Metal–Organic Framework-Based Composites for Dual Functionalities: Advances in Microwave Absorption and Flame Retardancy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Mechanism of EMA and Flame Retardant
2.1. EMA
2.2. Flame Retardant
3. EMA and Flame-Retardant Dual-Functional MOF Composites
3.1. Fe-MOF
3.2. Co-MOF
3.3. Ni-MOF
3.4. Polymetallic MOF
4. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, T.; Qi, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.-L.; Gong, X.; Chen, Y.; Qu, Y.; Peng, Q.; Zhong, W. Constructing mixed-dimensional lightweight flexible carbon foam/carbon nanotubes-based heterostructures: An effective strategy to achieve tunable and boosted microwave absorption. Carbon 2023, 206, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, X.; Gong, X.; Peng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xie, R.; Zhong, W. Microstructure optimization of core@shell structured MSe2/FeSe2@MoSe2 (M = Co, Ni) flower-like multicomponent nanocomposites towards high-efficiency microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 128, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhan, B.; He, M.; Qi, X.; Gong, X.; Yang, J.L.; Qu, Y.; Ding, J.; Zhong, W.; Gu, J. Interfacial Polarization Loss Improvement Induced by the Hollow Engineering of Necklace-like PAN/Carbon Nanofibers for Boosted Microwave Absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sheng, X.; Hao, S.; Liu, G.; Cai, R.; Xue, X.; Wang, Y. Construction of Fe0.64Ni0.36@graphite nanoparticles via corrosion-like transformation from NiFe2O4 and surface graphitization in flexible carbon nanofibers to achieve strong wideband microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 657, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinghui, Y. Low thickness electromagnetic wave absorbing polyurethane and IIR composites by interfacial polarization of multi-layer structure. J. Polym. Eng. 2024, 44, 651–658. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Pan, Y.-T.; Liu, L.; Song, P.; Yang, R. Metal-organic frameworks and their derivatives for sustainable flame-retardant polymeric materials. Adv. Nanocompos. 2025, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Nie, L.; Yan, X.; Li, J.; Qi, D. Ramie fiber reinforced composites with flame retardant structure design: Flammability, smoke suppression, and mechanical properties. J. Polym. Eng. 2022, 42, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Qiao, J.; Zheng, S.; Tian, H.; Li, B.; Liu, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F. Ternary Nickel/Molybdenum Dioxide/Carbon composited nanofibers for broadband and strong electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Gao, T.; He, W.; Liu, P. Electrospinning of hierarchical carbon fibers with multi-dimensional magnetic configurations toward prominent microwave absorption. Carbon 2023, 202, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, J.; Lu, M.; Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Feng, T.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, C.; Chen, X.; Kuang, S. MOF-derived LDH modified flame-retardant polyurethane sponge for high-performance oil-water separation: Interface engineering design based on bioinspiration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 444, 130398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, C.; She, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, H.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Preparation of ZIF67-modified phosphate compounds for enhancing fire safety of strandboards. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 483, 149393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Miao, W.; Pan, Y.T.; Song, P.; Gaan, S.; Ibarra, L.H.; Yang, R. Metal-Organic Frameworks: A Solution for Greener Polymeric Materials with Low Fire Hazards. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2024, 9, 2400768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Research progress of metal organic framework materials in anti-corrosion coating. J. Polym. Eng. 2024, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Pan, Y.-T.; Wang, W.; Yang, R. Surface modification of MOFs towards flame retardant polymer composites. RSC Appl. Interfaces 2025, 2, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ran, F.; Fan, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Lv, T.; Shao, L.; Xie, Z.; Liu, Y. Acidified bimetallic MOFs constructed Co/N co-doped low dimensional hybrid carbon networks for high-efficiency microwave absorption. Carbon 2021, 171, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, K.; Han, L.; Wu, T.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J. Ultra-strength polyurethane/MOF-derived composites with self-healing and recycling capabilities and highly efficient microwave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 1446–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Han, X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, P. MOFs derived magnetic porous carbon microspheres constructed by core-shell Ni@C with high-performance microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 88, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Cheng, C.; Li, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, Y. Fire-safe epoxy composite realized by MXenes based nanostructure with vertically arrayed MOFs derived from interfacial assembly strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 143039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Shi, C.; Qian, X.; Qin, Y.; Jing, J.; Che, H.; Ren, F.; Li, J.; Yu, B.; Zhou, K. Design of novel double-layer coated ammonium polyphosphate and its application in flame retardant thermoplastic polyurethanes. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 459, 141448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, B.; Xiao, G.; Cao, M.; Zhong, F.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, M.; Zou, R. Tri-source integrated adenosine triphosphate loaded BN in synergy with Cu-MOF to improve the fire safety of epoxy resin. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 394, 132258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.M.; Jo, Y.K.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, H.W.; Hwang, I.S.; Yoo, D.J. MOF-Based Chemiresistive Gas Sensors: Toward New Functionalities. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2206842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muratov, D.G.; Kozhitov, L.V.; Zaporotskova, I.V.; Popkova, A.V.; Sleptsov, V.V.; Zorin, A.V. Metal-organic frameworks and composites on their basis: Structure, synthesis methods, electrochemical properties and application prospects (a review). Mod. Electron. Mater. 2024, 10, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Song, Z.; Wang, T.; Feng, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, Y.; Wang, L. Bead-like flexible ZIF-67-derived Co@Carbon composite nanofibre mat for wideband microwave absorption in C-band. Carbon 2024, 216, 118573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Qiao, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, D.; Meng, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Wu, L.; Zeng, Z.; et al. ZIF-67-derived Co/C embedded boron carbonitride nanotubes for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liao, Z.; Han, X.; Ma, Y.; Feng, C.; Ma, M. Facile design of sea cucumber-like MOF-derived Fe-Co bimetallic autocatalytic carbon nanotube composites with enhanced microwave absorption properties. Synth. Met. 2023, 297, 117381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Du, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Cui, L.; Zhao, H.; Han, X. MOFs-derived multi-chamber carbon microspheres with enhanced microwave absorption. Carbon 2020, 157, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Bi, Y.; Tong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, P.; Wang, R.; Ma, Y.; Wu, G.; Liao, Z.; Chen, Y. Recent progress of MOF-derived porous carbon materials for microwave absorption. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 16572–16591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Song, X.; Pan, Y.T.; Sun, J.; Bifulco, A.; Yang, R. Dual function of carboxymethyl cellulose scaffold: A one-stone-two-birds strategy to prepare double-layer hollow ZIF-67 derivates for flame retardant epoxy composites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 674, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Zou, B.; Xiao, Y.; Qiu, S.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. Targeted modification of black phosphorus by MIL-53(Al) inspired by “Cannikin’s Law” to achieve high thermal stability of flame retardant polycarbonate at ultra-low additions. Compos. B Eng. 2022, 238, 109943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, P.; Hou, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Feng, C.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Huang, W.; et al. Composites Filled with Metal Organic Frameworks and Their Derivatives: Recent Developments in Flame Retardants. Polymers 2022, 14, 5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Song, X.; Song, K.; Geng, Z.; Pan, Y.T.; Song, P.; Yang, R. Synchronous preparation and modification of LDH hollow polyhedra by polydopamine: Synthesis and application. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 654, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Chen, S.; Han, Z.; Pan, Y.-T.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, R. Covalent metal-organic porous polymer on ZIF-67 realize anti-UV and highly stressed flame retardant epoxy composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 501, 157758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, X.; Shi, X.; Huang, M.; Li, X.; Zeng, Q.; Che, R. Recent progress of microwave absorption microspheres by magnetic-dielectric synergy. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 2136–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Jiao, Z.; Jiang, J.; Hou, Y.; Su, X.; Zhang, J.; Feng, C.; Ma, Y.; Ma, M.; Liu, J. Simple fabrication of cobalt-nickel alloy/carbon nanocomposite fibers for tunable microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 652, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Dong, F.; Wang, H.; Qu, Y.; Ding, J.; Ma, Y.; Ma, M.; Li, T. Fabrication of CuS/Fe3O4@polypyrrole flower-like composites for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 634, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, A.M.; Ross, G.F. Measurement of the Intrinsic Properties of Materials by Time-Domain Techniques. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1970, 19, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, W.B. Automatic measurement of complex dielectric constant and permeability at microwave frequencies. Proc. IEEE 1974, 62, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Jiao, Z.; Han, X.; Liu, J.; Ma, M.; Jiang, J.; Hou, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, C.; Ma, Y. Facile synthesis of FeNi nanoparticle-loaded carbon nanocomposite fibers for enhanced microwave absorption performance. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 175, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, A.; Qiu, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; He, S.; Huang, H. Carbonization of Ni@SiC@C nanoparticles reinforced PAN nanofibers for adjustable impedance matching. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Zhi, D.; Li, J.; Li, T.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Zhu, J.; Meng, F. Electromagnetic oscillation induced graphene-based aerogel microspheres with dual-chamber achieving high-performance broadband microwave absorption. Compos. B Eng. 2024, 271, 111149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Tian, X.; Jiang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, J.; Ma, L.; Qu, S. Design and synthesis of porous nitrogen-doped Co@C composites with broadband microwave absorption performance. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 130, 109424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Ning, M.; Raza, H.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, G.; Zheng, Q.; Che, R. Emerging Materials and Designs for Low- and Multi-Band Electromagnetic Wave Absorbers: The Search for Dielectric and Magnetic Synergy? Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, D.; Xie, Z.; Lu, S.; Liu, Y.; Liang, F. Recent Advances in Structural Design of Carbon/Magnetic Composites and their Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Applications. Small 2025, 2408570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Xia, L.; Ma, S.; Yin, Z.; Huang, Y. A Review on Metal-Organic Framework-Derived Porous Carbon-Based Novel Microwave Absorption Materials. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Su, X.; Feng, C.; Ma, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiao, Z.; Ma, M. Development of electromagnetic microwave absorbers in cementitious materials. Compos. Struct. 2023, 312, 116886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Sui, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, L. Improving the electromagnetic wave absorption properties of zinc ferrite-containing N-doped carbon composites by the introduction of Fe4N. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 900, 163355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Jia, C.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, H.; Jia, Z.; Wu, G. Integration of Multiple Heterointerfaces in a Hierarchical 0D@2D@1D Structure for Lightweight, Flexible, and Hydrophobic Multifunctional Electromagnetic Protective Fabrics. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Xiong, Z.; Gan, Z.; Liu, C.; Xie, Y. Microcapsule MOFs@MOFs derived porous “nut-bread” composites with broadband microwave absorption. Compos. B Eng. 2021, 224, 109170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi-Sarmad, M.; Samsami, S.; Ghaffarkhah, A.; Hashemi, S.A.; Ghasemi, S.; Amini, M.; Wuttke, S.; Rojas, O.; Tam, K.C.; Jiang, F.; et al. MOF-Based Electromagnetic Shields Multiscale Design: Nanoscale Chemistry, Microscale Assembly, and Macroscale Manufacturing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2304473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Fang, J.; Xu, C.; Cao, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, B.; Huang, M.; Wang, X.; Lv, H.; Che, R. One-Dimensional Magnetic FeCoNi Alloy Toward Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, B.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, P.; Liu, T. MOF-derived Co/CoO particles prepared by low temperature reduction for microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Ma, M.; Bi, Y.; Lu, C.; Feng, C.; Lyu, P.; Zhao, J.; Ma, Y. A review of carbon-based magnetic microwave-absorbing composites with one-dimensional structure. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 18243–18265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Ye, J.; Shi, L.; Feng, X. Magnetic CoFe alloy@C nanocomposites derived from ZnCo-MOF for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, S.; Sun, K.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Z.; Alshammari, A.S.; Helal, M.H.; El-Bahy, Z.M.; Yuan, Y.; Fan, R. Metal-organic framework derived carbon-based composites for high-performance microwave absorption. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2025, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Che, R. Hierarchical Engineering of Double-Shelled Nanotubes toward Hetero-Interfaces Induced Polarization and Microscale Magnetic Interaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2202588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Ye, F.; Kong, L.; Shen, Q.; Han, L.; Feng, L.; Yu, G.; Pan, Y.; Li, H. Graphene and MXene Nanomaterials: Toward High-Performance Electromagnetic Wave Absorption in Gigahertz Band Range. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Pan, Y.-T.; Zhou, K.; Song, P.; Yang, R. A new way to improve the fire safety of polyurethane composites with the assistance of metal–organic frameworks. RSC Appl. Polym. 2024, 2, 996–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Pan, Y.-T.; Zhang, J.; Song, P.; He, J.; Wang, D.-Y.; Yang, R. Metal–Organic Frameworks-Based Flame-Retardant System for Epoxy Resin: A Review and Prospect. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Zhang, Z.; Song, K.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Y.-T.; Qu, H.; Vahabi, H.; He, J.; Yang, R. Packaging of ZIF-8 into diatomite sealed by ionic liquid and its application in flame retardant polyurea composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 184, 108283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yuan, B.; Zhan, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhou, J.; Qi, C.; Lei, C.; Li, Y. Upgrading the pore-size scale of MIL-53 from microporous to macroporous for adsorbing triethyl phosphate and reducing the fire risk of polystyrene. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 159, 107003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Han, Z.; Song, X.; Pan, Y.T.; Geng, Z.; Vahabi, H.; Realinho, V.; Yang, R. Enhancing char formation of flame retardant epoxy composites: Onigiri-like ZIF-67 modification with carboxymethyl beta-cyclodextrin crosslinking. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 333, 121980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Song, X.; Chen, Z.; Pan, Y.-T.; Lai, X.; Wang, D.-Y.; Yang, R. Half etching of ZIF-67 towards open hollow nanostructure with boosted absorption ability for toxic smoke and fume in epoxy composites. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 41, e01024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, W.; Yao, M.; Wu, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Qu, H. Novel triazine-based metal-organic frameworks: Synthesis and mulifunctional application of flame retardant, smoke suppression and toxic attenuation on EP. Mater. Des. 2023, 226, 111664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, T.T.; Kang, F.R.; Zhou, T.B. Effect of Al-based metal-organic frameworks/halloysite nanotubes on the flame retardancy of silicone rubber foam. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, 54517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Gu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, R. Thermal degradation and flame retardancy prediction of Fe, Al, and Cu-based metal-organic framework and polyethylene terephthalate nanocomposites using DFT calculation. Polymer 2022, 263, 125496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, G.; Xu, X.; Tian, X.; Yan, J.; Su, X.; Yan, Y. Bio-Based Rigid Polyurethane Foams Modified with C-MOF/MWCNTs and TBPBP as Building Insulation Materials: Synergistic Effect and Corresponding Mechanism for Enhancing Fire and Smoke Safety. Polymers 2022, 14, 3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Liu, X.; Qiu, Z.; Cai, Z.; Diao, J.; Huang, Y. Hydrophobic and flame-retardant multifunctional foam for enhanced thermal insulation and broadband microwave absorption via a triple-continuous network of RGO/MWCNT-melamine composite. Carbon 2022, 196, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, D.; Tiwari, S.K.; Wei, F.; Chen, Y.; Thummavichai, K.; Wang, N.; Yan, C.; Zhu, Y. Implanting MOF Co-doped carbon nanotubes into PVP as flame-retardant to fabricate high performance PVA/SA aerogel nanocomposites. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qin, J.; Zhang, W.; Pan, Y.-T.; Wang, D.-Y.; Yang, R. Synthesis of a novel dual layered double hydroxide hybrid nanomaterial and its application in epoxy nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Cheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L. Epoxy Polymers Containing Metal–Organic Framework-Derived Layered Double Hydroxide and Black Phosphorus for Fire Resistance, Smoke Suppression, and Wear Resistance. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 14727–14736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.H.; Li, X.L.; Liu, Q.Y.; Wu, S.J.; Xie, W.M.; Zhao, N.; De La Vega, J.; Chen, M.J.; Wang, D.Y. Constructing Co-decorated layered double hydroxide via interfacial assembly and its application in flame-retardant epoxy resin. Compos. Commun. 2023, 43, 101712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, B.; Wei, F.; Guo, X.; Zhang, D.; Thummavichai, K.; Chen, D.; Wang, N.; Zhu, Y. Selective Laser Sintering of MXene-on-MOF (HKUST-1) Hybrids Enhanced Mechanical and Fire Safety Performances of Polyamide 12 Composites. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 9852–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Cai, L.; Shi, C.; Gao, F.; Yin, L.; Qian, X.; Zhou, K. Organic-inorganic hybrid engineering MXene derivatives for fire resistant epoxy resins with superior smoke suppression. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 161, 107109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Shi, C.; Qian, X.; Qin, Y.; Jing, J.; Che, H.; Ren, F.; Li, J.; Yu, B. Interface assembly of flower-like Ni-MOF functional MXene towards the fire safety of thermoplastic polyurethanes. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 163, 107187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wu, X.; Liu, Q.; Sun, S.; Cui, S.; Zhang, S.; Chen, C. Preparation of a novel Fe-MOF as the flame retardant synergist and its application in polystyrene. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2023, 35, e6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Hu, Q.; Yang, S.; Yan, S.; Gu, Y.; Ji, J.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. MOF-Fe@C Nanocomposites for Microwave Absorption. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2024, 26, 2400527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-R.; Li, Y.-M.; Chen, B.-B.; Hu, W.-J.; Wang, D.-Y. Highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorption Fe-MOF-rGO based composites with enhanced flame retardancy. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 918, 165516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Pan, Y.-T.; Guan, J.; Ardanuy, M.; Yang, R. A durable coating constructed by metal-organic framework and polyphosphazene for flame retardant cotton fabric with enhanced mechanical properties. Next Mater. 2024, 3, 100143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Qi, P.; Zhang, S.J.; Jiang, S.L.; Li, Y.C.; Sun, J.; Fei, B.; Gu, X.Y.; Zhang, S. A novel flame-retardant modification strategy for UiO66-NH2 by encapsulating triethyl phosphate: Preparation, characterization, and multifunctional application in poly (lactic acid). Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 30, 101550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Meng, C.; Liu, Q.; Li, N.; Yu, R.; Zeng, M. Fire-resistant iron-based phosphates/phosphorus-doped carbon composites derived from phytic acid-treated metal organic frameworks as high-efficiency microwave absorbers. Carbon 2022, 200, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y. Multifunctional three-dimensional porous MOFs derived Fe/C/carbon foam for microwave absorption, thermal insulation and infrared stealth. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 18861–18869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeraj, B.D.S.; Jayan, J.S.; Raman, A.; Saritha, A.; Joseph, K. Recent prospects and trends on zeolitic imidazolate frameworks for microwave absorption and EMI shielding applications. Synth. Met. 2023, 296, 117354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safak Boroglu, M.; Boz, I.; Kaya, B. Effect of new metal–organic framework (zeolitic imidazolate framework [ZIF-12]) in mixed matrix membranes on structure, morphology, and gas separation properties. J. Polym. Eng. 2021, 41, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Shi, C.; Chen, L.; Deng, L.; Qin, Y.; Che, H.; Jing, J.; Li, J.; Qian, X. Core-shell flame retardant/APP-PEI@MXene@ZIF-67: A nanomaterials self-assembly strategy towards reducing fire hazard of thermoplastic polyurethane. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 226, 110821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Tan, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, J.; Ji, G. Multifunctional Bulk Hybrid Foam for Infrared Stealth, Thermal Insulation, and Microwave Absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 28727–28737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y.; Lu, W. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of magnetic Co nanoparticles/CNTs/EG porous composites with waterproof, flame-retardant and thermal management functions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 17538–17552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
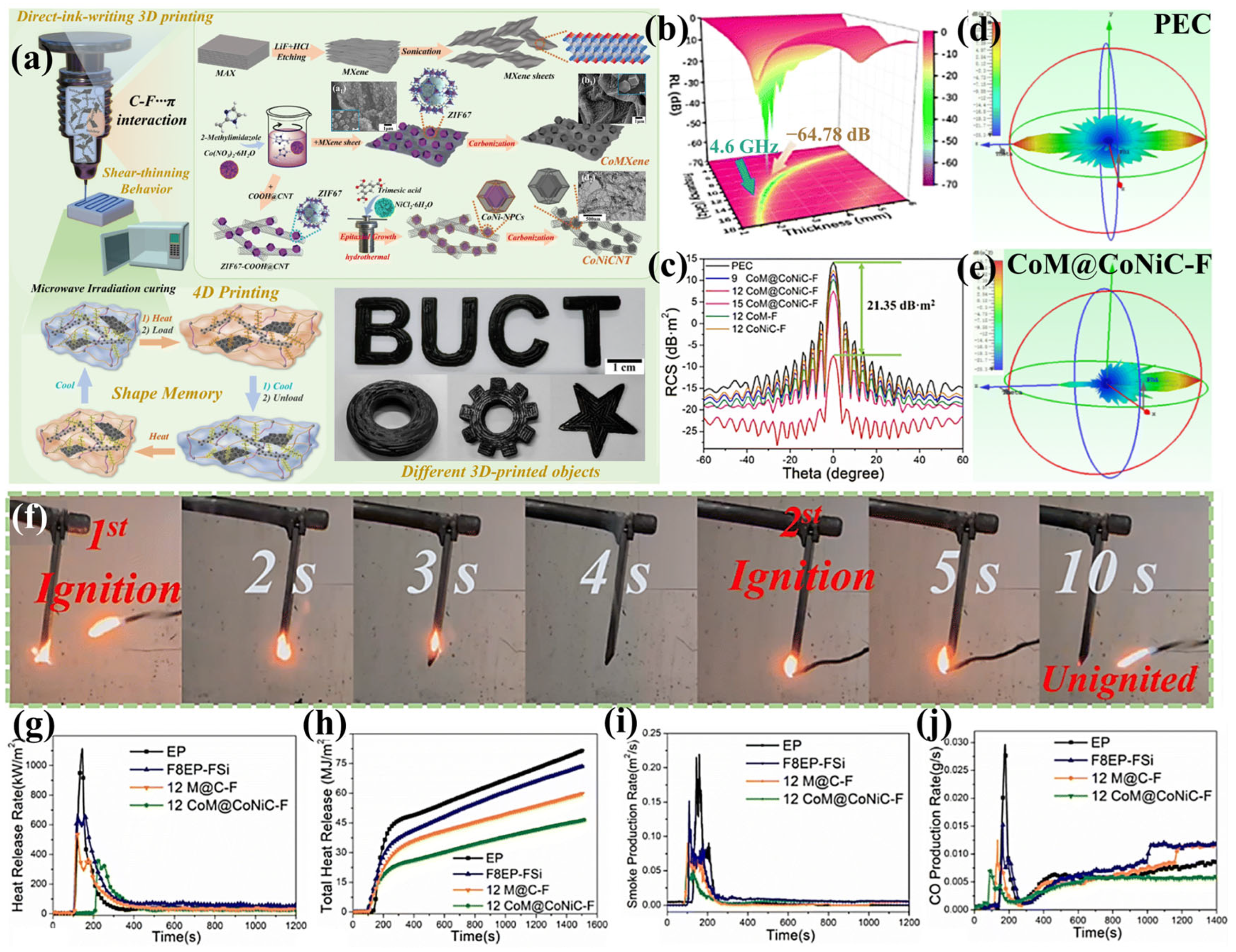
- Li, K.; Han, L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J. 4D printing MOF-derived/multi-fluorination nanocomposites for ultra-efficient electromagnetic wave absorption and robust environment adaptivity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 6302–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Diao, X.; Li, P.; Liu, P.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, G. Advanced multifunctional Co/N co-doped carbon foam-based phase change materials for wearable thermal management. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 485, 149858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
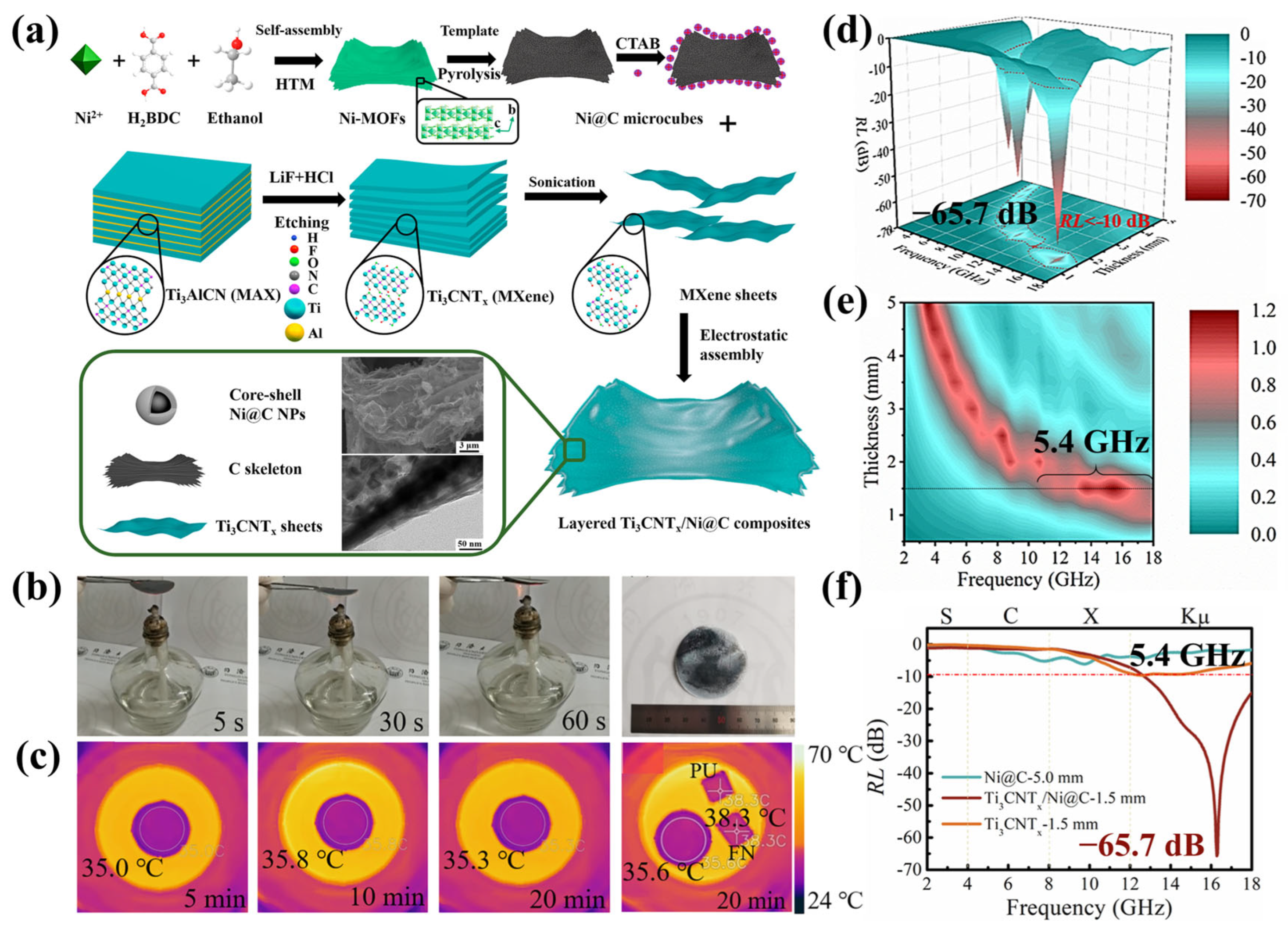
- Xiang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y.; Cai, L.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, X.; Dong, Y.; Lu, W. Efficient microwave absorption of MOFs derived laminated porous Ni@C nanocomposites with waterproof and infrared shielding versatility. Carbon 2021, 185, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y.; Cai, L.; Zhu, X.; Dong, Y.; Lu, W. Self-assembly of nano/microstructured 2D Ti3CNTx MXene-based composites for electromagnetic pollution elimination and Joule energy conversion application. Carbon 2022, 189, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, F.; Rao, Q.; Deng, J.; Cheng, L.; Zhong, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H.; Rao, G. Controllable Architecture of ZnO/FeNi Composites Derived from Trimetallic ZnFeNi Layered Double Hydroxides for High-Performance Electromagnetic Wave Absorbers. Small 2023, 19, 2300257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Liang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Hou, L.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, F. P-doped MOF-derived CoNi bimetallic sulfide electrocatalyst for highly-efficiency overall water splitting. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 931, 167575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Su, W.; Li, L.; Zhao, R.; Fu, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Guo, Q.; Ma, J. Cooperative Effect of ZIF-67-Derived Hollow NiCo-LDH and MoS2 on Enhancing the Flame Retardancy of Thermoplastic Polyurethane. Polymers 2022, 14, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Han, L.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J. Metal-Organic Framework Derived Multidimensional Carbon/Multifluorination Epoxy Nanocomposite with Electromagnetic Wave Absorption, Environmentally Adaptive, and Blue Energy Harvesting. Small Struct. 2023, 4, 2300210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Ge, D.; Lin, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Construction of heterogeneous interfaces modulating dielectric loss in MOF-derived FeCoNi/C confined carbon aerogels as multifunctional microwave absorbers. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 996, 174764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Li, Y.R.; Fang, H.P.; Deng, Y.; Wang, D.Y. Optimization Design of the Multidimensional Heterostructure toward Lightweight, Broadband, Highly Efficient, and Flame-Retarding Electromagnetic Wave-Absorbing Composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 51333–51345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Gao, C.; Song, C.; Liu, Z.; Fatehi, P.; Wang, S.; Kong, F. Wood-derived porous carbon foams filled with Ti3C2TxMXene/CoFe-MOF for electromagnetic shielding with flame retardant, heat insulation and excellent cycle stability. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 133, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Xu, N.; Cui, P.; Guo, L.; Ma, J.; Kang, Y.; Qin, L.; Wu, F.; Zhang, L.; et al. In situ Mechanical Foaming of Hierarchical Porous MoC for Assembling Ultra-light, Self-cleaning, Heat-insulation, Flame-retardant, and Infrared-stealth Device. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2414910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
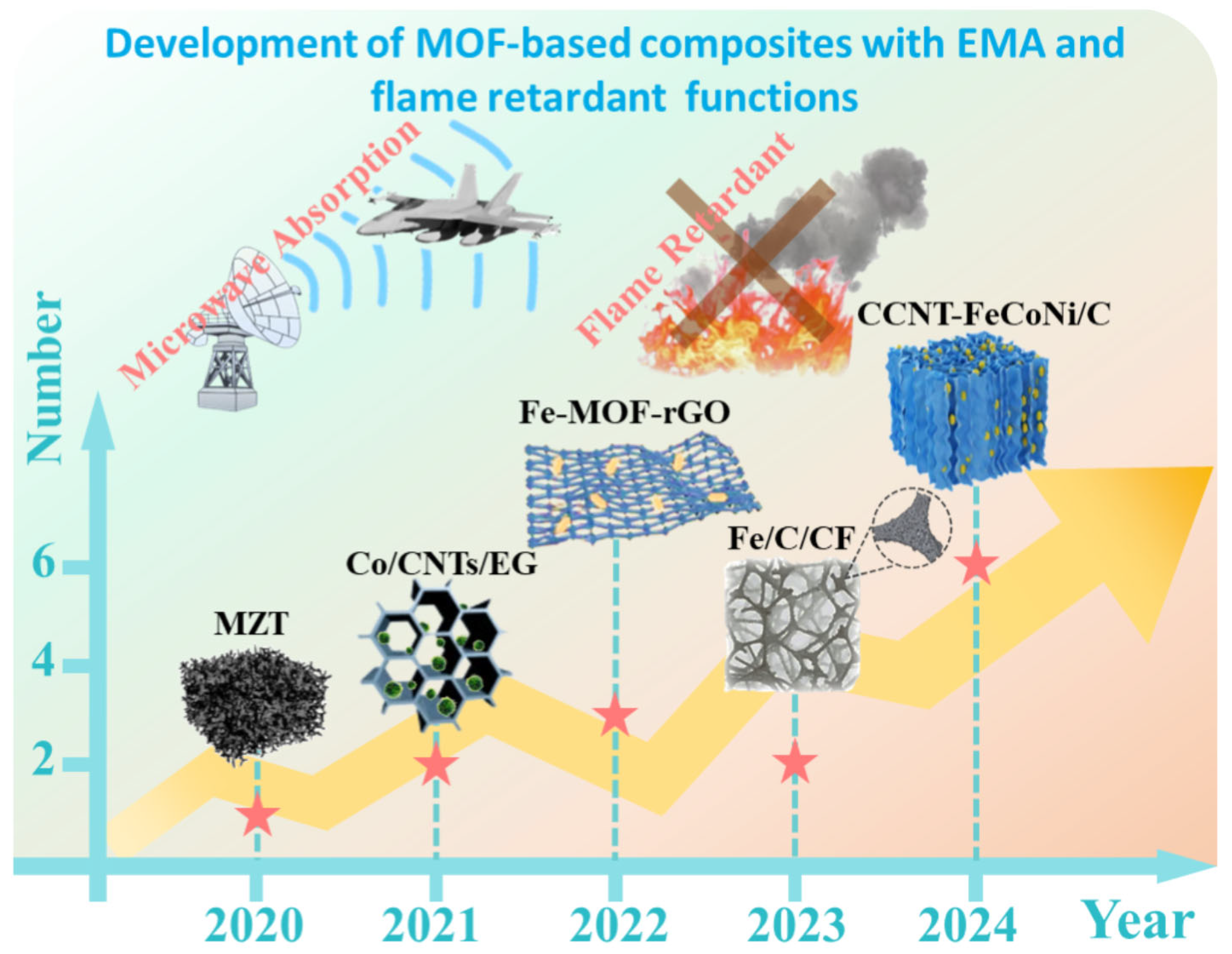










| Sample | Structure | Loading (wt.%) | RLmin/d (dB/mm) | EAB/d (GHz/mm) | Main Flame-Retardant and Thermal Insulation Results | Advantages/ Disadvantages | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-MOF-rGO | Heterostructure composed of 2D rGO and 3D Fe-MOF | 25 | −43.6/2.0 | 5.0/2.0 | Alcohol lamp burning 20 s without deformation; HRC, pHRR and THR decreased by 42.1%, 42.3% and 17.7%, respectively. | Lightweight, easy to prepare/high-proportion requirements | [77] |
| Fe2P4O12/P-C | Complex network structure composed of octahedral Fe2P4O12 and layered carbon | 30 | −67.6/2.0 | 5.76/2.1 | Alcohol lamp burning 180 s without deformation. | High-temperature fire resistance/complex preparation process and high-proportion requirements | [80] |
| Fe/C/CF | 3D porous structure composed of Fe/C nanocubes and carbon foam | - | −66.7/4.18 | 6.34/4.08 | Thermal insulation and infrared stealth. | Lightweight, easy to prepare/long-term stability and weather resistance to be proven | [81] |
| MZT | Highly ordered 3D pore network | 20 | −59.82/2.3 | 5.64/2.1 | Thermal insulation and infrared stealth. | Lightweight/requires precise control of calcining conditions | [85] |
| Co/CNTs/EG | 3D porous structure of urchin-like Co/CNTs distributed in honeycomb EG | 3 | −67.2/1.4 | 5.1/1.4 | Alcohol lamp burning 20 s without deformation; thermal insulation and infrared stealth. | Lightweight, low proportion/long-term stability and weather resistance to be proven | [86] |
| CoM@CoNiC-F | Multiphase structure composed of 2D CoMXene and 1D CoNiCNT | - | −64.78/2.3 | 4.6/1.7 | LOI was 30.8%; UL-94 V-0 rating; pHRR, THR, pSPR, and pCOP decreased by 70.71%, 43.11%, 71.69%, and 76.03%, respectively. (Heat flux was 35 kW/m2.) | Shape memory and 4D printing capability/complex preparation process | [87] |
| PW-CMF@Co/NC | 3D porous carbon foam structure with polyhedron growth, and the surface covered with dense carbon nanotubes | - | −57.93/3.0 | 3.85/3.0 | Alcohol lamp burning 60 s without deformation; heat conduction function; pHRR, THR, pSPR, and TSR were 82.3 kW/m2, 10.0 MJ/m2, 3.8 kW/m2, and 81.8 MJ/m2. (Heat flux was 50 kW/m2.) | Efficient photothermal conversion capability, excellent thermal storage stability/practical application limitations | [88] |
| Ni@C | Laminated porous structure formed by assembling 2D carbon sheets | 25 | −59.8/1.5 | 4.5/1.5 | Thermal insulation and infrared stealth. | Lightweight, hydrophobic/mechanical strength may be insufficient | [89] |
| Ti3CNTx/Ni@C | Layered porous structure composed of 2D MXene sheets and Ni@C microcubes. | 8 | −65.7/1.5 | 5.4/1.5 | Alcohol lamp burning 60 s without deformation; thermal insulation and infrared stealth. | Lightweight, low proportion/MXene easy to stack and agglomerate | [90] |
| CoC@FeNiG-F | Multidimensional carbon structure composed of 1D CNTs, 2D rGO, and 3D carbon skeleton | - | −75.19/2.4 | 3.95/2.4 | LOI was 31.2%; UL-94 V-0 rating; pHRR, THR, pSPR, and pCOP decreased by 68.77%, 36.53%, 48.39%, and 56.14%, respectively. (Heat flux was 35 kW/m2.) | Can be used for liquid–solid triboelectric nanogenerator/complex preparation process | [94] |
| CCNT-FeCoNi/C | 3D porous aerogel structure of FeCoNi alloy grown on the surface | 5 | −61.55/2.42 | 7.2/2.82 | Alcohol lamp burning 30 s without deformation; thermal insulation and infrared stealth. | Lightweight, low proportion/complex preparation process | [95] |
| CNT-rGO-Co/Ni-MOF | Multidimensional heterogeneous structures composed of CNT, rGO, and Co/Ni-MOF | 25 | −43.0/1.5 | 4.0/1.5 | Alcohol lamp burning 60 s without deformation; HRC, pHRR, and THR decreased by 59.2%, 52.6%, and 20.8%. | Lightweight, multi-mechanism synergies/high-proportion requirements | [96] |
| MMSW | Highly ordered cellular porous carbon foam structure | - | −58.2/2.0 | 5.8/2.0 | Alcohol lamp burning 90 s without deformation; thermal insulation. | Lightweight, excellent Joule thermal properties/mechanical strength may be insufficient | [97] |
| MoC-C | 3D foam structure containing a large number of bubbles and hierarchical pores | 15 | −47.56/2.5 | 4.4/2.5 | Alcohol lamp burning 20 s without deformation; thermal insulation and infrared stealth. | Lightweight, green preparation/mechanical strength may be insufficient | [98] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Jiang, J.; Li, Q.; Cao, J.; Sun, X.; Huo, S.; Pan, Y.-T.; Ma, M. Metal–Organic Framework-Based Composites for Dual Functionalities: Advances in Microwave Absorption and Flame Retardancy. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9030121
Hu J, Jiang J, Li Q, Cao J, Sun X, Huo S, Pan Y-T, Ma M. Metal–Organic Framework-Based Composites for Dual Functionalities: Advances in Microwave Absorption and Flame Retardancy. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(3):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9030121
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jinhu, Jialin Jiang, Qianlong Li, Jin Cao, Xiuhong Sun, Siqi Huo, Ye-Tang Pan, and Mingliang Ma. 2025. "Metal–Organic Framework-Based Composites for Dual Functionalities: Advances in Microwave Absorption and Flame Retardancy" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 3: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9030121
APA StyleHu, J., Jiang, J., Li, Q., Cao, J., Sun, X., Huo, S., Pan, Y.-T., & Ma, M. (2025). Metal–Organic Framework-Based Composites for Dual Functionalities: Advances in Microwave Absorption and Flame Retardancy. Journal of Composites Science, 9(3), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9030121









