Abstract
Ultrafine fibers from poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and their blends with different component ratios in the range of 0/100 to 100/0 wt.% were obtained, and their structure and dynamic properties were studied. The polymers were obtained via electrospinning in solution mode. The structure, morphology, and segmental dynamic behavior of the fibers were determined using optical microscopy, SEM, EPR, DSC, and IR spectroscopy. The low-temperature maximum on the DSC endotherms provided information on the state of the PVP hydrogen bond network, which made it possible to determine the enthalpies of thermal destruction of these bonds. The PHB/PVP fiber blend ratio significantly affected the structural and dynamic parameters of the system. Thus, at low concentrations of PVP (up to 9%) in the structure of ultra-fine fibers, the distribution of this polymer occurs in the form of tiny particles, which are crystallization centers, which causes a significant increase in the degree of crystallinity (χ) activation energy (Eact) and slowing down of molecular dynamics (τ). At higher concentrations of PVP, loose interphase layers were formed in the system, which caused a decrease in these parameters. The strongest changes in the concentration of hydrogen bonds occurred when PVP was added to the composition from 17 to 50%, which was due to the formation of intermolecular hydrogen bonds both in PVP and during the interaction of PVP and PHB. The diffusion coefficient of water vapor in the studied systems (D) decreased as the concentration of glassy PVP in the composition increased. The concentration of the radical decreased with an increase in the proportion of PVP, which can be explained by the glassy state of this polymer at room temperature. A characteristic point of the 50/50% mixture component ratio was found in the region where an inversion transition of PHB from a dispersion material to a dispersed medium was assumed. The conducted studies made it possible for the first time to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the effect of the component ratio on the structural and dynamic characteristics of the PHB/PVP fibrous material at the molecular scale.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, research has focused on developing a new generation of medical products, including biodegradable sutures, wound dressings, tissue engineering scaffolds, polymer implants, and controlled drug delivery systems [1,2]. Both poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB), a microbiologically derived polyester, and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), the most accessible synthetic biodegradable polyester, exhibit biocompatibility and retain their functional properties over extended periods. However, they degrade into natural metabolites in natural environments and living organisms. This enables the creation of materials for direct tissue contact. However, each specific application demands a tailored set of properties from the polymer product. The development of biodegradable polymer composites significantly broadens the potential applications of these systems. An effective method for controlling supramolecular structures involves molding composites from mixed polymer solutions [3,4,5,6]. Given that structural characteristics largely dictate the performance of polymeric materials and their suitability for medical or pharmacological applications, establishing the relationship between the composition of molding solutions and the resulting properties of PHB/PVP-based materials is a critical research objective.
The significant relevance of studying PHB/PVP polymer composites for biomedical development stems from their accessibility, enzymatic hydrolytic degradability in living organisms, and availability of shared solvents. This combination enables the fabrication of materials with tunable structures and performance characteristics through compositional variations [7]. In addition to a high degree of biocompatibility with the human organism, natural polymers are highly effective biostimulants, i.e., they activate the body’s defense mechanisms [8]. They are used to develop products such as controlled release systems for drug compounds, suture threads, endoprostheses, wound dressings, and matrices for tissue engineering. [9]. These products are used in surgery, cosmetology, traumatology, dentistry, oncology, and many other branches of medicine. The field of application of biodegradable materials determines the direction of development of polymers with the required complex properties [4,5,6,9].
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) are among the most extensively studied families of thermoplastic biodegradable polymers [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. This prominence stems not only from their environmentally favorable characteristics—biodegradability, biocompatibility, and renewability—but also from their relatively good thermal properties and processability via melt or solution-blending. Nevertheless, the key properties of these biopolymers, including mechanical strength, thermal stability, and barrier performance, require optimization to broaden their application scope.
Biodegradable polymeric biomaterials offer a key advantage in medical settings: their ability to degrade and be resorbed after fulfilling their functions.
To achieve targeted property modifications in PHB, various fillers are incorporated into its polymer matrix [19,20,21,22]. Research has demonstrated that introducing complexes with distinct stereoconfigurations and chemical structures into poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) fibers induces significant alterations in the polymer’s structural and dynamic properties. Crucially, the magnitude and direction of these changes are governed by the specific chemical structure of the additive. For example, in osteoprosthetics, the necessity arises to design bone tissue analogs in the form of composites, which, along with the advantages of modern implants, such as biocompatibility and controlled (bio)degradation, are characterized by additional therapeutic functions, providing targeted drug transportation [23,24].
Despite its advantages, PHB has drawbacks like high cost and brittleness. Blending and compositing are key strategies for enhancing their performance in biomedical and environmental applications [11,25,26,27,28,29,30]. Alternatively, copolymerization [30,31] enables the precise modulation of monomer ratios to tailor the physicochemical properties. For instance, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV)—with reduced crystallinity versus PHB—finds broader medical use.
Heteropolymers like PHBV degrade faster in vivo than homopolymers: PHB’s ~60% crystallinity decreases below 50% with 3HV incorporation. Modified PHBV fibers yield scaffolds that promote cell anchorage for bone regeneration. Studies have confirmed that PHBV scaffolds incorporating inorganic hydroxyapatite (HA) particles enhance osteoblast attachment [32]. Furthermore, PHBV’s biocompatibility and piezoelectricity make it suitable for spinal cord regeneration support.
To overcome these disadvantages of the PHB polymer, blended compositions with other biomedical polymers, such as PVP, have been used.
PVP has a unique complex of physicochemical, chemical, and biological properties that are valuable for its practical use. PVP has a rather high chemical resistance, which increases with increasing molecular weight of the polymer.
PVP exhibits unique solubility behavior, readily dissolving in both water and diverse organic solvents. This dual compatibility stems from its amphiphilic nature, possessing both hydrophilic and hydrophobic functional groups that enable interactions with various solvent systems.
Incorporating PVP into electrospun fibers is particularly valuable for medical and pharmaceutical applications owing to its biocompatibility, biodegradability, non-toxicity, and non-ionic character [33]. This polymer facilitates the following:
- Production of rapidly dissolving nanofibers
- Enhanced dissolution rates for poorly water-soluble drugs [34,35,36,37]. The high surface area of nanofibers accelerates drug dissolution, potentially increasing their bioavailability [38]. Additionally, amorphous PVP can molecularly interact with drugs, stabilizing them in amorphous forms, which further enhances solubility [39].
The unique properties imparted by nanoscale dimensions enable prolonged drug release, enhancing therapeutic efficacy and reducing cytotoxicity [40].
Nanofibrous scaffolds create optimal 3D frameworks for cell migration and proliferation, promoting a high tissue integration affinity. These matrices are widely utilized in biosensors and nanofilters, wound therapy, enzyme immobilization, sustained/targeted drug delivery systems, and other biomedical applications [41,42,43].
In miscible polymer blends, intermolecular interactions, such as hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole forces, and electrostatic attractions, significantly influence drug encapsulation and release kinetics [44,45]. PVP’s molecular structure facilitates hydrogen bonding between pyrrolidone rings upon hydration, evidenced by its characteristic O-H stretching band at 3200–3700 cm−1 [45]. Notably:
- -
- Low porosity promotes excessive H-bonding
- -
- H-bond formation reduces polymer free volume [44]
- -
- While individually weak, the cumulative H-bonds substantially retard drug release rates [46].
Crucially, drug-matrix interactions govern the release behavior. PVP’s chemical structure drives complex formation with diverse polymers via H-bonding [47], making it particularly effective for delivering poorly water-soluble compounds.
- -
- Suppresses drug crystallization
- -
- Enhances dissolution kinetics [41,42,47,48,49].
This complexation capability converts insoluble agents into bioavailable forms. Combined with their high surface area, which accelerates dissolution and potentially increases bioavailability [49], PVP-based systems offer powerful formulation strategies. In many cases, PVP is usually present as an important excipient but not the active ingredient. Recently, PVP has found many new applications due to its unusual properties.
Studies have been conducted on PGB-based fibrous materials containing chitosan [50], graphene oxide [51], polylactide [20,52], iron (III), zinc porphyrin, magnesium porphyrin, and porphyrin complexes [53,54].
These investigations demonstrate how low-MW additives and polymer blending influence the crystalline and amorphous phase structures of the fibers. Structural variations in fibers containing identical additive concentrations arise from differences in the intermolecular interaction strength between the additive and polymer polar groups. Specifically, the PHB-chitosan blends form hydrogen bonds between the PHB carbonyls and chitosan amides, significantly altering the fiber structural-dynamic parameters.
By varying the PHB/PVP blend ratios—and thereby controlling the polymer morphology and structure—composites with tailored physicochemical characteristics can be engineered.
The combination of dynamic and structural methods provides an effective approach for assessing semicrystalline polymer phases and their evolution in blends. Establishing composition-structure-property relationships in electrospun PHB/PVP fibers is essential for designing matrices with precisely controlled functionality.
The aim of the present work is to obtain data on the influence of the composition of the PHB/PVP blend obtained by the electrospinning method on the structural and dynamic parameters of this material using EPR, DSC, and IR spectroscopy. In addition, the diameter and cross-sectional geometry of the fibers based on these polymers were determined.
The primary objectives of this work are as follows:
- To investigate how the PHB/PVP blend composition affects the structural-dynamic parameters of electrospun materials using EPR, DSC, and IR spectroscopy.
- To characterize the fiber diameter and cross-sectional geometry of these polymer systems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Forming Solutions, Electrospinning of PHB/PVP
This work investigates blended compositions of biodegradable polymers, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP). The fibers were prepared using PHB (16F series) (Biomer Comp., Krailling, Germany), a white fine powder produced via microbiological synthesis (Mw = 4.6 × 105 g/mol; density = 1.248 g/cm3), and PVP (Central Drug House (CDH) Corp., New Delhi, India) (Mw = 3 × 105 g/mol; density = 1.2 g/cm3). PVP, PHB, and PHB/PVP blends were electrospun from CHCl3 solutions. The total concentration of both polymer components (PHB and PVP) in the initial molding solution was maintained at 7 wt.%, the voltage on the electrodes was 19 kV, the capillary diameter was 0.7 mm, and the distance from this capillary to the receiving anode was 18 cm.
The spinning solutions of PHB and PVP were prepared in chloroform at a temperature of 60 °C using an automatic magnetic stirrer. The total concentration of both polymer components (PHB and PVP) in the initial spinning solution was maintained constant at 7 wt.%. The composition of the PHB/PVP fiber was varied within the range of 0–100% (0, 3, 5, 9, 17, 35, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, and 100% PVP). The detailed ratios of the components in the mixtures are presented in Table 1. The fibers were obtained by electrospinning using a single-capillary laboratory setup (Figure 1) (the original setup manufactured at the Karpov Institute of Physical Chemistry, Moscow, Russia) with the following parameters: capillary diameter, 0.7 mm; electric current voltage, 12 kV; distance between electrodes, 18 cm; and solution conductivity, 10 μS/cm. The process of manufacturing the nonwoven material samples is shown in Figure 1.

Table 1.
Ratio of components in the mixtures.
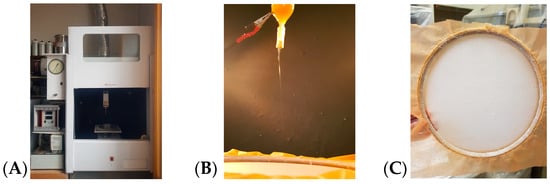
Figure 1.
The process of electrospinning fibers. (A) View of a single-capillary installation, (B) view of a capillary, and (C) finished nonwoven material.
The fiber geometry was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) using a Hitachi TM-3000 (Hitachi Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) at an accelerating voltage of 20 kV. Prior to imaging, the samples were sputter-coated with a 10–20 nm Au layer.
2.2. X-Band Electron Paramagnetic Resonance
X-band electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra were acquired using an EPR-V spectrometer (FIC CHF RAS, Moscow, Russia). The microwave power value did not exceed 1 mW to avoid saturation effects. The modulation amplitude was always significantly smaller than the resonance linewidth and did not exceed 0.5 Gs. The stable nitroxyl radical, TEMPO, was used as a spin probe.
Radical doping was performed via vapor-phase exposure at 60 °C for 1 h. Radical concentrations in the polymer matrices were quantified via EPR spectral integration, using a TEMPO/CCl4 vacuum solution (~1 × 10−3 mol/L) as the calibration standard.
The rotational correlation times (τ) of nitroxyl radicals within the range 5 × 10−11 < τ < 1 × 10−9 s were calculated from experimental spectra using the established relation [55].
where ΔH+ represents the spectral component linewidth in the weak-field region, and I+/I− denotes the intensity ratio between the weak- and strong-field components. The uncertainty in the τ measurements was ±5%. For correlation times within 1 × 10−9 < τ < 7 × 10−9 s, τ was calculated as follows: first, the effective (approximate) correlation time was determined from the experimental spectrum using the formula given above, and then the true correlation time was determined using a nomogram [56].
The radical adsorption equilibria in equal-mass samples were quantified using the WIN-EPR SIMFONIA software, version 1.2, is a product from Bruker. Spectral acquisition parameters (gain) were recorded, samples were weighed, and radical concentrations were calculated using software OriginPro 2025b.
2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
The samples were analyzed using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) on a DSC 204 F1 device from Netzsch (Netzsch GmbH & Co. KG, Selb, Germany) in an argon environment at a heating rate of 10 °C/min. The average statistical error in the measurement of the thermal effects was ±3%. The enthalpy of melting was calculated using the NETZSCH Proteus version 5.2.1 software. Thermal analysis was performed using a standard method. Peak separation was performed using NETZSCH Peak Separation 2006.01 software.
2.4. Sorption Capacity of Ultrafine PHB/PVP Fibers
The water sorption in the PHB/PVP fibers was measured gravimetrically using a McBain balance (quartz spiral sensitivity: 1.36 mm/mg). The electrospun mats were sectioned into specimens (≈5 × 3 cm2; 60–100 mg) and suspended in a thermostated vacuum chamber for isothermal gravimetry. The procedure followed an interval sorption protocol.
- Pre-treatment: 1-h evacuation to 0.1 mmHg (oil forevacuum pump) to remove ambient moisture
- Equilibration: Exposure to controlled water vapor pressures via a saturated inlet cylinder
- Measurement: Cathetometer recording of spiral elongation until equilibrium
- Pressure increment: Stepwise increases (0.8–0.9 activity range) with re-equilibration
This enabled:
- -
- Kinetic curve construction (mass gain vs. time) at discrete pressures
- -
- Equilibrium moisture uptake calculation
- -
- Water diffusion coefficient derivation
- -
- Sorption isotherm plotting (moisture uptake vs. vapor activity)
The diffusion coefficients were calculated as follows:
where tgα—tangent of diffusion kinetic curve slope angle [57],
D = tgαL2/5.784
L is the average fiber diameter (µm), and 5.784 is the coefficient, including the value of π and time dimensions.
2.5. IR Spectroscopy
The surface-layer PHB chain orientation and hydrogen bonding content were evaluated via FT-IR spectroscopy using attenuated total reflectance (ATR). Measurements were performed using a PerkinElmer Spectrum 100 spectrometer (PerkinElmer, Inc., Shelton, CT, USA) at the Collective Use Center’ New Materials and Technologies’ (IBCHF RAS, Moscow, Russia).
The spectra were acquired in the ATR mode (4000–650 cm−1 range) using a zinc selenide (ZnSe) crystal.
To determine the hydrogen bonding content, the 3408 cm−1 band was considered (its area was measured).
The optical densities of the 1228 cm−1 (crystallinity band) and 1182 cm−1 (disorder band) bands were measured to determine the fraction of rectified PHB chains on the surface of the samples [58,59].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Figure 1 shows the micrographs of the electrospun PHB and PVP nonwoven fiber materials.
The PHB fibers exhibited a bead-on-string morphology characterized by:
- -
- Elongated elliptical beads (25–30 μm longitudinal; 10–15 μm transverse dimensions)
- -
- Cylindrical fiber segments averaging 2–3 μm in diameter
This bead formation is attributed to PHB’s low electrical conductivity and high crystallization tendency during electrospinning.
The PVP materials displayed distinct morphologies (Figure 2):
- -
- Heterogeneous structures combining fibers (2–5 μm diameter) and fiber-like deposits
- -
- Resulting from a suboptimal molecular weight for stable electrospinning
The observed instability arises from intermittent transitions between
- Electrospraying (droplet formation)
- Mixed-mode ejection (simultaneous droplets/fibers)
- Stable fiber formation
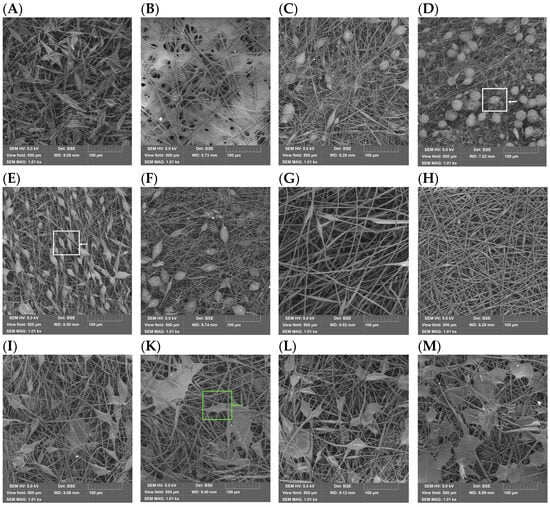
Figure 2.
SEM micrographs of electrospun nonwoven fiber materials: (A) PHB/PVP = 100/0, (B) 0/100, (C) 97/3, (D) 95/5, (E) 91/9, (F) 83/17, (G) 65/35, (H) 50/50, (I) 40/60, (K) 30/70, (L) 20/80, (M) 10/90 (Values denote mass ratios).
These regimes are governed by polymer-specific parameters, including solution concentration and molecular weight.
Micrographs of the PHB/PVP blended fiber materials show multiple thickenings with different geometries (green arrow—film structures; white arrow—round and elongated thickenings). These morphological differences arise from the distinct molecular interactions between the polar groups of both polymers during electrospinning under electrostatic stretching forces. The fiber diameters in the blends ranged from 0.5 to 5 μm, while the bead dimensions varied between 25 and 100 μm. Understanding the formation of PHB/PVP fibers requires an analysis of supramolecular structuring driven by polar group interactions.
3.2. Thermophysical Characteristics of PHB/PVP Composites
Blending PHB and PVP not only alters the fiber morphology but also modifies their thermophysical and structural characteristics. This work investigated the crystalline phase of PHB in PHB/PVP blends using DSC. Table 2 summarizes the composition-dependent parameters: PHB crystallinity (c), enthalpy of fusion (ΔH), PHB melting temperature (Tm), and hydrogen bond dissociation temperature (TD) of PVP. In all blended fiber material compositions (except for 100/0, 97/3, 95/5, and 0/100 PHB/PVP compositions), the DSC curves showed the presence of two melting peaks. The first peak represents the splitting of hydrogen bonds, and the second peak represents the melting of the PHB homopolymer.

Table 2.
DSC-derived characteristics of PHB/PVP blends: degree of crystallinity (χ), hydrogen bond dissociation enthalpy (ΔH, J/g), PHB melting temperature (Tm, °C), peak hydrogen bond disruption temperature (TD, °C).
We consider the binary system of PHB/PVP. The crystalline phase of these blended compositions was studied using DSC. The representative melting thermograms in Figure 3 depict: Pure PHB fibers, pure PVP fibers, and the 83/17 PHB/PVP blended composite.
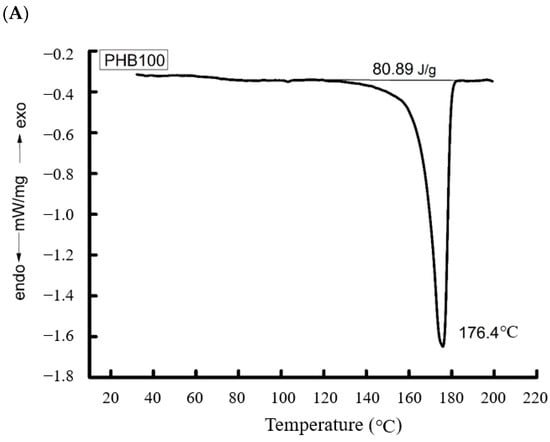
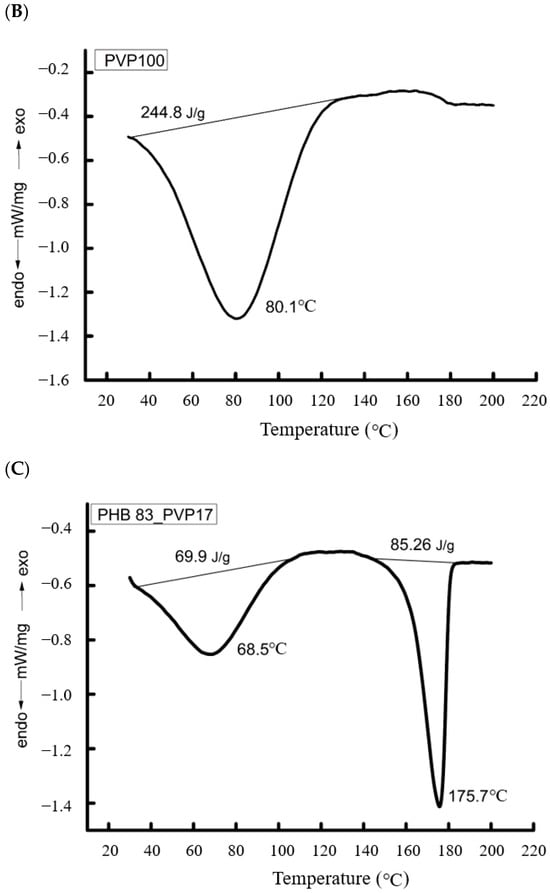
Figure 3.
Thermograms of blended compositions of ultrafine PHB/PVP fibers: (A)—PHB, (B)—PVP, (C)—PHB/PVP 83/17 (%).
PHB, which is highly crystalline, displays an asymmetric melting endotherm at 176.7 °C (Tm). This peak asymmetry indicates a broad distribution of crystallite sizes and structural imperfections. The specific fusion enthalpy (ΔH) was 80.9 J/g, corresponding to a crystallinity of 55.8% (Table 2).
The DSC thermograms of the PHB/PVP blends (91/9 to 10/90) consistently exhibited two endothermic peaks. The low-temperature peak corresponds to the disruption of hydrogen-bond networks, manifesting as a broad endotherm whose intensity reflects the energy of H-bond dissociation. Figure 4 presents the composition-dependent trends for
- -
- PHB crystallinity (χ)
- -
- Enthalpy of H-bond dissociation (ΔH)
- -
- Peak dissociation temperature (T)
Key crystallinity (χ) observations:
- -
- Increase from 55.8% to 69.8% at 3% PVP
- -
- Sharp decrease to 48.3% at 50% PVP
- -
- Transition point at 50/50 composition
- -
- Stabilization with minimal variation in χ at PVP > 50%
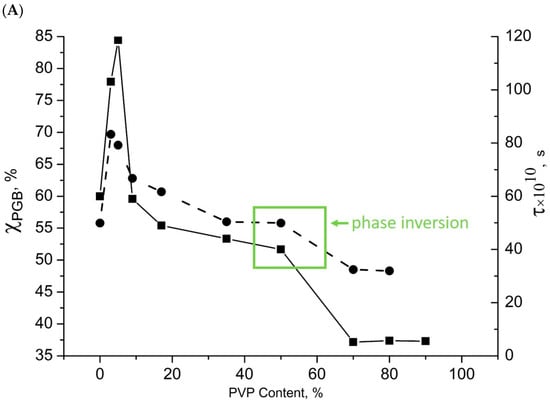

Figure 4.
Dependence on the content of PHB/PVP composition: (A)—χ (●), τ (■); (B)—ΔH (●), t0 (■).
At low PVP concentrations (≤3%) in ultrafine fibers, PVP is distributed as nanoscale particles that serve as crystallization nuclei. This significantly increased the PHB crystallinity (χ) due to the intermolecular PHB-PVP interactions. At higher PVP concentrations, PVP segregated into larger domains incapable of nucleating crystallization, while interphase layers formed. Hydrogen bonding between the PHB and PVP molecules prevented fiber crystallization, reducing χ as the PVP content increased. Similar patterns were obtained when studying the PHB/PLA mixture compositions [20].
The melting point of PHB decreased from 176.4 °C in pure fibers to ~175 °C in blends. This Tm depression correlated with the PVP content and reflected impaired crystallization. Reduced χ and Tm values indicate imperfect PHB crystallites in the binary mixtures. During crystallization, PVP molecules create steric hindrances to ideal chain packing in the crystallites and form hydrogen bonds, with both effects intensifying at higher PVP concentrations. Similar patterns were observed when studying the structure of mixed compositions of PHB with chitosan [41,50]. FTIR spectroscopy confirmed hydrogen bonding through broadened hydroxyl absorption bands shifted to 3450–3340 cm−1 compared to free hydroxyl groups at 3755 cm−1 [60].
If it is assumed that hydrogen bonds are formed only in PVP, then the dependence of ΔH on the structure of the composition will have the form of a straight line parallel to the x-axis. However, such dependence was observed only in the range from 50 to 100% PVP (стрелка, and the concentration of hydrogen bonds practically did not change (Figure 4). When the PHB concentration in the system increased from 50 to 83%, a sharp increase in ΔH was observed, and at higher PHB concentrations in the mixture, a sharp decrease in this parameter occurred. Earlier, it was noted that phase inversion occurred at a 50/50% composition (Figure 4, green arrow).
In blends with 50–100% PVP, the continuous phase consisted of highly hydrophilic PVP, where hydrogen bonds predominantly formed within the PVP network. The concentration of PHB/PVP hydrogen bonds remained low in this composition. It is proposed that hydrogen bonding occurs not only within PVP but also between the ester and hydroxyl groups of PHB and the carbonyl groups of PVP. In formulations with a high PVP content, the proportion of hydrogen bonds between PVP and PHB was small. As the proportion of PHB in the system increased, it increased in the PHB concentration range from 50 to 83%. It may be assumed that at low concentrations of PVP in the composition, when this polymer already forms a discrete phase in the mixture, the formation occurs in the form of finely dispersed formations, and the number of contacts with PHB is large. The result of such an interaction is a sharp increase in ΔH. The DSC peak maximum for hydrogen bond dissociation decreased from 80.1 °C to 54 °C with increasing PHB content (Figure 4), indicating weakened bonding interactions. Moisture absorption increased sharply at PVP contents ≥ 17%, facilitating hydrogen bond formation, with a dissociation temperature range of 20–130 °C.
These thermal transitions reveal a critical 50/50 composition threshold, where phase inversion occurs: PVP transitions from a continuous to a dispersed phase.
In pure PVP and PVP-rich blends (>50% PVP), dense hydrogen-bond networks efficiently retain water molecules. However, when the PHB content exceeded 50%, a sharp increase in ΔH occurred due to the formation of new hydrogen bonds between the PVP carbonyl groups and the PHB ester/hydroxyl moieties (main chain and terminal groups). Although weaker than intra-PVP hydrogen bonding, these interactions affect the free volume and molecular dynamics, which were analyzed via EPR.
Hydrogen bonds were formed only above 9% PVP content. Maximum bond concentration changes occurred at 17–50% PVP due to intermolecular bonding between the PVP carbonyls and PHB ester/terminal groups. Beyond 50% PVP, where PHB becomes the dispersed phase, changes gradually as the polymer contacts diminish.
Below 9% PVP, the PHB crystallinity improves significantly, and the crystallite fraction increases through PVP-nucleated crystallization. At higher PVP concentrations, the segregated PVP domains formed discrete phases. Interfacial layers develop hydrogen bonds between PHB ester/hydroxyl groups and PVP carbonyls, characterized by lower dissociation temperatures (80.1→54 °C) and reduced strength compared to pure PVP networks.
The 50/50 composition exhibited a sharp ΔH jump, reflecting both intra-PVP bond strengthening and new interpolymer bonding. These structural modifications should alter the segmental mobility, which will be examined through EPR analysis.
3.3. Study of the Surface of PHB/PVP Fiber Material by IR Spectroscopy
The surface structures of PHB, PVP, and their mixtures were monitored using IR spectroscopy. To determine the content of hydrogen bonds, the band in the range of 3433–3334 cm−1 was studied (its area was recorded). Figure 5 presents the FTIR spectra of the investigated polymer systems.
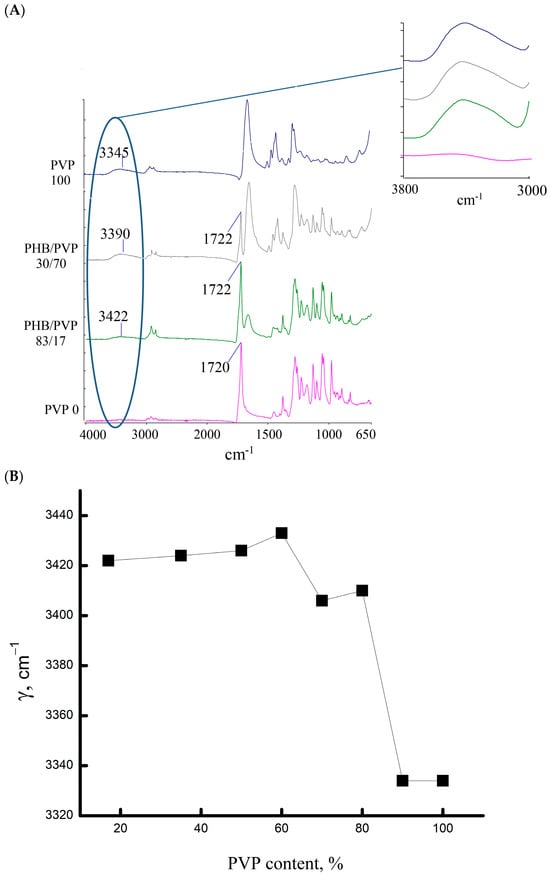
Figure 5.
IR spectra of multiple disturbed total internal reflection (MDTIR) compositions of PHB/PVP: (A) full IR spectra; (B) dependence of the frequency of the absorption band of hydroxyl groups bound by hydrogen bonds on the composition of the mixture.
FTIR spectra of PVP fibers and PHB/PVP blends exhibit characteristic hydrogen bonding peaks. Both pure PVP and the 10/90 PHB/PVP composition displayed the lowest frequency vibrations within the studied range. An increase in the PHB content shifted the absorption to higher frequencies, signifying progressively weaker hydrogen bonds. Consistent with the DSC data, systems containing > 50% PHB developed additional bonds between the PHB ester groups and PVP carbonyls, driving the sharp increase in ΔH observed in the thermal analysis.
3.4. Molecular Dynamics in Amorphous Regions of Electrospun PHB/PVP Composites
The structure and molecular dynamics of the amorphous regions in semicrystalline polymers are governed by the crystalline phase content. Blending highly crystalline PHB with amorphous PVP modifies both the PHB crystallinity (χ) and the mobility of the amorphous phase. Molecular dynamics were probed using EPR spectroscopy with the stable nitroxyl radical, TEMPO, as a molecular probe.
First, the effect of the blended composition of PHB/PVP on the molecular dynamics is considered.
The EPR spectra of the TEMPO radicals in both pure PHB and blended composites exhibited a superposition of two spectral components [61,62], corresponding to distinct radical populations characterized by correlation times τ1 and τ2. As shown in Figure 6, τ1 represents the molecular mobility in denser amorphous regions (designated as the slow component), while τ2 reflects faster mobility in less densely packed amorphous domains (identified as the fast component).
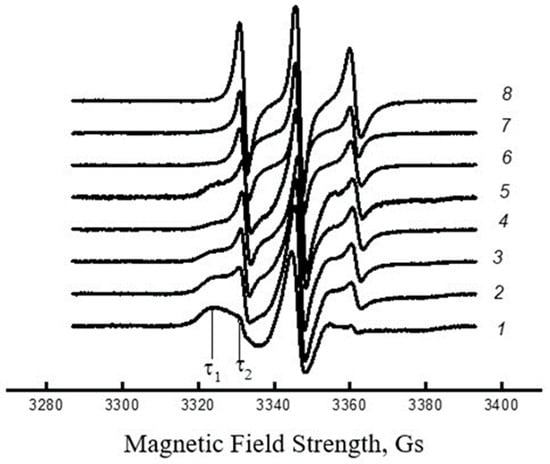
Figure 6.
EPR spectra of TEMPO radical in electrospun PHB/PVP composites: 1: 100/0, 2: 97/3, 3: 95/5, 4: 65/35, 5: 50/50, 6: 30/70, 7: 10/90, 8: 0/100%.
The heterogeneity of the amorphous regions arises from variations in the polymer packing density, resulting in distinct molecular dynamics. However, as demonstrated in [63], the characteristic mobility across probe rotation velocities can be represented by a single integral parameter, the relaxation time (τ).
PVP’s inherent rigidity, established previously, stems from its macromolecular structure and dense hydrogen-bonding network, creating high energy barriers to internal chain rotation. These barriers originate from steric hindrances in the segmental motion coupled with hydrogen bond formation. This glassy polymer matrix inhibits radical penetration, as evidenced by the low radical concentrations in the high-PVP samples (≤50%, Figure 7).
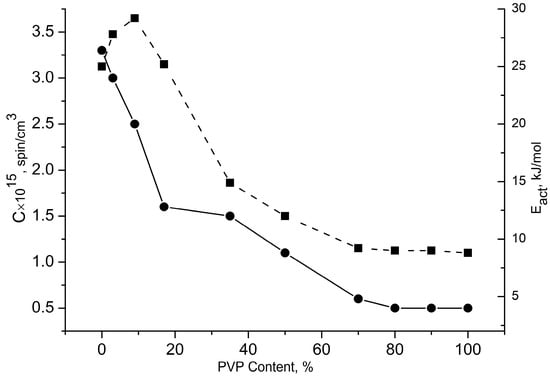
Figure 7.
Dependence of radical concentration Crad. on fiber material composition (●) and change in activation energy Eact. on the mixture concentration (■).
The equilibrium radical concentrations (Crad) in equal-mass samples were quantified using the Bruker WinEPR software. At the 50/50% phase inversion point, where the thermal properties shift the composition dependence, component incompatibility drives phase reversal. The addition of minor PVP (3.5%) reduced Crad due to the diminished amorphous regions. Higher PVP concentrations further decreased despite the increased amorphous content because the radicals were primarily adsorbed at the interfacial zones within the glassy PVP matrix. This effect culminates in a sharp Crad decline at 50/50% (Figure 7), where PVP’s glassy structure dominates.
Here also, as in the dependence of the system composition, a maximum located in the same concentration range (~3–5% PVP) is observed. The growth of c and τ at small additions of PVP and the sharp decrease in radical concentration are explained by the compaction of the mixture structure due to the formation of crystallites on the smallest particles of PVP, as there is an intermolecular interaction of polymers in the composition. It can be assumed that with an increase in the PVP concentration in the system, the particles increase in volume and can no longer perform the function of crystallite nucleation, and there is a loosening of the fiber structure due to the formation of interphase interlayers. This leads to a decrease in the crystallinity and alters the correlation times. Discontinuities in the radical concentration (Crad), hydrogen bond dissociation temperature, integral correlation time (τ), and PHB crystallinity (χ) occurred at a 50/50% composition (Figure 4), indicating phase inversion, where PHB transitioned from a continuous to a dispersed phase.
In addition to intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonding in PVP, blending with PHB introduces additional interactions through hydrogen bonding between the PHB ester groups and deacetylated PVP carbonyl groups. It is proposed that this partial disruption of the PVP hydrogen bond network reduces its compactness.
Further insights into the system dynamics emerge from temperature-dependent rotational diffusion studies. The activation energies (Eact) exhibited a characteristic discontinuity at the phase inversion point (50/50% PVP), consistent with the thermodynamic observations (Figure 7). Key trends include:
- -
- Eact increases with minor PVP additions (≤17%)
- -
- Progressive decrease occurs at intermediate PVP concentrations
- -
- A sharp drop at >50% PVP, followed by minimal concentration dependence.
The obtained dependences correlate well with the previously obtained dependences τ and c on the composition of the mixture. The nature of the temperature dependence varies with the composition. In PHB-rich systems, the radical correlation time (τ) increased during initial heating (≤40 °C), indicating the progressive activation of constrained amorphous domains as the thermal energy overcame the local mobility barriers. In samples with PVP contents greater than 50%, the temperature dependence was linear (Figure 8), which indicated a homogeneous structure in which the radical was sorbed. The observed regularity is due to the glassy state of the PVP matrix, and consequently, the low permeability of the radical.
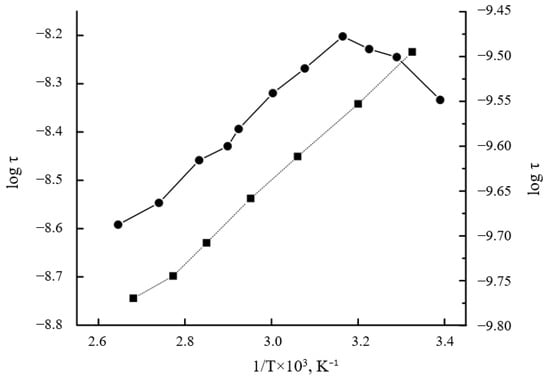
Figure 8.
Temperature dependence of the parameter τ for (●)—PHB/PVP 65/35% composition and (■)—initial PVP polymer.
Thus, increasing the PVP content to 9% (where the PHB crystallinity peaks and molecular dynamics slow) elevates the radical activation energy (Eact). This Eact increase corresponds to the structural reorganization of the intercrystalline amorphous phase, including the formation of interfacial layers with modified mobility. The densification of the amorphous regions—resulting from PVP-nucleated crystallite formation—provides a plausible mechanism for the observed energy barrier enhancement. At higher PHB contents in the mixture, a decrease in this parameter was observed in the region of compositions 50/50% PHB/PVP, similar to the previously presented laws c, DH, τ, and Crad. There is a kink in this dependency.
Molecular dynamics analysis of the PHB/PVP blends revealed composition-dependent trends.
- -
- At ≤9% PVP: Significant τ increase confirms slowed segmental dynamics due to enhanced crystallinity (Section 3.2), concurrent with sharp C decrease
- -
- At PVP concentrations > 9%, accelerated molecular mobility emerges through interfacial layer formation.
Notably, blending introduced novel hydrogen bonding between the PHB ester groups and the deacetylated PVP amino groups. This interaction likely disrupts PVP’s native hydrogen bond network, reducing its structural compactness. This fact is confirmed by the course of the downward branch of the dependence of the integral correlation time (τ). The glassy PVP matrix impedes radical penetration, as evidenced by low radical concentrations in samples with >50% PVP content, where phase inversion occurs. This transition fundamentally alters the composition-dependent thermal behavior. The parallel trends in Crad, χ, and τ reflect a unified structural-dynamic reorganization during phase inversion, specifically PHB’s transition from a dispersed phase to a continuous medium at 50/50% composition.
3.5. Analysis of Sorption Capacity of Ultrafine PHB/PVP Fibers
The sorption capacity is governed by polymer chemistry, morphology, surface characteristics, and porosity, with hydrolytic degradation kinetics primarily dependent on sorption-diffusion properties. For electrospun nonwoven materials, three factors dominate the sorption behavior: the specific surface area, fiber hydrophilicity, and material density. During sorption, water vapor first condenses on fiber surfaces and then diffuses into the fibrous matrix while inter-fiber voids remain vapor-filled; condensation within these voids yields unrealistic moisture absorption exceeding 100%. Given PVP’s high hydrophilicity, the sorption capacity increases proportionally with the PVP content. The sorption mechanism progresses sequentially: initial water molecule adsorption on fiber surfaces, followed by diffusion into the bulk, and culminating in physical and chemical interactions with polymer polar groups. The PHB/PVP nonwovens exhibited contrasting hydrophilicity-driven sorption profiles: semicrystalline PHB (55.8% crystallinity) demonstrated minimal moisture uptake despite its crystalline structure, whereas glassy PVP showed substantial absorption due to its inherent hydrophilicity. Figure 9 quantifies these differences using composition-dependent sorption isotherms, confirming PHB’s low capacity and the high performance of PVP.
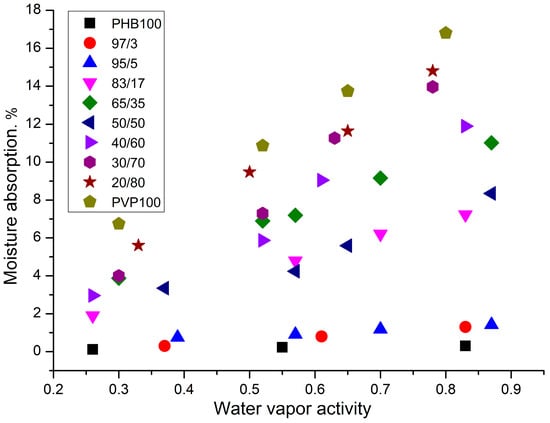
Figure 9.
Sorption isotherms of nonwoven fiber materials, PHB/PVP, from water vapor activity at 25 °C. The relative error in measuring water vapor sorption can be 10%.
All blended fiber materials exhibited intermediate water sorption capacities between those of pure PHB and PVP. The sorption capacity increased proportionally with the PVP content, demonstrating the direct composition-dependent behavior quantified in Figure 9.
This dependence is not monotonic. At low concentrations of PVP in the system (up to 9%) the values of sorption capacity remain at the same value and amount to ~0.8%, at addition of 17 and 50% of PVP in the composition this value immediately increases up to ~7% and only at higher content of PVP in the fibers of the mixture a sharp growth of sorption capacity of the system begins and it reaches 17%. Thus, in the region of 50/50%, as well as in previous studies on the change of t, DH, c, TD, and Crad. With a change in the mixture composition, there was a kink in the dependence of the sorption capacity on the composition of the mixture, which confirmed the conclusion regarding phase inversion in this range of polymer concentrations. Experimental limitations prevent the direct calculation of water vapor diffusion coefficients from sorption kinetics in nonwoven matrices. The electrospun fiber diameters (1–9 μm) enabled near-instantaneous sorption completion (~1 min), exceeding the instrumental resolution. While full kinetic tracing was unfeasible, diffusion coefficient ranges were estimated (Figure 10). These calculations revealed a sharp decrease in the diffusion coefficient (D) with increasing PVP content, which was attributable to the density enhancement from the incorporation of the glassy polymer.
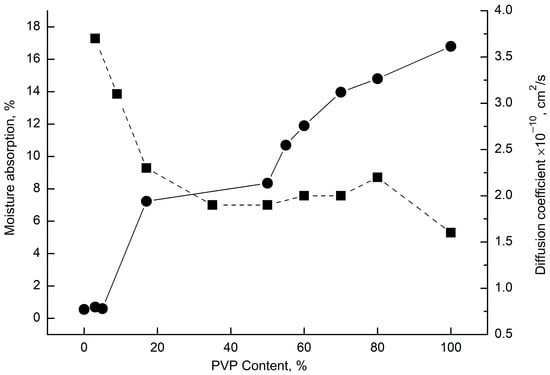
Figure 10.
Sorption isotherm of PHB/PVP nonwoven fibrous materials at 25 °C from the mixture composition at water vapor activity ~0.85 r.o.u. (●); diffusion coefficient (D) vs. blend composition (■).
Thus, the sorption analysis of electrospun PHB/PVP fibers reveals a critical paradox: despite the heightened water vapor activity in PVP-rich systems, the diffusion coefficient (D) decreases with increasing PVP content. This inverse relationship stems from the density reduction within the interfacial amorphous layers of the ultrafine fibers.
This section may be divided into subheadings. This section should provide a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation, and the experimental conclusions that can be drawn.
4. Conclusions
This paper shows that mixing PHB and PVP results in significant changes in the degree of PHB crystallinity (χ), activation energy (Eact), molecular dynamics (τ), concentration of hydrogen bonds in the bulk and on the surface of the fiber, concentration of radicals in amorphous regions (C), water sorption, and diffusion coefficient. Phase inversion occurred in the range of PHB/PVP 50/50% compositions. At low PVP concentrations in the structure of ultrafine fibers (up to 9%), the distribution of this polymer occurs in the form of tiny particles, which are crystallization centers, causing a significant increase in χ and τ (due to intermolecular interactions between PHB and PVP molecules). At higher PVP concentrations, the molecules segregated into particles of a sufficiently large size and could not act as crystallization centers. Loose interphase layers are formed, and consequently, χ, τ, and Eact decrease. A change in the degree of crystallinity is accompanied by a change in the molecular dynamics of the amorphous component. The concentration of the radical in the system decreases when PVP is added, since the proportion of the vitrified polymer in the composition with a low diffusion coefficient of the radical increases.
Weak changes in the presented parameters occurred at PVP concentrations above 50% (except for ΔH and TD, where a sharp increase began). The formation of hydrogen bonds was due to the presence of water vapor, and moisture absorption by the system began at a PVP content of 17%. Hydrogen bonds were formed in the range of 17–100% PVP in the mixture. Thus, changing the composition of biodegradable polyester films allows for targeted changes in the morphology of the polymer material, surface composition of the fibers, and their structural and dynamic parameters. The ability to regulate these parameters is a prerequisite for obtaining medical materials with specific properties. In the future, it is expected that, based on the studied systems, it will be possible to create biologically active materials with controlled drug release, as well as biodegradable polymer matrices promising for use in tissue engineering. Studies on the mixed composition of PHB/PVP have shown that mixed compositions containing up to 50% PVP lead to strengthening and increased stability of the composition. These studies have made it possible for the first time to carry out a comprehensive analysis of the effect of the component ratio on the structural and dynamic characteristics of the fibrous PHB/PVP material at the molecular level. Changing the composition of environmentally friendly fibrous biodegradable materials based on hydrophobic PHB and hydrophilic PVP allows for targeted changes in the morphology, surface composition, structural and dynamic parameters, and degree of hydrophilicity of the polymer fiber, which makes it possible to obtain stable materials for medical purposes, hygienic materials, matrices for the programmed release of biologically active substances, and ecosorbents that are promising for use in medicine, tissue engineering, and sustainable environmental protection. The ultra-thin fibrous materials studied are potentially intended for the development of innovative materials with different hydrophilic-hydrophobic balances for sustainable environmental chemistry, production, and mechanical engineering.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.A.V., A.A.P. and S.G.K.; methodology, I.A.V.; software, E.P.D.; validation, A.L.I., A.A.O. and A.A.V.; formal analysis, N.G.S.; investigation, A.G.F.; resources, A.A.V.; data curation, Y.K.L.; writing—original draft preparation, I.A.V. and A.A.V.; writing—review and editing, I.A.V., A.A.V. and A.L.I.; visualization, E.P.D.; supervision, S.G.K.; project administration, S.G.K.; funding acquisition, A.A.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Raw data can be provided upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The study was carried out using scientific equipment of the Center of Shared Usage «New Materials and Technologies» of Emanuel Institute of Biochemical Physics and the Common Use Centre of Plekhanov Russian University of Economics.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lins, L.C.; Padoin, N.; Pires, A.T.N.; Soares, C. Modeling Ketoprofen Release from PHB/Chitosan Composite Microparticles. Polym. Bull. 2016, 73, 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’brien, M.P.; Carnes, M.E.; Page, R.L.; Gaudette, G.R.; Pins, G.D. Designing Biopolymer Microthreads for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Curr. Stem Cell Rep. 2016, 2, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Iwata, T.; Tanaka, F.; Doi, Y. Crystal Structure and Enzymatic Degradation of Poly(4-Hydroxybutyrate). Macromolecules 2003, 36, 6401–6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi, I.; Venditti, I.; Trotta, F.; Punta, C. Environmental Safety of Nanotechnologies: The Eco-Design of Manufactured Nanomaterials for Environmental Remediation. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 864, 161181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Challenges and New Opportunities on Barrier Performance of Biodegradable Polymers for Sustainable Packaging. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 117, 101395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzi, F.; Puglia, D.; Torre, L. Natural Fiber Biodegradable Composites and Nanocomposites: A Biomedical Application. In Biomass, Biopolymer-Based Materials, and Bioenergy: Construction, Biomedical, and other Industrial Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Markova, N. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Electrospun Materials from Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) and Polyvinylpyrrolidone Containing Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester—“in” and “on” Strategies for Enhanced Solubility. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 545, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonartsev, A.P.; Bonartseva, G.A.; Reshetov, I.V.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Shaitan, K.V. Application of Polyhydroxyalkanoates in Medicine and the Biological Activity of Natural Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate). Acta Nat. 2019, 11, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieja, A.J.; Rostkowski, K.H.; Criddle, C.S. Distribution and Selection of Poly-3-Hydroxybutyrate Production Capacity in Methanotrophic Proteobacteria. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 62, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meereboer, K.W.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Review of Recent Advances in the Biodegradability of Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Bioplastics and Their Composites. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 5519–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebaldi, M.L.; Maia, A.L.C.; Poletto, F.; de Andrade, F.V.; Soares, D.C.F. Poly(-3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-3-Hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV): Current Advances in Synthesis Methodologies, Antitumor Applications and Biocompatibility. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 51, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobes, G.A.R.; Maysinger, D.; Marchessault, R.H. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Materials for Delivery Systems. Drug Deliv. J. Deliv. Target. Ther. Agents 1998, 5, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanoska-Dacikj, A.; Stachewicz, U. Smart Textiles and Wearable Technologies-Opportunities Offered in the Fight against Pandemics in Relation to Current COVID-19 State. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2020, 59, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sio, L.; Ding, B.; Focsan, M.; Kogermann, K.; Pascoal-Faria, P.; Petronella, F.; Mitchell, G.; Zussman, E.; Pierini, F. Personalized Reusable Face Masks with Smart Nano-Assisted Destruction of Pathogens for COVID-19: A Visionary Road. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2021, 27, 6112–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, M.; Papchenko, K.; Degli Esposti, M.; Tondi, G.; De Angelis, M.G.; Morselli, D.; Fabbri, P. Fully Biobased Polyhydroxyalkanoate/Tannin Films as Multifunctional Materials for Smart Food Packaging Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 28594–28605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, A.R.; Hazarika, P.; Duarah, R.; Goswami, R.; Hazarika, S. Biodegradable Electrospun Membranes for Sustainable Industrial Applications. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 11129–11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladhari, S.; Vu, N.-N.; Boisvert, C.; Saidi, A.; Nguyen-Tri, P. Recent Development of Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)-Based Materials for Antibacterial Applications: A Review. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 6, 1398–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muiruri, J.K.; Yeo, J.C.C.; Zhu, Q.; Ye, E.; Loh, X.J.; Li, Z. Poly(Hydroxyalkanoates): Applications and End-of-Life Strategies-Life Cycle Assessment Nexus. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 3387–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, S.G.; Ol’khov, A.A.; Zhul’kina, A.L.; Popov, A.A.; Iordanskii, A.L. Nonwoven Materials Based on Electrospun Ultrathin Fibers of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) and Complex Tin Chloride–Porphyrin. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2021, 63, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, S.G.; Ol’khov, A.A.; Popov, A.A.; Zhulkina, A.L.; Kosenko, R.Y.; Iordanskii, A.L. Study of the Effect of External Factors on the Structural and Dynamic Parameters of Film Materials Based on Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) and Polyactide. Nanobiotechnol. Rep. 2021, 16, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, S.G.; Chumakova, N.A.; Lobanov, A.V.; Olkhov, A.A.; Vetcher, A.A.; Iordanskii, A.L. Evaluation and Characterization of Ultrathin Poly(3-Hydroxibutirate) Fibers Loaded with Tetraphenylporphyrin and Its Complexes with Fe(III) and Sn(IV). Polymers 2022, 14, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, S.G.; Varyan, I.A.; Olkhov, A.A.; Tyubaeva, P.M.; Popov, A.A. A Feature of the Crystalline and Amorphous Structure of Ultra Thin Fibers Based on Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) Containing Minor Concentrations of Hemin and a Complex of Tetraphenylporphyrin with Iron. Polymers 2022, 14, 4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, B.; Kaur, J.; Lahooti, B.; Varahachalam, S.P.; Jayant, R.D.; Joshi, A. Drug-Releasing Nano-Bioimplants: From Basics to Current Progress. In Engineered Nanostructures for Therapeutics and Biomedical Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaetsu, I.; Yoshida, M.; Asano, M.; Yamanaka, H.; Imai, K.; Yuasa, H.; Mashimo, T.; Suzuki, K.; Katakai, R.; Oya, M. Biodegradable Implant Composites for Local Therapy. J. Control. Release 1987, 6, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tian, H.; Mao, J.; Ma, F.; Zhang, M.; Chen, F.; Yang, P. Preparation and Application of Chitosan-Based Medical Electrospun Nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 226, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swetha, T.A.; Bora, A.; Mohanrasu, K.; Balaji, P.; Raja, R.; Ponnuchamy, K.; Muthusamy, G.; Arun, A. A Comprehensive Review on Polylactic Acid (PLA)—Synthesis, Processing and Application in Food Packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briassoulis, D.; Tserotas, P.; Athanasoulia, I.-G. Alternative Optimization Routes for Improving the Performance of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) Based Plastics. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 318, 128555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmeiro-Sánchez, T.; O’fLaherty, V.; Lens, P.N. Polyhydroxyalkanoate Bio-Production and Its Rise as Biomaterial of the Future. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 348, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Briso, A.L.; Serrano-Aroca, Á. Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-co-3-Hydroxyvalerate): Enhancement Strategies for Advanced Applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samui, A.B.; Kanai, T. Polyhydroxyalkanoates Based Copolymers. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 522–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ramakrishna, S.; He, L.; Wu, G. Reactive Blends Based on Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Preparation and Biomedical Application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 1107–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, W.W.L.; Heng, P.W.S.; Thong, P.S.P.; Bhuvaneswari, R.; Hirt, W.; Kuenzel, S.; Soo, K.C.; Olivo, M. Improved Formulation of Photosensitizer Chlorin E6 Polyvinylpyrrolidone for Fluorescence Diagnostic Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy of Human Cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodorescu, M.; Bercea, M. Poly(Vinylpyrrolidone)—A Versatile Polymer for Biomedical and Beyond Medical Applications. Polym. Technol. Eng. 2015, 54, 923–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Giner, S.; Pérez-Masiá, R.; Lagaron, J.M. A Review on Electrospun Polymer Nanostructures as Advanced Bioactive Platforms. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 56, 500–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaljević, O.; Djuris, J.; Čalija, B.; Lavrič, Z.; Kristl, J.; Ibrić, S. Application of Miscibility Analysis and Determination of Soluplus Solubility Map for Development of Carvedilol-Loaded Nanofibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, P.; De Marco, I. The Use of Poly(N-Vinyl Pyrrolidone) in the Delivery of Drugs: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurakula, M.; Rao, G.K. Moving Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone Electrospun Nanofibers and Bioprinted Scaffolds toward Multidisciplinary Biomedical Applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 136, 109919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbata, P.; Berka, P.; Stránská, D.; Doležal, P.; Musilová, M.; Čižinská, L. Electrospun Drug Loaded Membranes for Sublingual Administration of Sumatriptan and Naproxen. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 457, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Kanjwal, M.A.; Lin, L.; Chronakis, I.S. Electrospun Polyvinyl-Alcohol Nanofibers as Oral Fast-Dissolving Delivery System of Caffeine and Riboflavin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 103, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulubayram, K.; Calamak, S.; Shahbazi, R.; Eroglu, I. Nanofibers Based Antibacterial Drug Design, Delivery and Applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 1930–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, S.G.; Ol’kHov, A.A.; Iordanskii, A.L.; Lomakin, S.M.; Shilkina, N.S.; Popov, A.A. Structural Dynamic Properties of Nonwoven Composite Mixtures Based on Ultrafine Tissues of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) with Chitosan. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 10, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharkova, I.; Staroverova, O.; Voinova, V.; Andreeva, N.; Shushckevich, A.; Sklyanchuk, E.; Kuzmicheva, G.; Bespalova, A.; Akulina, E.; Shaitan, K.; et al. Biocompatibility of Electrospun Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) and Its Composites Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Biomeditsinskaya Khimiya 2014, 60, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, M.; Kwiecień, M.; Kawalec, M.; Kurcok, P. Oxidative Degradation of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate). A New Method of Synthesis for the Malic Acid Copolymers. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 12809–12818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.; Du, N.; Guiver, M.D. Influence of Intermolecular Interactions on the Observable Porosity in Intrinsically Microporous Polymers. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 1763–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahma, A.; Munir, M.M.; Khairurrijal; Prasetyo, A.; Suendo, V.; Rachmawati, H. Intermolecular Interactions and the Release Pattern of Electrospun Curcumin-Polyvinyl(Pyrrolidone) Fiber. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.-M.; Li, K. Entrapment and Release Difference Resulting from Hydrogen Bonding Interactions in Niosome. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 403, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhou, G.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X. Electrospinning of Polymeric Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Applications. J. Control. Release 2014, 185, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Kong, L.; Gao, Y.; Gong, Y.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, X. Properties of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-3-Hydroxyhexanoate) Films Modified with Polyvinylpyrrolidone and Behavior of MC3T3-E1 Osteoblasts Cultured on the Blended Films. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2005, 16, 1395–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnatowski, A.; Sosnowski, M. Effect of PVP and Polybond Compatibilizers on Dynamic Properties of Polymer Blends Analyzed with DMTA. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2018, 12, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Nachev, N.; Spasova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Naydenov, M. Electrospun 5-Chloro-7-Iodo-8-Hydroxyquinoline (Clioquinol)-Containing Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate)/Polyvinylpyrrolidone Antifungal Materials Prospective as Active Dressings against Esca. Polymers 2022, 14, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, S.G.; Olkhov, A.A.; Varyan, I.A.; Popov, A.A.; Iordanskii, A.L. Effect of Drug Encapsulation and Hydrothermal Exposure on the Structure and Molecular Dynamics of the Binary System Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate)-Chitosan. Polymers 2023, 15, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, S.G.; Olkhov, A.A.; Varyan, I.A.; Shilkina, N.G.; Berlin, A.A.; Popov, A.A.; Iordanskii, A.L. Biocomposites Based on Electrospun Fibers of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) and Nanoplatelets of Graphene Oxide: Thermal Characteristics and Segmental Dynamics at Hydrothermal and Ozonation Impact. Polymers 2023, 15, 4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, S.G.; Ol’khov, A.A.; Chvalun, S.N.; Tyubaeva, P.M.; Popov, A.A.; Iordanskii, A.L. Comparative Structural Dynamic Analysis of Ultrathin Fibers of Poly-(3-Hydroxybutyrate) Modified by Tetraphenyl–Porphyrin Complexes with the Metals Fe. Nanotechnol. Russ. 2019, 14, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkhov, A.A.; Tyubaeva, P.M.; Vetcher, A.A.; Karpova, S.G.; Kurnosov, A.S.; Rogovina, S.Z.; Iordanskii, A.L.; Berlin, A.A. Aggressive Impacts Affecting the Biodegradable Ultrathin Fibers Based on Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate), Polylactide and Their Blends: Water Sorption, Hydrolysis and Ozonolysis. Polymers 2021, 13, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sysoeva, N.; Karmilov, A.; Buchachenko, A. NMR in Paramagnetic Complexes of Radicals with Organic Ligands. Chem. Phys. 1976, 15, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasserman, A.; Barashkova, I.; Yasina, L.; Pupov, V. Rotary and Progressive Diffusion of the Nitroxyl Radical in Amorphous Polymers. Polym. Sci. U.S.S.R. 1977, 19, 2389–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Olkhov, A.; E Mastalygina, E.; Iordanskii, A.L. Biopolymer Geotextiles Based on Mixtures of Polyhydroxybutyrate and Polylactic Acid. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1079, 052019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladkova, O.; Parkhats, M.; Gorbachova, A.; Terekhov, S. FTIR Spectra and Normal-Mode Analysis of Chlorin E6 and Its Degradation-Induced Impurities. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2010, 76, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ol’khov, A.A.; Tyubaeva, P.M.; Zernova, Y.N.; Kurnosov, A.S.; Karpova, S.G.; Iordanskii, A.L. Structure and Properties of Biopolymeric Fibrous Materials Based on Polyhydroxybutyrate–Metalloporphyrin Complexes. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2021, 91, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldstein, M.M.; Dormidontova, E.E.; Khokhlov, A.R. Pressure Sensitive Adhesives Based on Interpolymer Complexes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 42, 79–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ol’kHov, A.A.; Karpova, S.G.; Staroverova, O.V.; Kucherenko, E.L.; Ishchenko, A.A.; Iordanskii, A.L. Effect of External Factors on the Structure of Ultrathin Fibers of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) and Dipyridamole. Fibre Chem. 2016, 48, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaev, P.; Aliev, I.; Iordanskii, A.; Wasserman, A. Molecular Dynamics of the Spin Probes in Dry and Wet Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) Films with Different Morphology. Polymer 2001, 42, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobiev, A.K.; Bogdanov, A.V.; Yankova, T.S.; Chumakova, N.A. Spin Probe Determination of Molecular Orientation Distribution and Rotational Mobility in Liquid Crystals: Model-Free Approach. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 5875–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).