A New Sulfur-Containing Copolymer Created Through the Thermally Induced Radical Copolymerization of Elemental Sulfur with N2,N2-Diallylmelamine Comonomer for Potential CO2 Capture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Sulfur/NDAM Copolymers
2.3. Characterization of Crosslinked Sulfur Copolymer
2.4. CO2 Adsorption Testing
3. Results and Discussion
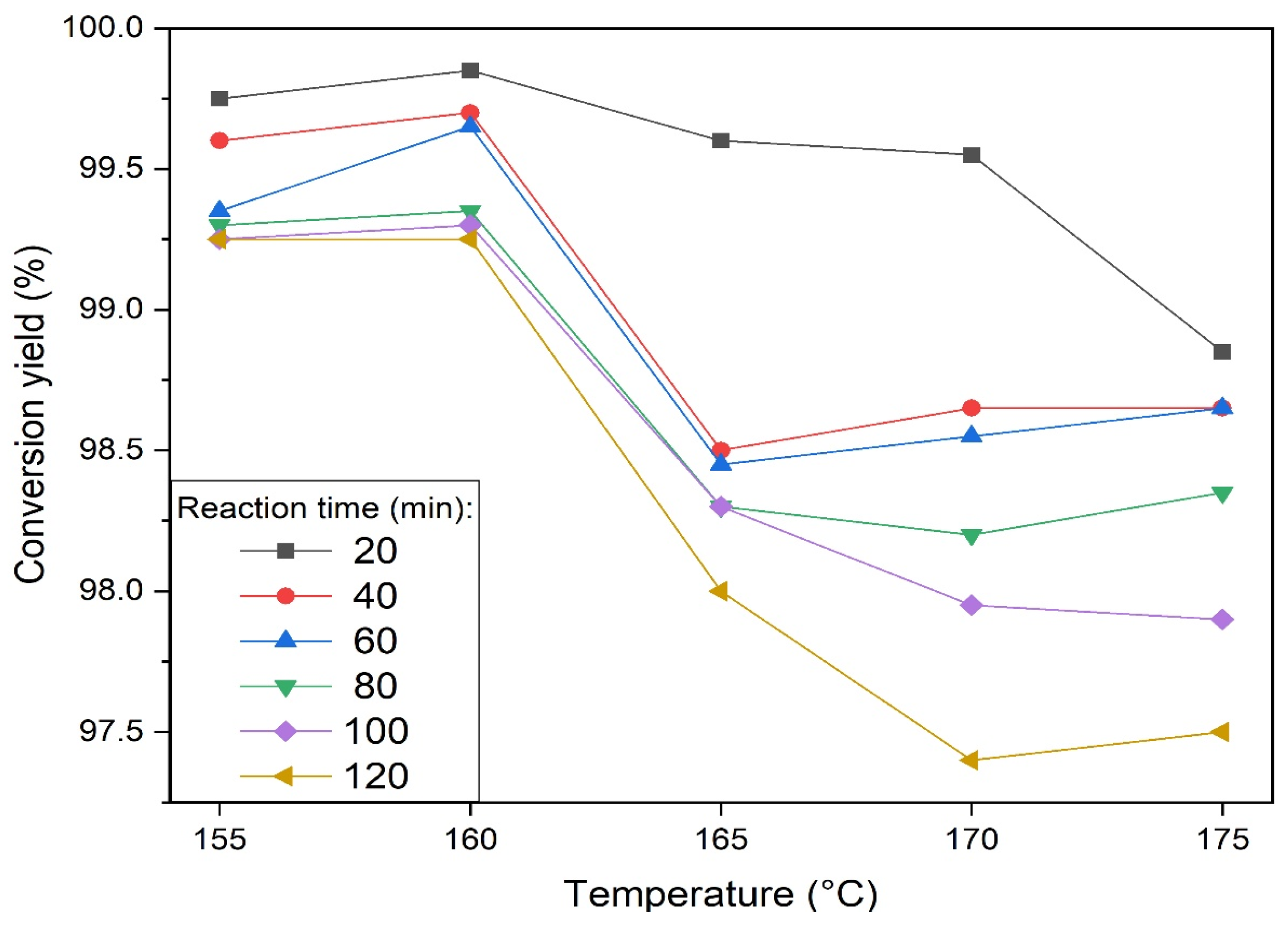
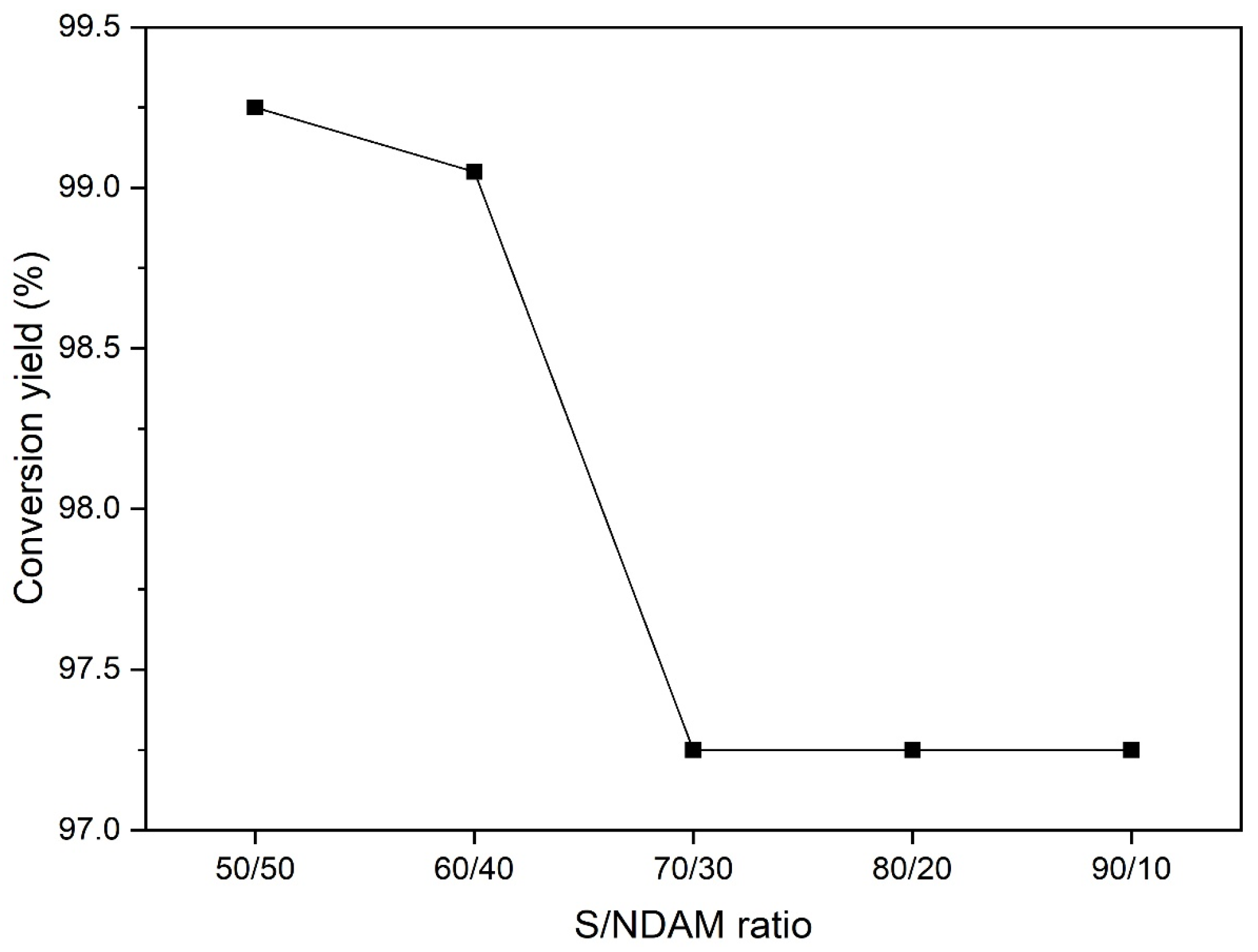
3.1. Selection of the Reaction Parameters of Sulfur with NDAM
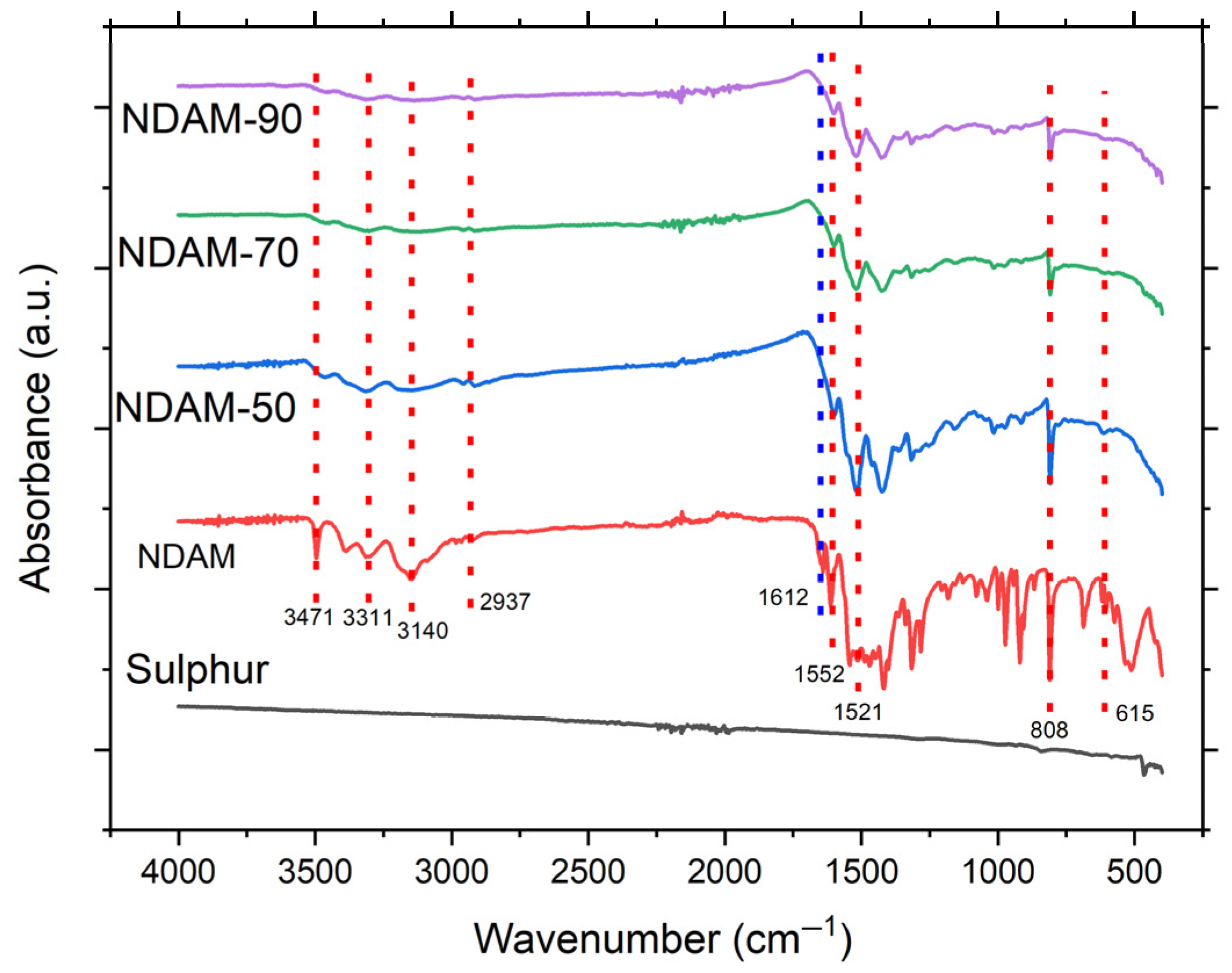
3.2. Chemical Composition of Copolymer
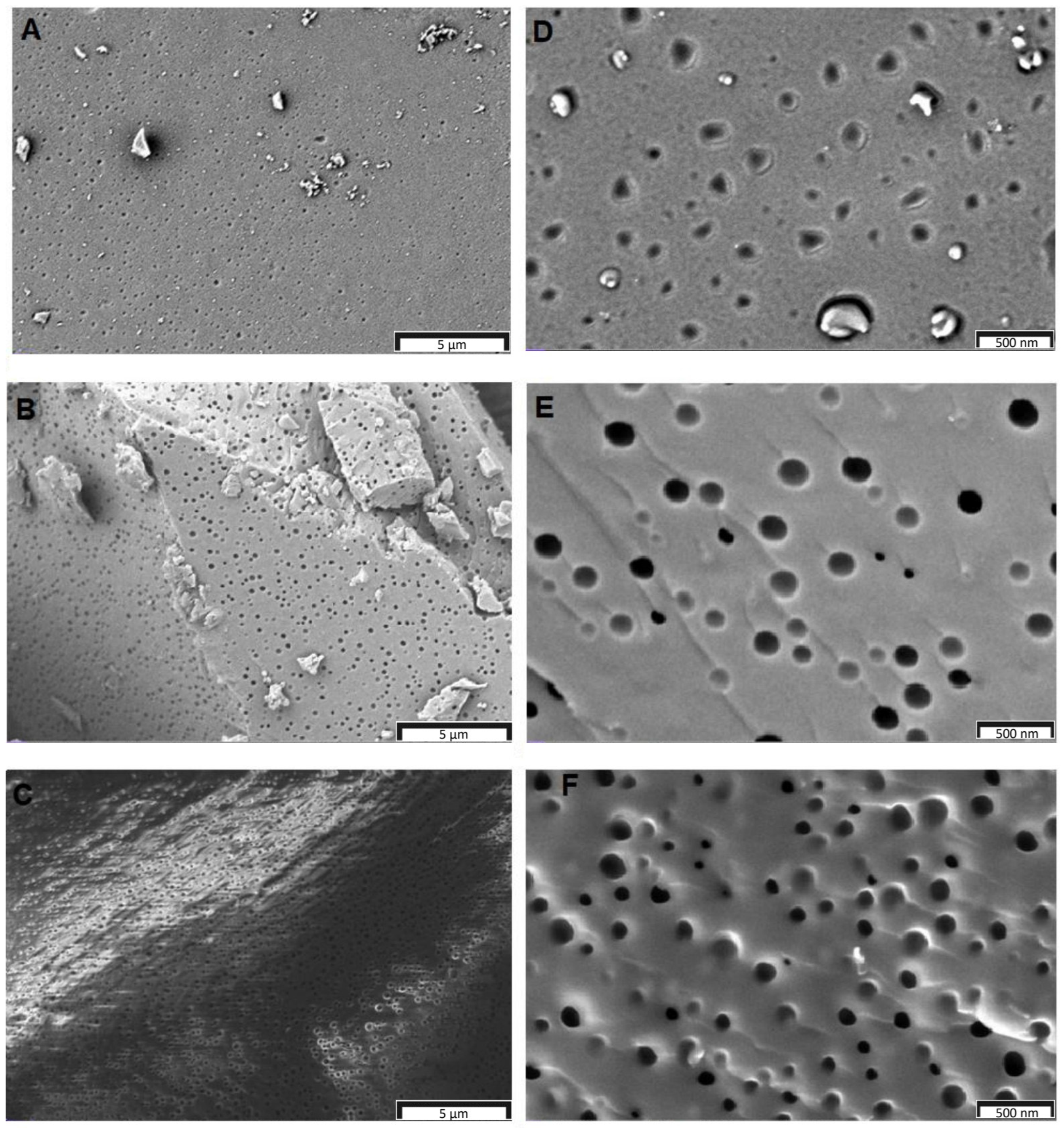
3.3. Surface Area and Pore Properties
3.4. Structural Properties
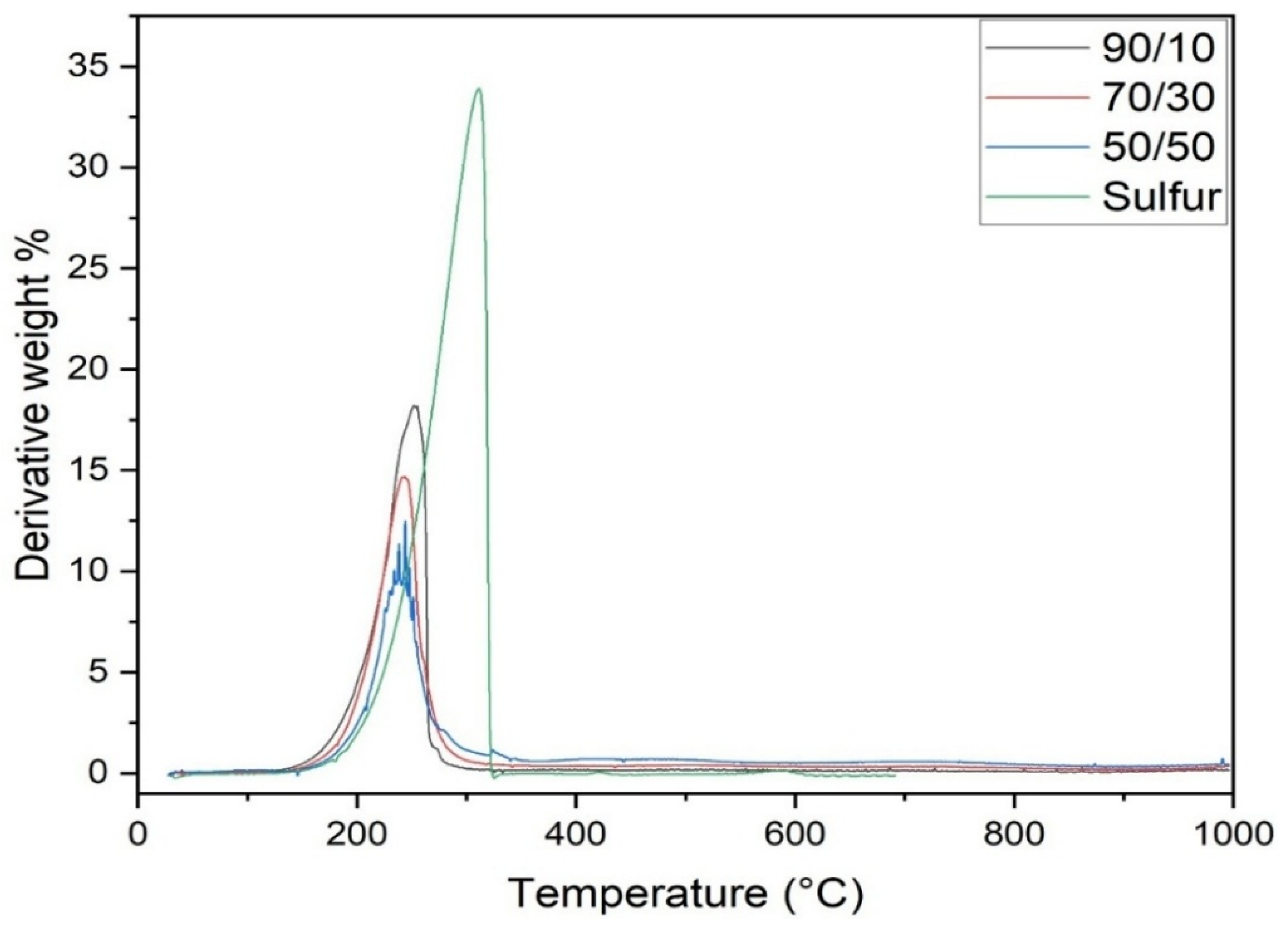
3.5. Thermal Properties
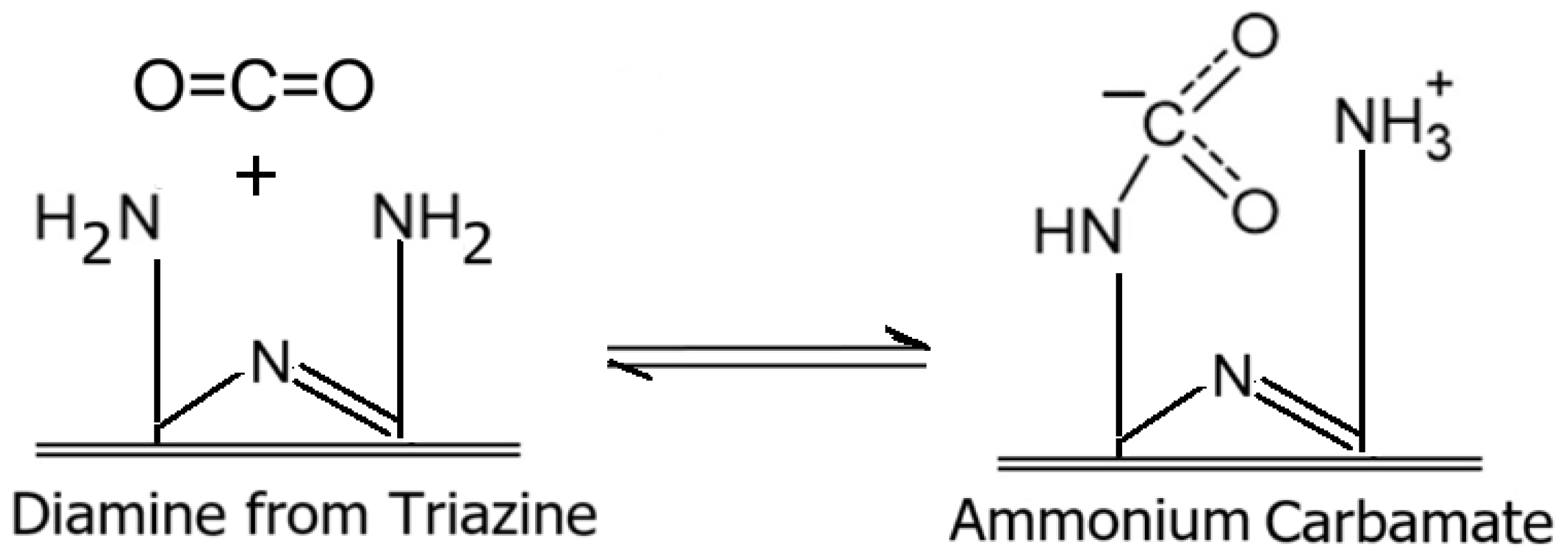
3.6. Evaluation of Aminated Sulfur-Containing Copolymer as Adsorbent for CO2 Adsorption
3.6.1. Effect of Sulfur Content
3.6.2. Effect of Porogen Content on CO2 Adsorption Capacity
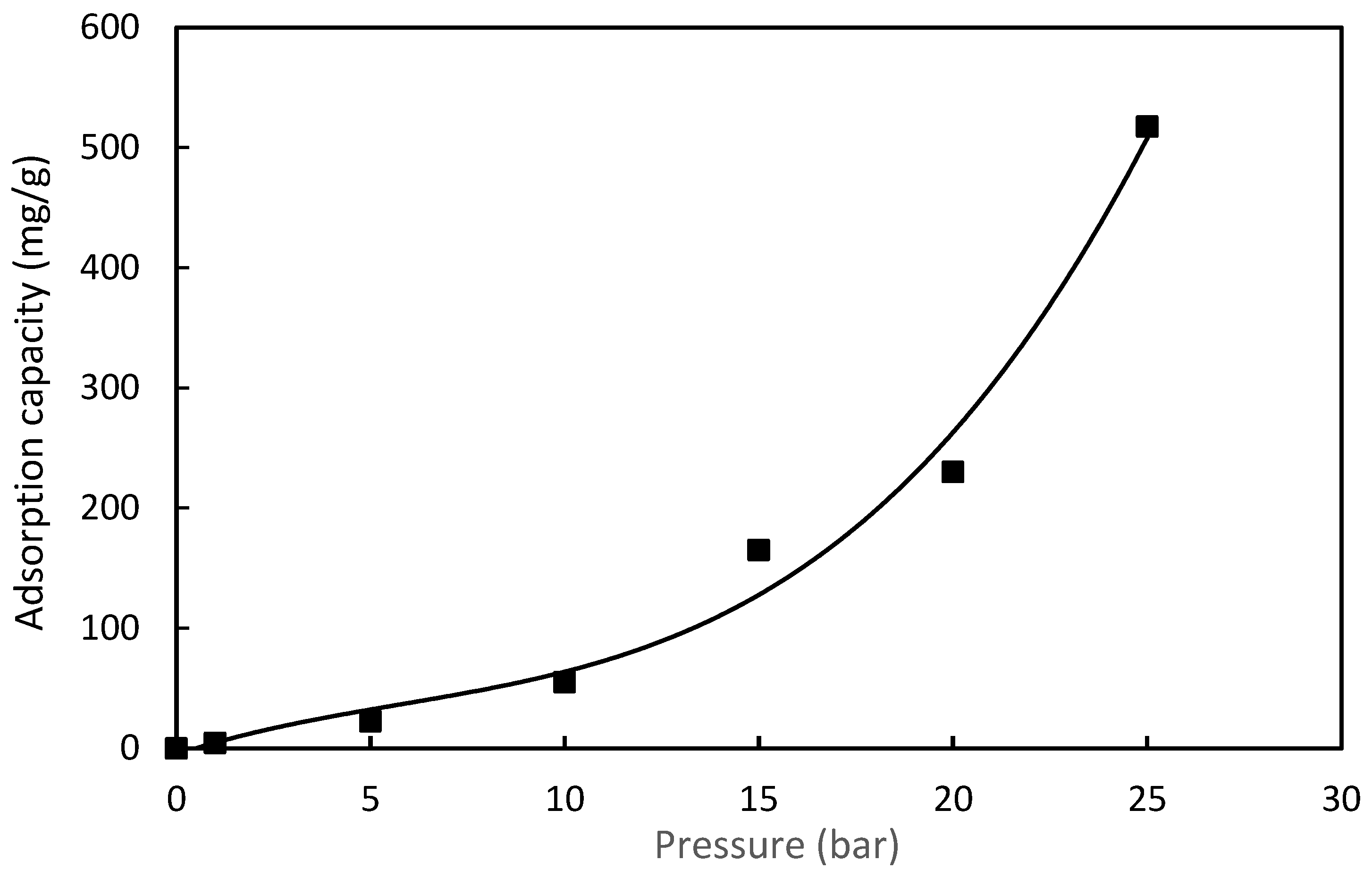
3.6.3. Effect of Pressure on CO2 Adsorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Msigwa, G.; Osman, A.I.; Fawzy, S.; Rooney, D.W.; Yap, P.S. Circular Economy Strategies for Combating Climate Change and Other Environmental Issues. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 21, 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenfeld, J.G.; Al-Ali, K.; Almheiri, S.; Slavens, A.F.; Calvet, N. Sustainable Applications Utilizing Sulfur, a by-Product from Oil and Gas Industry: A State-of-the-Art Review. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebiyi, F.M. Air Quality and Management in Petroleum Refining Industry: A Review. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2022, 4, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Nasef, M.M.; Yahya, W.Z.N. Copolymerization of Vegetable Oils and Bio-Based Monomers with Elemental Sulfur: A New Promising Route for Bio-Based Polymers. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2019, 13, 100158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, H. A Decade Development of Inverse Vulcanization Towards Green and Sustainable Practices. Polym. Rev. 2024, 64, 1211–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.K.; Karabay, B.; Karabay, L.C.; Cihaner, A. Elemental Sulfur-Based Polymeric Materials: Synthesis and Characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Griebel, J.J.; Dirlam, P.T.; Nguyen, N.A.; Glass, R.S.; Mackay, M.E.; Char, K.; Pyun, J. Inverse Vulcanization of Elemental Sulfur and Styrene for Polymeric Cathodes in Li-S Batteries. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2017, 55, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhou, C.; Wang, R.; Lan, F.; An, B.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X. Unveiling Inverse Vulcanized Polymers as Metal-Free, Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalysts for Cross-Coupling Reactions. Chinese Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 108832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griebel, J.J.; Namnabat, S.; Kim, E.T.; Himmelhuber, R.; Moronta, D.H.; Chung, W.J.; Simmonds, A.G.; Kim, K.J.; Van Der Laan, J.; Nguyen, N.A.; et al. New Infrared Transmitting Material via Inverse Vulcanization of Elemental Sulfur to Prepare High Refractive Index Polymers. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3014–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, D.A.; Nguyen, V.Q.; McClain, C.C.; Kung, F.H.; Baker, C.C.; Myers, J.D.; Hunt, M.P.; Kim, W.; Sanghera, J.S. Optical Properties of a Sulfur-Rich Organically Modified Chalcogenide Polymer Synthesized via Inverse Vulcanization and Containing an Organometallic Comonomer. ACS Macro Lett. 2019, 8, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuliu, Y.; Dong, W.; Huang, G.; Xie, H.; Yao, P.; Tan, J.; Mu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. Sulfur-Rich Norbornadiene-Derived Infrared Transparent Polymers by Inverse Vulcanization. Angew. Chem. 2025, 137, e202419446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, W.; Zhang, G. Transforming Element Sulfur to High Performance Closed-Loop Recyclable Polymer via Proton Transfer Enabled Anionic Hybrid Copolymerization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202414244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dop, R.A.; Neill, D.R.; Hasell, T. Antibacterial Activity of Inverse Vulcanized Polymers. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 5223–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.A.; Mulhall, R.; Goodman, S.; Fleming, G.; Allison, H.; Raval, R.; Hasell, T. Investigating the Antibacterial Properties of Inverse Vulcanized Sulfur Polymers. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5229–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, R.L.; Dop, R.A.; Sadler, E.; Lunt, A.M.; Neill, D.R.; Hasell, T.; Crick, C.R. Investigating the Viability of Sulfur Polymers for the Fabrication of Photoactive, Antimicrobial, Water Repellent Coatings. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 4153–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yan, P.; Li, X.; Miao, C.; Cai, S.; Ji, W.; Song, M.; Dodd, L.J.; Wu, X.; Hasell, T.; et al. Sulfur-Rich Polymers with Heating/UV Light-Responsive Shape Memory and Temperature-Modulated Self-Healing. Polym. Chem. 2023, 14, 3686–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor Ghumman, A.S.; Shamsuddin, R.; Nasef, M.M.; Maucieri, C.; Rehman, O.U.; Rosman, A.A.; Haziq, M.I.; Abbasi, A. Degradable Slow-Release Fertilizer Composite Prepared by Ex Situ Mixing of Inverse Vulcanized Copolymer with Urea. Agronomy 2022, 12, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wang, L.; Zan, X.; Zhang, L. Density-Adjustable Bio-Based Polysulfide Composite Prepared by Inverse Vulcanization and Bio-Based Fillers. Polymers 2020, 12, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Taghinezhad, S.F.; Mansourieh, M.; Xu, H.; Nasef, M.M.; Major, I. Inverse Vulcanized Sulfur-Styrene Polymers as Effective Plasticizers for Polystyrene. Polym. Test. 2024, 140, 108625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Ju, C.; Fan, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hadjichristidis, N. Inverse Vulcanization of Aziridines: Enhancing Polysulfides for Superior Mechanical Strength and Adhesive Performance. Angew. Chem. 2025, 137, e202418764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, P.; Guo, M.; Yu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Guo, B.; Zhou, G. Dual Functions of Inverse Vulcanized Copolymers as Both Vulcanizator and Interfacial Modifier for Improving the Mechanical Properties of Silica Reinforced Rubber Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2023, 239, 110075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.S.; Phan, A.; Olikagu, C.; Lee, T.; Loy, D.A.; Kwon, M.; Paik, H.; Hong, S.J.; Bang, J.; Parker, W.O.; et al. Segmented Polyurethanes and Thermoplastic Elastomers from Elemental Sulfur with Enhanced Thermomechanical Properties and Flame Retardancy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 22900–22907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, F.G.; Lisboa, L.S.; Chalker, J.M. Inverse Vulcanized Polymers for Sustainable Metal Remediation. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2023, 7, 2300010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, C.; Fu, Y.; Guo, T.; Yan, G.; Hu, J. Sulfur-Containing Adsorbent Made by Inverse Vulcanization of Sulfur/Oleylamine/Potato Starch for Efficient Removal of Hg(II) Ions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Jiang, X.; Liu, L.; Yin, C.; Wang, S.; Yang, X. Modification of High-sulfur Polymer Using a Mixture Porogen and Its Application as Advanced Adsorbents for Au(III) from Wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 328, 115437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Yahya, W.Z.N.; Nasef, M.M.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Ghumman, A.S.M.; Afolabi, H.K. Boron Removal by Glucamine-Functionalized Inverse Vulcanized Sulfur Polymer. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 177, 105311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherumukkil, S.; Agrawal, S.; Jasra, R.V. Sulfur Polymer as Emerging Advanced Materials: Synthesis and Applications. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202204428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amna, R.; Alhassan, S.M. A Comprehensive Exploration of Polysulfides, From Synthesis Techniques to Diverse Applications and Future Frontiers. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 4350–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Pyun, J.; Char, K. Recent Approaches for the Direct Use of Elemental Sulfur in the Synthesis and Processing of Advanced Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3249–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James Dodd, L. Inverse Vulcanisation: A New Starter’s Guide to an Emerging Field. RSC Appl. Polym. 2025, 3, 10–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.D.; Tennyson, A.G.; Smith, R.C. Sulfur-Containing Polymers Prepared from Fatty Acid-Derived Monomers: Application of Atom-Economical Thiol-Ene/Thiol-Yne Click Reactions and Inverse Vulcanization Strategies. Sustain. Chem. 2020, 1, 209–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.J.; Ren, W.M.; Lu, X.B. Copolymerization Involving Sulfur-Containing Monomers. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 14038–14083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyun, J.; Carrozza, C.F.; Silvano, S.; Boggioni, L.; Losio, S.; de Angelis, A.R.; O’Neil Parker, W. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Structural Characterization of Sulfur-Derived Copolymers from Inverse Vulcanization. Part 1: Styrene. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 60, 3471–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, I.; De Anastro, A.F.; Leonet, O.; Blazquez, J.A.; Grande, H.-J.; Pyun, J.; Mecerreyes, D. Sulfur Polymers Meet Poly(Ionic Liquid)s: Bringing New Properties to Both Polymer Families. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, 1800529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Nasef, M.M.; Yahya, W.Z.N.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Ghumman, A.S.M. Preparation and Characterization of Sulfur-Vinylbenzyl Chloride Polymer under Optimized Reaction Conditions Using Inverse Vulcanization. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 143, 110202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kleine, T.S.; Carothers, K.J.; Phan, D.D.; Glass, R.S.; Mackay, M.E.; Char, K.; Pyun, J. Functionalized Chalcogenide Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Polymers (CHIPs) via Inverse Vulcanization of Elemental Sulfur and Vinylanilines. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2290–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.J.; Griebel, J.J.; Kim, E.T.; Yoon, H.; Simmonds, A.G.; Ji, H.J.; Dirlam, P.T.; Glass, R.S.; Wie, J.J.; Nguyen, N.A.; et al. The Use of Elemental Sulfur as an Alternative Feedstock for Polymeric Materials. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, V.; Bear, J.C.; Rath, S.; Crick, C.R. Porous Sulfur Polymers for Effective Aqueous-Phase Organic Contaminant Removal. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadi, V.S.; Jena, K.K.; Khawaja, S.Z.; Ranagraj, V.M.; Alhassan, S.M. Preparation and Processing of Porous Sulfur Foams Having Low Thermal Conductivity. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 4397–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, M.; Kiskan, B.; Cengiz, E.C.; Demir-Cakan, R.; Yagci, Y. Inverse Vulcanization of Bismaleimide and Divinylbenzene by Elemental Sulfur for Lithium Sulfur Batteries. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 80, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Xiao, M.; Wang, S.; Han, D.; Song, S.; Chen, G.; Meng, Y. Sulfur-Rich Polymeric Materials with Semi-Interpenetrating Network Structure as a Novel Lithium-Sulfur Cathode. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 9280–9286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Dop, R.; Yan, P.; Neale, A.R.; Hardwick, L.J.; Hasell, T. Oxygen Heteroatom Enhanced Sulfur-Rich Polymers Synthesized by Inverse Vulcanization for High-Performance Lithium-Sulfur Batteries. J. Power Sources 2022, 545, 231921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Wang, H.; Dodd, L.J.; Hasell, T. Processable Crosslinked Terpolymers Made from Elemental Sulfur with Wide Range of Thermal and Mechanical Properties. Commun. Mater. 2023, 4, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Wu, X.; Berry, N.G.; Hasell, T. High Sulfur Content Polymers: The Effect of Crosslinker Structure on Inverse Vulcanization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2018, 56, 1777–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, V.; Bear, J.C.; Rath, S.; Crick, C.R. UV-Stable Photoactive Superhydrophobic Coatings Utilizing “Inverse Vulcanization” Sulfur Polymers. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 51, 104691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, D.J.; Jones, H.A.; Petcher, S.; Cervini, L.; Griffin, J.M.; Akhtar, R.; Hasell, T. Low Cost and Renewable Sulfur-Polymers by Inverse Vulcanisation, and Their Potential for Mercury Capture. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 11682–11692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.T.; Chung, W.J.; Lim, J.; Johe, P.; Glass, R.S.; Pyun, J.; Char, K. One-Pot Synthesis of PbS NP/Sulfur-Oleylamine Copolymer Nanocomposites via the Copolymerization of Elemental Sulfur with Oleylamine. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 3617–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayilan, M.; Kleine, T.S.; Carothers, K.J.; Griebel, J.J.; Frederick, K.M.; Loy, D.A.; Glass, R.S.; Mackay, M.E.; Char, K.; Pyun, J. Chalcogenide Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Polymer Resins: Amine Functional Prepolymers from Elemental Sulfur. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 58, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Seo, J.H.; Noh, G.Y.; Byun, W.; Kim, S.; Lee, W.; Park, S.; Kim, D.G.; Kim, Y.S. Inverse Vulcanization of Elemental Sulfur Catalyzed by Trialkyl Amines. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 4641–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrossamay, M.R.; Sun, G. A Study of Radical Graft Copolymerization on Polypropylene during Extrusion Using Two Peroxide Initiators. Polym. Int. 2010, 59, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hack, J.; Maeda, N.; Meier, D.M. Review on CO2 Capture Using Amine-Functionalized Materials. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 39520–39530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.J.R. The Rising Threat of Atmospheric CO2: A Review on the Causes, Impacts, and Mitigation Strategies. Environments 2023, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odunlami, O.A.A.; Vershima, D.A.A.; Oladimeji, T.E.E.; Nkongho, S.; Ogunlade, S.K.K.; Fakinle, B.S.S. Advanced Techniques for the Capturing and Separation of CO2—A Review. Results Eng. 2022, 15, 100512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattari, A.; Ramazani, A.; Aghahosseini, H.; Aroua, M.K. The Application of Polymer Containing Materials in CO2 Capturing via Absorption and Adsorption Methods. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 48, 101526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.M.; Kumar, S.V.; Alhassan, S.M. Porous Sulphur Copolymer for Gas-Phase Mercury Removal and Thermal Insulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crockett, M.P.; Evans, A.M.; Worthington, M.J.H.; Albuquerque, I.S.; Slattery, A.D.; Gibson, C.T.; Campbell, J.A.; Lewis, D.A.; Bernardes, G.J.L.; Chalker, J.M. Sulfur-Limonene Polysulfide: A Material Synthesized Entirely from Industrial By-Products and Its Use in Removing Toxic Metals from Water and Soil. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 1714–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasell, T.; Parker, D.J.; Jones, H.A.; McAllister, T.; Howdle, S.M. Porous Inverse Vulcanised Polymers for Mercury Capture. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 5383–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Zhao, W.; McBride, F.; Cai, D.; Dale, J.; Hasell, T. Mechanochemical Synthesis of Inverse Vulcanized Polymers. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghumman, A.S.M.; Nasef, M.M.; Shamsuddin, M.R.; Abbasi, A. Evaluation of Properties of Sulfur-Based Polymers Obtained by Inverse Vulcanization: Techniques and Challenges. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2020, 29, 1333–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleine, T.S.; Nguyen, N.A.; Anderson, L.E.; Namnabat, S.; Lavilla, E.A.; Showghi, S.A.; Dirlam, P.T.; Arrington, C.B.; Manchester, M.S.; Schwiegerling, J.; et al. High Refractive Index Copolymers with Improved Thermomechanical Properties via the Inverse Vulcanization of Sulfur and 1,3,5-Triisopropenylbenzene. ACS Macro Lett. 2016, 5, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Shui, H.; Peng, C.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y. Solubility of Elemental Sulfur in Pure Organic Solvents and Organic Solvent–Ionic Liquid Mixtures from 293.15 to 353.15 K. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2011, 312, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Sun, Y. Antimicrobial Polymers Containing Melamine Derivatives. II. Biocidal Polymers Derived from 2-Vinyl-4,6-Diamino-1,3,5-Triazine. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2005, 43, 4089–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghumman, A.S.M.; Shamsuddin, M.R.; Nasef, M.M.; Yahya, W.Z.N.; Ayoub, M.; Cheah, B.; Abbasi, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Sustainable Inverse Vulcanized Copolymers from Non-Edible Oil. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 1180–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Dai, Z.; Zhou, R.; Ke, Q.; Huang, C. Fabrication of Polypropylene-g-(Diallylamino Triazine) Bifunctional Nonwovens with Antibacterial and Air Filtration Activities by Reactive Extrusion and Melt-Blown Technology. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 3435095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amna, R.; Alhassan, S.M. Exploring Porous Sulfur Copolymers for Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewater: A Computational Study. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 138, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, D.A. Schwefel in Der Modernen Materialwissenschaft. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 15712–15729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaan, A.; Ghumman, M.; Shamsuddin, R.; Nasef, M.M.; Krivoborodov, E.G.; Ahmad, S.; Zanin, A.A.; Mezhuev, Y.O.; Abbasi, A.; Sabatini, V.; et al. A Degradable Inverse Vulcanized Copolymer as a Coating Material for Urea Produced under Optimized Conditions. Polymers 2021, 13, 4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Nasef, M.M.; Yahya, W.Z.N. Sulfur Based Polymers by Inverse Vulcanization: A Novel Path to Foster Green Chemistry. Green Mater. 2020, 8, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Yahya, W.Z.N.; Nasef, M.M.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Ghumman, A.S.M. Copolymerization of Palm Oil with Sulfur Using Inverse Vulcanization to Boost the Palm Oil Industry. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2021, 29, S1446–S1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Nasef, M.M.; Yahya, W.Z.N.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Ghumman, A.S. Preparation and Characterization of Green Polymer by Copolymerization of Corn Oil and Sulphur at Molten State. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2020, 29, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghumman, A.S.M.; Shamsuddin, R.; Nasef, M.M.; Nisa Yahya, W.Z.; Abbasi, A. Optimization of Synthesis of Inverse Vulcanized Copolymers from Rubber Seed Oil Using Response Surface Methodology. Polymer 2021, 219, 123553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, P.; Sandhu, N. A Review on Use of Elemental Sulphur in the Synthesis of Sulphur-Based Polymers. Mater. Today Proc. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadillah, G.; Saleh, T.A. Advances in Mesoporous Material for Adsorption and Photoconversion of CO2 in Environmental Pollution: Clean Environment and Clean Energy. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 29, 100812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, O.; Bolívar, C.; Ovalles, C.; García, J.J.; Espidel, Y. Reversible Adsorption of Carbon Dioxide on Amine Surface-Bonded Silica Gel. Inorganica Chim. Acta 1995, 240, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Tran, D.N.; Busche, B.J.; Fryxell, G.E.; Addleman, R.S.; Zemanian, T.S.; Aardahl, C.L. Ethylenediamine-Modified SBA-15 as Regenerable CO2 Sorbent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 3099–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Gao, Z.; Jing, Y.; Wang, Y. Adsorption of CO2 from Simulated Flue Gas on Pentaethylenehexamine-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Support Adsorbent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 14965–14974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.; Bhanja, P.; Bhaumik, A. A Triazine-Based Covalent Organic Polymer for Efficient CO2 Adsorption. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10050–10053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.; García-Díez, E.; Garcia, S.; Van Der Spek, M. The Impact of Binary Water–CO2 Isotherm Models on the Optimal Performance of Sorbent-Based Direct Air Capture Processes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 5377–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.H.; Huang, C.H.; Tan, C.S. A Review of CO2 Capture by Absorption and Adsorption. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 745–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambroz, F.; Macdonald, T.J.; Martis, V.; Parkin, I.P.; Ambroz, F.; Macdonald, T.J.; Parkin, I.P.; Martis, V. Evaluation of the BET Theory for the Characterization of Meso and Microporous MOFs. Small Methods 2018, 2, 1800173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, A.; Mellon, N.; Saqib, S.; Lee, S.P.; Bustam, M.A. Extension of BET Theory to CO2 Adsorption Isotherms for Ultra-Microporosity of Covalent Organic Polymers. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, A.; Ahmed, S.; Yusup, S. Adsorption Behaviour of Si-MCM-41 for CO2: Effect of Pressure and Temperature on Adsorption. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2014, 39, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, J.; Chen, L. Mixed Amine-Modified MCM-41 Sorbents for CO2 Capture. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2015, 37, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Zeng, W.; Kong, X. CO2 Adsorption of Aminopropyltrimethoxysilane-and-Tetraethylenepentamine-Co-Modified Mesoporous Silica Gel. Coatings 2025, 15, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcănescu, S.; Popa, A.; Verdeș, O.; Suba, M. Functionalized Ordered Mesoporous MCM-48 Silica: Synthesis, Characterization and Adsorbent for CO2 Capture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonmatoon, P.; Nokpho, P.; Piumsomboon, P.; Chalermsinsuwan, B. Enhanced CO2 Capture Performance Using Methyl Diethanolamine-Functionalized Silica Gels: Assessing CO2 Capture Capacity. Appl. Environ. Res. 2025, 47, 003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tsunoji, N.; Kumar, R.; Sukmana, N.C.; Sadakane, M. Minimizing Usage of Silane Coupling Agent for Amine-Grafted Mesoporous Silica CO2 Adsorbent. J. Porous Mater. 2024, 31, 1289–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| NaCl Content (wt%) | Total Pore Volume ×103 (cm3/g) | Means Pore Diameter (nm) | Surface Area (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 6.5 | 2.78 | 3.18 |
| 12.5 | 6.7 | 3.89 | 4.56 |
| 25.0 | 7.1 | 4.84 | 7.63 |
| 37.5 | 7.4 | 4.89 | 7.92 |
| 50.0 | 7.5 | 5.29 | 9.62 |
| Adsorbent Materials | Surface Area (m2/g) | CO2 Capacity (mg/g) | Mechanism of Adsorption | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCM 41 modified with TEPA and DEA on | 133.0 | 132 (1 bar, 70 °C) | Chemisorption/physisorption | [83] |
| Mesoporous silica gel modified with APTS/TEPA | 75.0 | 162 mg/g (1 bar, 70 °C) | Chemisorption/physisorption | [84] |
| Mesosilica MCM-48 modified with silane and EDA | 419 | 129 (1 bar, 30 °C) | Chemisorption/physisorption | [85] |
| Mesosilica gel modified with MDEA | 441.0 | 15.8 mg/g (1 bar, 70 °C) | Chemisorption/physisorption | [86] |
| Mesosilica (SBA-15) modified with APTMS | 170 | 24.0 (at 1 bar, 30 °C) | Chemisorption | [87] |
| Poly(S/NDAM) copolymer 50/50 (S/NDAM) | 9.62 | 19.0 (at 1 bar, 30 °C) | Chemisorption | This study |
| Poly(S/NDAM) copolymer 50/50 (S/NDAM) | 9.62 | 517.0 At 25 bar, 30 °C | Chemisorption | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Narendiran, D.; Sumadi, N.H.; Manzoor Ghumman, A.S.; Mohamad, N.A.; Nasef, M.M.; Abbasi, A.; Shamsuddin, R. A New Sulfur-Containing Copolymer Created Through the Thermally Induced Radical Copolymerization of Elemental Sulfur with N2,N2-Diallylmelamine Comonomer for Potential CO2 Capture. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9070362
Narendiran D, Sumadi NH, Manzoor Ghumman AS, Mohamad NA, Nasef MM, Abbasi A, Shamsuddin R. A New Sulfur-Containing Copolymer Created Through the Thermally Induced Radical Copolymerization of Elemental Sulfur with N2,N2-Diallylmelamine Comonomer for Potential CO2 Capture. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(7):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9070362
Chicago/Turabian StyleNarendiran, Dharrinesh, Nurul Hazirah Sumadi, Ali Shaan Manzoor Ghumman, Noor Ashikin Mohamad, Mohamed Mahmoud Nasef, Amin Abbasi, and Rashid Shamsuddin. 2025. "A New Sulfur-Containing Copolymer Created Through the Thermally Induced Radical Copolymerization of Elemental Sulfur with N2,N2-Diallylmelamine Comonomer for Potential CO2 Capture" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 7: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9070362
APA StyleNarendiran, D., Sumadi, N. H., Manzoor Ghumman, A. S., Mohamad, N. A., Nasef, M. M., Abbasi, A., & Shamsuddin, R. (2025). A New Sulfur-Containing Copolymer Created Through the Thermally Induced Radical Copolymerization of Elemental Sulfur with N2,N2-Diallylmelamine Comonomer for Potential CO2 Capture. Journal of Composites Science, 9(7), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9070362










