Effect of Surface Functional Groups and Calcium Ion Adsorption on Formation of Polystyrene/Apatite Core–Shell Microspheres by Aqueous Solution Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Immersion of PS Microspheres in Calcium Chloride (CaCl2) Solution
2.3. Preparation of 1.5m-SBF
- K2HPO4 3H2O (Nacalai Tesque, Kyoto, Japan) 0.342 g;
- MgCl2 6H2O (Hayashi Pure Chemical, Osaka, Japan) 0.458 g;
- 1 mmol mL−1 HCl (Hayashi Pure Chemical, Osaka, Japan) 52.5 mL;
- CaCl2 (Hayashi Pure Chemical, Osaka, Japan) 0.417 g.
2.4. Analysis of the Ca2+-PS Microspheres
2.5. Formation of PS/Apatite Core–Shell Microspheres by 1.5m-SBF Immersion
2.6. Characterization of the PS/Apatite Core–Shell Microspheres
3. Results and Discussion
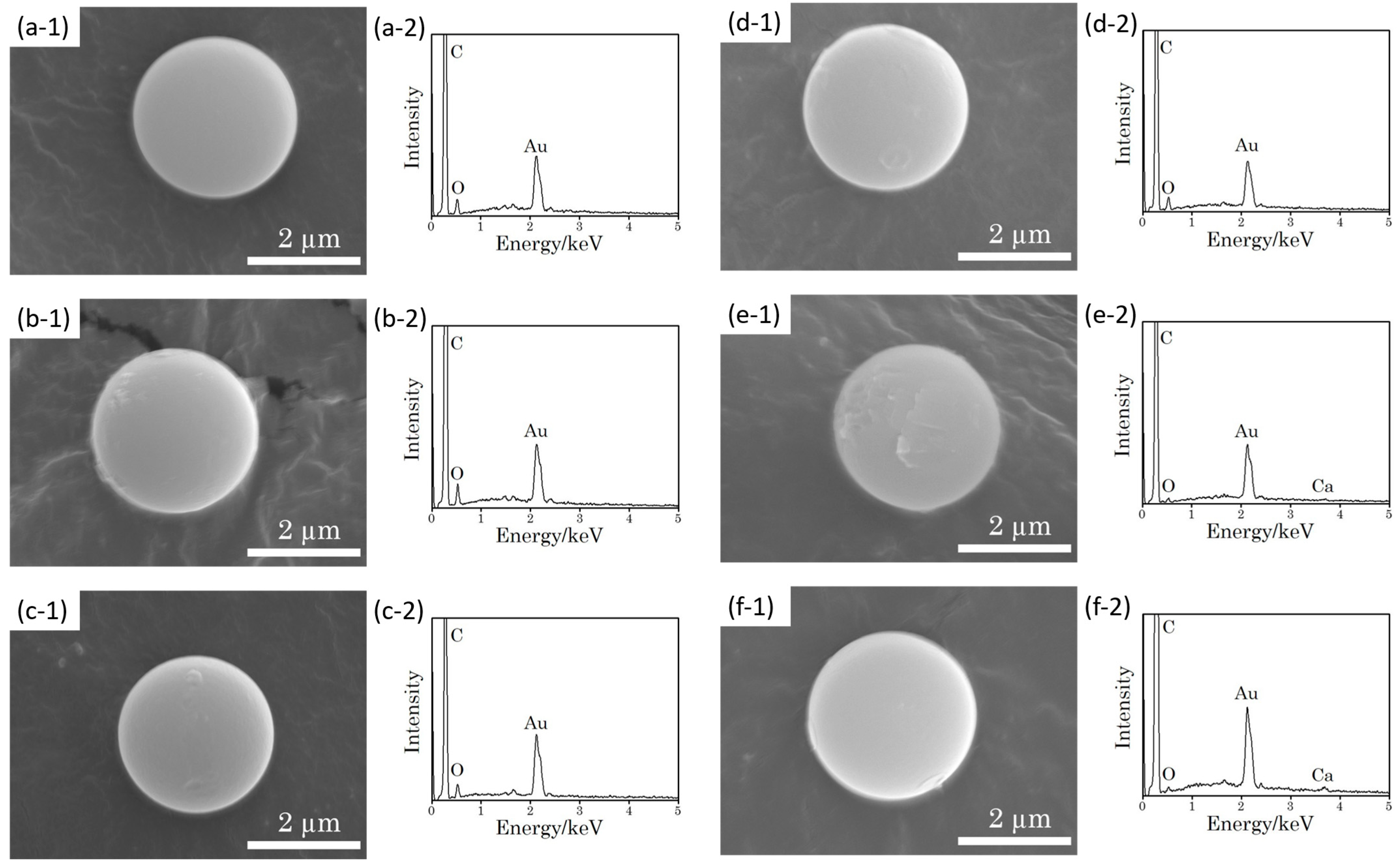
3.1. SEM Observation and EDX Analysis of the Ca2+-PS Microspheres
3.2. Surface Potential Measuremtnt of PS Microspheres
3.3. XPS Measurement of PS Microspheres
3.4. FT-IR Measurement After 1.5m-SBF Immersion
3.5. X-Ray Diffraction Measurement After 1.5m-SBF Immersion
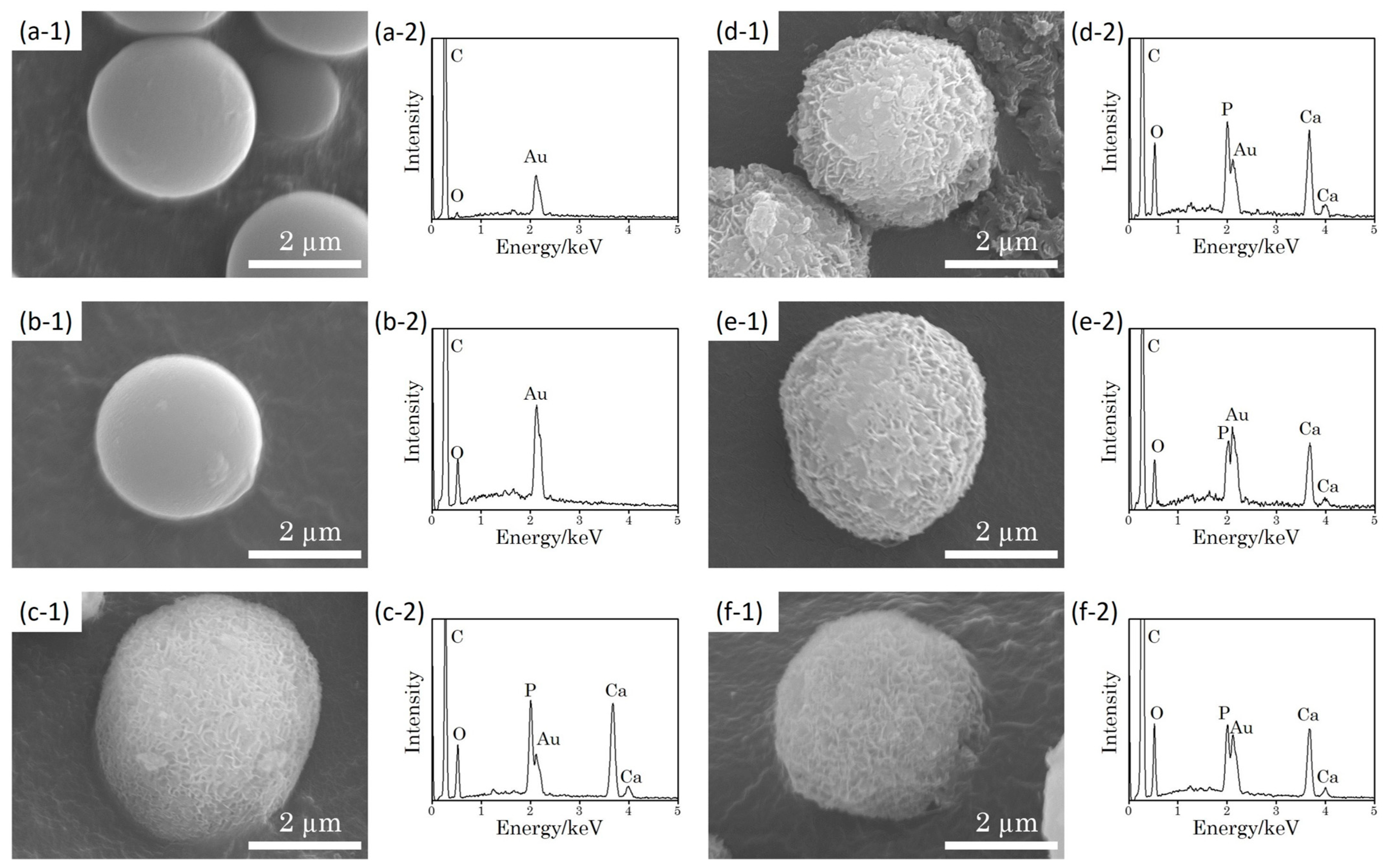
3.6. SEM Observation and EDX Analysis After 1.5m-SBF Immersion
3.7. TEM Observation and Film Thickness Evaluation After 1.5m-SBF Immersion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jarcho, M.J.; Kay, J.F.; Gumaer, K.I.; Doremus, R.H.; Drobeck, H.P. Tissue, cellular and subcellular events at bone-ceramic hydroxyapatite interface. J. Bioeng. 1977, 1, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- LeGeros, R.Z.; LeGeros, J.P. Hydroxyapatites. In An Introduction to Bioceramics, 2nd ed.; Hench, L.L., Ed.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2013; pp. 229–277. [Google Scholar]
- LeGeros, R.Z.; LeGeros, J.P. Hydroxyapatite. In Bioceramics and Their Clinical Applications; Kokubo, T., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 367–394. [Google Scholar]
- Oonishi, H.; Oonishi, H., Jr.; Kim, S.C. Clinical application of hydroxyapatite. In Bioceramics and Their Clinical Applications; Kokubo, T., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 606–687. [Google Scholar]
- Deligianni, D.D.; Katsala, N.D.; Koutsoukos, P.G.; Missirlis, Y.F. Effect of surface roughness of hydroxyapatite on human bone marrow cell adhesion, proliferation, differentiation and detachment strength. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzi, S.C.; Heath, D.J.; Coombes, A.G.A.; Bock, N.; Textor, M.; Downes, S. Biodegradable polymer/hydroxyapatite composites: Surface analysis and initial attachment of human osteoblasts. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 55, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarcho, M. Calcium phosphate ceramics as hard tissue prosthetics. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1981, 157, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiselius, A.; Hjerten, S.; Levin, O. Protein chromatography on calcium phosphate columns. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1956, 65, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liua, X.; Okada, M.; Maeda, H.; Fujii, S.; Furuzono, T. Hydroxyapatite/biodegradable poly(L-lactide–co-e-caprolactone) composite microparticles as injectable scaffolds by a Pickering emulsion route. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Lee, S.; Miyajima, T.; Kato, K.; Sugawara-Narutaki, A.; Sakurai, M.; Nagata, F. Evaluation of Drug-Loading Ability of Poly(Lactic Acid)/Hydroxyapatite Core–Shell Particles. Materials 2021, 14, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, S. Creation of carbonate apatite particles with drug treatable bone reproduction ability for bone defects treatment. Impact 2022, 2022, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, I.-M.; Krishnamra, N.; Charoenphandhu, N.; Hoonsawat, R.; Pon-On, W. Biomagnetic of Apatite-Coated Cobalt Ferrite: A Core–Shell Particle for Protein Adsorption and pH-Controlled Release. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokubo, T.; Takadama, H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.; Hibino, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Okada, H. Method for Stabilizing Calcium Phosphate Fine Particles, Process for Production of Calcium Phosphate Fine Particles by Utilizing the Method, and Use Thereof. U.S. Patent 8178066, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga, T.; Yabutsuka, T.; Takai, S.; Yao, T. Fabrication of Hydroxyapatite Microcapsules for Controlled Release of Hydrophobic Drug. Key Eng. Mater. 2016, 720, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Kokubo, T.; Yamamuro, T. Apatite coating on ceramics, metals and polymers utilizing a biological process. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1990, 1, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasband, W.S. ImageJ, U.S. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, M.D. Available online: https://imagej.net/ij/ (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Cuo, R.; Xie, C.; Liang, Q.; Xiao, X. Biomimetic mineralization of nanocrystalline hydroxyapatites on aminated modified polylactic acid microspheres to develop a novel drug delivery system for alendronate. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 110, 110655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanahashi, M.; Matsuda, T. Surface functional group dependence on apatite formation on self-assembled monolayers in a simulated body fluid. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 34, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Surface Functional Groups | Characteristics | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| None | Particles without any coating or special functional groups added to the particle surface | Normal |
| N(CH3)3+ | Particles with a positive zeta potential | NR3+ |
| NH2 | Particles stable in aqueous media | NH2 |
| COOH | Particles stable in aqueous media | COOH |
| Polyethylene glycol | Hydrophilic particles | PEG |
| Alkyl-OH | Hydrophilic particles | Alkyl-OH |
| Ion Concentration/μmol mL−1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood Plasma | 1.5SBF | 1.5m-SBF | |
| Na+ | 142.0 | 213.0 | 0.0 |
| K+ | 5.0 | 7.5 | 3.0 |
| Ca2+ | 2.5 | 3.8 | 3.8 |
| Mg2+ | 1.5 | 2.3 | 2.3 |
| Cl− | 103.0 | 221.7 | 12.0 |
| HCO3− | 27.0 | 6.3 | 0.0 |
| HPO42− | 1.0 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| SO42− | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yabutsuka, T.; Nakanishi, K.; Takai, S. Effect of Surface Functional Groups and Calcium Ion Adsorption on Formation of Polystyrene/Apatite Core–Shell Microspheres by Aqueous Solution Method. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9070323
Yabutsuka T, Nakanishi K, Takai S. Effect of Surface Functional Groups and Calcium Ion Adsorption on Formation of Polystyrene/Apatite Core–Shell Microspheres by Aqueous Solution Method. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(7):323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9070323
Chicago/Turabian StyleYabutsuka, Takeshi, Kota Nakanishi, and Shigeomi Takai. 2025. "Effect of Surface Functional Groups and Calcium Ion Adsorption on Formation of Polystyrene/Apatite Core–Shell Microspheres by Aqueous Solution Method" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 7: 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9070323
APA StyleYabutsuka, T., Nakanishi, K., & Takai, S. (2025). Effect of Surface Functional Groups and Calcium Ion Adsorption on Formation of Polystyrene/Apatite Core–Shell Microspheres by Aqueous Solution Method. Journal of Composites Science, 9(7), 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9070323






