Semi-Supervised Faster RCNN-Based Person Detection and Load Classification for Far Field Video Surveillance
Abstract
1. Introduction and Related Works
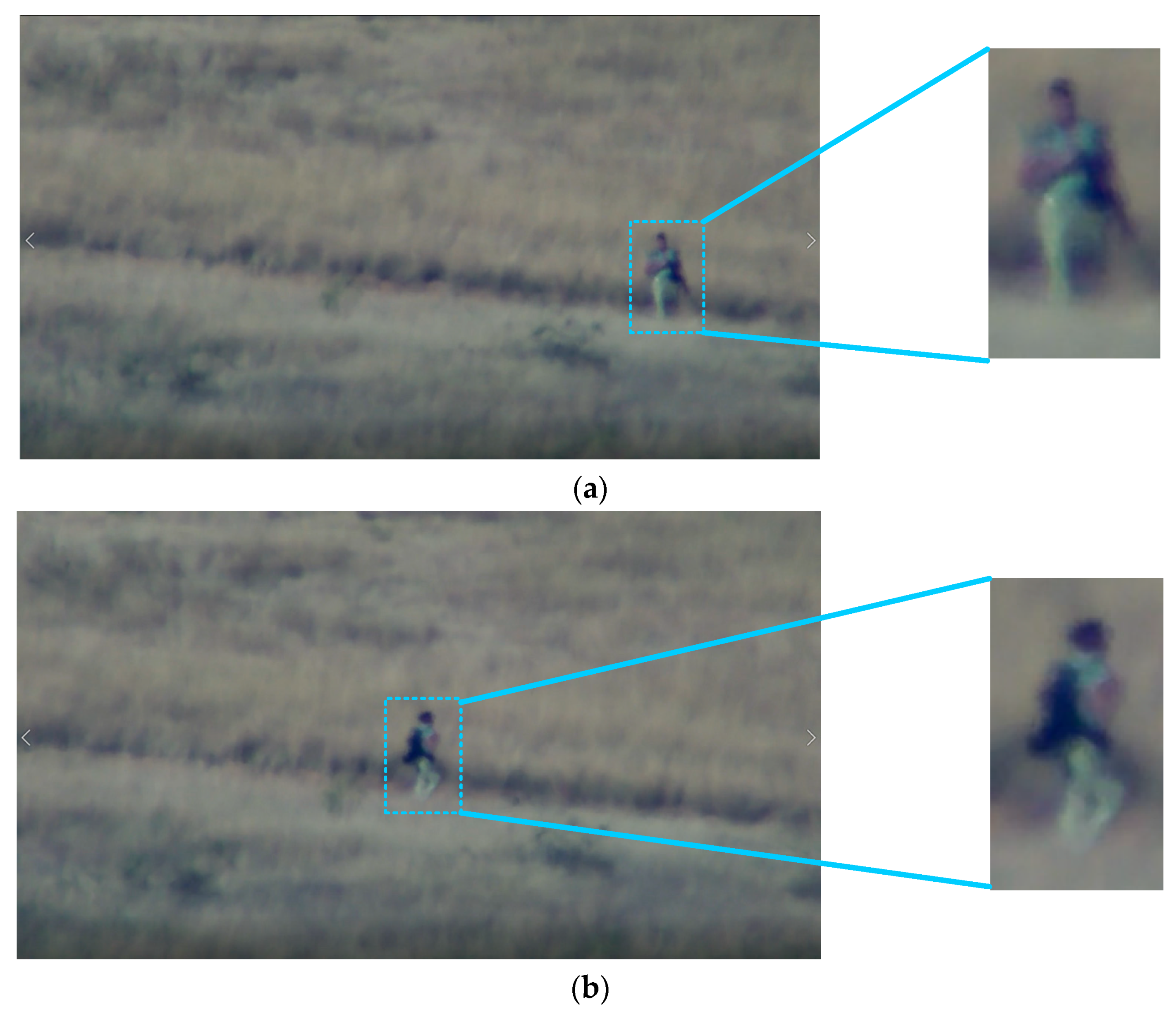
2. Far Field Video Dataset
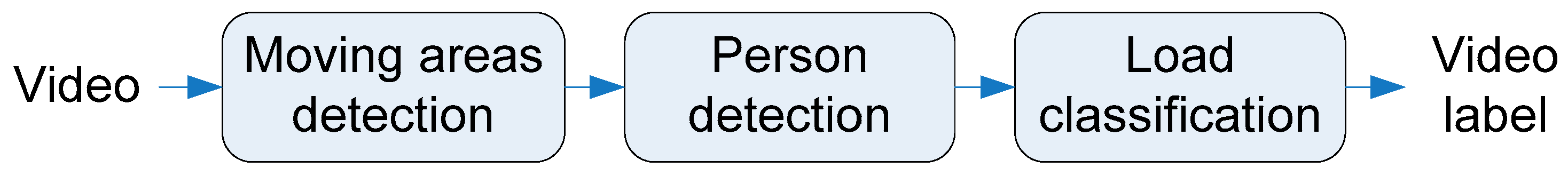
3. Developed Detection and Classification Approach
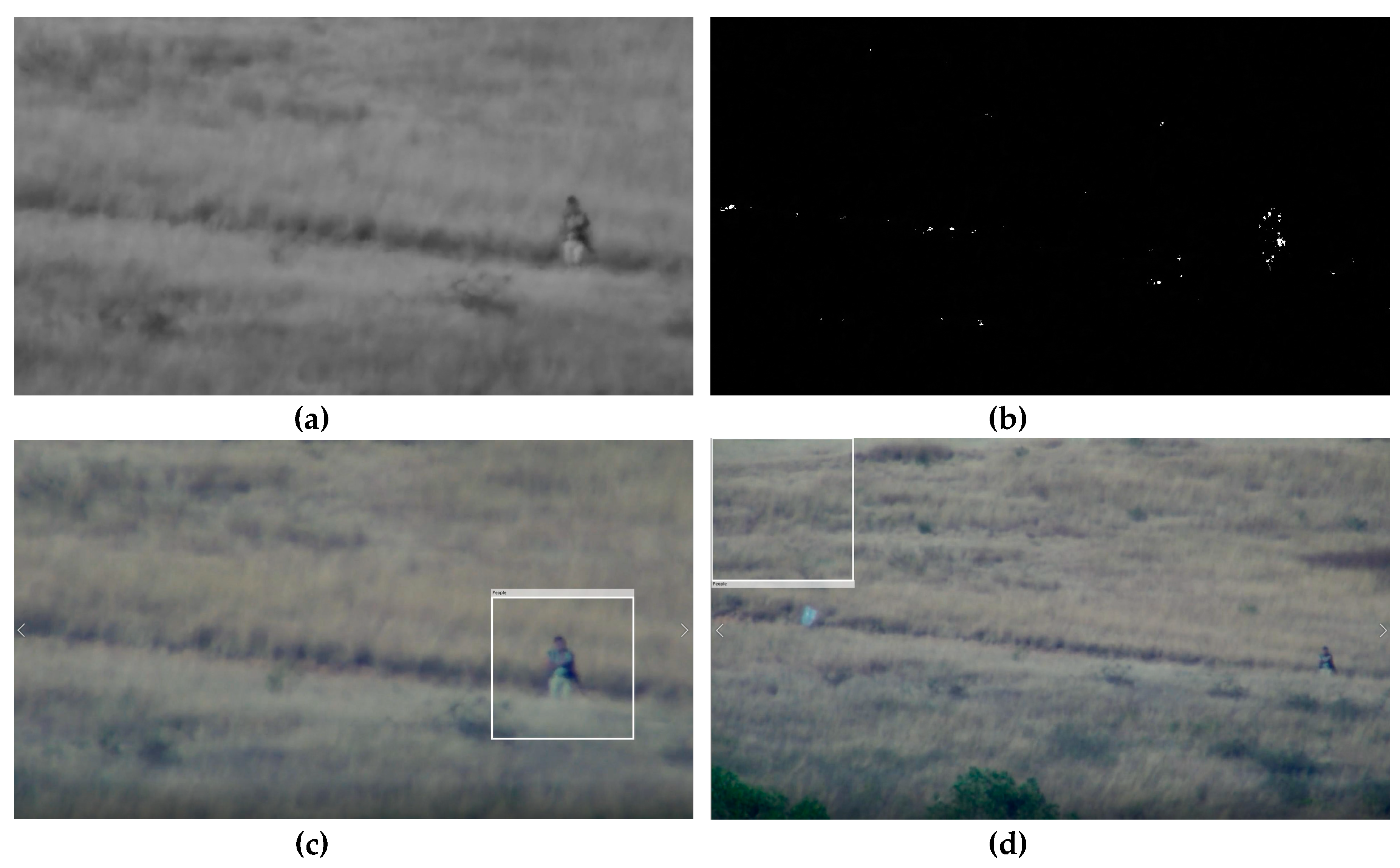
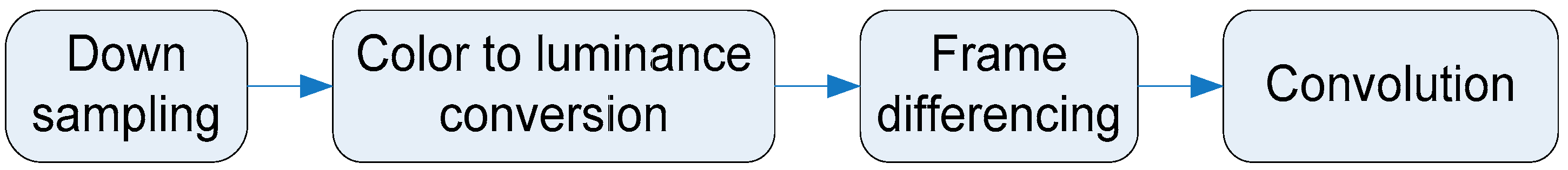
3.1. Moving Areas Detection
3.2. Person Detection
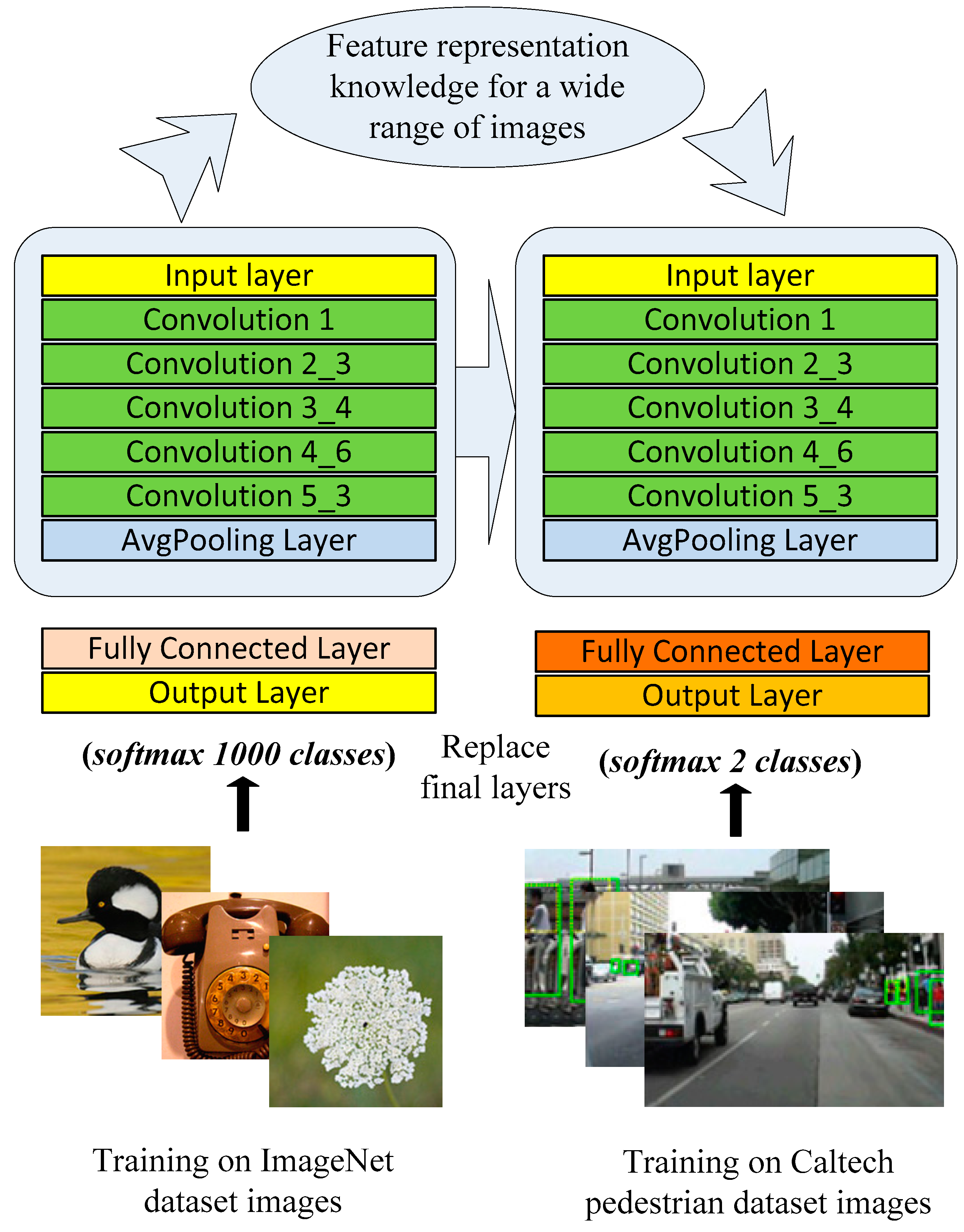
3.2.1. Faster RCNN Detector
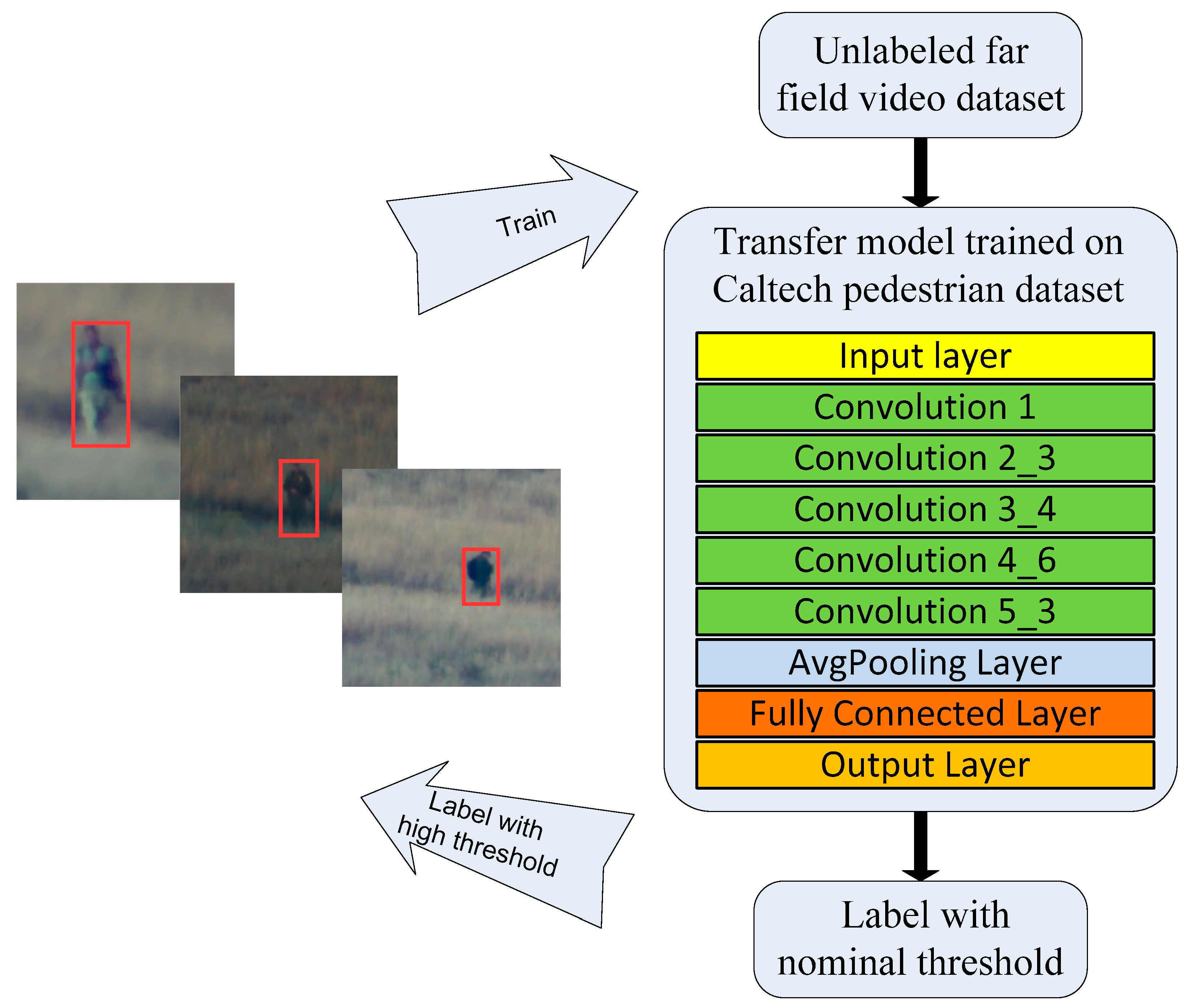
3.2.2. Semi-Supervised Faster RCNN (SF-RCNN) Detector
3.3. Load Classification
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Person Detection Results
4.2. Load Classification Results
4.3. Combined Detection and Classification Results
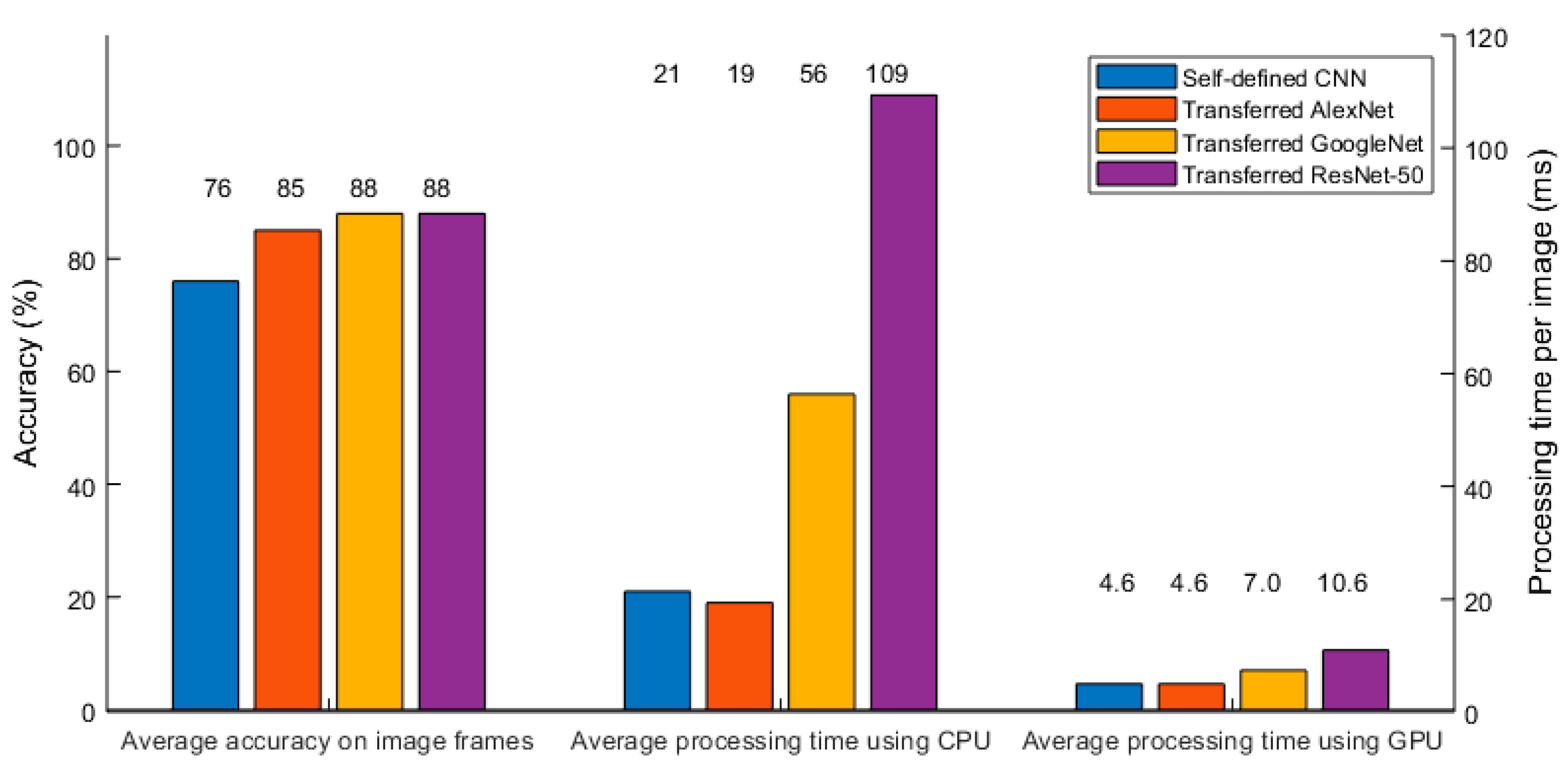
4.4. Real-Time Processing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Markets and Markets. Available online: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/video-surveillance-market-645.html (accessed on 20 February 2019).
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of Oriented Gradients for Human Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Dollar, P.; Wojek, C.; Shiele, B.; Perona, P. Pedestrian Detection: A Benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 304–311. [Google Scholar]
- Dollar, P.; Appel, R.; Belongie, S.; Perona, P. Fast Feature Pyramids for Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 1532–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.; Xia, J. Combining static and dynamic features for real-time moving pedestrian detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 3781–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Liu, B.; Li, R. Pedestrian object detection with fusion of visual attention mechanism and semantic computation. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.S.; Kim, B.G.; Hwang, Y.S.; Kwon, K.K. (2016) Fast multi-feature pedestrian detection algorithm based on histogram of oriented gradient using discrete wavelet transform. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2016, 75, 15229–15245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y. Research on the algorithm of pedestrian recognition in front of the vehicle based on SVM. In Proceedings of the 11th International Symposium on Distributed Computing and Applications to Business, Engineering and Science, DCABES 2012, Guilin, China, 19–22 October 2012; pp. 396–400. [Google Scholar]
- Chavez-Garcia, R.O.; Aycard, O. Multiple Sensor Fusion and Classification for Moving Object Detection and Tracking. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, T.X.; Yan, S. An HOG-LBP human detector with partial occlusion handling. In Proceedings of the IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 29 September–2 October 2009; pp. 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Roncancio, H.; Hernandes, A.C.; Becker, M. Vision-based system for pedestrian recognition using a tuned SVM classifier. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Engineering Applications, Bogota, Columbia, 2–4 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Choi, I.K.; Ko, M.S.; Bae, J.; Kwak, S.; Yoo, J. Vulnerable pedestrian detection and tracking using deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Electronics, Information, and Communication (ICEIC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–27 January 2018; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.L.; Song, Y.; Hao, X.; Shen, Y.; Qian, M. Multispectral pedestrian detection based on deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Xiamen, China, 22–25 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- González, A.; Fang, Z.; Socarras, Y.; Serrat, J.; Vázquez, D.; Xu, J.; López, A.M. Pedestrian Detection at Day/Night Time with Visible and FIR Cameras: A Comparison. Sensors 2016, 16, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosang, J.; Benenson, R.; Dollar, P.; Schiele, B. What Makes for Effective Detection Proposals? IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 814–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazil, G.; Yin, X.; Liu, X. Illuminating Pedestrians via Simultaneous Detection and Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4960–4969. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Laszewski, M.; Kehtarnavaz, N. Deep Learning-Based Person Detection and Classification for Far Field Video Surveillance. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE Dallas Circuits and Systems Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 2–12 November 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Dollár, P.; Wojek, C.; Schiele, B.; Perona, P. Pedestrian detection: An evaluation of the state of the art. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 34, 743–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwmans, T. Traditional and recent approaches in background modeling for foreground detection: An overview. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2014, 11, 31–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, C.; Grimson, W.E.L. Adaptive background mixture models for real-time tracking. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 23–25 June 1999; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Elgammal, A.; Harwood, D.; Davis, L. Non-Parametric Model for Background Subtraction. In Computer Vision-ECCV 2000; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2000; pp. 751–767. [Google Scholar]
- Heikkilä, M.; Pietikäinen, M.; Heikkilä, J. A texture-basedmethod for detectingmoving objects. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Kingston, UK, 7–9 September 2004; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga, S.; Shimada, A.; Nagahara, H.; Taniguchi, R. Statistical Local Difference Pattern for Background Modeling. IPSJ Trans. Comput. Vis. Appl. 2011, 3, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, M.; Mahmood, A.; Javed, S.; Jung, S.K. Unsupervised Deep Context Prediction for Background Estimation and Foreground Segmentation. Mach. Vision Appl. 2019, 30, 375–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minematsu, T.; Shimada, A.; Uchiyama, H.; Taniguchi, R.I. Analytics of Deep Neural Network-based Background Subtraction. J. Imaging 2018, 4, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmans, T.; Javed, S.; Sultana, M.; Jung, S.K. Deep neural network concepts for background subtraction: A systematic review and comparative evaluation. Neural Netw. 2019, 117, 8–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaee, M.; Dinh, D.T.; Rigoll, G. A deep convolutional neural network for video sequence background subtraction. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 76, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R. A short introduction to boosting. J. JSAI 1999, 14, 771–780. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, P.; Wang, W. Better region proposals for pedestrian detection with R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing, Chengdu, China, 27–30 Nov 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zitnick, C.L.; Dollar, P. Edge Boxes: Locating Object Proposals from Edges. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 391–405. [Google Scholar]
- Uijlings, J.R.R.; Van De Sande, K.E.A.; Gevers, T.; Smeulders, A.W.M. Selective search for object recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2013, 104, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Yang, Q. A Survey on Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2010, 22, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- ImageNet. Available online: http://www.image-net.org (accessed on 20 February 2019).
- Zhu, X.; Goldberg, A. Introduction to Semi-Supervised Learning. Synthesis lectures on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning; Morgan & Claypool: San Rafael, California, USA, 2009; pp. 1–130. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, Nevada, USA, 3–6 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going Deeper with Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mathworks. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/vision/examples/object-detection-using-faster-r-cnn-deep-learning.html (accessed on 20 February 2019).


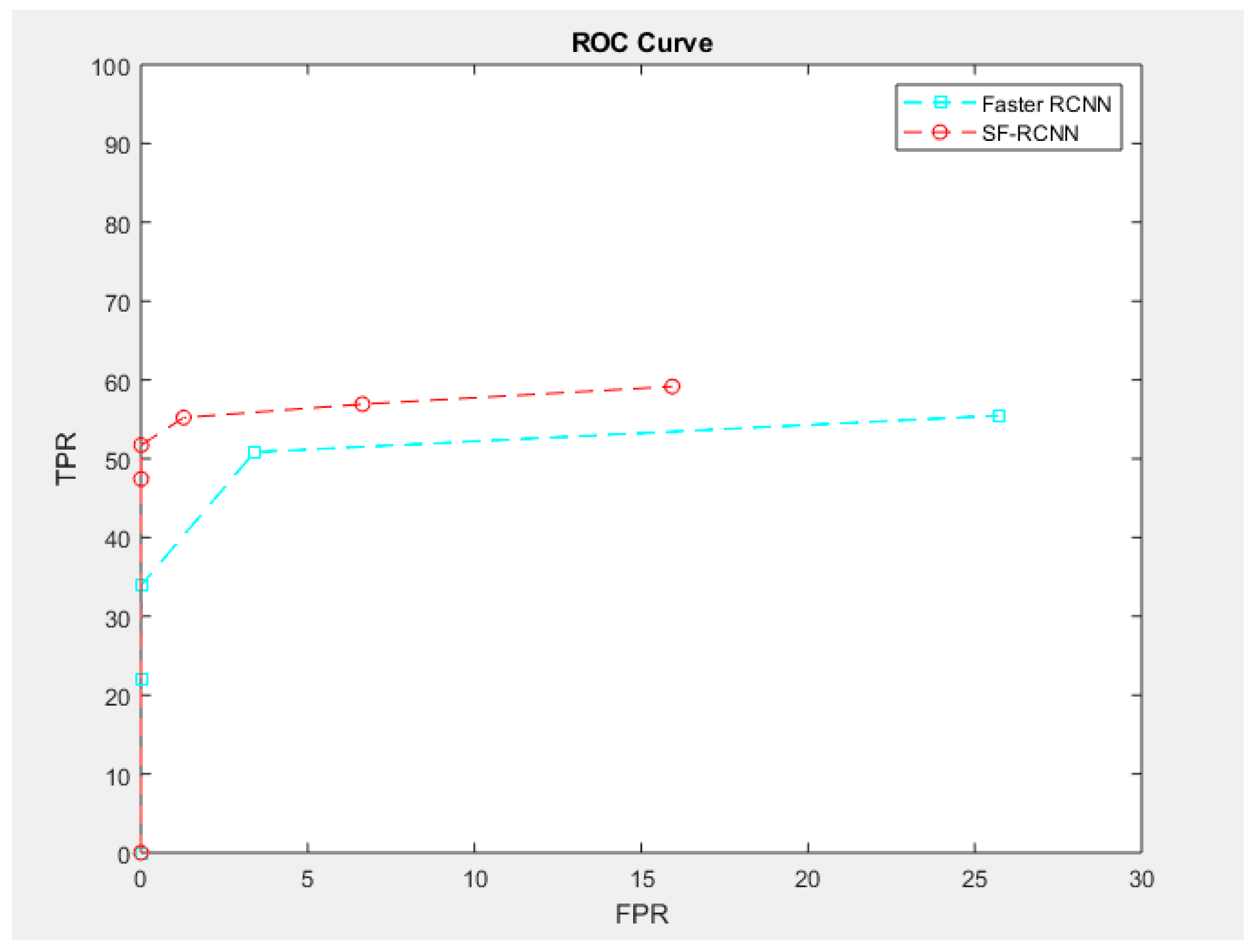
| Approach | Threshold | FPR | TPR | FNR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster RCNN | 0.95 | 0.006% | 21.9% | 78.06% |
| 0.6 | 0.03% | 34.06% | 64.94% | |
| 0.01 | 3.40% | 50.83% | 49.17% | |
| 0.001 | 25.71% | 55.47% | 44.53% | |
| Semi-Supervised Faster RCNN | 0.95 | 0.003% | 47.42% | 52.58% |
| 0.6 | 0.006% | 51.73% | 48.27% | |
| 0.01 | 1.28% | 55.21% | 44.79% | |
| 0.001 | 6.64% | 56.92% | 43.08% | |
| 0.0001 | 15.93% | 59.16% | 40.84% |
| Identified Class True Class | Long Arm | Bundle |
|---|---|---|
| Long Arm | 91.0% | 9.0% |
| Bundle | 9.3% | 90.7% |
| Identified Class True Class | Long Arm | Bundle |
|---|---|---|
| Long Arm | 92% | 8% |
| Bundle | 3.1% | 96.9% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, H.; Kehtarnavaz, N. Semi-Supervised Faster RCNN-Based Person Detection and Load Classification for Far Field Video Surveillance. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2019, 1, 756-767. https://doi.org/10.3390/make1030044
Wei H, Kehtarnavaz N. Semi-Supervised Faster RCNN-Based Person Detection and Load Classification for Far Field Video Surveillance. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction. 2019; 1(3):756-767. https://doi.org/10.3390/make1030044
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Haoran, and Nasser Kehtarnavaz. 2019. "Semi-Supervised Faster RCNN-Based Person Detection and Load Classification for Far Field Video Surveillance" Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction 1, no. 3: 756-767. https://doi.org/10.3390/make1030044
APA StyleWei, H., & Kehtarnavaz, N. (2019). Semi-Supervised Faster RCNN-Based Person Detection and Load Classification for Far Field Video Surveillance. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction, 1(3), 756-767. https://doi.org/10.3390/make1030044






