Statistical Analysis of Tensile Damage of Basalt Fiber Foam Concrete Based on DBSCAN Clustering Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Specimen Preparation
2.2. Design of Tensile Specimens
2.3. Uniaxial Quasi-Static Tensile Test
2.4. DBSCAN Clustering Method
3. Results and Discussion
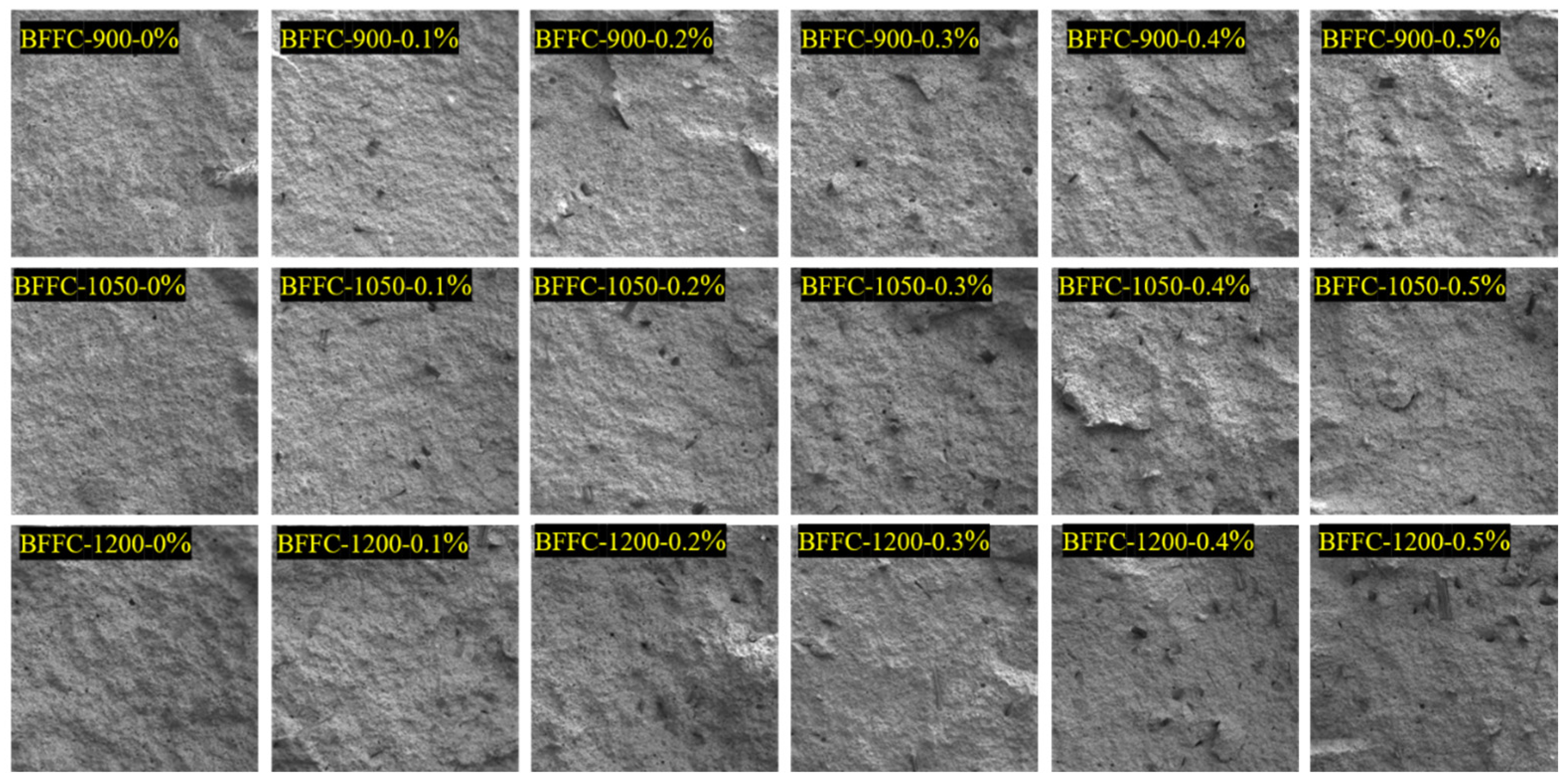
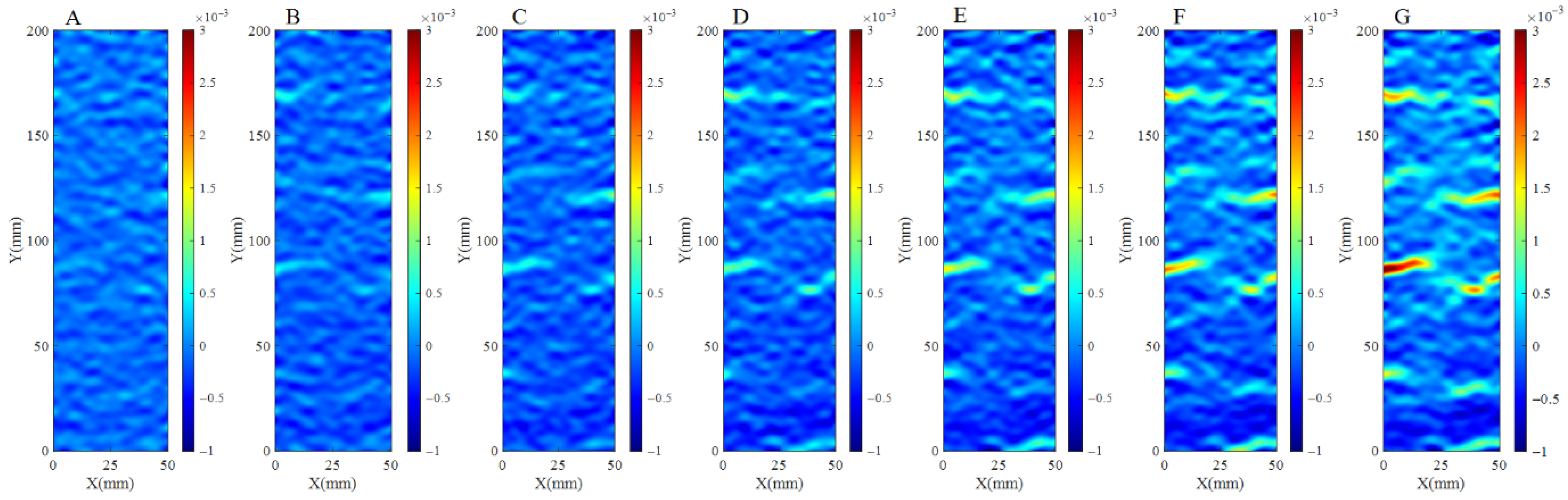
3.1. Tensile Damage Analysis
3.2. Ultimate Tensile Strength
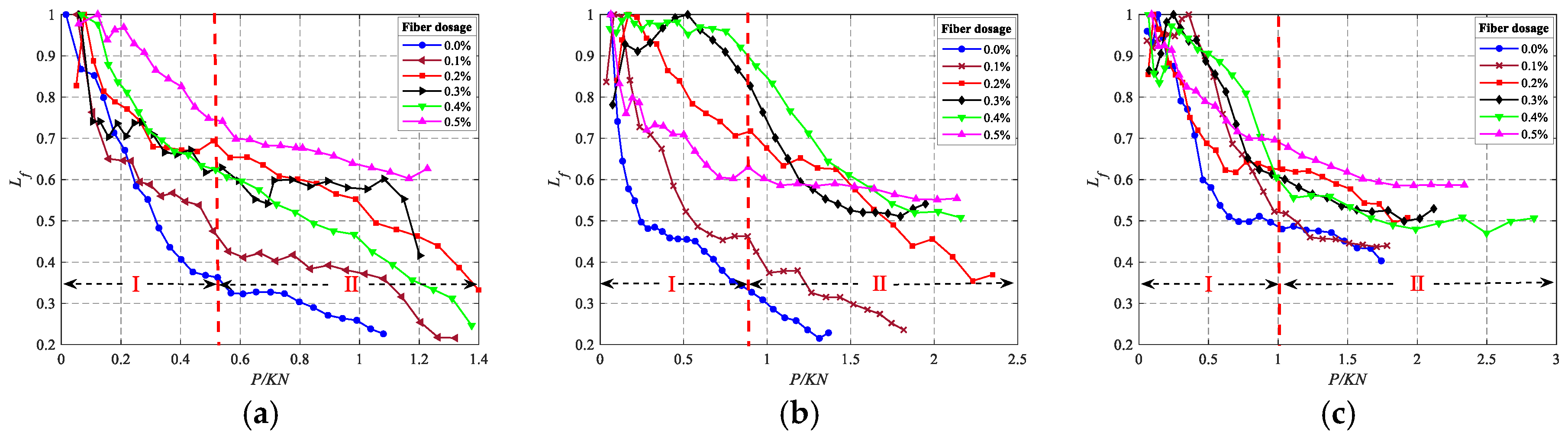
3.3. Statistical Analysis of the Strain Field Based on DBSCAN
3.3.1. Effect of Basalt Fibers on the
3.3.2. Effect of Basalt Fibers on the
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The experimental results of this study indicate that the addition of basalt fiber significantly enhances the ultimate tensile strength of basalt fiber foam concrete. The experiments demonstrate that, under three different matrix densities, the maximum tensile strength of specimens containing basalt fiber increased by 29.57%, 71.89%, and 61.57%, respectively, compared to the control group without fiber addition. It is worth noting that the experimental conclusions indicate that the optimal addition ratio of basalt fibers is not a fixed value but is closely related to the matrix density of the foam concrete. Under the three matrix density conditions studied in this research, the optimal addition ratio range of basalt fibers is 0.2–0.4%.
- (2)
- The statistical analysis results of this experiment show that the addition of basalt fibers not only effectively delays the damage process of the material but also increases the initial damage threshold load of the material. At the same time, the fibers disperse stress through their bridging action, promoting a more uniform stress distribution and effectively inhibiting the localization and concentration of damage (especially the rapid development of the main damage zone).
- (3)
- The damage degree factor and damage localization coefficient defined by the DIC-CA method in this paper can synchronously and quantitatively characterize two key dimensions of material damage: the former objectively reflects the overall damage accumulation of the material, while the latter precisely quantifies the degree of non-uniform spatial concentration of damage.
- (4)
- Although the DIC-CA method proposed in this paper demonstrates certain advantages in the quantitative analysis of material damage extent and strain localization, it also exhibits certain limitations. These limitations lie in the statistical analysis results being relatively sensitive to the two parameters of the DBSCAN clustering method, and to some extent also being influenced by the DIC computational parameters. The optimization of parameter combinations requires further research and exploration.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BFFC | Basalt Fiber Foam Concrete |
| FC | Foam Concrete |
| DIC | Digital Image Correlation |
| CA | Cluster Analysis |
References
- Hou, L.; Li, J.; Lu, Z. Influence of foaming agent on cement and foam concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 280, 122399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, M. Experimental research on the preparation and properties of foamed concrete using recycled waste concrete powder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 407, 133370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhasindrakrishna, K.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Pasupathy, K. Collapse of fresh foam concrete: Mechanisms and influencing parameters. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2021, 5, 104151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, C. Effect of superabsorbent polymer on the foam-stability of foamed concrete. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2022, 127, 104398. [Google Scholar]
- Majeed, S.; Mydin, M.; Bahrami, A. Development of ultra-lightweight foamed concrete modified with silicon dioxide (SiO2) nanoparticles: Appraisal of transport, mechanical, thermal, and microstructural properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 3308–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mydin, M.; Abdullah, M.; Sor, N. Thermal conductivity, microstructure and hardened characteristics of foamed concrete composite reinforced with raffia fiber. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mydin, M.; Jagadesh, P.; Bahrami, A. Use of calcium carbonate nanoparticles in production of nano-engineered foamed concrete. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Cao, K.; Sun, L. Review on the durability of polypropylene fibre-reinforced concrete. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6652077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakravan, H.; Latifi, M.; Jamshidi, M. Hybrid short fiber reinforcement system in concrete: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 142, 280e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambichik, M.; Abdul Samad, A.; Mohamad, N.; Mohd Ali, A.; Othuman Mydin, M.; Mohd Bosro, M. Effect of combining palm oil fuel ash (POFA) and rice husk ash (RHA) as partial cement replacement to the compressive strength of concrete. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2018, 10, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awang, H.; Mydin, M.; Roslan, A. Effects of fibre on drying shrinkage, compressive and flexural strength of lightweight foamed concrete. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 587, 144e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, A.; Tunc, U.; Bahrami, A. Use of waste glass powder toward more sustainable geopolymer concrete. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 8533–8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, C. Properties of foamed concrete with Ca(OH)2 as foam stabilizer. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2021, 118, 103985. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, M. Laboratory investigation of foamed concrete prepared by recycled waste concrete powder and ground granulated blast furnace slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Qu, N.; Li, J. Development and functional characteristics of novel foam concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 324, 126666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falliano, D.; Restuccia, L.; Gugliandolo, E. A simple optimized foam generator and a study on peculiar aspects concerning foams and foamed concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 268, 121101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, B.; Gil, A.M.; Bolina, F.L.; Tutikian, B.F. Thermal damage evaluation of full scale concrete columns exposed to high temperatures using scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. DYNA 2018, 85, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manica, G.C.; Bolina, F.L.; Tutikian, B.F.; Oliveira, M.; Moreir, M.A. Influence of curing time on the fire performance of solid reinforced concrete plates. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 2506–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J.; Zou, X. Experimental Study on Mechanical Properties of Basalt Fiber Concrete after Cryogenic Freeze-Thaw Cycles. Polymers 2023, 15, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzymski, F.; Musiał, M.; Trapko, T. Mechanical properties of fiber reinforced concrete with recycled fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 198, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Tayeh, B.; Aisheh Abu, Y.; Salih, M. Exploring the performance of steel fiber reinforced lightweight concrete: A case study review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e01968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaini, Z.; Rum, R.; Boon, K. Strength and fracture energy of foamed concrete incorporating rice husk ash and polypropylene mega-mesh 55. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 248, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugahed Amran, Y.; Alyousef, R.; Alabduljabbar, H.; Khudhair, M.; Hejazi, F.; Alaskar, A.; Alrshoudi, F.; Siddika, A. Performance properties of structural fibred foamed concrete. Results Eng. 2020, 5, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhu, J.; Sun, T.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Yin, W.; Han, J. Multiple effects of nanoCaCO3 and modified polyvinyl alcohol fiber on flexure-tension-resistant performance of engineered cementitious composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 303, 124426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakravan, H.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Synthetic fibers for cementitious composites: A critical and in-depth review of recent advances. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 207, 491–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, B.; Sathyan, D.; Madhavan, M.; Raj, A. Mechanical and durability properties of hybrid fiber reinforced foam concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 245, 118373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blythe, A.; Fox, B.; Nikzad, M.; Eisenbart, B.; Chai, B.X.; Blanchard, P. Evaluation of the failure mechanism in polyamide nanofiber veil toughened hybrid carbon/glass fiber composites. Materials 2022, 15, 8877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Choi, H.; Park, M. A review: Natural fiber composites selection in view of mechanical, light weight, and economic properties. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2015, 300, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazao, C.; Barros, J.; Camoes, A.; Alves, A.; Rocha, L. Corrosion effects on pullout behavior of hooked steel fibers in self-compacting concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 79, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shihada, S. Effect of polypropylene fibers on concrete fire resistance. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2021, 17, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Kim, T. Unveiling the underlying mechanisms of tensile behavior enhancement in fiber reinforced foam concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 398, 132509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, K.; Moreau, G.; Aboura, Z. Digital image correlation, acoustic emission and in-situ microscopy in order to understand composite compression damage behavior. Compos. Struct. 2020, 258, 113424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.Q.; Tabrizi, I.E.; Khan, R.M.A.; Tufani, A.; Yildiz, M. Microscopic analysis of failure in woven carbon fabric laminates coupled with digital image correlation and acoustic emission. Compos. Struct. 2019, 230, 111515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P. Subpixel displacement and deformation gradient measurement using digital image/speckle correlation (DISC). Opt. Eng. 2001, 40, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Guo, R.; Xia, H. Application of the mean intensity of the second derivative in evaluating the speckle patterns in digital image correlation. Opt. Laser Eng. 2014, 60, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Lu, Z.; Xie, H. Mean intensity gradient: An effective global parameter for quality assessment of the speckle patterns used in digital image correlation. Opt. Laser Eng. 2010, 48, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, M. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. Proc. Int. Conf. Knowl. Discov. Data Min. 1996, 96, 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Luchi, D.; Rodrigues, A.L.; Varejão, F.M. Sampling approaches for applying DBSCAN to large datasets. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2019, 117, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, M.; Seo, S.; Tran, H.; Khol, S. A novel method for acoustic emission source location in CFRP-concrete debonding using ΔT mapping and DBSCAN algorithm. Measurement 2024, 236, 115097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Lei, Z. Study on bending damage and failure of basalt fiber reinforced concrete under freeze-thaw cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 163, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, G.; Song, H. Experimental characterization of strain localization in rock. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 194, 1554–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
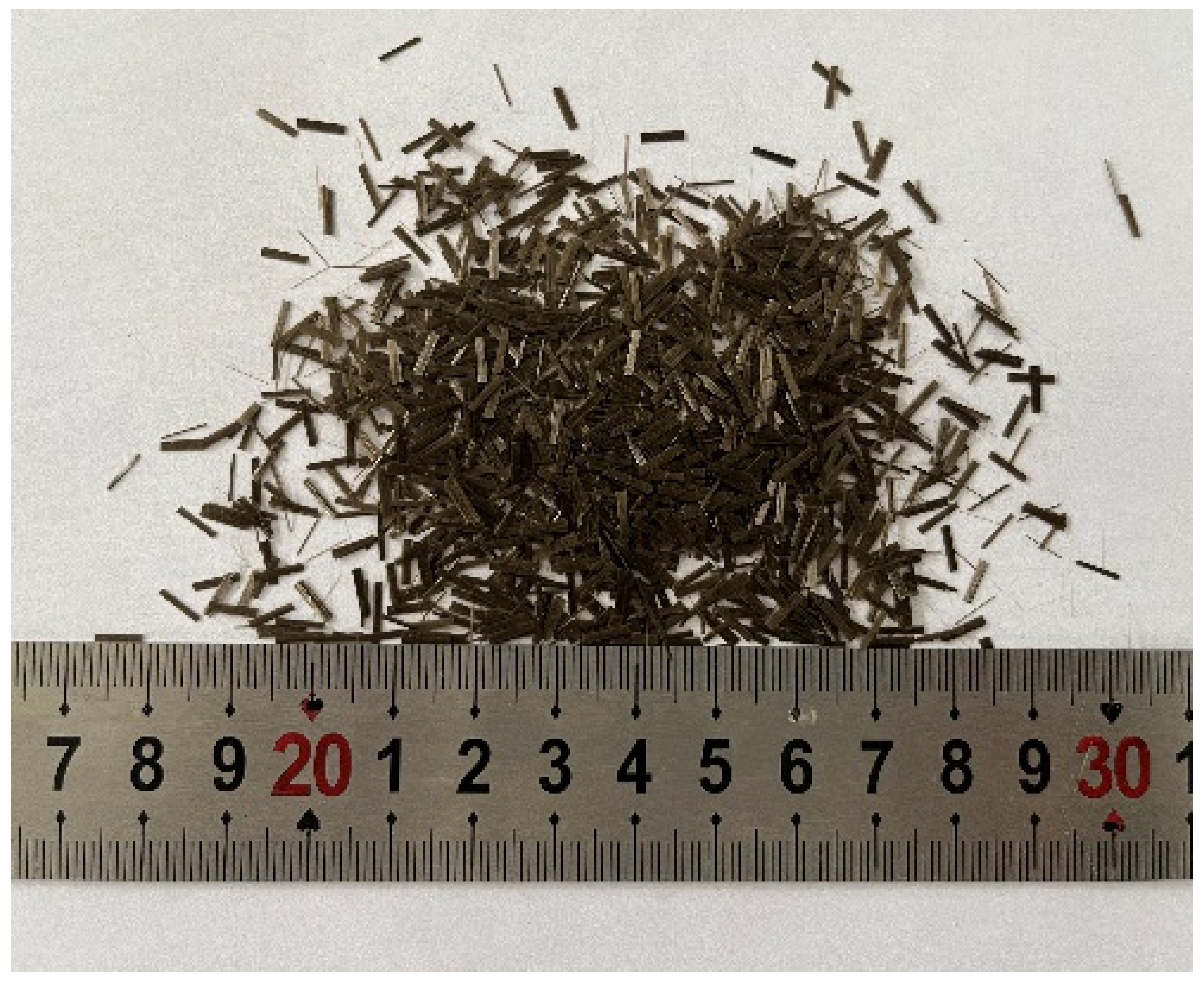
















| Diameter/μm | Tensile Strength/MPa | Elastic Modulus/GPa | Elongation/% | Density/(kg·m−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9–17 | 3000–4800 | 85–110 | 3.0–3.5% | 2.6–2.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Liu, C.; An, Y.; Ma, R.; Liu, Y. Statistical Analysis of Tensile Damage of Basalt Fiber Foam Concrete Based on DBSCAN Clustering Method. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9120694
Yu H, Liu C, An Y, Ma R, Liu Y. Statistical Analysis of Tensile Damage of Basalt Fiber Foam Concrete Based on DBSCAN Clustering Method. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(12):694. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9120694
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Hai, Changgeng Liu, Yangzhuang An, Rufeng Ma, and Yunpeng Liu. 2025. "Statistical Analysis of Tensile Damage of Basalt Fiber Foam Concrete Based on DBSCAN Clustering Method" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 12: 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9120694
APA StyleYu, H., Liu, C., An, Y., Ma, R., & Liu, Y. (2025). Statistical Analysis of Tensile Damage of Basalt Fiber Foam Concrete Based on DBSCAN Clustering Method. Journal of Composites Science, 9(12), 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9120694





