Antibacterial UV-Curable Gel with Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles for Regenerative Medicine in the Field of Orthopedics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Synthesis of HA—Acrylate–Gelatin Nanocomposite
3. Results and Discussion
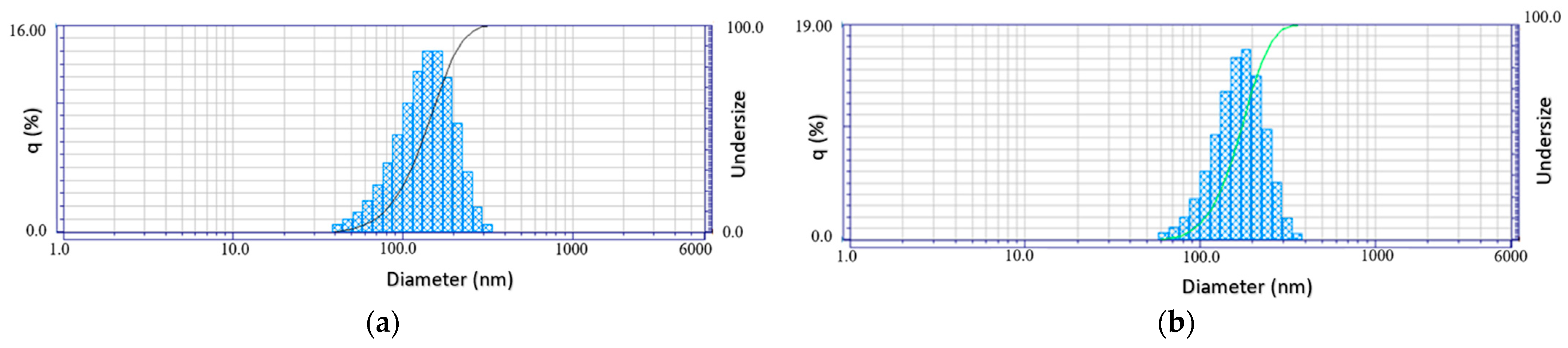
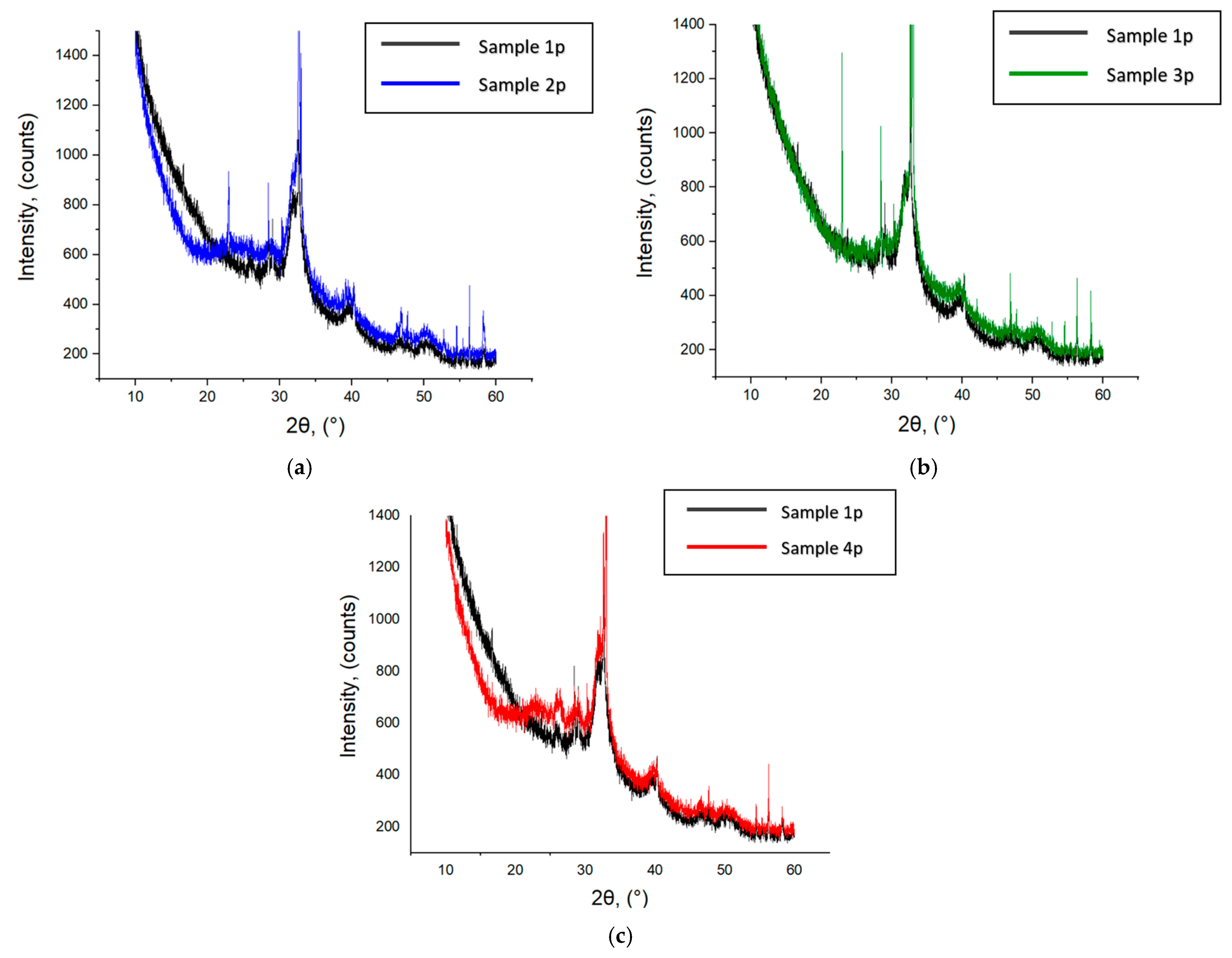
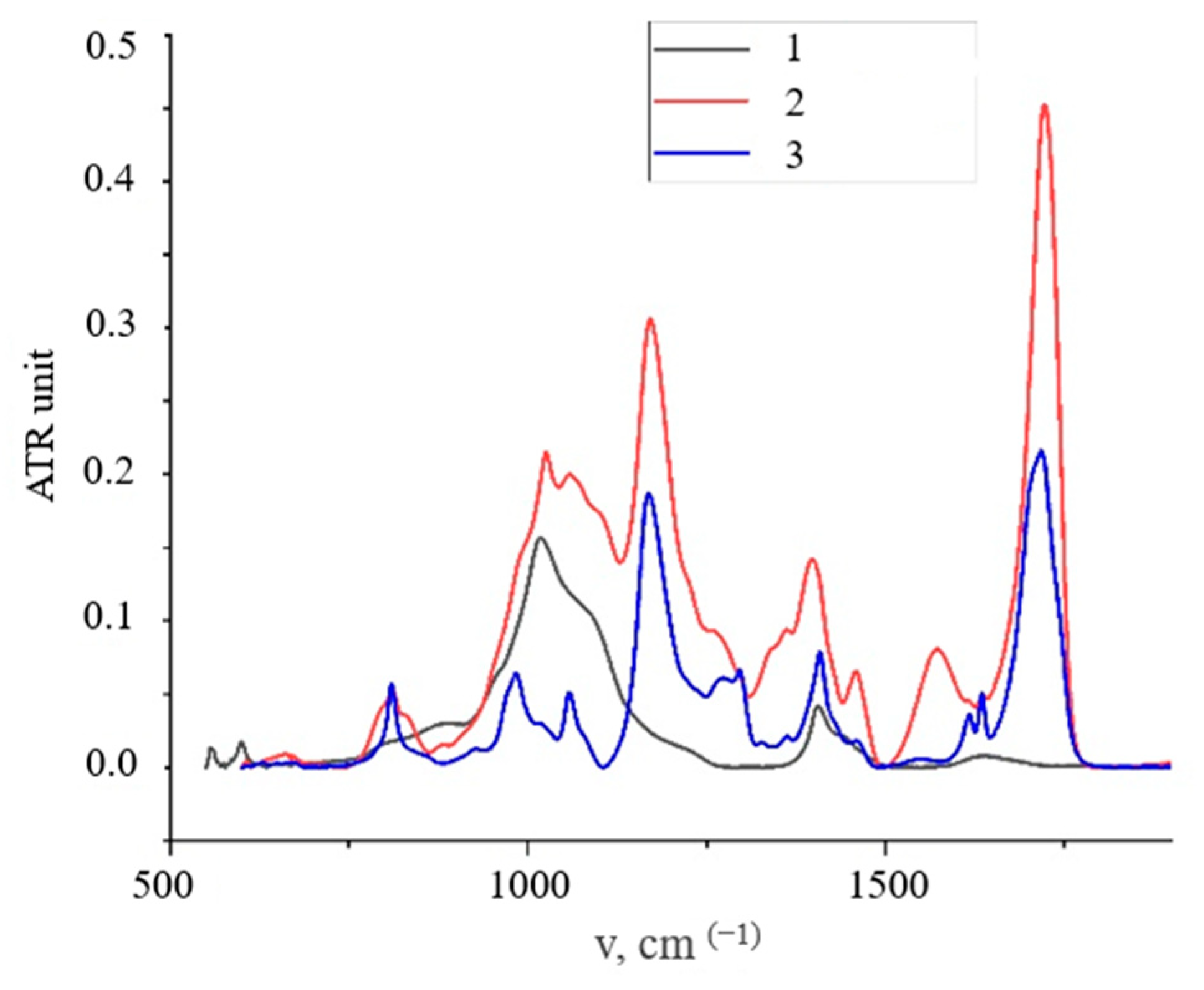
3.1. HA Nanoparticles
3.2. Wettability Angle and Water Sorption Rate of Nanocomposite Films
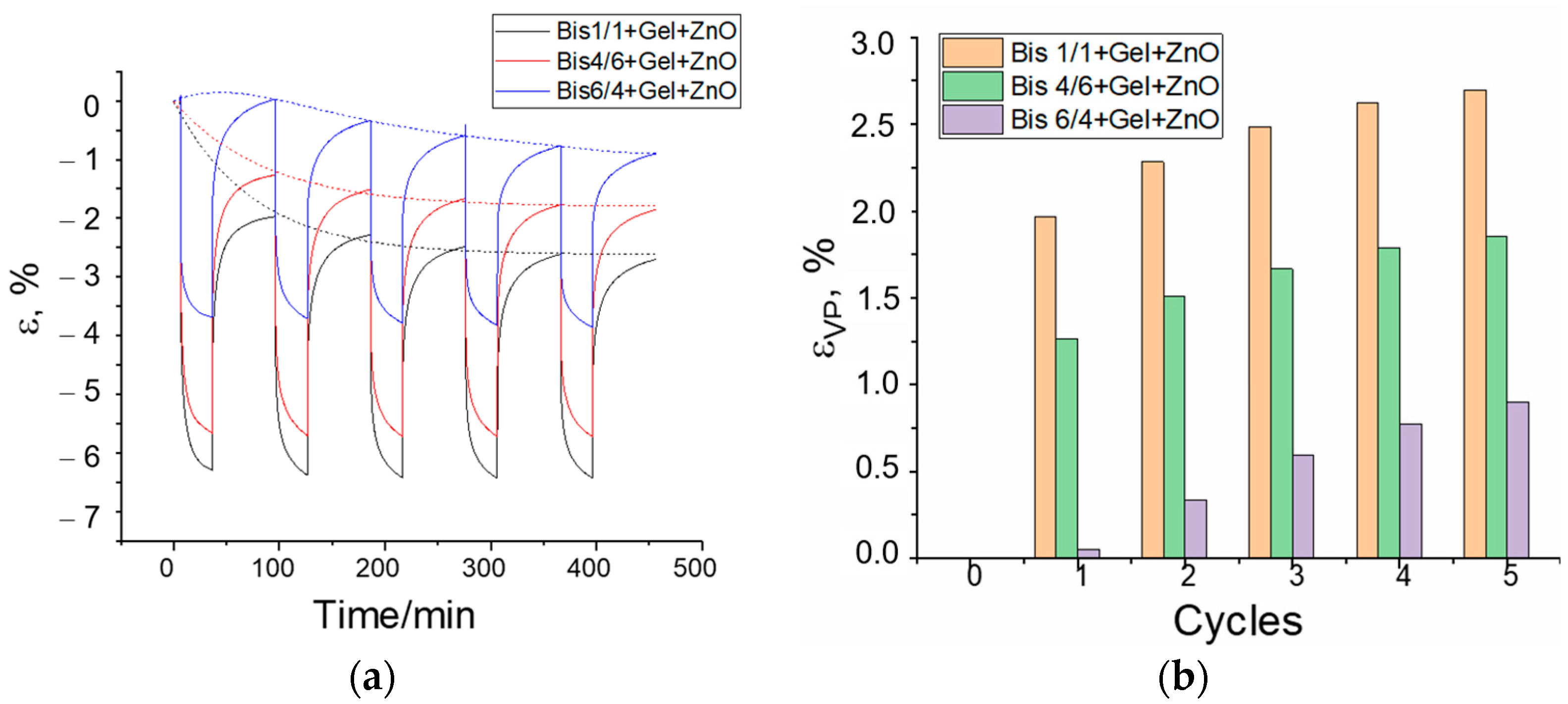
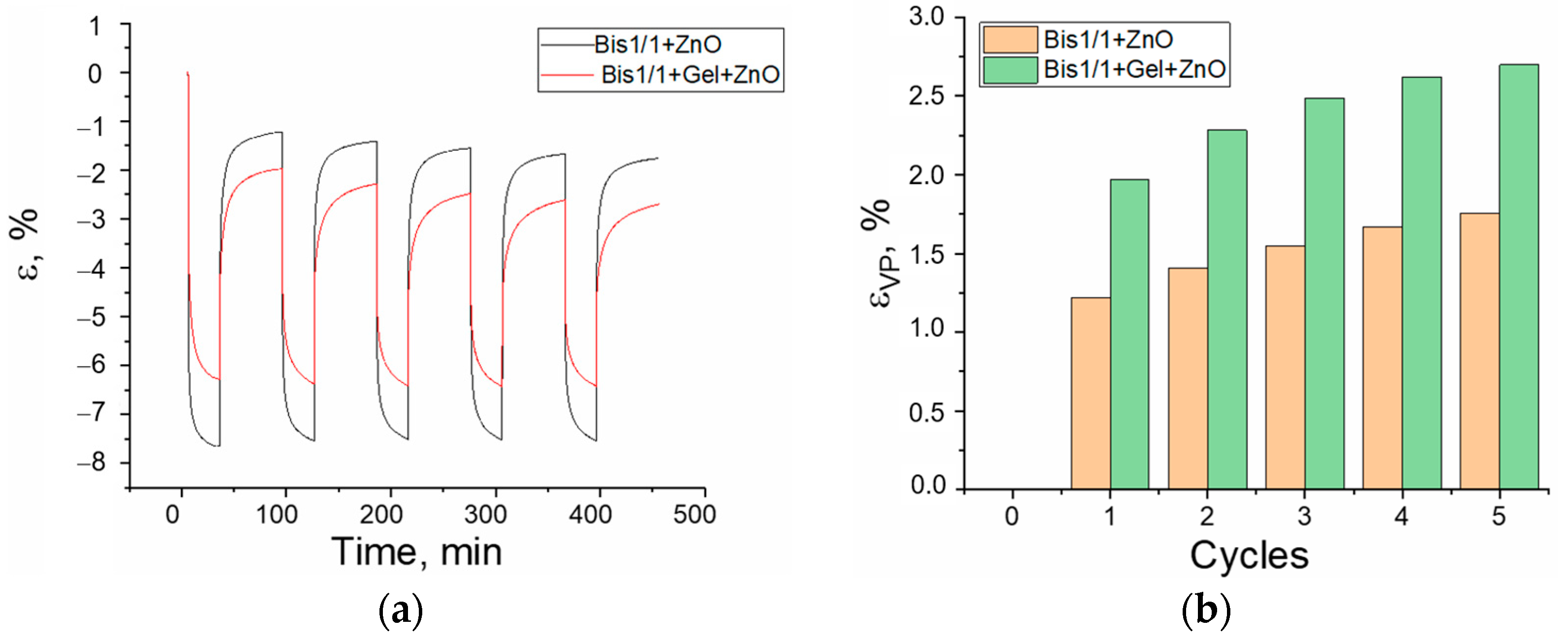
3.3. Creep/Recovery Test
- -
- The materials are liquid, but they are used without solvents, and they can be applied to a surface of any shape;
- -
- Materials are cured by a UV irradiation source;
- -
- Materials are biocompatible and, most importantly, partially resorbable. This property ensures that when composites are applied to a biological object or implant, there will always be a damping protective layer in which normal processes of bone and cartilage tissue development can take place.
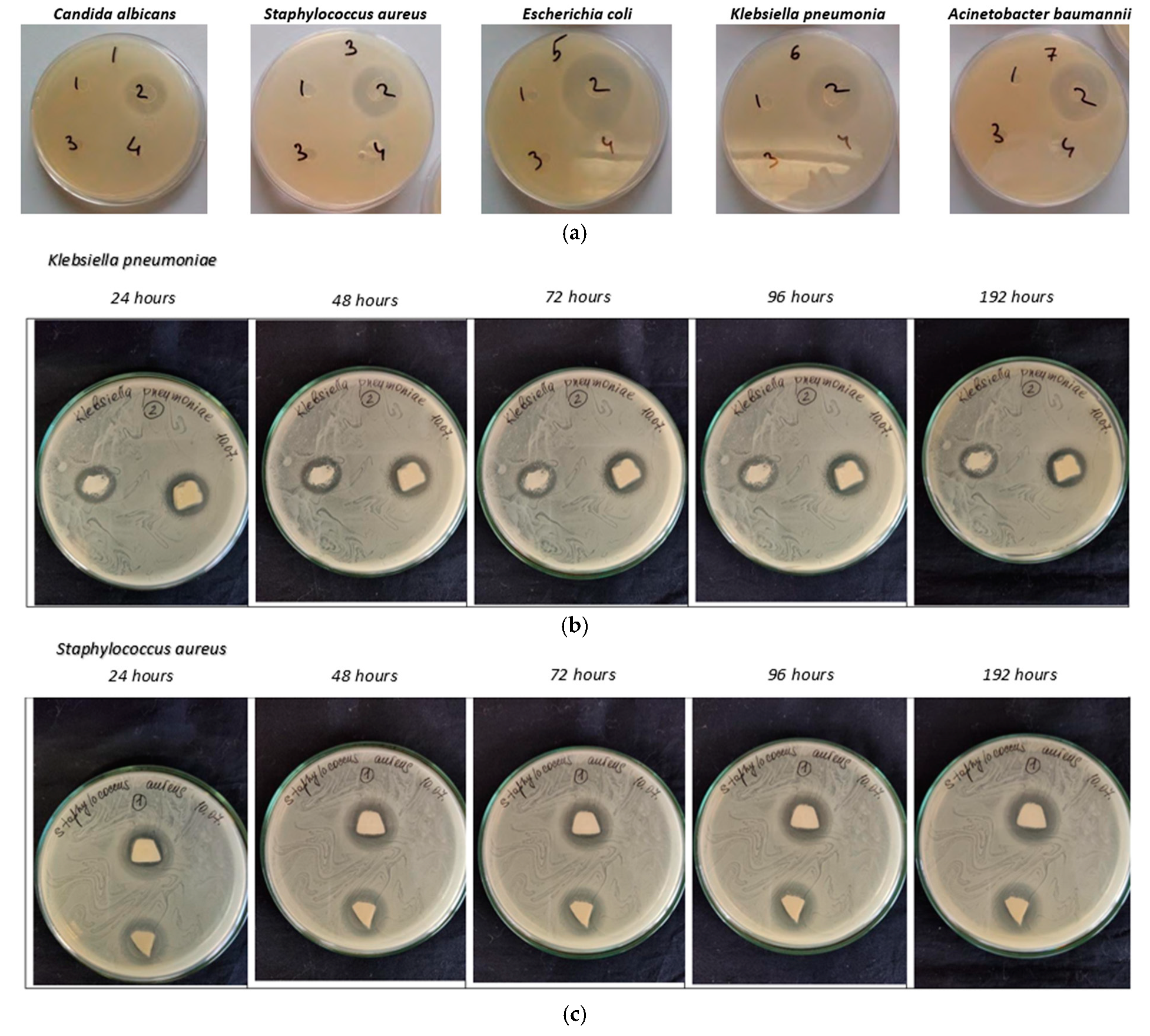
3.4. Antimicrobial Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ricotti, L.; Ciofani, G.; Mattoli, V.; Menciassi, A. Nano-Doped Matrices for Tissue Regeneration. In Advances in Regenerative Medicine; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; p. 295. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Berndt, C.C.; Gross, K.A.; Kucuk, A. Material fundamentals and clinical performance of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings: A review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 58, 570–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Goot, K.; Wolke, J.G.C.; Jancen, J.A. Calcium phosphate coatings for medical implants. Proc. Instn. Mech. Engrs. 1998, 212, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacefield, W.R.; Hench, L.L. The bonding of Bioglass® to a cobalt-chromium surgical implant alloy. Biomaterials 1986, 7, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehof, J.W.; Mahmood, J.; Takita, H.; Hof, M.V.; Kuboki, Y.; Spauwen, P.H.; Jansen, J.A. Ectopic bone formation in titanium mesh loaded with bone morphogenetic protein and coated with calcium phosphate. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2001, 108, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, A.E.; Patel, N.; Skepper, J.N.; Best, S.M.; Bonfield, W. Comparison of in vivo dissolution processes in hydroxyapatite and silicon-substituted hydroxyapatite bioceramics. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4609–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, A.E.; Patel, N.; Skepper, J.N.; Best, S.M.; Bonfield, W. Effect of sintered silicate-substituted hydroxyapatite on remodelling processes at the bone–implant interface. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 3303–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepla, E.; Besharat, L.K.; Palaia, G.; Tenore, G.; Migliau, G. Nano-hydroxyapatite and its applications in preventive, restorative and regenerative dentistry: A review of literature. Ann. Stomatol. 2014, 5, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, B.; Ghosh, D.; Sinha, M.K.; Sen, P.S.; Balla, V.K.; Das, N.; Basu, D. Doxorubicin-inter-calated nano-hydroxyapatite drug-delivery system for liver cancer: An animal model. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 9557–9566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Nanosized and nanocrystalline calcium orthophosphates. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Zhitomirsky, I. Electrophoretic deposition of composite hydroxyapatite-chitosan coatings. Mater. Charact. 2007, 57, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lim, B.K.; Sun, F.; Koh, K.; Ryu, S.C.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J. Preparation of high flexible composite film of hydroxyapatite and chitosan. Polym. Bull. 2009, 62, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Zhou, H.; Lee, J. Various preparation methods of highly porous hydroxyapatite/polymer nanoscale biocomposites for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 3813–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redepenning, J.; Venkataraman, G.; Chen, J.; Stafford, N. Electrochemical preparation of chitosan/hydroxyapatite composite coatings on titanium substrates. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2003, 66, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuyun, J.; Yubao, L.; Chengdong, X. Preparation and biological properties of a novel composite scaffold of nanohydroxyapatite/chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Sci. 2009, 16, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.Y.; Wang, M.; Cheung, W.L.; Ip, W.Y. Chapter 9—Selective laser sintering of poly (L-Lactide)/carbonated hydroxyapatite nanocomposite porous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. In Tissue Engineering; InTech: London, UK, 2010; pp. 179–204. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S. Recent Advances in Biocompatible Polymeric Materials for Tissue Engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 258–271. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Li, H. Design and Characterization of Biocompatible Polymeric Materials for Drug Delivery. Polym. Chem. 2024, 21, 367–380. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Chen, H.; Wu, Q. Biocompatible Polymeric Materials for Implantable Medical Devices. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2024, 42, 189–202. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, C.M.; Holmes, B.; Faucett, S.; Zhang, L.G. Three-Dimensional Printing of Nanomaterial Scaffolds for Complex Tissue Regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part B 2014, 21, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Chimal, R.; Arenas-Alatorre, J.Á.; Álvarez-Pérez, M.A. Nanoparticle-polymer composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 213, 113093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, G.; Clarke, J.; Picard, F.; Riches, P.; Jia, L.; Han, F.; Li, B.; Shu, W. 3D bioactive composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Bioact. Mater. 2018, 3, 278–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglio, M.; Salamanna, F.; Brogini, S.; Borsari, V.; Pagani, S.; Nicoli Aldini, N.; Giavaresi, G.; Fini, M. Histological, histomorphometrical, and biomechanical studies of bone-implanted medical devices: Hard resin embedding. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1804630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Calcium Orthophosphate-Based Bioceramics. Materials 2013, 6, 3840–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csarnovics, I.; Burunkova, J.; Sviazhina, D.; Oskolkov, E.; Alkhalil, G.; Orishak, E.; Nilova, L.; Szabo, I.; Rutka, P.; Bene, K.; et al. Development and study of biocompatible polyurethane-based polymer-metallic nanocomposites. J. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2020, 13, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulyashova, K.S.; Sharkeyev, Y.P. Preparation of synthetic hydroxyapatite for the formation of bio-coatings on medical implants. Chem. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 19, 447–453. [Google Scholar]
- Jongwattanapisan, P.; Charoenphandhu, N.; Krishnamra, N.; Thongbunchoo, J.; Tang, I.M.; Hoonsawat, R.; Smith, S.M.; Pon-On, W. In vitro study of the SBF and osteoblast-like cells on hydroxyapatite/chitosan–silica nanocomposite. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorozhkin, S.V.J. Calcium Orthophosphate-Containing Biocomposites and Hybrid Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications. Funct. Biomater. 2015, 6, 708–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Hariza, A.M.A.; Mohd Yunus, M.H.; Fauzi, M.B.; Murthy, J.K.; Tabata, Y.; Hiraoka, Y. The Fabrication of Gelatin–Elastin–Nanocellulose Composite Bioscaffold as a Potential Acellular Skin Substitute. Polymers 2023, 15, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soradech, S.; Nunthanid, J.; Sriamornsak, P.; Limmatvapirat, S.; Luangtana-anan, M. Factors affecting on the enhancement of mechanical properties of composite edible film based on Shellac and Gelatin. Thai J. Agric. Sci. 2011, 4, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- Afewerki, S.; Sheikhi, A.; Kannan, S.; Ahadian, S.; Khademhosseini, A. Gelatin-polysaccharide composite scaffolds for 3D cell culture and tissue engineering: Towards natural therapeutics. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2018, 4, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Shim, J.; Lee, H.G. Mechanical properties of gellan and gelatin composite film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 56, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Webster, T. (Eds.) Progress in Biology, Manufacturing, and Industry Perspectives; Orthopedic Biomaterials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibzadeh, F.; Sadraei, S.M.; Mansoori, R.; Chauhan, N.P.S.; Sargazi, G. Nanomaterials supported by polymers for tissue engineering applications: A review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, M.; Born, G.; Chaaban, M.; Scherberich, A. Natural polymeric scaffolds in bone regeneration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Katiyar, S.; Darshna Anand, A.; Singh, D.; Singh, B.N.; Mallick, S.P.; Mishra, A.; Srivastava, P. Design strategies for composite matrix and multifunctional polymeric scaffolds with enhanced bioactivity for bone tissue engineering. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1051678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiryaghoubi, N.; Fathi, M.; Pesyan, N.N.; Samiei, M.; Barar, J.; Omidi, Y. Bioactive polymeric scaffolds for osteogenic repair and bone regenerative medicine. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 1833–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| No | Nanocomposite | BisA/2Carboxylate [wt/wt] | SiO2 [wt%] | CaCl2 + H3PO4 [wt%] | Gelatin [wt%] | DMPA [wt%] | ZnO [wt%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bis1/1 + Gel + ZnO | 1/1 | 8 | 10 | 20 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 2 | Bis1/1 +ZnO | 1/1 | 8 | 10 | - | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 3 | Bis4/6 + Gel + ZnO | 4/6 | 8 | 10 | 20 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 4 | Bis4/6 + ZnO | 4/6 | 8 | 10 | - | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 5 | Bis6/4 + Gel + ZnO | 6/4 | 8 | 10 | 20 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| No | Composition of the Synthesis | Ca/P [wet %] |
|---|---|---|
| 1p | CaCl2 + H3PO4 | 1.67 |
| 2p | SiO2 + CaCl2 + H3PO4 | 2.19 |
| 3p | CaCl2 + H3PO4 + 2Car | 1.58 |
| 4p | SiO2 + CaCl2 + H3PO4 + 2Car | 1.66 |
| No | Sample | Average Crystallite Size, [nm] |
|---|---|---|
| 1p | HA powder | 4.05 |
| 2p | HA + SiO2 powder | 5.93 |
| 3p | HA particles in carboxylate | 12.63 |
| 4p | HA + SiO2 particles in carboxylate | 8.15 |
| No | Nanocomposite | Contact Angle [degree] | Sorption Rate [deg/min] | Weight Loss Due to Soaking [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bis1/1 + Gel + ZnO | 54.6 | 4.2 | 25 |
| 2 | Bis1/1 +ZnO | 67.5 | 2.4 | 10 |
| 3 | Bis4/6 + Gel + ZnO | 52.3 | 2.3 | 20 |
| 4 | Bis4/6 + ZnO | 62.2 | 1.8 | 26 |
| Microorganisms | Radius of Growth Suppression, mm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 96 h | 192 h | |
| Candida albicans | 17 × 19 | 16.5 × 18.5 | 15.5 × 18 | 14 × 16.5 | 14 × 15 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 14 × 16 | 13 × 14.5 | 12 × 14 | 12 × 14 | - |
| Escherichia coli | 22 × 23 | 20 × 20 | 18 × 19 | 17 × 17.5 | 17 × 17.5 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | Left 15 × 17 Right 18 × 18 | 15 × 17 18 × 18 | 14 × 16 16.5 × 17 | 13 × 16 16.5 × 17 | - 16.5 × 17 |
| Acinetobacter baumannii | Left 20 × 21 Right 21 × 21 | 19 × 19.5 20 × 20 | 19 × 19.5 20 × 20 | 19 × 19.5 20 × 20 | - 20 × 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burunkova, J.A.; Semykina, V.V.; Sitnikova, V.E.; Dolgintsev, D.M.; Zaripova, F.F.; Ponomareva, A.A.; Mizina, D.R.; Csick, A.; Kokenyesi, S.; Zhilenkov, A. Antibacterial UV-Curable Gel with Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles for Regenerative Medicine in the Field of Orthopedics. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9020065
Burunkova JA, Semykina VV, Sitnikova VE, Dolgintsev DM, Zaripova FF, Ponomareva AA, Mizina DR, Csick A, Kokenyesi S, Zhilenkov A. Antibacterial UV-Curable Gel with Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles for Regenerative Medicine in the Field of Orthopedics. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(2):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9020065
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurunkova, Julia A., Valeria V. Semykina, Vera E. Sitnikova, Dmitry M. Dolgintsev, Faliya F. Zaripova, Alina A. Ponomareva, Diana R. Mizina, Attila Csick, Sandor Kokenyesi, and Anton Zhilenkov. 2025. "Antibacterial UV-Curable Gel with Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles for Regenerative Medicine in the Field of Orthopedics" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 2: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9020065
APA StyleBurunkova, J. A., Semykina, V. V., Sitnikova, V. E., Dolgintsev, D. M., Zaripova, F. F., Ponomareva, A. A., Mizina, D. R., Csick, A., Kokenyesi, S., & Zhilenkov, A. (2025). Antibacterial UV-Curable Gel with Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles for Regenerative Medicine in the Field of Orthopedics. Journal of Composites Science, 9(2), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9020065







