Optimizing Nanosilica-Enhanced Polymer Synthesis for Drilling Fluids via Response Surface Methodology: Enhanced Fluid Performance Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of P-GS
2.3. Characterization of P-GS
2.4. Response Surface Methodology (RSM) Analysis of P-GS Synthesis Conditions
2.5. Preparation of Drilling Fluid
2.6. Filtration Property Tests
2.7. Rheological Property Measurement
2.8. Lubricity Testing of Drilling Fluids
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. RSM and Experimental Design
3.1.1. RSM Optimization of Optimal Synthesis Conditions
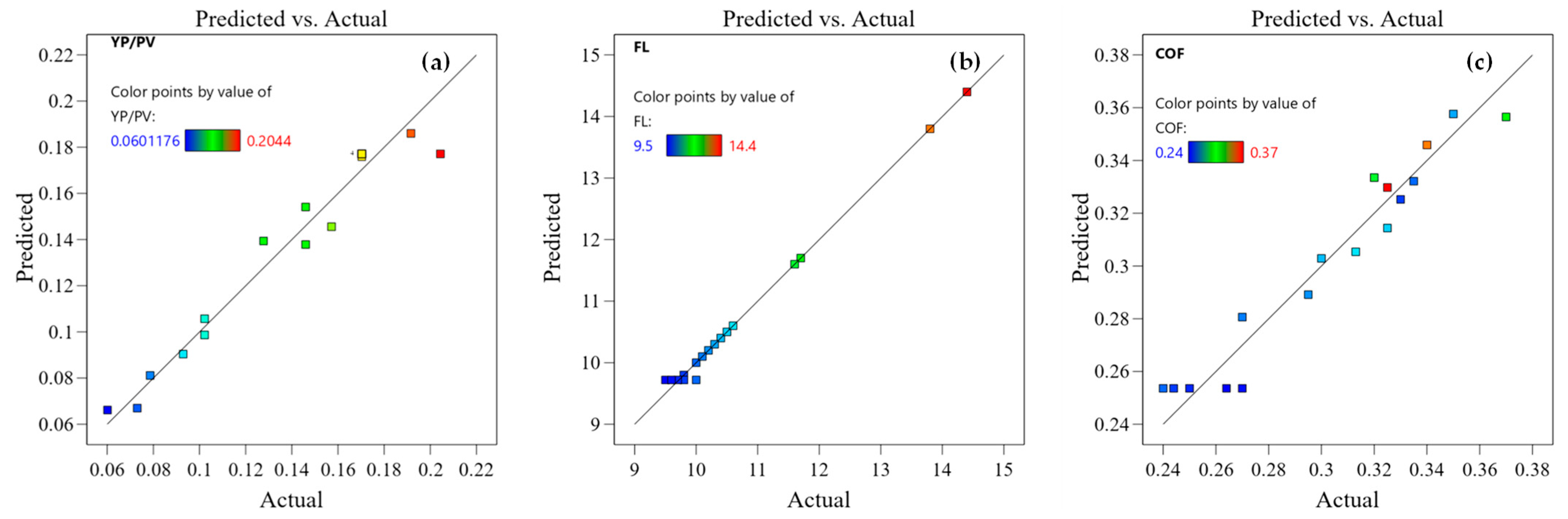
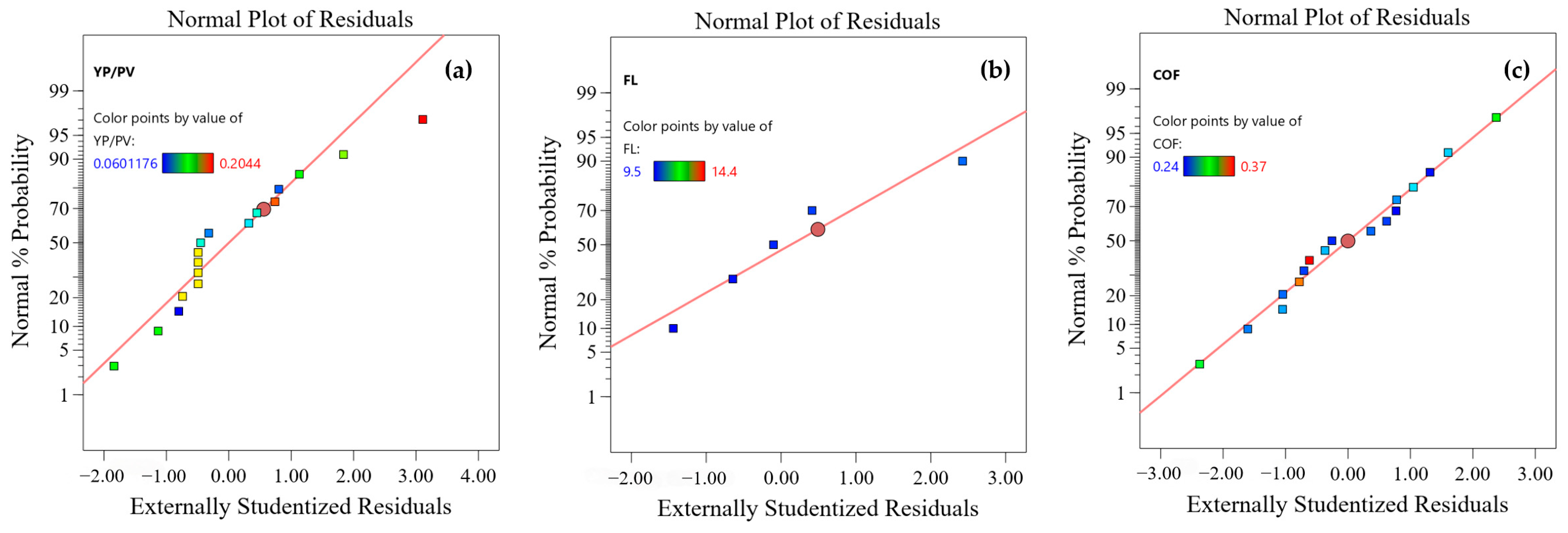
3.1.2. Experimental Results and Error Analysis of the Response Surface
- p-values below 0.05 indicate that the model is significant and statistically significant [32];
- R2 and adjusted R2 require values close to one [33];
- The coefficient of variance (CV) is the ratio of the standard error of the fit to the mean of the response values, which is required to be less than 10% for the common model to indicate the reproducibility of the model [34];
- A signal-to-noise ratio greater than four indicates that the model has sufficient accuracy [35].
3.1.3. Diagnostic Chart Assessment Model
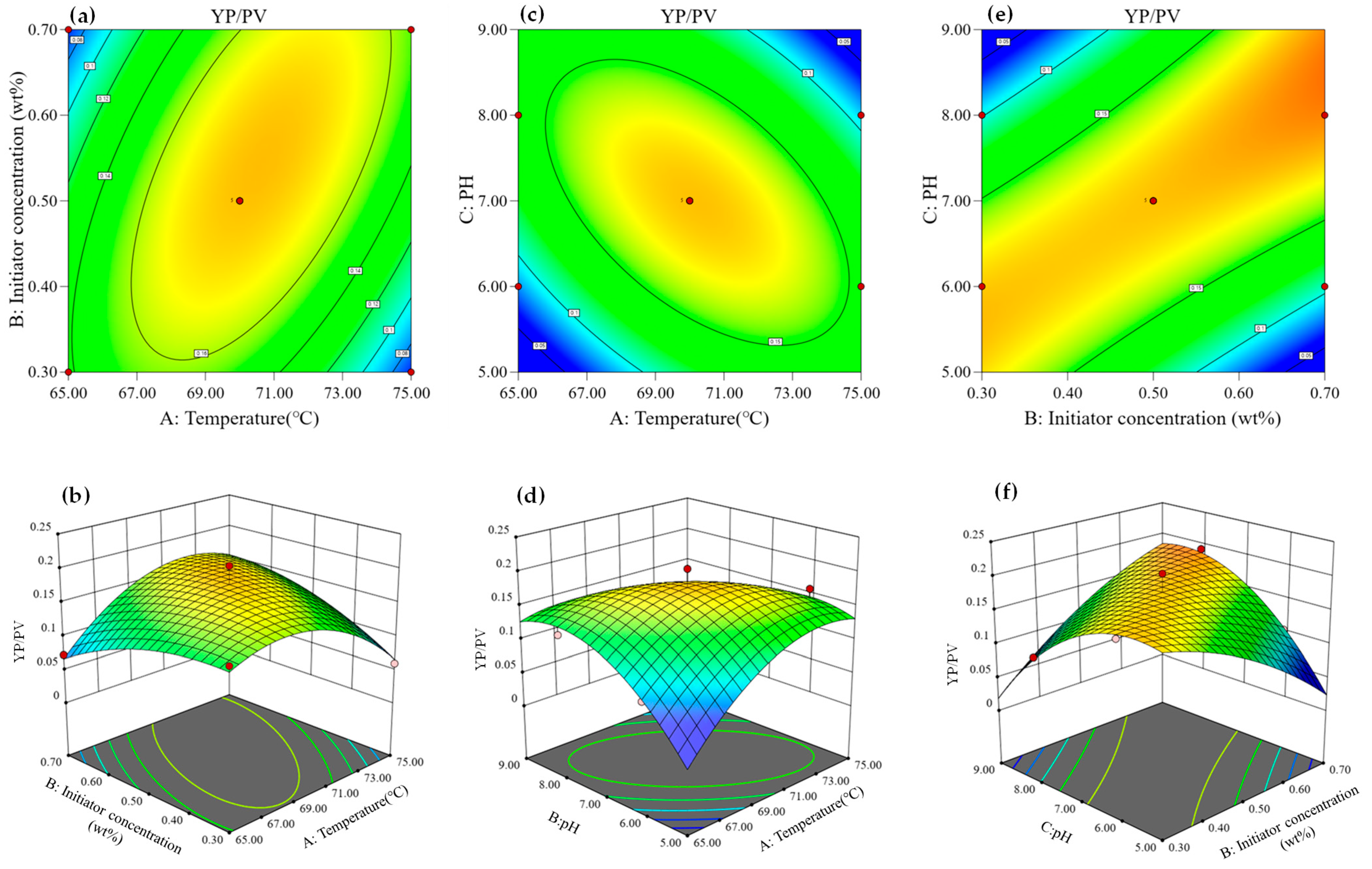
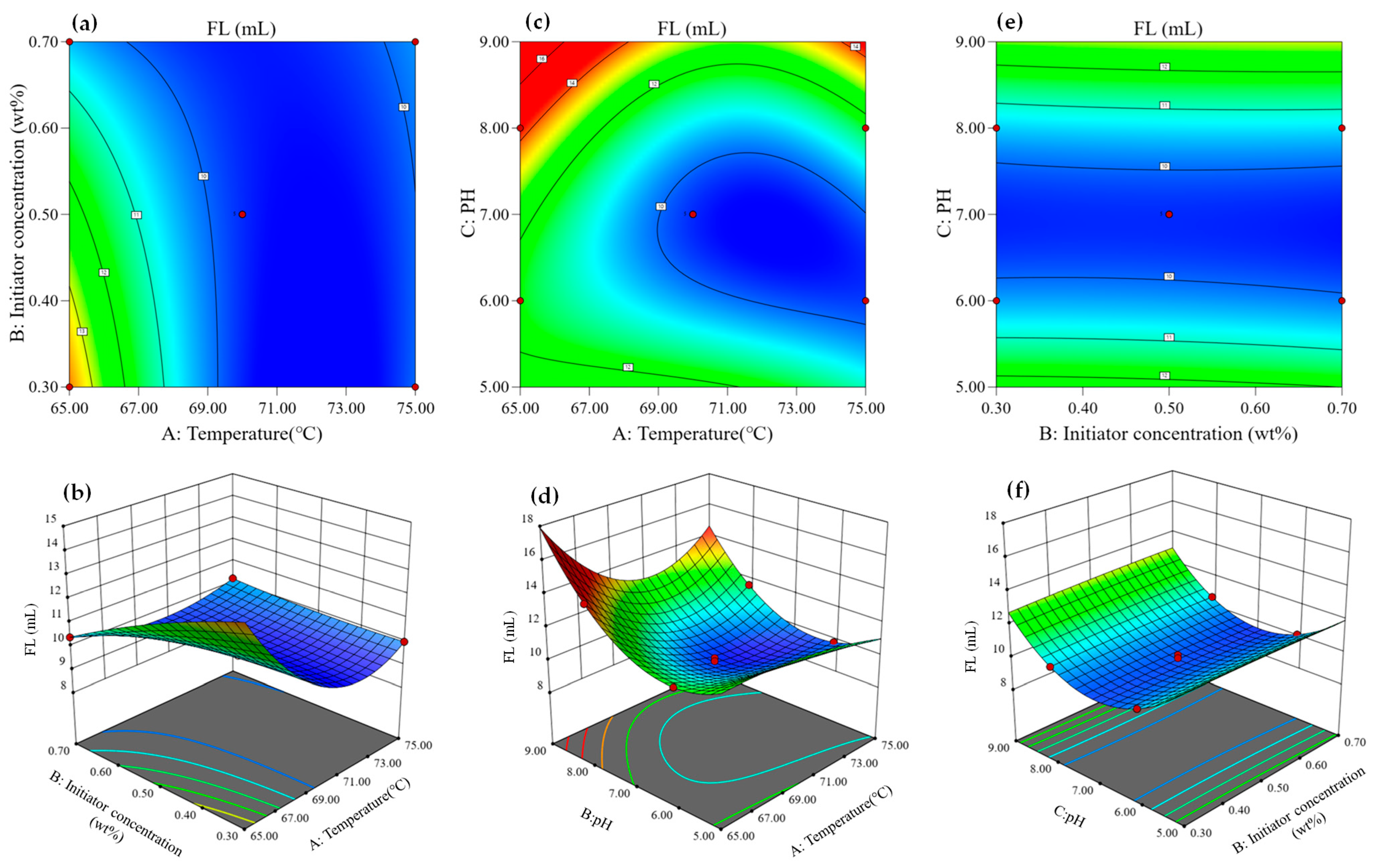
3.1.4. Effect of Variables on Response Values
- (1)
- Effect of variables on cutting-carrying capacity (YP/PV)
- (2)
- Effect of variables on drilling fluid filtration loss (FL)
- (3)
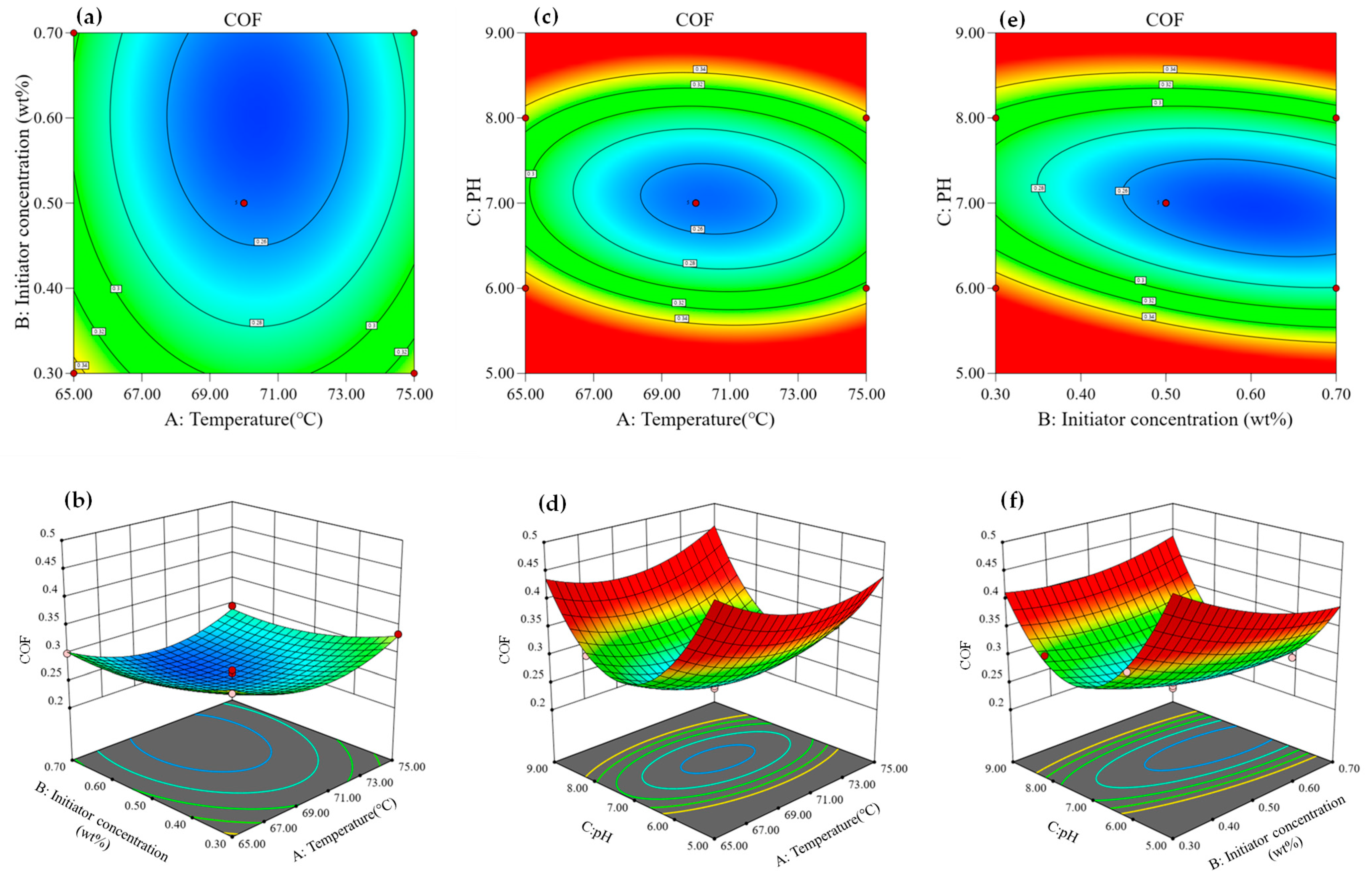
- Effect of variables on the coefficient of friction (CoF) of drilling fluids.
3.1.5. Optimized Results
3.2. Evaluation of Drilling Fluid Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caenn, R.; Chillingar, G.V. Drilling Fluids: State of the Art. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 1996, 14, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caenn, R.; Darley, H.C.H.; Gray, G.R.; Gray, G.R. Composition and Properties of Drilling and Completion Fluids, 6th ed.; Gulf Professional Pub: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-12-383858-2. [Google Scholar]
- Fink, J.K. Drilling Muds. In Petroleum Engineer’s Guide to Oil Field Chemicals and Fluids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 1–59. ISBN 978-0-12-383844-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.H.; Hackett, M.J.; Park, J.; Hyeon, T. Synthesis, Characterization, and Application of Ultrasmall Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, S.S.; Daraee, M.; Sobat, Z. Advanced Development in Upstream of Petroleum Industry Using Nanotechnology. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghian, G. Nanoparticles in Drilling Fluid: A Review of the State-of-the-Art. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 13, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulla, J.; Sahu, S.; Hayes, A. Nanotechnology: History and Future. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2015, 34, 1318–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vryzas, Z.; Kelessidis, V.C. Nano-Based Drilling Fluids: A Review. Energies 2017, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafati, R.; Smith, S.R.; Sharifi Haddad, A.; Novara, R.; Hamidi, H. Effect of Nanoparticles on the Modifications of Drilling Fluids Properties: A Review of Recent Advances. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 161, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelscher, K.P.; De Stefano, G.; Riley, M.; Young, S. Application of Nanotechnology in Drilling Fluids. In Proceedings of the SPE International Oilfield Nanotechnology Conference and Exhibition, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 12–14 June 2012; SPE: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2012; p. SPE-157031-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Desidery, L.; Lanotte, M. Polymers and Plastics: Types, Properties, and Manufacturing. In Plastic Waste for Sustainable Asphalt Roads; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 3–28. ISBN 978-0-323-85789-5. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.; Zhuang, G.; Li, Q.; Yuan, P.; Liu, D. Review of Nanoparticles in Water-Based Drilling Fluids: Innovations, Challenges, and Future Directions. Energy Fuels 2025, 39, 8800–8826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Pu, X.; Rong, K.; Yang, Y. Comb-Shaped Copolymer as Filtrate Loss Reducer for Water-Based Drilling Fluid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yan, Y.; Bai, G.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, F.; Shao, M.; Tian, X. Mechanisms for Stabilizing and Supporting Shale Fractures with Nanoparticles in Pickering Emulsion. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 164, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkatatny, S.; Tariq, Z.; Mahmoud, M. Real Time Prediction of Drilling Fluid Rheological Properties Using Artificial Neural Networks Visible Mathematical Model (White Box). J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 146, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; He, Y.; Cui, W.; Yang, L.; Ye, C. A Saturated Saltwater Drilling Fluid Based on Salt-Responsive Polyampholytes. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lv, K.; Sun, J.; Lu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Shen, H.; Wang, J. Enhancement of Thermal Stability of Drilling Fluid Using Laponite Nanoparticles under Extreme Temperature Conditions. Mater. Lett. 2019, 248, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Wang, W.; Ma, Y.; Huang, Y. Synthesis, Characterization and Properties of an Anionic Polymer for Water-Based Drilling Fluid as an Anti-High Temperature and Anti-Salt Contamination Fluid Loss Control Additive. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 2483–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, B.; Egwu, S.B.; Huang, Z. Polyanionic Cellulose/Hydrophilic Monomer Copolymer Grafted Silica Nanocomposites as HTHP Drilling Fluid-Loss Control Agent for Water-Based Drilling Fluids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 578, 152089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, Z.; Murtaza, M.; Mahmoud, M.; Aljawad, M.S.; Kamal, M.S. Machine Learning Approach to Predict the Dynamic Linear Swelling of Shales Treated with Different Waterbased Drilling Fluids. Fuel 2022, 315, 123282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kania, D.; Yunus, R.; Omar, R.; Abdul Rashid, S.; Mohamed Jan, B. Rheological Investigation of Synthetic-Based Drilling Fluid Containing Non-Ionic Surfactant Pentaerythritol Ester Using Full Factorial Design. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 625, 126700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashay, M.; Zirak, M.; Sheng, J.J.; Esmaeilnezhad, E. Properties Experimental Investigation of Water-Based Drilling Mud Contained Tragacanth Gum and Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 402, 124794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, R.; Kamal, I.; Salih, N.; Préat, A. Optimum Formulation Design and Properties of Drilling Fluids Incorporated with Green Uncoated and Polymer-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Ahmad, M.; Lashari, N. Optimizing Filtration Properties of Water Based Drilling Mud Systems Using Dually Modified Starch. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 454, 142022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malika, M.; Pargaonkar, A.; Sonawane, S.S. Experimental and Statistical Analysis of MWCNT Hybrid Nanofluid-Based Multi-Functional Drilling Fluid. Chem. Pap. 2023, 77, 6773–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, A.; Rajak, V.K.; Guria, C. Development of Functional Polymer-Based Clay-Free HPHT Drilling Fluid: Effect of Molecular Weight and Its Distribution on Drilling Fluid Performance. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2025, 246, 213616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Guria, C. Optimal Synthesis, Characterization, and Performance Evaluation of High-Pressure High-Temperature Polymer-Based Drilling Fluid: The Effect of Viscoelasticity on Cutting Transport, Filtration Loss, and Lubricity. SPE J. 2020, 25, 1333–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Yong, X. Synthesis and Characterization of Sodium Carboxymethyl Starch-Graft Acrylamide/1-Vinyl-2-Pyrrolidone Copolymers via Central Composite Design and Using as Filtration Loss Agent in Drilling Muds. Starch—Stärke 2021, 73, 2000151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakbari, F.S.; Mohyaldinn, M.E.; Mahmood, S.M.; Hassan, A.M.; Ashena, R.; Al-Fakih, A. A Statistics-Based Correlation for the Assessment of Water-Based Mud Performance: Yield Point Prediction. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2025, 50, 4927–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashay, M.; Zirak, M.; Sheng, J.J.; Ganat, T.; Esmaeilnezhad, E. Elevated Temperature and Pressure Performance of Water Based Drilling Mud with Green Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Biodegradable Polymer. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Mahfouz, A.; Ali, A.; Mubashir, M.; Hanbazazah, A.S.; Alsaady, M.; Show, P.L. Optimization of Viscosity of Titania Nanotubes Ethylene Glycol/Water-Based Nanofluids Using Response Surface Methodology. Fuel 2023, 347, 128334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maran, J.P.; Sivakumar, V.; Sridhar, R.; Thirugnanasambandham, K. Development of Model for Barrier and Optical Properties of Tapioca Starch Based Edible Films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordin, M.Y.; Venkatesh, V.C.; Sharif, S.; Elting, S.; Abdullah, A. Application of Response Surface Methodology in Describing the Performance of Coated Carbide Tools When Turning AISI 1045 Steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 145, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafari, S.; Aziz, H.A.; Isa, M.H.; Zinatizadeh, A.A. Application of Response Surface Methodology (RSM) to Optimize Coagulation–Flocculation Treatment of Leachate Using Poly-Aluminum Chloride (PAC) and Alum. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumar, M.; Mohan, D.; Rajendran, M. Optimization of Mix Proportions of Mineral Aggregates Using Box Behnken Design of Experiments. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2003, 25, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, K.; Dhamija, A.; Nam, I.-H.; Kim, Y.-M.; Chang, Y.-S. Decolourization of Reactive Black 5 by Laccase: Optimization by Response Surface Methodology. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 75, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajeri, L.; Aziz, H.A.; Isa, M.H.; Zahed, M.A. A Statistical Experiment Design Approach for Optimizing Biodegradation of Weathered Crude Oil in Coastal Sediments. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, J.; Xie, S.; Lv, K.; Huang, X.; Zong, J.; Zhang, Y. Controlling Filtration Loss of Water-Based Drilling Fluids by Anionic Copolymers with Cyclic Side Groups: High Temperature and Salt Contamination Conditions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 676, 132089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Ma, C.; Zhao, L.; Tchameni, A.P. Novel Thermo-Associating Polymer/Silica Nanocomposite as a Temperature-Resistant Rheology Modifier for Bentonite-Free Water-Based Drilling Fluids. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 222, 211426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoodi, S.; Al-Shargabi, M.; Wood, D.A.; Rukavishnikov, V.S.; Minaev, K.M. Thermally Stable and Salt-Resistant Synthetic Polymers as Drilling Fluid Additives for Deployment in Harsh Sub-Surface Conditions: A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 371, 121117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, T.; Yang, L.; Xie, C.; Jiang, G.; Wang, G.; Liu, Z.; He, X. Zwitterionic Silica-Based Hybrid Nanoparticles for Filtration Control in Oil Drilling Conditions. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 11052–11062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kania, D.; Yunus, R.; Omar, R.; Abdul Rashid, S.; Mohamad Jan, B. A Review of Biolubricants in Drilling Fluids: Recent Research, Performance, and Applications. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 135, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Amiri, A.; Polycarpou, A.A. Enhancements in the Tribological Performance of Environmentally Friendly Water-Based Drilling Fluids Using Additives. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 527, 146822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilgör, E.; Yilgör, I. Silicone Containing Copolymers: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1165–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Sun, Y.; Lin, D.; Feng, X.; Wang, F. Insights into the High Temperature-Induced Failure Mechanism of Bentonite in Drilling Fluid. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 445, 136680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Lin, L.; Gao, S.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, X.; Ren, H.; Luo, W. A Molecular Dynamics Study on Adsorption Mechanisms of Polar, Cationic, and Anionic Polymers on Montmorillonite. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 2010–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Design Factors | Design Variables | Horizontal Codes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Temperature/°C | A | 65 | 70 | 75 |
| Initiator concentration/wt.% | B | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 |
| pH | C | 5 | 7 | 9 |
| A | B | C | YP/PV | Error (YP/PV) (%) | FL | Error (FL) (%) | CoF | Error (CoF) (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best-fit optimization | 70.94 | 7.01 | 0.57 | 0.17767 | - | 9.58153 | - | 0.248849 | - | |
| Actual optimization | 70.9 | 7 | 0.57 | 0.17768 | - | 9.59283 | - | 0.248815 | - | |
| Run | 1 | 70.9 | 7 | 0.57 | 0.1825 | 2.71 | 9.5 | 0.97 | 0.250 | 0.48 |
| 2 | 70.9 | 7 | 0.57 | 0.1825 | 2.71 | 9.6 | 0.07 | 0.247 | 0.73 | |
| 3 | 70.9 | 7 | 0.57 | 0.1793 | 0.91 | 9.6 | 0.07 | 0.246 | 1.13 | |
| Average | 70.9 | 7 | 0.57 | 0.1814 | 2.1 | 9.53 | 0.65 | 0.388 | 0.78 | |
| Aging Temperatures | YP/PV | FL/mL | CoF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-GS | Base | P-GS | Base | P-GS | Base | |
| 25 °C | 0.146 | 0 | 11.5 | 25 | 0.25 | 0.35 |
| 120 °C | 0.15029 | 0.511 | 8.4 | 28.7 | 0.24 | 0.38 |
| 150 °C | 0.1825 | 0.511 | 9.4 | 32 | 0.25 | 0.425 |
| 180 °C | 0.511 | 0.511 | 14.4 | 35.3 | 0.28 | 0.45 |
| 210 °C | 0.554 | 0.511 | 20.3 | 37.8 | 0.32 | 0.49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, X.; Liu, N.; Zhao, X. Optimizing Nanosilica-Enhanced Polymer Synthesis for Drilling Fluids via Response Surface Methodology: Enhanced Fluid Performance Analysis. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9060263
Jia X, Liu N, Zhao X. Optimizing Nanosilica-Enhanced Polymer Synthesis for Drilling Fluids via Response Surface Methodology: Enhanced Fluid Performance Analysis. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(6):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9060263
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Xiangru, Nana Liu, and Xionghu Zhao. 2025. "Optimizing Nanosilica-Enhanced Polymer Synthesis for Drilling Fluids via Response Surface Methodology: Enhanced Fluid Performance Analysis" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 6: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9060263
APA StyleJia, X., Liu, N., & Zhao, X. (2025). Optimizing Nanosilica-Enhanced Polymer Synthesis for Drilling Fluids via Response Surface Methodology: Enhanced Fluid Performance Analysis. Journal of Composites Science, 9(6), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9060263






