Effect of T6 and T8 Ageing on the Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Graphene-Reinforced AA2219 Composites for Hydrogen Storage Tank Inner Liner Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Used
2.2. Methodology
2.3. Heat Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRD Analysis
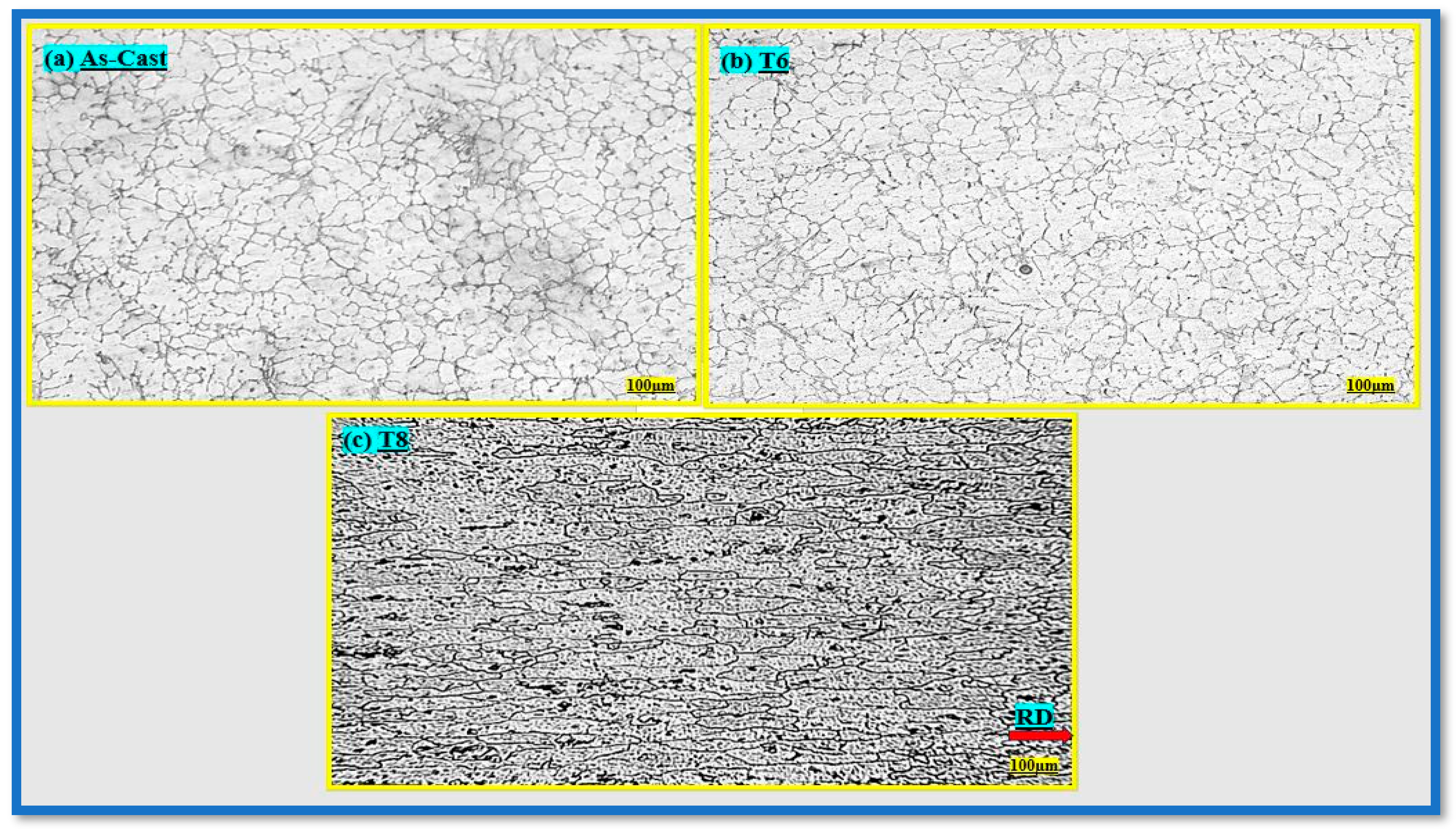
3.2. Optical Microscopy Analysis
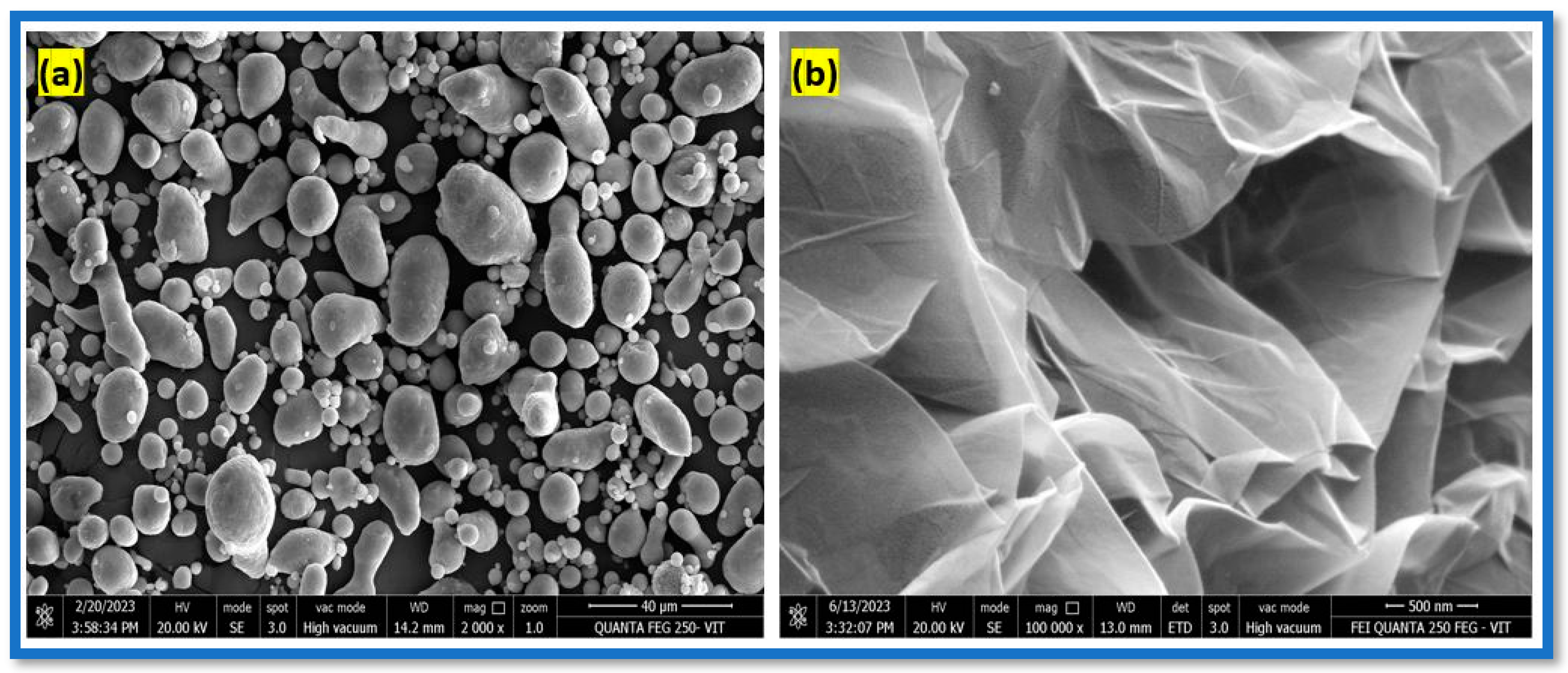
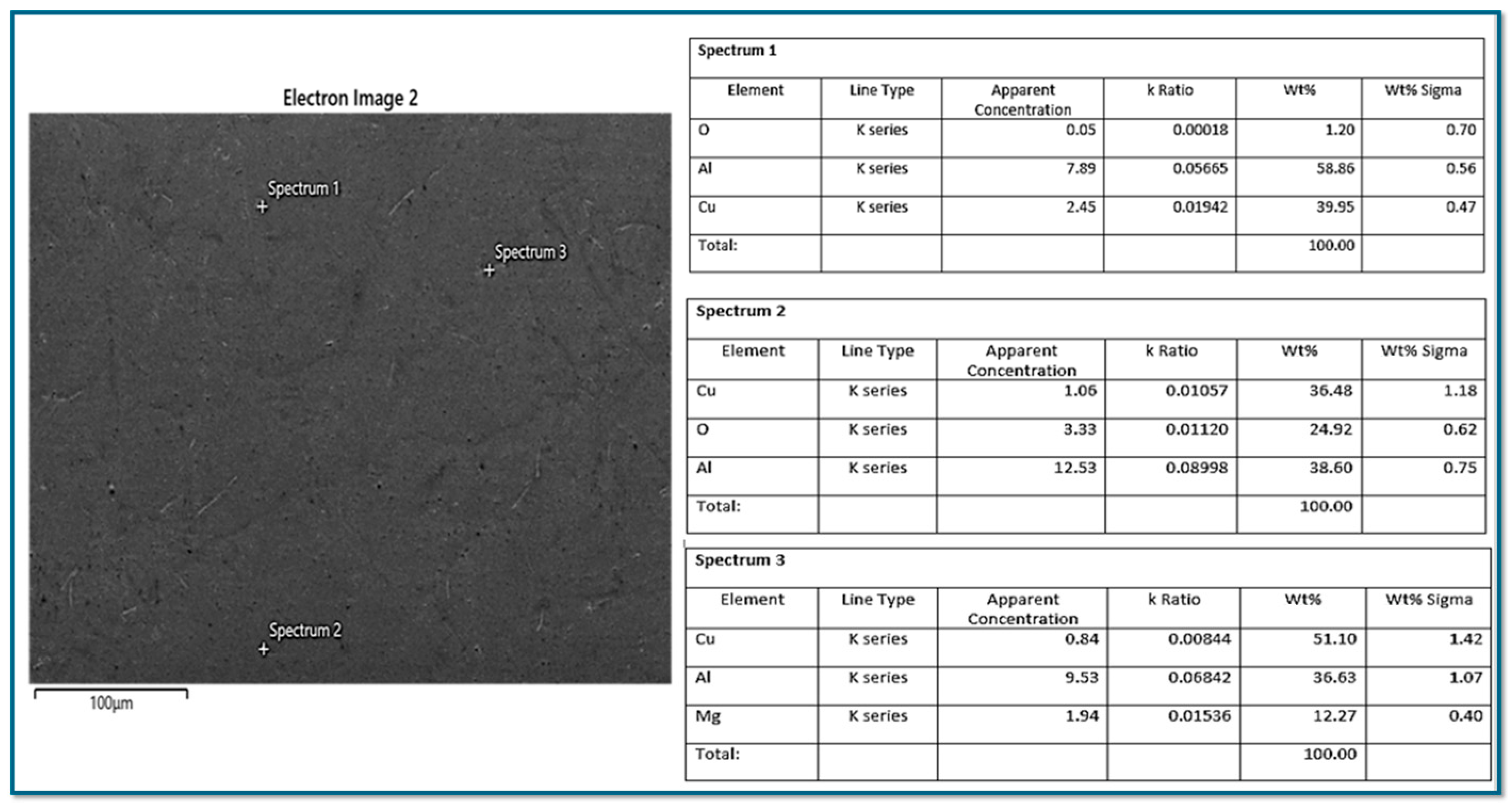
3.3. FE-SEM Analysis
3.4. Hardness Analysis
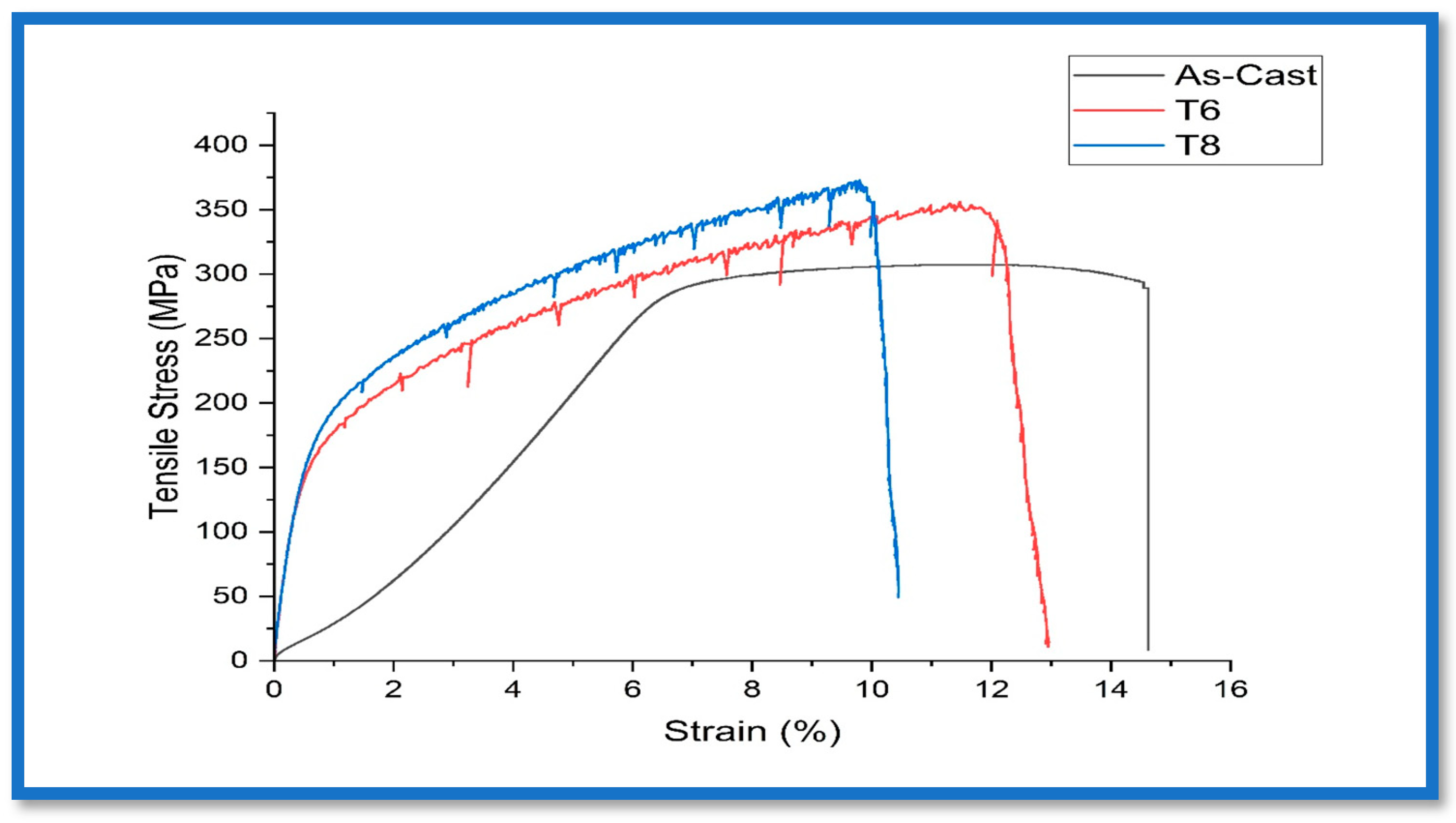
3.5. Ultimate Tensile Strength
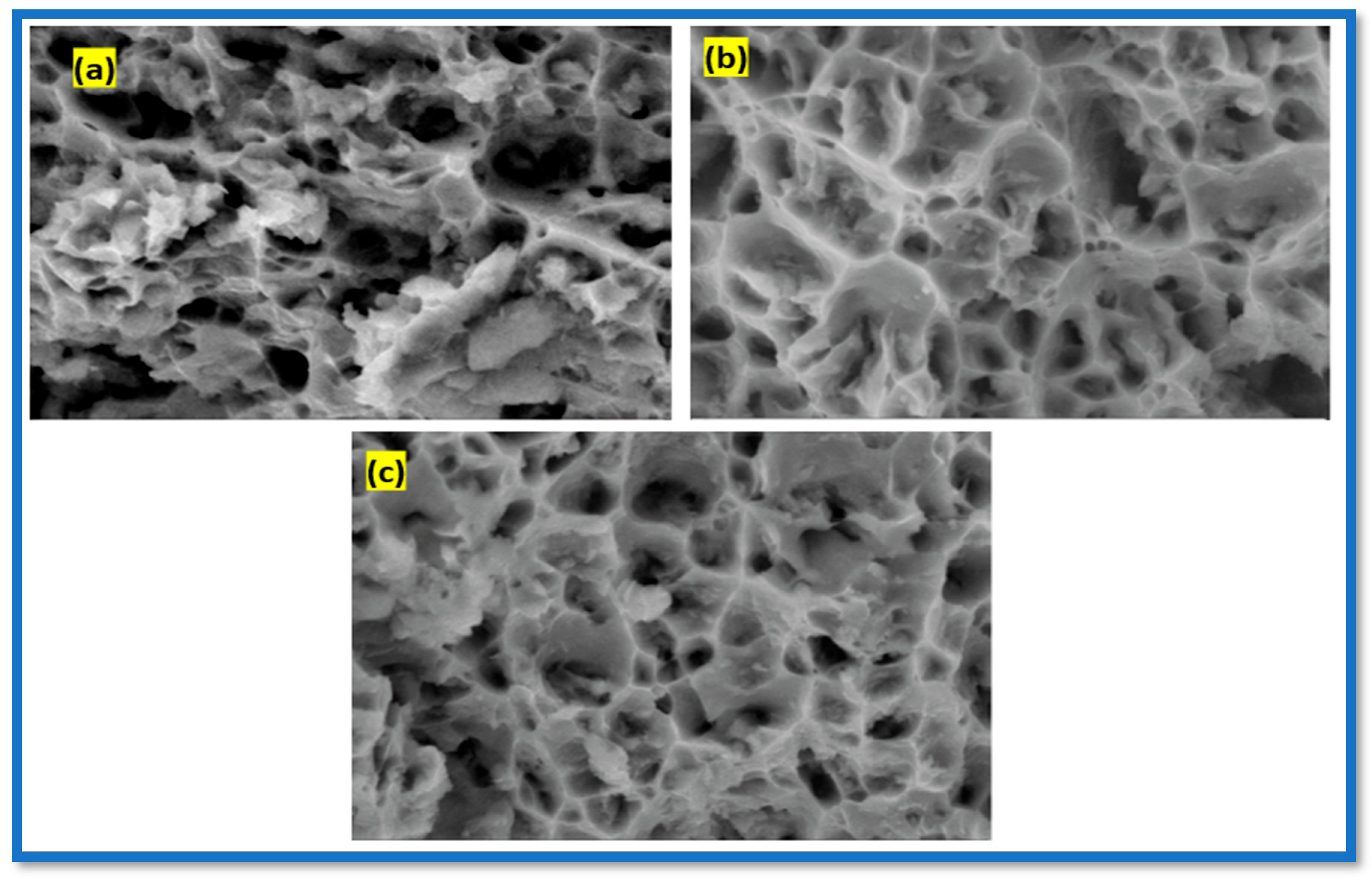
3.6. Tensile Fractography Analysis
3.7. Surface Energy Measurement
4. Conclusions
- The combination of high-energy ball milling, ultrasonic stirring, and squeeze casting successfully ensured uniform dispersion of 0.5 wt.% graphene in the AA2219 matrix, while also reducing porosity and improving interfacial bonding.
- The T6 heat-treated samples exhibited a significant increase in hardness to 114.2 HV and an ultimate tensile strength of 353.6 MPa owing to the formation of fine and coherent θ′ (Al2Cu) precipitates that enhanced strength while maintaining moderate ductility at 11.24%.
- The T8 samples achieved the best mechanical performance, with a maximum hardness of 131.3 HV and ultimate tensile strength of 371.5 MPa. This improvement is attributed to the combined effects of cold working and ageing, which introduced dense dislocations and a refined precipitate structure.
- Heat treatment led to marked grain refinement, with average grain sizes reducing from ~75 µm in the as-cast condition to ~50 µm after T6 treatment and further down to ~21 µm in the T8 condition, contributing significantly to strength enhancement.
- Fractography showed a clear transition from brittle fracture in the as-cast condition to ductile features such as deep dimples and microvoid coalescence in T6 and T8 samples, confirming improved toughness and energy absorption during fracture.
- The lightweight nature, improved strength, and excellent thermal stability of the developed composite make it a promising material for hydrogen storage tanks in aerospace propulsion systems, supporting safe and efficient fuel containment.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tenali, N.; Ganesan, G.; Babu, P.R. An investigation on the mechanical and tribological properties of an ultrasonic-assisted stir casting Al-Cu-Mg matrix-based composite reinforced with agro waste ash particles. Appl. Eng. Lett. 2024, 9, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstić, J.; Jovanović, J.; Gajević, S.; Miladinović, S.; Vaxevanidis, N.M.; Kiss, I.; Stojanović, B. Application of metal matrix nanocomposites in engineering. Adv. Eng. Lett. 2024, 3, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veličković, S.; Miladinović, S.; Stojanović, B.; Nikolić, R.R.; Hadzima, B.; Arsić, D. Influence of load and reinforcement content on selected tribological properties of Al/SiC/Gr hybrid composites. Prod. Eng. Arch. 2018, 18, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, A.; Qudeiri, J.A.; Abdudeen, A.; Ahammed, T.; Ziout, A. A review on AA 6061 metal matrix composites produced by stir casting. Materials 2021, 14, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthik, A.; Karunanithi, R.; Srinivasan, S.A.; Prashanth, M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of AA 2219-TiB2 composites by squeeze casting technique. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 27 Pt 3, 2574–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajith, K.M.; Nirmal, U. AA2219 aluminum alloy reinforced with graphene: An overview. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 086546. [Google Scholar]
- Ashwath, P.; Venkatraman, M.; Patel, A.; Xavior, M.A.; Batako, A. Innovation in sustainable composite research: Investigating graphene-reinforced MMCs for liquid hydrogen storage tanks in aerospace and space exploration. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 4313–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alidokht, S.A.; Salehi, M.T.; Besharati Givi, M.K. Recent progress on graphene-based nanocomposites for aerospace applications. Aerospace 2021, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavior, M.A.; Ranganathan, N.; Kumar, H.P.; Joel, J.; Ashwath, P. Mechanical properties evaluation of hot extruded AA 2024—Graphene nanocomposites. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 12519–12524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, F. Advances in the application of graphene-reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 111, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazhani, A.; Venkatraman, M.; Xavior, M.A.; Moganraj, A.; Batako, A.; Paulsamy, J.J.; Bavan, J.S. Synthesis and characterisation of graphene-reinforced AA 2014 MMC using squeeze casting method for lightweight aerospace structural applications. Mater. Des. 2023, 230, 111990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, S.; Prabu, S.B.; Marimuthu, P. Mechanical properties of graphene-reinforced aluminum composites. Metals 2020, 10, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z. Synthesis and strengthening mechanisms of graphene-aluminum composites. Carbon 2017, 120, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.V.; Asthana, R. Aluminum metal-matrix composites for automotive applications: An overview. JOM 2004, 56, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, L.; Yu, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y. Ultrasonic-assisted fabrication of aluminum-based composites: A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 52, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, J.; Looney, L.; Hashmi, M.S.J. Metal matrix composites: Production by the stir casting method. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1999, 92–93, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mula, S.; Padhi, P.; Panigrahi, S.C.; Mohapatra, N. Effect of SiC content on the properties of aluminum matrix composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 498, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Hwang, Y.J.; Lee, J.S. Recent advances in the preparation of graphene/aluminum composites by powder metallurgy routes. Metals 2021, 11, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Y.; Wang, G.; Lei, T. The effect of ball milling on dispersion and properties of graphene reinforced Al composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 862, 158171. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Dong, H.; Wang, S. Squeeze casting of aluminum alloys and composites. Metals 2020, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Kondoh, K.; Imai, H.; Umeda, J. Fabrication of graphene/aluminum composites by powder metallurgy and hot extrusion. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 820–826. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Anand, A.; Pandey, K.M. Ultrasonic cavitation for the preparation of graphene and its composites. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 56, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathiraja, P.; Anthony Xavior, M. Effect of B4C and graphene on the microstructural and mechanical properties of Al6061 matrix composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 31, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Huang, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, L. Homogeneous dispersion of graphene in aluminum matrix using ball-milling. Materials 2022, 15, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Wang, T.; Liu, Z. Effect of process parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties of graphene reinforced Al composites. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 65, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Nie, J.; Zhu, X. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of AA2219 aluminum alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 698, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, G.; Chen, B.; Huang, Z. Precipitation hardening of AA2219 and its composites. Metals 2021, 11, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Y. Mechanical behavior and fracture characteristics of graphene/aluminum composites. Materials 2020, 13, 4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Yang, H.; Yu, S. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of AA2219/SiC composites. Mater. Sci. Forum 2017, 877, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, X.; Xie, H.; Li, X. Fracture and strengthening mechanisms in graphene-reinforced aluminum composites. Acta Mater. 2019, 166, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wang, X.; Zhai, W.; Liu, L. Effect of graphene content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al matrix composites. Mater. Des. 2018, 142, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Lu, Y. Grain refinement and mechanical properties of graphene reinforced Al composites. Mater. Lett. 2020, 262, 127044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Chen, B.; Kondoh, K.; Wang, M. Fracture toughness improvement in graphene/Al composites. Crystals 2018, 8, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esawi, A.M.K.; Farag, M.M. Carbon nanotube reinforced composites: Processing and mechanical properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimian, M.; Ehsani, N.; Parvin, N.; Baharvandi, H.R. The effect of particle size, sintering temperature, and sintering time on the properties of Al–Al2O3 composites, made by powder metallurgy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 5387–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Cu | Si | Fe | Mg | Mn | Ti | Zn | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.98 | 0.13 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.32 | 0.05 | 0.05 | Bal |
| S. No: | Condition | Vickers Hardness (HV) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | As-Cast | 89.6 ± 3.2 |
| 2. | T6 | 114.2 ± 2.7 |
| 3. | T8 | 131.3 ± 3.0 |
| Condition | Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|
| As-Cast | 308.6 ± 6.5 | 13.68 |
| T6 | 353.6 ± 5.1 | 11.24 |
| T8 | 371.5 ± 4.8 | 8.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parasuraman, B.; Pazhani, A.; Michael, A.X.; Pitchaimuthu, S.; Batako, A. Effect of T6 and T8 Ageing on the Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Graphene-Reinforced AA2219 Composites for Hydrogen Storage Tank Inner Liner Applications. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9070328
Parasuraman B, Pazhani A, Michael AX, Pitchaimuthu S, Batako A. Effect of T6 and T8 Ageing on the Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Graphene-Reinforced AA2219 Composites for Hydrogen Storage Tank Inner Liner Applications. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(7):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9070328
Chicago/Turabian StyleParasuraman, Bharathiraja, Ashwath Pazhani, Anthony Xavior Michael, Sudhagar Pitchaimuthu, and Andre Batako. 2025. "Effect of T6 and T8 Ageing on the Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Graphene-Reinforced AA2219 Composites for Hydrogen Storage Tank Inner Liner Applications" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 7: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9070328
APA StyleParasuraman, B., Pazhani, A., Michael, A. X., Pitchaimuthu, S., & Batako, A. (2025). Effect of T6 and T8 Ageing on the Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Graphene-Reinforced AA2219 Composites for Hydrogen Storage Tank Inner Liner Applications. Journal of Composites Science, 9(7), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9070328









