A Review Focused on 3D Hybrid Composites from Glass and Natural Fibers Used for Acoustic and Thermal Insulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Properties of Fiber
2.1. Glass Fibers
Properties of Glass Fibers
2.2. Natural Fibers
2.2.1. Type of Natural Fibers
2.2.2. Environmental Impact
2.2.3. Properties and Advantages
2.2.4. Challenges and Considerations
2.3. Comparison of Glass and Natural Fibers
2.3.1. Acoustic and Thermal Properties
2.3.2. Mechanical Properties
2.3.3. Composition and Properties
2.3.4. Recycling and Environmental Impacts
2.3.5. Cost and Sustainability
3. 3D Hybrid Composites
3.1. Advanced Manufacturing of 3D Woven Fabrics
3.2. Mechanisms of Thermal and Acoustic Insulation
3D Hybrid Composites
3.3. Glass Fibers vs. Natural Fibers in 3D Composites
3.4. Emerging Trends in Bio-Based Fillers, Nano-Coatings, and Gradient Designs
3.5. Standardization Challenges
4. Challenges and Gaps in Applications for Vehicles and Buildings
4.1. Automotive and Aerospace Industries
4.2. Applications in Construction
5. Challenges and Future Studies
6. Conclusions
- -
- Glass fibers exhibit high tensile strengths of 3000–4500 MPa and thermal conductivity of ~0.045 W/m·K, making them ideal for structural applications in automotive and aerospace industries [28].
- -
- Natural fibers, such as jute, provide sound absorption coefficients (SAC) of 0.7–0.8 and thermal conductivity rates of 0.07–0.09 W/m·K, enhancing their sustainability and insulation performance [69].
- -
- -
- Bio-based fillers and nano-coatings reduce moisture absorption by 50% and improve fire resistance by delaying ignition by 120 s, addressing durability challenges [64].
- -
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carvalho, D.; Ferreira, N.; França, B.; Marques, R.; Silva, M.; Silva, S.; Silva, E.; Macário, D.; Barroso, L.; Silva, C.J.; et al. Advancing sustainability in the automotive industry: Bioprepregs and fully bio-based composites. Compos. Part C Open Access 2024, 14, 100459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gries, T.; Bettermann, I.; Blaurock, C.; Bündgens, A.; Dittel, G.; Emonts, C.; Gesché, V.; Glimpel, N.; Kolloch, M.; Grigat, N.; et al. Aachen Technology Overview of 3D Textile Materials and Recent Innovation and Applications. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2022, 29, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfaleh, I.; Abbassi, F.; Habibi, M.; Ahmad, F.; Guedri, M.; Nasri, M.; Garnier, C. A comprehensive review of natural fibers and their composites: An eco-friendly alternative to conventional materials. Results Eng. 2023, 19, 101271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Yang, Q.; Dai, H.; Deng, M.; Wang, H.; Hou, C.; Cheng, Z.; Gao, H. Effect of glass fiber on the mechanical and thermal insulation performances of kaolinite-based thermal insulator. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, T.; McCaa, D.; Rebandt, R.; Rusch, P.; Saha, P.; SAE Acoustical Materials Committee; SAE Thermal Materials Committee. Application of noise control and heat insulation materials and devices in the automotive industry. SAE Trans. 1995, 104, 2529–2546. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Pu, Y.; Thomas, V.M.; Yoo, C.G.; Ozcan, S.; Deng, Y.; Nelson, K.; Ragauskas, A.J. Recent advancements of plant-based natural fiber–reinforced composites and their applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 200, 108254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyavihalli Girijappa, Y.G.; Mavinkere Rangappa, S.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Siengchin, S. Natural fibers as sustainable and renewable resource for development of eco-friendly composites: A comprehensive review. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, H.-X.; Gao, X.-P.; Long, H.-R. Sound absorption properties of polyurethane-based warp-knitted spacer fabric composites. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2017, 42, 299–306. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, A.M. Preparation and studying of some properties of polymer composites reinforced with natural and artificial fibers. Iraqi J. Phys. 2016, 14, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, M.; Han, S. Thermal and acoustic properties of natural fiber reinforced composites for automobile applications. J. Mater. Eng. S 2009, 2, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, T.; Monaragala, R.; Needham, P.; Lay, E. Analysis of sound absorption of tuck spacer fabrics to reduce automotive noise. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yachmenev, V.G.; Calamari, T.A., Jr.; Parikh, D.V.; Yan, C.; Negulescu, I.I. Thermal insulation properties of kenaf and cotton nonwoven compositesfor automotive application. Europe 2004, 18, 19.2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, B.; Li, Y. Sound absorption characterization of natural materials and sandwich structure composites. Aerospace 2018, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, S.; Kaman, M.O. Pin loading effect on 3D spacer fabric-laminated composites produced vacuum infusion. J. Compos. Mater. 2022, 56, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandula, R.; Sanaka, S.P.; Ratna Prasad, A.V.; Reddy Konireddy, H. Thermo-physical and fire properties of natural fiber composites for energy saving applications. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 11845–11857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedkarimi, R.; Hasani, H.; Soltani, P.; Talebi, Z. Experimental and computational analysis of acoustic characteristics of warp-knitted spacer fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2020, 111, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, B.; Rahman, M.A.; Repon, M.R.; Rahman, M.M.; Haji, A.; Nawab, Y. Recent progress in thermal and acoustic properties of natural fiber reinforced polymer composites: Preparation, characterization, and data analysis. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 7235–7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Hossain, N.; Mim, J.J.; Rahman, S.M.; Iqbal, M.J.; Billah, M.; Chowdhury, M.A. Advances of composite materials in automobile applications—A review. J. Eng. Res. 2025, 13, 1001–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhisheng, L.; Dongmei, L.; Sheng, M.; Zhang, G.; Jianlong, L. Noise Impact and Improvement on Indoors Acoustic Comfort for the Building Adjacent to Heavy Traffic Road. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2013, 5, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Bhattacharjee, B. Thermal and noise insulation performance interaction of building envelope during building simulation optimization in tropical climates. Build. Environ. 2021, 200, 107948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, A.; Gokcekaya, O.; Billah, K.M.M.; Ertugrul, O.; Jiang, J.; Sun, J.; Hussain, S. Multi-material additive manufacturing: A systematic review of design, properties, applications, challenges, and 3D printing of materials and cellular metamaterials. Mater. Des. 2023, 226, 111661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallenberger, F.T.; Watson, J.C.; Li, H. Glass fibers. In Composites; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2001; pp. 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Yang, Z.; Lian, J.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Wu, Y.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, X. An all-natural, bioinspired, biodegradable electrical insulating composite based on lignocellulose and mica tailings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, S.; Mohapatra, S. Properties of glass-fiber hybrid composites: A review. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2017, 56, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Li, C.; Hu, Z.; Lv, H.; Zhang, J.; Meng, X. Preparation and application research of hybrid alkali-resistant glass fiber reinforced cement grout. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justin, S.; Thushanthan, K.; Tharmarajah, G. Durability and mechanical performance of glass and natural fiber-reinforced concrete in acidic environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 465, 140262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Bai, Y.; Liu, W.; Qi, Y.; Wang, J. Connections and structural applications of fibre reinforced polymer composites for civil infrastructure in aggressive environments. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 164, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, S.; Ivanova, T.A.; Mishra, R.K.; Müller, M.; Akhbari, M.; Hashjin, Z.E. Effect of Natural Fiber and Biomass on Acoustic Performance of 3D Hybrid Fabric-Reinforced Composite Panels. Materials 2024, 17, 5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, G.; Vaidya, U.; Wang, H. Past, present and future prospective of global carbon fibre composite developments and applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 250, 110463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siengchin, S. A review on lightweight materials for defence applications: Present and future developments. Def. Technol. 2023, 24, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, S.A.; Nazari, S.; Abbasi, M.; Kolahchi, R. Investigation of the bending behavior of 3D glass-fabric-reinforced composite panels as slabs in buildings. Earthq. Struct. 2019, 16, 569–573. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, D. Effect of fabric structures on the mechanical properties of 3-D textile composites. J. Ind. Text. 2006, 35, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirdehghan, A.; Nosraty, H.; Shokrieh, M.M.; Ghasemi, R.; Akhbari, M. Micromechanical modelling of the compression strength of three-dimensional integrated woven sandwich composites. J. Ind. Text. 2018, 48, 1399–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirdehghan, A.; Nosraty, H.; Shokrieh, M.M.; Akhbari, M. Manufacturing and drop-weight impact properties of three-dimensional integrated woven sandwich composite panels with hybrid core. J. Ind. Text. 2020, 51, 1183–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadighi, M.; Hosseini, S.A. Finite element simulation and experimental study on mechanical behavior of 3D woven glass fiber composite sandwich panels. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandramohan, D.; Marimuthu, K. A review on natural fibers. Int. J. Res. Rev. Appl. Sci. 2011, 8, 194–206. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Wang, B.; Dai, Z.; Shi, X.; Jin, Z.; Wang, H.; Jiang, X. New insights into the green cement composites with low carbon footprint: The role of biochar as cement additive/alternative. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 197, 107081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman MXiong, X.; Marek, J.; Yao, J.; Zhu, G. Electrospun nanofibrous membranes embedded with aerogel for advanced thermal and transport properties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 2583–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañete Vela, I.; Berdugo Vilches, T.; Berndes, G.; Johnsson, F.; Thunman, H. Co-recycling of natural and synthetic carbon materials for a sustainable circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firoozi, A.A.; Firoozi, A.A.; Oyejobi, D.O.; Avudaiappan, S.; Flores, E.S. Emerging trends in sustainable building materials: Technological innovations, enhanced performance, and future directions. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.K.; Pattanayak, A.K.; Mishra, R. Prediction of fabric drape behaviour using finite element method. J. Text. Eng. 2008, 54, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Hu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Chen, K.; Qiu, C.; Yang, J.; Yang, L. Investigation into the Reinforcement Modification of Natural Plant Fibers and the Sustainable Development of Thermoplastic Natural Plant Fiber Composites. Polymers 2024, 16, 3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, T.; Jamshaid, H.; Khan, M.Q.; Tichy, M.; Muller, M. Factors affecting acoustic properties of natural-fiber-based materials and composites: A review. Textiles 2021, 1, 55–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudabadi Farahani, M.; Asgharian Jeddi, A.A.; Jamshidi, M. Investigation of sound absorption of Warp Knitted Spacer Fabric with nanofiber coating. J. Text. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Pawar, U.S.; Chavan, S.S.; Mohite, D.D. Synthesis of glass FRP-natural fiber hybrid composites (NFHC) and its mechanical characterization. Discov. Sustain. 2024, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangoush, E.; Säilynoja, E.; Prinssi, R.; Lassila, L.; Vallittu, P.K.; Garoushi, S. Comparative evaluation between glass and polyethylene fiber reinforced composites: A review of the current literature. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2017, 9, e1408–e1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, K.K. Glass Fibers. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology; Buschow, K.H.J., Cahn, R.W., Flemings, M.C., Ilschner, B., Kramer, E.J., Mahajan, S., Veyssière, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 3541–3545. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, F.; Hossain, N.; Hasan, F.; Rahman, S.M.; Khan, S.; Saifullah, A.Z.A.; Chowdhury, M.A. Advances of natural fiber composites in diverse engineering applications—A review. Appl. Eng. Sci. 2024, 18, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Yang, T.; Mishra, R.; Militky, J. Transport properties of aerogel-based nanofibrous nonwoven fabrics. Fibers Polym. 2017, 17, 1709–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musthaq, M.A.; Dhakal, H.N.; Zhang, Z.; Barouni, A.; Zahari, R. The Effect of Various Environmental Conditions on the Impact Damage Behaviour of Natural-Fibre-Reinforced Composites (NFRCs)—A Critical Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.Y.; Al Rashid, A.; Arif, Z.U.; Ahmed, W.; Arshad, H.; Zaidi, A.A. Natural fiber reinforced composites: Sustainable materials for emerging applications. Results Eng. 2021, 11, 100263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xiong, X.; Venkataraman, M.; Novák, J. Investigation on sound absorption properties of aerogel/polymer nonwovens. J. Text. Inst. 2019, 110, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyam, S.; Patra, S. Innovations and challenges in adsorption-based wastewater remediation: A comprehensive review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, M.; Choudhary, P.; Krishnan, V.; Zafar, S. A review on recycling and reuse methods for carbon fiber/glass fiber composites waste from wind turbine blades. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 215, 108768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshood, T.D.; Nawanir, G.; Mahmud, F.; Mohamad, F.; Ahmad, M.H.; AbdulGhani, A. Sustainability of biodegradable plastics: New problem or solution to solve the global plastic pollution? Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 5, 100273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanrewaju, O.; Oladele, I.O.; Adelani, S.O. Recent advances in natural fiber reinforced metal/ceramic/polymer composites: An overview of the structure-property relationship for engineering applications. Hybrid Adv. 2025, 8, 100378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, H. Sound absorption behavior of knitted spacer fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2010, 80, 1949–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Choe, J. Development of the fire retardant glass fabric/carbonized phenolic composite. Compos. Struct. 2016, 148, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okur, N.; Yaradanakul, M.C. Development of hybrid layered structures based on natural fabric reinforced composites and warp knitted spacer fabric for acoustic applications. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 51 (Suppl. 2), 2216S–2245S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, V.; Militky, J.; Tunak, M. In-plane shear behavior of 3D spacer knitted fabrics. J. Ind. Text. 2016, 46, 868–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanikumar, K.; Prabhudass, J.; Sailesh, A. (Eds.) Experimental investigation of thermal properties of hybrid glass fiber-sisal reinforced epoxy composites. In Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Houston, TX, USA, 13–19 November 2015; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnasamy, B.; Shanmugam, N.; Subramanian, A.; Selvaraj, S.K.; Sakthivel, S.; Guru, R.; Admassu, Y. Sound-absorbing and thermal insulating properties of natural coir/jute hybrid composites for functional materials. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2024, 19, 15589250241270522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-H.; Pan, Y.-J.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Lin, Z.-I.; Lou, C.-W.; Lin, J.-H. 3D Fabric/Polyurethane Foam Composites Containing Various Fabrics: Property Evaluations. DEStech Trans. Eng. Technol. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, V.; Militky, J.; Davies, L.; Slater, S. Thermal and water vapor transmission through porous warp knitted 3D spacer fabrics for car upholstery applications. J. Text. Inst. 2018, 109, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onu, P.; Pradhan, A.; Mbohwa, C. The potential of industry 4.0 for renewable energy and materials development—The case of multinational energy companies. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, V.; Walther, G. Recycling and recovery infrastructures for glass and carbon fiber reinforced plastic waste from wind energy industry: A European case study. Waste Manag. 2021, 121, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Hao, H.; Lu, H.; Chow, C.L.; Lau, D. Exploring the development and applications of sustainable natural fiber composites: A review from a nanoscale perspective. Compos. Part B Eng. 2024, 276, 111369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Cock, L.; Guancha-Chalapud, M.A. Natural fibers for hydrogels production and their applications in agriculture. Acta Agron. 2017, 66, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Yu, K.; Qian, K. Sound insulation property of threedimensional spacer fabric composites. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2014, 22, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Maiti, S.; Islam, M.R.; Uddin, M.A.; Afroj, S.; Eichhorn, S.J.; Karim, N. Sustainable fiber-reinforced composites: A Review. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2022, 6, 2200258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, T.; Chaion, M.H.; Jalil, M.A.; Rafi, A.S.; Mushtari, F.; Dhar, A.K.; Hossain, S. Advancements and challenges in natural fiber-reinforced hybrid composites: A comprehensive review. SPE Polym. 2024, 5, 481–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siouta, L.; Apostolopoulou, M.; Bakolas, A. Natural Fibers in Composite Materials for Sustainable Building: A State-of-the-Art Review on Treated Hemp Fibers and Hurds in Mortars. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maganti, T.R.; Boddepalli, K.R. Optimization of mechanical and impact resistance of high strength glass fiber reinforced alkali activated concrete containing silica fume: An experimental and response surface methodology approach. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, J.; Salmon, S. Strategies and progress in synthetic textile fiber biodegradability. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, F.; Nisticò, A.; Tucci, F.; Carlone, P. Marine Application of Fiber Reinforced Composites: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Shi, J.; Cao, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, L.; Jiang, J. A Review on the Applications of Basalt Fibers and Their Composites in Infrastructures. Buildings 2025, 15, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Cao, X.; Wang, H. Infrastructure-Oriented Efficient Materials Implemented with Fibers. Buildings 2025, 15, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, R.; Xia, C.; Guo, H.F. Experimental Study on Effects of Laminated Structure on Acoustic Insulation Property of Composites. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 284–286, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, K.; Feng, Y.; Liang, L.; Chi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. Recent advances in thermal-conductive insulating polymer composites with various fillers. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 178, 107998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C423-23; Standard Test Method for Sound Absorption and Sound Absorption Coefficients by the Reverberation Room Method. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023.
- ISO 10534-2:1998; Acoustics—Determination of Sound Absorption Coefficient and Impedance in Impedance Tubes. International Standards Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- ASTM C518-21; Standard Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of the Heat Flow Meter Apparatus. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- ISO 8302:1991; Thermal Insulation—Determination of Steady-State Thermal Resistance and Related Properties—Guarded Hot Plate Apparatus. International Standards Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1991.


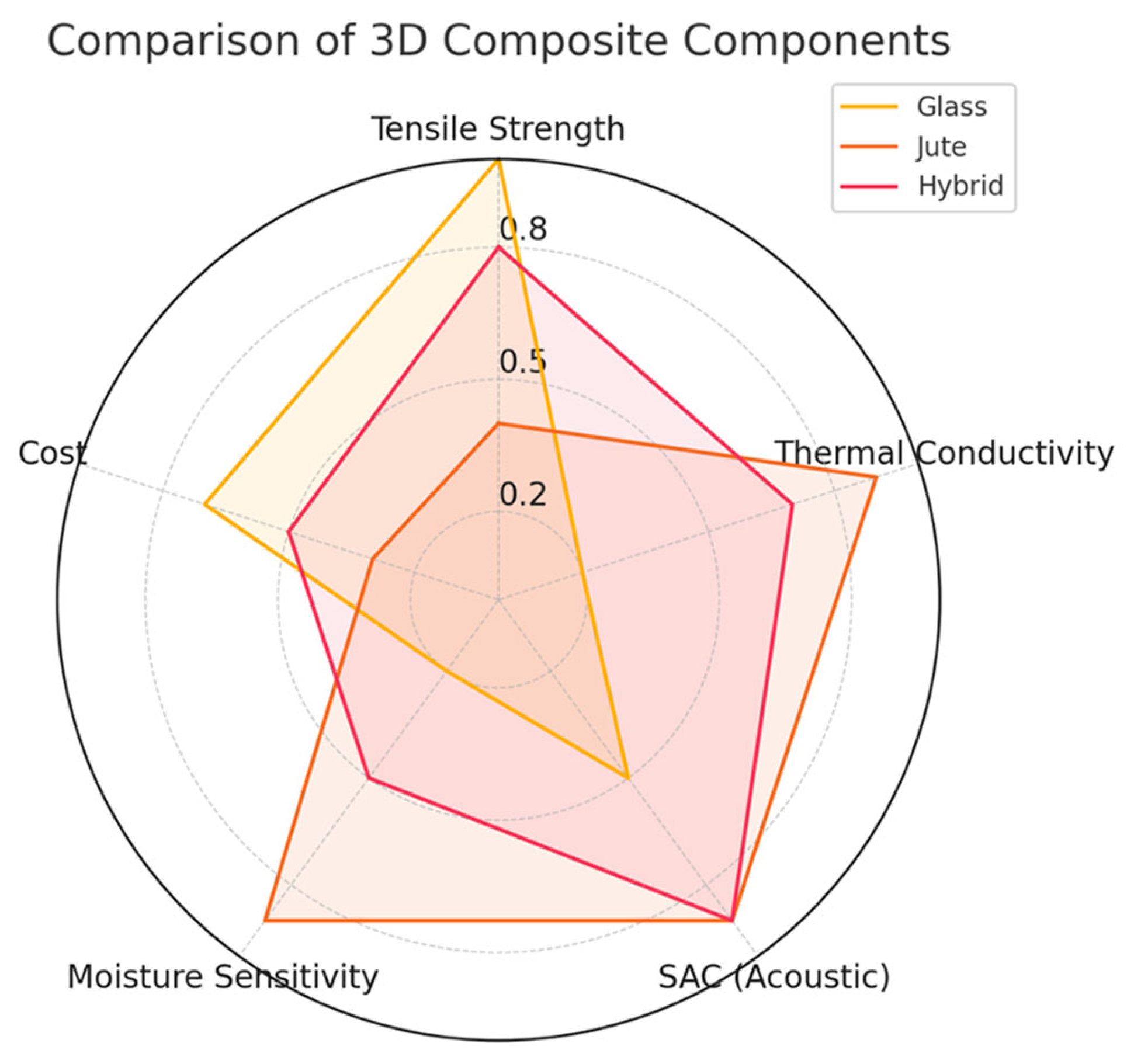

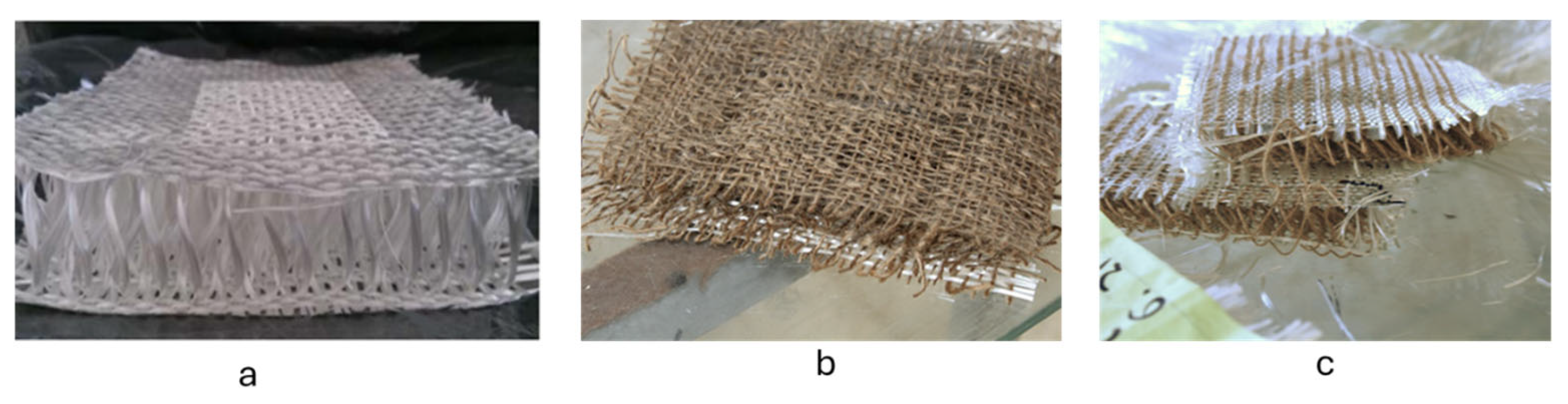

| Property | Glass Fibers | Natural Fibers (Jute) | Hybrid (50/50 Glass–Jute) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 3000–4500 | 400–800 | 1200–1800 | [4,22,28] |
| Young’s Modulus (Gpa) | 70–85 | 10–30 | 40–60 | [22,42] |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 0.04–0.05 | 0.07–0.09 | 0.05–0.06 | [9,25,61] |
| Moisture Absorption (%) | <0.1 | 12–15 | 5–8 (with treatments) | [6,50] |
| Application | Material | Sound Absorption (dB) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Panels | Glass Fiber | 30–35 (at 2000 Hz) | 0.04–0.05 | High heat resistance, poor damping |
| Jute–Glass Hybrid | 44.9 (at 10,000 Hz) | 0.05–0.06 | Balanced performance [28] | |
| Building Insulation | Hemp–Lime Composite | N/A | 0.06 | CO2 sequestration [38,40] |
| Parameter | Weaving | Knitting | Braiding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High (500–800 mPa) | Moderate (300–500 mPa) | High (400–700 mPa) |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High | Moderate-High |
| Production Speed | 10–50 cm/min | 50–200 cm/min | 5–30 m/min |
| Fiber Orientation | 0°/90° | Multi-directional | ±45° dominant |
| Typical Applications | Structural panels | Flexible composites | Tubular components |
| Parameter | Baseline Natural Fiber | Biomass-Enhanced | Nano-Coated | Combined Approach |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture Absorption | 12–15% | 10–12% | 5–7% | 4–6% |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.07–0.09 W/m·K | 0.05–0.06 W/m·K | 0.06–0.07 W/m·K | 0.04–0.05 W/m·K |
| Sound Absorption | 0.6–0.7 coeff. | 0.7–0.75 coeff. | 0.65–0.7 coeff. | 0.75–0.8 coeff. |
| Fire Resistance | Poor | Moderate | Good | Excellent |
| Application | Materials | Key Benefits | Performance Metrics | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMW i3 Door Panels | Flax–glass hybrid | 30% weight reduction | 22% better sound absorption at 1–2 kHz | [18,48] |
| Airbus A350 Wing Ribs | Carbon–aramid 3D weave | 25% part count reduction | 40% improved damage tolerance | [2,18] |
| Tesla Battery Enclosure | Basalt–glass 3D sandwich | 50% faster production | UL94 V0 fire rating | [63] |
| Siemens Wind Turbine | Recycled PET–glass 3D | 15% cost reduction | 12% higher fatigue life | [59] |
| Adidas Running Shoes | Flax–polyamide 3D knit | 100% biodegradable | 20% better energy return | [28,58] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nazari, S.; Ivanova, T.A.; Mishra, R.K.; Muller, M. A Review Focused on 3D Hybrid Composites from Glass and Natural Fibers Used for Acoustic and Thermal Insulation. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9080448
Nazari S, Ivanova TA, Mishra RK, Muller M. A Review Focused on 3D Hybrid Composites from Glass and Natural Fibers Used for Acoustic and Thermal Insulation. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(8):448. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9080448
Chicago/Turabian StyleNazari, Shabnam, Tatiana Alexiou Ivanova, Rajesh Kumar Mishra, and Miroslav Muller. 2025. "A Review Focused on 3D Hybrid Composites from Glass and Natural Fibers Used for Acoustic and Thermal Insulation" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 8: 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9080448
APA StyleNazari, S., Ivanova, T. A., Mishra, R. K., & Muller, M. (2025). A Review Focused on 3D Hybrid Composites from Glass and Natural Fibers Used for Acoustic and Thermal Insulation. Journal of Composites Science, 9(8), 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9080448








