generated content | |
| Methods and metrics for the detection of AI-generated content | |
| Lifelong learning for the responsible practice of AI | |
| Entrepreneurship and Innovation with AI (Evaluate, Create) | Critical thinking and analytical mindset |
| AI-first approaches to business strategy, operations, planning | |
| Recruiting and leading AI teams | |
| Fundamentals of IP, patents and commercialisation | |
| Pitching AI to investors | |
| Scaling AI solutions | |
| Presenting AI to non-technical audiences |
| Stakeholder Group | Foundational Knowledge of AI | Solving Problems Using AI | Ethical and Responsible Practice of AI | Entrepreneurship and Innovation with AI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coursework students | Describing the AI capabilities of a smartphone application | Understand complex topics using AI-based explanations | Guidelines for responsible use of Generative AI content in work, study, and personal settings | Recognising alternate career pathways for graduate employability |
| Research students | Unpacking the functionality of an AI research tool for lit review | Comparing research methods by expected outcomes | Ensuring the reproducibility of research outcomes when using AI-based research tools | Contributing a library of customised AI tools for discipline specific research activities |
| Academic staff | Recognising how AI-generated content can be included in assignment submissions | Integrating classroom experience into personalised, authentic assessments | Knowing the risks of bias, inaccuracies and fallacies when integrating AI into learning | Advocating and implementing personalised learner journeys that reduce attrition |
| Professional staff | Identifying opportunities for integrating AI into work activities | Using Generative AI for process automation | Preserving privacy, confidentiality and integrity of sensitive data when using AI tools | Progressing the digital transformation of institutional operations into AI transformation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Silva, D.; Jayatilleke, S.; El-Ayoubi, M.; Issadeen, Z.; Moraliyage, H.; Mills, N. The Human-Centred Design of a Universal Module for Artificial Intelligence Literacy in Tertiary Education Institutions. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2024, 6, 1114-1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/make6020051
De Silva D, Jayatilleke S, El-Ayoubi M, Issadeen Z, Moraliyage H, Mills N. The Human-Centred Design of a Universal Module for Artificial Intelligence Literacy in Tertiary Education Institutions. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction. 2024; 6(2):1114-1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/make6020051
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Silva, Daswin, Shalinka Jayatilleke, Mona El-Ayoubi, Zafar Issadeen, Harsha Moraliyage, and Nishan Mills. 2024. "The Human-Centred Design of a Universal Module for Artificial Intelligence Literacy in Tertiary Education Institutions" Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction 6, no. 2: 1114-1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/make6020051
APA StyleDe Silva, D., Jayatilleke, S., El-Ayoubi, M., Issadeen, Z., Moraliyage, H., & Mills, N. (2024). The Human-Centred Design of a Universal Module for Artificial Intelligence Literacy in Tertiary Education Institutions. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction, 6(2), 1114-1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/make6020051






